Seagrass-Watch. Activity Book
|
|
|
- Janis Gordon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Seagrass-Watch Activity Book
2 Sensational Seagrass Seagrass is one of the most important plants on earth. Seagrass is the only marine flowering plant. Seagrass is found in oceans throughout the world and is the basis for many important marine ecosystems. Seagrass meadows are commonly found along coastlines, on reef tops and in estuaries. Seagrass plants have roots, stems and leaves. The roots and horizontal stems (called rhizomes) are buried in the substrate and anchor the plant. Roots can be simple or branching, and have fine hairs to help absorb nutrients. Rhizomes form in segments, with leaves or vertical stems rising from the joins, which are called nodes or scars. Vertical (erect) stems are called shoots. They grow out of the sediment and have leaves. Sometimes the leaves are on a stalk, called a petiole. Seagrass have veins and air channels in their leaves and stems, so they can carry water, food and gases. Veins can be across the leaf blade or run parallel (longitudinal) to the leaf edge. At the base of a leaf is a sheath, which protects young leaves. At the other end of a leaf is the tip. Can you label the missing plant parts below from the following list? cross vein, oval leaf blade, rhizome, branching roots, stem, internode, leaf sheath, leaf tip 1:... longitudinal leaf vein leaf blade 2:... 3:... petiole node 4:... 5:... 6:... erect shoot root hair 7:... simple root 8:... 2
3 A special kind of grass They are called seagrass because most have flat, ribbon-like, grassy leaves. But they are not a true grass. There are around 60 different species of seagrass world-wide, and some do not look like grass at all. Seagrass range from the size of your fingernail to plants with leaves as long as 7 metres. Leaves of different seagrass species can be shaped like a flattened ribbon, look like a fern, a clover, or even like spaghetti. No matter what the shape, seagrass leaves rely on light to convert carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and sugar (photosynthesis). The sugar and oxygen are then available for use by other living organisms, making seagrass an important link in the food web. Can you identify the three seagrass species below from the following list? HD (Halophila decipiens) HO (Halophila ovalis) HS (Halophila spinulosa) oval shaped leaves oval shaped leaves in pairs oblong leaves arranged like fine hairs on leaf blade leaf edges & blade smooth a fern leaf edges jagged/saw-like can live on intertidal mud leaf edges jagged/saw-like able to live in low light flats able to live in low light CS (Cymodocea serrulata) wide stap-like leaves leaf tip rounded with jagged edge plants live in shallow water, not exposed at low tide HU (Halodule uninervis) strap-like leaves leaf tip has three points prominent single vein along middle of leaf SI (Syringodium isoetifolium) leaves spaghetti shaped leaf tip with single point plants live in shallow water, not exposed at low tide Species A:... Species B:... Species C:... 3
4 Food and shelter Seagrass is important because it is food and provides shelter for marine life. Within seagrass meadows, you can find animals such as prawns, crabs, starfish, marine slugs and seahorses. Hermit crabs are also common in seagrass meadows. Help the Hermit Crab find a new home 4
5 Biodiversity Seagrass meadows are very biodiverse. That means they include lots of different life forms (species). Seagrass meadows also have lots of animals living within them. About 40 times more animals occur in seagrass meadows than on bare sand. How many different animal and plant species can you count in the picture below? 5
6 Fisheries One of the most important roles of seagrass is providing a nursery and shelter area for fish and prawns which are valuable to recreational, commercial and indigenous fisheries. Juveniles of some important species which depend on seagrass meadows include fish such as perch, mullet, whiting, tailor, luderick, bream, flathead, snappers, emperors and sweetlips. Tiger prawns, king prawns and tropical rock lobsters also live in seagrass meadows as juveniles. Shellfish such as some oysters and pearl shell may be more likely to settle and survive where there is seagrass. What do all these animals have in common besides being valuable to fisheries? Red throat emperor / sweetlip adults live on coral reefs and lagoon areas are bottom feeders, mainly eating crabs, sea urchins, sand dollars and fish juveniles live in shallow water seagrass meadows, moving offshore as they grow change from female to male as they grow Tiger prawn adults live and spawn offshore on muddy or sandy bottoms mainly feed at night on molluscs, crustaceans and polychaete worms young prawns settle into and live in seagrass meadows estuarine fish are major predators of juveniles prawns Red emperor are part of the family of tropical snappers and sea perches adults live on coral reefs and sand flats. juveniles live in nearshore mangrove and seagrass habitats are predators which mainly feed at night Ornate tropical rock lobster adults live on coral or rocky reefs in spring mature adults congregate and migrate to deepwater spawning grounds adults spawn in summer in winter the postlarvae settle into seagrass meadows juveniles shelter and feed in seagrass meadows Illustrations courtesy Paul Lennon 6
7 Dugongs The dugong is a marine mammal which eats seagrass. Dugong can eat up to 40 kilograms of seagrass per day. When a dugong eats, it digs its snout into the sea-bed to uproot the seagrass, leaving a trail in the meadow where they have fed. Dugong can travel for great distances searching for food. They have a good memory and satellite tracking has shown that they can return hundreds of kilometres to a specific place. Two dugong have been tagged with satellite transmitters, which one will reach the seagrass meadow? 2 1 7
8 Sea Turtles Green sea turtles are marine reptiles that mainly feed on seagrass. They eat (crop) the leaves of the strap-like seagrass species. An adult green turtle eats about two kilograms of seagrass a day. 8
9 Word-Find Find the hidden words in the puzzle below. From the unused letters in the puzzle, reveal the name of the areas of the sea bottom on which marine flowering plants are present. Compass Crab Dredging Dugong Fishery Habitat Halodule Halophila Intertidal Nursery Quadrat Subtidal Transect Turtle Volunteer Water Quality Zostera W T U R T L E H T D S E A Y A G R I A A R R S H T R S S Y N S L A E A A E E H U R T S O N D R L R S A B E E A P S G E O Q R B T H R P H E I T D U U I I S T M I C N S U A N T D I I O L T G O L L B A A F D C A M E Z E I A T L A A D U G O N G T R D V O L U N T E E R Y C Q U A D R A T O W S 9
10 Seagrass Habitats Seagrasses need plenty of sun and clean water to grow. Seagrasses also live in locations sheltered from wave action. Species of seagrass are adapted to live in a variety of coastal marine habitats. Seagrasses are usually found growing in mud or sand, in subtidal areas (areas that are covered with salt water all the time). Subtidal areas can include very deep water (more than 15m depth). Some seagrass species can also be found in the intertidal region (covered by water during high tide and uncovered during low tide). Place the letter of each of the six seagrass species below in the correct box where you generally find that species. Hint: information on some species can be found on page 3. saltmarsh mangroves high tide mark low tide mark sand Intertidal Shallow subtidal Deep-water (>15m) a. b. c. Halophila spinulosa d. Halophila decipiens e. Cymodocea serrulata f. Halophila ovalis Zostera capricorni 10 Syringodium isoetifolium
11 Seagrass Tidal Search To live in intertidal regions (uncovered during low tide), seagrass must put up with getting too dry, too hot and too much sunlight. When the tide goes out, little pools of water are often left behind. Sometimes, small plants and animals get left behind too. Occasionally animals like dugongs can be stranded when the tide drops quickly. How many dugongs can you find hidden in this picture? 11
