An experimental study of inflatable offshore anchors in soft clay
|
|
|
- Silvester Hall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 An experimental study of inflatable offshore anchors in soft clay T.A. Newson and F.W. Smith Department of Civil Engineering, University of Dundee P. Brunning Stolt Offshore MS Ltd., Aberdeen Introduction Since many remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) are neutrally or positively bouyant, any activities that require any significant reaction load, e.g. in situ soil testing, are not possible without additional anchoring or clump weights. Whilst the majority of ROVs used by the offshore oil and gas industries have the necessary hydraulic and pneumatic control systems to employ anchors, previous attempts to develop seabed fixity have had variable success. These include standard anchor systems, such as helical screw, suction, duckbill and plate anchors. Any viable alternative must provide a cheap and reusable system that will provide sufficient pullout capacity and be able to operate in the demanding deep offshore environment. This project had the aim of determining whether a flexible, inflatable anchor system may provide sufficient uplift capacity to fix ROVs during offshore activities. A series of physical model tests have been used to assess the performance of the proposed anchor system in terms of pullout capacity and mobilisation distance. A limited range of anchor designs and operating conditions were investigated to provide data for this assessment. This paper describes the experimental methodology, anchor system and the testing of the system using an artificial clayey soil. Experimental methods Physical model testing was carried out in a large cylindrical steel container of 700 mm internal diameter and 1200 mm height. A series of tests involving constant velocity pullout of a range of anchors, with varying geometries was conducted. A large computer controlled screw jack was used to extract the Silt and siltation. Thomas Telford, London, 2001
2 2 Header - book title anchors and this was fixed to the top of the container using cross beams. The anchors were pulled out of the soil using a rigid hanger. The inflatable anchor system geometry is shown in Figure 1. The anchor consisted of a cylindrical steel tube (35 mm diameter, D) around which was fastened to a rubber membrane. Fluid or air can be pumped into the annular space between the tube and membrane to inflate it. The anchors were embedded to different depths (H) and the length of the inflatable section (L) was also varied. The fluid in the rubber membrane was pressurised by means of two screwed pistons, one of which may be driven by computer control to maintain a constant pressure. Constant volume was maintained by pressurising the system under computer control, then preventing further movement of the pistons. Soil H F To pressure - volume control L Inflatable membrane D Figure 1: Geometry of inflatable anchor system Computer control of the experiments was by means of HP-Vee programs. These monitored the inputs and took appropriate action to control the actuators. Values for load, pressure, travel etc were calculated, stored to disk and displayed on graphs as the experiment progressed. Where constant pressure was required any change in pressure in the system from a set value was used as feedback to drive the piston and thus bring the pressure back to the required value. Where constant volume testing was required a pressure was developed under computer control and then the actuator was disengaged to prevent any further change in fluid volume. The pressure-volume change relationship could also be investigated if necessary during an experiment. The anchor tests were conducted on a blend of Speswhite kaolin and Congleton sand. Congleton is a silicate sand with a uniform grading of subrounded particles, D 50 = 0.3 mm and specific gravity G s = The angle of repose of this soil is o. The range of densities for this soil are found to vary between ρ max = 1.78 t/m 3 and ρ min = 1.51 t/m 3. Speswhite kaolin clay is a
3 Header chapter title or author 3 commercially produced kaolin with G s = 2.68, liquid limit of 65% and plastic limit of 30 %. The angle of friction for this soil is 22 o. Clayey soils were created by mixing 50% sand and 50% clay at 70% moisture content (approximately 2 x liquid limit) and one dimensionally consolidating a sample in the cylindrical container. This blend of sand and clay was selected to represent the typical grading and behaviour of a North Sea deposit. Pressure was applied incrementally via a rigid top cap up to the required pressure, sufficient to create a sample with an undrained shear strength of 2-5 kpa. Prior to pullout, vane tests and moisture contents were performed. For this series of tests the anchors were pushed gently into the clay and left for two hours prior to inflation and pullout to dissipate excess pore pressures. The samples of clay were double drained (i.e. from top and bottom). Although the edges of the container were unlined, since the container was large enough to provide at least 10 diameters of soil on either side of the anchor, any influence due to the rigid boundary was thought to be insignificant. A range of model tests was conducted, with variations in geometry of the inflatable anchors and state of the soil. The variables investigated were stress history of the soil, inflation pressure (P), embedment ratio (H/L), anchor length (L), membrane thickness (t) and membrane surface roughness. A number of different forms of anchor were also tested for comparison, namely plate anchors and helical screw anchors. Only a limited range of the tests conducted will be reported herein. Further tests have been conducted on sand soils and these are reported elsewhere (Newson et al., 2003). Experimental results Results of pullout tests The pullout force against anchor displacement is shown for three tests (1A to 1C) conducted on a normally consolidated clayey soil sample with undrained shear strength of 1.5 to 2 kpa in Figure 2. These tests were conducted to investigate the rate of pullout, improvements of pullout capacity with excess pore pressure dissipation and the effect of inflation of the anchor. Test 1A used a 100 mm long (L) sand roughened anchor, embedded 140 mm (H), inflated to 150 kpa (P) and left for two hours (inflated) prior to pullout at a velocity (v) of mm/s. Test 1B used the same anchor, inflated to the same pressure, but pulled out at 3.81 mm/s immediately after inflation. Test 1C was not inflated and was again pulled out at 3.81 mm/s. For tests 1A and 1B the peak pullout loads were approximately 0.14 kn, with a mobilisation distance of the order of mm. Test 1C shows a similar mobilisation distance and a lower peak load of 0.05 kn. There appears to be very little difference between tests 1A and 1B, which suggests that for this clay mixture and state, there is marginal benefit in waiting a few hours prior to pullout. In fact, the coefficient of consolidation (c h ) for this
4 4 Header - book title type of material would be of the order of 1 to 10 m 2 /year, hence 50% dissipation of the excess pore pressures may be lie in the range of 1.5 to 15 hours. Comparison of test 1C with tests 1A and 1B shows the effect of inflation of the bladder, which appeared to increase the pullout capacity threefold. 0.3 Load (kn) Test 1A Test 1B Test 1C Displacement (mm) Figure 2: Force-displacement data for first series of pullout tests A second series of tests was conducted to further investigate the increases in pullout capacity associated with dissipation of excess pore pressures developed during anchor inflation. Figure 3 shows the data from two additional pullout tests 2A and 2B. These were conducted using a 100 mm anchor, embedded to 140 mm and inflated to 150 kpa. A higher consolidation pressure was used to create the sample and led to an undrained shear strength of 3.5 to 4 kpa. Test 2A was left inflated for 16 hours prior to pullout and test 2B was pulled out immediately after inflation. The pullout velocity (v) for both tests was 3.18 mm/s. Hence tests 1B and 2B are directly comparable. The pullout data for these two tests shows increases in capacity compared to the first series of tests, with test 2A peaking at 0.34 kn and test 2B at 0.26 kn. The mobilisation distances were comparable with those of the first series. Allowing the inflation excess pore pressures to dissipate significantly shows a 30% increase in pullout capacity for this soil and state.
5 Header chapter title or author 5 Load (kn) Test 2A Test 2B Displacement (mm) Figure 3: Force-displacement data for second series of pullout tests Volume-pressure relationships Since the volume-pressure relationship of the anchor can be monitored during inflation, the in situ stress-strain properties of the soil can be determined in a similar manner to the pressuremeter test using cavity expansion theory (e.g. Mair and Wood, 1987). This information may be used to estimate the uplift capacity of the anchor or for design and other purposes, e.g. upheaval buckling calculations. A typical volume-pressure curve (determined from the anchor system) for the clayey soil is shown in Figure 4. Analysis and interpretation of this data can provide a range of parameters, e.g. elastic (G, ν), angles of friction and dilation, lateral limit and in situ lateral pressures, undrained shear strength, etc.. Using this data, the shear modulus (G) can be estimated to be 650 kpa and assuming ν = 0.5, this gives a value of Young's modulus, E = 1950 kpa. Due to the extremely low horizontal effective stresses (since the anchor has a very shallow embedment) the uplift or in situ pressure is difficult to estimate. The limit pressure (p L ) for this test is approximately 15 kpa, which agrees with cavity expansion theory (e.g. Carter et al, 1986), which suggests a value of p L of 18 kpa:
6 6 Header - book title p L ( 1 K a ) G 2 = σ' h (1 + sin φ') (1) σ' h.sin φ' 1 where K a is the coefficient of active earth pressure and σ' h is the horizontal effective stress Pressure (kpa) Volume change (cm 3 ) Figure 4: Volume pressure relationship for inflation phase of anchor utilisation The undrained shear strength (c u ) can also be determined using equation (2) below (Mair and Wood, 1987). Assuming a value of N p =6 (taking G/c u approximately 200) then c u is 3.2 kpa, which is comparable with the vane test measurements. (pl σho ) cu = (2) N p where σ ho is the in situ horizontal total stress and N p is a pressuremeter constant (Marsland and Randolph, 1977). The dissipation of excess pore pressures due to inflation of the anchor (for test 2A) is shown in Figure 5. The graph shows a 50% drop in excess pore pressure in approximately eleven hours. Using the consolidation solution of Randolph and Wroth (1979) for a cylindrical cavity, the horizontal coefficient of consolidation (c h ) was determined to be 1.32 m 2 /year.
