DIMENSIONING WATER SUPPLY SYSTEM IN BUILDING
|
|
|
- Lauren Lynch
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Mamk Department of Energy and Environmental Technology, ET Double Degree Programme in Building Services T6615KA JukkaRäisä Water and sewage services in buildings DIMENSIONING WATER SUPPLY SYSTEM IN BUILDING 1. General Criteria for dimensioning of pipe network - Every tap gives adequate and steady water flow - No hydraulic hammer effects - Low noise, flow velocities are suitable If available pressure in the network (after main water meter) is greater than 500kPa, pressure must be dropped by installing of decompression valve which is then set to the pressure level required by dimensioning. If it is necessary, decompression valve in each flat is used. If pressure is kPa, could decompression valve be used depending on floor height and pressure losses of faucet in standard flow. If pressure level is too low (for instance high buildings), booster pumping is used. By the dimensioning used explications is fig 1. p0 Pressure level at connection point of distribution line and service line. (Water main pressure)
2 2 Local Waterworks announces the pressure (P0) in the distribution line. pn Pressure which is used to connection pipe and faucet flows. pn is calculated at the elevation of faucet. Pressure available at the level of the faucet overcomes the resistance of flow in the connection pipe and the faucet. The pressure pn is used in design by calculation. pn is calculated from po or by reducing from this. The pressure drop ( Hk) due to the difference in level between the water outlet and the distribution pipe, and the pressure losses in the service pipe, water meter, water heater and distribution pipes ( p). pn is calculated separately for the cold and warm water pipes. pa Available pressure after the decompression valve Pressure pn shall be calculated from pressure pa in same way, but level difference shall be calculated from level of the decompression valve, and pressure losses in site water pipe and water meter should not be taken into account.
3 3 Line 1 Line 2 connecting pipe main supply water meter service pipe distribution pipe Fig. 1 Definitions of terms used in designing water supply systems n number of storey s with water outlets K 1-4 water fittings 1-4 p pressure losses in pipe section
4 4 2. Dimensioning Dimensioning step by step: (1) Determine standard flow of each faucet (and connection pipe), position 3 dimensioning table 1 (2) Calculate sum of standard flow for each distribution section (Q). (3) Calculate the dimensioning flow (q) for each section of distribution pipe - hot and cold water separately, position 4. Dimensioning flow always define sum of standard flow. (4) Determine dimensions of distribution pipes, position 4, fig. 3 (Choose the tube diameter so, that flow velocity is 2,0m/s). (5) Determine dimensions of connecting pipes, position 5, dimensioning table 4 or 5 (Maximum flow usually 3 m/s). (6) Do the volume flow check which is based on calculations of pressure losses. Every faucet must provide water flow that is 70% - 150% from its standard flow. (0,70 qn q 1,50 qn). (7) The set point of decompression valve is based on calculations of pressure losses. (8) If pressure losses are too high then make larger pipe diameter. Or dropping pressure level shall be reduced by leaving off the decompression valve. Calculations of pressure losses make allowance for the changes in static pressure due to differences in elevation and pressure losses in pipes (service pipe, water meter, water heater, distribution line, connection line, pipes fittings, valves, faucets). Pressure losses are calculated by the dimensioning flow (q). If decompression valve, which is situated usually immediately after the water meter, is used, pressure losses before decompression valve is not necessary to be taken into account, if pressure difference pb-pa is at least 100kPa. The pressure loss in the decompression valve with the dimensioning flow shall be taken into account in design. Water works always do the dimensioning of the property s water meter and the service pipe.
5 5 TABLE 1 Standard flows for design Water outlet Standard flow q N, l/s Cold water Hot water Bath 0,3 0,3 Bidet 0,1 0,1 Sink 0,2 0,2 Sink unit (bucket sink) 0,2 0,2 Dishwasher, domestic 0,2 (0,2) Shower 0,2 0,2 Tap 0,2 0,2 Washing machine, domestic 0,2 Washing machine, in laundry room or similar 0,4 0,4 Garden valve In single family house DN 15 0,2 In block of flats DN 20 0,4 Wash basin 0,1 0,1 Urinal with flushing valve 0,4 Urinal with flushing tap 0,2 WC 0,1 WC with flushing valve 1,5 1) Grouped outlets Shower group n*0,14 1)2) n*0,14 1)2) Flushing valves in series for urinals 0,3+n*0,1 1)2) Flush taps in series for urinals 0,14+n*0,06 1)2) WC flushing valves coupled in series 1,3+n*0,2 1)2) Group of wash basins or trough basin 0,07+n*0,03 1)2) 0,07+n*0,03 1)2) Fire hydrant See Clause 2.9. Other industrial use To be calculated separately Notes to table 1: 1) Simultaneous demand is to be taken into account in accordance with Table 2. 2) n = number of fittings in the group. If the fitting has alternative outlets, the maximum flow is to be used in design. A device which supplies water for a consumer unit such as a washing machine through an easily demountable connection is also considered to be an outlet.
6 6 2.1 Dimensioning flow in distribution pipes The dimensioning flow of distribution pipe define is by sum of standard flows by formula 1. Dimensioning of distribution pipe is used fig.2 and table 2 dimensioning flows. In dimensioning of distribution pipe, a total standard flow of (Q) 0,8 dm 3 /s for cold water and 0,8 dm 3 /s for warm water may be appointed for each flat, single family house and similar even though the aggregate flow according to the table is more than 0,8 dm 3 /s. A separate pipe for kitchen or bathroom in a dwelling may be designed without consideration of the standard flow for a washing machine or dishwasher which is connected there, provided that the dimensioning flow of the pipe in question 0,2 dm 3 /s. In designing distribution pipes common to a number of dwellings, consideration shall be given to the flows which occur. The dimensioning flow in the distribution pipe is obtained from the formula: 1 q = dimensioning flow, dm 3 /s, also known as probable flow and design flow qn1 qm Θ Q A maximum standard flow in pipe being dimension (dm 3 /s) mean flow through valve in question, (dm 3 /s) probability that qm is used during peak consumption periods aggregated standard flows through the connected water outlets, (dm 3 /s) correction factor which takes account of the number of times that the dimension flow q is exceeded
7 7 Uncertainty 1 0,01 0,001 0,0001 Factor A 2,3 3,1 3,7 In calculating the dimensioning flow of distribution pipes in residential and office buildings, schools, hotels, hospitals and other similar buildings, the following values are to be used: qn1 = 0,2 dm 3 /s (without bath), 0,3 dm 3 /s (with bath) qm = 0,2 dm 3 /s Θ = 0,015 A = 3,1,, (2) Maximum q N1 in use is 0,3 dm 3 /s, even standard flow is greater. Values of the dimensioning flow (q) is calculated with these values is set out in Table 2. Aggregate standard flow Q, dm 3 /s Fig. 2, Dependence of the sum of standard flow and inner diameter of distribution pipe
8 1 The probability of the required flow (standard flow) not being reached shall be taken into consideration. 8
