Efficient Algorithms for finding a Trunk on a Tree Network and its Applications
|
|
|
- Harry Osborne
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Efficient Algoithms fo finding a Tunk on a Tee Netwok and its Applications Yamin Li, Shietung Peng Depatment of Compute Science Hosei Uniesity Tokyo Japan {yamin;speng}@k.hosei.ac.jp Wanming Chu Depatment of Compute Hadwae Uniesity of Aizu Aizu-Wakamatsu Japan w-chu@u-aizu.ac.jp Abstact Gien an edge-weighted tee T, a tunk is a path P in T which minimizes the sum of the distances of all etices in T fom P plus the weight of path P. In this pape, we gie efficient algoithms fo finding a tunk of T. The fist algoithm is a sequential algoithm which uns in O(n) time, whee n is the numbe of etices in T. The second algoithm is a paallel algoithm which uns in O(log n) time using O(n/ log n) pocessos on EREW PRAM model. We also pesent an application of tunk fo efficient multicast in wieless ad hoc netwoks.. Intoduction In netwok theoy, optimally locating a seice facility/infastuctue fo communication in a netwok has long been of geat inteest fo decades. Due to the aiety of facilities/infastuctues and diffeent citeia fo optimality, abundant optimization poblems in netwoks hae been defined and studied. The one that was extensiely studied in the liteatue is the coe-family, a path-shaped o teeshaped facility which minimizes the sum of the distances fom the facility to all etices in the netwok [6, 7, 8, 9]. Howee, in some applications fo wieless ad hoc netwoks, the citeia fo optimization ae diffeent with that of the taditional coe-family: Instead of meely minimizing the cumulatie distances, the cumulatie distances plus the weight of the facility, defined as the sum of the weights of all edges in the facility, should be minimized. The path that satisfies the aboe citeia of optimality in a tee netwok is called a tunk in this pape. The contibutions of this pape ae:. Show a new type of optimization poblem in tee netwoks;. Gie efficient algoithms, both sequential and paallel ones, fo constucting a tunk in a tee netwok; and 3. Gie an example application of the new optimization poblem in wieless ad hoc netwoks. The est of this pape is oganized into fie sections. In Section, we gie the necessay notation, definitions, and peliminay esults fo tunk. In Section 3 we gie the definition of the ooted tunk and theoetical backgound fo the design of efficient algoithms to constuct a tunk. The sequential algoithm and the paallel algoithm ae pesented in Sections 4 and 5, espectiely. We gie an application and conclude this pape in Section 6.. A Tunk of A Tee Let T = (V, E) be a fee tee. The size of T, T, is the numbe of etices in V. Each edge e E has an associated positie weight w(e). If w(e) = fo eey e E then T is unweighted, othewise weighted. Let P = (V, E ), V V and E E, be a path in T. Fo any two etices u, V, let P (u, ) be the unique path fom u to, and let the distance fom u to, d(u, ) = e E w(e). Let the degee of etex V, denoted as deg(), be the numbe of etices adjacent to. A leaf of T is a etex l V with deg(l) =. Fo any path P, let w(p ) = e E w(e) be the weight of path P. When P = P (u, ) we hae w(p ) = d(u, ). Fo V, we define the distance d(, P ) = min u V d(u, ), and the cumulatie distance δ(p ) = V d(, P ). When P is a single etex u, we hae δ(u) = V d(, u). A tunk is a path P in T which minimizes δ(p ) + w(p ). Notice that the coe that was taditionally studied in the liteatue is defined as a path P that minimizes δ(p ). Fo the tee in Figue, thee is a unique coe C = a b c d with δ(c) =. Howee, thee ae total six tunks P t : b c, b c d, b c e, a b c, a b c d, and a b c e with δ(p t ) + w(p t ) = 5.
2 d e c b a Lemma Let P (, w) be a path in subtee ST (, u). We hae δ(p (, w)) δ(p (u, w)) + w((, u)) and δ(p (, w)) = δ(p (u, w)) + w((, u)) if and only if u is a leaf. Figue. A simple example tee The unweighted tee in Figue shows that thee exists a tee T in which a coe is not a tunk and ice esa. Fo simplicity, we show only the calculation on the subtee as shown as in Figue, the contibution fom the same (ight) pat had been exluded. Let path P = a b c d (Figue (a)) and path P = x y (Figue (b)). Since δ(p ) = 5 and δ(p ) = 6, path P will be selected fo coe. Howee, since δ(p ) + w(p ) = = 9 and δ(p ) + w(p ) = 6 + = 8, P will be selected fo tunk. Poof: Fom the definition of δ(p ), we hae δ(p (, w)) = δ(p (u, w))+w((, u)) ST (u, ). ST (u, ) = if and only if u is a leaf. Theefoe, the lemma is tue. Fo each V (T ), thee ae N() subtees attached to though edges (, u) E, whee u N(). Let ST (u, ) be the subtee of T attached to though the edge (, u). Notice that ST (, u) is the subtee of T attached to u though the edge (u, ) (see Figue 3). ST (u, ) u ST (, u) y y x x P a P b c d (a) A coe of tee a b c 3 4 d Figue 3. ST (, u) and ST (u, ) in T 3. Rooted Tunk and Theoy of Tunk Fo efficiently constucting a tunk, we oient tee T into a ooted tee T with oot. Fo any etex T, we denote the paent of as p(), the subtee ooted at as T, and the numbe of etices in T as T. Let a ooted tunk P (, l 0 ) be a path fom oot to leaf l 0 which minimizes δ(p (, l)) + w(p (, l)) among all paths fom to leaf l in T. We show that the poblem of constucting a tunk in T can be educed to the poblem of constucting a ooted tunk in a ooted tee T. The following lemmas fom the theoetical backgound fo the eduction. (b) A tunk of tee Figue. A tee in which a coe is not a tunk and ice esa In geneal, the two end-etices of a tunk may not necessaily be leaes. Let 0 be an end-etex of tunk P. Fo A, B V, let A/B = {u u A, u B}. Let N() be the set of etices adjacent to in T. By Lemma, the etices in N( 0 )/P must be leaes of T, and the extension of P to any leaf in N() must be a tunk. Theefoe, without loss of geneality, we assume that the end-etices of a tunk ae leaes. Lemma Let ooted tee T be an oientation of T and P (, l 0 ) a ooted tunk in T. Then P (, l 0 ) P (l, l ) fo any tunk P (l, l ) in T. Poof: Assume that P (, l 0 ) P (l, l ) = fo a tunk P (l, l ). Let i be the closest etex in P (, l 0 ) to P (l, l ) and j the closest etex in P (l, l ) to P (, l 0 ) (see Figue 4). Let path C = P (l 0, i) P (i, j) P (j, l ). Since P (, l 0 ) is a ooted tunk, δ(p (l 0, i)) + w(p (l 0, i))) δ(p (l, i))+w(p (l, i)). Since i is not a leaf, by Lemma, we hae δ(p (l, i)) + w(p (l, i)) < δ((p (l, j)) + w(p (l, j)). Simila, we hae δ(p (l 0, j)) + w(p (l 0, j)) < δ((p (l 0, i)) + w(p (l 0, i)). Fom these equations, we get δ(p (l 0, j)) + w(p (l 0, j)) < δ((p (l, j)) + w(p (l, j)). This implies δ(c) + w(c) < δ(p (l, l )) + w(p (l, l )), a
3 contadiction to the fact that P (l, l )) is a tunk. Theefoe, the lemma must be tue. l i j In Figue 6, we fist show an example tee T with an abitaily selected etex in Figue 6(a). Then, in Figue 6(b), we show the ooted tee T and a ooted tunk P (, l 0 ) in T. We hae δ(p (, l 0 )) + w(p (, l 0 )) = = 3. Finally in Figue 6(c), we show the ooted tee T l0 and a ooted tunk P (l 0, l 0 ) in T l0. The path P (l 0, l 0) is a tunk in T, and we hae δ(p (l 0, l 0)) + w(p (l 0, l 0)) = = 6. l 0 l 3 Figue 4. P (, l 0 ) is a ooted tunk in T and P (l, l ) is a tunk Theoem Let ooted tee T be an oientation of T and P (, l 0 ) a ooted tunk in T. Then a ooted tunk in ooted tee T l0, a new oientation of T, is a tunk in T. (a) T l 0 l 0 (b) T Poof: Let P (l 0, l 0) be a ooted tunk in T l0. Assume that P (l, l ) is a tunk in T. Fom Lemma, P (l 0, l 0) P (l, l ). Let P (i, j) = P (l 0, l 0) P (l, l ), whee i is the etex in P (i, j) closest to etices l 0 and l (see figue 5). Since P (, l 0 ) is a ooted tunk, we hae δ(p (l 0, i)) + w(p (l 0, i)) δ(p (l, i)) + w(p (l, i)). Similaly, Since P (l 0, l 0) is a ooted tunk, we hae δ(p (l 0, j)) + w(p (l 0, j)) δ(p (l, j)) +w(p (l, j)). Theefoe, we get δ(p (l 0, l 0)) + w(p (l 0, l 0)) δ(p (l, l )) + w(p (l, l )). We conclude that P (l 0, l 0) is a tunk in T. l 0 l 0 l j Figue 5. P (i, j) = P (l 0, l 0) P (l, l ) Fom Theoem, the poblem of constucting a tunk in T can be soled as follows: i. Oient tee T into a ooted tee T with an abitay etex ;. Constuct a ooted tunk P (, l 0 ) in T ; 3. Re-oient T into T l0 ; 4. Constuct a ooted tunk in T l0. l l 0 (c) T l0 Figue 6. (a) An example tee; (b) a ooted tunk in T ; (c) a ooted tunk in T l0 which is a tunk in T It was well known that oientation of a tee can be done optimally both sequentially and in paallel. The key fo an efficient algoithm to constuct a tunk lies on efficiently constucting a ooted tunk. We pesent two optimal algoithms, sequentially and in paallel, fo constucting a ooted tunk in a ooted tee T in the next two sections, espectiely. Based on these two algoithms, the poblem of constucting a tunk in tee T can be soled optimally both sequentially and in paallel. 4. Sequential algoithm fo finding a ooted tunk In ode to find min l is a leaf in T {δ(p (, l))+w(p (, l))}, the alue of T fo eey node and δ(l) fo eey leaf l in T should be computed in adance. Computing T fo eey node in O(n) time is tiial. We show in the 6
4 following lemma, Lemma 3, that δ(l), fo eey leaf l in T can be computed in O(n) time Lemma 3 Gien a weighted tee T, δ() fo V (T ) can be computed in O(n) time Poof: Fist, we oient T into a ooted tee T in O(n) time. δ() can be computed in O(n) time though a post-ode taesal of T by the fomula δ() = V (T ) d(, ) = V (T )/{} w((, p())) T. Then, δ() fo all can be computed in O(n) time though a pe-ode taesal of T by the fomula δ() = δ(p()) w((, p())) ( T (n T )) = δ(p()) w((, p())) ( T n). The sequential algoithm fo finding a ooted tunk of a ooted tee T woks fom bottom up: once the ooted tunks of all subtees T w, whee node w is a child of node, hae been found, the ooted tunk of subtee T can be computed. Computing a ooted tunk of subtee T is done as follows: Let,..., k be the childen of in T. Let P (l i, i ) be the ooted tunk in subtee T i. Fom the fomula δ(p (l i, )) + w(p (l i, )) = δ(p (l i, i )) + w(p (l i, i )) w((, i )) ( T i ), the algoithm computes δ(p (l i, )) + w(p (l i, )) and finds the minimum fo all i, i k. The path that eaches this minimum fo is a ooted tunk in subtee T. The algoithm is descibed fomally in Algoithm. Fo finding a ooted tunk in T, we simply call Find ooted tunk(t ). Algoithm (Find ooted tunk(t )) Input: ooted tee T Output: leaf l and δ(p (l, )) + w(p (l, )) /* P (l, ) is a ooted tunk in T. */ begin if is a leaf then etun ((, δ()) else /* assume i, i k ae the childen of. */ fo i to k do (l i, alue i ) Find ooted tunk(t i ); endfo min min i k {alue i w((, i )) ( T i )}; min leaf l j ; /*alue j w((, j )) ( T j ) = min*/ etun(min leaf, min); endif end Figue 7 and Figue 8 show how the algoithm woks fo the example tee T in Figue 6(b) and T l0 in Figue 6(c), espectiely. Theoem A ooted tunk in a ooted tee T can be found in O(n) time Figue 7. A woking example fo Algoithm Figue 8. A woking example fo Algoithm Poof: Fom the definition of ooted tunk and the fomula δ(p (l, p()))+w(p (l, p())) = δ(p (l, ))+w(p (l, )) w((p(), )) ( T ), it is easy to see that Algoithm finds a ooted tunk in T. The algoithm pefoms a post-ode taesal of T with O() computations pe step. Theefoe, ooted tunk in T can be found in O(n) time. Coollay A tunk in a tee T can be found in O(n) time. Poof: The ooted T can be obtained fom an oientation of tee T in O(n) time. Fom Theoem, finding a ooted tunk in a ooted tee takes O(n) time. A tunk can be found by pefoming twice the pocess of a tee oientation followed by finding a ooted tunk in the ooted tee. Theefoe, the coollay is tue. 5. Paallel algoithm fo finding a ooted tunk The paallel computation model used in this pape is EREW PRAM. A PRAM consists of a collection of autonomous pocessos, each haing access to a common memoy. At each step, eey pocesso pefoms the same instuction, with a numbe of pocessos masked out. In the