12 Seagrass Food Webs In a seagrass meadow as elsewhere, all the living things are connected to each other. Lets look at an example. In a reef lagoon green turtles eat seagrass, and sharks eat the green turtles. This is called a food chain. eaten by eaten by seagrass green turtle shark Energy Energy in a food chain moves from the plant to the first animal, and on to the second animal. At each stage energy is used by many things. Seagrass uses some of it s energy to flower and make seeds. The dugong uses energy to breed and move about. drift & export leaf fragments green turtle herbivorous fish epiphytes sponges sinking & decay dissolved organic matter zooplankton phytoplankton dugong juvenile fish & prawns sea urchin detritus sea cucumber crab roots binding sediments worms Food chains tell us about one feeding relationship. In a place like a seagrsss meadow there are many different feeding relationships which are connected together to form a food web. Food webs are not fixed because feeding relationships can change. In the food web above many of the plants and animals depend on each other. 12
13 Seagrass Food Webs Can you construct a food web? Use the structure below and write the name of each plant or animal group in it s correct location in the food web. Facts to help you: Tick off the groups when arrows show the movement of energy you have used them: food chains start with a plant giant perch are large predators that are found in tidal waters crab pelican where they feed on prawns and surface fish such as garfish dugong are marine mammals that graze on seagrass crocodile prawns garfish eat plants detritus sea perch molluscs and worms eat seagrass detritus dugong seagrass whiting are a fish that forage for burrowing benthic animals such as worms garfish shark sea birds such as pelicans prey on whiting giant perch whiting sharks prey on large fish, such as sea perch, and marine molluscs worms mammals crocodiles prey on large fish, such as giant perch, and marine mammals prawns feed primarily at night, on benthic animals such as molluscs and polychaete worms crabs are scavengers, eating worms and prawns detritus includes the organic material from decomposing plants sea perch consume mainly crabs, followed by prawns and benthic fish dugong crocodile start here seagrass garfish molluscs giant perch detritus prawns shark worms crab sea perch pelican whiting 13
14 Damaging seagrass Seagrass meadows are fragile ecosystems. Worldwide there is concern that seagrass meadows are being lost due to the activities of people. People can damage or destroy seagrass by pollution (sewage, oil spills and coastal runoff) and physical destruction (dredging, boat propellers and anchors/moorings). Physical damage can cause scars within a seagrass meadow. Damage can be both natural or by people. Below is a birds eye view of an intertidal seagrass meadow. Can you identify what caused the damage (scars) to the meadow? How many scars have been caused by: dugongs feeding... shorebirds feeding... boat propellers... boat anchors... boats swinging on moorings... digging for bait worms... Help stop the damage There are many ways you can help stop damage to seagrass meadows: don t litter; be aware when applying fertilizers and pesticides, as excess amounts can wash down gutters and drains to the sea; when boating, slow down and avoid shallow areas; support marine conservation program; learn about these special marine habitats and volunteer to monitor their health by joining Seagrass-Watch. 14
15 Seagrass Monitoring: Spot the difference We can see if seagrass meadows are healthy by watching them over time this is called monitoring. Seagrass-Watch is a seagrass monitoring program which measures seagrass health and makes us aware of any damage or loss. How observant are you? Can you spot the ten things different between the two pictures below? 15
16 Seagrass Monitoring One way we can monitor seagrass is to measure the amount or cover of seagrass within a square frame (quadrat) and compare this over time. In each of the quadrats below, measure the percentage of each seagrass species (Halophila and Zostera) and add them together to make up the total cover. Each grid is equal to 1%. Legend Halophila Zostera % Halophila = % Zostera = TOTAL COVER = Q1. Q2. % Halophila = % Zostera = TOTAL COVER = Q3. % Halophila = Q4. % Halophila = % Zostera = % Zostera = TOTAL COVER = TOTAL COVER = 16
17 Seagrass Mapping Seagrasses can form extensive meadows, similar to grasslands. These meadows occur along our coastlines, particularly in sheltered, shallow waters of estuaries, bays and lagoons, as well as on reef tops and on the sheltered sides of many off- shore islands. One way to monitor seagrass meadows is to map them over time. From the three maps below, calculate the area of each seagrass meadow for each year and plot the results in a stacked bar graph below. Each grid equals 1 hectare. Why do you think meadows would change between years? Muddy River 2000 Legend Halophila meadow mudbank Zostera meadow land 50 area of seagrass (hectares)
18 Word Scramble 1. ANDS PHAILOHAL ITMORNO MSACOCP EMALPS TEUVELONR CBRA HLULODAE ZRTAEOS DOOF DRSGNIMIOYU DTAARQU TADAEHTSE TECNASRT TULRET IBTATAH AOESSHER HPATES OGGUND MYEOOCCAD SGRASSAE RANPW 18
19 Crossword 1 Across 1. Sampling intertidal seagrass meadows is best done at low 2. This marine mammal eats seagrass 5. Seagrass fruits contain _ 8. A set of information used to identify seagrass (or a device to lock a door) 9. The hollow tube used to collect seagrass seeds is a _ 11. Global Positioning System (initials) 12. A transect is set up using a 50m measure 14. Device that holds a boat in place at sea 19. A square frame that the seagrass percent covers are estimated within 20. You use them to measure canopy height 21. Image taken as a permanent record of percent covers within a quadrat. Down 1. Quadrats are placed along a 50m 3. This marine reptile eats seagrass 4. Seagrass meadows act as _ areas for baby prawns and fish 6. During a cyclone, be prepared for a tidal _ 7. Seagrass species with many cross veins and rounded leaf tip (ZC) 10. Fish eggs 13. Seagrass with 3 pointed leaf tip 15. A group of whales 16. A marine flowering plant 17. Used for sifting sediment to find seeds 18. A crustacean that uses seagrass meadows as a nursery area 19
20 Crossword 2 Across Down 1. Species of Cymodocea with a distinctly jagged leaf tip 1. Species of Halophila which has a lateral shoot bearing pairs of opposite 5. number of points on the leaf tip of Halodule leaflets (fern-like) uninervis 2. Seagrass structures used to anchor the 6. Repeated observation of a site to detect plant and absorb nutrients change 3. Growing tip of a seagrass 10. Genus of seagrass whos leaves are round in 4. Stalk of Halophila ovalis leaves cross-section (spaghetti like) 6. Open expanses of intertidal mud 12. A paper form used to record field data in a 7. Species of Cymodocea with rounded leaf tip set format 13. Self-Contained Underwater Breathing 8. Soil/matter that settles to the bottom of a water body Apparatus 16. Beneath the low watermark 17. Structure which encloses the growing end of 9. Single leaf structure arising immediately from the horizontal rhizome unique to the genus Zostera a stem and protects young leaves 11. A fixed unit, usually square, used for sampling 14. A cylindrical sample of benthos and substratum obtained by the use of a hollow tube 15. Satellite-based navigation system Hint: you can find information on seagrass identification by visiting 20
21 Local Eyes: Global Wise Seagrass-Watch is a global scientific seagrass assessment and monitoring program. Which of the following Seagrass-Watch regions or countries is missing? Australia Bali Bangladesh Bowen Broome Cairns China Cooktown Eritrea Fiji Fitzroy Flores Gizo Gladstone Gold Coast Great Sandy Strait Hervey Bay India Indonesia Japan Karimunjawa Kavieng Komodo Kosrae Lau Mackay Madang Malaysia Manado Micronesia Mission Beach Moreton bay Mornington Island Napranum New Caledonia Noosa Ovalau Palau Papua New Guinea Philippines Pohnpei Rotuma Sabah Shoalwater Bay Singapore Solomon Islands Thailand Torres Strait Townsville Viet Nam Viti Levu Whitsundays H Z K O S R A E N O T S D A L G O V G M T C B T J M T M A C K A Y O R Z T I F U J P A P U A N E W G U I N E A W N S I N D D N E Q D E H N E W C A L E D O N I A V N G Y B A P A L A U T B G I Z O R E R O A L S I N D O N E S I A A B A L I P P V L A I Y G O J P A I L A R T S U A N A A S D N A L S I N O M O L O S K B C H N L I E G B S U D S D N A L I A H T D O I A N S A R P Y A I S E N O R C I M N P H U O H P E S Y A P H I L I P P I N E S C V T R O T U M A D E V M L J X D D W U Y E G N R A S Z N B N U I J I F N O O S A L N A E W J A P A N U H E R V E Y B A Y I I E K L D E O J A O S S T E S Y F S F T N R O A M N A C Q R T T T N M N J E S I R T M O E W X E D G N E I V A K W R K V O I O H A I S Y A L A M R H Z M Z O Q B M R D S A B A H C O O K T O W N D L T K B E O D A N A M B S J G L A M X T F L 21