9 9 2.2 Pressures and pressure losses Units of the pressures: Water column pressure mwp (Fin: mvp) International System of Units (SI) N/m 2 = Pa (Pascal) It is an appropriate unit to used kpa for dimensioning of water supply system. 1,0 mwp = 10 kpa 2.3 Available static pressure p st Difference of static pressure (= static pressure loss) h st +H 2 h st H 2 +H 1 H 1 0-level Fig. 4.1 Difference of static pressure (= static pressure loss) h st Difference of static pressure is calculated by formula: (3) hst H2 H1 difference of static pressure, m mwp kpa point of sight level 2, m point of sight level 1, m
10 10 Dimensioning of water supply systems are interested available static pressure p st. Water main pressure (+H 2 ) Point of sight level (+H 1 ) p st H 2 H 1 Fig. 4.2 Available static pressure p st Available static pressure is calculated by formula: (4) pst p0 H1 available static pressure, m mwp kpa water main pressure, m point of sight level, m 2.4 Pressure losses due to flow rate 5 Fig. 4.3 Local pressure loss of pipe section The local pressure loss of the pipe section is calculated following formula. (5) 0,5 (6) p local pressure loss, kpa
11 11 R l Z pd friction loss per one meter of pipe, kpa/m pipe length, m the pipe part s single (local) resistance pressure loss, kpa sum of pipe part's coefficients depended on the nature of local resistance dynamic pressure, kpa density of the fluid, kg/m 3 v rate of flow, m/s Pressure losses in distribution pipes: Σ Σ (7) (8) p sum of the local pressure losses, kpa Available pressure p n Σ (9) pn pst p available pressure for the connection pipe and faucet. (Static pressure is calculated to the elevation of faucet.), kpa available static pressure of the faucet height, kpa sum of local pressure losses from the connection point of municipal water work and service pipe to the beginning of the connection pipe which is gone at the issue faucet, kpa Faucet, P v Connection pipe, P k p st P n H p Distribution line, p Fig Available pressure p n
12 Pressure losses in the connection pipe: Pressure losses of the connection pipe are calculated the same way as pressure losses of distribution pipe section. (10) 0,5 (11) p R l Z pd local pressure loss, kpa friction loss per one meter of pipe, kpa/m length of connection pipe, m the pipe part s single (local) resistance pressure loss, kpa sum of pipe part's coefficients depended on the nature of local resistance dynamic pressure, kpa density of the fluid, kg/m 3 v rate of flow, m/s Distribution pipe FAUCET p vn p TBE Manifold Connection pipe p KN Fig Pressure losses in connection pipe When you have dimensioned flexible plastic pipe as PEX-pipe, you may be used following formula: (12)
13 13 TABLE 4 Connection pipes for outer diameter of copper pipes. The maximum length standard value is given for hydraulic hammer s decreasing. Standard flow, qn Pipe size* Velocity Friction loss per one Maximum length of dm 3 /s d u x e m / s meter of pipe, kpa/m connection pipe, m 0,1 10 x0,8 1,8 9, x 1,0 1,3 3, x 1,0 0,8 1 >10 0,2 12 x 1,0 2,6 14, x 1,0 1,5 3,8 5 0,3 15 x 1,0 2,3 8, x 1,0 1,5 2,8 5 0,4 18 x 1,0 2 4, x 1,0 1,3 1,5 10 * Pipe size du x e = outer diameter of pipe and thickness of pipe wall, mm TABLE 5 Connection pipes for inner diameter of plastic pipes. The maximum length standard value is given for hydraulic hammer s decreasing. Standard flow, qn Inner diameter Velocity Friction loss per one Maximum length of meter of pipe, dm 3 /s of pipe, mm m / s kpa/m connection pipe, m 0,1 10 1,3 2, ) 0,9 1,1 15 0,2 10 2,6 8, ) 1,8 3, ,5 2,5 20 0,3 10 3,8 18, ) 2,7 7, ,3 5,1 15 0, , ) 2 3, ) 1,3 1, ,3 1,1 20 1) Multilayer pipe
14 14 The pressure loss in the water fittings and in its connection pipe with standard flow can be calculated by following formula: (13) p nn p kn p v the total pressure loss in the water fittings and in the connection pipe with standard flow, kpa the pressure loss in the connection pipe with standard flow, kpa the pressure loss in the water fittings with standard flow, kpa The flow from the water fittings can be calculated by following formula: (14) q flow from the water fitting, dm 3 /s p n p nn q N the water fittings and connection pipe s pressure on the water fittings level, kpa. the total pressure loss in the water fittings and in the connection pipe with standard flow, kpa standard flow in the water fitting, dm 3 /s. The friction losses in the copper and plastic pipes are calculated according to fig. 8 and fig. 10. The coefficient of the local pressure loss in the pipe equipment and in the pipe system s fittings due to local resistance can be taken from table 6. Or it can be given by manufacturer and from the hand books. The value of the pressure loss pv in the water fittings with standard flow qn can be given by manufacturer, but it must be at least 150 kpa anyway.
15 15 TABLE 6 Local pressure losses due to local resistance: (the coefficient of loss) Pipe fittings r/d or direction of flow Local resistance coefficient Comment Bend r is radius of curvature d is inner diameter Elbow The local resistance Branch Direction coefficient relates to rate of flow after the branch. Direction Direction
16 16
17 17
18 18 Correction coefficient for the different temperatures: Roughness: 0,0005 Fig. Pressure loss diagram of Uponor PEX and Uponor CombiPEX PN 10
19 The requisite pressure pa If there is needed to use decompression valve, the requisite pressure pa is calculated following formula: (15) NOTE! Remember right sign of 100 (16) Fig Requisite pressure p a
SIZING OF WATER PIPING SYSTEM
 SIZING OF WATER PIPING SYSTEM (This appendix is informative and is not part of the code.) SECTION AP101 GENERAL AP101.1 Scope. AP101.1.1 This appendix outlines two procedures for sizing a water piping
SIZING OF WATER PIPING SYSTEM (This appendix is informative and is not part of the code.) SECTION AP101 GENERAL AP101.1 Scope. AP101.1.1 This appendix outlines two procedures for sizing a water piping
SIZING OF WATER PIPING SYSTEM
 SIZING OF WATER PIPING SYSTEM The provisions contained in this appendix are not mandatory unless specifically referenced in the adopting ordinance. E101.1 Scope. SECTION E101 GENERAL E101.1.1 This appendix
SIZING OF WATER PIPING SYSTEM The provisions contained in this appendix are not mandatory unless specifically referenced in the adopting ordinance. E101.1 Scope. SECTION E101 GENERAL E101.1.1 This appendix
APPENDIX A RECOMMENDED RULES FOR SIZING THE WATER SUPPLY SYSTEM CHART A 1.2 FRICTION LOSSES FOR DISK-TYPE WATER METERS 1-1/2"
 RECOMMENDED RULES FOR SIZING THE WATER SUPPLY SYSTEM Because of the variable conditions encountered, it is impractical to lay down definite detailed rules of procedure for determining the sizes of water
RECOMMENDED RULES FOR SIZING THE WATER SUPPLY SYSTEM Because of the variable conditions encountered, it is impractical to lay down definite detailed rules of procedure for determining the sizes of water
APPENDIX A RECOMMENDED RULES FOR SIZING THE WATER SUPPLY SYSTEMS CHART A-1 FRICTION LOSSES FOR DISK-TYPE WATER METERS 1-1/2"
 RECOMMENDED RULES FOR SIZING THE WATER SUPPLY SYSTEMS Because of the variable conditions encountered, it is impractical to lay down definite detailed rules of procedure for determining the sizes of water
RECOMMENDED RULES FOR SIZING THE WATER SUPPLY SYSTEMS Because of the variable conditions encountered, it is impractical to lay down definite detailed rules of procedure for determining the sizes of water
appendix a recommended rules For sizing the water supply system PRE-PRINT Chart a 1.2 FriCtion losses For Disk-type water Meters
 recommended rules For sizing the water supply system Because of the variable conditions encountered, it is impractical to lay down definite detailed rules of procedure for determining the sizes of water