5 EREW PRAM model, a memoy location cannot be simultaneously accessed by moe than one pocess. Two techniques of paallel computation fo tees, paallel Eule-tou and tee contaction that ae intoduced biefly below, will be used in the poposed paallel algoithm. Gien a tee T, the Eule path of T is a linea list of n diected edges, whee n = V (T ). We descibe Eule tou biefly as follows: Fo each etex in V (T ), we set next(u i ) = u (i+)mod k fo 0 i k, whee k = deg() and u i, 0 i k, ae the neighbos of in T (see Figue 9). Fo tee oientation with oot, we set next(u deg() ) = end of list. By applying the optimal list anking algoithm [], each edge in T can be oiented away fom the oot by assigning it the diection of one of its two diected edges in the Eule path which has lage ank. We conclude that tee T can be oiented into a ooted tee T in O(log n) time using O(n/ log n) pocessos on an EREW PRAM. 3 Figue 9. An Eule tou The tee contaction is a paallel technique on a ooted tee T which educes T in paallel to its oot by a sequence of etex emoals. The tee contaction algoithm of Abahamson et al. [], which will be used in ou algoithm, is descibed biefly below. Fist, the ooted tee T should be pesented as a binay tee though the standad tansfomation in which a node with k > childen is pesented as a binay subtee of hight k with k dummy nodes of (see Figue 0). 3 dummy Figue 0. A binay tee pesentation of a tee A tee contaction sequence of length s is defined as a set of binay tees {BT i i s} such that BT i is obtained fom BT i by one of the following two opeations:. pune(): leaf in BT i is emoed; 3. bypass(): a non-oot node in BT i with only one child is emoed and the paent of becomes the paent of the unique child of. It was showed in [] that eey binay tee has an optimal contaction sequence of length O(log n) and this sequence can be obtained in O(log n) time using O(n/ log n) pocessos on an EREW PRAM. The following lemma shows that δ() fo all V (T ) can be computed efficiently in paallel. Lemma 4 Gien a ooted tee T, T and δ() fo all V (T ) can be computed in O(log n) time using O(n/ log n) pocessos on an EREW PRAM. Poof: The numbe of nodes in subtee T ooted at, T, fo all V (T ), can be computed in paallel using Eule-tou technique as follows: Fo the diected edges e oiented away fom oot, set f(e) = 0; and fo the diected edges e oiented towad, set f(e ) =. Then, pefom paallel pefix computation of f on the list of Eule tou and let the esult be the function g. It is easy to see that g(e 0) equals to T, whee e 0 = (, u) is the unique diected edge stating fom that is oiented towad. δ() fo all V (T ) can be computed in paallel using tee contaction and expansion techniques. Fist, we show that δ() can be computed in paallel using tee contaction as follows: Fo binay tee BT in the sequence of tee contaction, set f() = if is a leaf; othewise, f() = 0. While pefoming pune(), whee is a leaf in BT i, we set f(p()) = f(p())+w((, p()) T. While pefoming bypass(), whee has a unique child u in T i, we set f(p()) = f(p()) + w((, p()) T and w((u, p()) = w((, p()) + w((u, )), whee (u, p()) is a new edge ceated by bypass opeation. It is easy to see fom the definition of δ that f() = δ() while tee contaction is done. Finally, δ() fo can be computed in paallel though the tee expansion technique which is the inese pocess of tee contaction. The tee expansion expands to T though in pune and in bypass opeations. Initially, we set g() = δ(). While pefoming in pune() to ceate a child u of, we set g(u) = g()+w((u, )) (n T u ) (w((u, )) and T u ae kept in while pefoming pune(u)). Similaly, while pefoming in bypass(), we set g(u) = g() + w((u, )) (n T u ) and w((u, z)) = w((, z)) w((u, )), whee z is the unique child of geneated by bypass(u) in tee contaction. Fom the fomula δ() = δ(p()) + w((, p()) (n T ), it is easy to see that afte tee expansion is done, g() = δ() fo eey T. Next, we use the tee contaction technique on T to compute in paallel the alue min{δ(p (, l))+w(p (, l))}, whee l is a leaf in T. Fo each node in BT i, a binay tee in the sequence of tees geneated by the tee
6 Algoithm (Paallel ooted tunk(t )) Input: ooted tee T Output: min{δ(p (, l)) + w(p (, l))}, whee l is a leaf in T begin In paallel, compute δ(l) fo all leaf l T ; Tansfe T into a binay tee pesentation; fo each node T do if is a dummy node then w(, p()) = 0; if is a leaf then f() = δ() else f() = ; g() = 0; endfo Pefom tee contaction to geneate a sequence of binay tees {BT i i s}, whee BT is a binay epesentation of T and BT s = {}; /* BT i is obtained fom BT i by pune() o bypass() opeations. */ fo each pune() do f(p()) = min{f(p()), f() w((, p()) (n T )} + g(); endfo fo each bypass() do f(p()) = min{f(p()), f() w((, p()) (n T )} + g(); w((u, p()) = w((, p()) + w((u, )); /* u is the unique child of. */ g(u) = g(u) + w(, p()) ( T T u ); endfo etun(f()); end contaction, we compute two functions, f() and g(). If is a leaf in BT i, the alue of function f() epesents min{δ(p (, l)) + w(p (, l))}, whee l is a leaf in T, the subtee of T ooted at. Theefoe, when tee contaction ends, f() will be the answe we want. The function g() is used to adjust the distance saing ceated by path extension fom to p() whee edge (, p()) is an edge ceated by the bypass opeation. We will explain this effect in details late. Initially, in BT, we set f() = δ() if is a leaf, othewise, f() = ; g() = 0 fo all. Then, fo each pune(), we should update the alue of f(p()) by the fomula f(p()) = min{f(p()), f() w((, p()) (n T )}; And, fo each bypass(), we should update the alue of f(p()) by the fomula f(p()) = min{f(p()), f() w((, p()) (n T )} and gie the new edge (u, p()) weight w((, p()) + w((u, )) so that, when pefom pune(u) the distance saing fo the path extension fom u to p() calculated by the fomula w(u, p()) (n T u ) will be coect. Howee, the effect of the nodes in T on the distance saing due to the path extension fom u to p() is oe-calculated in the fomula (the distance saing due to the path extension fo the nodes in T is w(u, ), not w(u, p())). Theefoe, a facto g(u) = w(, p()) ( T T u ) is needed to compensate this oe-calculation. That is, the update fomula fo f(p()) should be f(p()) = min{f(p()), f() w((, p()) (n T )} + g(). The algoithm is shown in Algoithm. Figue shows how the algoithm woks fo the example tee T in Figue 6(b). Notice that BT 3 comes fom BT by a bypass(). Fom the algoithm, we get f(p()) = 5 (0 8 ) = 4, w(u, p()) = + =, and g(u) = 8 6 =. Duing the pune(u) opeation in BT 4, we get f(p(u)) = min{4, 58 (0 6 )+} = 34. Finally, since BT 6 = {} comes fom BT 5 by a pune opeation, we get f() = min{58, 34 (0 6 ) + 0} = 3. Theoem 3 Gien a ooted tee T, min{δ(p (, l)) + w(p (, l))}, whee l is any leaf in T, can be computed in O(log n) time using O(n/ log n) pocessos on an EREW PRAM. Poof: We apply tee contaction on tee T with O() additional computations of functions f and g on BT i, i s, while pefoming pune and bypass opeations. Initially, we set g() = 0 and f() = δ() if is a leaf in BT ; othewise f() =. If is a dummy
7 9 9 dummy u dummy p() Poof: The leaf l 0 that achiees the minimum alue in Theoem 3 can be obtained easily with O() additional bookkeeping pocess pe etex while pefoming pune and bypass opeations. Coollay 3 A tunk in a tee T can be found in O(log n) time using O(n/ log n) pocessos on an EREW PRAM. (a) BT = T (binay) 74 4 u g(u) dummy = p() (c) BT 3 : Bypass (b) BT : Pune 58 4 u 58 g(u) 5 = f() = 74 (0 3 ) = 58 (d) BT 4 : Pune Poof: The oientation of tee T and finding a ooted tunk in a ooted tee take O(log n) time using O(n/ log n) pocessos on an EREW PRAM. A tunk can be found by pefoming twice the pocess of a tee oientation followed by finding a ooted tunk in the ooted tee. Theefoe, the coollay is tue. 6. An Application and Concluding emaks 58 p(u) 34 (e) BT 5 : Pune 3 (e) BT 6 : Pune Figue. A woking example fo Algoithm node, since and p() ae identical in the oiginal tee, we should set w(, p()) = 0. While pefoming pune(), whee is a leaf, we set f(p()) = min{f(p()), f() w((, p()) (n T )} + g(), whee the compensation facto g() is intoduced by the bypass opeation as explained befoe. The aboe fomula fo updating f(p()) comes fom the fact δ(p()) + w(p (p(), l) = δ(p (, l) + w(p (, l)) w((, p()) (n T ) fo any path P (, l) T. While pefoming bypass(), whee has a unique child u in T i, we set f(p()) = min{f(p()), f() w((, p()) (n T )} + g() and w((u, p()) = w((, p())+w((u, )), whee (u, p()) is a new edge ceated by bypass opeation. We also modify the compensation facto g() by setting g() = g() + w(, p()) ( T T u ). Simila to the poof of Lemma 4, it is easy to eify that f() = min{δ(p (, l))+w(p (, l))} while tee contaction is done. Coollay A ooted tunk in a ooted tee T can be found in O(log n) time using O(n/ log n) pocessos on an EREW PRAM. The concept of tunk in tee netwoks has applications on efficient multicast fo wieless ad hoc netwoks. Oelay multicast potocols [3, 4, 5] ae used fo efficient multicast at application laye. It constucts a itual mesh spanning all membe nodes of a multicast goup and employs standad unicast outing to fulfill multicast functionality. A spanning tee T on the itual mesh, an weighted tee in which the weight of an edge (u, ) is the numbe of hops fom u to in the oiginal netwok, is commonly used by oelay multicast potocols fo efficient multicast. Howee, maintaining the spanning tee fo mobile ad hoc netwoks is expensie. A path in the tee can be used to educed the cost fo maintenance due to its simple, linea stuctue. The total cost fo multicast using a path P contains two pats: the cost fo boadcasting inside P and the cost fo unicasting fom the nodes inside P to the nodes outside. Fomally speaking, the cost of the fist pat is e P w(e) and the cost of the second pat is V (T ) d(, P ). Theefoe, the poblem of finding a path with minimum communication cost is exactly the poblem of finding a tunk in T. Figue shows a tunk of a spanning tee on a itual mesh of size 50 in an ad hoc wieless netwok of 00 nodes. The solid cycles in the figue epesent the goup membes and the tunk is maked with thickest lines. We had pesented a new optimization poblem, its solutions and efficient algoithms on theoetical models. We also showed a possible application on communication in ad hoc wieless netwoks. It is inteesting to deelop efficient algoithms fo constucting a tunk in tee netwoks on the models that un asynchonously and use local infomation only.