7 Header chapter title or author 7 c h 2 D.T50 2 = (3) t 50 where D is the cavity diameter, T 50 is the time factor and t 50 the time associated with 50% pore pressure dissipation. 1 Normalised pwp (u/uo) Root Time (s) Figure 5: Excess pore pressure dissipation following membrane expansion Discussion The experimental data suggest that the pullout capacity of the inflatable anchor system will increase for stiffer, stronger clays and increased membrane pressures. Improvements in pullout capacity were also seen for long waiting periods after membrane inflation prior to pullout, although a shorter two-hour waiting period was found to result in the same pullout capacity. Hence the undrained shear strength and soil density (and therefore pullout capacity) may be improved by membrane loading, but for application offshore on ROVs long waiting periods are not practical. Varying the rate of pullout to determine whether a variation between drained and undrained states could be found, proved to yield the same pullout capacity. Closer inspection of the rates (limited by the gearing of the screw jack), using the dimensionless group v.l/ch suggested that both rates lay within the undrained range (Finnie, 1993). In order to achieve drained pullout of the anchor, a rate less than mm/hour would be required.
8 8 Header - book title A number of studies have been reported in the literature related to soil nails, anchors and piles subjected to uplift/tensile forces (e.g. Dickin & Leung, 1990; Merrifield & Williams, 1988). Those that have investigated pressure grouted anchors or nails, and enlarged base piles may be appropriate for interpreting and predicting the behaviour of the inflatable anchors. Ignoring the friction along the smooth steel section of the anchor we may estimate the pullout capacity (F uo ) of the membrane (when uninflated, e.g. test 1C) using: F uo = α.c u. A 1 (4) where A 1 is the membrane surface area (π.d o.l), D o is the uninflated membrane diameter, L is the membrane length and α is the adhesion factor, which can vary between 0.25 and 1. Again, ignoring the friction along the smooth steel section of the anchor the pullout capacity (F ui ) of the membrane when inflated (e.g. test 1B) maybe better estimated using: F ui = N c.c u.a 2 (5) where N c is a bearing capacity factor, A 2 is the projected cross-sectional area of the inflated membrane (π.d 2 i /4) and D i is the inflated membrane diameter. The ratio of the uninflated to inflated pullout capacities (ψ) is therefore found from: Fuo 4. α.l ψ = = 2 (6) Fui D.n.N where n is the ratio of the inflated to uninflated membrane diameter (i.e. D i = D o.n) Assuming that the inflated section causes a flow mechanism similar to the t- bar or ball penetrometer (Randolph and Houlsby, 1984; Stewart and Randolph, 1994) then the bearing capacity factor N c would be approximately In the tests presented herein, L = 140 mm and D o = 35 mm, and the volume change during inflation was approximately 35 cm 3. Hence the value of n is approximately 1.2. Assuming full adhesion α = 1.0 and equation [6] suggests the ratio of the uninflated to inflated pullout capacity is This compares favourably with the observed pullouts shown in Figure 3 of approximately 1/3. Similar values of bearing capacity factor (N c ) were presented by Meyerhof and Adams (1968) for enlarged base piles in clay soils based on experimental data and mathematical analysis. Their work further suggested that below embedment ratios of H/D o of 4, the failure mechanism changes from a deep to a shallow case and the bearing capacity factor (and pullout capacity) reduces quickly. For example, for H/D o of 1 N c can vary from 2 to 8 for the cases of stiff and soft clay respectively. It should be noted that in the aforementioned discussion no account has been taken of breakaway of the soil below the anchor on pullout. The flow o c
9 Header chapter title or author 9 mechanism of Randolph and Houlsby (1984) assumes the soil will flow completely around the object closing at the back, with no detachment. This would occur if the interface at the bottom of the anchor could sustain tension due to suction (or adhesion), or if the initial stresses were large enough to ensure that the stresses behind the anchor were compressive up to the failure load. In common with the tests completed on the sand samples (Newson et al., 2003) the mobilisation distances (δ f ) for peak load were found to be quite high for the majority of tests with δ fw / w (H+L) being approximately 20 %. The relative stiffness of the membrane was found to contribute considerably to this distance in the sand tests, as was increasing the roughness of the membrane. This suggests that the same may be true of the clayey soil and these reductions in mobilisation distance may be a function of the compressibility of the flexible membrane under loading (the overall volume is constant but the shape may vary) and changes in the deformation mechanism of the soil. However, the mechanisms of failure of the anchor system are currently unknown and this aspect should be investigated further to provide more accurate design for utilisation of the anchor system and to suggest improvements of the geometry. The effects of soil disturbance due to installation of the anchor also need to be investigated. Conclusions Based on the preliminary data shown herein, the inflatable anchor system shows considerable promise for offshore use for soft clayey soils. The additional benefits of monitoring the pressure-volume relationship during inflation have also been demonstrated, allowing the determination of a range of soil parameters to provide information for design and for optimisation of waiting time prior to loading the anchors. Further testing needs to be conducted at full scale to verify these findings. Acknowledgements The work described in this paper was supported by funds from Stolt Offshore Ltd and this support is gratefully acknowledged. The authors also wish to thank the technical staff of the Department of Civil Engineering at the University of Dundee for all their help. References 1. Carter, J.P., Booker, J.R. and Yeung, S.K. (1986) Cavity expansion in cohesive frictional soils. Geotechnique, 36(3), Dickin, E.A. and Leung, C.F. (1990) Performance of piles with enlarged bases subject to uplift forces. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 27, Finnie, I.M. (1993). Performance of shallow foundations in calcareous soil. PhD Thesis, University of Western Australia, Australia.