recommended rules For sizing the water supply system Because of the variable conditions encountered, it is impractical to lay down definite detailed rules of procedure for determining the sizes of water
High Performance BSP Dial Up Pattern Pressure Reducing Valve
 See our full range online at: www.vip-ltd.co.uk High Performance BSP Dial Up Pattern Pressure Reducing Valve VIP Product Code 31/0103 FUNCTION Pressure reducing valves are devices which, when installed
See our full range online at: www.vip-ltd.co.uk High Performance BSP Dial Up Pattern Pressure Reducing Valve VIP Product Code 31/0103 FUNCTION Pressure reducing valves are devices which, when installed
Old-Exam.Questions-Ch-14 T072 T071
 Old-Exam.Questions-Ch-14 T072 Q23. Water is pumped out of a swimming pool at a speed of 5.0 m/s through a uniform hose of radius 1.0 cm. Find the mass of water pumped out of the pool in one minute. (Density
Old-Exam.Questions-Ch-14 T072 Q23. Water is pumped out of a swimming pool at a speed of 5.0 m/s through a uniform hose of radius 1.0 cm. Find the mass of water pumped out of the pool in one minute. (Density
Experiment 8: Minor Losses
 Experiment 8: Minor Losses Purpose: To determine the loss factors for flow through a range of pipe fittings including bends, a contraction, an enlargement and a gate-valve. Introduction: Energy losses
Experiment 8: Minor Losses Purpose: To determine the loss factors for flow through a range of pipe fittings including bends, a contraction, an enlargement and a gate-valve. Introduction: Energy losses
Pre-adjustable pressure reducing valves with self-contained cartridge
 Pre-adjustable pressure reducing valves with self-contained cartridge 535..H series ACCREDITED ISO 91 FM 15 15/17 GB replaces 15/1GB Function Pressure reducing valves are devices which, when installed
Pre-adjustable pressure reducing valves with self-contained cartridge 535..H series ACCREDITED ISO 91 FM 15 15/17 GB replaces 15/1GB Function Pressure reducing valves are devices which, when installed
RESIDENTIAL WATER DISTRIBUTION
 RESIDENTIAL WATER DISTRIBUTION This case study demonstrates the steady-state simulation of the fresh water (drinking water) reticulation system in a small village. WATER RETICULATION Page1 WATER RETICULATION
RESIDENTIAL WATER DISTRIBUTION This case study demonstrates the steady-state simulation of the fresh water (drinking water) reticulation system in a small village. WATER RETICULATION Page1 WATER RETICULATION
Tous fluid flow systems. Further details on specific piping systems
 CHAPTER 33 PIPE SIZING Pressure Drop Equations... 33.1 WATER PIPING... 33.3 Flow Rate Limitations... 33.3 Hydronic System Piping... 33.4 Service Water Piping... 33.6 STEAM PIPING... 33.9 Low-Pressure Steam
CHAPTER 33 PIPE SIZING Pressure Drop Equations... 33.1 WATER PIPING... 33.3 Flow Rate Limitations... 33.3 Hydronic System Piping... 33.4 Service Water Piping... 33.6 STEAM PIPING... 33.9 Low-Pressure Steam
Read Only Document Not For Distribution
 Appendix B Sizing the Building Water Supply System B.1 General...229 B.2 Preliminary Information...229 B.2.1 General...229 B.2.2 Materials For System...229 B.2.3 Characteristics Of The Water Supply...229
Appendix B Sizing the Building Water Supply System B.1 General...229 B.2 Preliminary Information...229 B.2.1 General...229 B.2.2 Materials For System...229 B.2.3 Characteristics Of The Water Supply...229
CALEFFI. Pre-adjustable pressure reducing valves with self-contained cartridge series 01085/17 GB. replaces 01085/14 GB
 Pre-adjustable pressure reducing valves with self-contained cartridge - series CCREDITED ISO 9 FM CLEFFI /7 GB replaces / GB Function Pressure reducing valves are devices which, when installed on private
Pre-adjustable pressure reducing valves with self-contained cartridge - series CCREDITED ISO 9 FM CLEFFI /7 GB replaces / GB Function Pressure reducing valves are devices which, when installed on private
WATER PRESSURE REDUCER (SBD)
 WATER PRESSURE REDUCER (SBD) December 2016 PRODUCTS Product Code Connection Size Range of Products Max. Input Pressure Pressure Setting Range 340308 1/4" SBD 340315 1/2" SBD 340415 1/2" with sleeve coupling
WATER PRESSURE REDUCER (SBD) December 2016 PRODUCTS Product Code Connection Size Range of Products Max. Input Pressure Pressure Setting Range 340308 1/4" SBD 340315 1/2" SBD 340415 1/2" with sleeve coupling
Rules for Classification and Construction Additional Rules and Guidelines 3 Machinery Installations
 VI Rules for Classification and Construction Additional Rules and Guidelines 3 Machinery Installations 6 Guidelines for the Construction, Equipment and Testing of Closed Fuel Oil Overflow Systems Edition
VI Rules for Classification and Construction Additional Rules and Guidelines 3 Machinery Installations 6 Guidelines for the Construction, Equipment and Testing of Closed Fuel Oil Overflow Systems Edition
CALEFFI. Inclined pressure reducing valves series 01024/17 GB. replaces 01024/14 GB
 Inclined pressure reducing valves 533 series RIT ISO 91 FM 15 LFFI /17 G replaces /1 G Function Pressure reducing valves are installed in residential water system to reduce and stabilise inlet pressure
Inclined pressure reducing valves 533 series RIT ISO 91 FM 15 LFFI /17 G replaces /1 G Function Pressure reducing valves are installed in residential water system to reduce and stabilise inlet pressure
Applications of Bernoulli s principle. Principle states that areas with faster moving fluids will experience less pressure
 Applications of Bernoulli s principle Principle states that areas with faster moving fluids will experience less pressure Artery o When blood flows through narrower regions of arteries, the speed increases
Applications of Bernoulli s principle Principle states that areas with faster moving fluids will experience less pressure Artery o When blood flows through narrower regions of arteries, the speed increases
ACCREDITED H series Inclined pressure reducing valve sizes DN 15 (1/2 ) and DN 20 (3/4 )
 Inclined pressure reducing valves 533..H series RIT ISO 91 FM LFFI /17 G replaces / G Function Pressure reducing valves are installed in residential water systems to reduce and stabilise inlet pressure
Inclined pressure reducing valves 533..H series RIT ISO 91 FM LFFI /17 G replaces / G Function Pressure reducing valves are installed in residential water systems to reduce and stabilise inlet pressure
Water Hammer Arrestors
 Water Hammer rrestors watts.com What is Water Hammer? T he noise from banging pipes is caused by shocks of high speed water flowing in the piping system when a fixture is suddenly closed. Sudden stoppage
Water Hammer rrestors watts.com What is Water Hammer? T he noise from banging pipes is caused by shocks of high speed water flowing in the piping system when a fixture is suddenly closed. Sudden stoppage
Instruction Manual. Pipe Friction Training Panel
 Instruction Manual HL 102 Pipe Friction Training Panel 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 HL 102 Instruction Manual This manual must be kept by the unit. Before operating the unit: - Read this manual. - All
Instruction Manual HL 102 Pipe Friction Training Panel 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 HL 102 Instruction Manual This manual must be kept by the unit. Before operating the unit: - Read this manual. - All
Enter your parameter set number (1-27)
 1- Helium balloons fly and balloons with air sink. Assume that we want to get a balloon that is just floating in the air, neither rising nor falling, when a small weight is placed hanging in the balloon.
1- Helium balloons fly and balloons with air sink. Assume that we want to get a balloon that is just floating in the air, neither rising nor falling, when a small weight is placed hanging in the balloon.