8 47 30 a f 8 5d 43 a b c c e c f b 6 36 b e d a 4f e c 3a d 3f c 4e e 5 5 d a 6 3c f b e d f 7 3b 3 6 4b 4d a 58 Figue. A tunk of a spanning tee on itual mesh Refeences [] K. Abahamson, N. Dadoun, D. G. Kikpatick, and T. Pzytycka. A simple paallel tee contaction algoithm. Jounal of Algoithms, 0():87 30, Jun [] R. Cole and U. Vishkin. Appoximate paallel scheduling. pat i: The basic technique with applications to optimal paallel list anking in logaithmic time. SIAM Jounal of Computing, 7():8 4, 988. [3] C. Codeio, H. Gossain, and D. Agawal. Multicast oe wieless mobile ad hoc netwoks: Pesent and futue diections. IEEE Netwok, 7():5 59, Jan [4] C. Gui and P. Mohapata. Efficient oelay multicast fo mobile ad hoc netwoks. In Poceedings of IEEE Wieless Communications and Netwoking Confeence (WCNC003), Ma [5] J. Janotti, D. Giffod, K. Johnson, M. Kaashoek, and J. O Toole. Oecast: Reliable multicasting with an oelay netwok. In Poceedings of 4th Symp. Opeating Systems Design and Implementation, pages 97, Oct [6] C. A. Mogan and P. J. Slate. A linea algoithm fo a coe of a tee. Jounal of Algoithms, (3):47 58, 980. [7] S. Peng and W. Lo. A simple optimal paallel algoithm fo a coe of a tee. Jounal of Paallel amd Distibuted Computing, 0(3):388 39, 994. [8] S. Peng and W. Lo. Efficient algoithms fo finding a coe with a specific length. Jounal of Algoithms, 0(3): , 996. [9] S. Peng, A. B. Stephens, and Y. Yesha. Algoithms fo a coe and k-tee coe of a tee. Jounal of Algoithms, 5():43 59, Jul. 993.
Red-Black Trees Goodrich, Tamassia Red-Black Trees 1
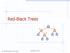 Red-Black Tees 8 00 Goodich, Tamassia Red-Black Tees 1 Fom (,) to Red-Black Tees A ed-black tee is a epesentation of a (,) tee by means of a binay tee whose nodes ae coloed ed o black In compaison with
Red-Black Tees 8 00 Goodich, Tamassia Red-Black Tees 1 Fom (,) to Red-Black Tees A ed-black tee is a epesentation of a (,) tee by means of a binay tee whose nodes ae coloed ed o black In compaison with
Fundamental Algorithms for System Modeling, Analysis, and Optimization
 Fundamental Algoithms fo System Modeling, Analysis, and Optimization Edwad A. Lee, Jaijeet Roychowdhuy, Sanjit A. Seshia UC Bekeley EECS 44/44 Fall With thanks to R. K. Bayton, K. Keutze, N. Shenoy, and
Fundamental Algoithms fo System Modeling, Analysis, and Optimization Edwad A. Lee, Jaijeet Roychowdhuy, Sanjit A. Seshia UC Bekeley EECS 44/44 Fall With thanks to R. K. Bayton, K. Keutze, N. Shenoy, and
Noncrossing Trees and Noncrossing Graphs
 Noncossing Tees and Noncossing Gaphs William Y. C. Chen and Shey H. F. Yan Cente fo Combinatoics, LPMC, Nanai Univesity, 300071 Tianjin, P.R. China chen@nanai.edu.cn, huifangyan@eyou.com Submitted: Sep
Noncossing Tees and Noncossing Gaphs William Y. C. Chen and Shey H. F. Yan Cente fo Combinatoics, LPMC, Nanai Univesity, 300071 Tianjin, P.R. China chen@nanai.edu.cn, huifangyan@eyou.com Submitted: Sep
arxiv:cs/ v1 [cs.ds] 8 Dec 1998
![arxiv:cs/ v1 [cs.ds] 8 Dec 1998 arxiv:cs/ v1 [cs.ds] 8 Dec 1998](/thumbs/79/79557328.jpg) Minimum Cuts in Nea-Linea Time David R. Kage Febuay 1, 2008 axiv:cs/9812007v1 [cs.ds] 8 Dec 1998 Abstact We significantly impove known time bounds fo solving the minimum cut poblem on undiected gaphs.
Minimum Cuts in Nea-Linea Time David R. Kage Febuay 1, 2008 axiv:cs/9812007v1 [cs.ds] 8 Dec 1998 Abstact We significantly impove known time bounds fo solving the minimum cut poblem on undiected gaphs.