10 10 Header - book title 4. Mair, R.J. and Wood, D.M. (1987) Pressuremeter testing: methods and interpretation. CIRIA Ground Engineering Report, Butterworths, pp Majer, J. (1955) Zur Berechnung von Zugfundamenten. Osterreichische Bauzeitschrift, 10(5), Marsland, A. and Randolph, M.F. (1977). Comparisons of the results from pressuremeter tests and large in-situ plate tests on London Clay. Geotechnique, 27(2), Meyerhof, G.G. and Adams, J.I. (1968) The ultimate uplift capacity of foundations. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 5(4), Merrifield, C.M. and Williams, A.R. (1988) Pullout capacity and load displacement characteristics of vertical anchorages modelled in the centrifuge. Centrifuge 88 Conference, Newson, T.A., Smith, F.W., Brunning, P. and Gallacher, S. (2003) An experimental study of inflatable offshore anchors. ISOPE 2003 Conference, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA. (Paper # 2003-JSC-127). 10. Randolph, M.F. and Houlsby, G.T. (1984) The limiting pressure on a circular pile loaded laterally in cohesive soil, Geotechnique, 34(4), Randolph, M.F. and Wroth, C.P. (1979). An analytical solution for the consolidation around a driven pile. Int. J. Num. Anal. Methods Geomech., 3, Stewart, D.P. and Randolph, M.F. (1994) T-bar penetration testing in soft clay ASCE Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 120(12),
The tensile capacity of suction caissons in sand under rapid loading
 Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics: ISFOG 25 Gourvenec & Cassidy (eds) 25 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 415 3963 X The tensile capacity of suction caissons in sand under rapid loading Guy T. Houlsby,
Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics: ISFOG 25 Gourvenec & Cassidy (eds) 25 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 415 3963 X The tensile capacity of suction caissons in sand under rapid loading Guy T. Houlsby,
Vertical Uplift Capacity of a Group of Equally Spaced Helical Screw Anchors in Sand
 SECM/15/080 Vertical Uplift Capacity of a Group of Equally Spaced Helical Screw Anchors in Sand S. Mukherjee 1* and Dr. S. Mittal 2 1 Amity University, Noida, India 2 Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee,
SECM/15/080 Vertical Uplift Capacity of a Group of Equally Spaced Helical Screw Anchors in Sand S. Mukherjee 1* and Dr. S. Mittal 2 1 Amity University, Noida, India 2 Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee,
Pressuremeters in Geotechnical Design
 Pressuremeters in Geotechnical Design B.G. CLARKE Department of Civil Engineering University of Newcastle upon Tyne BLACK1E ACADEMIC & PROFESSIONAL An Imprint of Chapman & Hall London Glasgow Weinheim
Pressuremeters in Geotechnical Design B.G. CLARKE Department of Civil Engineering University of Newcastle upon Tyne BLACK1E ACADEMIC & PROFESSIONAL An Imprint of Chapman & Hall London Glasgow Weinheim
UNIT-I SOIL EXPLORATION
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : Geotechnical Engineering - II (16CE127) Year & Sem: III-B.Tech & II-Sem
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : Geotechnical Engineering - II (16CE127) Year & Sem: III-B.Tech & II-Sem
Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
 43 Module 3: Lecture - 5 on Compressibility and Consolidation Contents Stresses in soil from surface loads; Terzaghi s 1-D consolidation theory; Application in different boundary conditions; Ramp loading;
43 Module 3: Lecture - 5 on Compressibility and Consolidation Contents Stresses in soil from surface loads; Terzaghi s 1-D consolidation theory; Application in different boundary conditions; Ramp loading;
OMAE INVESTIGATING THE RESPONSE OF OFFSHORE FOUNDATIONS IN SOFT CLAY SOILS
 Proceedings of OMAE st International Conference on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering June 3-8, Oslo, Norway OMAE-857 INVESTIGATING THE RESPONSE OF OFFSHORE FOUNDATIONS IN SOFT CLAY SOILS B.W. Byrne
Proceedings of OMAE st International Conference on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering June 3-8, Oslo, Norway OMAE-857 INVESTIGATING THE RESPONSE OF OFFSHORE FOUNDATIONS IN SOFT CLAY SOILS B.W. Byrne
Theory of a vertically loaded Suction Pile in CLAY
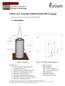 11 Theory of a vertically loaded Suction Pile in CLAY Mainly based on the et Norske Veritas NV-RP-E303 1. Convention Water COG h L Soil COG t Figure 1 Suction Pile Figure 2 Suction pile with main parameters
11 Theory of a vertically loaded Suction Pile in CLAY Mainly based on the et Norske Veritas NV-RP-E303 1. Convention Water COG h L Soil COG t Figure 1 Suction Pile Figure 2 Suction pile with main parameters
Analysis of dilatometer test in calibration chamber
 Analysis of dilatometer test in calibration chamber Lech Bałachowski Gdańsk University of Technology, Poland Keywords: calibration chamber, DMT, quartz sand, FEM ABSTRACT: Because DMT in calibration test
Analysis of dilatometer test in calibration chamber Lech Bałachowski Gdańsk University of Technology, Poland Keywords: calibration chamber, DMT, quartz sand, FEM ABSTRACT: Because DMT in calibration test
SOIL ANCHORS ETSAB/UPC J.Llorens - ETSAB/UPC PASSIVE ANCHORS - ANTECEDENTS
 SOIL ANCHORS ignasi.llorens@upc.edu ETSAB/UPC - 2013 PASSIVE ANCHORS - ANTECEDENTS Antecedents of passive anchors can be found in Nature. Roots feed plants and provide uplift resistance against the wind
SOIL ANCHORS ignasi.llorens@upc.edu ETSAB/UPC - 2013 PASSIVE ANCHORS - ANTECEDENTS Antecedents of passive anchors can be found in Nature. Roots feed plants and provide uplift resistance against the wind
CHAPTER 5: VACUUM TEST WITH VERTICAL DRAINS
 CHAPTER 5: VACUUM TEST WITH VERTICAL DRAINS 5.1 Introduction Using surcharging as the sole soil consolidation mean can take a long time to reach the desired soil settlement. Soil consolidation using prefabricated
CHAPTER 5: VACUUM TEST WITH VERTICAL DRAINS 5.1 Introduction Using surcharging as the sole soil consolidation mean can take a long time to reach the desired soil settlement. Soil consolidation using prefabricated
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON OPTIMUM INSTALLATION DEPTH OF PVD UNDER VACUUM CONSOLIDATION ABSTRACT
 EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON OPTIMUM INSTALLATION DEPTH OF PVD UNDER VACUUM CONSOLIDATION EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON OPTIMUM INSTALLATION DEPTH OF PVD UNDER VACUUM CONSOLIDATION J.-C CHAI i), N. MIURA
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON OPTIMUM INSTALLATION DEPTH OF PVD UNDER VACUUM CONSOLIDATION EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON OPTIMUM INSTALLATION DEPTH OF PVD UNDER VACUUM CONSOLIDATION J.-C CHAI i), N. MIURA
Learn more at
 Full scale model tests of a steel catenary riser C. Bridge 1, H. Howells 1, N. Toy 2, G. Parke 2, R. Woods 2 1 2H Offshore Engineering Ltd, Woking, Surrey, UK 2 School of Engineering, University of Surrey,
Full scale model tests of a steel catenary riser C. Bridge 1, H. Howells 1, N. Toy 2, G. Parke 2, R. Woods 2 1 2H Offshore Engineering Ltd, Woking, Surrey, UK 2 School of Engineering, University of Surrey,
Influence of Settlement on Bearing Capacity Analysis of Shallow Foundations on Sandy Clays in the Niger Delta, Nigeria
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Applied Engineering and Scientific Research, 201, 2 (4):20-27 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN: 22 0041 Influence
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Applied Engineering and Scientific Research, 201, 2 (4):20-27 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN: 22 0041 Influence
CONE PENETRATION TESTS
 February 25, 2015 John Doe, P.E. Acme Engineering and Testing 1234 Test Avenue, Suite 204 Lake Wales, FL 33853 Re: Sample CPT Soundings Dear Mr. Doe, Direct Push Services, LLC (DPS) was retained by Acme
February 25, 2015 John Doe, P.E. Acme Engineering and Testing 1234 Test Avenue, Suite 204 Lake Wales, FL 33853 Re: Sample CPT Soundings Dear Mr. Doe, Direct Push Services, LLC (DPS) was retained by Acme
City, University of London Institutional Repository
 City Research Online City, University of London Institutional Repository Citation: Gorasia, R. J., McNamara, A. M. & Rettura, D. (212). Reducing driving forces for pressed-in. Proceedings of the Institution
City Research Online City, University of London Institutional Repository Citation: Gorasia, R. J., McNamara, A. M. & Rettura, D. (212). Reducing driving forces for pressed-in. Proceedings of the Institution
Typical factors of safety for bearing capacity calculation in different situations
 Typical factors of safety for bearing capacity calculation in different situations Density of soil: In geotechnical engineering, one deals with several densities such as dry density, bulk density, saturated
Typical factors of safety for bearing capacity calculation in different situations Density of soil: In geotechnical engineering, one deals with several densities such as dry density, bulk density, saturated
Bearing Capacity and Settlement Response of PMS Tanks on Cohesionless Soil Lithology in Lekki, Lagos of Nigeria
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Applied Engineering and Scientific Research,, ():- (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN: 8 Bearing Capacity and
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Applied Engineering and Scientific Research,, ():- (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN: 8 Bearing Capacity and
Suction caisson extraction resistance in Gulf of Guinea clay
 Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics III Meyer (Ed.) 2015 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN: 978-1-138-02848-7 Suction caisson extraction resistance in Gulf of Guinea clay C. Gaudin, M.F. Randolph, S.
Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics III Meyer (Ed.) 2015 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN: 978-1-138-02848-7 Suction caisson extraction resistance in Gulf of Guinea clay C. Gaudin, M.F. Randolph, S.
