Suction caisson extraction resistance in Gulf of Guinea clay
|
|
|
- Barrie Gallagher
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics III Meyer (Ed.) 2015 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN: Suction caisson extraction resistance in Gulf of Guinea clay C. Gaudin, M.F. Randolph, S. Gourvenec, C.D. O Loughlin & D.J. White Centre for Offshore Foundation Systems, The University of Western Australia, Australia J.-L. Colliat TOTAL E&P, Pau, France ABSTRACT: This paper presents the results and interpretation of a series of centrifuge tests performed to model the extraction of stiffened and unstiffened suction caissons in Angola clay. Parameters investigated during the testing programme included (i) the setup time after installation, which varied between 0 and 360 days, and (ii) the extraction rate, which spanned over three orders of magnitude. The interpretation revealed fundamental aspects of the caisson behaviour notably associated with the installation soil kinematics, and its influence during the subsequent extraction on both the internal and external friction, and their evolution with setup time. The effect of setup time can be reasonably approximated using conventional cavity expansion theory followed by radial consolidation. The effect of the extraction rate can be assessed using a total stress analysis but accounting for both strain rate effects and consolidation occurring while mobilising the peak extraction resistance. Recommended friction factors and bearing capacity factors are provided accounting for the parameters investigated. 1 INTRODUCTION The capacity of suction caissons is governed by different mechanisms associated with soil softening/ hardening at the wall interface and soil kinematics around the tip and stiffeners. These mechanisms are relatively well understood (see notably Andersen et al. 2005), but depend strongly on the caisson geometry and the mechanical characteristics of the soil. Establishing geotechnical design parameters therefore remains challenging and may require modelling exercises to account for specific features of the caisson geometry or soil conditions encountered at the site. In 2006, Total E&P initiated a centrifuge testing programme undertaken by IFSTTAR (formerly LCPC) to assist in the design of suction caissons used in an oil development in the Gulf of Guinea, offshore Angola. The programme was prompted by the specific features of the Gulf of Guinea seabed material, which notably exhibits a high plasticity index (from 70 to 150), a yield stress ratio greater than 1 (associated with post-sedimentation structural and bonding effects), and a high sensitivity (from 3 to 6). A comprehensive review of Gulf of Guinea sediment characteristics is presented in Colliat et al. (2010a). The centrifuge test programme focused on the installation of suction caissons with and without internal stiffeners, and the subsequent sealed extraction capacity, as a function of loading rate and postinstallation consolidation time (Colliat et al. 2010b). Results provided insights into the suction caisson performance, but also raised issues, notably related to the very low inferred interface friction (when compared to the soil remoulded strength) and a limited dependence of the caisson capacity on the setup time. To investigate further and potentially settle these issues, a second set of centrifuge tests, featuring a nearly identical testing programme was performed at UWA. That programme is the subject of this paper. Gaudin et al. (2014) presented the first part of the testing outcomes, focusing on the installation results and on the effect of the internal ring stiffeners on the penetration resistance. It was demonstrated that very limited soil flow occurred around the ring stiffeners as water became trapped between the stiffeners. This results in essentially zero inner skin friction, so the penetration resistance could be accurately predicted assuming a nominal internal friction, τ in = 1 kpa above the first stiffener, an external friction factor, α ex = τ ex /s u of 0.3, a caisson skirt tip bearing factor of 7.5 and a bearing factor on the first stiffener (only) increasing from 5 to 15 with penetration depth to account for the additional work to extrude the soil plug as the caisson penetrates. This result was on contrast with IFSTTAR results where a gap between the stiffeners and the wall allowed water to freely move along the wall so inner skin friction could be generated. The paper presents the second part of the testing outcomes, focusing on the extraction capacity as a function of ring stiffeners, setup time and pullout rate. It highlights the importance of strain rate effects and strength recovery. 251
2 2 CENTRIFUGE MODELLING The centrifuge soil sample characteristics, suction caisson models and testing procedure have been presented extensively in Gaudin et al. (2014) and are covered here in brief. Table 1. Suction caisson prototype dimensions. 2.1 Soil sample characteristics Gulf of Guinea clay was mixed with fresh water to reconstitute normally consolidated samples with similar water content profile to that in-situ. Shear strength profiles, inferred from in-flight T-bar penetrometer tests performed at normalised velocity v/d of 0.25, have a strength at mudline of s um = 1.3 kpa and strength gradients k ranging from 1 kpa/m to 1.4 kpa/m during the course of tests conducted in each sample. The latter value aligns with lower bound shear strength profiles measured in-situ. Caisson capacities have been scaled to reflect an average strength gradient of 1.2 kpa/m. Piezocone dissipation tests indicated a coefficient of consolidation c v of about 3 m 2 /year at σ v = 55 kpa. However, significant other differences were observed between the centrifuge samples and in-situ soil. These relate notably to the shear strength ratio, s u /σ vo, and the soil sensitivity, S t, which were both significantly lower for the centrifuge samples ( 0.28 against 0.45 and 1.7 against 3 6, respectively). Laboratory tests showed that the differences were not due to different salinity of the pore fluid (the centrifuge sample being reconstituted with added fresh water), but from structural and bonding effects, present in-situ, which could not be recreated by the sample reconstitution process. An important feature of Gulf of Guinea clay is its relatively high strength rate dependency. The increase in shear strength per log cycle increase in shearing rate range from 16 to 19%, based on CU triaxial tests performed over six orders of magnitude of strain rates (Colliat et al. 2010a). 