Depth-first search and strong connectivity in Coq
 1 Depth-fist seach and stong connectivity in Coq Januay 9, 2015 2 The poblem Finding the stongly connected components of a diected gaph. Pedagogical value: The fist nontivial gaph algoithm. Pactical value:
1 Depth-fist seach and stong connectivity in Coq Januay 9, 2015 2 The poblem Finding the stongly connected components of a diected gaph. Pedagogical value: The fist nontivial gaph algoithm. Pactical value:
Design Engineering Challenge: The Big Dig Contest Platter Strategies: Ball Liberation
 Poblem Set 4: Unifom Cicula Motion Design Engineeing Challenge: The Big Dig.007 Contest Platte Stategies: Ball Libeation Oeall Notes: You ae not equied to pefom the actual analysis in this poblem set,
Poblem Set 4: Unifom Cicula Motion Design Engineeing Challenge: The Big Dig.007 Contest Platte Stategies: Ball Libeation Oeall Notes: You ae not equied to pefom the actual analysis in this poblem set,
Multi-Robot Flooding Algorithm for the Exploration of Unknown Indoor Environments
 2010 IEEE Intenational Confeence on Robotics and Automation Anchoage Convention Distict May 3-8, 2010, Anchoage, Alaska, USA Multi-Robot Flooding Algoithm fo the Exploation of Unknown Indoo Envionments
2010 IEEE Intenational Confeence on Robotics and Automation Anchoage Convention Distict May 3-8, 2010, Anchoage, Alaska, USA Multi-Robot Flooding Algoithm fo the Exploation of Unknown Indoo Envionments
A CONCEPTUAL WHEELED ROBOT FOR IN-PIPE INSPECTION Ioan Doroftei, Mihaita Horodinca, Emmanuel Mignon
 A CONCEPTUAL WHEELED ROBOT FOR IN-PIPE INSPECTION Ioan Dooftei, Mihaita Hoodinca, Emmanuel Mignon Univesité Libe de Buxelles Active Stuctues Laboatoy 50, Av. F.D.Roosevelt, B-1050, Bussels, Belgium. Email:
A CONCEPTUAL WHEELED ROBOT FOR IN-PIPE INSPECTION Ioan Dooftei, Mihaita Hoodinca, Emmanuel Mignon Univesité Libe de Buxelles Active Stuctues Laboatoy 50, Av. F.D.Roosevelt, B-1050, Bussels, Belgium. Email:
Incorporating Location, Routing and Inventory Decisions in Dual Sales Channel - A Hybrid Genetic Approach
 Incopoating Location, Routing and Inventoy Decisions in Dual Sales Channel - A Hybid Genetic Appoach Chia-lin Hsieh 1, Shu-hsien Liao 2, Wei-chung Ho 2 1 Depatment of Statistics and Actuaial Science, Aletheia
Incopoating Location, Routing and Inventoy Decisions in Dual Sales Channel - A Hybid Genetic Appoach Chia-lin Hsieh 1, Shu-hsien Liao 2, Wei-chung Ho 2 1 Depatment of Statistics and Actuaial Science, Aletheia
Rearranging trees for robust consensus
 Poceedings of the IEEE Conf. on Decision and Contol, Olando, FL, 011 Reaanging tees fo obust consensus Geoge Foest Young, Luca Scadovi and Naomi Ehich Leonad Abstact In this pape, we use the H nom associated
Poceedings of the IEEE Conf. on Decision and Contol, Olando, FL, 011 Reaanging tees fo obust consensus Geoge Foest Young, Luca Scadovi and Naomi Ehich Leonad Abstact In this pape, we use the H nom associated
Multi-Robot Forest Coverage
 Multi-Robot Foest Coveage Xiaoming Zheng Sonal Jain Sven Koenig David Kempe Depatment of Compute Science Univesity of Southen Califonia Los Angeles, CA 90089-0781, USA {xiaominz, sonaljai, skoenig, dkempe}@usc.edu
Multi-Robot Foest Coveage Xiaoming Zheng Sonal Jain Sven Koenig David Kempe Depatment of Compute Science Univesity of Southen Califonia Los Angeles, CA 90089-0781, USA {xiaominz, sonaljai, skoenig, dkempe}@usc.edu
The Solution to the Bühlmann - Straub Model in the case of a Homogeneous Credibility Estimators
 5 Economy Infomatics, -4/005 The Solution to the Bühlmann - Staub Model in the case of a Homogeneous Cedibility Estimatos Lect. Viginia ATANASIU Mathematics Depatment, Academy of Economic Studies Oiginal
5 Economy Infomatics, -4/005 The Solution to the Bühlmann - Staub Model in the case of a Homogeneous Cedibility Estimatos Lect. Viginia ATANASIU Mathematics Depatment, Academy of Economic Studies Oiginal
EC-FRM: An Erasure Coding Framework to Speed up Reads for Erasure Coded Cloud Storage Systems
 215 44th Intenational Confeence on Paallel Pocessing EC-FRM: An Easue Coding Famewok to Speed up Reads fo Easue Coded Cloud Stoage Systems Yingxun Fu, Jiwu Shu *, and Zhiong Shen Tsinghua National Laboatoy
215 44th Intenational Confeence on Paallel Pocessing EC-FRM: An Easue Coding Famewok to Speed up Reads fo Easue Coded Cloud Stoage Systems Yingxun Fu, Jiwu Shu *, and Zhiong Shen Tsinghua National Laboatoy
10 Torque. Lab. What You Need To Know: Physics 211 Lab
 b Lab 10 Toque What You Need To Know: F (a) F F Angula Systems Evey lab up to this point has dealt with objects moving in the linea system. In othe wods, objects moving in a staight line. Now we ae going
b Lab 10 Toque What You Need To Know: F (a) F F Angula Systems Evey lab up to this point has dealt with objects moving in the linea system. In othe wods, objects moving in a staight line. Now we ae going
Cyclostrophic Balance in Surface Gravity Waves: Essay on Coriolis Effects
 Jounal of Oceanogaphy, Vol. 53, pp. 311 to 315. 1997 Shot Contibution Cyclostophic Balance in Suface Gavity Waves: Essay on Coiolis Effects KERN E. KENYON 4632 Noth Lane Del Ma, CA 92014-4134, U.S.A. (Received
Jounal of Oceanogaphy, Vol. 53, pp. 311 to 315. 1997 Shot Contibution Cyclostophic Balance in Suface Gavity Waves: Essay on Coiolis Effects KERN E. KENYON 4632 Noth Lane Del Ma, CA 92014-4134, U.S.A. (Received
OPTIMAL SCHEDULING MODELS FOR FERRY COMPANIES UNDER ALLIANCES
 Jounal of Maine Science and Technology, Vol. 15, No. 1, pp. 53-66 (2007) 53 OPTIMAL SCHEDULING MODELS FOR FERRY COMPANIES UNDER ALLIANCES Shangyao Yan*, Chia-Hung Chen**, Hsin-Yen Chen*** and Tze-Chiang
Jounal of Maine Science and Technology, Vol. 15, No. 1, pp. 53-66 (2007) 53 OPTIMAL SCHEDULING MODELS FOR FERRY COMPANIES UNDER ALLIANCES Shangyao Yan*, Chia-Hung Chen**, Hsin-Yen Chen*** and Tze-Chiang
Faster Nearest Neighbors: Voronoi Diagrams and k-d Trees
 154 25 Jonathan Richad Shewchuk Faste Neaest Neighbos: Voonoi Diagams and k-d Tees SPEEDING UP NEAREST NEIGHBOR CLASSIFIERS Can we pepocess taining pts to obtain sublinea quey time? 2 5 dimensions: Voonoi
154 25 Jonathan Richad Shewchuk Faste Neaest Neighbos: Voonoi Diagams and k-d Tees SPEEDING UP NEAREST NEIGHBOR CLASSIFIERS Can we pepocess taining pts to obtain sublinea quey time? 2 5 dimensions: Voonoi
Cheat-Proof Playout for Centralized and Distributed Online Games
 Cheat-Poof Playout fo Centalized and Distibuted Online Games Nathaniel E. Baughman Bian Neil Levine baughman@cs.umass.edu bian@cs.umass.edu Depatment of Compute Science Univesity of Massachusetts Amhest,
Cheat-Poof Playout fo Centalized and Distibuted Online Games Nathaniel E. Baughman Bian Neil Levine baughman@cs.umass.edu bian@cs.umass.edu Depatment of Compute Science Univesity of Massachusetts Amhest,
An Auction Based Mechanism for On-Demand Transport Services
 An Auction Based Mechanism fo On-Demand Tanspot Sevices Malcolm Egan, Ni Oen and Michal Jakob Abstact Recently, a new class of tanspot sevices, exemplified by Ube and Lyft has emeged. Such sevices use
An Auction Based Mechanism fo On-Demand Tanspot Sevices Malcolm Egan, Ni Oen and Michal Jakob Abstact Recently, a new class of tanspot sevices, exemplified by Ube and Lyft has emeged. Such sevices use
CS3350B Computer Architecture. Lecture 6.2: Instructional Level Parallelism: Hazards and Resolutions
 CS3350B Compute Achitectue Winte 2015 Lectue 6.2: Instuctional Level Paallelism: Hazads and Resolutions Mac Moeno Maza www.csd.uwo.ca/couses/cs3350b [Adapted fom lectues on Compute Oganization and Design,
CS3350B Compute Achitectue Winte 2015 Lectue 6.2: Instuctional Level Paallelism: Hazads and Resolutions Mac Moeno Maza www.csd.uwo.ca/couses/cs3350b [Adapted fom lectues on Compute Oganization and Design,
The Study About Stopping Distance of Vehicles
 Intenational Jounal of Infomation Engineeing and Applications 018; 1(1): 18- http://www.aascit.og/jounal/infomation The Study About Stopping Distance of Vehicles Zhao Chun-xue School of Mathematics and
Intenational Jounal of Infomation Engineeing and Applications 018; 1(1): 18- http://www.aascit.og/jounal/infomation The Study About Stopping Distance of Vehicles Zhao Chun-xue School of Mathematics and
Lecture Topics. Overview ECE 486/586. Computer Architecture. Lecture # 9. Processor Organization. Basic Processor Hardware Pipelining
 EE 486/586 ompute chitectue Lectue # 9 asic Pocesso Hadwae Pipelining Refeence: ppendix : Section.1 Lectue Topics Sping 2015 Potland State Univesity Oveview Pocesso Oganization typical computing task consists
EE 486/586 ompute chitectue Lectue # 9 asic Pocesso Hadwae Pipelining Refeence: ppendix : Section.1 Lectue Topics Sping 2015 Potland State Univesity Oveview Pocesso Oganization typical computing task consists
Experiment #10 Bio-Physics Pre-lab Comments, Thoughts and Suggestions
 Expeient #10 Bio-Physics Pe-lab Coents, Thoughts and Suggestions The pupose of this pape is to povide you with soe infoation which ay be useful fo solving the pe-lab questions and pefoing the lab. I will
Expeient #10 Bio-Physics Pe-lab Coents, Thoughts and Suggestions The pupose of this pape is to povide you with soe infoation which ay be useful fo solving the pe-lab questions and pefoing the lab. I will
Trees & Routing (1) BFS
 Tees & Routing (1) BFS Why (spanning) tees? Spanning Tee Given a gaph G=(V,E), a Spanning Tee of G is an acyclic subgaph, spanning all the nodes in V. Spanning Tee Given a gaph G=(V,E), a Spanning Tee
Tees & Routing (1) BFS Why (spanning) tees? Spanning Tee Given a gaph G=(V,E), a Spanning Tee of G is an acyclic subgaph, spanning all the nodes in V. Spanning Tee Given a gaph G=(V,E), a Spanning Tee
Design and Simulation Model for Compensated and Optimized T-junctions in Microstrip Line
 Intenational Jounal of Advanced Reseach in Compute Engineeing & Technology (IJARCET) Volume 3 Issue, Decembe 4 Design and Simulation Model fo Compensated and Optimized T-junctions in Micostip Line Alok
Intenational Jounal of Advanced Reseach in Compute Engineeing & Technology (IJARCET) Volume 3 Issue, Decembe 4 Design and Simulation Model fo Compensated and Optimized T-junctions in Micostip Line Alok
Torque. Physics 2. Prepared by Vince Zaccone For Campus Learning Assistance Services at UCSB
 Toque Physics Toque Toque is what causes angula acceleation (just like a foce causes linea acceleation) Toque Toque is what causes angula acceleation (just like a foce causes linea acceleation) Fo a toque
Toque Physics Toque Toque is what causes angula acceleation (just like a foce causes linea acceleation) Toque Toque is what causes angula acceleation (just like a foce causes linea acceleation) Fo a toque
Data Sheet. Linear bearings
 Data Pack G Issued Septembe 1999 1502325042 Data Sheet Linea beaings Instument ball beaings and shafts The RS ange of instument quality ball bushing beaings ae fo 1 8in, 3 16in and 1 4in shafts. Each beaing
Data Pack G Issued Septembe 1999 1502325042 Data Sheet Linea beaings Instument ball beaings and shafts The RS ange of instument quality ball bushing beaings ae fo 1 8in, 3 16in and 1 4in shafts. Each beaing
British Prime Minister Benjamin Disraeli once remarked that
 GABREL COSTA, MCHAEL HUBER, & OHN SACCOMAN Cumulative Home Run Fequency and the Recent Home Run Explosion Bitish Pime Ministe Benjamin Disaeli once emaked that thee ae thee kinds of falsehoods: lies, damned
GABREL COSTA, MCHAEL HUBER, & OHN SACCOMAN Cumulative Home Run Fequency and the Recent Home Run Explosion Bitish Pime Ministe Benjamin Disaeli once emaked that thee ae thee kinds of falsehoods: lies, damned
Angle-restricted Steiner arborescences for flow map layout Buchin, K.A.; Speckmann, B.; Verbeek, K.A.B.
