1.5 THE LAND BREEZE CHARACTERISTICS IN ISRAEL DURING THE SUMMER BY THE MM5 MODEL
|
|
|
- Leon Gyles Murphy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1. THE LAND BREEZE CHARACTERISTICS IN ISRAEL DURING THE SUMMER BY THE MM MODEL S. Berkovic and Y. Feliks Department of Mathematics, Israel Institute for Biological Research P.O.B 19, Ness-Ziona, Israel 1. Introduction During the summer (mainly July and August) the sea-land breeze circulation is the most prominent flow. The Persian trough is the dominant synoptic system in the lower levels. At the beginning of the night the land breeze develops along the coast due to sea-land differential cooling. Later, as the katabatic wind arrives from the western slopes of the mountain ridges, the wind intensity increases and becomes southeast. The mountains are 3 km inland in the south and approach the coast in the north. This paper describes the land breeze and the katabatic wind along the coast in Israel during July 1994 as obtained from MM simulations. 2. Model Setup The standard PSU/NCAR MM model version 3.2 (Dudhia 2) was run for 4 one-way nested domains starting at a resolution of 4 km over the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea down to 2 km for the center to the north of the Israeli coast (fig 1). 26 vertical levels were applied, 11 levels under 2 km above the ground. The model initial and boundary conditions were taken from the GEOS-1 Multi Year Assimilation Data Mediterranean subset (Da-Silva and Alpert 1996) and AVHRR sea surface temperature (WOCE satellite Data CD-ROM, Version 1.1) data set, with a time resolution of 6 hours. The model was Rosh 69 8 Fig 1: 4, 18, 6 and 2 km MM modeling domains. On the right, the topography of the studied area and locations of important points. TA(pt. 9 ) == Tel-Aviv, N( pt. 24 ) ==Netanya Rosh ( pt. 69 ) ==Rosh-Hanikra, A( pt. 9) == Akko (Acre), H( pt. 47) == Ha-Hoterim, MC == Mount Carmel * Corresponding author address: S. Berkovic, IIBR, Ness-Ziona, Israel; berkovic@iibr.gov.il A 9 Haifa 2 MC H N 24 TA 3km Height m
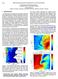
2 initialized at Z and run for 36 hours every day during July The physical parameterizations used were: Grell cumulus scheme, MRF boundary layer scheme, Five layer soil temperature model, Dudhia simple ice microphysical scheme and Cloud-radiation scheme. The model output was saved every hour. The analysis of the time series is presented in the next section. 3. Results The land breeze is a wind with an eastern component due to katabatic wind and differential cooling, therefore, it is defined as the component of the offshore wind orthogonal to the coastline. The calculated land breeze characteristics along the coast were: 1. The land breeze imum intensity. 2. The land breeze start, imum intensity and end times 3. Duration of the land breeze, as derived from end and start times. The nocturnal wind is weak (< 2 m/s) and might change from offshore to onshore wind for a imum period of 3 hours. The start time is defined as the first time an offshore wind is found after at least 4 hours of onshore wind. The land breeze blows during the night, therefore we inspect two days. The end time is found by going backwards in time from 14Z on the next day, it is the last hour at which land breeze is found, if there is an onshore wind from the end time to 14Z on the next day. This definition allows the occurrence of short periods (< 3 hours) of an onshore wind during the duration of the land breeze. The land breeze parameters were calculated from model output of the finest domain at the lowest sigma level (~ m above the ground). The average of the imum intensity of the land breeze, u, v, and the wind intensity at the imum time, along the coastline from S to N, is shown in Fig. 2a. The strongest imum land breeze intensity is 2.4 m/s south of Haifa around Atlit (point 44,4). The weakest imum land breeze is.8 m/s around Haifa (point 49). m/s a m/s u v speed b Tel-Aviv Netanya Haifa Rosh-Hanikra Fig 2: a. The average imum land breeze intensity ( black), and the average u (green),v(red) and speed(blue) at the time of the imum land breeze along the coastline from S to N. ( point 9 == Tel Aviv, point ==Netanya, Point 2 == Haifa, point 69 == Rosh Hanikra). b. The variance.
3 The influence of the coastline curvature is seen by the varying contribution of the u and v horizontal wind components (u from W to E, v from S to N). The contribution of u increases at the northern points (-7) where the coastline is straight and goes from south to north. The variance of the parameters ( Fig 2.b) changes significantly along the coast probably as a result of the topography. In areas of complex terrain: Haifa, Akko (Acre) and Rosh Hanikra (points ) the highest variance ~1 m/s was found. In areas of flat terrain and straight coastline: from Tel-Aviv to Netanya (points 1-24) the smallest variance.3-. m/s was found. McPherson 197 explained the asymmetric flow above a rectangular bay as a result of Coriolis and the pressure gradient forces counter acting on one side of the bay and co acting on the other side. Gilliam et al 24 pointed out the special flow where the coastline has cusps. Furthermore, the katabatic wind adds to the curvature effect, it strengthens the wind s intensity and broadens the variance of the wind direction. The average start, imum and end times of the land breeze are shown in fig 3a. The land breeze starts at 19-23Z. North of Rosh Hanikra (points 68-8) the start time is earlier: 19-2Z, probably as a result of the proximity of steep mountains to the coast. The latest start time is 23Z around the Carmel area where steep mountain and curved coastline meet. The average land breeze imum time is 1-3Z, from Rosh-Hanikra and further north it is earlier: 23-1Z. The average end time is -6Z, from Rosh-Hanikra and further north it is earlier: 4- Z. The variance (Fig3b) of the start time is 2-2. hours. The variance of the imum time is hours. The variance of the end time is ~ 1 hour from Tel-Aviv to Ha-Hotrim, south of the Carmel (point 47), around Acre it increases to 1. hour and further north from Rosh-Hanikra it increases to hours. GMT ave start end start end urs ho var start end start end Fig 3: a. The average start, imum intensity and end times of the land breeze along the coastline from S to N. b. The variance.
4 The Carmel area is a singular point as a result of its unique topography and needs further study. The greatest variance of start and end times was found there, which indicates a different flow. The duration of the land breeze is 7-1 hours and its variance is 2-4 hours. Further statistical information is gained from the histograms of the start, imum and end times of the land breeze at the following : Tel-Aviv (point 9), Netanya (point 24), Haifa bay (point ) and Rosh-Hanikra (point 69) (Fig 4). The distribution of the end time is narrower than the distribution of the start and the imum time. At all the points, the most frequent hours of the start (21-23Z), imum (3-4Z) and end times (4-Z) agree within 1 hour. The average values of the imum time are 1-2 hours earlier than the most frequent hours of the imum time. The average and the most frequent hours of the start and end times are the same. Tel-Aviv pt _t 4 end_t 4 Netanya pt 24 4 _t 4 end_t pt 2 3 Haifa bay _t 2 3 end_t 2 3 Rosh-Hanikra Fig4: start, imum intensity and end time histograms of the land breeze at the : Tel-Aviv, Netanya, Haifa bay and Rosh-Hanikra.