2.2 Suction caisson models Two suction caisson models were manufactured, with overall geometry summarised in Table 1 in prototype dimensions (at a scaling ratio of 1:200). The models represent an 8 m diameter and 24 m long prototype suction caisson, used to anchor riser towers in Site C of block B17, offshore Angola (Colliat et al., 2007). The unstiffened caisson model, labelled USC, featured a flush skirt, 0.08 m thick, slightly thicker than the m used in-situ (due to machining constraints). No surface treatment was applied on the skirt, resulting in a relatively smooth interface. The stiffened caisson model, labelled SC, featured 5 horizontal ring stiffeners 0.58 m wide (measured in the horizontal plane, as compared to m in-situ) and 0.2 m thick (measured in the vertical plane). The first ring stiffener is located 4 m from the base of the caisson, with the subsequent stiffeners spaced 4 m apart. The model caissons were machined from a full block of duraluminium. There were no gaps between the stiffeners and the caisson inner surface where water could travel freely up the inner skirt. This was demonstrated in Gaudin et al. (2014) to influence significantly the soil kinematics around the stiffeners, resulting in very little soil flow round the stiffeners. 2.3 Testing programme and procedure The testing programme included 11 tests featuring vented and sealed extraction, at normalised pullout rates of vd/c v of 0.42 and 168.2, and after consolidation prototype periods of 0, 30 and 366 days. Four of these cases were performed using the unstiffened caisson (USC) and eight used the stiffened caisson (SC). Note that vd/c v = corresponds to fully undrained conditions and that the difference in extraction rates translates into a difference in undrained strength of about 44% (based on 17% increase in strength per log cycle increase in rate). For tests at vd/c v = 168.2, the interpretation uses the strength inferred from T-bar tests without rate correction. The test names reflect the sample the test was performed in (S1 or S2), the type of caisson (stiffened SC or unstiffened USC), the test number, the extraction mode (s for sealed or v for vented) and the extraction rate (q for vd/c v = or s for 0.42). Following penetration (either jacked or by selfweight followed by suction), the suction caisson was maintained in place ( z = 0) for the required consolidation period, before being pulled out under displacement control at the targeted velocity v. The purpose of the vented extraction tests was to provide direct insight into changes in external and internal friction (since no plug uplift takes place) with setup time and pullout rate. The vented tests enable the post-consolidation changes in friction factor to be isolated, at least for the combined internal and external friction (separate assessment can be made assuming an internal to external friction ratio). 252
3 Table 2. Summary of extraction results. Peak Consol. Extract. extract. period rate resist. Proto. T v Extract. vd/c v Tests (d) ( ) mode ( ) F e (MN) S1-USC4vq V S2-USC4vs 0 0 V S1-SC5vq V S2-SC5vs V S2-SC7vs V S2-USC3sq S S1-SC1sq S S2-SC1sq S S1-SC2ss S S2-SC2ss S S2-SC6ss S RESULTS 3.1 Summary of results Table 2 presents the peak extraction resistance for each test. The time factor T v characterising the level of consolidation for each test is introduced and defined as c v t/d 2 eq, where t is the consolidation time and D eq the caisson equivalent diameter (Randolph 2003). Although there are some anomalies, the following trends are noted: Effect of sealing. Sealed extraction of the stiffened caissons evidently exhibits higher capacity than vented extraction due to the base resistance of the soil plug. Effect of stiffeners on internal friction. For vented extraction, unstiffened caissons have a higher extraction resistance than stiffened caissons. This indicates that the stiffened caissons have lower inner friction, even after recovery post-installation. Effect of stiffeners on external friction and plug uplift resistance. By contrast, for sealed extraction, stiffened caissons exhibit higher capacity than unstiffened caissons, indicating higher external friction (taking plug uplift resistance as unaffected). Observed effect of extraction rate. The capacity of both vented and sealed caissons is reduced by the 500-fold reduction in extraction rate in the slow tests. The magnitude of this effect depends on the presence of stiffeners and the consolidation period. Capacity is reduced by about for the vented stiffened caissons (comparing S1-SC5vq with S2- SC5vs and S2-SC7vs) and with the low end of this range observed at shorter consolidation times. The effect of rate is only 1.2 for vented unstiffened caissons, although this comparison is made for different consolidation times (comparing (S1-USC4vq and S2-USC4vs). The sealed stiffened caissons exhibit a reduction in capacity with decreasing extraction rate of 1.05 after 30 days of consolidation (see tests S1-SC1sq and S1-SC2ss) and of about 1.65 after about 366 days consolidation (see tests S2-SC1sq and S2-SC2ss). Theoretical effect of extraction rate. Direct allowance for strain rate effects via the typical soil element response (Colliat et al. 2010) suggests a ratio of about 1.44 between the two different extraction rates (at identical consolidation time). Evidently, for both the vented and sealed extraction, other factors influence the caisson capacity. Effect of consolidation time. For vd/c v = 168.2, there is an evident increase of stiffened caisson extraction resistance with consolidation time of about 1.4 from 27.2 days of consolidation (test S1-SC1sq) to 357 (test S2-SC1sq). No effect of consolidation time is observed for vd/c v = Back calculation of design parameters Vented rapid extraction. Design parameters are first calculated for vd/c v = and 32 days of consolidation. According to the consolidation solution of Teh and Houlsby (1991), about 30% of full primary consolidation is expected after 32 days for the conditions considered in this study. The predicted extraction