 Angle-esticted Steine aboescences fo flow ma layout Buchin, K.A.; Seckmann, B.; Vebeek, K.A.B. Published in: Abst. 27th Euoean Woksho on Comutational Geomety (EuoCG) Published: 01/01/2011 Document Vesion
Angle-esticted Steine aboescences fo flow ma layout Buchin, K.A.; Seckmann, B.; Vebeek, K.A.B. Published in: Abst. 27th Euoean Woksho on Comutational Geomety (EuoCG) Published: 01/01/2011 Document Vesion
Range Extension Control System for Electric Vehicles Based on Front and Rear Driving Force Distribution Considering Load Transfer
 Range Extension Contol System fo Electic Vehicles Based on and Diving Foce Distibution Consideing Load Tansfe Sho Egami and Hioshi Fujimoto The Univesity of Tokyo 5--5, Kashiwanoha, Kashiwa, Chiba, 227-856
Range Extension Contol System fo Electic Vehicles Based on and Diving Foce Distibution Consideing Load Tansfe Sho Egami and Hioshi Fujimoto The Univesity of Tokyo 5--5, Kashiwanoha, Kashiwa, Chiba, 227-856
An integrated supply chain design model with random disruptions consideration
 Afican Jounal of Business Management Vol. 4(1), pp. 393-401, 18 Septembe, 010 Available online at http://www.academicounals.og/ajbm ISSN 1993-833 010 Academic Jounals Full Length Reseach Pape An integated
Afican Jounal of Business Management Vol. 4(1), pp. 393-401, 18 Septembe, 010 Available online at http://www.academicounals.og/ajbm ISSN 1993-833 010 Academic Jounals Full Length Reseach Pape An integated
Lesson 33: Horizontal & Vertical Circular Problems
 Lesson 33: Hoizontal & Vetical Cicula Poblems Thee ae a wide vaiety of questions that you do if you apply you knowledge of cicula motion coectly. The tough pat is figuing out how to set them up. You need
Lesson 33: Hoizontal & Vetical Cicula Poblems Thee ae a wide vaiety of questions that you do if you apply you knowledge of cicula motion coectly. The tough pat is figuing out how to set them up. You need
Carnegie Mellon University Forbes Ave., Pittsburgh, PA command as a point on the road and pans the camera in
 Panacea: An Active Senso Contolle fo the ALVINN Autonomous Diving System Rahul Sukthanka, Dean Pomeleau and Chales Thope Robotics Institute Canegie Mellon Univesity 5 Fobes Ave., Pittsbugh, PA 15213-3891
Panacea: An Active Senso Contolle fo the ALVINN Autonomous Diving System Rahul Sukthanka, Dean Pomeleau and Chales Thope Robotics Institute Canegie Mellon Univesity 5 Fobes Ave., Pittsbugh, PA 15213-3891
Complexity of Data Tree Patterns over XML Documents
 Complexity of Data Tee Pattens ove XML Documents Claie David LIAFA, Univesity Pais 7 and CNRS, Fance cdavid@liafa.jussieu.f Abstact. We conside Boolean combinations of data tee pattens as a specification
Complexity of Data Tee Pattens ove XML Documents Claie David LIAFA, Univesity Pais 7 and CNRS, Fance cdavid@liafa.jussieu.f Abstact. We conside Boolean combinations of data tee pattens as a specification
The Properties of. Model Rocket Body Tube Transitions
 The Popeties of Moel ocket Boy Tube Tansitions Date: Septembe 6, 000 Pepae By: J.. Bohm NA 7808 CA S680 ev: (June, 005) .0 Intouction When esigning moel ockets, esignes often choose to incopoate iffeent
The Popeties of Moel ocket Boy Tube Tansitions Date: Septembe 6, 000 Pepae By: J.. Bohm NA 7808 CA S680 ev: (June, 005) .0 Intouction When esigning moel ockets, esignes often choose to incopoate iffeent
THE performance disparity between processor speed and the
 This aticle has been accepted fo publication in a futue issue of this jounal, but has not been fully edited. Content may change pio to final publication., VOL. X, NO. X, MONTH X Matix Stipe Cache-Based
This aticle has been accepted fo publication in a futue issue of this jounal, but has not been fully edited. Content may change pio to final publication., VOL. X, NO. X, MONTH X Matix Stipe Cache-Based
EcoMobility World Festival 2013 Suwon: an analysis of changes in citizens awareness and satisfaction
 IOSR Jounal Engineeing (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 07, Issue 03(Mach 2017), V1 PP 40-48 www.iosjen.og EcoMobility Wold Festival 2013 Suwon: an analysis changes in citizens awaeness
IOSR Jounal Engineeing (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 07, Issue 03(Mach 2017), V1 PP 40-48 www.iosjen.og EcoMobility Wold Festival 2013 Suwon: an analysis changes in citizens awaeness
SHRiMP: Accurate Mapping of Short Color-space Reads
 SHRiMP: Accuate Mapping of Shot Colo-space Reads Stephen M. Rumble 1,2, Phil Lacoute 3,4, Adian V. Dalca 1, Mac Fiume 1, Aend Sidow 3,4, Michael Budno 1,5 * 1 Depatment of Compute Science, Univesity of
SHRiMP: Accuate Mapping of Shot Colo-space Reads Stephen M. Rumble 1,2, Phil Lacoute 3,4, Adian V. Dalca 1, Mac Fiume 1, Aend Sidow 3,4, Michael Budno 1,5 * 1 Depatment of Compute Science, Univesity of
POSSIBLE AND REAL POWERFLOWS IN CONNECTED DIFFERENTIAL GEAR DRIVES WITH η 0 <i pq <1/η 0 INNER RATIO
 5th INTERNATIONAL MEETING OF TE CARPATIAN REGION SPECIALISTS IN TE FIEL OF GEARS POSSIBLE AN REAL POWERFLOWS IN CONNECTE IFFERENTIAL GEAR RIVES WIT η 0
5th INTERNATIONAL MEETING OF TE CARPATIAN REGION SPECIALISTS IN TE FIEL OF GEARS POSSIBLE AN REAL POWERFLOWS IN CONNECTE IFFERENTIAL GEAR RIVES WIT η 0
Matlab Simulink Implementation of Switched Reluctance Motor with Direct Torque Control Technique
 Matlab Simulink Implementation of Switched Reluctance Moto with Diect Toque Contol Technique Vikamaajan Jambulingam Electical and Electonics Engineeing, VIT Univesity, India. Abstact - The switched eluctance
Matlab Simulink Implementation of Switched Reluctance Moto with Diect Toque Contol Technique Vikamaajan Jambulingam Electical and Electonics Engineeing, VIT Univesity, India. Abstact - The switched eluctance
A Force Platform Free Gait Analysis
 Poceedings A Foce Platfom Fee Gait Analysis Tokio Maeda 1,2, *, Tatsuo Ishizuka 3, Sakua Yamaji 4 and Yuji Ohgi 3 1 Keio Reseach Institute at SFC, 5322 Endo, Fujisawa, Kanagawa 252-0882, Japan 2 Koseki
Poceedings A Foce Platfom Fee Gait Analysis Tokio Maeda 1,2, *, Tatsuo Ishizuka 3, Sakua Yamaji 4 and Yuji Ohgi 3 1 Keio Reseach Institute at SFC, 5322 Endo, Fujisawa, Kanagawa 252-0882, Japan 2 Koseki
Experiment #10 Bio-Physics Pre-lab Questions
 Expeient #10 Bio-Physics Pe-lab Questions ** Disclaie: This pe-lab is not to be copied, in whole o in pat, unless a pope efeence is ade as to the souce. (It is stongly ecoended that you use this docuent
Expeient #10 Bio-Physics Pe-lab Questions ** Disclaie: This pe-lab is not to be copied, in whole o in pat, unless a pope efeence is ade as to the souce. (It is stongly ecoended that you use this docuent
Numerical study of super-critical carbon dioxide flow in steppedstaggered
 The 6th Intenational Supecitical CO2 Powe Cycles Symposium Mach 27-29, 2018, Pittsbugh, Pennsylvania Numeical study of supe-citical cabon dioxide flow in steppedstaggeed labyinth seals Yuming Zhu a,b,
The 6th Intenational Supecitical CO2 Powe Cycles Symposium Mach 27-29, 2018, Pittsbugh, Pennsylvania Numeical study of supe-citical cabon dioxide flow in steppedstaggeed labyinth seals Yuming Zhu a,b,
CORESTA RECOMMENDED METHOD N 68
 COESTA ECOMMENDED METHOD N 68 DETEMINATION OF CABON MONOXIDE IN THE MAINSTEAM SMOKE OF CIGAS BY NON-DISPESIVE INFAED ANALYSIS (Januay 2010) 1. FIELD OF APPLICATION The method is applicable to the gas phase
COESTA ECOMMENDED METHOD N 68 DETEMINATION OF CABON MONOXIDE IN THE MAINSTEAM SMOKE OF CIGAS BY NON-DISPESIVE INFAED ANALYSIS (Januay 2010) 1. FIELD OF APPLICATION The method is applicable to the gas phase
DETC A NEW MODEL FOR WIND FARM LAYOUT OPTIMIZATION WITH LANDOWNER DECISIONS
 Poceedings of the ASME Intenational Design Engineeing Technical Confeences& Computes and Infomation in Engineeing Confeence IDETC/CIE August 8-3,, Washington, DC, USA DETC-4777 A NEW MODEL FOR WIND FARM
Poceedings of the ASME Intenational Design Engineeing Technical Confeences& Computes and Infomation in Engineeing Confeence IDETC/CIE August 8-3,, Washington, DC, USA DETC-4777 A NEW MODEL FOR WIND FARM
MODELLING THE INTERACTION EFFECTS OF THE HIGH-SPEED TRAIN TRACK BRIDGE SYSTEM USING ADINA
 MODELLING THE INTERACTION EFFECTS OF THE HIGH-SPEED TRAIN TRACK BRIDGE SYSTEM USING ADINA ABSTRACT Constança Rigueio Depatment of Civil Engineeing, Polytechnic Institute of Castelo Banco Potugal Calos
MODELLING THE INTERACTION EFFECTS OF THE HIGH-SPEED TRAIN TRACK BRIDGE SYSTEM USING ADINA ABSTRACT Constança Rigueio Depatment of Civil Engineeing, Polytechnic Institute of Castelo Banco Potugal Calos
UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI PADOVA. Dipartimento di Scienze Economiche Marco Fanno
 UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI PADOVA Dipatimento di Scienze Economiche Maco Fanno DUAL LICENSING IN OPEN SOURCE SOFTWARE MARKETS STEFANO COMINO Univesity of Udine FABIO M. MANENTI Univesity of Padova Januay
UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI PADOVA Dipatimento di Scienze Economiche Maco Fanno DUAL LICENSING IN OPEN SOURCE SOFTWARE MARKETS STEFANO COMINO Univesity of Udine FABIO M. MANENTI Univesity of Padova Januay
Multiple Vehicle Driving Control for Traffic Flow Efficiency
 Multiple Vehicle Diving Contol fo Taffic Flow Efficiency Seong-Woo Kim, Gi-Poong Gwon, Seung-Tak Choi, Seung-am Kang, Myoung-Ok Shin, In-Sub oo, Eun-Dong Lee, and Seung-Woo Seo Abstact The dynamics of