Drum Centrifuge Model Tests Comparing the Performance of Spudcans and Caissons in Kaolin Clay
 Drum Centrifuge Model Tests Comparing the Performance of Spudcans and Caissons in Kaolin Clay by M.J. Cassidy and B.W. Byrne Report No. OUEL 48/ University of Oxford Department of Engineering Science Parks
Drum Centrifuge Model Tests Comparing the Performance of Spudcans and Caissons in Kaolin Clay by M.J. Cassidy and B.W. Byrne Report No. OUEL 48/ University of Oxford Department of Engineering Science Parks
Cubzac-les-Ponts Experimental Embankments on Soft Clay
 Cubzac-les-Ponts Experimental Embankments on Soft Clay GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. www.geo-slope.com 1, 7 - th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada TP T Main: +1 3 9 Fax: +1 3 39 Introduction In the 197 s, a series
Cubzac-les-Ponts Experimental Embankments on Soft Clay GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. www.geo-slope.com 1, 7 - th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada TP T Main: +1 3 9 Fax: +1 3 39 Introduction In the 197 s, a series
THE EFFECT OF EMBEDMENT DEPTH ON BEARING CAPACITY OF STRIP FOOTING IN COHESIVE FRICTIONAL MEDIUM
 Proceedings of the 4 th International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2018), 9~11 February 2018, KUET, Khulna, Bangladesh (ISBN-978-984-34-3502-6) THE EFFECT OF EMBEDMENT
Proceedings of the 4 th International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2018), 9~11 February 2018, KUET, Khulna, Bangladesh (ISBN-978-984-34-3502-6) THE EFFECT OF EMBEDMENT
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 CIVIL ENGINEERING Tutorial Question Bank Name : FOUNDATION ENGINEERING Code : A60126 Class : III B. Tech II Semester Branch
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 CIVIL ENGINEERING Tutorial Question Bank Name : FOUNDATION ENGINEERING Code : A60126 Class : III B. Tech II Semester Branch
OP CHECKLIST FOR 1D CONSOLIDATION LABORATORY TEST
 Page 1 of 5 WORK INSTRUCTIONS FOR ENGINEERS NHB Compiled by : LSS Checked by : GSS Approved by : OP-3-31. CHECKLIST FOR 1D CONSOLIDATION LABORATORY TEST Page 2 of 5 31.0 CHECKLIST ITEMS *(refer to respective
Page 1 of 5 WORK INSTRUCTIONS FOR ENGINEERS NHB Compiled by : LSS Checked by : GSS Approved by : OP-3-31. CHECKLIST FOR 1D CONSOLIDATION LABORATORY TEST Page 2 of 5 31.0 CHECKLIST ITEMS *(refer to respective
Ground Failure Mechanism of Micoropiled-raft
 Ground Failure Mechanism of Micoropiled-raft T. H. Hwang 1), H. J. Kim 2), and * J.H. Shin 3) 1), 2), 3) Department of Civil Engineering, Konkuk University, Seoul 143-701, Korea 3) jhshin@konkuk.ac.kr
Ground Failure Mechanism of Micoropiled-raft T. H. Hwang 1), H. J. Kim 2), and * J.H. Shin 3) 1), 2), 3) Department of Civil Engineering, Konkuk University, Seoul 143-701, Korea 3) jhshin@konkuk.ac.kr
PUSH PIER SYSTEMS STABILITY. SECURITY. INTEGRITY. Push Pier Systems PN #MBPPT
 PUSH PIER SYSTEMS STABILITY. SECURITY. INTEGRITY. PN #MBPPT Push Pier Systems About Foundation Supportworks is a network of the most experienced and knowledgeable foundation repair and new construction
PUSH PIER SYSTEMS STABILITY. SECURITY. INTEGRITY. PN #MBPPT Push Pier Systems About Foundation Supportworks is a network of the most experienced and knowledgeable foundation repair and new construction
V-H-M Yield Surface describing Soil Structure Interaction of Sub-sea Structures and Wind Turbines on Caisson Foundations in Soft Clays
 NGM 2016 Reykjavik Proceedings of the 17 th Nordic Geotechnical Meeting Challenges in Nordic Geotechnic 25 th 28 th of May V-H-M Yield Surface describing Soil Structure Interaction of Sub-sea Structures
NGM 2016 Reykjavik Proceedings of the 17 th Nordic Geotechnical Meeting Challenges in Nordic Geotechnic 25 th 28 th of May V-H-M Yield Surface describing Soil Structure Interaction of Sub-sea Structures
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad CIVIL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 00 04 CIVIL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name Course Code Regulation Course Structure Course Coordinator Course Faculty
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 00 04 CIVIL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name Course Code Regulation Course Structure Course Coordinator Course Faculty
Reinforced Soil Retaining Walls-Design and Construction
 Lecture 32 Reinforced Soil Retaining Walls-Design and Construction Prof. G L Sivakumar Babu Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560012 Example calculation An 8 m high
Lecture 32 Reinforced Soil Retaining Walls-Design and Construction Prof. G L Sivakumar Babu Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560012 Example calculation An 8 m high
SUCTION CAISSON FOUNDATIONS FOR OFFSHORE WIND TURBINES
 SUCTION CAISSON FOUNDATIONS FOR OFFSHORE WIND TURBINES Felipe A. Villalobos Oxford University felipe.villalobos@eng.ox.ac.uk Guy T. Houlsby Oxford University guy.houlsby@eng.ox.ac.uk Byron W. Byrne Oxford
SUCTION CAISSON FOUNDATIONS FOR OFFSHORE WIND TURBINES Felipe A. Villalobos Oxford University felipe.villalobos@eng.ox.ac.uk Guy T. Houlsby Oxford University guy.houlsby@eng.ox.ac.uk Byron W. Byrne Oxford
Displacement-based calculation method on soil-pile interaction of PHC pipe-piles
 Seattle, WA Displacement-based calculation method on soil-pile interaction of PHC pipe-piles Dr. Huang Fuyun Fuzhou University 31 st May, 217 Outline Background ing introduction ing results Simple calculation
Seattle, WA Displacement-based calculation method on soil-pile interaction of PHC pipe-piles Dr. Huang Fuyun Fuzhou University 31 st May, 217 Outline Background ing introduction ing results Simple calculation
OMAE INVESTIGATING NOVEL FOUNDATIONS FOR OFFSHORE WINDPOWER GENERATION
 Proceedings of OMAE 2 21 st International Conference on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering June 23-28, 22 Oslo, Norway OMAE22-28423 INVESTIGATING NOVEL FOUNDATIONS FOR OFFSHORE WINDPOWER GENERATION
Proceedings of OMAE 2 21 st International Conference on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering June 23-28, 22 Oslo, Norway OMAE22-28423 INVESTIGATING NOVEL FOUNDATIONS FOR OFFSHORE WINDPOWER GENERATION
Irrigation &Hydraulics Department lb / ft to kg/lit.
 CAIRO UNIVERSITY FLUID MECHANICS Faculty of Engineering nd Year CIVIL ENG. Irrigation &Hydraulics Department 010-011 1. FLUID PROPERTIES 1. Identify the dimensions and units for the following engineering
CAIRO UNIVERSITY FLUID MECHANICS Faculty of Engineering nd Year CIVIL ENG. Irrigation &Hydraulics Department 010-011 1. FLUID PROPERTIES 1. Identify the dimensions and units for the following engineering
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 14 Fluids Fluids at rest pressure vs. depth Pascal s principle Archimedes s principle Buoynat forces Fluids in motion: Continuity & Bernoulli equations 1. How deep
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 14 Fluids Fluids at rest pressure vs. depth Pascal s principle Archimedes s principle Buoynat forces Fluids in motion: Continuity & Bernoulli equations 1. How deep
Application of Expansive Soil Geotechnical Procedures
 Application of Expansive Soil Geotechnical Procedures FPA PRESENTATION John T. Bryant, Ph.D., P.G., P.E with Robert L. Lytton, Ph.D., PE. And Mr. Dean Read HOUSTON, TEXAS WEDNESDAY DECEMBER 10, 2008 2008
Application of Expansive Soil Geotechnical Procedures FPA PRESENTATION John T. Bryant, Ph.D., P.G., P.E with Robert L. Lytton, Ph.D., PE. And Mr. Dean Read HOUSTON, TEXAS WEDNESDAY DECEMBER 10, 2008 2008
DAMAGE TO STORAGE TANKS CAUSED BY THE 2011 TOHOKU EARTHQUAKE AND TSUNAMI AND PROPOSAL FOR STRUCTURAL ASSESSMENT METHOD FOR CYLINDRICAL STORAGE TANKS
 DAMAGE TO STORAGE TANKS CAUSED BY THE 2011 TOHOKU EARTHQUAKE AND TSUNAMI AND PROPOSAL FOR STRUCTURAL ASSESSMENT METHOD FOR CYLINDRICAL STORAGE TANKS Takashi Ibata Isho Nakachi Dr. Kazuo Ishida Junichi
DAMAGE TO STORAGE TANKS CAUSED BY THE 2011 TOHOKU EARTHQUAKE AND TSUNAMI AND PROPOSAL FOR STRUCTURAL ASSESSMENT METHOD FOR CYLINDRICAL STORAGE TANKS Takashi Ibata Isho Nakachi Dr. Kazuo Ishida Junichi