resistance for vented test S1-USC4vq is calculated as the sum of the internal and external friction, and reverse end bearing at the skirt tip for which a bearing factor of N c,tip = 7.5 is adopted. The experimental result is best fitted by assuming external and internal friction factors of α ex = 0.87 and α in = 0.53, respectively, i.e. 2.3 times the value deduced from penetration (see Gaudin et al. 2014). The ratio α ex /α in was taken as 1.63 (although this figure may not be strictly appropriate for the present tests), following Jeanjean et al. (2006) who observed lower consolidation inside the caisson from centrifuge model tests featuring double-wall caisson. The exercise is repeated for the stiffened caisson, assuming a nominal internal friction above the first stiffener of 1 kpa (resulting from no soil flow round the stiffeners during penetration). This yields an external friction factor of Predicted and measured extraction resistances are compared in Figure 1. Vented slow extraction. For tests at vd/c v = 0.42, there is uncertainty about the exact drainage conditions, and hence what intrinsic differences in frictional capacity might be expected between rapid (undrained) and slow (quasi-drained) extraction. The difference in capacity observed for the unstiffened caissons is relatively small. There is also evidence (essentially for piles), that drained and undrained shaft capacities show little differences, with similar changes in normal effective stresses. The soil caisson system is not a constant stress system, but more closely resembles a constant volume system. Accordingly, drained shearing may reduce the normal effective stress due to volumetric collapse of the sheared material, just as undrained shearing reduces the normal effective stress due to generation of excess pore pressure. In practice, the drained capacity might be estimated as a function of the effective stress σ h and the drained friction angle 253
4 Figure 1. Vented unstiffened and stiffened caissons predicted and measured extraction resistances for vd/c v = δ r. However, following the above consideration and acknowledging the difficulty in predicting both the change in effective stresses and the interface friction angle, it is more convenient to use the same friction factor approach to predict the slow capacity, noting that αs u = σ h tanδ r. Another advantage of this approach is the ability to account directly for strain rate effects. Figure 2 presents the predicted extraction resistance for both the stiffened and unstiffened caisson. The extraction resistance has been factored down by 44% to account for a reduction in strength of 44% due to the difference in strain rates. In contrast to test S1-USC4vq, identical internal and external friction factors are assumed for test S2-USC4vs since extraction was performed immediately after penetration. For the unstiffened caisson, a friction factor of 0.86 provides the best fit. This value is higher than the average value of 0.7 obtained for the faster test S1-USC4vq (Fig. 1, combining internal and external friction factors), which experienced a higher (initial) consolidation time (32 days against 0). There is however an evident time effect at vd/c v = 0.42, due to the long period required for the peak extraction resistance to be mobilised. For test S2-UCS4vs, although extraction began after 32 days of consolidation, the peak extraction resistance was only mobilised after 509 days, potentially resulting in about 78% of consolidation (against the estimated 30% for the fast 32-day test, S1-USC4vq). However, if consolidation is assumed to take place, the assumption of identical external and internal friction factors may no longer be valid.assuming the same distribution, as for test S1-USC4vq, would result in external and internal friction factors of α ex = 1.08 and α in = 0.65 (after 78% consolidation) compared to the values of α ex = 0.87 and α in = 0.53 (after 30% of consolidation).this is broadly consistent. Figure 2. Vented unstiffened and stiffened caissons, predicted and measured extraction resistances for vd/c v = 0.42, accounting for strain rate effects. Sealed extraction. The capacity of the sealed suction caisson is subsequently predicted assuming passive suction is mobilised (as demonstrated by the pore pressures of about kpa at caisson base, not presented in the paper). The net undrained uplift capacity of the caisson (i.e. excluding the caisson submerged weight) is expressed as the sum of a reverse end bearing component at the caisson base and the external friction along the caisson skirt, noting that the overburden component at the tip level is cancelled by the weight of the soil plug. The data were fitted using a value of 5 for the plug bearing capacity N c,plug. This is lower than the range of suggested (Andersen et al. 2005), but reflects the limited displacements (averaging around 0.1D) required to reach peak capacity, essentially accounting for the fact that full mobilisation of the reverse end bearing component does not coincide with the peak of the overall extraction resistance. For 32 days of consolidation, back calculated values of the external friction factor α ex are 0.4 and 0.6 for the unstiffened and stiffened caissons, respectively. The value of 0.6 for the stiffened caisson is consistent with the value of 0.54 obtained for unstiffened vented extraction. For the unstiffened caisson a lower value of α ex of 0.4 is required, assuming a plug bearing factor identical to the stiffened caisson (an assumption justified by pore pressure measurements at the base, not presented in the paper). This value is consistent with the values inferred for the stiffened caisson, assuming that slower consolidation takes place for the latter (as discussed later in the paper). However, it contrasts with the value of α ex = 0.87 obtained for the vented extraction. A possible explanation relates to the test 254