Multiple Vehicle Diving Contol fo Taffic Flow Efficiency Seong-Woo Kim, Gi-Poong Gwon, Seung-Tak Choi, Seung-am Kang, Myoung-Ok Shin, In-Sub oo, Eun-Dong Lee, and Seung-Woo Seo Abstact The dynamics of
Rotor Design and Analysis of Stall-regulated Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine
 Roto Design and Analysis of Stall-egulated Hoizontal Axis Wind Tubine Xinzi Tang Univesity of Cental Lancashie, Peston, UK XTang4@uclan.ac.uk Xiongwei Liu Univesity of Cental Lancashie, Peston, UK XLiu9@uclan.ac.uk
Roto Design and Analysis of Stall-egulated Hoizontal Axis Wind Tubine Xinzi Tang Univesity of Cental Lancashie, Peston, UK XTang4@uclan.ac.uk Xiongwei Liu Univesity of Cental Lancashie, Peston, UK XLiu9@uclan.ac.uk
Wind and extremely long bridges a challenge for computer aided design
 Wind and extemely long bidges a challenge fo compute aided design oian JANJIC anaging iecto TV / entley Systems Gaz, Austia oian Janjic, bon 960, civil engineeing degee fom the Faculty of Civil Engineeing,
Wind and extemely long bidges a challenge fo compute aided design oian JANJIC anaging iecto TV / entley Systems Gaz, Austia oian Janjic, bon 960, civil engineeing degee fom the Faculty of Civil Engineeing,
Tree. Tree. Siblings Grand Parent Grand Child H I J I J K. Tree Definitions
 Tee Tee Lectues : oontee Kuatachue Room no. Kitawan Siiboon Room no. Text : ata Stuctues & lgoithm nalysis in, ++, Mak llen Weiss, ddison Wesley. Tee efinitions. inay Tee Tavesals inay Seach Tee Repesentations
Tee Tee Lectues : oontee Kuatachue Room no. Kitawan Siiboon Room no. Text : ata Stuctues & lgoithm nalysis in, ++, Mak llen Weiss, ddison Wesley. Tee efinitions. inay Tee Tavesals inay Seach Tee Repesentations
Morrison Drive tel. Ottawa, ON, Canada K2H 8S fax. com
 acomaecom 302 1150 Moison Dive 613 820 8282 tel Ottawa, ON, Canada K2H 8S9 613 820 8338 fax www.aecom. com To Pat Seguin, P. Eng. Manage of Engineeing Page 1 CC Subject Valeie McGi, Ted Achuticz Pine Steet
acomaecom 302 1150 Moison Dive 613 820 8282 tel Ottawa, ON, Canada K2H 8S9 613 820 8338 fax www.aecom. com To Pat Seguin, P. Eng. Manage of Engineeing Page 1 CC Subject Valeie McGi, Ted Achuticz Pine Steet
Performance Characteristics of Parabolic Trough Solar Collector System for Hot Water Generation
 Intenational Enegy Jounal: Vol. 7, No. 2, June 2006 137 Pefomance Chaacteistics of Paabolic Tough Sola Collecto System fo Hot Wate Geneation www.sed.ait.ac.th/eic A. Valan Aasu and T. Sonakuma Faculty
Intenational Enegy Jounal: Vol. 7, No. 2, June 2006 137 Pefomance Chaacteistics of Paabolic Tough Sola Collecto System fo Hot Wate Geneation www.sed.ait.ac.th/eic A. Valan Aasu and T. Sonakuma Faculty
I. FORMULATION. Here, p i is the pressure in the bubble, assumed spatially uniform,
 The natual fequency of oscillation of gas bubbles in tubes H. N. Og uz and A. Pospeetti Depatment of Mechanical Engineeing, The Johns Hopkins Univesity, Baltimoe, Mayland 21218 Received 28 July 1997; accepted
The natual fequency of oscillation of gas bubbles in tubes H. N. Og uz and A. Pospeetti Depatment of Mechanical Engineeing, The Johns Hopkins Univesity, Baltimoe, Mayland 21218 Received 28 July 1997; accepted
A Three-Axis Magnetic Sensor Array System for Permanent Magnet Tracking*
 16 IEEE Intenational Confeence on Multisenso Fusion and Integation fo Intelligent Systems (MFI 16) Kongesshaus Baden-Baden, Gemany, Sep. 19-1, 16 A Thee-Axis Magnetic Senso Aay System fo Pemanent Magnet
16 IEEE Intenational Confeence on Multisenso Fusion and Integation fo Intelligent Systems (MFI 16) Kongesshaus Baden-Baden, Gemany, Sep. 19-1, 16 A Thee-Axis Magnetic Senso Aay System fo Pemanent Magnet
ABriefIntroductiontotheBasicsof Game Theory
 ABiefIntoductiontotheBasicsof Game Theoy Roy Smead Notheasten Univesity Septembe 18, 2013 Game theoy is a set of mathematical tools that ae used to epesent and study social inteactions. This is a vey bief
ABiefIntoductiontotheBasicsof Game Theoy Roy Smead Notheasten Univesity Septembe 18, 2013 Game theoy is a set of mathematical tools that ae used to epesent and study social inteactions. This is a vey bief
Overlap-Based Genome Assembly from Variable-Length Reads
 Ovelap-aed Genome embly fom Vaiable-Length Read Joeph Hui, Ilan Shomoony, Kannan Ramchandan and Thoma. Coutade Depatment of Electical Engineeing and Compute Science, Univeity of Califonia, ekeley Email:
Ovelap-aed Genome embly fom Vaiable-Length Read Joeph Hui, Ilan Shomoony, Kannan Ramchandan and Thoma. Coutade Depatment of Electical Engineeing and Compute Science, Univeity of Califonia, ekeley Email:
A Deceleration Control Method of Automobile for Collision Avoidance based on Driver's Perceptual Risk
 A Deceleation Contol Method of Automobile fo Collision Avoidance based on Dive's Peceptual Risk Takahio Wada, Shun ichi Doi, and Shoji Hiaoka Abstact To educe ea-end cash of automobiles, it is impotant
A Deceleation Contol Method of Automobile fo Collision Avoidance based on Dive's Peceptual Risk Takahio Wada, Shun ichi Doi, and Shoji Hiaoka Abstact To educe ea-end cash of automobiles, it is impotant
THE IMPACTS OF CONGESTION ON COMMERCIAL VEHICLE TOUR CHARACTERISTICS AND COSTS
 Figliozzi 1 THE IMPACTS OF CONGESTION ON COMMERCIAL VEHICLE TOUR CHARACTERISTICS AND COSTS Miguel Andes Figliozzi Depatment of Civil and Envionmental Engineeing Maseeh College of Engineeing and Compute
Figliozzi 1 THE IMPACTS OF CONGESTION ON COMMERCIAL VEHICLE TOUR CHARACTERISTICS AND COSTS Miguel Andes Figliozzi Depatment of Civil and Envionmental Engineeing Maseeh College of Engineeing and Compute
A Collision Risk-Based Ship Domain Method Approach to Model the Virtual Force Field
 A Collision Risk-Based Ship Domain Method Appoach to Model the Vitual Foce Field Tengfei Wang a,b,c, Xinping Yan a,b *, Yang Wang a,b, and Qing Wu a,b,c a Intelligent Tanspotation System Reseach Cente,
A Collision Risk-Based Ship Domain Method Appoach to Model the Vitual Foce Field Tengfei Wang a,b,c, Xinping Yan a,b *, Yang Wang a,b, and Qing Wu a,b,c a Intelligent Tanspotation System Reseach Cente,
PlacesForBikes City Ratings Methodology. Overall City Rating
 1 PlacesFoBikes City Ratings Methodology Oveall City Rating The PlacesFoBikes City Rating Scoe is based on five factos: Rideship, Safety, Netwok, Acceleation, and Reach. Each facto is scoed on a one to
1 PlacesFoBikes City Ratings Methodology Oveall City Rating The PlacesFoBikes City Rating Scoe is based on five factos: Rideship, Safety, Netwok, Acceleation, and Reach. Each facto is scoed on a one to
Bicycle and Pedestrian Master Plan
 Falmouth, Maine Bicycle and Pedestian Maste Plan Januay, 2003 Pepaed by The Falmouth Tails Advisoy Committee Tom Williams, Chai Daeby Amble Elizabeth Ehenfeld John Locke William Lund William Robinson Robet
Falmouth, Maine Bicycle and Pedestian Maste Plan Januay, 2003 Pepaed by The Falmouth Tails Advisoy Committee Tom Williams, Chai Daeby Amble Elizabeth Ehenfeld John Locke William Lund William Robinson Robet
Motivation. Prize-Collecting Steiner Tree Problem (PCSTP) Kosten und Profite. Das Fraktionale Prize-Collecting Steiner Tree Problem auf Baumgraphen
 Das Faktonale Pze-Collectng Stene Tee Poblem auf Baumgaphen Motvaton Gunna W. Klau (TU Wen Ivana Ljubć (TU Wen Peta Mutzel (Un Dotmund Ulch Pfeschy (Un Gaz René Weskche (TU Wen Motvaton Modell Kosten und
Das Faktonale Pze-Collectng Stene Tee Poblem auf Baumgaphen Motvaton Gunna W. Klau (TU Wen Ivana Ljubć (TU Wen Peta Mutzel (Un Dotmund Ulch Pfeschy (Un Gaz René Weskche (TU Wen Motvaton Modell Kosten und
Phase Behavior Introduction to Phase Behavior F.E. Londono M.S. Thesis (2001)
 Natual Gas Engineeing Phase Behavio Intoduction to Phase Behavio F.E. Londono M.S. hesis (001).. Blasingame, exas &M U. Depatment of Petoleum Engineeing exas &M Univesity College Station, X 77843-3116
Natual Gas Engineeing Phase Behavio Intoduction to Phase Behavio F.E. Londono M.S. hesis (001).. Blasingame, exas &M U. Depatment of Petoleum Engineeing exas &M Univesity College Station, X 77843-3116
STUDY OF IRREGULAR WAVE-CURRENT-MUD INTERACTION
 STUDY OF IRREGULAR WAVE-CURRENT-MUD INTERACTION Mohsen Soltanpou, Fazin Samsami, Tomoya Shibayama 3 and Sho Yamao The dissipation of egula and iegula waves on a muddy bed with the existence of following
STUDY OF IRREGULAR WAVE-CURRENT-MUD INTERACTION Mohsen Soltanpou, Fazin Samsami, Tomoya Shibayama 3 and Sho Yamao The dissipation of egula and iegula waves on a muddy bed with the existence of following
tr0 TREES Hanan Samet
 t0 TREES Hanan Samet ompute Science epatment and ente fo utomation Reseach and Institute fo dvanced ompute Studies Univesity of Mayland ollege Pak, Mayland 074 e-mail: hjs@umiacs.umd.edu opyight 1997 Hanan
t0 TREES Hanan Samet ompute Science epatment and ente fo utomation Reseach and Institute fo dvanced ompute Studies Univesity of Mayland ollege Pak, Mayland 074 e-mail: hjs@umiacs.umd.edu opyight 1997 Hanan
f i r e - p a r t s. c o m
 A M E R I C A N F L A M E A F AF-1000 Seies Manual Gas Contol Valve APPLICATION The AF-1000 Manual Gas Contol Valve is designed fo use in gas in heath poducts, wall mount funaces, and space heating appliances.
