Strength assessment during shallow penetration of a sphere in clay
|
|
|
- Carol Hart
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Morton, J. P. et al. (24) Géotechnique Letters 4, , Strength assessment during shallo penetration of a sphere in clay J. P. MORTON*, C. D. O LOUGHLIN* and D. J. WHITE* Strength interpretation from the measured penetration resistance of full-flo penetrometers, such as the T-bar and ball, is generally based on a constant bearing capacity factor associated ith a deep flo-round mechanism. This approach may underestimate the strength of near-surface sediments, hich is becoming increasingly important for the design of offshore infrastructure such as pipelines, steel catenary risers and mudmats. This paper describes a series of centrifuge experiments designed to capture the change in the capacity factor of a ball penetrometer during shallo penetration. A rigorous consideration of soil buoyancy is provided. This is an important consideration in soils ith a higher strength to self-eight ratio because a cavity is formed by the passage of the ball and remains open to greater depths. The depth at hich a full-flo mechanism develops is related to the dimensionless strength ratio, expressed as the ratio of the undrained shear strength to the effective unit eight and penetrometer diameter. This observation forms the basis for proposed formulations that describe the evolution of the bearing capacity factor ith depth for different dimensionless strength ratios. These formulations can be used to determine more accurately the undrained shear strength of near-surface soil over the range of dimensionless strength ratios that is of interest to offshore applications. KEYWORDS: bearing capacity; centrifuge modelling; penetrometers; shear strength; site investigation ICE Publishing: all rights reserved NOTATION A s c v D F buoy F s H c k m N b N b-deep N b-shallo q b q m q net Q s s u u v op a c9 s v s9 v projected area of the sphere shaft area coefficient of vertical consolidation diameter of penetrometer soil buoyancy evolving soil resistance cavity depth undrained shear strength gradient plastic volumetric strain ratio bearing capacity factor deep bearing capacity factor shallo bearing capacity factor buoyancy resistance measured bearing pressure net penetration resistance soil resistance undrained shear strength hydrostatic pore pressure penetration rate ball invert depth normalised operative depth net area ratio of the load cell core to the shaft area effective unit eight of the soil overburden pressure vertical effective stress INTRODUCTION For a deeply embedded ball penetrometer, a full-flo mechanism that is symmetrical above and belo the ball is operative and the undrained shear strength, s u, can be interpreted from the measured bearing pressure, q m, Manuscript received 4 July 24; first decision 6 August 24; accepted 5 September 24. Published online at.geotechniqueletters.com on October 24. *Centre for Offshore Foundation Systems, University of Western Australia, Perth, WA, Australia according to s u 5q m /N b-deep. Hoever, at shallo penetration depths, a full-flo mechanism does not develop and s u should be interpreted from the measured penetration resistance using a bearing capacity factor N b-shallo,n b-deep. Adopting an appropriate N b-shallo, and accounting for its evolution to N b-deep ith depth, is an important aspect of quantifying s u over the upper 2 m of the seabed. This is critical for the design of almost all shalloly embedded offshore infrastructure (Puech et al., 2) including subsea pipelines, steel catenary risers and mudmats. Large-deformation finite-element (LDFE) analyses on a T-bar (White et al., 2; Tho et al., 22), spudcan (Hossain et al., 25) and ball penetrometer (Zhou et al., 23) have shon that the transition depth from N b-shallo to N b-deep is dependent on the dimensionless strength ratio s u /c9d, here c9 is the effective unit eight of the soil and D is the diameter of the penetrometer. Higher strength ratios are associated ith a delay in the transition to a steady N b-deep. Correlations for the transition depth and N b-shallo have been derived and, in the case of the T-bar and ball, a basis for correcting penetration data ithin the shallo zone has been proposed (White et al., 2; Zhou et al., 23). Hoever, from the perspective of a spherical penetrometer, hich is the focus of this paper, the range of strength ratios previously examined (s u /c9d52?95 44?25 (Zhou et al., 23)) is narroer than the range that is of practical interest for offshore problems. For example, a 25 mm diameter freefall spherical penetrometer (for measuring the strength of the seabed (Morton & O Loughlin, 22)) penetrating very soft soil is associated ith lo values of s u /c9d approaching? at one diameter embedment, hereas an 8 mm piezoball penetrating the seabed ith a crust strength of <2 kpa is associated ith high values of s u /c9d, approaching 4. The motivation for this study as to experimentally capture the variation in N b-shallo ith depth for a ball penetrometer embedding into clay over a ide range of s u /c9d. The experimental data are combined ith reinterpreted 262 Donloaded by [ University Of Western Australia] on [23//5]. Copyright ICE Publishing, all rights reserved.
2 Strength assessment during shallo penetration of a sphere in clay 263 LDFE results (Zhou et al., 23) and form the basis of a ne correlation that describes the evolution of N b ith depth. EXPERIMENTAL DETAILS The problem is addressed through centrifuge tests carried out at g in the University of Western Australia (UWA) beam centrifuge. The penetration resistance response and the degree of hole-closure ere analysed for nine penetrometer tests using a?3 mm diameter ball ith a 4?8 mm diameter shaft, penetrating a kaolin clay sample ith a progressively higher overconsolidation ratio (OCR). A constant penetration rate of mm/s as adopted such that the non-dimensional velocity vd/c v <3 (v is the penetration rate, D is the sphere diameter and c v is the coefficient of vertical consolidation <2?8 m 2 /year (Cocjin et al., 24)) and the response is primarily undrained (House et al., 2). A video recording observed the progressive hole-closure during each test and provided a means of determining the depth at hich the cavity, formed by the passage of the ball, closed over. The experimental arrangement is shon in Fig.. EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE Preparation of clay specimen The sample as prepared by mixing kaolin poder ith ater in a vacuum mixer at a moisture content equal to tice the liquid limit (2%). A drainage sand layer at the base of the sample alloed to-ay drainage during self-eight consolidation in the centrifuge at g, and vertical drains in the corners of the sample ensured there as no hydraulic gradient over the height of the sample. A nominal mm layer of free ater as maintained throughout testing. In order to investigate the range of s u /c9d of interest (spanning to orders of magnitude), the local s u as progressively increased by scraping a 2 mm layer of clay from the surface of the sample beteen each consecutive penetration test (see Fig. 2). This had the effect of increasing the OCR of the clay and increasing s u relative to the (ne) sample surface. Theoretical basis for interpretation of measured ball penetration resistance As the ball penetrates the soil, the measured bearing pressure q m includes the evolving soil resistance q s, expressed in terms of N b, and the resistance due to soil buoyancy, q b Fig. 2. A scraped soil sample before a test q m ~q s zq b ~N b s u z F buoy () here F buoy is the soil buoyancy force and is the projected area of the sphere. If the ball is deeply embedded such that the soil flos around the ball during penetration, the buoyancy force can be calculated from Archimedes principle; that is, the buoyancy force is the volume of the displaced soil multiplied by the effective unit eight of the soil, F buoy 5 (pd 3 /6)c9. Hoever, during initial penetration, the soil does not flo around the ball. Instead, a cavity is created above the ball and the soil that ould have filled this void is instead accommodated by heave at the soil surface. To capture this heave effect, a simple multiplier can be applied on F buoy, as proposed previously for the penetration of cylindrical and spherical geometries (e.g. Merifield et al., 29; White et al., 2; Chatterjee et al., 22; Zhou et al., 23). An alternative approach to derive this multiplier directly, is to consider the ork required to lift the soil that is displaced by the incrementally advancing ball. This can be done by assuming a cavity geometry formed by the advancing ball, hich is approximated here as an inverted cone for all considered values of s u /c9d, prompted by camera observations (e.g. see Fig. 3) and supported by LDFE simulations (Zhou et al., 23). At a ball invert depth of #?5D (Fig. 4(a)), all of the soil displaced by the advancing ball is lifted to the soil surface. The ork done then becomes the eight of the Actuator Ball penetrometer Camera Water Kaolin clay Sand Fig.. Experimental arrangement in the beam centrifuge Donloaded by [ University Of Western Australia] on [23//5]. Copyright ICE Publishing, all rights reserved.