22 Solutions Sensational Seagrass: 1=leaf tip; 2=oval leaf blade; 3=cross vein; 4=leaf sheath; 5=stem; 6=internode; 7=rhizome; 8=branching roots A special kind of grass: species A = HS, species B = HU, species C = HO Biodiversity: 15 (4 fish, 3 seagrass, 1 crab, 1 scallop, 2 snails, 1 prawn, 1 marine mammal, 1 starfish, 1 sand dollar) Fisheries: adults live offshore, juveniles live in nearshore seagrass meadows Dugong maze: tagged dugong number 2 Mapping continued..: The change in meadows between years may be due to: runoff (poor water quality) from Muddy River. Increased turbidity could cause the loss of Halophila meadow and some of intertidal Zostera meadow (in 1999). Increased nutrients could aid expansion of intertidal Zostera in Word scramble: 1. sand, 2. Halophila, 3. monitor, 4. compass, 5. sample, 6. volunteer, 7. crab, 8. Halodule, 9. Zostera, 10. food, 11. Syringodium, 12. quadrat, 13. datasheet, 14. transect, 15. turtle, 16. habitat, 17. seahorse, 18. gastropod, 19. dugong, 20. Cymodocea, 21. seagrass, 22. prawn Crossword 1: Word find: seagrass meadows Habitats: intertidal = d & e; shallow subtidal = c & f; deep-water = a & b Tide Pool Search: 18 Food web: dugong crocodile seagrass garfish molluscs giant perch Crossword 2: detritus prawns shark worms crab sea perch pelican whiting Damaging scars: 6 dugongs feeding trails (wavy lines); 2 bird feeding areas (groups of dots); 8 boat propellers (straight lines or arcs); 3 boat anchors (squares); 1 boat swinging on its mooring (semi-circle); 1 bait worm digging area (dashed rectangle). Spot the difference: Flying bird missing, ruler shorter, mans tongue not poking out, less wrinkles on back of mans shirt, no hair on mans legs, no flash on camera, pocket missing from ladies shorts, pocket missing from backpack, ripple missing from around ladies legs, island in background smaller Local Eyes: Global Wise: missing region is Torres Strait for more information, visit Monitoring: Q1, Halophila=8, Zostera=45, TOTAL=53 Q2, Halophila=0.5, Zostera=30, TOTAL=30.5 Q3, Halophila=25, Zostera=36, TOTAL=61 Q4, Halophila=40, Zostera=12, TOTAL=52 Mapping: 50 area of seagrass (hectares) Booklet by Len McKenzie, Rudi Yoshida & Jane Mellors. Produced by Seagrass-Watch HQ Supported by the Australian Government s Marine and Tropical Sciences Research Facility (Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts) represented in North Queensland by the Reef and Rainforest Research Centre and the Queensland Department of Primary Industries & Fisheries. 22
23 Seagrass-Watch HQ, PO Box 5396 Cairns QLD 4870 AUSTRALIA Phone: Fax: hq@seagrasswatch.org Web: This bookmark is the property of... Seagrass-Watch HQ, PO Box 5396 Cairns QLD 4870 AUSTRALIA Phone: Fax: hq@seagrasswatch.org Web: This bookmark is the property of... Seagrass-Watch HQ, PO Box 5396 Cairns QLD 4870 AUSTRALIA Phone: Fax: hq@seagrasswatch.org Web: This bookmark is the property of... Seagrass-Watch HQ, PO Box 5396 Cairns QLD 4870 AUSTRALIA Phone: Fax: hq@seagrasswatch.org Web: This bookmark is the property of... Seagrass-Watch HQ, PO Box 5396 Cairns QLD 4870 AUSTRALIA Phone: Fax: hq@seagrasswatch.org Web: This bookmark is the property of...
24 Make your own bookmark. Colour the images and cut out along dotted line.
Seagrass-Watch. Activity Book. Junior Edition
 Seagrass-Watch Activity Book Junior Edition Sensational Seagrass Seagrass are flowering plants that live in the sea. There are many different kinds of seagrasses and some do not look like grass at all.
Seagrass-Watch Activity Book Junior Edition Sensational Seagrass Seagrass are flowering plants that live in the sea. There are many different kinds of seagrasses and some do not look like grass at all.
Marine Ecosystems. Aquatic Ecosystems Section 2
 Marine Ecosystems Marine ecosystems are located mainly in coastal areas and in the open ocean. Organisms that live in coastal areas adapt to changes in water level and salinity. Organisms that live in
Marine Ecosystems Marine ecosystems are located mainly in coastal areas and in the open ocean. Organisms that live in coastal areas adapt to changes in water level and salinity. Organisms that live in
SALINITY. It's the amount of dissolved salts the water contains.
 AQUATIC ECOSYSTEMS SALINITY The types of organisms in an aquatic ecosystem depend upon the water s Salinity. It's the amount of dissolved salts the water contains. Salinity determines the two main aquatic
AQUATIC ECOSYSTEMS SALINITY The types of organisms in an aquatic ecosystem depend upon the water s Salinity. It's the amount of dissolved salts the water contains. Salinity determines the two main aquatic
Seagrass: Global Conservation Challenges
 Seagrass: Global Conservation Challenges Len McKenzie 1 & Richard Unsworth 2 1 James Cook University, Cairns, Queensland, Australia 2 Swansea University, Swansea, Wales, United Kingdom photo courtesy Ria
Seagrass: Global Conservation Challenges Len McKenzie 1 & Richard Unsworth 2 1 James Cook University, Cairns, Queensland, Australia 2 Swansea University, Swansea, Wales, United Kingdom photo courtesy Ria
Habitat Fact Sheets. Rocky habitats are dominated by seaweeds and often mussels, which rely on the rocks for attachment.
 Habitat Fact Sheets Habitats in the Gulf of Maine serve many important roles for the environment and for humans as well. These include: cycling nutrients, filtering pollution, trapping sediments, storing
Habitat Fact Sheets Habitats in the Gulf of Maine serve many important roles for the environment and for humans as well. These include: cycling nutrients, filtering pollution, trapping sediments, storing
Warm-up # 7 A day 5/17 - B day 5/18 UPDATE YOUR TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Warm-up # 7 A day 5/17 - B day 5/18 UPDATE YOUR TABLE OF CONTENTS Question: List all examples of surface water on Earth. Answer: Rivers and streams, lakes and reservoirs, (ponds) wetlands, estuaries and
Warm-up # 7 A day 5/17 - B day 5/18 UPDATE YOUR TABLE OF CONTENTS Question: List all examples of surface water on Earth. Answer: Rivers and streams, lakes and reservoirs, (ponds) wetlands, estuaries and
Examples of estuaries include bays, sounds, salt marshes, mangrove forests, mud flats, swamps, inlets, and sloughs.
 An estuary is a partially enclosed body of water where incoming seawater is mixed with fresh water coming from the land. Examples of estuaries include bays, sounds, salt marshes, mangrove forests, mud
An estuary is a partially enclosed body of water where incoming seawater is mixed with fresh water coming from the land. Examples of estuaries include bays, sounds, salt marshes, mangrove forests, mud
Sample page. Contents
 Contents Part A: Mangroves and seagrasses 5 A1. What do mangroves look like? 5 A2. Which animals use mangroves for shelter? 7 A3. How do mangroves grow? 8 A4. How do mangroves reproduce? 10 A5. Which animals
Contents Part A: Mangroves and seagrasses 5 A1. What do mangroves look like? 5 A2. Which animals use mangroves for shelter? 7 A3. How do mangroves grow? 8 A4. How do mangroves reproduce? 10 A5. Which animals
Lecture Benthic Ecology
 Lecture Benthic Ecology Benthos Unlike the drifting plankton and swimming nekton, benthic organisms commonly referred to as benthos live on or near the ocean bottom A benthic habitat may be shallow or
Lecture Benthic Ecology Benthos Unlike the drifting plankton and swimming nekton, benthic organisms commonly referred to as benthos live on or near the ocean bottom A benthic habitat may be shallow or
WHAT ARE ECOSYSTEMS? Dr. V. N. Nayak Professor of Marine Biology (Retd)
 WHAT ARE ECOSYSTEMS? Dr. V. N. Nayak Professor of Marine Biology (Retd) An ECOSYSTEM is an interacting system of plant, animals, and humans and the surrounding environment. An ecosystem contains living
WHAT ARE ECOSYSTEMS? Dr. V. N. Nayak Professor of Marine Biology (Retd) An ECOSYSTEM is an interacting system of plant, animals, and humans and the surrounding environment. An ecosystem contains living
Definitions. The environment is the biological, chemical, physical, and social conditions that surround organisms.