5 Summary The start, imum intensity and end times of the land breeze along the coast were calculated. It starts earlier in the northern part of the coast probably as a result of the proximity of the mountains to the coast. The distribution of start and imum times is broader than the end time distribution. The average imum intensity of the land breeze is about 2 m/s at a height of m above the ground. The Israeli coastline is straight except near Haifa (in the north) where the coastline curves sharply to form the bay and there the Carmel Mountain reaches the coast. In this region the land breeze has a different behavior and the imum land breeze intensity is found there. References Da-Silva A. and Alpert P., 1996: Documentation of the multi-year GEOS-1 assimilation data subset for the Northern Africa, the Mediterranean and the Middle East, NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center, Data Assimilation Office Note 96-24pp. Dudhia J., Gill D., Guo Y. and Manning K., 2: PSU/NCAR Mesoscale modeling system tutorial class notes and Users guide Gilliam R. C., Raman S. and Niyogi D. T. S., 24: Observational and numerical study of the influence of large-scale flow direction and coastline shape on sea-breeze evolution. Boundary-Layer Meteorology 111:27-3. McPherson R. D., 197: A numerical study on the effect of a coastal irregularity on the sea breeze. J Appl. Meteor. 9,
1 INTRODUCTION. Figure 2: Synoptical situation at the beginning of the simulation: 5th January 1999 at 12UTC.
 2.2 NOCTURNAL CIRCULATIONS UNDER WEAK PRESSURE GRADIENTS IN THE ISLAND OF MALLORCA J. Cuxart and M.A. Jiménez Universitat de les Illes Balears, Spain 1 INTRODUCTION To study the local nocturnal circulations
2.2 NOCTURNAL CIRCULATIONS UNDER WEAK PRESSURE GRADIENTS IN THE ISLAND OF MALLORCA J. Cuxart and M.A. Jiménez Universitat de les Illes Balears, Spain 1 INTRODUCTION To study the local nocturnal circulations
Climatology of the 10-m wind along the west coast of South American from 30 years of high-resolution reanalysis
 Climatology of the 10-m wind along the west coast of South American from 30 years of high-resolution reanalysis David A. Rahn and René D. Garreaud Departamento de Geofísica, Facultad de Ciencias Físicas
Climatology of the 10-m wind along the west coast of South American from 30 years of high-resolution reanalysis David A. Rahn and René D. Garreaud Departamento de Geofísica, Facultad de Ciencias Físicas
P2.25 SUMMER-TIME THERMAL WINDS OVER ICELAND: IMPACT OF TOPOGRAPHY. Bergen
 P2.25 SUMMER-TIME THERMAL WINDS OVER ICELAND: IMPACT OF TOPOGRAPHY Haraldur Ólafsson 1 and Hálfdán Ágústsson 2 1 University of Iceland, Bergen School of Meteorology, Geophysical Institute, University of
P2.25 SUMMER-TIME THERMAL WINDS OVER ICELAND: IMPACT OF TOPOGRAPHY Haraldur Ólafsson 1 and Hálfdán Ágústsson 2 1 University of Iceland, Bergen School of Meteorology, Geophysical Institute, University of
OBSERVATIONAL AND NUMERICAL STUDY ON THE INFLUENCE OF LARGE-SCALE FLOW DIRECTION AND COASTLINE SHAPE ON SEA-BREEZE EVOLUTION
 OBSERVATIONAL AND NUMERICAL STUDY ON THE INFLUENCE OF LARGE-SCALE FLOW DIRECTION AND COASTLINE SHAPE ON SEA-BREEZE EVOLUTION ROBERT C. GILLIAM, SETHU RAMAN and DEV DUTTA S. NIYOGI Department of Marine,
OBSERVATIONAL AND NUMERICAL STUDY ON THE INFLUENCE OF LARGE-SCALE FLOW DIRECTION AND COASTLINE SHAPE ON SEA-BREEZE EVOLUTION ROBERT C. GILLIAM, SETHU RAMAN and DEV DUTTA S. NIYOGI Department of Marine,
6.28 PREDICTION OF FOG EPISODES AT THE AIRPORT OF MADRID- BARAJAS USING DIFFERENT MODELING APPROACHES
 6.28 PREDICTION OF FOG EPISODES AT THE AIRPORT OF MADRID- BARAJAS USING DIFFERENT MODELING APPROACHES Cecilia Soriano 1, Darío Cano 2, Enric Terradellas 3 and Bill Physick 4 1 Universitat Politècnica de
6.28 PREDICTION OF FOG EPISODES AT THE AIRPORT OF MADRID- BARAJAS USING DIFFERENT MODELING APPROACHES Cecilia Soriano 1, Darío Cano 2, Enric Terradellas 3 and Bill Physick 4 1 Universitat Politècnica de
Idealized WRF model sensitivity simulations of sea breeze types and their effects on offshore windfields: Supplementary material
 Idealized WRF model sensitivity simulations of sea breeze types and their effects on offshore windfields: Supplementary material Authors: C. J. Steele, S. R. Dorling, R. von Glasow and J. Bacon Synoptic
Idealized WRF model sensitivity simulations of sea breeze types and their effects on offshore windfields: Supplementary material Authors: C. J. Steele, S. R. Dorling, R. von Glasow and J. Bacon Synoptic
Numerical Approach on the Mechanism of Precipitation-Topography Relationship in Mountainous Complex Terrain
 Numerical Approach on the Mechanism of Precipitation-Topography Relationship in Mountainous Complex Terrain Yoshiharu, S. 1, S. Miyata 2, E. Nakakita 3 and M. Hasebe 4 1 Faculty of Engineering, Utsunomiya
Numerical Approach on the Mechanism of Precipitation-Topography Relationship in Mountainous Complex Terrain Yoshiharu, S. 1, S. Miyata 2, E. Nakakita 3 and M. Hasebe 4 1 Faculty of Engineering, Utsunomiya
Numerical Study of Diurnal Circulations of Tropical Coastal Site Visakhapatnam Using the ARW MesoScale Model
 (An ISO 3297: 2007 Certified Organization Numerical Study of Diurnal Circulations of Tropical Coastal Site Visakhapatnam Using the ARW MesoScale Model 1 V. LakshmanaRao, 2P.Satish 1 Assistant Professor,
(An ISO 3297: 2007 Certified Organization Numerical Study of Diurnal Circulations of Tropical Coastal Site Visakhapatnam Using the ARW MesoScale Model 1 V. LakshmanaRao, 2P.Satish 1 Assistant Professor,
An Analysis of the South Florida Sea Breeze Circulation: An Idealized Study
 An Analysis of the South Florida Sea Breeze Circulation: An Idealized Study John Cangialosi University of Miami/RSMAS Abstract This experiment is an idealized study (removal of mean large scale flow) to
An Analysis of the South Florida Sea Breeze Circulation: An Idealized Study John Cangialosi University of Miami/RSMAS Abstract This experiment is an idealized study (removal of mean large scale flow) to
Characterization of Boundary-Layer Meteorology During DISCOVER-AQ
 Characterization of Boundary-Layer Meteorology During DISCOVER-AQ Daniel M. Alrick and Clinton P. MacDonald Sonoma Technology, Inc. Gary A. Morris St. Edward s University for Texas Air Quality Research
Characterization of Boundary-Layer Meteorology During DISCOVER-AQ Daniel M. Alrick and Clinton P. MacDonald Sonoma Technology, Inc. Gary A. Morris St. Edward s University for Texas Air Quality Research
1.6 HIGH RESOLUTION SIMULATIONS OF THE ISLAND-INDUCED CIRCULATIONS FOR THE ISLAND OF HAWAII DURING HaRP. Yang Yang and Yi-Leng Chen*
 1.6 HIGH RESOLUTION SIMULATIONS OF THE ISLAND-INDUCED CIRCULATIONS FOR THE ISLAND OF HAWAII DURING HaRP Yang Yang and Yi-Leng Chen* Department of Meteorology University of Hawaii at Manoa Honolulu, Hawaii
1.6 HIGH RESOLUTION SIMULATIONS OF THE ISLAND-INDUCED CIRCULATIONS FOR THE ISLAND OF HAWAII DURING HaRP Yang Yang and Yi-Leng Chen* Department of Meteorology University of Hawaii at Manoa Honolulu, Hawaii
10.6 Eddy Formation and Shock Features Associated with a Coastally Trapped Disturbance
 10.6 Eddy Formation and Shock Features Associated with a Coastally Trapped Disturbance William T. Thompson and Stephen D. Burk Naval Research Laboratory Monterey, California 1. Introduction On 28 August
10.6 Eddy Formation and Shock Features Associated with a Coastally Trapped Disturbance William T. Thompson and Stephen D. Burk Naval Research Laboratory Monterey, California 1. Introduction On 28 August
Local nocturnal circulations in the island of Majorca: mesoscale modelling and verification
 Tethys, 3, 67 73, 2006 www.tethys.cat ISSN-1139-3394 DOI:10.3369/tethys.2006.3.09 Journal edited by ACAM (Associació Catalana de Meteorologia) Local nocturnal circulations in the island of Majorca: mesoscale