3 264 Morton, O Loughlin and White s u, q net /N b-deep : kpa q net 2 N b-deep Normalised depth, ŵ op + DZ scrape s u Transition points Fig. 3. Ball penetrometer and cavity after a penetration test 8 2 Base sand drainage layer displaced soil multiplied by the distance beteen the centroidal height of the embedded ball (a spherical cap) and the soil surface. For?5D. # H c + D, here H c is the cavity depth, only some of the soil displaced by the advancing ball is lifted to the surface. The remainder fills part of the cavity created by the increment of ball penetration, as shon in Fig. 4(b). In this case, the ork done is calculated by adding the gain in potential energy by these to separate elements of soil, resulting in the profile of soil buoyancy ith embedment given in Fig. 4(c). The net penetration resistance q net can be calculated using the measured resistance q m from equation () by correcting for the unequal pore pressure and overburden pressure effects due to the shaft behind the ball (Chung & Randolph, 24) q net ~q m {½s v {u ({a)š A s (2) here s v is the overburden pressure, u is the hydrostatic pore pressure, A s is the shaft area and the parameter a is the net area ratio of the load cell core to the shaft area (a 5?8 for the tests considered here). For a deeply embedded ball, q net and hence the inferred s u corresponds to the mid-height of the ball due to the depth symmetry of the flo-round mechanism. For a shalloly embedded ball, here the full-flo mechanism is not fully developed, the normalised operative depth ^ op is assumed to vary linearly up to the depth here a full floround mechanism occurs, in a similar manner to that Fig. 5. Comparison of strength profiles of Ladd et al. (977) and q net /N b-deep profiles proposed for a shalloly embedded T-bar (White et al., 2) ^ op ~ D {: 5 H c zd D {: 5 (3) Omitted from the above theoretical frameork is any consideration of ho N b evolves during shallo to deep penetration. This has been purposely excluded from the preceding discussion and ill be formulated later in the paper to reflect the experimental results presented in the folloing section. RESULTS AND COMPARISONS In-flight video camera observations The camera as synchronised ith the data acquisition system such that visual observations could be relayed to the measured penetration response. For loer values of s u /c9d, here the open cavity depth as loer and could be captured by the camera, the instances hen soil floed over the ball ere consistent ith the transitional depths inferred from the penetration profiles shon in Fig. 5 (and discussed in the next section). This observation is at variance ith the LDFE results reported by Zhou et al. (23), hich indicate that more penetration is required to establish a deep failure mechanism after full flo of soil over the top of the ball. Change in elevation of soil mass centroid F buoy /c'd Soil flo to surface Displaced soil Partial soil flo D' Soil surface H c Normalised invert depth, /D (a) Displaced soil (b) 3. (c) Fig. 4. Schematic illustration of soil buoyancy due to (a) the sphere and (b) the sphere and conical cavity. (c) Buoyancy function for a typical cavity depth Donloaded by [ University Of Western Australia] on [23//5]. Copyright ICE Publishing, all rights reserved.
4 Strength assessment during shallo penetration of a sphere in clay here s v is the current vertical effective stress, determined from the c9 profile ith depth and the varying acceleration level ithin the centrifuge (93g to 5g over the depth of penetration), and m is the plastic volumetric strain ratio (Schofield & Wroth, 968). The normally consolidated undrained strength ratio (su =s v )nc 5?3, as determined from ball penetrometer tests before scraping the soil surface (i.e. OCR5) using the commonly adopted Nb-deep5?5 (Chung & Randolph, 24). The ratio (su =s v )nc increases to?5 if the measured resistance (hich ignores shaft effects) is considered, similar to (su =s v )nc 5?6 reported by Richardson et al. (29) and Hu et al. (24), and equivalent to an undrained strength gradient ith prototype depth, k5 kpa/m, hich is typical for UWA kaolin. The best agreement beteen equation (4) and the experimental qnet/nb-deep profiles in the overconsolidated samples as obtained using m5 (rather than the commonly reported m5?8), hich reflects the minimal selling time permitted beteen each soil scrape and the subsequent penetration test. Deep mechanism transition depth ^ deep-op are also shon The normalised transition depths in Fig. 5, and ere selected as the depths here the qnet/nb-deep experimental data ere judged to have reached su predicted using equation (4). The final to profiles do not reach the predicted su profile due to the proximity of ^ deep-op are approximated the base drainage sand layer and in these instances on the basis of the Nb variation ith ^ deep-op are also shon in depth, discussed later. Values of Fig. 6 alongside previously reported T-bar (White et al., 2), spudcan (Hossain et al., 25) and ball (Zhou et al., 23) data, but reinterpreted to account for the definition of operative depth adopted here. Further reinterpretation of the ball data of Zhou et al. (23) as made to ascertain ^ deep-op assessed as hen Nb became effectively constant (to ithin,5% of the final value) rather than reaching the limit, hich is difficult to judge and is approached asymptotically. The experimental ball data reported here, together ith the reinterpreted Zhou et al. (23) ball data, no form a unique ^ deep-op and su/c9d for a ball penetrelationship beteen ^ deep-op ), rometer (here su is the undrained strength at hich can be described using c d{a ^ deep-op ~az b su z (5) cd z½(su =c D)=e f Present study Zhou et al. (23), Ball reinterpreted Normalised transition depth, ŵdeep-op Undrained shear strength profiles As discussed earlier, the OCR of the sample as incrementally increased by scraping an additional 2 mm from the sample surface beteen penetration tests. The strength of the sample can then be assumed to vary ith depth according to equation (4), proposed by Ladd et al. (977) su su ~s v OCRm (4) s v nc White et al. (2), T-bar Hossain et al. (25), Spudcan Equation (5)... Normalised strength, su/c'd Fig. 6. Effect of strength ratio su/c9d on transition depth here the fitting constants a56?3, b5?2, c5?3, d5?52, e54?9 and f5?5. Shallo bearing capacity factors Figure 7 shos the experimental variation in Nb ith depth for each penetration test, obtained by dividing qnet by su from equation (4). Each Nb profile follos the same trend, commencing at zero at the soil surface and reaching a steady Nb-deep at the transition depth, hich is entirely dependent on su/c9d. This variation in Nb ith depth can be fitted using equation (6) (also shon on Fig. 7)!p ^ op Nb-shallo ~Nb-deep (6) ^ deep-op and p~:49 su c D {: (7) Nb Normalised operative depth, ŵop During shallo penetration, little or no heave as observed on the soil surface, particularly for tests ith higher values of su/c9d. This is considered to be due to the axisymmetric flo mechanism of the ball, hich reduces the heave compared ith plane strain flo for a cylindrical T-bar or pipeline (Stanier & White, 24). In light of this observation, enhancement of Fbuoy in equation () to account for heave of the soil surface, as considered by Merifield et al. (29), Randolph & White (28) and Stanier & White (24), as not included Equation (6) 3 Nb variation 4 Transition points 5 6 Fig. 7. Measured variation in normalised bearing factor ith normalised embedment depth and equation fit Donloaded by [ University Of Western Australia] on [23//5]. Copyright ICE Publishing, all rights reserved.
5 266 Morton, O Loughlin and White CONCLUSIONS This paper reports on centrifuge tests in hich a ball as penetrated into clay under undrained conditions over s u /c9d5?7 to 2?7 (at the transition depth). The depth at hich an open cavity, formed by the passage of the ball, closed over is considered to indicate the transitional depth ^ deep-op here a full flo-round mechanism develops. A novel analytical solution for the soil buoyancy in the case of an open conical hole has been developed. This rigorous approach is necessary to avoid significant errors in the determination of strength during shallo penetration in soils ith a lo strength to self-eight ratio. For instance, in a clay ith zero mudline strength and an undrained shear strength ratio of s u =s v 5?25, the buoyancy resistance increases to almost 7% of the geotechnical resistance during shallo penetration, and is independent of the penetrometer diameter at all penetration depths. Data from centrifuge experiments, combined ith reinterpreted data from LDFE analyses, sho a unique relationship beteen ^ deep-op and s u /c9d examined over the range s u /c9d<? to 4. Equations that describe the change in ^ deep-op and the capacity factor N b ith s u /c9d are proposed. These equations offer a more rigorous and reliable means of assessing soil strength in the upper fe metres of the seabed. Acknoledgements This ork forms part of the activities of the Centre for Offshore Foundation Systems (COFS), currently supported as a node of the Australian Research Council Centre of Excellence for Geotechnical Science and Engineering and as a Centre of Excellence by the Lloyd s Register Foundation. The Lloyd s Register Foundation invests in science, engineering and technology for public benefit, orldide. REFERENCES Chatterjee, S., Randolph, M. F. & White, D. J. (22). The effects of penetration rate and strain softening on the vertical penetration resistance of seabed pipelines. Géotechnique 62, No. 7, Chung, S. F. & Randolph, M. F. (24). Penetration resistance in soft clay for different shaped penetrometers. Proc. 2nd Int. Conf. on Site Characterisation, Porto 2, No., Cocjin, M. J., Gourvenec, S. M., White, D. J. & Randolph, M. F. (24). Tolerably mobile subsea foundations observations of performance. Géotechnique, in press. Hossain, M. S., Hu, Y., Randolph, M. F. & White, D. J. (25). Limiting cavity depth for spudcan foundations penetrating clay. Géotechnique 55, No. 9, House, A. R., Oliveria, J. R. M. S. & Randolph, M. F. (2). Evaluating the coefficient of consolidation using penetration tests. Int. J. Phys. Model. Geotech., No. 3, Hu, P., Stainer, S. A., Cassidy, M. J. & Wang, D. (24). Predicting peak resistance of spudcan penetrating sand overlying clay. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Engng ASCE 4, No Ladd, C. C., Foot, R., Ishihara, K., Schlosser, F. & Poulos, H. G. (977). Stress deformation and strength characteristics. Proc. 9th Int. Conf. Soil Mech. Found. Engng, Tokyo 2, Merifield, R., White, D. J. & Randolph, M. F. (29). The effect of surface heave on the response of partially-embedded pipelines on clay. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Engng ASCE 35, No. 6, Morton, J. P. & O Loughlin, C. D. (22). Dynamic penetration of a sphere in clay. Proc. 7th Int. Conf. on Offshore Site Investigation and Geotechnics, London 7, Puech, A., Orozco-Calderón, M. & Foray, P. (2). Mini T-bar testing at shallo penetration. Proc. Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics, Perth, Randolph, M. F. & White, D. J. (28). Pipeline embedment in deep ater: processes and quantitative assessment. Proc. Offshore Tech. Conf., Houston, 6. Richardson, M. D., O Loughlin, C. D., Randolph, M. F. & Gaudin, C. (29). Setup folloing installation of dynamic anchors in normally consolidated clay. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Engng ASCE 35, No. 4, Schofield, A. N. & Wroth, C. P. (968). Critical state soil mechanics. London: McGra-Hill. Stanier, S. A. & White, D. J. (24). Shallo penetrometer penetration resistance. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Engng ASCE, in press. Tho, K. K., Leung, C. F., Cho, Y. K. & Palmer, A. C. (22). Deep cavity flo mechanism of pipe penetration in clay. Can. Geotech. J. 49, No., White, D. J., Gaudin, C., Boylan, N. & Zhou, H. (2). Interpretation of T-bar penetrometer tests at shallo embedment and in very soft soil. Can. Geotech. J. 47, No. 2, Zhou, H., Hossain, M. S., Hu, Y. & Liu, H. (23). Behaviour of a ball penetrometer in uniform single and double layer clays. Géotechnique 63, No. 8, WHAT DO YOU THINK? To discuss this paper, please up to 5 ords to the editor at journals@ice.org.uk. Your contribution ill be forarded to the author(s) for a reply and, if considered appropriate by the editorial panel, ill be published as a discussion. Donloaded by [ University Of Western Australia] on [23//5]. Copyright ICE Publishing, all rights reserved.