 Marine Ecosystems Definitions An ecosystem is a geographically specified system of organisms (including humans), the environment, and the processes that control its dynamics. The environment is the biological,
Marine Ecosystems Definitions An ecosystem is a geographically specified system of organisms (including humans), the environment, and the processes that control its dynamics. The environment is the biological,
Oceans Humans both depend on it and threaten it with their activities
 Oceans Humans both depend on it and threaten it with their activities Oceans Water covers nearly ¾ of the Earth s surface More than 50% of the world s population lives within an hour of the coast Oceans
Oceans Humans both depend on it and threaten it with their activities Oceans Water covers nearly ¾ of the Earth s surface More than 50% of the world s population lives within an hour of the coast Oceans
Harbours, bays and estuaries. at the edges of land and sea
 Harbours, bays and estuaries at the edges of land and sea Our prized snapper Snapper are fish that live not too far offshore mainly around the coasts of the North Island. They are one of New Zealand s
Harbours, bays and estuaries at the edges of land and sea Our prized snapper Snapper are fish that live not too far offshore mainly around the coasts of the North Island. They are one of New Zealand s
CHAPTER 11.1 THE WORLD OCEAN MARINE BIOMES NOTES
 CHAPTER 11.1 THE WORLD OCEAN MARINE BIOMES NOTES 1. The world ocean can be divided into zones both and. The,, and zones that apply to large lakes also apply to the ocean. 2. In addition to the depth zones,
CHAPTER 11.1 THE WORLD OCEAN MARINE BIOMES NOTES 1. The world ocean can be divided into zones both and. The,, and zones that apply to large lakes also apply to the ocean. 2. In addition to the depth zones,
dugon) ) and Seagrass in Thailand: Present Status and Future Challenges Kanjana Adulyanukosol Sombat Poovachiranon Mickmin Charuchida
 Dugong ( (Dugong dugon) ) and Seagrass in Thailand: Present Status and Future Challenges Kanjana Adulyanukosol Sombat Poovachiranon Mickmin Charuchida Phuket Marine Biological Center (PMBC) Department
Dugong ( (Dugong dugon) ) and Seagrass in Thailand: Present Status and Future Challenges Kanjana Adulyanukosol Sombat Poovachiranon Mickmin Charuchida Phuket Marine Biological Center (PMBC) Department
Oceans Alive Resource Book
 E-BOOK CODE: REAU5023 Special School Photocopy Master Edition Oceans Alive Resource Book Image courtesy Microsoft Design Gallery by Sandy Tasker Contents OCEANS ALIVE Contents... 3 The Wonderful World
E-BOOK CODE: REAU5023 Special School Photocopy Master Edition Oceans Alive Resource Book Image courtesy Microsoft Design Gallery by Sandy Tasker Contents OCEANS ALIVE Contents... 3 The Wonderful World
Key Stage 1 ACTIVITY BOOK Ages 5-7
 Key Stage 1 ACTIVITY BOOK Ages 5-7 Teacher Answer Booklet Hi! My name is Seamor. Answer my questions as we go around the aquarium. Front Room 1. What colour are the Crawfish in the front room? Orange/Brown
Key Stage 1 ACTIVITY BOOK Ages 5-7 Teacher Answer Booklet Hi! My name is Seamor. Answer my questions as we go around the aquarium. Front Room 1. What colour are the Crawfish in the front room? Orange/Brown
Restoration of Eelgrass to Upper Casco Bay: Feasibility Tests in Hilary A. Neckles US Geological Survey Augusta, ME
 Restoration of Eelgrass to Upper Casco Bay: Feasibility Tests in 2015 Hilary A. Neckles US Geological Survey Augusta, ME hneckles@usgs.gov Robert J. Orth Eelgrass: Zostera marina * marine flowering plant
Restoration of Eelgrass to Upper Casco Bay: Feasibility Tests in 2015 Hilary A. Neckles US Geological Survey Augusta, ME hneckles@usgs.gov Robert J. Orth Eelgrass: Zostera marina * marine flowering plant
Coastal areas have become increasingly under threat in recent years. Climate change is having a huge effect on coastal areas, making them much more
 Why are some coastal environments under threat? Coastal areas have become increasingly under threat in recent years. Climate change is having a huge effect on coastal areas, making them much more likely
Why are some coastal environments under threat? Coastal areas have become increasingly under threat in recent years. Climate change is having a huge effect on coastal areas, making them much more likely
Types of Freshwater Ecosystems. Streams originate from underground water. Rivers form when streams join together. Freshwater Biome
 Definition Streams originate from underground water sources Types of Freshwater Ecosystems Streams Rivers Rivers form when streams join together Freshwater Lakes Ponds Basic Characteristics Directional
Definition Streams originate from underground water sources Types of Freshwater Ecosystems Streams Rivers Rivers form when streams join together Freshwater Lakes Ponds Basic Characteristics Directional
For Creative Minds. Salt Marsh Plants and Animals
 For Creative Minds The For Creative Minds educational section may be photocopied or printed from our website by the owner of this book for educational, non-commercial uses. Cross-curricular teaching activities,
For Creative Minds The For Creative Minds educational section may be photocopied or printed from our website by the owner of this book for educational, non-commercial uses. Cross-curricular teaching activities,
PHYLUM: PLATHYHELMINTHES
 PHYLUM: PLATHYHELMINTHES FLATWORMS Free living (living independently i.e. not attached) Bilaterally symmetrical with a definite front and back, and with left and right sides. Mobile creeping animals. Concentration
PHYLUM: PLATHYHELMINTHES FLATWORMS Free living (living independently i.e. not attached) Bilaterally symmetrical with a definite front and back, and with left and right sides. Mobile creeping animals. Concentration
Let s take a closer look at estuaries and learn why they are important.
 ave you ever wondered what happens where a river or stream flows into the ocean? When fresh water meets saltwater in a protected bay or inlet, a partially enclosed body of water called an estuary often
ave you ever wondered what happens where a river or stream flows into the ocean? When fresh water meets saltwater in a protected bay or inlet, a partially enclosed body of water called an estuary often
Exploring Tide Pools. Exploring Tide Pools. Visit for thousands of books and materials.
 Exploring Tide Pools A Reading A Z Level R Leveled Reader Word Count: 1,617 LEVELED READER R Exploring Tide Pools Written by Trica Oshant Hawkins Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials.
Exploring Tide Pools A Reading A Z Level R Leveled Reader Word Count: 1,617 LEVELED READER R Exploring Tide Pools Written by Trica Oshant Hawkins Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials.
The mangroves. The mangrove environment. The excursion
 The mangroves Now you are going to investigate an environment that you may have experienced the mangrove swamp. You will use this environment to practise writing food chains. To do this, you are going
The mangroves Now you are going to investigate an environment that you may have experienced the mangrove swamp. You will use this environment to practise writing food chains. To do this, you are going
Seagrass Surveys in Kampot
 Coastal Annual Forum 23 rd October 2014 Sihanoukville, Cambodia Seagrass Surveys in Kampot Presentation by Louis Bourne INTERNATIONAL UNION FOR CONSERVATION OF NATURE Presentation Overview Location and
Coastal Annual Forum 23 rd October 2014 Sihanoukville, Cambodia Seagrass Surveys in Kampot Presentation by Louis Bourne INTERNATIONAL UNION FOR CONSERVATION OF NATURE Presentation Overview Location and
Marine Environments. Copyright 2011 LessonSnips
 Marine Environments I must go down to the seas again, for the call of the running tide Is a wild call and a clear call that may not be denied Excerpt from a poem by John Masefield Continents and islands
Marine Environments I must go down to the seas again, for the call of the running tide Is a wild call and a clear call that may not be denied Excerpt from a poem by John Masefield Continents and islands
Front Room. 1. There are several different types of flatfish in the pier tank. Name two species of flatfish you can see. and
 Key Stage 2 Lower ACTIVITY BOOK Ages 7-9 Name: Class: Date: Front Room Welcome to Anglesey Sea Zoo! Hi! My name is Seamor, and in this activity book my friends and I will give you lots of fun facts about
Key Stage 2 Lower ACTIVITY BOOK Ages 7-9 Name: Class: Date: Front Room Welcome to Anglesey Sea Zoo! Hi! My name is Seamor, and in this activity book my friends and I will give you lots of fun facts about
Over the next few weeks, we will be learning all about the Coral Reef Ecosystems that surround much of the Australian coastline.
 Over the next few weeks, we will be learning all about the Coral Reef Ecosystems that surround much of the Australian coastline. You will need to complete the tasks set out below and hand them in at the
Over the next few weeks, we will be learning all about the Coral Reef Ecosystems that surround much of the Australian coastline. You will need to complete the tasks set out below and hand them in at the
What do animals eat?
 What do animals eat? Name: Class: No. 1. Use the words in the box to finish the sentences about carnivores. eat animals meat carnivores are animals that eat Draw a picture of what a carnivore eats. only.
What do animals eat? Name: Class: No. 1. Use the words in the box to finish the sentences about carnivores. eat animals meat carnivores are animals that eat Draw a picture of what a carnivore eats. only.
Fish Texas AQUATIC ECOSYSTEMS
 27 Additionally, healthy aquatic communities in Texas rivers, reservoirs and estuaries provide unparalleled recreational opportunities to millions of Texans. Our fresh and saltwater environments vary from
27 Additionally, healthy aquatic communities in Texas rivers, reservoirs and estuaries provide unparalleled recreational opportunities to millions of Texans. Our fresh and saltwater environments vary from
Why protect seagrass beds?