Field Testing of Suction Caissons at Bothkennar and Luce Bay
 Field Testing of Suction Caissons at Bothkennar and Luce Bay by G.T. Houlsby, R.B. Kelly, J. Huxtable and B.W. Byrne Report No. OUEL 2276/5 University of Oxford Department of Engineering Science Parks
Field Testing of Suction Caissons at Bothkennar and Luce Bay by G.T. Houlsby, R.B. Kelly, J. Huxtable and B.W. Byrne Report No. OUEL 2276/5 University of Oxford Department of Engineering Science Parks
from ocean to cloud HEAVY DUTY PLOUGH PERFORMANCE IN VERY SOFT COHESIVE SEDIMENTS
 HEAVY DUTY PLOUGH PERFORMANCE IN VERY SOFT COHESIVE SEDIMENTS Geoff Holland, Sarah Dzinbal (Alcatel-Lucent Submarine Networks) Email: geoff.holland@alcatel-lucent.com Alcatel-Lucent Submarine Networks
HEAVY DUTY PLOUGH PERFORMANCE IN VERY SOFT COHESIVE SEDIMENTS Geoff Holland, Sarah Dzinbal (Alcatel-Lucent Submarine Networks) Email: geoff.holland@alcatel-lucent.com Alcatel-Lucent Submarine Networks
The single bore multiple anchor system
 A D Barley 1 The single bore multiple anchor system Eur.Ing. A D BARLEY, Director of Engineering, Keller Ground Engineering, Wetherby, UK INTRODUCTION An anchor tendon with a 10m fixed length in soil or
A D Barley 1 The single bore multiple anchor system Eur.Ing. A D BARLEY, Director of Engineering, Keller Ground Engineering, Wetherby, UK INTRODUCTION An anchor tendon with a 10m fixed length in soil or
Construction Dewatering
 Construction Dewatering Introduction The control of groundwater is one of the most common and complicated problems encountered on a construction site. Construction dewatering can become a costly issue
Construction Dewatering Introduction The control of groundwater is one of the most common and complicated problems encountered on a construction site. Construction dewatering can become a costly issue
E.2 CAP SETTLEMENT RA D AND OUTBOARD
 DRAFT ONONDAGA LAKE CAPPING, DREDGING AND HABITAT INTERMEDIATE DESIGN E.2 CAP SETTLEMENT RA D AND OUTBOARD Parsons P;\Honeywell-SYR\444576 2008 Capping\09 Reports\9.1 Capping and Dredge Area & Depth IDS\Appendices\Appendix
DRAFT ONONDAGA LAKE CAPPING, DREDGING AND HABITAT INTERMEDIATE DESIGN E.2 CAP SETTLEMENT RA D AND OUTBOARD Parsons P;\Honeywell-SYR\444576 2008 Capping\09 Reports\9.1 Capping and Dredge Area & Depth IDS\Appendices\Appendix
382. Fellenius, B.H. and Terceros, M.H., Information on the single pile, static loading tests at B.E.S.T. Proceedings of the 3rd Bolivian
 382. Fellenius, B.H. and Terceros, M.H., 2017. Information on the single pile, static loading tests at B.E.S.T. Proceedings of the 3rd Bolivian International Conference on Deep Foundations, Santa Cruz
382. Fellenius, B.H. and Terceros, M.H., 2017. Information on the single pile, static loading tests at B.E.S.T. Proceedings of the 3rd Bolivian International Conference on Deep Foundations, Santa Cruz
Lateral Load Analysis Considering Soil-Structure Interaction. ANDREW DAUMUELLER, PE, Ph.D.
 Lateral Load Analysis Considering Soil-Structure Interaction ANDREW DAUMUELLER, PE, Ph.D. Overview Introduction Methods commonly used to account for soil-structure interaction for static loads Depth to
Lateral Load Analysis Considering Soil-Structure Interaction ANDREW DAUMUELLER, PE, Ph.D. Overview Introduction Methods commonly used to account for soil-structure interaction for static loads Depth to
Experimental Investigations of the Cyclic Response of Suction Caissons in Sand B.W. Byrne and G.T. Houlsby
 OTC 12194 Experimental Investigations of the Cyclic Response of Suction Caissons in Sand B.W. Byrne and G.T. Houlsby Copyright 2, Offshore Technology Conference This paper was prepared for presentation
OTC 12194 Experimental Investigations of the Cyclic Response of Suction Caissons in Sand B.W. Byrne and G.T. Houlsby Copyright 2, Offshore Technology Conference This paper was prepared for presentation
m v = 1.04 x 10-4 m 2 /kn, C v = 1.29 x 10-2 cm 2 /min
 2.10 Problems Example 2.1: Design of Shallow Foundation in Saturated Clay Design a square footing to support a column load of 667 kn. The base of the footing will be located 1 m below the ground level
2.10 Problems Example 2.1: Design of Shallow Foundation in Saturated Clay Design a square footing to support a column load of 667 kn. The base of the footing will be located 1 m below the ground level
Comparison and Sensitivity Investigations of a CALM and SALM Type Mooring System for Wave Energy Converters
 J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 214, 2, 93-122; doi:1.339/jmse2193 Article OPEN ACCESS Journal of Marine Science and Engineering ISSN 277-1312 www.mdpi.com/journal/jmse Comparison and Sensitivity Investigations of a
J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 214, 2, 93-122; doi:1.339/jmse2193 Article OPEN ACCESS Journal of Marine Science and Engineering ISSN 277-1312 www.mdpi.com/journal/jmse Comparison and Sensitivity Investigations of a
Cyclic loading of shallow offshore foundations on sand
 Cyclic loading of shallow offshore foundations on sand B.W. Byrne, G.T. Houlsby & C.M. Martin Department of Engineering Science, The University of Oxford, United Kingdom ABSTRACT: A significant challenge
Cyclic loading of shallow offshore foundations on sand B.W. Byrne, G.T. Houlsby & C.M. Martin Department of Engineering Science, The University of Oxford, United Kingdom ABSTRACT: A significant challenge
Department of Civil & Geological Engineering GEOE Engineering Geology
 Department of Civil & Geological Engineering GEOE 218.3 Engineering Geology Assignment #3, Head, Pore Pressure & Effective Stress Due 08 Oct, 2010 NOTE: Numbered subscripts indicate depth, in metres, below
Department of Civil & Geological Engineering GEOE 218.3 Engineering Geology Assignment #3, Head, Pore Pressure & Effective Stress Due 08 Oct, 2010 NOTE: Numbered subscripts indicate depth, in metres, below
STIFFNESS INVESTIGATION OF PNEUMATIC CYLINDERS. A. Czmerk, A. Bojtos ABSTRACT
 59 th ILMENAU SCIENTIFIC COLLOQUIUM Technische Universität Ilmenau, 11 15 September 2017 URN: urn:nbn:de:gbv:ilm1-2017iwk-148:6 STIFFNESS INVESTIGATION OF PNEUMATIC CYLINDERS A. Czmerk, A. Bojtos Budapest
59 th ILMENAU SCIENTIFIC COLLOQUIUM Technische Universität Ilmenau, 11 15 September 2017 URN: urn:nbn:de:gbv:ilm1-2017iwk-148:6 STIFFNESS INVESTIGATION OF PNEUMATIC CYLINDERS A. Czmerk, A. Bojtos Budapest
Stress and deformation of offshore piles under structural and wave loading
 Stress and deformation of offshore piles under structural and wave loading Author Eicher, Jackie, Guan, Hong, Jeng, Dong-Sheng Published 2003 Journal Title Ocean Engineering DOI https://doi.org/10.1016/s0029-8018(02)00031-8
Stress and deformation of offshore piles under structural and wave loading Author Eicher, Jackie, Guan, Hong, Jeng, Dong-Sheng Published 2003 Journal Title Ocean Engineering DOI https://doi.org/10.1016/s0029-8018(02)00031-8
Supporting Capacity of Short Suction Anchor based on Numerical Modeling
 The 2012 World Congress on Advances in Civil, Environmental, and Materials Research (ACEM 12) Seoul, Korea, August 26-30, 2012 Supporting Capacity of Short Suction Anchor based on Numerical Modeling *Jaehun
The 2012 World Congress on Advances in Civil, Environmental, and Materials Research (ACEM 12) Seoul, Korea, August 26-30, 2012 Supporting Capacity of Short Suction Anchor based on Numerical Modeling *Jaehun
SOIL IMPROVEMENT BY VACUUM PRELOADING FOR A POWER PLANT PROJECT IN VIETNAM
 18 th Southeast Asian Geotechnical & Inaugural AGSSEA Conference 29-31 May 213, Singapore Leung, Goh & Shen (eds) SOIL IMPROVEMENT BY VACUUM PRELOADING FOR A POWER PLANT PROJECT IN VIETNAM GOUW TJIE-LIONG
18 th Southeast Asian Geotechnical & Inaugural AGSSEA Conference 29-31 May 213, Singapore Leung, Goh & Shen (eds) SOIL IMPROVEMENT BY VACUUM PRELOADING FOR A POWER PLANT PROJECT IN VIETNAM GOUW TJIE-LIONG
An Innovative Solution for Water Bottling Using PET
 An Innovative Solution for Water Bottling Using PET A. Castellano, P. Foti, A. Fraddosio, S. Marzano, M.D. Piccioni, D. Scardigno* DICAR Politecnico di Bari, Italy *Via Orabona 4, 70125 Bari, Italy, scardigno@imedado.poliba.it