5 Table 3. Design parameters after 30 days of consolidation. Table 4. Measured and back-calculated friction factors. Caisson Extract. N c,tip N c,plug α ex α in Unstiff. Vented 7.5 N/A Sealed N/A N/A Stiff. Vented 7.5 N/A 0.54 (1 kpa) Sealed N/A N/A procedure for the vented caisson, whereas penetration was undertaken beyond touchdown, pushing the plug within the soil and generating higher excess pore pressures around the caisson that would take longer to dissipate. For extraction at vd/c v = 0.42, α ex = 1.27, 1.01 and 1.28 is calculated for tests S1-SC2ss, S2-SC2ss and S2-SC6ss, respectively (accounting for strain rate effects). These values are relatively high, but consistent with the value of 1.17 obtained after 366 days for stiffened caisson tests at vd/c v = The calculated friction factors are summarised in Table 3 for tests at vd/c v = and 30 days of consolidation. 4 DISCUSSION 4.1 Effect of internal ring stiffeners Internal ring stiffeners have an effect on the suction caisson capacity. Comparison of tests S2-USC3sq and S2-SC1sq indicates that the stiffeners increased the undrained vertical sealed capacity by a ratio of Analysis of both the penetration (see Gaudin et al. 2014) and extraction stages has demonstrated that the internal friction is reduced to nearly zero. The water entrapped between the ring stiffeners prevents full flow around the stiffeners, limiting the contribution of the internal friction to the total penetration resistance to less than 5%. There is no regain of internal friction with consolidation (demonstrated from the vented extraction results). However, this does not affect the undrained uplift capacity of the sealed stiffened caisson, which was measured to be 64% higher than for the unstiffened caisson, after 366 days of consolidation, indicating a higher external friction for stiffened caissons. This is most likely related to the soil flow during penetration. Due to the presence of the stiffeners, more soil is expected to flow outside the caisson, generating (after consolidation) higher effective stresses along the caisson external walls and, consequently, higher friction (although a longer time scale for consolidation). For the vented extraction (i.e. without contribution of the plug uplift), the higher soil displacement and external friction is overshadowed by the negligible internal friction, resulting in the unstiffened caisson exhibiting a higher vented undrained uplift capacity by a factor of Effect of consolidation time and pullout rate Interpretation of piezocone tests performed in the centrifuge samples yielded a t 50 time of about 95 days for Cons. time (d) T v = c v t/d 2 eq U = u/ u i (%) 0% 30% 73% 78% 84% 89% α ex CET Stiff Sea Stiff Ven. Unstif. 0.4 Sea. Unstif Ven. the caissons, and t 90 of more than 1500 days. Accordingly, significant setup is expected between 30 and 366 days, the two consolidation periods used during testing. Indeed, the capacity of sealed stiffened caissons extracted at vd/c v = increases by a ratio of 1.41 after 366 days of consolidation. This translates into an increase in external friction factor from 0.60 to The latter value is slightly higher than the value predicted using conventional cylindrical cavity expansion theory (CET) for open piles (Randolph 2003). The prediction is presented in Table 4 for the full consolidation range, assuming a residual interface friction angle δ r of 21 (obtained from direct shear tests performed at 0.05 mm/min), a rigidity index G/s u of 100 relevant for Gulf of Guinea clay (Low et al. 2010), and a remoulded strength immediately after penetration of 0.3 (consistent with the friction factor of 0.3 back calculated during penetration). The cavity expansion analysis captures reasonably well the increase in external friction factor with consolidation time for the stiffened caisson, and can be used confidently for design, provided that the soil sensitivity used is corrected to reflect the estimated friction factor at zero consolidation. As discussed, the difference in extraction rate results in a difference in shear strength of about 44%, which does not totally account for the measured differences in capacity. During slow extraction, the peak resistance is reached after a significant time, comparable with consolidation times. As a result, excess pore pressure present at the beginning of the process will dissipate further, adding consolidation to what was already achieved during the post-installation consolidation phase. The superposition of these two aspects (consolidation and strain rate) explains the increase in difference in uplift capacity between tests performed at vd/c v = and vd/c v = Slow extraction tests experienced a much greater degree of consolidation by the time failure occurred, resulting in a larger setup and higher friction, which balances the reduction in strength due to strain rate. This is illustrated symbolically in Fig. 3, where a constant difference in capacity is observed provided that the consolidation time is corrected to reflect the time to reach peak capacity. The point is further demonstrated in Table 4, where friction 255
6 Figure 3. rates. Combined effects of consolidation time and strain ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This work forms part of the activities of the Centre for Offshore Foundation Systems (COFS), currently supported as a node of the Australian Research Council Centre of Excellence for Geotechnical Science and Engineering. The centrifuge programme and subsequent interpretation were funded by Total E&P, which support is gratefully acknowledged. Centrifuge tests were performed with the assistance of Manuel Palacios, Dave Jones and John Breen. REFERENCES Figure 4. Evolution of external and internal friction factors with time factor. factors calculated for test at vd/c v = 0.42, accounting for rate effects and corrected for additional consolidation, are compared with cavity expansion solutions. The agreement is convincing. 5 CONCLUDING REMARKS Figure 4 presents the set of recommended friction factors gathered in Table 4 as a function of time factor, T v. These values are believed appropriate for design of suction caissons in Block 17 in the Gulf of Guinea, offshore Angola, acknowledging that the absolute values of α back-calculated from the model tests need to be reduced due to strain rate effects, depending on the actual penetration or extraction rates of the caisson. The model caisson tests induce very high shear strain rates along the shaft, which can be estimated as 20 to 40 times the ratio v/d (Einav and Randolph 2006). This gives an average strain rate of about 30%/s for tests at vd/c v = 168.2, which is 4 orders of magnitude higher than typical laboratory strain rates. This would require α to be factored by 0.6 for design, reducing the value at 900 days from an average 1.14 to 0.69, a value closer to the range of reported by Colliat & Colliard (2010) and suggested by Andersen & Jostad (2002) for full consolidation. Andersen K.H. & Jostad H.P Shear strength along outside wall of suction anchors in clay after installation. Proc. of the 12th International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conf., Kitakyushu. Japan, Andersen K.H., Murff J.D., Randolph M.F., Clukey E.C., Erbrich C.T., Jostad H.P., Hansen B., Aubeny C., Sharma P. & Supachawarote C Suction anchors for deepwater applications. 