 Why protect seagrass beds? Fish need healthy places to live, feed and reproduce. They also need corridors or pathways to migrate between these places. Those places that supply fishes with their life cycle
Why protect seagrass beds? Fish need healthy places to live, feed and reproduce. They also need corridors or pathways to migrate between these places. Those places that supply fishes with their life cycle
Key Stage 1 ACTIVITY BOOK Ages 5-7
 Key Stage 1 ACTIVITY BOOK Ages 5-7 Name: Class: Date: Hi! My name is Seamor. Answer my questions as we go around the aquarium. Front Room 1. What colour are the Crawfish in the front room? 2. Draw a line
Key Stage 1 ACTIVITY BOOK Ages 5-7 Name: Class: Date: Hi! My name is Seamor. Answer my questions as we go around the aquarium. Front Room 1. What colour are the Crawfish in the front room? 2. Draw a line
Seagrasses of the Virgin Islands
 Seagrasses of the Virgin Islands Seagrasses are flowering plants that live underwater. These marine plants resemble the land species of grasses in that they have long blade-like leaves. Seagrasses grow
Seagrasses of the Virgin Islands Seagrasses are flowering plants that live underwater. These marine plants resemble the land species of grasses in that they have long blade-like leaves. Seagrasses grow
Secret Gardens under the Sea: What. They Important? SEA PLEASE KEEP OFF GRASS
 the Earth and its Resources Published: 01 February 2018 doi:10.3389/frym.2018.00002 SEA PLEASE KEEP OFF GRASS Secret Gardens under the Sea: What Are and Why Are They Important? Leanne Claire Cullen-Unsworth
the Earth and its Resources Published: 01 February 2018 doi:10.3389/frym.2018.00002 SEA PLEASE KEEP OFF GRASS Secret Gardens under the Sea: What Are and Why Are They Important? Leanne Claire Cullen-Unsworth
Seagrass-Watch Proceedings of a workshop for monitoring seagrass habitats in the Noosa region, South East Queensland CWA Hall, Tewantin 9-10 March
 Seagrass-Watch Proceedings of a workshop for monitoring seagrass habitats in the Noosa region, South East Queensland CWA Hall, Tewantin 9-10 March 2013 Len McKenzie & Rudi Yoshida First Published 2013
Seagrass-Watch Proceedings of a workshop for monitoring seagrass habitats in the Noosa region, South East Queensland CWA Hall, Tewantin 9-10 March 2013 Len McKenzie & Rudi Yoshida First Published 2013
Diving Deeper, discovering how the marine environment ticks!
 1 Diving Deeper Diving Deeper, discovering how the marine environment ticks! The Marine Environment Over 3,000 million years ago, life may have begun in the sea as simple bacteria. As ancient time progressed,
1 Diving Deeper Diving Deeper, discovering how the marine environment ticks! The Marine Environment Over 3,000 million years ago, life may have begun in the sea as simple bacteria. As ancient time progressed,
Review of the current impacts of Dredge Spoil Islands and water circulation on adjacent seagrass beds Swansea Flats
 Office of the Lake Macquarie and Catchment Co-ordinator Review of the current impacts of Dredge Spoil Islands and water circulation on adjacent seagrass beds Swansea Flats March 2004 TABLE OF CONTENTS
Office of the Lake Macquarie and Catchment Co-ordinator Review of the current impacts of Dredge Spoil Islands and water circulation on adjacent seagrass beds Swansea Flats March 2004 TABLE OF CONTENTS
LiMPETS Sandy Beach Monitoring Classroom Presentation - SCRIPT
 LiMPETS Sandy Beach Monitoring Classroom Presentation - SCRIPT I m really excited to talk to you about the LiMPETS program for which you guys will participate as marine scientists. LiMPETS stands for Long-Term
LiMPETS Sandy Beach Monitoring Classroom Presentation - SCRIPT I m really excited to talk to you about the LiMPETS program for which you guys will participate as marine scientists. LiMPETS stands for Long-Term
Questions # 4 7 refer to Figure # 2 (page 321, Fig )
 Shoreline Community College OCEANOGRAPHY 101 Fall 2006 Sample Exam # 3 Instructor: Linda Khandro Questions # 1 3 refer to Figure # 1 (page 284, Fig 11.7) 1. At which position is the moon in its new moon
Shoreline Community College OCEANOGRAPHY 101 Fall 2006 Sample Exam # 3 Instructor: Linda Khandro Questions # 1 3 refer to Figure # 1 (page 284, Fig 11.7) 1. At which position is the moon in its new moon
Seagrass-Watch Guidelines for Torres Strait Land & Sea Rangers
 Seagrass-Watch Guidelines for Torres Strait Land & Sea Rangers Port Kennedy Association Hall, Thursday Island 26 th February 2007 Len McKenzie & Jane Mellors Department of Primary Industries & Fisheries,
Seagrass-Watch Guidelines for Torres Strait Land & Sea Rangers Port Kennedy Association Hall, Thursday Island 26 th February 2007 Len McKenzie & Jane Mellors Department of Primary Industries & Fisheries,
Seventh Grade. Maui Ocean Center Learning Worksheet. Name: Our mission is to foster understanding, wonder and respect for Hawai i s Marine Life.
 Name: Maui Ocean Center Learning Worksheet Seventh Grade Our mission is to foster understanding, wonder and respect for Hawai i s Marine Life. Based on benchmarks SC.6.3.1, SC. 7.3.1, SC. 7.3.2, SC. 7.5.4
Name: Maui Ocean Center Learning Worksheet Seventh Grade Our mission is to foster understanding, wonder and respect for Hawai i s Marine Life. Based on benchmarks SC.6.3.1, SC. 7.3.1, SC. 7.3.2, SC. 7.5.4
UMVERSITI MALAYSIA SABAW
 UMVERSITI MALAYSIA SABAW Community and Education-based monitoring sf seagrass in Sabah, Malaysia A workshop organized by Borneo Marine Research Institute, University of Malaysia, Sa ba h. in collaboration
UMVERSITI MALAYSIA SABAW Community and Education-based monitoring sf seagrass in Sabah, Malaysia A workshop organized by Borneo Marine Research Institute, University of Malaysia, Sa ba h. in collaboration
Learning Pad Launch Portal S & T Activities Producers and Consumers activity
 Activities Producers and Consumers activity Google DCDSB. Click on the DCDSB website. Near the top of the screen, click on Students. Down the right side of the screen, click on the LaunchPad Learning Portal
Activities Producers and Consumers activity Google DCDSB. Click on the DCDSB website. Near the top of the screen, click on Students. Down the right side of the screen, click on the LaunchPad Learning Portal
Sustainable Recreational Fishing Student Activity Workbook 6.2. Sustainable Recreational Fishing
 Sustainable Recreational Fishing! Activity zone 1 - Recreational Fishing Panel Fishing is a popular pastime for more millions Australians each year but is not the only way to enjoy our lakes and coastline.
Sustainable Recreational Fishing! Activity zone 1 - Recreational Fishing Panel Fishing is a popular pastime for more millions Australians each year but is not the only way to enjoy our lakes and coastline.