An Innovative Solution for Water Bottling Using PET A. Castellano, P. Foti, A. Fraddosio, S. Marzano, M.D. Piccioni, D. Scardigno* DICAR Politecnico di Bari, Italy *Via Orabona 4, 70125 Bari, Italy, scardigno@imedado.poliba.it
An Introduction to Deep Foundations
 An Introduction to Deep Foundations J. Paul Guyer, P.E., R.A. Paul Guyer is a registered mechanical engineer, civil engineer, fire protection engineer and architect with over 35 years experience in the
An Introduction to Deep Foundations J. Paul Guyer, P.E., R.A. Paul Guyer is a registered mechanical engineer, civil engineer, fire protection engineer and architect with over 35 years experience in the
OTC Copyright 2008, Offshore Technology Conference
 OTC 19545 Comparison of Jackup Rig Spudcan Penetration Methods in Clay David Menzies, Fugro-McClelland Marine Geosciences, Inc., and Richard Roper, ENSCO International, Inc. Copyright 2008, Offshore Technology
OTC 19545 Comparison of Jackup Rig Spudcan Penetration Methods in Clay David Menzies, Fugro-McClelland Marine Geosciences, Inc., and Richard Roper, ENSCO International, Inc. Copyright 2008, Offshore Technology
DEVELOPMENT OF A ROBUST PUSH-IN PRESSUREMETER
 DEVELOPMENT OF A ROBUST PUSH-IN PRESSUREMETER Roger Failmezger, P.E. In-Situ Soil Testing, L.C., Lancaster, Virginia, USA ABSTRACT A push-in pressuremeter was developed using slotted steel casing with
DEVELOPMENT OF A ROBUST PUSH-IN PRESSUREMETER Roger Failmezger, P.E. In-Situ Soil Testing, L.C., Lancaster, Virginia, USA ABSTRACT A push-in pressuremeter was developed using slotted steel casing with
Performance of Anchors for Floating Offshore Windfarms
 Geotechnical Engineering for US Offshore Wind Infrastructure Boston April 25, 2016 Performance of Anchors for Floating Offshore Windfarms Charles Aubeny Texas A&M University Background: Multi-Line Attachment
Geotechnical Engineering for US Offshore Wind Infrastructure Boston April 25, 2016 Performance of Anchors for Floating Offshore Windfarms Charles Aubeny Texas A&M University Background: Multi-Line Attachment
Offshore engineering science
 Offshore engineering science In this research stream theoretical models advanced geotechnical models and new numerical techniques were used in applied offshore engineering topics such as loading, design
Offshore engineering science In this research stream theoretical models advanced geotechnical models and new numerical techniques were used in applied offshore engineering topics such as loading, design
The Benefits Of Composite Materials In Deepwater Riser Applications. 26 th March 2015 Hassan Saleh Senior Engineer 2H Offshore Engineering Ltd
 The Benefits Of Composite Materials In Deepwater Riser Applications 26 th March 2015 Hassan Saleh Senior Engineer 2H Offshore Engineering Ltd Composite Benefits and Challenges Composite Materials offer
The Benefits Of Composite Materials In Deepwater Riser Applications 26 th March 2015 Hassan Saleh Senior Engineer 2H Offshore Engineering Ltd Composite Benefits and Challenges Composite Materials offer
On the Bearing Capacity of Suction Bucket Foundations in Saturated Sand
 The Open Ocean Engineering Journal,,, 45-49 45 Open Access On the Bearing Capacity of Suction Bucket Foundations in Saturated Sand Bintian Jiao* Xiaobing Lu and Zhongmin Shi Institute of Mechanics, Chinese
The Open Ocean Engineering Journal,,, 45-49 45 Open Access On the Bearing Capacity of Suction Bucket Foundations in Saturated Sand Bintian Jiao* Xiaobing Lu and Zhongmin Shi Institute of Mechanics, Chinese
Static and Dynamic Behaviour of the VersaBolt. Presented by Denis Champaigne VP Technical Services MMTI
 Static and Dynamic Behaviour of the VersaBolt Presented by Denis Champaigne VP Technical Services MMTI General Description The VersaBolt is designed for ground support conditions that are subject to static
Static and Dynamic Behaviour of the VersaBolt Presented by Denis Champaigne VP Technical Services MMTI General Description The VersaBolt is designed for ground support conditions that are subject to static
Influence of Fly Ash Content on Compaction Characteristics of Fly Ash Clay Mixture
 Jordan Journal of Civil Engineering, Volume, No. 1, 16 Influence of Fly Ash Content on Compaction Characteristics of Fly Ash Clay Mixture Ashis Kumar Bera 1)* and Sayan Kundu 2) 1) Associate Professor
Jordan Journal of Civil Engineering, Volume, No. 1, 16 Influence of Fly Ash Content on Compaction Characteristics of Fly Ash Clay Mixture Ashis Kumar Bera 1)* and Sayan Kundu 2) 1) Associate Professor
GEOTECHNICAL PERFORMANCE OF SPUDCAN FOUNDATIONS
 Guidance Notes on Geotechnical Performance of Spudcan Foundations GUIDANCE NOTES ON GEOTECHNICAL PERFORMANCE OF SPUDCAN FOUNDATIONS JANUARY 2017 (Updated March 2018 see next page) American Bureau of Shipping
Guidance Notes on Geotechnical Performance of Spudcan Foundations GUIDANCE NOTES ON GEOTECHNICAL PERFORMANCE OF SPUDCAN FOUNDATIONS JANUARY 2017 (Updated March 2018 see next page) American Bureau of Shipping
Numerical Simulations of a Train of Air Bubbles Rising Through Stagnant Water
 Numerical Simulations of a Train of Air Bubbles Rising Through Stagnant Water Hong Xu, Chokri Guetari ANSYS INC. Abstract Transient numerical simulations of the rise of a train of gas bubbles in a liquid
Numerical Simulations of a Train of Air Bubbles Rising Through Stagnant Water Hong Xu, Chokri Guetari ANSYS INC. Abstract Transient numerical simulations of the rise of a train of gas bubbles in a liquid
RIGID RISERS FOR TANKER FPSOs
 RIGID RISERS FOR TANKER FPSOs Stephen A. Hatton 2H Offshore Engineering Ltd. SUMMARY Recent development work on the subject of dynamic rigid (steel pipe) risers demonstrates that their scope of application
RIGID RISERS FOR TANKER FPSOs Stephen A. Hatton 2H Offshore Engineering Ltd. SUMMARY Recent development work on the subject of dynamic rigid (steel pipe) risers demonstrates that their scope of application
Strength assessment during shallow penetration of a sphere in clay
 Morton, J. P. et al. (24) Géotechnique Letters 4, 262 266, http://dx.doi.org/.68/geolett.4.49 Strength assessment during shallo penetration of a sphere in clay J. P. MORTON*, C. D. O LOUGHLIN* and D. J.
Morton, J. P. et al. (24) Géotechnique Letters 4, 262 266, http://dx.doi.org/.68/geolett.4.49 Strength assessment during shallo penetration of a sphere in clay J. P. MORTON*, C. D. O LOUGHLIN* and D. J.
World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology International Journal of Mechanical and Mechatronics Engineering Vol:6, No:1, 2012
 Perfect Plastic Deformation of a Circular Thin Bronze Plate due to the Growth and Collapse of a Vapour Bubble M.T. Shervani-Tabar, M. Rezaee and E. Madadi Kandjani Abstract Dynamics of a vapour bubble
Perfect Plastic Deformation of a Circular Thin Bronze Plate due to the Growth and Collapse of a Vapour Bubble M.T. Shervani-Tabar, M. Rezaee and E. Madadi Kandjani Abstract Dynamics of a vapour bubble
Desaturating sand deposit by air injection for reducing liquefaction potential
 Desaturating sand deposit by air injection for reducing liquefaction potential M. Ishihara, M. Okamura & T. Oshita Public Works Research Institute, Tsukuba City, Japan. ABSTRACT: It has been known that
Desaturating sand deposit by air injection for reducing liquefaction potential M. Ishihara, M. Okamura & T. Oshita Public Works Research Institute, Tsukuba City, Japan. ABSTRACT: It has been known that
Formation level = m. Foundation level = m. Height of the wall above the Ground Level = 7.42 m
 DESIGN OF RETAINING WALL INTRODUCTION: This wall is designed for active earth pressure and live load surcharge pressure The loads for the purpose of design are calculated per meter length of wall. BASIC
DESIGN OF RETAINING WALL INTRODUCTION: This wall is designed for active earth pressure and live load surcharge pressure The loads for the purpose of design are calculated per meter length of wall. BASIC
For a cantilever pile wall shown in Figure 1, assess the performance of the system and answer the following questions.