Tethys, 3, 67 73, 2006 www.tethys.cat ISSN-1139-3394 DOI:10.3369/tethys.2006.3.09 Journal edited by ACAM (Associació Catalana de Meteorologia) Local nocturnal circulations in the island of Majorca: mesoscale
ATMS 310 Tropical Dynamics
 ATMS 310 Tropical Dynamics Introduction Throughout the semester we have focused on mid-latitude dynamics. This is not to say that the dynamics of other parts of the world, such as the tropics, are any
ATMS 310 Tropical Dynamics Introduction Throughout the semester we have focused on mid-latitude dynamics. This is not to say that the dynamics of other parts of the world, such as the tropics, are any
Synoptic features of orographically enhanced heavy rainfall on the east coast of Korea associated with Typhoon Rusa (2002)
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L02803, doi:10.1029/2006gl028592, 2007 Synoptic features of orographically enhanced heavy rainfall on the east coast of Korea associated
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L02803, doi:10.1029/2006gl028592, 2007 Synoptic features of orographically enhanced heavy rainfall on the east coast of Korea associated
Sea and Land Breezes METR 4433, Mesoscale Meteorology Spring 2006 (some of the material in this section came from ZMAG)
 Sea and Land Breezes METR 4433, Mesoscale Meteorology Spring 2006 (some of the material in this section came from ZMAG) 1 Definitions: The sea breeze is a local, thermally direct circulation arising from
Sea and Land Breezes METR 4433, Mesoscale Meteorology Spring 2006 (some of the material in this section came from ZMAG) 1 Definitions: The sea breeze is a local, thermally direct circulation arising from
Local Winds. Please read Ahrens Chapter 10
 Local Winds Please read Ahrens Chapter 10 Scales of Motion Microscale: meters Turbulent eddies Formed by mechanical disturbance or convection Lifetimes of minutes Mesoscale: km s to 100 s of km s Local
Local Winds Please read Ahrens Chapter 10 Scales of Motion Microscale: meters Turbulent eddies Formed by mechanical disturbance or convection Lifetimes of minutes Mesoscale: km s to 100 s of km s Local
Winds and Ocean Circulations
 Winds and Ocean Circulations AT 351 Lab 5 February 20, 2008 Sea Surface Temperatures 1 Temperature Structure of the Ocean Ocean Currents 2 What causes ocean circulation? The direction of most ocean currents
Winds and Ocean Circulations AT 351 Lab 5 February 20, 2008 Sea Surface Temperatures 1 Temperature Structure of the Ocean Ocean Currents 2 What causes ocean circulation? The direction of most ocean currents
Darwin s mid-evening surge
 Darwin s mid-evening surge Gerald L. Thomsen and Roger K. Smith Meteorological Institute, University of Munich, Germany November 11, 2009 Corresponding author: Gerald Thomsen, gerald@meteo.physik.uni-muenchen.de
Darwin s mid-evening surge Gerald L. Thomsen and Roger K. Smith Meteorological Institute, University of Munich, Germany November 11, 2009 Corresponding author: Gerald Thomsen, gerald@meteo.physik.uni-muenchen.de
10.6 The Dynamics of Drainage Flows Developed on a Low Angle Slope in a Large Valley Sharon Zhong 1 and C. David Whiteman 2
 10.6 The Dynamics of Drainage Flows Developed on a Low Angle Slope in a Large Valley Sharon Zhong 1 and C. David Whiteman 2 1Department of Geosciences, University of Houston, Houston, TX 2Pacific Northwest
10.6 The Dynamics of Drainage Flows Developed on a Low Angle Slope in a Large Valley Sharon Zhong 1 and C. David Whiteman 2 1Department of Geosciences, University of Houston, Houston, TX 2Pacific Northwest
Goals for today: continuing Ch 8: Atmospheric Circulation and Pressure Distributions. 26 Oct., 2011
 Goals for today: 26 Oct., 2011 continuing Ch 8: Atmospheric Circulation and Pressure Distributions Examples of synoptic scale and mesoscale circulation systems that are driven by geographic diversity in
Goals for today: 26 Oct., 2011 continuing Ch 8: Atmospheric Circulation and Pressure Distributions Examples of synoptic scale and mesoscale circulation systems that are driven by geographic diversity in
ASSESSMENT OF SEA BREEZE CHARACTERISTICS FROM SODAR ECHOGRAMS
 ASSESSMENT OF SEA BREEZE CHARACTERISTICS FROM SODAR ECHOGRAMS SUNEETHA RANI. JUPUDI Prof. M. PURNACHANDRA RAO Department of Physics, Andhra University, Visakhapatnam, India. ABSTRACT The SODAR echograms
ASSESSMENT OF SEA BREEZE CHARACTERISTICS FROM SODAR ECHOGRAMS SUNEETHA RANI. JUPUDI Prof. M. PURNACHANDRA RAO Department of Physics, Andhra University, Visakhapatnam, India. ABSTRACT The SODAR echograms
Development and propagation of a pollution gradient in the marine boundary layer during INDOEX (1999)
 Development and propagation of a pollution gradient in the marine boundary layer during INDOEX (1999) Matthew Simpson and Sethu Raman Department of Marine, Earth, and Atmospheric Sciences, North Carolina
Development and propagation of a pollution gradient in the marine boundary layer during INDOEX (1999) Matthew Simpson and Sethu Raman Department of Marine, Earth, and Atmospheric Sciences, North Carolina
Darwin s mid-evening surge
 Australian Meteorological and Oceanographic Journal 60 (2010) 25-36 Darwin s mid-evening surge Gerald L. Thomsen and Roger K. Smith Meteorological Institute, University of Munich, Germany (Manuscript received
Australian Meteorological and Oceanographic Journal 60 (2010) 25-36 Darwin s mid-evening surge Gerald L. Thomsen and Roger K. Smith Meteorological Institute, University of Munich, Germany (Manuscript received
Wind: Small-scale and Local Systems
 Wind: Small-scale and Local Systems Scales of Atmospheric Motion Atmospheric motions/phenomena occur on many diverse spatial and temporal scales. Weather forecasters tend to focus on Mesoscale and synoptic
Wind: Small-scale and Local Systems Scales of Atmospheric Motion Atmospheric motions/phenomena occur on many diverse spatial and temporal scales. Weather forecasters tend to focus on Mesoscale and synoptic
+ R. gr T. This equation is solved by the quadratic formula, the solution, as shown in the Holton text notes given as part of the class lecture notes:
 Homework #4 Key: Physical explanations 1.The way water drains down a sink, counterclockwise or clockwise, is independent of which hemisphere you are in. A draining sink is an example of vortex in cyclostrophic
Homework #4 Key: Physical explanations 1.The way water drains down a sink, counterclockwise or clockwise, is independent of which hemisphere you are in. A draining sink is an example of vortex in cyclostrophic
Influence of Heat Transport by Sea Breezes on Inland Temperature in the Osaka Area
 Academic Article Journal of Heat Island Institute International Vol. 9-2 (2) Influence of Heat Transport by Sea Breezes on Inland Temperature in the Osaka Area Atsumasa Yoshida* Junichi Yashiro* Xinbo
Academic Article Journal of Heat Island Institute International Vol. 9-2 (2) Influence of Heat Transport by Sea Breezes on Inland Temperature in the Osaka Area Atsumasa Yoshida* Junichi Yashiro* Xinbo
Abstract. 1 Introduction
 On the atmospheric stability in the Athens Basin M. Petrakis,* P. Kassomenos,* S. Lykoudis,* V. Synodinou^ "National Observatory ofathens, Institute of Meteorology and Physics of the Atmospheric Environment,
On the atmospheric stability in the Athens Basin M. Petrakis,* P. Kassomenos,* S. Lykoudis,* V. Synodinou^ "National Observatory ofathens, Institute of Meteorology and Physics of the Atmospheric Environment,
August 1990 H. Kondo 435. A Numerical Experiment on the Interaction between Sea Breeze and
 August 1990 H. Kondo 435 A Numerical Experiment on the Interaction between Sea Breeze and Valley Wind to Generate the so-called "Extended Sea Breeze" By Hiroaki Kondo National Research Institute for Pollution
August 1990 H. Kondo 435 A Numerical Experiment on the Interaction between Sea Breeze and Valley Wind to Generate the so-called "Extended Sea Breeze" By Hiroaki Kondo National Research Institute for Pollution