Construction, Fitting and Testing of Closed Fuel Overflow Systems
 Construction, Fitting and Testing of Closed Fuel Overflow Systems 2014 This latest edition incorporates all rule changes. The latest revisions are shown with a vertical line. The section title is framed
Construction, Fitting and Testing of Closed Fuel Overflow Systems 2014 This latest edition incorporates all rule changes. The latest revisions are shown with a vertical line. The section title is framed
SIZING AND CAPACITIES OF GAS PIPING Reserved
 APPENDIX A (IFGS) SIZING AND CAPACITIES OF GAS PIPING Reserved 2003 INTERNATIONAL RESIDENTIAL CODE 529R APPENDIX A SIZING AND CAPACITIES OF GAS PIPING This page left intentionally blank. 530R 2003 INTERNATIONAL
APPENDIX A (IFGS) SIZING AND CAPACITIES OF GAS PIPING Reserved 2003 INTERNATIONAL RESIDENTIAL CODE 529R APPENDIX A SIZING AND CAPACITIES OF GAS PIPING This page left intentionally blank. 530R 2003 INTERNATIONAL
Pressure reducing valves
 Pressure reducing valves series 60-6 - 6-66 cert. n 000 ISO 9001 06/01 G Replaces 06/97 G Function Pressure reducers are devices which, when installed on a water system, reduce and stabilise the pressure
Pressure reducing valves series 60-6 - 6-66 cert. n 000 ISO 9001 06/01 G Replaces 06/97 G Function Pressure reducers are devices which, when installed on a water system, reduce and stabilise the pressure
Fluid Flow. Link. Flow» P 1 P 2 Figure 1. Flow Model
 Fluid Flow Equipment: Water reservoir, output tubes of various dimensions (length, diameter), beaker, electronic scale for each table. Computer and Logger Pro software. Lots of ice.temperature probe on
Fluid Flow Equipment: Water reservoir, output tubes of various dimensions (length, diameter), beaker, electronic scale for each table. Computer and Logger Pro software. Lots of ice.temperature probe on
SIZING AND CAPACITIES OF GAS PIPING
 APPENDIX A (IFGS) SIZING AND CAPACITIES OF GAS PIPING (This appendix is informative and is not part of the code. This appendix is an excerpt from the 2003 International Fuel Gas Code, coordinated with
APPENDIX A (IFGS) SIZING AND CAPACITIES OF GAS PIPING (This appendix is informative and is not part of the code. This appendix is an excerpt from the 2003 International Fuel Gas Code, coordinated with
Irrigation &Hydraulics Department lb / ft to kg/lit.
 CAIRO UNIVERSITY FLUID MECHANICS Faculty of Engineering nd Year CIVIL ENG. Irrigation &Hydraulics Department 010-011 1. FLUID PROPERTIES 1. Identify the dimensions and units for the following engineering
CAIRO UNIVERSITY FLUID MECHANICS Faculty of Engineering nd Year CIVIL ENG. Irrigation &Hydraulics Department 010-011 1. FLUID PROPERTIES 1. Identify the dimensions and units for the following engineering
A centrifugal pump consists of an impeller attached to and rotating with the shaft and a casing that encloses the impeller.
 Centrifugal pump How centrifugal pumps work A centrifugal pump consists of an impeller attached to and rotating with the shaft and a casing that encloses the impeller. In centrifugal pump, liquid is forced
Centrifugal pump How centrifugal pumps work A centrifugal pump consists of an impeller attached to and rotating with the shaft and a casing that encloses the impeller. In centrifugal pump, liquid is forced
SPH 4C Unit 4 Hydraulics and Pneumatic Systems
 SPH 4C Unit 4 Hydraulics and Pneumatic Systems Properties of Fluids and Pressure Learning Goal: I can explain the properties of fluids and identify associated units. Definitions: Fluid: A substance that
SPH 4C Unit 4 Hydraulics and Pneumatic Systems Properties of Fluids and Pressure Learning Goal: I can explain the properties of fluids and identify associated units. Definitions: Fluid: A substance that
SIZING AND CAPACITIES OF GAS PIPING
 APPENDIX A (IFGS) SIZING AND CAPACITIES OF GAS PIPING (This appendix is adopted as part of the code.) A.1 General. To determine the size of piping used in a gas piping system, the following factors must
APPENDIX A (IFGS) SIZING AND CAPACITIES OF GAS PIPING (This appendix is adopted as part of the code.) A.1 General. To determine the size of piping used in a gas piping system, the following factors must
ACCREDITED. Function. series 5360/
 Pressure reducing valves series 360-36 - 36-366 RIT ISO 900 FM 6 LFFI 06/7 G replaces dp 06/0 G Function Pressure reducing valves are devices which, when installed on a private plumbing system, reduce
Pressure reducing valves series 360-36 - 36-366 RIT ISO 900 FM 6 LFFI 06/7 G replaces dp 06/0 G Function Pressure reducing valves are devices which, when installed on a private plumbing system, reduce
Unsteady Flow in Pipes
 The Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Civil Engineering Department Hydraulics - ECIV 3322 Chapter 4 Unsteady Flow in Pipes Water Hammer Phenomenon in pipelines A sudden change of flow rate
The Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Civil Engineering Department Hydraulics - ECIV 3322 Chapter 4 Unsteady Flow in Pipes Water Hammer Phenomenon in pipelines A sudden change of flow rate
CVEN 311 Fluid Dynamics Fall Semester 2011 Dr. Kelly Brumbelow, Texas A&M University. Final Exam
 CVEN 311 Fluid Dynamics Fall Semester 2011 Dr. Kelly Brumbelow, Texas A&M University Final Exam 8 pages, front & back, not including reference sheets; 21 questions An excerpt from the NCEES Fundamentals
CVEN 311 Fluid Dynamics Fall Semester 2011 Dr. Kelly Brumbelow, Texas A&M University Final Exam 8 pages, front & back, not including reference sheets; 21 questions An excerpt from the NCEES Fundamentals
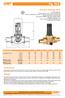 Fig. Art. 515 121 Pressure reducing valve DVGW approved pressure: max. 25 bar (362,50 psi) Outlet pressure adjustable between 1,5 bar (21,8 psi) and 6 bar (87 psi) Factory pre-set to 4 bar ( psi) Temperature
Fig. Art. 515 121 Pressure reducing valve DVGW approved pressure: max. 25 bar (362,50 psi) Outlet pressure adjustable between 1,5 bar (21,8 psi) and 6 bar (87 psi) Factory pre-set to 4 bar ( psi) Temperature
REGISTRATION EXAMINATION, JUNE 2017 CERTIFYING PLUMBER ANSWER SCHEDULE
 No. 9195 REGISTRATION EXAMINATION, JUNE 2017 CERTIFYING PLUMBER ANSWER SCHEDULE Plumbers, Gasfitters and Drainlayers Board, 2017. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced by any
No. 9195 REGISTRATION EXAMINATION, JUNE 2017 CERTIFYING PLUMBER ANSWER SCHEDULE Plumbers, Gasfitters and Drainlayers Board, 2017. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced by any
Hours / 100 Marks Seat No.