1st Int. Symp. Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics. Gourvenec & Cassidy (Eds) Colliat J.-L., Colliard D Set-up of suction piles in deepwater Gulf of Guinea clays. Proc. of the 2nd International Symposium on Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics. Gourvenec & White (Eds) Colliat J.-L., Dendani H. & Schroeder, K Installation of suction piles at deepwater sites in Angola. Proc. 6th Int. Offshore Site Investigation and Geotechnics Conf.: Confronting New Challenges and Sharing Knowledge, London, England Colliat J.-L., Dendani H., PuechA. & Nauroy J.-F. 2010a. Gulf of Guinea deepwater sediments: Geotechnical properties, design issues and installation experiences. 2nd Int. Symp. Frontiers in offshore Geotechnics, Gourvenec & White (Eds) Colliat J.-L., Dendani H., Jostad H.P., Andersen K.H., Thorel L., Garnier, J. & Rault, G. 2010b. Centrifuge testing of suction piles in deepwater Nigeria clay Effect of stiffeners and setup time. 2nd Int. Symp. Frontiers in offshore Geotechnics, Gourvenec & White (Eds) Einav I. & Randolph M.F Effect of strain rate on mobilised strength and thickness of curved shear bands. Géotechnique. 56(7): Gaudin C., O Loughlin C.D., Hossain M.S., Randolph M.F. & Colliat J.-L Installation of suction caissons in Gulf of Guinea clay. Proc. of the 8th International Conf. on Physical Modelling in Geotechnics, Perth, Australia. 1: Jeanjean P., Znidarcic D., Phillips R., Ko H. Y., Pfister S. & Schroeder K Centrifuge testing on suction anchors: double-wall, stiff clays, and layered soil profile. Offshore Technology Conf., Houston. OTC Low H.E., Lunne T., Andersen K.H., Sjursen M.A., Li X. & Randolph M.F Estimation of intact and remoulded undrained shear strength from penetration tests in soft clays. Géotechnique. 60(11): Randolph M.F Science and empiricism in pile foundation design. Géotechnique. 53(10): Teh C.I. & Houlsby G. T An analytical study of the cone penetration test in clay. Géotechnique. 41(1):
The tensile capacity of suction caissons in sand under rapid loading
 Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics: ISFOG 25 Gourvenec & Cassidy (eds) 25 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 415 3963 X The tensile capacity of suction caissons in sand under rapid loading Guy T. Houlsby,
Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics: ISFOG 25 Gourvenec & Cassidy (eds) 25 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 415 3963 X The tensile capacity of suction caissons in sand under rapid loading Guy T. Houlsby,
Theory of a vertically loaded Suction Pile in CLAY
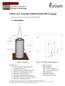 11 Theory of a vertically loaded Suction Pile in CLAY Mainly based on the et Norske Veritas NV-RP-E303 1. Convention Water COG h L Soil COG t Figure 1 Suction Pile Figure 2 Suction pile with main parameters
11 Theory of a vertically loaded Suction Pile in CLAY Mainly based on the et Norske Veritas NV-RP-E303 1. Convention Water COG h L Soil COG t Figure 1 Suction Pile Figure 2 Suction pile with main parameters
Learn more at
 Full scale model tests of a steel catenary riser C. Bridge 1, H. Howells 1, N. Toy 2, G. Parke 2, R. Woods 2 1 2H Offshore Engineering Ltd, Woking, Surrey, UK 2 School of Engineering, University of Surrey,
Full scale model tests of a steel catenary riser C. Bridge 1, H. Howells 1, N. Toy 2, G. Parke 2, R. Woods 2 1 2H Offshore Engineering Ltd, Woking, Surrey, UK 2 School of Engineering, University of Surrey,
CHAPTER 5: VACUUM TEST WITH VERTICAL DRAINS
 CHAPTER 5: VACUUM TEST WITH VERTICAL DRAINS 5.1 Introduction Using surcharging as the sole soil consolidation mean can take a long time to reach the desired soil settlement. Soil consolidation using prefabricated
CHAPTER 5: VACUUM TEST WITH VERTICAL DRAINS 5.1 Introduction Using surcharging as the sole soil consolidation mean can take a long time to reach the desired soil settlement. Soil consolidation using prefabricated
Installation and Monotonic Pullout of a Suction Caisson Anchor in. Calcareous Silt
 1 Submitted January 2016, Revised May 2016 2 3 4 Installation and Monotonic Pullout of a Suction Caisson Anchor in Calcareous Silt 5 6 Kai Xiang Koh 1, Muhammad Shazzad Hossain 2 and Youngho Kim 3 7 8
1 Submitted January 2016, Revised May 2016 2 3 4 Installation and Monotonic Pullout of a Suction Caisson Anchor in Calcareous Silt 5 6 Kai Xiang Koh 1, Muhammad Shazzad Hossain 2 and Youngho Kim 3 7 8
Pressuremeters in Geotechnical Design
 Pressuremeters in Geotechnical Design B.G. CLARKE Department of Civil Engineering University of Newcastle upon Tyne BLACK1E ACADEMIC & PROFESSIONAL An Imprint of Chapman & Hall London Glasgow Weinheim
Pressuremeters in Geotechnical Design B.G. CLARKE Department of Civil Engineering University of Newcastle upon Tyne BLACK1E ACADEMIC & PROFESSIONAL An Imprint of Chapman & Hall London Glasgow Weinheim
Installation of Stiffened Caissons in Nonhomogeneous Clays Published in: DOI: Document Version General rights Take down policy
 Installation of Stiffened Caissons in Nonhomogeneous Clays Zhou, M., Hossain, M., Hu, Y., & Liu, H. (2016). Installation of Stiffened Caissons in Nonhomogeneous Clays. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmentral
Installation of Stiffened Caissons in Nonhomogeneous Clays Zhou, M., Hossain, M., Hu, Y., & Liu, H. (2016). Installation of Stiffened Caissons in Nonhomogeneous Clays. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmentral
Strength assessment during shallow penetration of a sphere in clay
 Morton, J. P. et al. (24) Géotechnique Letters 4, 262 266, http://dx.doi.org/.68/geolett.4.49 Strength assessment during shallo penetration of a sphere in clay J. P. MORTON*, C. D. O LOUGHLIN* and D. J.