Suction caisson extraction resistance in Gulf of Guinea clay
 Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics III Meyer (Ed.) 2015 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN: 978-1-138-02848-7 Suction caisson extraction resistance in Gulf of Guinea clay C. Gaudin, M.F. Randolph, S.
Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics III Meyer (Ed.) 2015 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN: 978-1-138-02848-7 Suction caisson extraction resistance in Gulf of Guinea clay C. Gaudin, M.F. Randolph, S.
Learn more at
 Full scale model tests of a steel catenary riser C. Bridge 1, H. Howells 1, N. Toy 2, G. Parke 2, R. Woods 2 1 2H Offshore Engineering Ltd, Woking, Surrey, UK 2 School of Engineering, University of Surrey,
Full scale model tests of a steel catenary riser C. Bridge 1, H. Howells 1, N. Toy 2, G. Parke 2, R. Woods 2 1 2H Offshore Engineering Ltd, Woking, Surrey, UK 2 School of Engineering, University of Surrey,
ON-BOTTOM STABILITY CALCULATIONS FOR FIBRE OPTIC SUBMARINE CABLES
 ON-BOTTOM STABILITY CALCULATIONS FOR FIBRE OPTIC SUBMARINE CABLES Inge Vintermyr (Nexans ray AS) Email: Nexans ray AS, PO.Box 6450 Etterstad, N-0605 Oslo, ray. Abstract: This
ON-BOTTOM STABILITY CALCULATIONS FOR FIBRE OPTIC SUBMARINE CABLES Inge Vintermyr (Nexans ray AS) Email: Nexans ray AS, PO.Box 6450 Etterstad, N-0605 Oslo, ray. Abstract: This
CHAPTER 5: VACUUM TEST WITH VERTICAL DRAINS
 CHAPTER 5: VACUUM TEST WITH VERTICAL DRAINS 5.1 Introduction Using surcharging as the sole soil consolidation mean can take a long time to reach the desired soil settlement. Soil consolidation using prefabricated
CHAPTER 5: VACUUM TEST WITH VERTICAL DRAINS 5.1 Introduction Using surcharging as the sole soil consolidation mean can take a long time to reach the desired soil settlement. Soil consolidation using prefabricated
The tensile capacity of suction caissons in sand under rapid loading
 Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics: ISFOG 25 Gourvenec & Cassidy (eds) 25 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 415 3963 X The tensile capacity of suction caissons in sand under rapid loading Guy T. Houlsby,
Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics: ISFOG 25 Gourvenec & Cassidy (eds) 25 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 415 3963 X The tensile capacity of suction caissons in sand under rapid loading Guy T. Houlsby,
MODELLING ANCILLARIES: WEIR COEFFICIENTS
 WaPUG USER NOTE No 27 MODELLING ANCILLARIES: WEIR COEFFICIENTS David Balmforth, MWH 1. SCOPE This user note gives advice on the choice of coefficient for overflo eirs and orifices hen modelling storm seage
WaPUG USER NOTE No 27 MODELLING ANCILLARIES: WEIR COEFFICIENTS David Balmforth, MWH 1. SCOPE This user note gives advice on the choice of coefficient for overflo eirs and orifices hen modelling storm seage
Analysis of dilatometer test in calibration chamber
 Analysis of dilatometer test in calibration chamber Lech Bałachowski Gdańsk University of Technology, Poland Keywords: calibration chamber, DMT, quartz sand, FEM ABSTRACT: Because DMT in calibration test
Analysis of dilatometer test in calibration chamber Lech Bałachowski Gdańsk University of Technology, Poland Keywords: calibration chamber, DMT, quartz sand, FEM ABSTRACT: Because DMT in calibration test
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON OPTIMUM INSTALLATION DEPTH OF PVD UNDER VACUUM CONSOLIDATION ABSTRACT
 EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON OPTIMUM INSTALLATION DEPTH OF PVD UNDER VACUUM CONSOLIDATION EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON OPTIMUM INSTALLATION DEPTH OF PVD UNDER VACUUM CONSOLIDATION J.-C CHAI i), N. MIURA
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON OPTIMUM INSTALLATION DEPTH OF PVD UNDER VACUUM CONSOLIDATION EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON OPTIMUM INSTALLATION DEPTH OF PVD UNDER VACUUM CONSOLIDATION J.-C CHAI i), N. MIURA
Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
 43 Module 3: Lecture - 5 on Compressibility and Consolidation Contents Stresses in soil from surface loads; Terzaghi s 1-D consolidation theory; Application in different boundary conditions; Ramp loading;
43 Module 3: Lecture - 5 on Compressibility and Consolidation Contents Stresses in soil from surface loads; Terzaghi s 1-D consolidation theory; Application in different boundary conditions; Ramp loading;
Offshore engineering science
 Offshore engineering science In this research stream theoretical models advanced geotechnical models and new numerical techniques were used in applied offshore engineering topics such as loading, design
Offshore engineering science In this research stream theoretical models advanced geotechnical models and new numerical techniques were used in applied offshore engineering topics such as loading, design
OMAE INVESTIGATING THE RESPONSE OF OFFSHORE FOUNDATIONS IN SOFT CLAY SOILS
 Proceedings of OMAE st International Conference on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering June 3-8, Oslo, Norway OMAE-857 INVESTIGATING THE RESPONSE OF OFFSHORE FOUNDATIONS IN SOFT CLAY SOILS B.W. Byrne
Proceedings of OMAE st International Conference on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering June 3-8, Oslo, Norway OMAE-857 INVESTIGATING THE RESPONSE OF OFFSHORE FOUNDATIONS IN SOFT CLAY SOILS B.W. Byrne
Pressuremeters in Geotechnical Design
 Pressuremeters in Geotechnical Design B.G. CLARKE Department of Civil Engineering University of Newcastle upon Tyne BLACK1E ACADEMIC & PROFESSIONAL An Imprint of Chapman & Hall London Glasgow Weinheim
Pressuremeters in Geotechnical Design B.G. CLARKE Department of Civil Engineering University of Newcastle upon Tyne BLACK1E ACADEMIC & PROFESSIONAL An Imprint of Chapman & Hall London Glasgow Weinheim
CONE PENETRATION TESTS
 February 25, 2015 John Doe, P.E. Acme Engineering and Testing 1234 Test Avenue, Suite 204 Lake Wales, FL 33853 Re: Sample CPT Soundings Dear Mr. Doe, Direct Push Services, LLC (DPS) was retained by Acme
February 25, 2015 John Doe, P.E. Acme Engineering and Testing 1234 Test Avenue, Suite 204 Lake Wales, FL 33853 Re: Sample CPT Soundings Dear Mr. Doe, Direct Push Services, LLC (DPS) was retained by Acme
Vertical Uplift Capacity of a Group of Equally Spaced Helical Screw Anchors in Sand
 SECM/15/080 Vertical Uplift Capacity of a Group of Equally Spaced Helical Screw Anchors in Sand S. Mukherjee 1* and Dr. S. Mittal 2 1 Amity University, Noida, India 2 Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee,
SECM/15/080 Vertical Uplift Capacity of a Group of Equally Spaced Helical Screw Anchors in Sand S. Mukherjee 1* and Dr. S. Mittal 2 1 Amity University, Noida, India 2 Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee,
An experimental study of inflatable offshore anchors in soft clay