 17421 15116 3 Hours / 100 Seat No. Instructions (1) All Questions are Compulsory. (2) Answer each next main Question on a new page. (3) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (4)
17421 15116 3 Hours / 100 Seat No. Instructions (1) All Questions are Compulsory. (2) Answer each next main Question on a new page. (3) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (4)
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 14 Fluids Fluids at rest pressure vs. depth Pascal s principle Archimedes s principle Buoynat forces Fluids in motion: Continuity & Bernoulli equations 1. How deep
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 14 Fluids Fluids at rest pressure vs. depth Pascal s principle Archimedes s principle Buoynat forces Fluids in motion: Continuity & Bernoulli equations 1. How deep
ART24 Differential Pressure Control Valve (DPCV)
 ART24 Differential Pressure Technical Data and Installation Instructions Page 1 PN 16 Main features: ART24 is used for balancing the flow in cooling, heating and domestic water systems. ART24 is a differential
ART24 Differential Pressure Technical Data and Installation Instructions Page 1 PN 16 Main features: ART24 is used for balancing the flow in cooling, heating and domestic water systems. ART24 is a differential
Chapter 14 Fluids Mass Density Pressure Pressure in a Static Fluid Pascal's Principle Archimedes' Principle
 Chapter 14 Fluids Mass Density Pressure Pressure in a Static Fluid Pascal's Principle Archimedes' Principle Fluids in Motion The Equation of Continuity DEFINITION OF MASS DENSITY The mass density ρ is
Chapter 14 Fluids Mass Density Pressure Pressure in a Static Fluid Pascal's Principle Archimedes' Principle Fluids in Motion The Equation of Continuity DEFINITION OF MASS DENSITY The mass density ρ is
Chapter 13 Fluids. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 13 Fluids Phases of Matter Density and Specific Gravity Pressure in Fluids Atmospheric Pressure and Gauge Pressure Pascal s Principle Units of Chapter 13 Measurement of Pressure; Gauges and the
Chapter 13 Fluids Phases of Matter Density and Specific Gravity Pressure in Fluids Atmospheric Pressure and Gauge Pressure Pascal s Principle Units of Chapter 13 Measurement of Pressure; Gauges and the
SIZING AND CAPACITIES OF GAS PIPING
 (IFGS) SIZING AND CAPACITIES OF GAS PIPING (This appendix is informative and is not part of the code. This appendix is an excerpt from the 2006 International Fuel Gas Code, coordinated with the section
(IFGS) SIZING AND CAPACITIES OF GAS PIPING (This appendix is informative and is not part of the code. This appendix is an excerpt from the 2006 International Fuel Gas Code, coordinated with the section
SUMMARY PROBLEMS CAUSED BY BACKFLOW IN PIPE SYSTEMS.
 Page 1 of 11 SUMMARY There are many problems derived from a reverse flow in a piping system. A solution presented in this paper is the WaStop inline check valve. The paper aims to explain some of the important
Page 1 of 11 SUMMARY There are many problems derived from a reverse flow in a piping system. A solution presented in this paper is the WaStop inline check valve. The paper aims to explain some of the important
Unit Test Review. Pressure Valve Pump Surfactant Viscosity Plimsoll line Density Units for density Neutral buoyancy Pipeline pig
 Pressure Valve Pump Surfactant Viscosity Plimsoll line Density Units for density Neutral buoyancy Pipeline pig Unit Test Review 4. What properties affect or change the density of a substance? 5. Describe
Pressure Valve Pump Surfactant Viscosity Plimsoll line Density Units for density Neutral buoyancy Pipeline pig Unit Test Review 4. What properties affect or change the density of a substance? 5. Describe
Automatic balancing valves ASV
 Automatic balancing valves ASV ASV-P ASV-PV ASV-PV ASV-PV ASV-I ASV-M 15-40 15-40 50 65-100 15-50 15-50 Description / Application ASV balancing valves are used for dynamic hydronic balance in heating and
Automatic balancing valves ASV ASV-P ASV-PV ASV-PV ASV-PV ASV-I ASV-M 15-40 15-40 50 65-100 15-50 15-50 Description / Application ASV balancing valves are used for dynamic hydronic balance in heating and
Technical Information. ips. 11 Compensating for expansion and contraction
 Technical Information System design 1 Dimensions of plastic piping systems 2 Sizing pipes 3 Pressure loss in pipe 5 Pressure loss in fittings and valves 8 Water hammer 9 Thermal expansion and contraction
Technical Information System design 1 Dimensions of plastic piping systems 2 Sizing pipes 3 Pressure loss in pipe 5 Pressure loss in fittings and valves 8 Water hammer 9 Thermal expansion and contraction
SIZING AND CAPACITIES OF GAS PIPING
 SIZING AND CAPACITIES OF GAS PIPING A.1 General piping considerations. The first goal of determining the pipe sizing for a fuel gas piping system is to make sure that there is sufficient gas pressure at
SIZING AND CAPACITIES OF GAS PIPING A.1 General piping considerations. The first goal of determining the pipe sizing for a fuel gas piping system is to make sure that there is sufficient gas pressure at
Shri Krishna Test House, B-70/1, Gali No. 8, New Modern Shahdara, Mansarover Park, Delhi. Discipline Mechanical Testing Issue Date
 Last Amended on - Page 1 of 14 I. PERFORMANCE TEST 1. Domestic gas Stove for use with L.P.G. General Cl. 4, IS:5116 & Cl.4.1.1 of IS:4246 Material Cl. 5 of IS:5116 Design for Maintenance Cl. 6.2, 6.3,
Last Amended on - Page 1 of 14 I. PERFORMANCE TEST 1. Domestic gas Stove for use with L.P.G. General Cl. 4, IS:5116 & Cl.4.1.1 of IS:4246 Material Cl. 5 of IS:5116 Design for Maintenance Cl. 6.2, 6.3,
Automatic balancing valves ASV
 Automatic balancing valves ASV ASV-PV ASV-PV ASV-PV ASV-BD ASV-M DN 15-40 DN 50 DN 65-100 DN 15-50 DN 15-50 Description / Application ASV balancing valves are used for dynamic hydronic balance in heating
Automatic balancing valves ASV ASV-PV ASV-PV ASV-PV ASV-BD ASV-M DN 15-40 DN 50 DN 65-100 DN 15-50 DN 15-50 Description / Application ASV balancing valves are used for dynamic hydronic balance in heating
Pressure surge absorption
 Pressure surge absorption Product range for drinking water, waste water and the chemical industry With remote monitoring, everything is fully under control. Willy Zahnd, WARET AG PRESSURE SURGE ABSORPTION
Pressure surge absorption Product range for drinking water, waste water and the chemical industry With remote monitoring, everything is fully under control. Willy Zahnd, WARET AG PRESSURE SURGE ABSORPTION
Description. Functions. Technical data. Applications. Tests. On-Off 2 levels float control valve, closing at high level and opening at low level.
 DN 0 to 1000 - Serie K3 0 On-Off levels float control valve, closing at high level and opening at low level. Functions Prevents overflowing and closes at a constant and adjustable high level. Remains closed
DN 0 to 1000 - Serie K3 0 On-Off levels float control valve, closing at high level and opening at low level. Functions Prevents overflowing and closes at a constant and adjustable high level. Remains closed
Integral type Differential pressure flowmeter VNT Series
 Integral type Differential pressure flowmeter VNT Series OUTLINE VH series Wafer-Cone differential pressure flowmeter and high precision differential pressure transmitter are integrated into one flowmeter.
Integral type Differential pressure flowmeter VNT Series OUTLINE VH series Wafer-Cone differential pressure flowmeter and high precision differential pressure transmitter are integrated into one flowmeter.
SPECIFICATIONS & INSTALLATION GUIDE ANOTHER QUALITY PRODUCT BY FORZA GLOBAL WATER CRIMP EDITION: 0001
 WATER CRIMP TM SPECIFICATIONS & INSTALLATION GUIDE ANOTHER QUALITY PRODUCT BY FORZA GLOBAL EDITION: 0001 2 WATER CRIMP FORZA GLOBAL are the manufacturers and distributors of FORZA PE-Xa PIPING Systems
WATER CRIMP TM SPECIFICATIONS & INSTALLATION GUIDE ANOTHER QUALITY PRODUCT BY FORZA GLOBAL EDITION: 0001 2 WATER CRIMP FORZA GLOBAL are the manufacturers and distributors of FORZA PE-Xa PIPING Systems
Slide 1 / What is the density of an aluminum block with a mass of 4050 kg and volume of 1.5 m 3?