Morton, J. P. et al. (24) Géotechnique Letters 4, 262 266, http://dx.doi.org/.68/geolett.4.49 Strength assessment during shallo penetration of a sphere in clay J. P. MORTON*, C. D. O LOUGHLIN* and D. J.
OMAE INVESTIGATING THE RESPONSE OF OFFSHORE FOUNDATIONS IN SOFT CLAY SOILS
 Proceedings of OMAE st International Conference on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering June 3-8, Oslo, Norway OMAE-857 INVESTIGATING THE RESPONSE OF OFFSHORE FOUNDATIONS IN SOFT CLAY SOILS B.W. Byrne
Proceedings of OMAE st International Conference on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering June 3-8, Oslo, Norway OMAE-857 INVESTIGATING THE RESPONSE OF OFFSHORE FOUNDATIONS IN SOFT CLAY SOILS B.W. Byrne
An experimental study of inflatable offshore anchors in soft clay
 An experimental study of inflatable offshore anchors in soft clay T.A. Newson and F.W. Smith Department of Civil Engineering, University of Dundee P. Brunning Stolt Offshore MS Ltd., Aberdeen Introduction
An experimental study of inflatable offshore anchors in soft clay T.A. Newson and F.W. Smith Department of Civil Engineering, University of Dundee P. Brunning Stolt Offshore MS Ltd., Aberdeen Introduction
Performance of Anchors for Floating Offshore Windfarms
 Geotechnical Engineering for US Offshore Wind Infrastructure Boston April 25, 2016 Performance of Anchors for Floating Offshore Windfarms Charles Aubeny Texas A&M University Background: Multi-Line Attachment
Geotechnical Engineering for US Offshore Wind Infrastructure Boston April 25, 2016 Performance of Anchors for Floating Offshore Windfarms Charles Aubeny Texas A&M University Background: Multi-Line Attachment
Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
 43 Module 3: Lecture - 5 on Compressibility and Consolidation Contents Stresses in soil from surface loads; Terzaghi s 1-D consolidation theory; Application in different boundary conditions; Ramp loading;
43 Module 3: Lecture - 5 on Compressibility and Consolidation Contents Stresses in soil from surface loads; Terzaghi s 1-D consolidation theory; Application in different boundary conditions; Ramp loading;
CONE PENETRATION TESTS
 February 25, 2015 John Doe, P.E. Acme Engineering and Testing 1234 Test Avenue, Suite 204 Lake Wales, FL 33853 Re: Sample CPT Soundings Dear Mr. Doe, Direct Push Services, LLC (DPS) was retained by Acme
February 25, 2015 John Doe, P.E. Acme Engineering and Testing 1234 Test Avenue, Suite 204 Lake Wales, FL 33853 Re: Sample CPT Soundings Dear Mr. Doe, Direct Push Services, LLC (DPS) was retained by Acme
INCLINED LOAD CAPACITY OF SUCTION CAISSON IN CLAY
 INCLINED LOAD CAPACITY OF SUCTION CAISSON IN CLAY by CHAIRAT SUPACHAWAROTE This thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy at The University of Western Australia School of Civil and Resource
INCLINED LOAD CAPACITY OF SUCTION CAISSON IN CLAY by CHAIRAT SUPACHAWAROTE This thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy at The University of Western Australia School of Civil and Resource
DNVGL-RP-E303 Edition April 2017
 RECOMMENDED PRACTICE DNVGL-RP-E303 Edition April 2017 Geotechnical design and installation of suction anchors in clay The electronic pdf version of this document, available free of charge from http://www.dnvgl.com,
RECOMMENDED PRACTICE DNVGL-RP-E303 Edition April 2017 Geotechnical design and installation of suction anchors in clay The electronic pdf version of this document, available free of charge from http://www.dnvgl.com,
Supporting Capacity of Short Suction Anchor based on Numerical Modeling
 The 2012 World Congress on Advances in Civil, Environmental, and Materials Research (ACEM 12) Seoul, Korea, August 26-30, 2012 Supporting Capacity of Short Suction Anchor based on Numerical Modeling *Jaehun
The 2012 World Congress on Advances in Civil, Environmental, and Materials Research (ACEM 12) Seoul, Korea, August 26-30, 2012 Supporting Capacity of Short Suction Anchor based on Numerical Modeling *Jaehun
Offshore engineering science
 Offshore engineering science In this research stream theoretical models advanced geotechnical models and new numerical techniques were used in applied offshore engineering topics such as loading, design
Offshore engineering science In this research stream theoretical models advanced geotechnical models and new numerical techniques were used in applied offshore engineering topics such as loading, design