Role of detailed wind-topography interaction in orographic rainfall
 Q. J. R. Meteorol. SOC. (99), 7, pp. 4-46.77.:.8.(4.3) Role of detailed wind-topography interaction in orographic rainfall By P. ALPERT and H. SHAFIR Department of Geophysics and Planetary Sciences, Raymond
Q. J. R. Meteorol. SOC. (99), 7, pp. 4-46.77.:.8.(4.3) Role of detailed wind-topography interaction in orographic rainfall By P. ALPERT and H. SHAFIR Department of Geophysics and Planetary Sciences, Raymond
An Observational Study of the Summer Mediterranean Sea- Breeze-Front Penetration into the Complex Topography of the. Jordan-Rift-Valley
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 An Observational Study of the Summer Mediterranean Sea- Breeze-Front Penetration into the Complex Topography of the Jordan-Rift-Valley By: R. Naor 1, O. Potchter 2, H. Shafir
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 An Observational Study of the Summer Mediterranean Sea- Breeze-Front Penetration into the Complex Topography of the Jordan-Rift-Valley By: R. Naor 1, O. Potchter 2, H. Shafir
Scales of Atmospheric Motion. The atmosphere features a wide range of circulation types, with a wide variety of different behaviors
 Scales of Atmospheric Motion The atmosphere features a wide range of circulation types, with a wide variety of different behaviors Typically, the best way to classify these circulations is according to:
Scales of Atmospheric Motion The atmosphere features a wide range of circulation types, with a wide variety of different behaviors Typically, the best way to classify these circulations is according to:
Impact of Sea Breeze Fronts on Urban Heat Island & Air Quality in Texas
 Impact of Sea Breeze Fronts on Urban Heat Island & Air Quality in Texas Xiao-Ming Hu Center for Analysis and Prediction of Storms, School of Meteorology University of Oklahoma July 14, 2015 at LanZhou
Impact of Sea Breeze Fronts on Urban Heat Island & Air Quality in Texas Xiao-Ming Hu Center for Analysis and Prediction of Storms, School of Meteorology University of Oklahoma July 14, 2015 at LanZhou
Figure 1. Modeling domains used in WRF-ARW
 SIMULATION OF TRANSPORT AND DISPERSION OF POLLUTANTS FROM ELEVATED POINT SOURCES IN MISSISSIPPI GULF COAST USING A MESOSCALE ATMOSPHERIC DISPERSION MODELING SYSTEM Venkata Srinivas Challa, Jayakumar Indracanti,
SIMULATION OF TRANSPORT AND DISPERSION OF POLLUTANTS FROM ELEVATED POINT SOURCES IN MISSISSIPPI GULF COAST USING A MESOSCALE ATMOSPHERIC DISPERSION MODELING SYSTEM Venkata Srinivas Challa, Jayakumar Indracanti,
Coastal effects on radar propagation in atmospheric ducting conditions
 Meteorol. Appl. 13, 53 62 (2006) Coastal effects on radar propagation in atmospheric ducting conditions doi:10.1017/s1350482705001970 B. W. Atkinson & M. Zhu Department of Geography, Queen Mary, University
Meteorol. Appl. 13, 53 62 (2006) Coastal effects on radar propagation in atmospheric ducting conditions doi:10.1017/s1350482705001970 B. W. Atkinson & M. Zhu Department of Geography, Queen Mary, University
Low level coastal jet
 MetOcean analysis of a low-level coastal jet off the Norwegian coast. EERA DeepWind'2014 Deep Sea Offshore Wind R&D Conference, Trondheim, 22-24 January 2014 Harokopio University Konstantinos Christakos,
MetOcean analysis of a low-level coastal jet off the Norwegian coast. EERA DeepWind'2014 Deep Sea Offshore Wind R&D Conference, Trondheim, 22-24 January 2014 Harokopio University Konstantinos Christakos,
Influence of NOx/VOC emission-reduction on ozone levels in the Mediterranean area
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION JOINT RESEARCH CENTRE ENVIRONMENT INSTITUTE Environmental Modelling Task Force Influence of NOx/VOC emission-reduction on ozone levels in the Mediterranean area C. Cuvelier, P. Thunis
EUROPEAN COMMISSION JOINT RESEARCH CENTRE ENVIRONMENT INSTITUTE Environmental Modelling Task Force Influence of NOx/VOC emission-reduction on ozone levels in the Mediterranean area C. Cuvelier, P. Thunis
Scales of Atmospheric Motion
 Lecture 12 Local Wind Systems Scales of Atmospheric Motion Small turbulent eddies (swirls) A synoptic eddy 1 Coriolis Effect The larger the scale, the longer the life time. Wind shear and turbulent eddy
Lecture 12 Local Wind Systems Scales of Atmospheric Motion Small turbulent eddies (swirls) A synoptic eddy 1 Coriolis Effect The larger the scale, the longer the life time. Wind shear and turbulent eddy
9/25/2014. Scales of Atmospheric Motion. Scales of Atmospheric Motion. Chapter 7: Circulation of the Atmosphere
 Chapter 7: Circulation of the Atmosphere The Atmosphere: An Introduction to Meteorology, 12 th Lutgens Tarbuck Lectures by: Heather Gallacher, Cleveland State University Scales of Atmospheric Motion Small-
Chapter 7: Circulation of the Atmosphere The Atmosphere: An Introduction to Meteorology, 12 th Lutgens Tarbuck Lectures by: Heather Gallacher, Cleveland State University Scales of Atmospheric Motion Small-
Thermally-forced Circulations. Presented by: Daran Rife NCAR RAL 26 Jul 2005
 Thermally-forced Circulations Presented by: Daran Rife NCAR RAL 26 Jul 2005 Thermally-driven Winds: Some Basic Concepts A class of mesoscale circulations driven by horizontal gradients in surface heating
Thermally-forced Circulations Presented by: Daran Rife NCAR RAL 26 Jul 2005 Thermally-driven Winds: Some Basic Concepts A class of mesoscale circulations driven by horizontal gradients in surface heating
Breeze Circulation in the Crimean Region Atmosphere
 Breeze Circulation in the Crimean Region Atmosphere V.V. Efimov, O.I. Komarovskaya Marine Hydrophysical Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences, Sevastopol, Russian Federation e-mail: vefim.38@mail.ru Using
Breeze Circulation in the Crimean Region Atmosphere V.V. Efimov, O.I. Komarovskaya Marine Hydrophysical Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences, Sevastopol, Russian Federation e-mail: vefim.38@mail.ru Using
Conditions for Offshore Wind Energy Use
 Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg Institute of Physics Energy Meteorology Group Detlev Heinemann Conditions for Offshore Wind Energy Use Detlev Heinemann ForWind Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg
Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg Institute of Physics Energy Meteorology Group Detlev Heinemann Conditions for Offshore Wind Energy Use Detlev Heinemann ForWind Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg
The Cooling Effect of Green Strategies Proposed in the Hanoi Master Plan for Mitigation of Urban Heat Island
 The Cooling Effect of Green Strategies Proposed in the Hanoi Master Plan for Mitigation of Urban Heat Island Andhang Rakhmat Trihamdani, M.Eng. [Grad. School for IDEC, Hiroshima Univ., Japan] andhang.rt@gmail.com
The Cooling Effect of Green Strategies Proposed in the Hanoi Master Plan for Mitigation of Urban Heat Island Andhang Rakhmat Trihamdani, M.Eng. [Grad. School for IDEC, Hiroshima Univ., Japan] andhang.rt@gmail.com
QUARTERLY JOURNAL ROYAL METEOROLOGICAL SOCIETY
 QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF THE ROYAL METEOROLOGICAL SOCIETY Vol. 132 APRIL 2006 Part A No. 616 Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. (2006), 132, pp. 691 707 doi: 10.1256/qj.05.126 Simulations of low-level convergence lines
QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF THE ROYAL METEOROLOGICAL SOCIETY Vol. 132 APRIL 2006 Part A No. 616 Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. (2006), 132, pp. 691 707 doi: 10.1256/qj.05.126 Simulations of low-level convergence lines
The dynamics of heat lows over flat terrain
 The dynamics of heat lows over flat terrain Roger K. Smith, Thomas Spengler presented by Julia Palamarchuk, Ukraine, Odessa Split Workshop in Atmospheric Physics and Oceanography, May 22-30, Split, Croatia