 Question 1 For a cantilever pile wall shown in Figure 1, assess the performance of the system and answer the following questions. Figure 1 - Cantilever Pile Wall i. Estimate the net resulting horizontal
Question 1 For a cantilever pile wall shown in Figure 1, assess the performance of the system and answer the following questions. Figure 1 - Cantilever Pile Wall i. Estimate the net resulting horizontal
Saturated-Unsaturated Consolidation
 Introduction Saturated-Unsaturated Consolidation This example looks at the volume change behavior of a saturated-unsaturated column under loading, wetting and drying conditions. Feature Highlights GeoStudio
Introduction Saturated-Unsaturated Consolidation This example looks at the volume change behavior of a saturated-unsaturated column under loading, wetting and drying conditions. Feature Highlights GeoStudio
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING Volume 1, No 4, 2010
 Effect of geometric dimensions on the transmission coefficient of floating breakwaters Mohammad Hosein Tadayon, Khosro Bargi 2, Hesam Sharifian, S. Reza Hoseini - Ph.D student, Department of Civil Engineering,
Effect of geometric dimensions on the transmission coefficient of floating breakwaters Mohammad Hosein Tadayon, Khosro Bargi 2, Hesam Sharifian, S. Reza Hoseini - Ph.D student, Department of Civil Engineering,
REPORT GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION FOR THE PROPOSED BLOCK-7 SUB-STATION SY NO-225, NEAR RAYACHERLU VILLAGE
 REPORT ON GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION FOR THE PROPOSED BLOCK-7 SUB-STATION SY NO-225, NEAR RAYACHERLU VILLAGE CLIENT: KARNATAKA SOLAR POWER DEVELOPMENT CORPORATION BANGALORE 0 GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION
REPORT ON GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION FOR THE PROPOSED BLOCK-7 SUB-STATION SY NO-225, NEAR RAYACHERLU VILLAGE CLIENT: KARNATAKA SOLAR POWER DEVELOPMENT CORPORATION BANGALORE 0 GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION
Experimental Determination of Temperature and Pressure Profile of Oil Film of Elliptical Journal Bearing
 International Journal of Advanced Mechanical Engineering. ISSN 2250-3234 Volume 4, Number 5 (2014), pp. 469-474 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Experimental Determination of Temperature
International Journal of Advanced Mechanical Engineering. ISSN 2250-3234 Volume 4, Number 5 (2014), pp. 469-474 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Experimental Determination of Temperature
Rotary air valves used for material feed and explosion protection are required to meet the criteria of NFPA 69 (2014)
 Rotary air valves used for material feed and explosion protection are required to meet the criteria of NFPA 69 (2014) 12.2.4.2. 12.2.4.2 rotary valve design criteria (close clearance) 12.2.4.3 THE DESIGN
Rotary air valves used for material feed and explosion protection are required to meet the criteria of NFPA 69 (2014) 12.2.4.2. 12.2.4.2 rotary valve design criteria (close clearance) 12.2.4.3 THE DESIGN
Using sea bed roughness as a wave energy dissipater
 Island Sustainability II 203 Using sea bed roughness as a wave energy dissipater T. Elgohary 1, R. Elgohary 1 & M. Hagrass 2 1 Department of Civil Engineering (Irrigation and Hydraulic), The Tenth of Ramadan
Island Sustainability II 203 Using sea bed roughness as a wave energy dissipater T. Elgohary 1, R. Elgohary 1 & M. Hagrass 2 1 Department of Civil Engineering (Irrigation and Hydraulic), The Tenth of Ramadan
CIVE 554/650. Geotechnical Engineering. Rock. Soil. Water. Site Investigation Techniques. CIVE Knight 1. 1/8/2006 CIVE Knight 1
 CIVE 554/650 Site Investigation Techniques 1/8/2006 CIVE 554 - Knight 1 Geotechnical Engineering Soil Rock Water 1/8/2006 CIVE 554 - Knight 2 CIVE 554 - Knight 1 Key Soil Engineering Properties Compressibility
CIVE 554/650 Site Investigation Techniques 1/8/2006 CIVE 554 - Knight 1 Geotechnical Engineering Soil Rock Water 1/8/2006 CIVE 554 - Knight 2 CIVE 554 - Knight 1 Key Soil Engineering Properties Compressibility
APPLICATION OF PUSHOVER ANALYSIS ON EARTHQUAKE RESPONSE PREDICATION OF COMPLEX LARGE-SPAN STEEL STRUCTURES
 APPLICATION OF PUSHOVER ANALYSIS ON EARTHQUAKE RESPONSE PREDICATION OF COMPLEX LARGE-SPAN STEEL STRUCTURES J.R. Qian 1 W.J. Zhang 2 and X.D. Ji 3 1 Professor, 3 Postgraduate Student, Key Laboratory for
APPLICATION OF PUSHOVER ANALYSIS ON EARTHQUAKE RESPONSE PREDICATION OF COMPLEX LARGE-SPAN STEEL STRUCTURES J.R. Qian 1 W.J. Zhang 2 and X.D. Ji 3 1 Professor, 3 Postgraduate Student, Key Laboratory for
An integrated three-dimensional model of wave-induced pore pressure and effective stresses in a porous seabed: II. Breaking waves
 An integrated three-dimensional model of wave-induced pore pressure and effective stresses in a porous seabed: II. Breaking waves Author Jeng, D., Zhang, Hong Published 2005 Journal Title Ocean Engineering
An integrated three-dimensional model of wave-induced pore pressure and effective stresses in a porous seabed: II. Breaking waves Author Jeng, D., Zhang, Hong Published 2005 Journal Title Ocean Engineering
Figure 1 FSM 250 roof anchor system
 Report No.: 15111045 Date: 27.11.15 Engineers Report FSM 250 Roof Anchor Overview Methodology AS/NZS 1891.4:2009 Loading Anchorage Application Analysis Parameters Acceptance Criteria Results Conclusions
Report No.: 15111045 Date: 27.11.15 Engineers Report FSM 250 Roof Anchor Overview Methodology AS/NZS 1891.4:2009 Loading Anchorage Application Analysis Parameters Acceptance Criteria Results Conclusions
Stability of Pipeline and details of Anchor blocks
 Stability of Pipeline and details of Anchor blocks For Offshore pipeline laying at Gulf of Kutch, Gujarat. Client WELSPUN (I) LTD, Gujarat EPC Contactor PATEL CONSTRUCTION CO. Consultants Prof. R. Sundaravadivelu
Stability of Pipeline and details of Anchor blocks For Offshore pipeline laying at Gulf of Kutch, Gujarat. Client WELSPUN (I) LTD, Gujarat EPC Contactor PATEL CONSTRUCTION CO. Consultants Prof. R. Sundaravadivelu
Homework of chapter (3)
 The Islamic University of Gaza, Civil Engineering Department, Fluid mechanics-discussion, Instructor: Dr. Khalil M. Al Astal T.A: Eng. Hasan Almassri T.A: Eng. Mahmoud AlQazzaz First semester, 2013. Homework
The Islamic University of Gaza, Civil Engineering Department, Fluid mechanics-discussion, Instructor: Dr. Khalil M. Al Astal T.A: Eng. Hasan Almassri T.A: Eng. Mahmoud AlQazzaz First semester, 2013. Homework
Assistant Lecturer Anees Kadhum AL Saadi
 Pressure Variation with Depth Pressure in a static fluid does not change in the horizontal direction as the horizontal forces balance each other out. However, pressure in a static fluid does change with
Pressure Variation with Depth Pressure in a static fluid does not change in the horizontal direction as the horizontal forces balance each other out. However, pressure in a static fluid does change with
Effect of Fluid Density and Temperature on Discharge Coefficient of Ogee Spillways Using Physical Models
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Effect of Fluid Density and Temperature on Discharge Coefficient of Ogee Spillways Using Physical Models M. SREENIVASULU REDDY 1 DR Y. RAMALINGA REDDY 2 Assistant Professor, School of
RESEARCH ARTICLE Effect of Fluid Density and Temperature on Discharge Coefficient of Ogee Spillways Using Physical Models M. SREENIVASULU REDDY 1 DR Y. RAMALINGA REDDY 2 Assistant Professor, School of
Critical Pool Level and Stability of Slopes in Granular Soils
 TECHNICAL NOTES Critical Pool Level and Stability of Slopes in Granular Soils Radoslaw L. Michalowski, F.ASCE 1 Abstract: The influence of pore-water pressure and the pool water pressure on stability of
TECHNICAL NOTES Critical Pool Level and Stability of Slopes in Granular Soils Radoslaw L. Michalowski, F.ASCE 1 Abstract: The influence of pore-water pressure and the pool water pressure on stability of