Drum Centrifuge Model Tests Comparing the Performance of Spudcans and Caissons in Kaolin Clay
 Drum Centrifuge Model Tests Comparing the Performance of Spudcans and Caissons in Kaolin Clay by M.J. Cassidy and B.W. Byrne Report No. OUEL 48/ University of Oxford Department of Engineering Science Parks
Drum Centrifuge Model Tests Comparing the Performance of Spudcans and Caissons in Kaolin Clay by M.J. Cassidy and B.W. Byrne Report No. OUEL 48/ University of Oxford Department of Engineering Science Parks
OTC Copyright 2008, Offshore Technology Conference
 OTC 19545 Comparison of Jackup Rig Spudcan Penetration Methods in Clay David Menzies, Fugro-McClelland Marine Geosciences, Inc., and Richard Roper, ENSCO International, Inc. Copyright 2008, Offshore Technology
OTC 19545 Comparison of Jackup Rig Spudcan Penetration Methods in Clay David Menzies, Fugro-McClelland Marine Geosciences, Inc., and Richard Roper, ENSCO International, Inc. Copyright 2008, Offshore Technology
On the Bearing Capacity of Suction Bucket Foundations in Saturated Sand
 The Open Ocean Engineering Journal,,, 45-49 45 Open Access On the Bearing Capacity of Suction Bucket Foundations in Saturated Sand Bintian Jiao* Xiaobing Lu and Zhongmin Shi Institute of Mechanics, Chinese
The Open Ocean Engineering Journal,,, 45-49 45 Open Access On the Bearing Capacity of Suction Bucket Foundations in Saturated Sand Bintian Jiao* Xiaobing Lu and Zhongmin Shi Institute of Mechanics, Chinese
INSTALLATION CONSTRAINTS OF SUCTION ASSISTED FOUNDATIONS AND ANCHORS FOR OFFSHORE ENERGY DEVELOPMENT
 Geotec., Const. Mat. & Env., DOI: https://doi.org/10.21660/2018.47.3695 ISSN: 2186-2982 (Print), 2186-2990 (Online), Japan INSTALLATION CONSTRAINTS OF SUCTION ASSISTED FOUNDATIONS AND ANCHORS FOR OFFSHORE
Geotec., Const. Mat. & Env., DOI: https://doi.org/10.21660/2018.47.3695 ISSN: 2186-2982 (Print), 2186-2990 (Online), Japan INSTALLATION CONSTRAINTS OF SUCTION ASSISTED FOUNDATIONS AND ANCHORS FOR OFFSHORE
STRIDE PROJECT Steel Risers in Deepwater Environments Achievements
 STRIDE PROJECT Steel Risers in Deepwater Environments Achievements 1999-21 Neil Willis Principal Engineer 2H Offshore Engineering 6 th Annual Deepwater Technologies and Developments Conference 21 The presentation
STRIDE PROJECT Steel Risers in Deepwater Environments Achievements 1999-21 Neil Willis Principal Engineer 2H Offshore Engineering 6 th Annual Deepwater Technologies and Developments Conference 21 The presentation
Vertical Uplift Capacity of a Group of Equally Spaced Helical Screw Anchors in Sand
 SECM/15/080 Vertical Uplift Capacity of a Group of Equally Spaced Helical Screw Anchors in Sand S. Mukherjee 1* and Dr. S. Mittal 2 1 Amity University, Noida, India 2 Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee,
SECM/15/080 Vertical Uplift Capacity of a Group of Equally Spaced Helical Screw Anchors in Sand S. Mukherjee 1* and Dr. S. Mittal 2 1 Amity University, Noida, India 2 Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee,
Typical factors of safety for bearing capacity calculation in different situations
 Typical factors of safety for bearing capacity calculation in different situations Density of soil: In geotechnical engineering, one deals with several densities such as dry density, bulk density, saturated
Typical factors of safety for bearing capacity calculation in different situations Density of soil: In geotechnical engineering, one deals with several densities such as dry density, bulk density, saturated
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON OPTIMUM INSTALLATION DEPTH OF PVD UNDER VACUUM CONSOLIDATION ABSTRACT
 EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON OPTIMUM INSTALLATION DEPTH OF PVD UNDER VACUUM CONSOLIDATION EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON OPTIMUM INSTALLATION DEPTH OF PVD UNDER VACUUM CONSOLIDATION J.-C CHAI i), N. MIURA
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON OPTIMUM INSTALLATION DEPTH OF PVD UNDER VACUUM CONSOLIDATION EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON OPTIMUM INSTALLATION DEPTH OF PVD UNDER VACUUM CONSOLIDATION J.-C CHAI i), N. MIURA
Suction anchor foundations for tension and taut leg floaters in deep waters. Tension Leg Platform. Taut Leg Platform. upper chain. risers.