 An experimental study of inflatable offshore anchors in soft clay T.A. Newson and F.W. Smith Department of Civil Engineering, University of Dundee P. Brunning Stolt Offshore MS Ltd., Aberdeen Introduction
An experimental study of inflatable offshore anchors in soft clay T.A. Newson and F.W. Smith Department of Civil Engineering, University of Dundee P. Brunning Stolt Offshore MS Ltd., Aberdeen Introduction
Installation of Stiffened Caissons in Nonhomogeneous Clays Published in: DOI: Document Version General rights Take down policy
 Installation of Stiffened Caissons in Nonhomogeneous Clays Zhou, M., Hossain, M., Hu, Y., & Liu, H. (2016). Installation of Stiffened Caissons in Nonhomogeneous Clays. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmentral
Installation of Stiffened Caissons in Nonhomogeneous Clays Zhou, M., Hossain, M., Hu, Y., & Liu, H. (2016). Installation of Stiffened Caissons in Nonhomogeneous Clays. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmentral
Cubzac-les-Ponts Experimental Embankments on Soft Clay
 Cubzac-les-Ponts Experimental Embankments on Soft Clay GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. www.geo-slope.com 1, 7 - th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada TP T Main: +1 3 9 Fax: +1 3 39 Introduction In the 197 s, a series
Cubzac-les-Ponts Experimental Embankments on Soft Clay GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. www.geo-slope.com 1, 7 - th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada TP T Main: +1 3 9 Fax: +1 3 39 Introduction In the 197 s, a series
Drum Centrifuge Model Tests Comparing the Performance of Spudcans and Caissons in Kaolin Clay
 Drum Centrifuge Model Tests Comparing the Performance of Spudcans and Caissons in Kaolin Clay by M.J. Cassidy and B.W. Byrne Report No. OUEL 48/ University of Oxford Department of Engineering Science Parks
Drum Centrifuge Model Tests Comparing the Performance of Spudcans and Caissons in Kaolin Clay by M.J. Cassidy and B.W. Byrne Report No. OUEL 48/ University of Oxford Department of Engineering Science Parks
Desaturating sand deposit by air injection for reducing liquefaction potential
 Desaturating sand deposit by air injection for reducing liquefaction potential M. Ishihara, M. Okamura & T. Oshita Public Works Research Institute, Tsukuba City, Japan. ABSTRACT: It has been known that
Desaturating sand deposit by air injection for reducing liquefaction potential M. Ishihara, M. Okamura & T. Oshita Public Works Research Institute, Tsukuba City, Japan. ABSTRACT: It has been known that
Digital Computer Simulation of a Reciprocating Compressor-A Simplified Analysis
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1972 Digital Computer Simulation of a Reciprocating Compressor-A Simplified Analysis D.
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1972 Digital Computer Simulation of a Reciprocating Compressor-A Simplified Analysis D.
SPE Effect of Initial Water Saturation on Spontaneous Water Imbibition Kewen Li, SPE, Kevin Chow, and Roland N. Horne, SPE, Stanford University
 SPE 7677 Effect of Initial Water Saturation on Spontaneous Water Imbibition Keen Li, SPE, Kevin Cho, and Roland N. Horne, SPE, Stanford University Copyright, Society of Petroleum Engineers Inc. This paper
SPE 7677 Effect of Initial Water Saturation on Spontaneous Water Imbibition Keen Li, SPE, Kevin Cho, and Roland N. Horne, SPE, Stanford University Copyright, Society of Petroleum Engineers Inc. This paper
Design of a High Efficiency Scroll Wrap Profile for Alternative Refrigerant R410A
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1998 Design of a High Efficiency Scroll Wrap Profile for Alternative Refrigerant R410A J.
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1998 Design of a High Efficiency Scroll Wrap Profile for Alternative Refrigerant R410A J.
Research on ESC Hydraulic Control Unit Property and Pressure Estimation
 Research on ESC Hydraulic Control Unit Property and Pressure Estimation Liu Wei, Ding Haitao *, and Guo Konghui State Key Libratory of Automobile Dynamic Simulation, Jilin University, Changchun 30025,
Research on ESC Hydraulic Control Unit Property and Pressure Estimation Liu Wei, Ding Haitao *, and Guo Konghui State Key Libratory of Automobile Dynamic Simulation, Jilin University, Changchun 30025,
Title Tsunami during 2011 East Japan Eart. The final publication is available より本文ファイルは に公開.
 Title Combined Failure Mechanism of a Bre Tsunami during 2011 East Japan Eart Author(s) Iai, Susumu Citation Geotechnical, Geological and Earthq 37: 177-186 Issue Date 2015-04-16 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/198459
Title Combined Failure Mechanism of a Bre Tsunami during 2011 East Japan Eart Author(s) Iai, Susumu Citation Geotechnical, Geological and Earthq 37: 177-186 Issue Date 2015-04-16 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/198459
STRIDE PROJECT Steel Risers in Deepwater Environments Achievements
 STRIDE PROJECT Steel Risers in Deepwater Environments Achievements 1999-21 Neil Willis Principal Engineer 2H Offshore Engineering 6 th Annual Deepwater Technologies and Developments Conference 21 The presentation
STRIDE PROJECT Steel Risers in Deepwater Environments Achievements 1999-21 Neil Willis Principal Engineer 2H Offshore Engineering 6 th Annual Deepwater Technologies and Developments Conference 21 The presentation
Critical Pool Level and Stability of Slopes in Granular Soils
 TECHNICAL NOTES Critical Pool Level and Stability of Slopes in Granular Soils Radoslaw L. Michalowski, F.ASCE 1 Abstract: The influence of pore-water pressure and the pool water pressure on stability of
TECHNICAL NOTES Critical Pool Level and Stability of Slopes in Granular Soils Radoslaw L. Michalowski, F.ASCE 1 Abstract: The influence of pore-water pressure and the pool water pressure on stability of
OTC Copyright 2008, Offshore Technology Conference
 OTC 19545 Comparison of Jackup Rig Spudcan Penetration Methods in Clay David Menzies, Fugro-McClelland Marine Geosciences, Inc., and Richard Roper, ENSCO International, Inc. Copyright 2008, Offshore Technology
OTC 19545 Comparison of Jackup Rig Spudcan Penetration Methods in Clay David Menzies, Fugro-McClelland Marine Geosciences, Inc., and Richard Roper, ENSCO International, Inc. Copyright 2008, Offshore Technology
m v = 1.04 x 10-4 m 2 /kn, C v = 1.29 x 10-2 cm 2 /min
 2.10 Problems Example 2.1: Design of Shallow Foundation in Saturated Clay Design a square footing to support a column load of 667 kn. The base of the footing will be located 1 m below the ground level
2.10 Problems Example 2.1: Design of Shallow Foundation in Saturated Clay Design a square footing to support a column load of 667 kn. The base of the footing will be located 1 m below the ground level
Suction anchor foundations for tension and taut leg floaters in deep waters. Tension Leg Platform. Taut Leg Platform. upper chain. risers.