The dynamics of heat lows over flat terrain Roger K. Smith, Thomas Spengler presented by Julia Palamarchuk, Ukraine, Odessa Split Workshop in Atmospheric Physics and Oceanography, May 22-30, Split, Croatia
Summary of Lecture 10, 04 March 2008 Introduce the Hadley circulation and examine global weather patterns. Discuss jet stream dynamics jet streams
 Summary of Lecture 10, 04 March 2008 Introduce the Hadley circulation and examine global weather patterns. Discuss jet stream dynamics jet streams arise because the Coriolis force prevents Hadley-type
Summary of Lecture 10, 04 March 2008 Introduce the Hadley circulation and examine global weather patterns. Discuss jet stream dynamics jet streams arise because the Coriolis force prevents Hadley-type
2. THE NEW ENGLAND AIR QUALITY STUDY
 P2.4 NEW ENGLAND COASTAL AIR POLLUTION DISPERSION MODELING Michael Tjernström * and Mark Žagar Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden Wayne Angevine CIRES, University of Colorado, and NOAA Aeronomy Laboratory,
P2.4 NEW ENGLAND COASTAL AIR POLLUTION DISPERSION MODELING Michael Tjernström * and Mark Žagar Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden Wayne Angevine CIRES, University of Colorado, and NOAA Aeronomy Laboratory,
2.4. Applications of Boundary Layer Meteorology
 2.4. Applications of Boundary Layer Meteorology 2.4.1. Temporal Evolution & Prediction of the PBL Earlier, we saw the following figure showing the diurnal evolution of PBL. With a typical diurnal cycle,
2.4. Applications of Boundary Layer Meteorology 2.4.1. Temporal Evolution & Prediction of the PBL Earlier, we saw the following figure showing the diurnal evolution of PBL. With a typical diurnal cycle,
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 Numerical investigation of the formation of elevated pollution layers over the Los Angeles air basin Rong Lu, R.P. Turco Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of California, Los Angeles, 405 Hilgard
Numerical investigation of the formation of elevated pollution layers over the Los Angeles air basin Rong Lu, R.P. Turco Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of California, Los Angeles, 405 Hilgard
Local Winds & Microclimates. Unit 2- Module 1
 Local Winds & Microclimates Unit 2- Module 1 Objectives Overview of local winds (sea & land breezes, valley winds) Overview of microclimates (valley, urban, woodland) Local Winds Local Winds Local winds
Local Winds & Microclimates Unit 2- Module 1 Objectives Overview of local winds (sea & land breezes, valley winds) Overview of microclimates (valley, urban, woodland) Local Winds Local Winds Local winds
INTRODUCTION * Corresponding author address: Michael Tjernström, Stockholm University, Department of Meteorology, SE-
 4.12 NEW ENGLAND COASTAL BOUNDARY LAYER MODELING Mark Žagar and Michael Tjernström * Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden Wayne Angevine CIRES, University of Colorado, and NOAA Aeronomy Laboratory,
4.12 NEW ENGLAND COASTAL BOUNDARY LAYER MODELING Mark Žagar and Michael Tjernström * Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden Wayne Angevine CIRES, University of Colorado, and NOAA Aeronomy Laboratory,
Parameterizations (fluxes, convection)
 Parameterizations (fluxes, convection) Heinke Schlünzen Meteorological Institute, University of Hamburg New resolutions - new challenges What is the current status? Surface fluxes Convection Towards improving
Parameterizations (fluxes, convection) Heinke Schlünzen Meteorological Institute, University of Hamburg New resolutions - new challenges What is the current status? Surface fluxes Convection Towards improving
Observations and Modeling of Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction over the California Current System
 Observations and Modeling of Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction over the California Current System Cape Blanco Dudley Chelton 1, Xin Jin 2, Jim McWilliams 2 & Tracy Haack 3 1 Oregon State University
Observations and Modeling of Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction over the California Current System Cape Blanco Dudley Chelton 1, Xin Jin 2, Jim McWilliams 2 & Tracy Haack 3 1 Oregon State University
TEMPERATURE BEHAVIOR during WINTER in ANTARCTICA
 TEMPERATURE BEHAVIOR during WINTER in ANTARCTICA The temperature behaviour during winter in Antarctica was investigated. Special attention was devoted to anomalous strong warmings, ranging between 20 and
TEMPERATURE BEHAVIOR during WINTER in ANTARCTICA The temperature behaviour during winter in Antarctica was investigated. Special attention was devoted to anomalous strong warmings, ranging between 20 and
Effects of an Inclined Land Surface on the Land and Sea Breeze Circulation: A Numerical Experiment. By Tomb Asai
 December 1978 T. Asai and S. Mitsumoto 559 Effects of an Inclined Land Surface on the Land and Sea Breeze Circulation: A Numerical Experiment By Tomb Asai Ocean Research Institute, University of Tokyo
December 1978 T. Asai and S. Mitsumoto 559 Effects of an Inclined Land Surface on the Land and Sea Breeze Circulation: A Numerical Experiment By Tomb Asai Ocean Research Institute, University of Tokyo
STUDY OF LOCAL WINDS IN MOUNTAINOUS COASTAL AREAS BY MULTI- SENSOR SATELLITE DATA
 STUDY OF LOCAL WINDS IN MOUNTAINOUS COASTAL AREAS BY MULTI- SENSOR SATELLITE DATA Werner Alpers Institute of Oceanography, University of Hamburg, Bundesstrasse 53, D-20146 Hamburg, Germany E-mail: alpers@ifm.uni-hamburg.de
STUDY OF LOCAL WINDS IN MOUNTAINOUS COASTAL AREAS BY MULTI- SENSOR SATELLITE DATA Werner Alpers Institute of Oceanography, University of Hamburg, Bundesstrasse 53, D-20146 Hamburg, Germany E-mail: alpers@ifm.uni-hamburg.de
Numerical Study of the Wind Waves Effect on Air-sea Fluxes in the Yellow Sea during the Cold Wave Events
 Numerical Study of the Wind Waves Effect on Air-sea Fluxes in the Yellow Sea during the Cold Wave Events Jianhong WANG Jialin SHI Chunsheng MIAO Mo PENG, Jianmin SHENG NUIST & JMEMFC Liverpool, UK, 10-15
Numerical Study of the Wind Waves Effect on Air-sea Fluxes in the Yellow Sea during the Cold Wave Events Jianhong WANG Jialin SHI Chunsheng MIAO Mo PENG, Jianmin SHENG NUIST & JMEMFC Liverpool, UK, 10-15
Scales of Atmospheric Motion Scale Length Scale (m) Time Scale (sec) Systems/Importance Molecular (neglected)
 Supplement Wind, Fetch and Waves Scales of Atmospheric Motion Scale Length Scale (m) Time Scale (sec) Systems/Importance Molecular 10-7 - 10-2 10-1 (neglected) Coriolis not important Turbulent 10-2 10
Supplement Wind, Fetch and Waves Scales of Atmospheric Motion Scale Length Scale (m) Time Scale (sec) Systems/Importance Molecular 10-7 - 10-2 10-1 (neglected) Coriolis not important Turbulent 10-2 10
Seasonal Evaluation of Temperature Inversion
 Seasonal Evaluation of Temperature Inversion Kandil, H A 1, Kader M M. A 2, Moaty, A A. 2, Elhadidi, B 3, Sherif, A.O. 3 The seasonal evaluation of the temperature inversion over Cairo-Egypt is examined
Seasonal Evaluation of Temperature Inversion Kandil, H A 1, Kader M M. A 2, Moaty, A A. 2, Elhadidi, B 3, Sherif, A.O. 3 The seasonal evaluation of the temperature inversion over Cairo-Egypt is examined
Tidal regime along Vietnam coast under impacts of sea level rise
 VNU Journal of Science, Earth Sciences 28 (2012) 133-139 Tidal regime along Vietnam coast under impacts of sea level rise Tran Thuc, Duong Hong Son* Vietnam Institute of Meteorology, Hydrology and Environment
VNU Journal of Science, Earth Sciences 28 (2012) 133-139 Tidal regime along Vietnam coast under impacts of sea level rise Tran Thuc, Duong Hong Son* Vietnam Institute of Meteorology, Hydrology and Environment
A case study of boundary layer ventilation by convection and coastal processes
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006jd007984, 2007 A case study of boundary layer ventilation by convection and coastal processes H. F. Dacre, 1 S. L.