Seagrasses: Vital Habitat in Texas Estuaries
 Seagrasses: Vital Habitat in Texas Estuaries Cindy Hobson Water Resources Branch Coastal Fisheries Division Texas Parks and Wildlife Department February 17, 2015 Why Care About Seagrass? Sustain coastal
Seagrasses: Vital Habitat in Texas Estuaries Cindy Hobson Water Resources Branch Coastal Fisheries Division Texas Parks and Wildlife Department February 17, 2015 Why Care About Seagrass? Sustain coastal
Dinner Dilemma [Grades 3-5]
![Dinner Dilemma [Grades 3-5] Dinner Dilemma [Grades 3-5]](/thumbs/93/112477039.jpg) Dinner Dilemma [Grades 3-5] Georgia Standards of Excellence Addressed: S4L1. Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information about the roles of organisms and the flow of energy within an ecosystem. a. Develop
Dinner Dilemma [Grades 3-5] Georgia Standards of Excellence Addressed: S4L1. Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information about the roles of organisms and the flow of energy within an ecosystem. a. Develop
Seagrass Educators Handbook By Len McKenzie (Seagrass-Watch HQ/DPI&F), Feb 2008
 Seagrass-Watch Seagrass Educators Handbook By Len McKenzie (Seagrass-Watch HQ/DPI&F), Feb 2008 This handbook provides educators with information on what seagrasses are, their plant morphology and anatomy,
Seagrass-Watch Seagrass Educators Handbook By Len McKenzie (Seagrass-Watch HQ/DPI&F), Feb 2008 This handbook provides educators with information on what seagrasses are, their plant morphology and anatomy,
Seagrass-Watch Proceedings of a workshop for monitoring seagrass habitats in the Kimberley region, Western Australia Department of Parks and Wildlife
 Seagrass-Watch Proceedings of a workshop for monitoring seagrass habitats in the Kimberley region, Western Australia Department of Parks and Wildlife (DPaW) - Broome Work Centre Broome, Western Australia
Seagrass-Watch Proceedings of a workshop for monitoring seagrass habitats in the Kimberley region, Western Australia Department of Parks and Wildlife (DPaW) - Broome Work Centre Broome, Western Australia
Marine Ecosystems. Objectives. Key Terms SECTION 2
 SECTION 2 Marine Ecosystems Marine ecosystems of the world are made up of a wide variety of plant and animal communities. Marine ecosystems are located mainly in coastal areas and in the open ocean. Organisms
SECTION 2 Marine Ecosystems Marine ecosystems of the world are made up of a wide variety of plant and animal communities. Marine ecosystems are located mainly in coastal areas and in the open ocean. Organisms
Lesson 10: Oyster Reefs and Their Inhabitants
 Lesson 10: Oyster Reefs and Their Inhabitants Focus Question: What animals use oyster reefs for habitats? Objective: observe properties of animals found within a bag of oysters; Infer about the quality
Lesson 10: Oyster Reefs and Their Inhabitants Focus Question: What animals use oyster reefs for habitats? Objective: observe properties of animals found within a bag of oysters; Infer about the quality
Seagrass-Watch Proceedings of a workshop for monitoring seagrass habitats in South East Queensland QPWS, Moreton Bay Manly Office August 2013 Len
 Seagrass-Watch Proceedings of a workshop for monitoring seagrass habitats in South East Queensland QPWS, Moreton Bay Manly Office August 2013 Len McKenzie & Rudi Yoshida First Published 2013 Seagrass Watch
Seagrass-Watch Proceedings of a workshop for monitoring seagrass habitats in South East Queensland QPWS, Moreton Bay Manly Office August 2013 Len McKenzie & Rudi Yoshida First Published 2013 Seagrass Watch
1. Distribute the activity sheet, and allow 20 minutes for the first use.
 A LOCAL WAY OF LEARNING Title: MISSING MANGROVE MESSAGE Author: Eulalie R. Rivera Elementary School Environmental Education Team Grade Level: 4-6 Concepts: 2.Ecosystem 6.Resources 9.Change Disciplines:
A LOCAL WAY OF LEARNING Title: MISSING MANGROVE MESSAGE Author: Eulalie R. Rivera Elementary School Environmental Education Team Grade Level: 4-6 Concepts: 2.Ecosystem 6.Resources 9.Change Disciplines:
A North Australian Food Web Game
 A North Australian Food Web Game by Barbara E. Wueringer, Hannah Cook and Jillian Morris Brake with special thanks to Stirling Peverell and Paul Lennon SARA The Food Web Game V 1.4 November 2018 2 Author
A North Australian Food Web Game by Barbara E. Wueringer, Hannah Cook and Jillian Morris Brake with special thanks to Stirling Peverell and Paul Lennon SARA The Food Web Game V 1.4 November 2018 2 Author
5/8/2018. Estuaries are classified by: > Mode of formation e.g. glaciers, deposition, sea level rise. > Patterns of water circulation
 Prepared by Diana Wheat-LBCC Compare and contrast the various types of estuaries, including their origin, size, shape, and general location on earth. Distinguish and describe the different types of habitats
Prepared by Diana Wheat-LBCC Compare and contrast the various types of estuaries, including their origin, size, shape, and general location on earth. Distinguish and describe the different types of habitats
Barnacles attach to hard surfaces and use their legs to catch tiny particles of food, including plankton from the water around them.
 Food Web Resources - Food Chain Cards Barnacles attach to hard surfaces and use their legs to catch tiny particles of food, including plankton from the water around them Barnacle Edible crabs use their
Food Web Resources - Food Chain Cards Barnacles attach to hard surfaces and use their legs to catch tiny particles of food, including plankton from the water around them Barnacle Edible crabs use their
Puget Sound Shorelines. Waves and coastal processes. Puget Sound shorelines: Effects of beach armoring
 Puget Sound Shorelines Puget Sound shorelines: Effects of beach armoring Waves and coastal processes Factors affecting wave energy hitting the coast Processes transporting sediment along coastlines What
Puget Sound Shorelines Puget Sound shorelines: Effects of beach armoring Waves and coastal processes Factors affecting wave energy hitting the coast Processes transporting sediment along coastlines What
Mark L. Botton and Robert E. Loveland. The Importance of Horseshoe Crabs in the Ecology of Delaware Bay: More than Just Bird Food?
 Mark L. Botton and Robert E. Loveland The Importance of Horseshoe Crabs in the Ecology of Delaware Bay: More than Just Bird Food? Getting Beyond the Bird Food Paradigm: Other Ecological Roles for HSC s
Mark L. Botton and Robert E. Loveland The Importance of Horseshoe Crabs in the Ecology of Delaware Bay: More than Just Bird Food? Getting Beyond the Bird Food Paradigm: Other Ecological Roles for HSC s
FACT SHEET#4: SOME ANIMALS IN THE MANGROVE SWAMP
 FACT SHEET#4: SOME ANIMALS IN THE MANGROVE SWAMP SOME ANIMALS IN THE MANGROVE SWAMP A mangrove swamp is home to many animals. Below are some animals that can be commonly found in the mangrove swamp, and
FACT SHEET#4: SOME ANIMALS IN THE MANGROVE SWAMP SOME ANIMALS IN THE MANGROVE SWAMP A mangrove swamp is home to many animals. Below are some animals that can be commonly found in the mangrove swamp, and
Ocean Environmental Science Art Workshop
 Ocean Environmental Science Art Workshop An integrated learning module for primary schools designed and facilitated by the artist Angela Rossen The images here show the workshop with the students in Year
Ocean Environmental Science Art Workshop An integrated learning module for primary schools designed and facilitated by the artist Angela Rossen The images here show the workshop with the students in Year
Part 4: Ocean Life Zones
 Part 4: Ocean Life Zones 1 Factors that Affect Life in the Ocean 1. Amount of sunlight 2. Temperature of the water 3. Water pressure How does depth affect each of these? Where would you expect to find
Part 4: Ocean Life Zones 1 Factors that Affect Life in the Ocean 1. Amount of sunlight 2. Temperature of the water 3. Water pressure How does depth affect each of these? Where would you expect to find
Saltwater detective guide
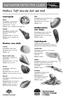 Saltwater detective guide Molluscs: Soft muscular foot and shell Gastropods Snail Description: rounded shell, grey/brown/cream colours. Various sizes: 5 30 mm Habitat: sand or mudflats and Whelk Description:
Saltwater detective guide Molluscs: Soft muscular foot and shell Gastropods Snail Description: rounded shell, grey/brown/cream colours. Various sizes: 5 30 mm Habitat: sand or mudflats and Whelk Description:
Port Curtis and Rodds Bay seagrass and benthic macro-invertebrate community baseline survey
 INFORMATION SERIES QI03058 Port Curtis and Rodds Bay seagrass and benthic macro-invertebrate community baseline survey November/December 2002 M A Rasheed R Thomas A J Roelofs K M Neil and S P Kerville