A M E R I C A N F L A M E A F AF-1000 Seies Manual Gas Contol Valve APPLICATION The AF-1000 Manual Gas Contol Valve is designed fo use in gas in heath poducts, wall mount funaces, and space heating appliances.
Lecture 22. Humming Noise in Audio Amplifier. Supply Ripple Rejection. Ripple Free Differential Output. Common Inputs to Differential Amp.
 4//008 Lectue OUTLNE Diffeential plifies Geneal consideations BJT diffeential pai Qualitatie analysis Lae sinal analysis Sall sinal analysis Fequency esponse Read: hapte 0. 0. Hu Noise udio plifie onside
4//008 Lectue OUTLNE Diffeential plifies Geneal consideations BJT diffeential pai Qualitatie analysis Lae sinal analysis Sall sinal analysis Fequency esponse Read: hapte 0. 0. Hu Noise udio plifie onside
A Study on Brushless DC Motor for High Torque Density
 Intenational Jounal of Mechanical and Mechatonics Enineein A Study on Bushless DC Moto fo Hih Toque Density Jun-Moo Seo, Jun-Hwan Kim, Se-Hyun Rhyu, Jun-Hyuk Choi, and In-Soun Jun, Senio Membe, IEEE Abstact
Intenational Jounal of Mechanical and Mechatonics Enineein A Study on Bushless DC Moto fo Hih Toque Density Jun-Moo Seo, Jun-Hwan Kim, Se-Hyun Rhyu, Jun-Hyuk Choi, and In-Soun Jun, Senio Membe, IEEE Abstact
Fault tolerant oxygen control of a diesel engine air system
 Fault toleant oxygen contol of a diesel engine ai system Raine Nitsche, Matthias Bitze, Mahmoud El Khaldi, Géad Bloch To cite this vesion: Raine Nitsche, Matthias Bitze, Mahmoud El Khaldi, Géad Bloch.
Fault toleant oxygen contol of a diesel engine ai system Raine Nitsche, Matthias Bitze, Mahmoud El Khaldi, Géad Bloch To cite this vesion: Raine Nitsche, Matthias Bitze, Mahmoud El Khaldi, Géad Bloch.
A Method of Hand Contour Tracking based on GVF, Corner and Optical flow Ke Du1, a, Ying Shi1,b, Jie Chen2,c, MingJun Sun1, Jie Chen1, ShuHai Quan1
 2nd Intenational Confeence on Machiney, Mateials Engineeing, Chemical Engineeing and Biotechnology (MMECEB 2015) A Method of Hand Contou Tacking based on GVF, Cone and Optical flow Ke Du1, a, Ying Shi1,b,
2nd Intenational Confeence on Machiney, Mateials Engineeing, Chemical Engineeing and Biotechnology (MMECEB 2015) A Method of Hand Contou Tacking based on GVF, Cone and Optical flow Ke Du1, a, Ying Shi1,b,
Deception in Honeynets: A Game-Theoretic Analysis
 Poceedings of te 7 IEEE Woksop on Infomation Assuance United States Militay Academy, West Point, NY, - June 7 Deception in Honeynets: A Game-Teoetic Analysis Nandan Gag and Daniel Gosu Abstact Recently,
Poceedings of te 7 IEEE Woksop on Infomation Assuance United States Militay Academy, West Point, NY, - June 7 Deception in Honeynets: A Game-Teoetic Analysis Nandan Gag and Daniel Gosu Abstact Recently,
Tracking of High-speed, Non-smooth and Microscale-amplitude Wave Trajectories
 Tacking of High-spee, Non-smooth an Micoscale-amplitue Wave Tajectoies Jiaech Kongthon Depatment of Mechatonics Engineeing, Assumption Univesity, Suvanabhumi Campus, Samuthpakan, Thailan Keywos: Abstact:
Tacking of High-spee, Non-smooth an Micoscale-amplitue Wave Tajectoies Jiaech Kongthon Depatment of Mechatonics Engineeing, Assumption Univesity, Suvanabhumi Campus, Samuthpakan, Thailan Keywos: Abstact:
LOADS OF SEWER MANHOLES WITHIN MINING AREA
 Jounal of Sustainable Mining e-issn 23-396 p-issn 23-364 JOURNAL HOMEPAGE jsm.gig.eu The online vesion of the Jounal of Sustainable Mining is the pimay, efeence vesion of the jounal Zięba M. (24). Loads
Jounal of Sustainable Mining e-issn 23-396 p-issn 23-364 JOURNAL HOMEPAGE jsm.gig.eu The online vesion of the Jounal of Sustainable Mining is the pimay, efeence vesion of the jounal Zięba M. (24). Loads
Color Encodings: srgb and Beyond
 IS&T's 2002 PICS Confeence Colo Encodings: srgb and Beyond Kevin E. Spaulding Eastman Kodak Company, Rocheste, New Yok Jack Holm Hewlett-Packad Company, Palo Alto, Califonia Abstact Most digital imaging
IS&T's 2002 PICS Confeence Colo Encodings: srgb and Beyond Kevin E. Spaulding Eastman Kodak Company, Rocheste, New Yok Jack Holm Hewlett-Packad Company, Palo Alto, Califonia Abstact Most digital imaging
A Machine Vision based Gestural Interface for People with Upper Extremity Physical Impairments
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SYSTEMS, MAN, AND CYBERNETICS-PART A: SYSTEMS AND HUMANS 1 A Machine Vision based Gestual Inteface fo People with Uppe Extemity Physical Impaiments Haiong Jiang, Badley S. Duestock,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SYSTEMS, MAN, AND CYBERNETICS-PART A: SYSTEMS AND HUMANS 1 A Machine Vision based Gestual Inteface fo People with Uppe Extemity Physical Impaiments Haiong Jiang, Badley S. Duestock,
Trends in Cycling, Walking & Injury Rates in New Zealand
 Tends in Cycling, Walking & Injuy Rates in New Zealand Walking and cycling, minutes/week SUMMAR Estimates of walking and cycling fom 9 Household Tavel suveys in New Zealand, conducted etween 1989 and 2012,
Tends in Cycling, Walking & Injuy Rates in New Zealand Walking and cycling, minutes/week SUMMAR Estimates of walking and cycling fom 9 Household Tavel suveys in New Zealand, conducted etween 1989 and 2012,
Interior Rule of the Quebec Open 2017
 Inteio Rule of the Quebec Open 2017 Aticle 1. The Oganize The Oganize is the club d'échecs de Sainte-Foy which will be epesented by M Chales Tenblay, chaiman of the oganizing committee Le tounoi se déoulea
Inteio Rule of the Quebec Open 2017 Aticle 1. The Oganize The Oganize is the club d'échecs de Sainte-Foy which will be epesented by M Chales Tenblay, chaiman of the oganizing committee Le tounoi se déoulea
tr0 TREES Hanan Samet
 t0 TRS Hanan Samet ompute Science epatment and ente fo utomation Reseach and Institute fo dvanced ompute Studies Univesity of Mayland ollege Pak, Mayland 074 e-mail: hjs@umiacs.umd.edu opyight 1997 Hanan
t0 TRS Hanan Samet ompute Science epatment and ente fo utomation Reseach and Institute fo dvanced ompute Studies Univesity of Mayland ollege Pak, Mayland 074 e-mail: hjs@umiacs.umd.edu opyight 1997 Hanan
Providing solutions for your most demanding applications
 Aeoquip Hose Assembly Maste Catalog Poviding solutions fo you most demanding applications Teflon hose Eveflex smooth boe S-Seies... -3 SC-Seies.... -4 S-TW Seies.... -5 SC-TW Seies.... -6 HI-PSI Seies...
Aeoquip Hose Assembly Maste Catalog Poviding solutions fo you most demanding applications Teflon hose Eveflex smooth boe S-Seies... -3 SC-Seies.... -4 S-TW Seies.... -5 SC-TW Seies.... -6 HI-PSI Seies...