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006jd007984, 2007 A case study of boundary layer ventilation by convection and coastal processes H. F. Dacre, 1 S. L.
Idealized Numerical Modeling of a Land/Sea Breeze
 Idealized Numerical Modeling of a Land/Sea Breeze Jeremy A. Gibbs School of Meteorology, University of Oklahoma 3 December 2008 1 Introduction With references in the Bible, the land and sea breeze is one
Idealized Numerical Modeling of a Land/Sea Breeze Jeremy A. Gibbs School of Meteorology, University of Oklahoma 3 December 2008 1 Introduction With references in the Bible, the land and sea breeze is one
Measurement of Coastal & Littoral Toxic Material Tracer Dispersion. Dr. Robert E. Marshall T41 NSWCDD
 Measurement of Coastal & Littoral Toxic Material Tracer Dispersion Dr. Robert E. Marshall robert.e.marshall@navy.mil T41 NSWCDD Mouth of the Piankatank River Chesapeake Bay Model this for CB defense? Ground
Measurement of Coastal & Littoral Toxic Material Tracer Dispersion Dr. Robert E. Marshall robert.e.marshall@navy.mil T41 NSWCDD Mouth of the Piankatank River Chesapeake Bay Model this for CB defense? Ground
Time Dependent Wave Setup During Hurricanes on the Mississippi Coast. D. Slinn, A. Niedoroda,, R. Dean, R. Weaver, C. Reed, and J. Smith.
 Time Dependent Wave Setup During Hurricanes on the Mississippi Coast D. Slinn, A. Niedoroda,, R. Dean, R. Weaver, C. Reed, and J. Smith. 1 Motivation TO UNDERSTAND THE APPARENT DIFFERENCE IN WAVE SET-UP
Time Dependent Wave Setup During Hurricanes on the Mississippi Coast D. Slinn, A. Niedoroda,, R. Dean, R. Weaver, C. Reed, and J. Smith. 1 Motivation TO UNDERSTAND THE APPARENT DIFFERENCE IN WAVE SET-UP
P2.17 OBSERVATIONS OF STRONG MOUNTAIN WAVES IN THE LEE OF THE MEDICINE BOW MOUNTAINS OF SOUTHEAST WYOMING
 P2.17 OBSERVATIONS OF STRONG MOUNTAIN WAVES IN THE LEE OF THE MEDICINE BOW MOUNTAINS OF SOUTHEAST WYOMING Larry D. Oolman 1, Jeffrey R. French 1, Samuel Haimov 1, David Leon 1, and Vanda Grubišić 2 1 University
P2.17 OBSERVATIONS OF STRONG MOUNTAIN WAVES IN THE LEE OF THE MEDICINE BOW MOUNTAINS OF SOUTHEAST WYOMING Larry D. Oolman 1, Jeffrey R. French 1, Samuel Haimov 1, David Leon 1, and Vanda Grubišić 2 1 University
The dryline is a mesoscale phenomena whose development and evaluation is strongly linked to the PBL.
 2.2. Development and Evolution of Drylines The dryline is a mesoscale phenomena whose development and evaluation is strongly linked to the PBL. Text books containing sections on dryline: The Dry Line.
2.2. Development and Evolution of Drylines The dryline is a mesoscale phenomena whose development and evaluation is strongly linked to the PBL. Text books containing sections on dryline: The Dry Line.
THE WAVE CLIMATE IN THE BELGIAN COASTAL ZONE
 THE WAVE CLIMATE IN THE BELGIAN COASTAL ZONE Toon Verwaest, Flanders Hydraulics Research, toon.verwaest@mow.vlaanderen.be Sarah Doorme, IMDC, sarah.doorme@imdc.be Kristof Verelst, Flanders Hydraulics Research,
THE WAVE CLIMATE IN THE BELGIAN COASTAL ZONE Toon Verwaest, Flanders Hydraulics Research, toon.verwaest@mow.vlaanderen.be Sarah Doorme, IMDC, sarah.doorme@imdc.be Kristof Verelst, Flanders Hydraulics Research,
Coastal Perturbations of Marine-Layer Winds, Wind Stress, and Wind Stress Curl along California and Baja California in June 1999
 1152 JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY VOLUME 34 Coastal Perturbations of Marine-Layer Winds, Wind Stress, and Wind Stress Curl along California and Baja California in June 1999 DARKO KORAČIN Desert Research
1152 JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY VOLUME 34 Coastal Perturbations of Marine-Layer Winds, Wind Stress, and Wind Stress Curl along California and Baja California in June 1999 DARKO KORAČIN Desert Research
Air Pressure and Wind
 Air Pressure and Wind 19.1 Understanding Air Pressure Air Pressure Defined Air pressure is the pressure exerted by the weight of air. Air pressure is exerted in all directions down, up, and sideways. The
Air Pressure and Wind 19.1 Understanding Air Pressure Air Pressure Defined Air pressure is the pressure exerted by the weight of air. Air pressure is exerted in all directions down, up, and sideways. The
EXTREME WIND GUSTS IN LARGE-EDDY SIMULATIONS OF TROPICAL CYCLONES
 The National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) is sponsored by the National Science Foundation (NSF) EXTREME WIND GUSTS IN LARGE-EDDY SIMULATIONS OF TROPICAL CYCLONES George Bryan National Center
The National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) is sponsored by the National Science Foundation (NSF) EXTREME WIND GUSTS IN LARGE-EDDY SIMULATIONS OF TROPICAL CYCLONES George Bryan National Center
NAVAL POSTGRADUATE SCHOOL THESIS
 NAVAL POSTGRADUATE SCHOOL MONTEREY, CALIFORNIA THESIS FACTORS INFLUENCING THE STRUCTURE OF THE MONTEREY BAY SEA BREEZE by Emily M. Duvall March 2004 Thesis Advisor: Second Reader: Wendell A. Nuss David
NAVAL POSTGRADUATE SCHOOL MONTEREY, CALIFORNIA THESIS FACTORS INFLUENCING THE STRUCTURE OF THE MONTEREY BAY SEA BREEZE by Emily M. Duvall March 2004 Thesis Advisor: Second Reader: Wendell A. Nuss David
The Persian Gulf summertime low-level jet over sloping terrain
 Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 138: 145 157, January 2012 A The Persian Gulf summertime low-level jet over sloping terrain E. M. Giannakopoulou* and R. Toumi
Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 138: 145 157, January 2012 A The Persian Gulf summertime low-level jet over sloping terrain E. M. Giannakopoulou* and R. Toumi
Sea Breeze, Coastal Upwelling Modeling to Support Offshore Wind Energy Planning and Operations
 Sea Breeze, Coastal Upwelling Modeling to Support Offshore Wind Energy Planning and Operations Greg Seroka, Travis Miles, Rich Dunk, Josh Kohut, Scott Glenn Center for Ocean Observing Leadership Rutgers
Sea Breeze, Coastal Upwelling Modeling to Support Offshore Wind Energy Planning and Operations Greg Seroka, Travis Miles, Rich Dunk, Josh Kohut, Scott Glenn Center for Ocean Observing Leadership Rutgers
General Coastal Notes + Landforms! 1
 General Coastal Notes + Landforms! 1 Types of Coastlines: Type Description Primary Coast which is essentially in the same condition when sea level stabilized Coastline after the last ice age, younger.