INFORMATION SERIES QI03058 Port Curtis and Rodds Bay seagrass and benthic macro-invertebrate community baseline survey November/December 2002 M A Rasheed R Thomas A J Roelofs K M Neil and S P Kerville
Dr. Prakash N. Mesta
 Coastal Wetland Monitoring Dr. Prakash N. Mesta prakashhonavar@gmail.com Coastal Ecosystem is diverse in nature Most of the world human population p settled in Coastal region. Cities & Industries established
Coastal Wetland Monitoring Dr. Prakash N. Mesta prakashhonavar@gmail.com Coastal Ecosystem is diverse in nature Most of the world human population p settled in Coastal region. Cities & Industries established
A DAY AT THE WHITNEY LAB The Whitney Laboratory for Marine Bioscience An Institute for Marine Research and Biotechnology
 A DAY AT THE WHITNEY LAB The Whitney Laboratory for Marine Bioscience An Institute for Marine Research and Biotechnology STUDENT NAME: What s For Lunch? The Mission In this activity, you will make an educated
A DAY AT THE WHITNEY LAB The Whitney Laboratory for Marine Bioscience An Institute for Marine Research and Biotechnology STUDENT NAME: What s For Lunch? The Mission In this activity, you will make an educated
Seagrass-Watch. Len McKenzie
 Seagrass-Watch Proceedings of a Workshop for Mapping and Monitoring Seagrass Habitats in North East Arnhem Land, Northern Territory 18 th 20 th October 2008 Len McKenzie Seagrass-Watch HQ Table of Contents
Seagrass-Watch Proceedings of a Workshop for Mapping and Monitoring Seagrass Habitats in North East Arnhem Land, Northern Territory 18 th 20 th October 2008 Len McKenzie Seagrass-Watch HQ Table of Contents
The Great Barrier Reef
 The Great Barrier Reef The Great Barrier Reef Where are the most biologically diverse places on the planet? If I asked you this question, you might guess the Amazon rainforest in Brazil or the jungles
The Great Barrier Reef The Great Barrier Reef Where are the most biologically diverse places on the planet? If I asked you this question, you might guess the Amazon rainforest in Brazil or the jungles
Green crabs: invaders in the Great Marsh Featured scientist: Alyssa Novak from the Center for Coastal Studies/Boston University
 Name Green crabs: invaders in the Great Marsh Featured scientist: Alyssa Novak from the Center for Coastal Studies/Boston University Research Background: Marshes are areas along the coast that flood with
Name Green crabs: invaders in the Great Marsh Featured scientist: Alyssa Novak from the Center for Coastal Studies/Boston University Research Background: Marshes are areas along the coast that flood with
ZOOPLANKTON. Zooplankton: 2. Crustaceans Copepods. Diverse -- protozoans and others
 ZOOPLANKTON Diverse -- protozoans and others Nutrition modes: Herbivores (graze on phytoplankton) Carnivores (predators) Radiolaria Foraminifera Zooplankton: 1. Protozoans: Foraminifera and Radiolarians
ZOOPLANKTON Diverse -- protozoans and others Nutrition modes: Herbivores (graze on phytoplankton) Carnivores (predators) Radiolaria Foraminifera Zooplankton: 1. Protozoans: Foraminifera and Radiolarians
Underwater Secrets of a Marine Protected Area. A Lesson Plan for Grades 4 to 8. Power Point Prepared by Susan Miller
 Underwater Secrets of a Marine Protected Area A Lesson Plan for Grades 4 to 8 Power Point Prepared by Susan Miller Photographs by Jerry Loomis, California State Parks Ranger Josh Pederson, MPA SIMoN Steve
Underwater Secrets of a Marine Protected Area A Lesson Plan for Grades 4 to 8 Power Point Prepared by Susan Miller Photographs by Jerry Loomis, California State Parks Ranger Josh Pederson, MPA SIMoN Steve
Chapter 15 : Fisheries and Aquaculture
 Chapter 15 : Fisheries and Aquaculture identify the importance of marine ecosystems to Newfoundland and Labrador. Include: Note - oceans and greenhouse gas control : oceans surface (photic zone) abundant
Chapter 15 : Fisheries and Aquaculture identify the importance of marine ecosystems to Newfoundland and Labrador. Include: Note - oceans and greenhouse gas control : oceans surface (photic zone) abundant
Prof.Dr.Hanan M Mitwally, Marine Biology. Objectives
 Definition. Benthos & Nekton Objectives Some forms of phyto-benthos. Relationship between size of organisms and abundance. Marine Animals. Marine invertebrates. Coral reefs Marine vertebrates. Fish Mammals.
Definition. Benthos & Nekton Objectives Some forms of phyto-benthos. Relationship between size of organisms and abundance. Marine Animals. Marine invertebrates. Coral reefs Marine vertebrates. Fish Mammals.
5 th Grade Science Pre-assessment Organisms & Environments Unit 5 KEY
 5 th Grade Science Pre-assessment Organisms & Environments Unit 5 KEY 1. Sun Grass Grasshopper Spider Bird Using the food chain above, how would a large decrease in the spider population affect the other
5 th Grade Science Pre-assessment Organisms & Environments Unit 5 KEY 1. Sun Grass Grasshopper Spider Bird Using the food chain above, how would a large decrease in the spider population affect the other
Activity 4: Investigating marine ecosystems
 Activity 4: Investigating marine ecosystems Let s learn about feeding behaviours and relationships in the marine environment CURRICULUM LINKS Learning areas Learning intention Success criteria Science:
Activity 4: Investigating marine ecosystems Let s learn about feeding behaviours and relationships in the marine environment CURRICULUM LINKS Learning areas Learning intention Success criteria Science:
Marine Math. A 4 th Grade Field Trip Guide to The Texas State Aquarium STUDENT BOOKLET
 Marine Math A 4 th Grade Field Trip Guide to The Texas State Aquarium STUDENT BOOKLET Copyright Erin Saenz, 2010. Permission granted for educational purposes only. This permission does not extend to copying
Marine Math A 4 th Grade Field Trip Guide to The Texas State Aquarium STUDENT BOOKLET Copyright Erin Saenz, 2010. Permission granted for educational purposes only. This permission does not extend to copying
The Ocean and Fisheries
 Visualizing Environmental Science The Ocean and Fisheries Chapter 11 Chapter 7 [chapter [chapter opener opener image] Copyright The Global Ocean Patterns of circulation Winds over the ocean produce currents
Visualizing Environmental Science The Ocean and Fisheries Chapter 11 Chapter 7 [chapter [chapter opener opener image] Copyright The Global Ocean Patterns of circulation Winds over the ocean produce currents
Kuala Lawas INTRODUCTION. Why is Kuala Lawas IMPORTANT? DISTRIBUTION OF SEAGRASS IN THE WATERS OF LAWAS, SARAWAK.
 DISTRIBUTION OF SEAGRASS IN THE WATERS OF LAWAS, SARAWAK. Oswald Braken TISEN, James BALI, Samantha KWAN, Shirley NANING, Eda IZANIE. Regional Meeting on Conservation & Management of Sea Turtle Foraging
DISTRIBUTION OF SEAGRASS IN THE WATERS OF LAWAS, SARAWAK. Oswald Braken TISEN, James BALI, Samantha KWAN, Shirley NANING, Eda IZANIE. Regional Meeting on Conservation & Management of Sea Turtle Foraging
Dr. Kim Peyton. (w/ some modifications by Dr. Bruland) University of Hawai i Mānoa
 The Seagrasses Dr. Kim Peyton (w/ some modifications by Dr. Bruland) University of Hawai i Mānoa Department t of Botany 1 Outline Anatomy Characteristics Taxonomy, systematics, &evolution Distribution
The Seagrasses Dr. Kim Peyton (w/ some modifications by Dr. Bruland) University of Hawai i Mānoa Department t of Botany 1 Outline Anatomy Characteristics Taxonomy, systematics, &evolution Distribution
Dewees Island Game Fish & Shellfish
 Dewees Island Game Fish & Shellfish Red Drum Also called: spottail, spottail bass, channel bass, redfish, puppy drum Limit: 2 per person, per day Size: 15-inch minimum, 24-inch maximum Remarks: Red drum
Dewees Island Game Fish & Shellfish Red Drum Also called: spottail, spottail bass, channel bass, redfish, puppy drum Limit: 2 per person, per day Size: 15-inch minimum, 24-inch maximum Remarks: Red drum
Marine Math. A 5 th Grade Field Trip Guide to The Texas State Aquarium STUDENT BOOKLET
 Marine Math A 5 th Grade Field Trip Guide to The Texas State Aquarium STUDENT BOOKLET Copyright Erin Saenz, 2010. Permission granted for educational purposes only. This permission does not extend to copying
Marine Math A 5 th Grade Field Trip Guide to The Texas State Aquarium STUDENT BOOKLET Copyright Erin Saenz, 2010. Permission granted for educational purposes only. This permission does not extend to copying
SEAGRASS SURVEY CALATAGAN
 SEAGRASS SURVEY CALATAGAN Conducted with the sponsorship of the CAP Oceans Foundation Angela Quiros, PH.D Candidate University of California Santa Cruz and Cori Hume, Leslie Hart, Ian Jacobson, Jordan