 Case history: Soil investigation for offshore suction anchors anchor foundations for tension and taut leg floaters in deep waters Alternative anchors for floating structures pile Over last 5 - years anchoring
Case history: Soil investigation for offshore suction anchors anchor foundations for tension and taut leg floaters in deep waters Alternative anchors for floating structures pile Over last 5 - years anchoring
Stress and deformation of offshore piles under structural and wave loading
 Stress and deformation of offshore piles under structural and wave loading Author Eicher, Jackie, Guan, Hong, Jeng, Dong-Sheng Published 2003 Journal Title Ocean Engineering DOI https://doi.org/10.1016/s0029-8018(02)00031-8
Stress and deformation of offshore piles under structural and wave loading Author Eicher, Jackie, Guan, Hong, Jeng, Dong-Sheng Published 2003 Journal Title Ocean Engineering DOI https://doi.org/10.1016/s0029-8018(02)00031-8
GEOTECHNICAL PERFORMANCE OF SPUDCAN FOUNDATIONS
 Guidance Notes on Geotechnical Performance of Spudcan Foundations GUIDANCE NOTES ON GEOTECHNICAL PERFORMANCE OF SPUDCAN FOUNDATIONS JANUARY 2017 (Updated March 2018 see next page) American Bureau of Shipping
Guidance Notes on Geotechnical Performance of Spudcan Foundations GUIDANCE NOTES ON GEOTECHNICAL PERFORMANCE OF SPUDCAN FOUNDATIONS JANUARY 2017 (Updated March 2018 see next page) American Bureau of Shipping
Learn more at
 STRIDE JIP Phase III SUT Talk 15th November 2 Offshore VIV monitoring (vortex induced vibration) Catenary riser interaction with deepwater seabeds 3 Full Scale Riser Monitoring To get real measurements
STRIDE JIP Phase III SUT Talk 15th November 2 Offshore VIV monitoring (vortex induced vibration) Catenary riser interaction with deepwater seabeds 3 Full Scale Riser Monitoring To get real measurements
Bearing Capacity and Settlement Response of PMS Tanks on Cohesionless Soil Lithology in Lekki, Lagos of Nigeria
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Applied Engineering and Scientific Research,, ():- (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN: 8 Bearing Capacity and
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Applied Engineering and Scientific Research,, ():- (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN: 8 Bearing Capacity and
Influence of Settlement on Bearing Capacity Analysis of Shallow Foundations on Sandy Clays in the Niger Delta, Nigeria
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Applied Engineering and Scientific Research, 201, 2 (4):20-27 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN: 22 0041 Influence
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Applied Engineering and Scientific Research, 201, 2 (4):20-27 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN: 22 0041 Influence
SUMMARY OF SUBSURFACE STRATIGRAPHY AND MATERIAL PROPERTIES
 Page 1 of 101 Written by: Ming Zhu Date: 08/20/2008 Reviewed by: R. Kulasingam/J. Beech Date: 08/20/2008 SUMMARY OF SUBSURFACE STRATIGRAPHY AND MATERIAL PROPERTIES 1. INTRODUCTION This Summary of Subsurface
Page 1 of 101 Written by: Ming Zhu Date: 08/20/2008 Reviewed by: R. Kulasingam/J. Beech Date: 08/20/2008 SUMMARY OF SUBSURFACE STRATIGRAPHY AND MATERIAL PROPERTIES 1. INTRODUCTION This Summary of Subsurface
COURSE NUMBER: ME 321 Fluid Mechanics I Fluid statics. Course teacher Dr. M. Mahbubur Razzaque Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering BUET
 COURSE NUMBER: ME 321 Fluid Mechanics I Fluid statics Course teacher Dr. M. Mahbubur Razzaque Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering BUET 1 Fluid statics Fluid statics is the study of fluids in
COURSE NUMBER: ME 321 Fluid Mechanics I Fluid statics Course teacher Dr. M. Mahbubur Razzaque Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering BUET 1 Fluid statics Fluid statics is the study of fluids in
The Adequacy of Pushover Analysis to Evaluate Vulnerability of Masonry Infilled Steel Frames Subjected to Bi-Directional Earthquake Loading
 The Adequacy of Pushover Analysis to Evaluate Vulnerability of Masonry Infilled Steel Frames Subjected to Bi-Directional Earthquake Loading B.Beheshti Aval & M. Mohammadzadeh K.N.Toosi University of Technology,
The Adequacy of Pushover Analysis to Evaluate Vulnerability of Masonry Infilled Steel Frames Subjected to Bi-Directional Earthquake Loading B.Beheshti Aval & M. Mohammadzadeh K.N.Toosi University of Technology,
City, University of London Institutional Repository
 City Research Online City, University of London Institutional Repository Citation: Gorasia, R. J., McNamara, A. M. & Rettura, D. (212). Reducing driving forces for pressed-in. Proceedings of the Institution
City Research Online City, University of London Institutional Repository Citation: Gorasia, R. J., McNamara, A. M. & Rettura, D. (212). Reducing driving forces for pressed-in. Proceedings of the Institution
Blast Damage Consideratons for Horizontal Pressure Vessel and Potential for Domino Effects
 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 26, 2012 Guest Editors: Valerio Cozzani, Eddy De Rademaeker Copyright 2012, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-17-4; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian
A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 26, 2012 Guest Editors: Valerio Cozzani, Eddy De Rademaeker Copyright 2012, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-17-4; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian
Installation and Monotonic Pullout of a Suction Caisson Anchor in. Calcareous Silt
 1 Submitted January 2016, Revised May 2016 2 3 4 Installation and Monotonic Pullout of a Suction Caisson Anchor in Calcareous Silt 5 6 Kai Xiang Koh 1, Muhammad Shazzad Hossain 2 and Youngho Kim 3 7 8
1 Submitted January 2016, Revised May 2016 2 3 4 Installation and Monotonic Pullout of a Suction Caisson Anchor in Calcareous Silt 5 6 Kai Xiang Koh 1, Muhammad Shazzad Hossain 2 and Youngho Kim 3 7 8
Numerical Simulations of a Train of Air Bubbles Rising Through Stagnant Water
 Numerical Simulations of a Train of Air Bubbles Rising Through Stagnant Water Hong Xu, Chokri Guetari ANSYS INC. Abstract Transient numerical simulations of the rise of a train of gas bubbles in a liquid
Numerical Simulations of a Train of Air Bubbles Rising Through Stagnant Water Hong Xu, Chokri Guetari ANSYS INC. Abstract Transient numerical simulations of the rise of a train of gas bubbles in a liquid
Strength and Deformation Behavior of Soft Bangkok Clay
 Geotechnical Testing Journal, Vol. 26, No. 4 Paper ID GTJ8933_264 Available online at: www.astm.org T. H. Seah 1 and K. C. Lai 2 Strength and Deformation Behavior of Soft Bangkok Clay ABSTRACT: The influence
Geotechnical Testing Journal, Vol. 26, No. 4 Paper ID GTJ8933_264 Available online at: www.astm.org T. H. Seah 1 and K. C. Lai 2 Strength and Deformation Behavior of Soft Bangkok Clay ABSTRACT: The influence
SOIL-STRUCTURE INTERACTION ANALYSIS OF THE MANHATTAN BRIDGE FOUNDATIONS
 10NCEE Tenth U.S. National Conference on Earthquake Engineering Frontiers of Earthquake Engineering July 21-25, 2014 Anchorage, Alaska SOIL-STRUCTURE INTERACTION ANALYSIS OF THE MANHATTAN BRIDGE FOUNDATIONS
10NCEE Tenth U.S. National Conference on Earthquake Engineering Frontiers of Earthquake Engineering July 21-25, 2014 Anchorage, Alaska SOIL-STRUCTURE INTERACTION ANALYSIS OF THE MANHATTAN BRIDGE FOUNDATIONS
UNIT-I SOIL EXPLORATION
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : Geotechnical Engineering - II (16CE127) Year & Sem: III-B.Tech & II-Sem
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : Geotechnical Engineering - II (16CE127) Year & Sem: III-B.Tech & II-Sem
Bottom End-Closure Design Optimization of DOT-39 Non-Refillable Refrigerant Cylinders
 Y. Kisioglu a) Department of Mechanical Education, Kocaeli University, Izmit, Kocaeli, 41100, Turkey J. R. Brevick Industrial and Systems Engineering, The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio G. L. Kinzel
Y. Kisioglu a) Department of Mechanical Education, Kocaeli University, Izmit, Kocaeli, 41100, Turkey J. R. Brevick Industrial and Systems Engineering, The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio G. L. Kinzel
AIRFLOW GENERATION IN A TUNNEL USING A SACCARDO VENTILATION SYSTEM AGAINST THE BUOYANCY EFFECT PRODUCED BY A FIRE
 - 247 - AIRFLOW GENERATION IN A TUNNEL USING A SACCARDO VENTILATION SYSTEM AGAINST THE BUOYANCY EFFECT PRODUCED BY A FIRE J D Castro a, C W Pope a and R D Matthews b a Mott MacDonald Ltd, St Anne House,
- 247 - AIRFLOW GENERATION IN A TUNNEL USING A SACCARDO VENTILATION SYSTEM AGAINST THE BUOYANCY EFFECT PRODUCED BY A FIRE J D Castro a, C W Pope a and R D Matthews b a Mott MacDonald Ltd, St Anne House,
THE EFFECT OF EMBEDMENT DEPTH ON BEARING CAPACITY OF STRIP FOOTING IN COHESIVE FRICTIONAL MEDIUM
 Proceedings of the 4 th International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2018), 9~11 February 2018, KUET, Khulna, Bangladesh (ISBN-978-984-34-3502-6) THE EFFECT OF EMBEDMENT
Proceedings of the 4 th International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2018), 9~11 February 2018, KUET, Khulna, Bangladesh (ISBN-978-984-34-3502-6) THE EFFECT OF EMBEDMENT
Experimental Investigation of a Model Jack-Up Unit on Clay
 Proceedings of the Eleventh (21) h~ternational Offshore and Polar Engineerblg Conference Stavanget; Norway, June 17-22, 21 Copyright 21 by The International Society of Offshore and Polar Engineers ISBN
Proceedings of the Eleventh (21) h~ternational Offshore and Polar Engineerblg Conference Stavanget; Norway, June 17-22, 21 Copyright 21 by The International Society of Offshore and Polar Engineers ISBN
An Introduction to Deep Foundations
 An Introduction to Deep Foundations J. Paul Guyer, P.E., R.A. Paul Guyer is a registered mechanical engineer, civil engineer, fire protection engineer and architect with over 35 years experience in the
An Introduction to Deep Foundations J. Paul Guyer, P.E., R.A. Paul Guyer is a registered mechanical engineer, civil engineer, fire protection engineer and architect with over 35 years experience in the
Autodesk Moldflow Communicator Process settings
 Autodesk Moldflow Communicator 212 Process settings Revision 1, 3 March 211. Contents Chapter 1 Process settings....................................... 1 Profiles.................................................