 Slide 1 / 68 1 What is the density of an aluminum block with a mass of 4050 kg and volume of 1.5 m 3? Slide 2 / 68 2 What is the mass of a rectangular shaped ice block with dimensions of 0.04m x 0.05m
Slide 1 / 68 1 What is the density of an aluminum block with a mass of 4050 kg and volume of 1.5 m 3? Slide 2 / 68 2 What is the mass of a rectangular shaped ice block with dimensions of 0.04m x 0.05m
DN300 DN2000 C Plunger Valve
 ל DN300 DN2000 C Plunger Valve P.O.B 46 MOSHAV SHTULA WESTERN GALILEE 2286500 Tl. +972-(0)77-6656101, Fax. +972-(0)77-6656196 Website: www.saisanketvalves.com www.saisanket.com email: saisanket@saisanket.com
ל DN300 DN2000 C Plunger Valve P.O.B 46 MOSHAV SHTULA WESTERN GALILEE 2286500 Tl. +972-(0)77-6656101, Fax. +972-(0)77-6656196 Website: www.saisanketvalves.com www.saisanket.com email: saisanket@saisanket.com
Types of Forces. Pressure Buoyant Force Friction Normal Force
 Types of Forces Pressure Buoyant Force Friction Normal Force Pressure Ratio of Force Per Unit Area p = F A P = N/m 2 = 1 pascal (very small) P= lbs/in 2 = psi = pounds per square inch Example: Snow Shoes
Types of Forces Pressure Buoyant Force Friction Normal Force Pressure Ratio of Force Per Unit Area p = F A P = N/m 2 = 1 pascal (very small) P= lbs/in 2 = psi = pounds per square inch Example: Snow Shoes
Applied Fluid Mechanics
 Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Chapter 9 Fluids and Buoyant Force
 Chapter 9 Fluids and Buoyant Force In Physics, liquids and gases are collectively called fluids. 3/0/018 8:56 AM 1 Fluids and Buoyant Force Formula for Mass Density density mass volume m V water 1000 kg
Chapter 9 Fluids and Buoyant Force In Physics, liquids and gases are collectively called fluids. 3/0/018 8:56 AM 1 Fluids and Buoyant Force Formula for Mass Density density mass volume m V water 1000 kg
Versions. Benefits. Balancing DN15-32 DN40 DN50 DN15, DN20, DN25, DN32, DN40, DN50. Dimensions
 Ballorex Delta Description The Ballorex Delta is a differential pressure control valve used in hydronic heating or cooling systems. By ensuring a constant differential pressure across motorized or static
Ballorex Delta Description The Ballorex Delta is a differential pressure control valve used in hydronic heating or cooling systems. By ensuring a constant differential pressure across motorized or static
Assistant Lecturer Anees Kadhum AL Saadi
 Pressure Variation with Depth Pressure in a static fluid does not change in the horizontal direction as the horizontal forces balance each other out. However, pressure in a static fluid does change with
Pressure Variation with Depth Pressure in a static fluid does not change in the horizontal direction as the horizontal forces balance each other out. However, pressure in a static fluid does change with
Pumping Systems for Landscaping Pumps, Controls and Accessories. Mark Snyder, PE
 October 21, 2010 Pumping Systems for Landscaping Pumps, Controls and Accessories Mark Snyder, PE Pump Station Design Purpose of Pump Stations Pump stations are designed to boost water pressure from a lower
October 21, 2010 Pumping Systems for Landscaping Pumps, Controls and Accessories Mark Snyder, PE Pump Station Design Purpose of Pump Stations Pump stations are designed to boost water pressure from a lower
Static Fluids. **All simulations and videos required for this package can be found on my website, here:
 DP Physics HL Static Fluids **All simulations and videos required for this package can be found on my website, here: http://ismackinsey.weebly.com/fluids-hl.html Fluids are substances that can flow, so
DP Physics HL Static Fluids **All simulations and videos required for this package can be found on my website, here: http://ismackinsey.weebly.com/fluids-hl.html Fluids are substances that can flow, so
Baker maric flow control valves
 Gate Valves 1 Baker maric flow control valves A - W - E - 2 Baker Maric Flow Control Valves Ever since water has been piped there has been a definite need for a practical, accurate, self cleaning and inexpensive
Gate Valves 1 Baker maric flow control valves A - W - E - 2 Baker Maric Flow Control Valves Ever since water has been piped there has been a definite need for a practical, accurate, self cleaning and inexpensive
Residential Pressure Booster Systems
 Residential Pressure Booster Systems HOW IT WORKS When the pressure available is insuffi cient it is necessary to install a boosting system. FLUX BOOSTING SYSTEM starts and stops according to the user
Residential Pressure Booster Systems HOW IT WORKS When the pressure available is insuffi cient it is necessary to install a boosting system. FLUX BOOSTING SYSTEM starts and stops according to the user
STAD Series. Balancing and control valves. Technical Data Sheet. WattsIndustries.com
 STAD Series Balancing and control valves Technical Data Sheet WattsIndustries.com Description STAD Series variable-orifice threaded valves are designed for flow control and monitoring in climate control
STAD Series Balancing and control valves Technical Data Sheet WattsIndustries.com Description STAD Series variable-orifice threaded valves are designed for flow control and monitoring in climate control
Gas Physics Pressure and Flow Topics Covered:
 Gas Physics Pressure and Flow Topics Covered: Molecular Theory of Gases Definition of Pressure The Gas Laws Definition of Flow Definition of Pressure Drop Gas Physics Pressure and Flow Topics Covered:
Gas Physics Pressure and Flow Topics Covered: Molecular Theory of Gases Definition of Pressure The Gas Laws Definition of Flow Definition of Pressure Drop Gas Physics Pressure and Flow Topics Covered:
H16 Losses in Piping Systems
 H16 Losses in Piping Systems The equipment described in this manual is manufactured and distributed by TECQUIPMENT LIMITED Suppliers of technological laboratory equipment designed for teaching. BONSALL
H16 Losses in Piping Systems The equipment described in this manual is manufactured and distributed by TECQUIPMENT LIMITED Suppliers of technological laboratory equipment designed for teaching. BONSALL
Wirsbo / AquaPEX. AquaPEX Tube. White Coils. White Straight Lengths. Wirsbo AquaPEX plus Tubing. Red Coils. Blue Coils PAGE 055-1
 2011 Wirsbo / AquaPEX PAGE 055-1 Code# Description Pkg Mfg# AquaPEX Tubing AquaPEX Tube Wirsbo AquaPEX tubing is used in hot and cold potable water distribution systems and Uponor residential fire safety
2011 Wirsbo / AquaPEX PAGE 055-1 Code# Description Pkg Mfg# AquaPEX Tubing AquaPEX Tube Wirsbo AquaPEX tubing is used in hot and cold potable water distribution systems and Uponor residential fire safety
Installation and operation Manual. Bermad Surge Anticipation Valve. Model No 435
 Instruction manual Bermad surge anticipation manual Model No 435 Installation and operation Manual Bermad Surge Anticipation Valve Model No 435 Bermad Water Technologies Rev 0 5/05/2015 7 Inglewood Drive,
Instruction manual Bermad surge anticipation manual Model No 435 Installation and operation Manual Bermad Surge Anticipation Valve Model No 435 Bermad Water Technologies Rev 0 5/05/2015 7 Inglewood Drive,
1. The principle of fluid pressure that is used in hydraulic brakes or lifts is that:
 University Physics (Prof. David Flory) Chapt_15 Thursday, November 15, 2007 Page 1 Name: Date: 1. The principle of fluid pressure that is used in hydraulic brakes or lifts is that: A) pressure is the same
University Physics (Prof. David Flory) Chapt_15 Thursday, November 15, 2007 Page 1 Name: Date: 1. The principle of fluid pressure that is used in hydraulic brakes or lifts is that: A) pressure is the same
3. A fluid is forced through a pipe of changing cross section as shown. In which section would the pressure of the fluid be a minimum?