General Coastal Notes + Landforms! 1 Types of Coastlines: Type Description Primary Coast which is essentially in the same condition when sea level stabilized Coastline after the last ice age, younger.
COASTAL MORPHODYNAMICS
 COASTAL MORPHODYNAMICS PATRICIA CHARDÓN-MALDONADO, PHD, EIT Miguel Canals, Jack A. Puleo, Alec Torres-Freyermuth & Jens Figlus March 9, 2017 OUTLINE INTRODUCTION Meteorological Phenomena Forcing Conditions
COASTAL MORPHODYNAMICS PATRICIA CHARDÓN-MALDONADO, PHD, EIT Miguel Canals, Jack A. Puleo, Alec Torres-Freyermuth & Jens Figlus March 9, 2017 OUTLINE INTRODUCTION Meteorological Phenomena Forcing Conditions
OCEANOGRAPHY STUDY GUIDE
 OCEANOGRAPHY STUDY GUIDE Chapter 2 Section 1 1. Most abundant salt in ocean. Sodium chloride; NaCl 2. Amount of Earth covered by Water 71% 3. Four oceans: What are they? Atlantic, Pacific, Arctic, Indian
OCEANOGRAPHY STUDY GUIDE Chapter 2 Section 1 1. Most abundant salt in ocean. Sodium chloride; NaCl 2. Amount of Earth covered by Water 71% 3. Four oceans: What are they? Atlantic, Pacific, Arctic, Indian
WEATHER SYSTEMS OF MIDDLE LATITUDES
 CHAPTER 10 WEATHER SYSTEMS OF MIDDLE LATITUDES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. In equal volumes, which one of the following air masses exerts the highest surface air pressure? a. cp *b. A c. mp d. ct e. mt
CHAPTER 10 WEATHER SYSTEMS OF MIDDLE LATITUDES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. In equal volumes, which one of the following air masses exerts the highest surface air pressure? a. cp *b. A c. mp d. ct e. mt
Investigation of local flow features in Istanbul. Part I: high-resolution sensitivity simulations
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CLIMATOLOGY Int. J. Climatol. (215) Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com) DOI: 1.12/joc.4248 Investigation of local flow features in Istanbul. Part
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CLIMATOLOGY Int. J. Climatol. (215) Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com) DOI: 1.12/joc.4248 Investigation of local flow features in Istanbul. Part
Sophie Bastin (*), Philippe Drobinski IPSL, Paris, France;
 1.7 TEMPERATURE AND WIND VELOCITY OSCILLATIONS ALONG A GENTLE SLOPE DURING SEA-BREEZE EVENTS. Sophie Bastin (), Philippe Drobinski IPSL, Paris, France; 1. INTRODUCTION The flow structure at Vallon d Ol
1.7 TEMPERATURE AND WIND VELOCITY OSCILLATIONS ALONG A GENTLE SLOPE DURING SEA-BREEZE EVENTS. Sophie Bastin (), Philippe Drobinski IPSL, Paris, France; 1. INTRODUCTION The flow structure at Vallon d Ol
Chapter. Air Pressure and Wind
 Chapter Air Pressure and Wind 19.1 Understanding Air Pressure Air Pressure Defined Air pressure is the pressure exerted by the weight of air. 19.1 Understanding Air Pressure Air Pressure Defined Air pressure
Chapter Air Pressure and Wind 19.1 Understanding Air Pressure Air Pressure Defined Air pressure is the pressure exerted by the weight of air. 19.1 Understanding Air Pressure Air Pressure Defined Air pressure
The Diurnal Distribution of Lightning over North Florida and Its Relation to the Prevailing Low-Level Flow
 729 The Diurnal Distribution of Lightning over North Florida and Its Relation to the Prevailing Low-Level Flow JOSEPH P. CAMP Department of Meteorology, The Florida State University, Tallahassee, Florida
729 The Diurnal Distribution of Lightning over North Florida and Its Relation to the Prevailing Low-Level Flow JOSEPH P. CAMP Department of Meteorology, The Florida State University, Tallahassee, Florida
The influence of synoptic scale flow on sea breeze induced surface winds and calm zones
 PUBLISHED BY THE INTERNATIONAL METEOROLOGICAL INSTITUTE IN STOCKHOLM SERIES A DYNAMIC METEOROLOGY AND OCEANOGRAPHY Tellus (2010), 62A, 209 217 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved C 2009 The Authors
PUBLISHED BY THE INTERNATIONAL METEOROLOGICAL INSTITUTE IN STOCKHOLM SERIES A DYNAMIC METEOROLOGY AND OCEANOGRAPHY Tellus (2010), 62A, 209 217 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved C 2009 The Authors
Tidal influence on offshore and coastal wind resource predictions at North Sea. Barbara Jimenez 1,2, Bernhard Lange 3, and Detlev Heinemann 1.