Autodesk Moldflow Communicator 212 Process settings Revision 1, 3 March 211. Contents Chapter 1 Process settings....................................... 1 Profiles.................................................
Research Reports. The University of Western Australia 41
 Research Reports The University of Western Australia 41 Research Reports Numerical modelling techniques A variety of conventional numerical analyses have been conducted in 2011 to investigate the behaviours
Research Reports The University of Western Australia 41 Research Reports Numerical modelling techniques A variety of conventional numerical analyses have been conducted in 2011 to investigate the behaviours
Application of Expansive Soil Geotechnical Procedures
 Application of Expansive Soil Geotechnical Procedures FPA PRESENTATION John T. Bryant, Ph.D., P.G., P.E with Robert L. Lytton, Ph.D., PE. And Mr. Dean Read HOUSTON, TEXAS WEDNESDAY DECEMBER 10, 2008 2008
Application of Expansive Soil Geotechnical Procedures FPA PRESENTATION John T. Bryant, Ph.D., P.G., P.E with Robert L. Lytton, Ph.D., PE. And Mr. Dean Read HOUSTON, TEXAS WEDNESDAY DECEMBER 10, 2008 2008
ISOLATION OF NON-HYDROSTATIC REGIONS WITHIN A BASIN
 ISOLATION OF NON-HYDROSTATIC REGIONS WITHIN A BASIN Bridget M. Wadzuk 1 (Member, ASCE) and Ben R. Hodges 2 (Member, ASCE) ABSTRACT Modeling of dynamic pressure appears necessary to achieve a more robust
ISOLATION OF NON-HYDROSTATIC REGIONS WITHIN A BASIN Bridget M. Wadzuk 1 (Member, ASCE) and Ben R. Hodges 2 (Member, ASCE) ABSTRACT Modeling of dynamic pressure appears necessary to achieve a more robust
Saturated-Unsaturated Consolidation
 Introduction Saturated-Unsaturated Consolidation This example looks at the volume change behavior of a saturated-unsaturated column under loading, wetting and drying conditions. Feature Highlights GeoStudio
Introduction Saturated-Unsaturated Consolidation This example looks at the volume change behavior of a saturated-unsaturated column under loading, wetting and drying conditions. Feature Highlights GeoStudio
TACKLING JACK-UP RIG NO-GO LOCATIONS. Prakasha Kuppalli ABSTRACT
 TACKLING JACK-UP RIG NO-GO LOCATIONS Prakasha Kuppalli ABSTRACT Jack-up rigs are deployed for drilling and work-over (maintenance) of offshore oil and gas wells for producing hydrocarbons. Rigs drill through
TACKLING JACK-UP RIG NO-GO LOCATIONS Prakasha Kuppalli ABSTRACT Jack-up rigs are deployed for drilling and work-over (maintenance) of offshore oil and gas wells for producing hydrocarbons. Rigs drill through
Calibration and Validation of the Shell Fatigue Model Using AC10 and AC14 Dense Graded Hot Mix Asphalt Fatigue Laboratory Data
 Article Calibration and Validation of the Shell Fatigue Model Using AC10 and AC14 Dense Graded Hot Mix Asphalt Fatigue Laboratory Data Mofreh Saleh University of Canterbury, Private Bag 4800, Christchurch,
Article Calibration and Validation of the Shell Fatigue Model Using AC10 and AC14 Dense Graded Hot Mix Asphalt Fatigue Laboratory Data Mofreh Saleh University of Canterbury, Private Bag 4800, Christchurch,
Theory of a vertically loaded Suction Pile in CLAY
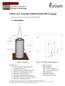 11 Theory of a vertically loaded Suction Pile in CLAY Mainly based on the et Norske Veritas NV-RP-E303 1. Convention Water COG h L Soil COG t Figure 1 Suction Pile Figure 2 Suction pile with main parameters
11 Theory of a vertically loaded Suction Pile in CLAY Mainly based on the et Norske Veritas NV-RP-E303 1. Convention Water COG h L Soil COG t Figure 1 Suction Pile Figure 2 Suction pile with main parameters
DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF A RIG FOR THE PRESSURE TESTING OF WEAK VESSELS AND SUBSEQUENT WORK RELATING TO THE STRENGTH OF FLAT PLATES
 DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF A RIG FOR THE PRESSURE TESTING OF WEAK VESSELS AND SUBSEQUENT WORK RELATING TO THE STRENGTH OF FLAT PLATES D.F. Pilkington Ph.D. B.Sc(Eng)*, G Piatt B.Sc.*, G. Norton B.Sc.**
DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF A RIG FOR THE PRESSURE TESTING OF WEAK VESSELS AND SUBSEQUENT WORK RELATING TO THE STRENGTH OF FLAT PLATES D.F. Pilkington Ph.D. B.Sc(Eng)*, G Piatt B.Sc.*, G. Norton B.Sc.**
Critical face pressure and backfill pressure in shield TBM tunneling on soft ground
 Critical face pressure and backfill pressure in shield TBM tunneling on soft ground Kiseok Kim 1), Juyoung Oh 2), Hyobum Lee 3) and Hangseok Choi 4) 1), 3), 4) Department of civil engineering, Korea University,
Critical face pressure and backfill pressure in shield TBM tunneling on soft ground Kiseok Kim 1), Juyoung Oh 2), Hyobum Lee 3) and Hangseok Choi 4) 1), 3), 4) Department of civil engineering, Korea University,
Laboratory studies of water column separation
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Laboratory studies of water column separation To cite this article: R Autrique and E Rodal 2013 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 52
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Laboratory studies of water column separation To cite this article: R Autrique and E Rodal 2013 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 52
Experimental Investigation of Clear-Water Local Scour at Pile Groups
 Experimental Investigation of Clear-Water Local Scour at Pile Groups B. Ataie-Ashtiani 1 and A. A. Beheshti 2 Abstract: Experiments of local scour around pile groups are carried out under steady clear-water
Experimental Investigation of Clear-Water Local Scour at Pile Groups B. Ataie-Ashtiani 1 and A. A. Beheshti 2 Abstract: Experiments of local scour around pile groups are carried out under steady clear-water
CENGRS GEOTECHNICA PVT. LTD. Job No Sheet No. 1
 CENGRS GEOTECHNICA PVT. LTD. Job No. 214030 Sheet No. 1 INTERIM REPORT ON GEOTECHNICAL INVESTIGATION FOR PROPOSED 66 KV GRID PLOT AT G-7, DWARKA, NEW DELHI. 1.0 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Project Description M/s.
CENGRS GEOTECHNICA PVT. LTD. Job No. 214030 Sheet No. 1 INTERIM REPORT ON GEOTECHNICAL INVESTIGATION FOR PROPOSED 66 KV GRID PLOT AT G-7, DWARKA, NEW DELHI. 1.0 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Project Description M/s.