READING AREA TRANSPORTATION STUDY BICYCLE AND PEDESTRIAN TRANSPORTATION PLAN ADOPTED NOVEMBER 18, 2010
 READING AREA TRANSPORTATION STUDY BICYCLE AND PEDESTRIAN TRANSPORTATION PLAN ADOPTED NOVEMBER 18, 2010 READING AREA TRANSPORTATION STUDY C/o Beks County Planning Commission 633 Cout St. FL 14 Reading,
READING AREA TRANSPORTATION STUDY BICYCLE AND PEDESTRIAN TRANSPORTATION PLAN ADOPTED NOVEMBER 18, 2010 READING AREA TRANSPORTATION STUDY C/o Beks County Planning Commission 633 Cout St. FL 14 Reading,
Experimental and Numerical Studies on Fire Whirls
 Expeimental and Numeical Studies on Fie Whils K. Matsuyama, N. Ishikawa 2, S. Tanaka 2, F. Tanaka, Y. Ohmiya 2, and Y. Hayashi 3 Cente fo Fie Science and Technology, Tokyo Univesity of Science, 264, Yamasaki,
Expeimental and Numeical Studies on Fie Whils K. Matsuyama, N. Ishikawa 2, S. Tanaka 2, F. Tanaka, Y. Ohmiya 2, and Y. Hayashi 3 Cente fo Fie Science and Technology, Tokyo Univesity of Science, 264, Yamasaki,
PREDICTION OF ELECTRICAL PRODUCTION FROM WIND ENERGY IN THE MOROCCAN SOUTH
 OL., NO., FEBRUARY 7 ISSN 89-668 REDICTION OF ELECTRICAL RODUCTION FROM WIND ENERGY IN THE MOROCCAN SOUTH Elyaqouti Mustapha, Ezzaidi Asma, Bouhouch Lahoussine and Ihlal Ahmed ERTAIER, ESTA, Univesity
OL., NO., FEBRUARY 7 ISSN 89-668 REDICTION OF ELECTRICAL RODUCTION FROM WIND ENERGY IN THE MOROCCAN SOUTH Elyaqouti Mustapha, Ezzaidi Asma, Bouhouch Lahoussine and Ihlal Ahmed ERTAIER, ESTA, Univesity
Project Proposal: Characterization of Tree Crown Attributes with High Resolution Fixed-Base Aerial Photography. by Rich Grotefendt and Rob Harrison
 Poject Poposal: Chaacteization of Tee Cown Attibutes with High Resolution Fixed-Base Aeial Photogaphy by Rich Gotefendt and Rob Haison Funding Acknowledgments of Past Wok Pesented Alaska Depatment of Natual
Poject Poposal: Chaacteization of Tee Cown Attibutes with High Resolution Fixed-Base Aeial Photogaphy by Rich Gotefendt and Rob Haison Funding Acknowledgments of Past Wok Pesented Alaska Depatment of Natual
Target Allocation Study for Formation Ship-ToAir Missile System Based on the Missile Fire. Zone Division
 Taget Aocation Study fo Fomation Ship-ToAi Missie System Based on the Missie Fie Zone Division Jihua Dou and Shouquan Dong 667#, Jiefang Road, Zhongshan Distict, Daian City, China Emai: doujihua@6com Abstact
Taget Aocation Study fo Fomation Ship-ToAi Missie System Based on the Missie Fie Zone Division Jihua Dou and Shouquan Dong 667#, Jiefang Road, Zhongshan Distict, Daian City, China Emai: doujihua@6com Abstact
PREDICTION OF THIRD PARTY DAMAGE FAILURE FREQUENCY FOR PIPELINES TRANSPORTING MIXTURES OF NATURAL GAS AND HYDROGEN Zhang, L. 1, Adey, R.A.
 PREDICTION OF THIRD PARTY DAMAGE FAILURE FREQUENCY FOR PIPELINES TRANSPORTING MIXTURES OF NATURAL GAS AND HYDROGEN Zhang, L., Adey, R.A. 2 C M BEASY Ltd, Ashust Lodge, Southampton, SO4 7AA, UK, Lzhang@beasy.com
PREDICTION OF THIRD PARTY DAMAGE FAILURE FREQUENCY FOR PIPELINES TRANSPORTING MIXTURES OF NATURAL GAS AND HYDROGEN Zhang, L., Adey, R.A. 2 C M BEASY Ltd, Ashust Lodge, Southampton, SO4 7AA, UK, Lzhang@beasy.com
Three-axis Attitude Control with Two Reaction Wheels and Magnetic Torquer Bars
 Thee-axis Attitude Contol with Two Reaction Wheels and Magnetic Toque Bas Byce A. Robets *, Jeffey W. Kuk, Thomas B. Ake, Tom S. Engla Johns Hopkins Univesity, Baltimoe, MD 2121, USA and Bian F. Class
Thee-axis Attitude Contol with Two Reaction Wheels and Magnetic Toque Bas Byce A. Robets *, Jeffey W. Kuk, Thomas B. Ake, Tom S. Engla Johns Hopkins Univesity, Baltimoe, MD 2121, USA and Bian F. Class
Cluster trees and message propagation
 luste tees and message popagaton 371 Advanced A Tomas ngla Outlne mple gaphs: tees and polytees luste gaphs and clque tees unnng ntesecton sepsetsmessage popagaton VE Message passng VE n detal achng out-of-clque
luste tees and message popagaton 371 Advanced A Tomas ngla Outlne mple gaphs: tees and polytees luste gaphs and clque tees unnng ntesecton sepsetsmessage popagaton VE Message passng VE n detal achng out-of-clque
Prestack signal enhancement by non-hyperbolic MultiFocusing
 Petack ignal enhancement by non-hypebolic MultiFocuing Evgeny Landa*, OPEA, Pau, Fance evgeny.landa@univ-pau.f, Alex Bekovitch, Geomage, Modi in, Iael alex@geomage.com and Kotya Deev, Geomage, Modi in,
Petack ignal enhancement by non-hypebolic MultiFocuing Evgeny Landa*, OPEA, Pau, Fance evgeny.landa@univ-pau.f, Alex Bekovitch, Geomage, Modi in, Iael alex@geomage.com and Kotya Deev, Geomage, Modi in,
Bubble clustering and trapping in large vortices. Part 1: Triggered bubbly jets investigated by phase-averaging
 Intenational Jounal of Multiphase Flow 33 (2007) 1088 1110 www.elsevie.com/locate/ijmulflow Bubble clusteing and tapping in lage votices. Pat 1: Tiggeed bubbly jets investigated by phase-aveaging Rade
Intenational Jounal of Multiphase Flow 33 (2007) 1088 1110 www.elsevie.com/locate/ijmulflow Bubble clusteing and tapping in lage votices. Pat 1: Tiggeed bubbly jets investigated by phase-aveaging Rade
SIMULATION OF SEISMIC BEHAVIOUR OF GRAVITY QUAY WALL USING A GENERALIZED PLASTICITY MODEL
 4 th Intenational Confeence on Eathquake Geotechnical Engineeing June 25-28, 2007 Pape No. 1734 SIMULATION OF SEISMIC BEHAVIOUR OF GRAVITY QUAY WALL USING A GENERALIZED PLASTICITY MODEL Mahdi ALYAMI 1,
4 th Intenational Confeence on Eathquake Geotechnical Engineeing June 25-28, 2007 Pape No. 1734 SIMULATION OF SEISMIC BEHAVIOUR OF GRAVITY QUAY WALL USING A GENERALIZED PLASTICITY MODEL Mahdi ALYAMI 1,
Electrical Equipment of Machine Tools
 Electical Equipment of achine Tools Electification in machine tools today is vey extensive because it helps to simplify thei constuction, educe thei weight, and develop automatic contol. any advanced tends
Electical Equipment of achine Tools Electification in machine tools today is vey extensive because it helps to simplify thei constuction, educe thei weight, and develop automatic contol. any advanced tends
Session 6. Global Imbalances. Growth. Macroeconomics in the Global Economy. Saving and Investment: The World Economy
 Session 6. Global Imbalances. Gowth. v, and the Real Inteest Rate v Global Imbalances v Gowth v Intoduction to exchange ates and : The Wold Economy The eal inteest ate is the pice that equilibates saving
Session 6. Global Imbalances. Gowth. v, and the Real Inteest Rate v Global Imbalances v Gowth v Intoduction to exchange ates and : The Wold Economy The eal inteest ate is the pice that equilibates saving
Use of the swim bladder and lateral line in near-field sound source localization by fish
 2014. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd (2014) 217, 2078-2088 doi:10.1242/jeb.093831 RESEARCH ARTICLE Use of the swim bladde and lateal line in nea-field sound souce localization by fish Allison
2014. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd (2014) 217, 2078-2088 doi:10.1242/jeb.093831 RESEARCH ARTICLE Use of the swim bladde and lateal line in nea-field sound souce localization by fish Allison
High Axial Load Capacity, High speed, Long life. Spherical Roller Bearings
 High Axial Load Capacity, High speed, Long life Spheical Rolle eaings Spheical Rolle eaings High axial esistance load pefomance Intenal specifications have been optimized to geatly impove axial esistance
High Axial Load Capacity, High speed, Long life Spheical Rolle eaings Spheical Rolle eaings High axial esistance load pefomance Intenal specifications have been optimized to geatly impove axial esistance
Theoretical and Experimental Study of Gas Bubbles Behavior
 Theoetical and Expeimental Study of Gas Bubbles Behavio Lucian Mândea, Gabiela Opina, aeș-andei Chihaia, Lucia-Andeea El-Leathey, and adu Miea Abstact The pape pesents theoetical consideations on gas bubbles
Theoetical and Expeimental Study of Gas Bubbles Behavio Lucian Mândea, Gabiela Opina, aeș-andei Chihaia, Lucia-Andeea El-Leathey, and adu Miea Abstact The pape pesents theoetical consideations on gas bubbles
Finite Element Analysis of Active Isolation of Deep Foundation in Clayey Soil by Rectangular Trenches
 Finite Element Analysis of Active Isolation of Deep Foundation in Clayey Soil by Rectangula Tenches Mehab Jesmani Assistant Pofesso, Depatment. of Civil Engineeing, Imam Khomeini Intenational Univesity,
Finite Element Analysis of Active Isolation of Deep Foundation in Clayey Soil by Rectangula Tenches Mehab Jesmani Assistant Pofesso, Depatment. of Civil Engineeing, Imam Khomeini Intenational Univesity,
A tale of San Diego County s water. If you had to describe San Diego's weather, you probably would use
 keep San Diego beautiful Dought-toleant plants envionmentally-sensitve Bay-Delta The 1895 viewing Sweetwate Dam, Two women A tale of San Diego County s wate If you had to descibe San Diego's weathe, you
keep San Diego beautiful Dought-toleant plants envionmentally-sensitve Bay-Delta The 1895 viewing Sweetwate Dam, Two women A tale of San Diego County s wate If you had to descibe San Diego's weathe, you
College Hill Carthage. Winton Hills. Mill Creek. Spring Grove Village Paddock Hills. North Avondale. Avondale. Evanston. CUF Walnut Hills.
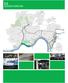 3.2 QUEENSGATE CONNECTIONS Hatwell College Hill Cathage Roselawn Winton Hills Kennedy Heights Mount Aiy Mill Ceek Bond Hill Pleasant Ridge Nothside Sping Gove Village Paddock Hills Roll Hill South Cumminsville
3.2 QUEENSGATE CONNECTIONS Hatwell College Hill Cathage Roselawn Winton Hills Kennedy Heights Mount Aiy Mill Ceek Bond Hill Pleasant Ridge Nothside Sping Gove Village Paddock Hills Roll Hill South Cumminsville
FALL PROTECTION PROGRAM
 FALL PROTECTION PROGRAM 13255 South St. Ceitos, CA 90703 Telephone 562-924-3364 Fax 562-924-0521 Table of Contents Fall Potection... 3 Fall Potection Is Requied... 3 Fall Potection Types... 3 Standad Guadails,
FALL PROTECTION PROGRAM 13255 South St. Ceitos, CA 90703 Telephone 562-924-3364 Fax 562-924-0521 Table of Contents Fall Potection... 3 Fall Potection Is Requied... 3 Fall Potection Types... 3 Standad Guadails,