Strength and Deformation Behavior of Soft Bangkok Clay
 Geotechnical Testing Journal, Vol. 26, No. 4 Paper ID GTJ8933_264 Available online at: www.astm.org T. H. Seah 1 and K. C. Lai 2 Strength and Deformation Behavior of Soft Bangkok Clay ABSTRACT: The influence
Geotechnical Testing Journal, Vol. 26, No. 4 Paper ID GTJ8933_264 Available online at: www.astm.org T. H. Seah 1 and K. C. Lai 2 Strength and Deformation Behavior of Soft Bangkok Clay ABSTRACT: The influence
REPORT GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION FOR THE PROPOSED BLOCK-1 SUB-STATION SY NO-44, NEAR KYATAGANACHERLU VILLAGE
 REPORT ON GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION FOR THE PROPOSED BLOCK-1 SUB-STATION SY NO-44, NEAR KYATAGANACHERLU VILLAGE CLIENT: KARNATAKA SOLAR POWER DEVELOPMENT CORPORATION BANGALORE 0 GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION
REPORT ON GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION FOR THE PROPOSED BLOCK-1 SUB-STATION SY NO-44, NEAR KYATAGANACHERLU VILLAGE CLIENT: KARNATAKA SOLAR POWER DEVELOPMENT CORPORATION BANGALORE 0 GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION
STUDY ON UPWARD MOVEMENT OF FINES FROM SANDY SEABED UNDER CYCLIC WATER PRESSURE CHANGE DUE TO WAVES
 C- Fourth International Conference on Scour and Erosion STUDY ON UPWARD MOVEMENT OF FINES FROM SANDY SEABED UNDER CYCLIC WATER PRESSURE CHANGE DUE TO WAVES Takashi TSUCHIDA, Akihiro MATSUI and Ryoichi
C- Fourth International Conference on Scour and Erosion STUDY ON UPWARD MOVEMENT OF FINES FROM SANDY SEABED UNDER CYCLIC WATER PRESSURE CHANGE DUE TO WAVES Takashi TSUCHIDA, Akihiro MATSUI and Ryoichi
INVESTIGATION OF INSTALLATION TORQUE AND TORQUE-TO-CAPACITY RELATIONSHIP OF SCREW-PILES AND HELICAL ANCHORS
 University of Massachusetts Amherst ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst Geotechnical Engineering Masters Projects Civil and Environmental Engineering 2015 INVESTIGATION OF INSTALLATION TORQUE AND TORQUE-TO-CAPACITY
University of Massachusetts Amherst ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst Geotechnical Engineering Masters Projects Civil and Environmental Engineering 2015 INVESTIGATION OF INSTALLATION TORQUE AND TORQUE-TO-CAPACITY
STRIDE PROJECT Steel Risers in Deepwater Environments Achievements
 STRIDE PROJECT Steel Risers in Deepwater Environments Achievements 1999-21 Neil Willis Principal Engineer 2H Offshore Engineering 6 th Annual Deepwater Technologies and Developments Conference 21 The presentation
STRIDE PROJECT Steel Risers in Deepwater Environments Achievements 1999-21 Neil Willis Principal Engineer 2H Offshore Engineering 6 th Annual Deepwater Technologies and Developments Conference 21 The presentation
Copyright ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA , United States.
 LastD 4429 93 standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because it may not be technically possible to adequately
LastD 4429 93 standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because it may not be technically possible to adequately
Investigation of Stresses in Ring Stiffened Circular Cylinder
 International Journal of Engineering and Technical Research (IJETR) ISSN: 2321-869, Volume-2, Issue-9, September 214 Investigation of Stresses in Ring Stiffened Circular Cylinder Neetesh N. Thakre, Dr.
International Journal of Engineering and Technical Research (IJETR) ISSN: 2321-869, Volume-2, Issue-9, September 214 Investigation of Stresses in Ring Stiffened Circular Cylinder Neetesh N. Thakre, Dr.
Global Buckling Design for Flexible Flowlines
 Global Buckling Design for Flexible Flowlines Challenges, Approach and Lessons Learned Mostafa Tantawi 1 Agenda Background to flexible lines Mechanical behavior of Flexible vs Steel. Why flexible buckling
Global Buckling Design for Flexible Flowlines Challenges, Approach and Lessons Learned Mostafa Tantawi 1 Agenda Background to flexible lines Mechanical behavior of Flexible vs Steel. Why flexible buckling
and its weight (in newtons) when located on a planet with an acceleration of gravity equal to 4.0 ft/s 2.
 1.26. A certain object weighs 300 N at the earth's surface. Determine the mass of the object (in kilograms) and its weight (in newtons) when located on a planet with an acceleration of gravity equal to
1.26. A certain object weighs 300 N at the earth's surface. Determine the mass of the object (in kilograms) and its weight (in newtons) when located on a planet with an acceleration of gravity equal to
H16 Losses in Piping Systems
 H16 Losses in Piping Systems The equipment described in this manual is manufactured and distributed by TECQUIPMENT LIMITED Suppliers of technological laboratory equipment designed for teaching. BONSALL
H16 Losses in Piping Systems The equipment described in this manual is manufactured and distributed by TECQUIPMENT LIMITED Suppliers of technological laboratory equipment designed for teaching. BONSALL
INSTALLATION CONSTRAINTS OF SUCTION ASSISTED FOUNDATIONS AND ANCHORS FOR OFFSHORE ENERGY DEVELOPMENT
 Geotec., Const. Mat. & Env., DOI: https://doi.org/10.21660/2018.47.3695 ISSN: 2186-2982 (Print), 2186-2990 (Online), Japan INSTALLATION CONSTRAINTS OF SUCTION ASSISTED FOUNDATIONS AND ANCHORS FOR OFFSHORE
Geotec., Const. Mat. & Env., DOI: https://doi.org/10.21660/2018.47.3695 ISSN: 2186-2982 (Print), 2186-2990 (Online), Japan INSTALLATION CONSTRAINTS OF SUCTION ASSISTED FOUNDATIONS AND ANCHORS FOR OFFSHORE
Tension Cracks. Topics Covered. Tension crack boundaries Tension crack depth Query slice data Thrust line Sensitivity analysis.
 Tension Cracks 16-1 Tension Cracks In slope stability analyses with cohesive soils, tension forces may be observed in the upper part of the slope. In general, soils cannot support tension so the results
Tension Cracks 16-1 Tension Cracks In slope stability analyses with cohesive soils, tension forces may be observed in the upper part of the slope. In general, soils cannot support tension so the results
Research on Shear Test methods of bonded steel bolts
 Research on Shear Test methods of bonded steel bolts *Quan Xueyou 1), Li Xiongsong 2) and Luo Chujie 2) 1), 2) School of Civil Engineering, Chongqing University 1), 2) Key Laboratory of New Technology
Research on Shear Test methods of bonded steel bolts *Quan Xueyou 1), Li Xiongsong 2) and Luo Chujie 2) 1), 2) School of Civil Engineering, Chongqing University 1), 2) Key Laboratory of New Technology
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING Volume 3, No 1, 2012
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING Volume 3, No 1, 2012 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Research article ISSN 0976 4399 ABSTRACT Scour
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING Volume 3, No 1, 2012 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Research article ISSN 0976 4399 ABSTRACT Scour
AIR EJECTOR WITH A DIFFUSER THAT INCLUDES BOUNDARY LAYER SUCTION
 Engineering MECHANICS, Vol. 20, 2013, No. 3/4, p. 213 220 213 AIR EJECTOR WITH A DIFFUSER THAT INCLUDES BOUNDARY LAYER SUCTION Václav Dvořák* The article deals with axial-symmetric subsonic air-to-air
Engineering MECHANICS, Vol. 20, 2013, No. 3/4, p. 213 220 213 AIR EJECTOR WITH A DIFFUSER THAT INCLUDES BOUNDARY LAYER SUCTION Václav Dvořák* The article deals with axial-symmetric subsonic air-to-air
The Relationship between the Depth Embedded Pipe Pile and the Force of Clamping Jaw
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS The Relationship between the Depth Embedded Pipe Pile and the Force of Clamping Jaw To cite this article: Yu Wentai et al 018
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS The Relationship between the Depth Embedded Pipe Pile and the Force of Clamping Jaw To cite this article: Yu Wentai et al 018