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Fluid Mechanics 1. A cork has weight mg and density 5% of water s density. A string is tied around the cork and attached to the bottom of a water-filled container. The
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Fluid Mechanics 1. A cork has weight mg and density 5% of water s density. A string is tied around the cork and attached to the bottom of a water-filled container. The
DAV - P. Product Catalogue DAV - P. Air release & Vacuum Break Valves. (Plastic Air Valves) DAV - P. Edition 2012
 Product Catalogue DAV - P DAV - P Air release & Vacuum Break Valves Edition 1 DAV - P (Plastic Air Valves) DAV Series Overview General The presence of trapped air in a pressurized pipeline can have serious
Product Catalogue DAV - P DAV - P Air release & Vacuum Break Valves Edition 1 DAV - P (Plastic Air Valves) DAV Series Overview General The presence of trapped air in a pressurized pipeline can have serious
HL Article. Air admittance valves DN50 DN75
 100 165 177 HL Article Air admittance valves 48 DN50 EAN 9003076 + HL Air admittance valves Basic about design and installation Air admittance valves nowadays are part of nearly every drainage system.
100 165 177 HL Article Air admittance valves 48 DN50 EAN 9003076 + HL Air admittance valves Basic about design and installation Air admittance valves nowadays are part of nearly every drainage system.
CHAPTER 9 Fluids. Units
 CHAPTER 9 Fluids Units Fluids in Motion; Flow Rate and the Equation of Continuity Bernoulli s Equation Applications of Bernoulli s Principle Viscosity Flow in Tubes: Poiseuille s Equation, Blood Flow Surface
CHAPTER 9 Fluids Units Fluids in Motion; Flow Rate and the Equation of Continuity Bernoulli s Equation Applications of Bernoulli s Principle Viscosity Flow in Tubes: Poiseuille s Equation, Blood Flow Surface
Exercise 2-3. Flow Rate and Velocity EXERCISE OBJECTIVE C C C
 Exercise 2-3 EXERCISE OBJECTIVE C C C To describe the operation of a flow control valve; To establish the relationship between flow rate and velocity; To operate meter-in, meter-out, and bypass flow control
Exercise 2-3 EXERCISE OBJECTIVE C C C To describe the operation of a flow control valve; To establish the relationship between flow rate and velocity; To operate meter-in, meter-out, and bypass flow control
Operating instructions Pitot Static Tube
 Operating instructions Pitot Static Tube halstrup-walcher GmbH Stegener Straße 10 D-79199 Kirchzarten, Germany Phone: +49 (0) 76 61/39 63-0 Fax: +49 (0) 76 61/39 63-99 E-mail: info@halstrup-walcher.de
Operating instructions Pitot Static Tube halstrup-walcher GmbH Stegener Straße 10 D-79199 Kirchzarten, Germany Phone: +49 (0) 76 61/39 63-0 Fax: +49 (0) 76 61/39 63-99 E-mail: info@halstrup-walcher.de
Hours / 100 Marks Seat No.
 17421 21415 3 Hours / 100 Marks Seat No. Instructions : (1) All Questions are compulsory. (2) Answer each next main Question on a new page. (3) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary.
17421 21415 3 Hours / 100 Marks Seat No. Instructions : (1) All Questions are compulsory. (2) Answer each next main Question on a new page. (3) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary.
SAV. Safety Shut-off Valve. Safety Shut-off Valve Type SAV
 SAV Safety Shut-off Valve Safety Shut-off Valve Type SAV Direct acting shut-off device with adjustable setpoint springs for over-pressure and underpressure monitoring In compliance with EN 14382 Inlet
SAV Safety Shut-off Valve Safety Shut-off Valve Type SAV Direct acting shut-off device with adjustable setpoint springs for over-pressure and underpressure monitoring In compliance with EN 14382 Inlet
Third measurement MEASUREMENT OF PRESSURE
 1. Pressure gauges using liquids Third measurement MEASUREMENT OF PRESSURE U tube manometers are the simplest instruments to measure pressure with. In Fig.22 there can be seen three kinds of U tube manometers
1. Pressure gauges using liquids Third measurement MEASUREMENT OF PRESSURE U tube manometers are the simplest instruments to measure pressure with. In Fig.22 there can be seen three kinds of U tube manometers
THE IMPACT ON ENERGY CONSUMPTION CAUSED BY PRESSURE DROP IN A COMPRESSED AIR SYSTEM
 THE IMPACT ON ENERGY CONSUMPTION CAUSED BY PRESSURE DROP IN A COMPRESSED AIR SYSTEM What is pressure drop in a compressed air utility? Pressure drop is a term used to characterize the reduction in air
THE IMPACT ON ENERGY CONSUMPTION CAUSED BY PRESSURE DROP IN A COMPRESSED AIR SYSTEM What is pressure drop in a compressed air utility? Pressure drop is a term used to characterize the reduction in air
Webassign 1 2.notebook. September 30, 2015
 1. Question DetailsCJ9 11.P.055. [2029001] A patient recovering from surgery is being given fluid intravenously. The fluid has a density of 1070 kg/m 3, and9.99 10 4 m 3 of it flows into the patient every
1. Question DetailsCJ9 11.P.055. [2029001] A patient recovering from surgery is being given fluid intravenously. The fluid has a density of 1070 kg/m 3, and9.99 10 4 m 3 of it flows into the patient every
1. All fluids are: A. gases B. liquids C. gases or liquids D. non-metallic E. transparent ans: C
 Chapter 14: FLUIDS 1 All fluids are: A gases B liquids C gases or liquids D non-metallic E transparent 2 Gases may be distinguished from other forms of matter by their: A lack of color B small atomic weights
Chapter 14: FLUIDS 1 All fluids are: A gases B liquids C gases or liquids D non-metallic E transparent 2 Gases may be distinguished from other forms of matter by their: A lack of color B small atomic weights
Ballorex Dynamic Description. Versions. Benefits. Balancing
 Ballorex Dynamic Description The Ballorex Dynamic valve is a combined pressure independent flow limiter and control valve which maintains a constant flow independently of pressure changes in heating or
Ballorex Dynamic Description The Ballorex Dynamic valve is a combined pressure independent flow limiter and control valve which maintains a constant flow independently of pressure changes in heating or
Fluid Mechanics. Liquids and gases have the ability to flow They are called fluids There are a variety of LAWS that fluids obey
 Fluid Mechanics Fluid Mechanics Liquids and gases have the ability to flow They are called fluids There are a variety of LAWS that fluids obey Density Regardless of form (solid, liquid, gas) we can define
Fluid Mechanics Fluid Mechanics Liquids and gases have the ability to flow They are called fluids There are a variety of LAWS that fluids obey Density Regardless of form (solid, liquid, gas) we can define
. In an elevator accelerating upward (A) both the elevator accelerating upward (B) the first is equations are valid
 IIT JEE Achiever 2014 Ist Year Physics-2: Worksheet-1 Date: 2014-06-26 Hydrostatics 1. A liquid can easily change its shape but a solid cannot because (A) the density of a liquid is smaller than that of
IIT JEE Achiever 2014 Ist Year Physics-2: Worksheet-1 Date: 2014-06-26 Hydrostatics 1. A liquid can easily change its shape but a solid cannot because (A) the density of a liquid is smaller than that of
Use equation for the cylindrical section and equation or for the ends.