 Tidal influence on offshore and coastal wind resource predictions at North Sea Barbara Jimenez 1,2, Bernhard Lange 3, and Detlev Heinemann 1. 1 ForWind - Center for Wind Energy Research, University of
Tidal influence on offshore and coastal wind resource predictions at North Sea Barbara Jimenez 1,2, Bernhard Lange 3, and Detlev Heinemann 1. 1 ForWind - Center for Wind Energy Research, University of
Outline. Wind Turbine Siting. Roughness. Wind Farm Design 4/7/2015
 Wind Turbine Siting Andrew Kusiak 2139 Seamans Center Iowa City, Iowa 52242-1527 andrew-kusiak@uiowa.edu Tel: 319-335-5934 Fax: 319-335-5669 http://www.icaen.uiowa.edu/~ankusiak Terrain roughness Escarpments
Wind Turbine Siting Andrew Kusiak 2139 Seamans Center Iowa City, Iowa 52242-1527 andrew-kusiak@uiowa.edu Tel: 319-335-5934 Fax: 319-335-5669 http://www.icaen.uiowa.edu/~ankusiak Terrain roughness Escarpments
PGF. Pressure Gradient. Wind is horizontal movement of the air or other word air in motion. Forces affecting winds 2/14/2017
 Winds Wind is horizontal movement of the air or other word air in motion. Forces affecting winds 1. Pressure gradient force a. High pressure flows to low pressure b. Pressure gradient = difference in pressure
Winds Wind is horizontal movement of the air or other word air in motion. Forces affecting winds 1. Pressure gradient force a. High pressure flows to low pressure b. Pressure gradient = difference in pressure
Are Advanced Wind Flow Models More Accurate? A Test of Four Models
 Are Advanced Wind Flow Models More Accurate? A Test of Four Models Philippe Beaucage, PhD Senior Research Scientist Michael C. Brower, PhD Chief Technical Officer Brazil Wind Power Conference 2012 Albany
Are Advanced Wind Flow Models More Accurate? A Test of Four Models Philippe Beaucage, PhD Senior Research Scientist Michael C. Brower, PhD Chief Technical Officer Brazil Wind Power Conference 2012 Albany
Simulations of the Summer Hydrometeorological Processes of Lake Kinneret
 95 Simulations of the Summer Hydrometeorological Processes of Lake Kinneret RONI AVISSAR AND HAI PAN Center for Environmental Prediction, Department of Environmental Sciences, Rutgers The State University
95 Simulations of the Summer Hydrometeorological Processes of Lake Kinneret RONI AVISSAR AND HAI PAN Center for Environmental Prediction, Department of Environmental Sciences, Rutgers The State University
10.2 ATMOSPHERIC ROTORS: AIRCRAFT IN SITU AND CLOUD RADAR MEASUREMENTS IN T-REX
 10.2 ATMOSPHERIC ROTORS: AIRCRAFT IN SITU AND CLOUD RADAR MEASUREMENTS IN T-REX Vanda Grubišić 1, Larry Armi 2, Joachim Kuettner 3, Samuel Haimov 4, Larry Oolman 4, Rick Damiani 4, and Brian Billings 1
10.2 ATMOSPHERIC ROTORS: AIRCRAFT IN SITU AND CLOUD RADAR MEASUREMENTS IN T-REX Vanda Grubišić 1, Larry Armi 2, Joachim Kuettner 3, Samuel Haimov 4, Larry Oolman 4, Rick Damiani 4, and Brian Billings 1
Thermally driven mesoscale flows simulations and measurements
 Boreal Environment Research : 6 64 7 ISSN 9-695 (print) ISSN 797-469 (online) helsinki 8 December 7 Thermally driven mesoscale flows simulations and measurements Karin Törnblom, Hans Bergström and Cecilia
Boreal Environment Research : 6 64 7 ISSN 9-695 (print) ISSN 797-469 (online) helsinki 8 December 7 Thermally driven mesoscale flows simulations and measurements Karin Törnblom, Hans Bergström and Cecilia
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint. Chapter 15 Earth Science, 12e Tarbuck/Lutgens
 Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 15 Earth Science, 12e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 15 Earth Science, 12e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
S-190 Intro to Wildland Fire Behavior
 S-190 Intro to Wildland Fire Behavior Unit 2 Objectives 1. List the indicators of an approaching cold front & describe the expected wind changes. 2. List 3 common foehn wind conditions & the areas in which
S-190 Intro to Wildland Fire Behavior Unit 2 Objectives 1. List the indicators of an approaching cold front & describe the expected wind changes. 2. List 3 common foehn wind conditions & the areas in which
Sensitivity of Coastal Currents Near Pt. Conception to Forcing by Three Different Winds: ECMWF, COAMPS and Blended SSM/I-ECMWF-Buoy Winds
 Sensitivity of Coastal Currents Near Pt. Conception to Forcing by Three Different Winds: ECMWF, COAMPS and Blended SSM/I-ECMWF-Buoy Winds Changming Dong and Lie-Yauw Oey* Program in Atmospheric & Oceanic
Sensitivity of Coastal Currents Near Pt. Conception to Forcing by Three Different Winds: ECMWF, COAMPS and Blended SSM/I-ECMWF-Buoy Winds Changming Dong and Lie-Yauw Oey* Program in Atmospheric & Oceanic
Chapter 2: wind. Wind conditions are an important consideration for anyone who travels by water. 1. Introduction. 2. How Wind is Formed
 Chapter 2: wind Wind conditions are an important consideration for anyone who travels by water. 1. Introduction Wind conditions are an important consideration for anyone who travels by water. Vessels of
Chapter 2: wind Wind conditions are an important consideration for anyone who travels by water. 1. Introduction Wind conditions are an important consideration for anyone who travels by water. Vessels of
The total precipitation (P) is determined by the average rainfall rate (R) and the duration (D),
 Orographic precipitation Common ingredients of heavy orographic precipitation The total precipitation (P) is determined by the average rainfall rate (R) and the duration (D), P = RD. (1) The rainfall rate
Orographic precipitation Common ingredients of heavy orographic precipitation The total precipitation (P) is determined by the average rainfall rate (R) and the duration (D), P = RD. (1) The rainfall rate
Typhoon Vamei: An Equatorial Tropical Cyclone Formation
 1 Typhoon Vamei: An Equatorial Tropical Cyclone Formation C.-P. Chang, Ching-Hwang Liu 1, Hung-Chi Kuo 2 Department of Meteorology, Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, CA Abstract. Due to the diminishing
1 Typhoon Vamei: An Equatorial Tropical Cyclone Formation C.-P. Chang, Ching-Hwang Liu 1, Hung-Chi Kuo 2 Department of Meteorology, Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, CA Abstract. Due to the diminishing
Mountain Forced Flows
 Mountain Forced Flows Jeremy A. Gibbs University of Oklahoma gibbz@ou.edu February 3, 2015 1 / 45 Overview Orographic Precipitation Common Ingredients of Heavy Orographic Precipitation Formation and Enhancement
Mountain Forced Flows Jeremy A. Gibbs University of Oklahoma gibbz@ou.edu February 3, 2015 1 / 45 Overview Orographic Precipitation Common Ingredients of Heavy Orographic Precipitation Formation and Enhancement
Numerical Simulations of the Effects of Coastlines on the Evolution of Strong, Long-Lived Squall Lines
 1710 M O N T H L Y W E A T H E R R E V I E W VOLUME 135 Numerical Simulations of the Effects of Coastlines on the Evolution of Strong, Long-Lived Squall Lines TODD P. LERICOS* AND HENRY E. FUELBERG Department
1710 M O N T H L Y W E A T H E R R E V I E W VOLUME 135 Numerical Simulations of the Effects of Coastlines on the Evolution of Strong, Long-Lived Squall Lines TODD P. LERICOS* AND HENRY E. FUELBERG Department
Lecture 14. Heat lows and the TCZ
 Lecture 14 Heat lows and the TCZ ITCZ/TCZ and heat lows While the ITCZ/TCZ is associated with a trough at low levels, it must be noted that a low pressure at the surface and cyclonic vorticity at 850 hpa
Lecture 14 Heat lows and the TCZ ITCZ/TCZ and heat lows While the ITCZ/TCZ is associated with a trough at low levels, it must be noted that a low pressure at the surface and cyclonic vorticity at 850 hpa
Lecture 13 March 24, 2010, Wednesday. Atmospheric Pressure & Wind: Part 4
 Lecture 13 March 24, 2010, Wednesday Atmospheric Pressure & Wind: Part 4 Synoptic scale winds Mesoscale winds Microscale winds Air-sea interactions The largest synoptic scale wind. Monsoon: Arabic for
Lecture 13 March 24, 2010, Wednesday Atmospheric Pressure & Wind: Part 4 Synoptic scale winds Mesoscale winds Microscale winds Air-sea interactions The largest synoptic scale wind. Monsoon: Arabic for
Currents measurements in the coast of Montevideo, Uruguay
 Currents measurements in the coast of Montevideo, Uruguay M. Fossati, D. Bellón, E. Lorenzo & I. Piedra-Cueva Fluid Mechanics and Environmental Engineering Institute (IMFIA), School of Engineering, Research
Currents measurements in the coast of Montevideo, Uruguay M. Fossati, D. Bellón, E. Lorenzo & I. Piedra-Cueva Fluid Mechanics and Environmental Engineering Institute (IMFIA), School of Engineering, Research