SEAGRASS SURVEY CALATAGAN Conducted with the sponsorship of the CAP Oceans Foundation Angela Quiros, PH.D Candidate University of California Santa Cruz and Cori Hume, Leslie Hart, Ian Jacobson, Jordan
Middle to Upper Primary Grades 3 to 6
 Booklet Coastal Discovery Middle to Upper Primary Grades 3 to 6 Student Name:... School:... Beach:... Date:... 1 Additional copies of the Coastal Discovery booklets can be downloaded from the Cradle Coast
Booklet Coastal Discovery Middle to Upper Primary Grades 3 to 6 Student Name:... School:... Beach:... Date:... 1 Additional copies of the Coastal Discovery booklets can be downloaded from the Cradle Coast
Reef Watch Guidelines
 Reef Watch Guidelines What is Reef Watch? Reef watch is a simple one-dive-one-survey method to record the health of coral reefs. The method is easily learnt and it is even easier to participate in the
Reef Watch Guidelines What is Reef Watch? Reef watch is a simple one-dive-one-survey method to record the health of coral reefs. The method is easily learnt and it is even easier to participate in the
 OCTOPUS Found throughout the world in tropical, warm and cold temperate waters - the octopus is a bottom dweller, spending much of its life in hiding, usually in a hole among rocks. All octopus species
OCTOPUS Found throughout the world in tropical, warm and cold temperate waters - the octopus is a bottom dweller, spending much of its life in hiding, usually in a hole among rocks. All octopus species
SCRIPPS BIRCH AQUARIUM WORKSHEET
 SCRIPPS BIRCH AQUARIUM WORKSHEET Name 1. Read over the Student Learning Outcomes and associated General Questions on this page, and refer back and take notes on this page as you walk through the aquarium,
SCRIPPS BIRCH AQUARIUM WORKSHEET Name 1. Read over the Student Learning Outcomes and associated General Questions on this page, and refer back and take notes on this page as you walk through the aquarium,
Activity Book. Help protect our soil, air, woods, waters, and wildlife
 A program of the Izaak Activity Book Activities to educate and encourage future conservation leaders Recommended Ages: 6 to 8 Find the hidden pictures. See back cover. Help protect our soil, air, woods,
A program of the Izaak Activity Book Activities to educate and encourage future conservation leaders Recommended Ages: 6 to 8 Find the hidden pictures. See back cover. Help protect our soil, air, woods,
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level *4245615796* MARINE SCIENCE 9693/03 Paper 3 A2 Structured Questions May/June 2015 1 hour 30 minutes Candidates
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level *4245615796* MARINE SCIENCE 9693/03 Paper 3 A2 Structured Questions May/June 2015 1 hour 30 minutes Candidates
Species Conclusions Table
 Conclusions Table Project Name: Chesapeake Landing HOA- Breakwaters (NAO-14-0283) Date: February 25, 2014 /Resource Name Loggerhead sea turtle (Caretta caretta) Conclusion ESA Section 7 / Eagle Act Determination
Conclusions Table Project Name: Chesapeake Landing HOA- Breakwaters (NAO-14-0283) Date: February 25, 2014 /Resource Name Loggerhead sea turtle (Caretta caretta) Conclusion ESA Section 7 / Eagle Act Determination
Seagrass-Watch Proceedings of Workshops for Monitoring Seagrass Habitats in South East Queensland
 Seagrass-Watch Proceedings of Workshops for Monitoring Seagrass Habitats in South East Queensland Capalaba Baseball Club, Sheldon, Brisbane 24 th November 2007 & Gecko House, Currumbin, Gold Coast 25 th
Seagrass-Watch Proceedings of Workshops for Monitoring Seagrass Habitats in South East Queensland Capalaba Baseball Club, Sheldon, Brisbane 24 th November 2007 & Gecko House, Currumbin, Gold Coast 25 th
SCI-3 MMS Science Review Quiz #1 Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions
 SCI-3 MMS Science Review Quiz #1 Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:218C58 1 Some birds fly south for the winter. Birds know when and where to fly because of A hibernation B mimicry
SCI-3 MMS Science Review Quiz #1 Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:218C58 1 Some birds fly south for the winter. Birds know when and where to fly because of A hibernation B mimicry
Any Age. Ocean Animals. Express Lapbook SAMPLE PAGE. A Journey Through Learning
 A J T L Any Age Ocean Animals Express Lapbook Mini Lapbook, Study Guide, Activities, and Crafts A Journey Through Learning www.ajourneythroughlearning.com Copyright 2013 A Journey Through Learning 1 Authors-Paula
A J T L Any Age Ocean Animals Express Lapbook Mini Lapbook, Study Guide, Activities, and Crafts A Journey Through Learning www.ajourneythroughlearning.com Copyright 2013 A Journey Through Learning 1 Authors-Paula
LK Increasing knowledge on sea grass habitats and dugong distribution at selected sites in North Western Sri Lanka Project progress July2016
 LK6-2132 Increasing knowledge on sea grass habitats and dugong distribution at selected sites in North Western Sri Lanka Project progress July2016 ORCA Ocean Resources Conservation Association This is
LK6-2132 Increasing knowledge on sea grass habitats and dugong distribution at selected sites in North Western Sri Lanka Project progress July2016 ORCA Ocean Resources Conservation Association This is
Kelp Forest Conservation Food web activity
 Kelp Forest Conservation Food web activity Activity Steps Cut out the kelp forest food web organisms cards. Have students form small groups. Pass out one food web organism and to each group. Using a blank
Kelp Forest Conservation Food web activity Activity Steps Cut out the kelp forest food web organisms cards. Have students form small groups. Pass out one food web organism and to each group. Using a blank
Proceedings of the 7th Internationa. SEASTAR2000 workshop) (2012):
 Title Productivity and Distribution of Se Davao Gulf Author(s) NOEL, HELEN W.; LUCERO, RUTH S.; SA PARCASIO JR; LABIS, PETER Y.; LUCER Proceedings of the 7th Internationa Citation SEASTAR2000 and Asian
Title Productivity and Distribution of Se Davao Gulf Author(s) NOEL, HELEN W.; LUCERO, RUTH S.; SA PARCASIO JR; LABIS, PETER Y.; LUCER Proceedings of the 7th Internationa Citation SEASTAR2000 and Asian
Lobsters, Crab and Shrimp
 Lobsters, Crab and Shrimp Crustaceans Phylum: Arthropoda ( jointed feet ) Invertebrate Exoskeleton (made of chitin) protects body and provides a place for muscles to attach to. Segmented body Jointed appendages
Lobsters, Crab and Shrimp Crustaceans Phylum: Arthropoda ( jointed feet ) Invertebrate Exoskeleton (made of chitin) protects body and provides a place for muscles to attach to. Segmented body Jointed appendages
Chloe is a Civil Engineer
 Chloe the Crab Chloe is a Civil Engineer Civil engineers design bridges, roads, skyscrapers and other things you see every day. The tools Chloe uses are: Computer Scale Plans Books Count the Crabs 2 3
Chloe the Crab Chloe is a Civil Engineer Civil engineers design bridges, roads, skyscrapers and other things you see every day. The tools Chloe uses are: Computer Scale Plans Books Count the Crabs 2 3
Tide Pools Starfish eating a mussel
 Tide Pools Lesson 6 T ide pools form in rocks where water collects in depressions in the rocks during low tide. A variety of plants and animals live their entire life in a tide pool. Many animals that
Tide Pools Lesson 6 T ide pools form in rocks where water collects in depressions in the rocks during low tide. A variety of plants and animals live their entire life in a tide pool. Many animals that
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level *9180775193* MARINE SCIENCE 9693/03 Paper 3 A2 Structured Questions May/June 2017 1 hour 30 minutes Candidates
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level *9180775193* MARINE SCIENCE 9693/03 Paper 3 A2 Structured Questions May/June 2017 1 hour 30 minutes Candidates
Coral Reef Basics and Its Impact on Ocean Life
 2012 Coral Reef Basics and Its Impact on Ocean Life Biology 1010 Professor LynneGilbert-Norton 4/25/2012 Contents Introduction... 2 Coral Explained... 2 Evolution... 3 Eating Habits... 4 Location... 4
2012 Coral Reef Basics and Its Impact on Ocean Life Biology 1010 Professor LynneGilbert-Norton 4/25/2012 Contents Introduction... 2 Coral Explained... 2 Evolution... 3 Eating Habits... 4 Location... 4
no-take zone 1 of 5 Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary, California
 This website would like to remind you: Your browser (Apple Safari 4) is out of date. Update your browser for more security, comfort and the best experience on this site. Encyclopedic Entry no-take zone
This website would like to remind you: Your browser (Apple Safari 4) is out of date. Update your browser for more security, comfort and the best experience on this site. Encyclopedic Entry no-take zone