Supporting Capacity of Short Suction Anchor based on Numerical Modeling
 The 2012 World Congress on Advances in Civil, Environmental, and Materials Research (ACEM 12) Seoul, Korea, August 26-30, 2012 Supporting Capacity of Short Suction Anchor based on Numerical Modeling *Jaehun
The 2012 World Congress on Advances in Civil, Environmental, and Materials Research (ACEM 12) Seoul, Korea, August 26-30, 2012 Supporting Capacity of Short Suction Anchor based on Numerical Modeling *Jaehun
Cyclic loading of shallow offshore foundations on sand
 Cyclic loading of shallow offshore foundations on sand B.W. Byrne, G.T. Houlsby & C.M. Martin Department of Engineering Science, The University of Oxford, United Kingdom ABSTRACT: A significant challenge
Cyclic loading of shallow offshore foundations on sand B.W. Byrne, G.T. Houlsby & C.M. Martin Department of Engineering Science, The University of Oxford, United Kingdom ABSTRACT: A significant challenge
INTERACTION BETWEEN WIND-DRIVEN AND BUOYANCY-DRIVEN NATURAL VENTILATION Bo Wang, Foster and Partners, London, UK
 INTERACTION BETWEEN WIND-DRIVEN AND BUOYANCY-DRIVEN NATURAL VENTILATION Bo Wang, Foster and Partners, London, UK ABSTRACT Ventilation stacks are becoming increasingly common in the design of naturally
INTERACTION BETWEEN WIND-DRIVEN AND BUOYANCY-DRIVEN NATURAL VENTILATION Bo Wang, Foster and Partners, London, UK ABSTRACT Ventilation stacks are becoming increasingly common in the design of naturally
The Challenge of Wave Scouring Design for the Confederation Bridge
 13: Coastal and Ocean Engineering ENGI.8751 Undergraduate Student Forum Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science, Memorial University, St. John s, NL, Canada MARCH 2013 Paper Code. (13 - walsh) The Challenge
13: Coastal and Ocean Engineering ENGI.8751 Undergraduate Student Forum Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science, Memorial University, St. John s, NL, Canada MARCH 2013 Paper Code. (13 - walsh) The Challenge
Department of Civil & Geological Engineering GEOE Engineering Geology
 Department of Civil & Geological Engineering GEOE 218.3 Engineering Geology Assignment #3, Head, Pore Pressure & Effective Stress Due 08 Oct, 2010 NOTE: Numbered subscripts indicate depth, in metres, below
Department of Civil & Geological Engineering GEOE 218.3 Engineering Geology Assignment #3, Head, Pore Pressure & Effective Stress Due 08 Oct, 2010 NOTE: Numbered subscripts indicate depth, in metres, below
Numerical simulation of an intermediate sized bubble rising in a vertical pipe
 Computational Methods in Multiphase Flow V 111 Numerical simulation of an intermediate sized bubble rising in a vertical pipe J. Hua 1, S. Quan 2 & J. Nossen 1 1 Department of Process and Fluid Flow Technology,
Computational Methods in Multiphase Flow V 111 Numerical simulation of an intermediate sized bubble rising in a vertical pipe J. Hua 1, S. Quan 2 & J. Nossen 1 1 Department of Process and Fluid Flow Technology,
E.2 CAP SETTLEMENT RA D AND OUTBOARD
 DRAFT ONONDAGA LAKE CAPPING, DREDGING AND HABITAT INTERMEDIATE DESIGN E.2 CAP SETTLEMENT RA D AND OUTBOARD Parsons P;\Honeywell-SYR\444576 2008 Capping\09 Reports\9.1 Capping and Dredge Area & Depth IDS\Appendices\Appendix
DRAFT ONONDAGA LAKE CAPPING, DREDGING AND HABITAT INTERMEDIATE DESIGN E.2 CAP SETTLEMENT RA D AND OUTBOARD Parsons P;\Honeywell-SYR\444576 2008 Capping\09 Reports\9.1 Capping and Dredge Area & Depth IDS\Appendices\Appendix
FC-CIV HIDRCANA: Channel Hydraulics Flow Mechanics Review Fluid Statics
 FC-CIV HIDRCANA: Channel Hydraulics Flow Mechanics Review Fluid Statics Civil Engineering Program, San Ignacio de Loyola University Objective Calculate the forces exerted by a fluid at rest on plane or
FC-CIV HIDRCANA: Channel Hydraulics Flow Mechanics Review Fluid Statics Civil Engineering Program, San Ignacio de Loyola University Objective Calculate the forces exerted by a fluid at rest on plane or
THE STABILITY OF THE PIPELINE LAID ON A PORO-ELASTIC SEABED
 www.arpapress.com/volumes/vol17issue1/ijrras_17_1_04.pdf THE STABILITY OF THE PIPELINE LAID ON A PORO-ELASTIC SEABED Ren Yanrong Science School, Beijing Institute of Civil Engineering and Architecture,
www.arpapress.com/volumes/vol17issue1/ijrras_17_1_04.pdf THE STABILITY OF THE PIPELINE LAID ON A PORO-ELASTIC SEABED Ren Yanrong Science School, Beijing Institute of Civil Engineering and Architecture,
Copyright ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA , United States.
 LastD 4429 93 standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because it may not be technically possible to adequately
LastD 4429 93 standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because it may not be technically possible to adequately
Flow and Mixing in the Liquid between Bubbles
 Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2009 Boston Flow and Mixing in the Liquid between Bubbles Bruce A. Finlayson, Professor Emeritus of Chemical Engineering Department of Chemical Engineering,
Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2009 Boston Flow and Mixing in the Liquid between Bubbles Bruce A. Finlayson, Professor Emeritus of Chemical Engineering Department of Chemical Engineering,
A FINITE ELEMENT PROCEDURE TO MODEL THE EFFECT OF HYDROSTATIC TESTING ON SUBSEQUENT FATIGUE CRACK GROWTH
 Proceedings of the International Pipeline Conference & Exposition IPC216 September 26-3, 216, Calgary, Alberta, Canada IPC216-64563 A FINITE ELEMENT PROCEDURE TO MODEL THE EFFECT OF HYDROSTATIC TESTING
Proceedings of the International Pipeline Conference & Exposition IPC216 September 26-3, 216, Calgary, Alberta, Canada IPC216-64563 A FINITE ELEMENT PROCEDURE TO MODEL THE EFFECT OF HYDROSTATIC TESTING
Presented to the International Technical Rescue Symposium, November Abstract
 Presented to the International Technical Rescue Symposium, November 21 Presented by: Chuck Weber, PMI Quality Manager Abstract This paper presents the results of 162 individual drop tests performed at
Presented to the International Technical Rescue Symposium, November 21 Presented by: Chuck Weber, PMI Quality Manager Abstract This paper presents the results of 162 individual drop tests performed at
Mat-Supported Jack-Up Foundation On Soft Clay Overturning Storm Stability
 Mat-Supported Jack-Up Foundation On Soft Clay Overturning Storm Stability W.P. Stewart, with support from various companies and consultants. Stewart Technology Associates Abstract The Maleo Producer is
Mat-Supported Jack-Up Foundation On Soft Clay Overturning Storm Stability W.P. Stewart, with support from various companies and consultants. Stewart Technology Associates Abstract The Maleo Producer is
Workshop 1: Bubbly Flow in a Rectangular Bubble Column. Multiphase Flow Modeling In ANSYS CFX Release ANSYS, Inc. WS1-1 Release 14.
 Workshop 1: Bubbly Flow in a Rectangular Bubble Column 14. 5 Release Multiphase Flow Modeling In ANSYS CFX 2013 ANSYS, Inc. WS1-1 Release 14.5 Introduction This workshop models the dispersion of air bubbles
Workshop 1: Bubbly Flow in a Rectangular Bubble Column 14. 5 Release Multiphase Flow Modeling In ANSYS CFX 2013 ANSYS, Inc. WS1-1 Release 14.5 Introduction This workshop models the dispersion of air bubbles
Vibration Related Testing for Hermetic Compressor Development
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1978 Vibration Related Testing for Hermetic Compressor Development J. P. Elson Follo this
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1978 Vibration Related Testing for Hermetic Compressor Development J. P. Elson Follo this
Friction properties of the face of a hand-held tennis racket
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 34 (2012 ) 544 549 9 th Conference of the International Sports Engineering Association (ISEA) Friction properties of the face of a hand-held
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 34 (2012 ) 544 549 9 th Conference of the International Sports Engineering Association (ISEA) Friction properties of the face of a hand-held
Analysis of Shear Lag in Steel Angle Connectors
 University of New Hampshire University of New Hampshire Scholars' Repository Honors Theses and Capstones Student Scholarship Spring 2013 Analysis of Shear Lag in Steel Angle Connectors Benjamin Sawyer
University of New Hampshire University of New Hampshire Scholars' Repository Honors Theses and Capstones Student Scholarship Spring 2013 Analysis of Shear Lag in Steel Angle Connectors Benjamin Sawyer
REPORT GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION FOR THE PROPOSED BLOCK-7 SUB-STATION SY NO-225, NEAR RAYACHERLU VILLAGE
 REPORT ON GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION FOR THE PROPOSED BLOCK-7 SUB-STATION SY NO-225, NEAR RAYACHERLU VILLAGE CLIENT: KARNATAKA SOLAR POWER DEVELOPMENT CORPORATION BANGALORE 0 GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION
REPORT ON GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION FOR THE PROPOSED BLOCK-7 SUB-STATION SY NO-225, NEAR RAYACHERLU VILLAGE CLIENT: KARNATAKA SOLAR POWER DEVELOPMENT CORPORATION BANGALORE 0 GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION
DNVGL-RP-E303 Edition April 2017
 RECOMMENDED PRACTICE DNVGL-RP-E303 Edition April 2017 Geotechnical design and installation of suction anchors in clay The electronic pdf version of this document, available free of charge from http://www.dnvgl.com,
RECOMMENDED PRACTICE DNVGL-RP-E303 Edition April 2017 Geotechnical design and installation of suction anchors in clay The electronic pdf version of this document, available free of charge from http://www.dnvgl.com,
Appendix E BACKGROUND TO STRAIN GAUGE AND EXTENSOMETER CALIBRATIONS. R. Frederking and D. Sudom
 Appendix E BACKGROUND TO STRAIN GAUGE AND EXTENSOMETER CALIBRATIONS R. Frederking and D. Sudom Table of contents 1. Strain Gauge Calibrations... 1 1.1 Variation of strain gauge factor with location around
Appendix E BACKGROUND TO STRAIN GAUGE AND EXTENSOMETER CALIBRATIONS R. Frederking and D. Sudom Table of contents 1. Strain Gauge Calibrations... 1 1.1 Variation of strain gauge factor with location around
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF PIPELINE GLOBAL WALKING WITH SPANNING AND LATERAL BUCKLING
 Proceedings of the ASME 2014 33rd International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE2014 June 8-13, 2014, San Francisco, California, USA OMAE2014-24159 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF PIPELINE
Proceedings of the ASME 2014 33rd International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE2014 June 8-13, 2014, San Francisco, California, USA OMAE2014-24159 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF PIPELINE
Fluid-Structure Interaction Analysis of a Flow Control Device
 Abaqus Technology Brief Fluid-Structure Interaction Analysis of a Control Device TB-06-FSI-2 Revised: April 2007. Summary The Vernay VernaFlo flow controls are custom-designed fluid flow management devices
Abaqus Technology Brief Fluid-Structure Interaction Analysis of a Control Device TB-06-FSI-2 Revised: April 2007. Summary The Vernay VernaFlo flow controls are custom-designed fluid flow management devices
ANALYSIS OF THE POSITIVE FORCES EXHIBITING ON THE MOORING LINE OF COMPOSITE-TYPE SEA CAGE
 194 He, W., Li, C.: Analysis of the positive forces exhibiting on ANALYSIS OF THE POSITIVE FORCES EXHIBITING ON THE MOORING LINE OF COMPOSITE-TYPE SEA CAGE Wei He 1* Chunliu Li 2 1 Ocean College, Agricultural
194 He, W., Li, C.: Analysis of the positive forces exhibiting on ANALYSIS OF THE POSITIVE FORCES EXHIBITING ON THE MOORING LINE OF COMPOSITE-TYPE SEA CAGE Wei He 1* Chunliu Li 2 1 Ocean College, Agricultural
Pressure Plate Drying and Wetting
 1 Introduction Pressure Plate Drying and Wetting This air flow example illustrates how the process of axis translation, which is used in pressure plates to measure the water content function, can be modeled.