 Solution 13.1 See section 13.3.4, equations 13.7 to 13.18 Solution 13.2 Use equation 13.34. (a) rigid constant C = 0.43 (b) free to rotate, C = 0.56 Solution 13.3 See section 13.5.1 Use equation 13.39
Solution 13.1 See section 13.3.4, equations 13.7 to 13.18 Solution 13.2 Use equation 13.34. (a) rigid constant C = 0.43 (b) free to rotate, C = 0.56 Solution 13.3 See section 13.5.1 Use equation 13.39
Correction of Pressure Drop in Steam and Water System in Performance Test of Boiler
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Correction of Pressure Drop in Steam and Water System in Performance Test of Boiler To cite this article: Jinglong Liu et al 2018
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Correction of Pressure Drop in Steam and Water System in Performance Test of Boiler To cite this article: Jinglong Liu et al 2018
SPECIFICATIONS & INSTALLATION GUIDE ANOTHER QUALITY PRODUCT BY FORZA GLOBAL WATER CRIMP EDITION: 0001
 WATER CRIMP TM SPECIFICATIONS & INSTALLATION GUIDE ANOTHER QUALITY PRODUCT BY FORZA GLOBAL EDITION: 0001 2 WATER CRIMP FORZA GLOBAL are the manufacturers and distributors of FORZA PE-Xa PIPING Systems
WATER CRIMP TM SPECIFICATIONS & INSTALLATION GUIDE ANOTHER QUALITY PRODUCT BY FORZA GLOBAL EDITION: 0001 2 WATER CRIMP FORZA GLOBAL are the manufacturers and distributors of FORZA PE-Xa PIPING Systems
AP B Fluids Practice Problems. Multiple Choice. Slide 2 / 43. Slide 1 / 43. Slide 4 / 43. Slide 3 / 43. Slide 6 / 43. Slide 5 / 43
 Slide 1 / 43 Slide 2 / 43 P Fluids Practice Problems Multiple hoice Slide 3 / 43 1 Two substances mercury with a density 13600 kg/m 3 and alcohol with a density 0.8 kg/m 3 are selected for an experiment.
Slide 1 / 43 Slide 2 / 43 P Fluids Practice Problems Multiple hoice Slide 3 / 43 1 Two substances mercury with a density 13600 kg/m 3 and alcohol with a density 0.8 kg/m 3 are selected for an experiment.
Homework of Chapter (4.2,4.3)
 Dead Line: Saturday (24/3/2018) The Islamic University of Gaza, Instructors: Dr. Khalil M. Al Astal Civil Engineering Department, Hydraulics -Discussion, Second semester, 2018. T.A: Eng. Mohammed AbuRahma
Dead Line: Saturday (24/3/2018) The Islamic University of Gaza, Instructors: Dr. Khalil M. Al Astal Civil Engineering Department, Hydraulics -Discussion, Second semester, 2018. T.A: Eng. Mohammed AbuRahma
General Performance Data Hose Ref Minimum Bend. Safety Pressure at 20 C (BAR) Working Pressure at. Flow Rate at 3 bar (lit/min) Working Pressure
 The Classic range provides a safe and taint free conveyance of potable water supplies for Domestic and Commercial plumbing applications. The range is designed to achieve robust and flexible solutions with
The Classic range provides a safe and taint free conveyance of potable water supplies for Domestic and Commercial plumbing applications. The range is designed to achieve robust and flexible solutions with
Installation, commissioning and servicing instructions
 488.03 www.reece.com.au Pressure reducing s Installation, commissioning and servicing instructions Function Pressure reducing s are installed in residential water systems to reduce and stabilise inlet
488.03 www.reece.com.au Pressure reducing s Installation, commissioning and servicing instructions Function Pressure reducing s are installed in residential water systems to reduce and stabilise inlet
627 Series Pressure Reducing Regulators
 627 Series Pressure Reducing Regulators Introduction The 627 Series direct-operated pressure reducing regulators (Figure 1) are for low and high-pressure systems. These regulators can be used with natural
627 Series Pressure Reducing Regulators Introduction The 627 Series direct-operated pressure reducing regulators (Figure 1) are for low and high-pressure systems. These regulators can be used with natural
Combination Air Valve
 Combination Air Valve For Sewage and Wastewater Model C50 Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual (IOM) Table of Contents General... Page 2 Safety... Page 2 Operational Data... Page 3 Materials
Combination Air Valve For Sewage and Wastewater Model C50 Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual (IOM) Table of Contents General... Page 2 Safety... Page 2 Operational Data... Page 3 Materials
Department of Civil & Geological Engineering GEOE Engineering Geology
 Department of Civil & Geological Engineering GEOE 218.3 Engineering Geology Assignment #3, Head, Pore Pressure & Effective Stress Due 08 Oct, 2010 NOTE: Numbered subscripts indicate depth, in metres, below
Department of Civil & Geological Engineering GEOE 218.3 Engineering Geology Assignment #3, Head, Pore Pressure & Effective Stress Due 08 Oct, 2010 NOTE: Numbered subscripts indicate depth, in metres, below
SECTION 8 HYDRAULIC MODEL
 SECTION 8 HYDRAULIC MODEL 8-1 General A computer model of the City s water system was utilized to aid in the evaluation of the adequacy of the existing facilities under present and future demand conditions.
SECTION 8 HYDRAULIC MODEL 8-1 General A computer model of the City s water system was utilized to aid in the evaluation of the adequacy of the existing facilities under present and future demand conditions.
MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science FLUID MECHANICS LABORATORY PIPE FRICTION
 MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science FLUID MECHANICS LABORATORY PIPE FRICTION Objective To estimate the fluid pressure drops and roughness specifications for copper
MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science FLUID MECHANICS LABORATORY PIPE FRICTION Objective To estimate the fluid pressure drops and roughness specifications for copper
(Refer Slide Time: 2:16)
 Fluid Machines. Professor Sankar Kumar Som. Department Of Mechanical Engineering. Indian Institute Of Technology Kharagpur. Lecture-23. Diffuser and Cavitation. Good morning and welcome you all to this
Fluid Machines. Professor Sankar Kumar Som. Department Of Mechanical Engineering. Indian Institute Of Technology Kharagpur. Lecture-23. Diffuser and Cavitation. Good morning and welcome you all to this
PHYSICS - CLUTCH CH 17: FLUID MECHANICS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com INTRO TO DENSITY LIQUIDS and GASES are types of. So we use the term to refer generally to both Liquids AND Gases. The DENSITY of a material is a measure of how tight the molecules
!! www.clutchprep.com INTRO TO DENSITY LIQUIDS and GASES are types of. So we use the term to refer generally to both Liquids AND Gases. The DENSITY of a material is a measure of how tight the molecules
APRIL 2017 Level 3 Advanced Technical Diploma in Plumbing (450) Level 3 Plumbing Theory Exam
 *82025350417* 8202-535 APRIL 2017 Level 3 Advanced Technical Diploma in Plumbing (450) Level 3 Plumbing Theory Exam If provided, stick your candidate barcode label here. Candidate name (first, last) First
*82025350417* 8202-535 APRIL 2017 Level 3 Advanced Technical Diploma in Plumbing (450) Level 3 Plumbing Theory Exam If provided, stick your candidate barcode label here. Candidate name (first, last) First
Water Hammer Arresters Standard PDI-WH 201 Revised 2006
 Water Hammer Arresters Standard PDI-WH 201 Revised 2006 Certification Sizing Placement Reference Data THE PLUMBING AND DRAINAGE INSTITUTE 800 Turnpike Street, Suite 300 North Andover, MA 01845 Phone: (800)
Water Hammer Arresters Standard PDI-WH 201 Revised 2006 Certification Sizing Placement Reference Data THE PLUMBING AND DRAINAGE INSTITUTE 800 Turnpike Street, Suite 300 North Andover, MA 01845 Phone: (800)