1 Introduction Pressure Plate Drying and Wetting This air flow example illustrates how the process of axis translation, which is used in pressure plates to measure the water content function, can be modeled.
REPORT GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION FOR THE PROPOSED BLOCK-1 SUB-STATION SY NO-44, NEAR KYATAGANACHERLU VILLAGE
 REPORT ON GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION FOR THE PROPOSED BLOCK-1 SUB-STATION SY NO-44, NEAR KYATAGANACHERLU VILLAGE CLIENT: KARNATAKA SOLAR POWER DEVELOPMENT CORPORATION BANGALORE 0 GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION
REPORT ON GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION FOR THE PROPOSED BLOCK-1 SUB-STATION SY NO-44, NEAR KYATAGANACHERLU VILLAGE CLIENT: KARNATAKA SOLAR POWER DEVELOPMENT CORPORATION BANGALORE 0 GEO-TECHNICAL INVESTIGATION
V-H-M Yield Surface describing Soil Structure Interaction of Sub-sea Structures and Wind Turbines on Caisson Foundations in Soft Clays
 NGM 2016 Reykjavik Proceedings of the 17 th Nordic Geotechnical Meeting Challenges in Nordic Geotechnic 25 th 28 th of May V-H-M Yield Surface describing Soil Structure Interaction of Sub-sea Structures
NGM 2016 Reykjavik Proceedings of the 17 th Nordic Geotechnical Meeting Challenges in Nordic Geotechnic 25 th 28 th of May V-H-M Yield Surface describing Soil Structure Interaction of Sub-sea Structures
HCMTCB MATERIALS SAMPLING & TESTING PERFORMANCE CHECKLIST
 HCMTCB MATERIALS SAMPLING & TESTING PERFORMANCE CHECKLIST Release Date: January 7, 2014 Sampling Coarse Aggregate PERFORMANCE CHECKLIST AASHTO T-2 Sampling of Aggregates Sampling From A Stockpile 1 When
HCMTCB MATERIALS SAMPLING & TESTING PERFORMANCE CHECKLIST Release Date: January 7, 2014 Sampling Coarse Aggregate PERFORMANCE CHECKLIST AASHTO T-2 Sampling of Aggregates Sampling From A Stockpile 1 When
Aalborg Universitet. Published in: Proceedings of Offshore Wind 2007 Conference & Exhibition. Publication date: 2007
 Aalborg Universitet Design Loads on Platforms on Offshore wind Turbine Foundations with Respect to Vertical Wave Run-up Damsgaard, Mathilde L.; Gravesen, Helge; Andersen, Thomas Lykke Published in: Proceedings
Aalborg Universitet Design Loads on Platforms on Offshore wind Turbine Foundations with Respect to Vertical Wave Run-up Damsgaard, Mathilde L.; Gravesen, Helge; Andersen, Thomas Lykke Published in: Proceedings
Hardware Triaxial and Consolidation Testing Systems Pressure Measurement and Control
 25 GDS Helpsheet Hardware Triaxial and Consolidation Testing Systems Pressure Measurement and Control World Leaders in Computer Controlled Testing Systems for Geotechnical Engineers and Geologists 1. Digital
25 GDS Helpsheet Hardware Triaxial and Consolidation Testing Systems Pressure Measurement and Control World Leaders in Computer Controlled Testing Systems for Geotechnical Engineers and Geologists 1. Digital
Behavior of Square Footing Resting on Reinforced Sand Subjected to Static Load
 IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 3 Issue 02 July 2016 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 Behavior of Square Footing Resting on Reinforced Sand Subjected to Static
IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 3 Issue 02 July 2016 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 Behavior of Square Footing Resting on Reinforced Sand Subjected to Static
SEMI-SPAN TESTING IN WIND TUNNELS
 25 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES SEMI-SPAN TESTING IN WIND TUNNELS S. Eder, K. Hufnagel, C. Tropea Chair of Fluid Mechanics and Aerodynamics, Darmstadt University of Technology
25 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES SEMI-SPAN TESTING IN WIND TUNNELS S. Eder, K. Hufnagel, C. Tropea Chair of Fluid Mechanics and Aerodynamics, Darmstadt University of Technology
Module 3: Hydrostatic forces on submerged bodies Lecture 7: Calculation of horizontal component, buoyancy. Forces on submerged bodies (continued)
 Forces on submerged bodies (continued) Buoyancy file:///d /Web%20Course/Dr.%20Nishith%20Verma/local%20server/fluid_mechanics/lecture7/7_1.htm[5/9/2012 3:05:26 PM] Forces on submerged bodies (continued)
Forces on submerged bodies (continued) Buoyancy file:///d /Web%20Course/Dr.%20Nishith%20Verma/local%20server/fluid_mechanics/lecture7/7_1.htm[5/9/2012 3:05:26 PM] Forces on submerged bodies (continued)
EN M '
 THE AMERICAN SOCIETY OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERS 345 E. 47th St New York, N.Y. 10017 The Society shall not be responsible for statements or opinions advancedin papers or &Scission at meetings of the Society
THE AMERICAN SOCIETY OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERS 345 E. 47th St New York, N.Y. 10017 The Society shall not be responsible for statements or opinions advancedin papers or &Scission at meetings of the Society
Effect of Coiled Capillary Tube Pitch on Vapour Compression Refrigeration System Performance
 Effect of Coiled Capillary Tube Pitch on Vapour Compression Refrigeration System Performance Mutalubi Aremu Akintunde Federal University of Technology, Department of Mechanical Engineering Akure, Ondo
Effect of Coiled Capillary Tube Pitch on Vapour Compression Refrigeration System Performance Mutalubi Aremu Akintunde Federal University of Technology, Department of Mechanical Engineering Akure, Ondo
EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF VAPOUR BUBBLE GROWING ON A HEATED SURFACE
 EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF VAPOUR BUBBLE GROWING ON A HEATED SURFACE T.A. KOWALEWSKI, R. TRZCIŃSKI, A. CYBULSKI 1, J. PAKLEZA, M.-C. DULUC 2 ABSTRACT Using high speed video camera and numerical processing
EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF VAPOUR BUBBLE GROWING ON A HEATED SURFACE T.A. KOWALEWSKI, R. TRZCIŃSKI, A. CYBULSKI 1, J. PAKLEZA, M.-C. DULUC 2 ABSTRACT Using high speed video camera and numerical processing
A model for the bubble lift-off diameter in subcooled boiling flow in a horizontal channel
 Advances in Fluid Mechanics X 215 A model for the bubble lift-off diameter in subcooled boiling flow in a horizontal channel S. Shabannejad & N. Ashgriz Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering,
Advances in Fluid Mechanics X 215 A model for the bubble lift-off diameter in subcooled boiling flow in a horizontal channel S. Shabannejad & N. Ashgriz Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering,
INSTALLATION CONSTRAINTS OF SUCTION ASSISTED FOUNDATIONS AND ANCHORS FOR OFFSHORE ENERGY DEVELOPMENT
 Geotec., Const. Mat. & Env., DOI: https://doi.org/10.21660/2018.47.3695 ISSN: 2186-2982 (Print), 2186-2990 (Online), Japan INSTALLATION CONSTRAINTS OF SUCTION ASSISTED FOUNDATIONS AND ANCHORS FOR OFFSHORE
Geotec., Const. Mat. & Env., DOI: https://doi.org/10.21660/2018.47.3695 ISSN: 2186-2982 (Print), 2186-2990 (Online), Japan INSTALLATION CONSTRAINTS OF SUCTION ASSISTED FOUNDATIONS AND ANCHORS FOR OFFSHORE