 Case history: Soil investigation for offshore suction anchors anchor foundations for tension and taut leg floaters in deep waters Alternative anchors for floating structures pile Over last 5 - years anchoring
Case history: Soil investigation for offshore suction anchors anchor foundations for tension and taut leg floaters in deep waters Alternative anchors for floating structures pile Over last 5 - years anchoring
Aalborg Universitet. Published in: Proceedings of Offshore Wind 2007 Conference & Exhibition. Publication date: 2007
 Aalborg Universitet Design Loads on Platforms on Offshore wind Turbine Foundations with Respect to Vertical Wave Run-up Damsgaard, Mathilde L.; Gravesen, Helge; Andersen, Thomas Lykke Published in: Proceedings
Aalborg Universitet Design Loads on Platforms on Offshore wind Turbine Foundations with Respect to Vertical Wave Run-up Damsgaard, Mathilde L.; Gravesen, Helge; Andersen, Thomas Lykke Published in: Proceedings
SUCTION CAISSON FOUNDATIONS FOR OFFSHORE WIND TURBINES
 SUCTION CAISSON FOUNDATIONS FOR OFFSHORE WIND TURBINES Felipe A. Villalobos Oxford University felipe.villalobos@eng.ox.ac.uk Guy T. Houlsby Oxford University guy.houlsby@eng.ox.ac.uk Byron W. Byrne Oxford
SUCTION CAISSON FOUNDATIONS FOR OFFSHORE WIND TURBINES Felipe A. Villalobos Oxford University felipe.villalobos@eng.ox.ac.uk Guy T. Houlsby Oxford University guy.houlsby@eng.ox.ac.uk Byron W. Byrne Oxford
Comparison and Sensitivity Investigations of a CALM and SALM Type Mooring System for Wave Energy Converters
 J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 214, 2, 93-122; doi:1.339/jmse2193 Article OPEN ACCESS Journal of Marine Science and Engineering ISSN 277-1312 www.mdpi.com/journal/jmse Comparison and Sensitivity Investigations of a
J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 214, 2, 93-122; doi:1.339/jmse2193 Article OPEN ACCESS Journal of Marine Science and Engineering ISSN 277-1312 www.mdpi.com/journal/jmse Comparison and Sensitivity Investigations of a
UNIT-I SOIL EXPLORATION
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : Geotechnical Engineering - II (16CE127) Year & Sem: III-B.Tech & II-Sem
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : Geotechnical Engineering - II (16CE127) Year & Sem: III-B.Tech & II-Sem
Desaturating sand deposit by air injection for reducing liquefaction potential
 Desaturating sand deposit by air injection for reducing liquefaction potential M. Ishihara, M. Okamura & T. Oshita Public Works Research Institute, Tsukuba City, Japan. ABSTRACT: It has been known that
Desaturating sand deposit by air injection for reducing liquefaction potential M. Ishihara, M. Okamura & T. Oshita Public Works Research Institute, Tsukuba City, Japan. ABSTRACT: It has been known that
Bearing Capacity and Settlement Response of PMS Tanks on Cohesionless Soil Lithology in Lekki, Lagos of Nigeria
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Applied Engineering and Scientific Research,, ():- (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN: 8 Bearing Capacity and
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Applied Engineering and Scientific Research,, ():- (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN: 8 Bearing Capacity and
Influence of Settlement on Bearing Capacity Analysis of Shallow Foundations on Sandy Clays in the Niger Delta, Nigeria
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Applied Engineering and Scientific Research, 201, 2 (4):20-27 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN: 22 0041 Influence
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Applied Engineering and Scientific Research, 201, 2 (4):20-27 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN: 22 0041 Influence
DESIGN AND INSTALLATION OF DRAG ANCHORS AND PLATE ANCHORS
 Guidance Notes on Design and Installation of Drag Anchors and Plate Anchors GUIDANCE NOTES ON DESIGN AND INSTALLATION OF DRAG ANCHORS AND PLATE ANCHORS MARCH 2017 American Bureau of Shipping Incorporated
Guidance Notes on Design and Installation of Drag Anchors and Plate Anchors GUIDANCE NOTES ON DESIGN AND INSTALLATION OF DRAG ANCHORS AND PLATE ANCHORS MARCH 2017 American Bureau of Shipping Incorporated
Anchors for Floating Structures Don Murff, TAMU/OTRC
 Anchors for Floating Structures Don Murff, TAMU/OTRC Floating structures that are moored impose a variety of load conditions on the anchor system. These loads range from vertical uplift loads for a TLP
Anchors for Floating Structures Don Murff, TAMU/OTRC Floating structures that are moored impose a variety of load conditions on the anchor system. These loads range from vertical uplift loads for a TLP
Learn more at
 STRIDE JIP Phase III SUT Talk 15th November 2 Offshore VIV monitoring (vortex induced vibration) Catenary riser interaction with deepwater seabeds 3 Full Scale Riser Monitoring To get real measurements
STRIDE JIP Phase III SUT Talk 15th November 2 Offshore VIV monitoring (vortex induced vibration) Catenary riser interaction with deepwater seabeds 3 Full Scale Riser Monitoring To get real measurements
Analysis of dilatometer test in calibration chamber
 Analysis of dilatometer test in calibration chamber Lech Bałachowski Gdańsk University of Technology, Poland Keywords: calibration chamber, DMT, quartz sand, FEM ABSTRACT: Because DMT in calibration test
Analysis of dilatometer test in calibration chamber Lech Bałachowski Gdańsk University of Technology, Poland Keywords: calibration chamber, DMT, quartz sand, FEM ABSTRACT: Because DMT in calibration test
E.2 CAP SETTLEMENT RA D AND OUTBOARD
 DRAFT ONONDAGA LAKE CAPPING, DREDGING AND HABITAT INTERMEDIATE DESIGN E.2 CAP SETTLEMENT RA D AND OUTBOARD Parsons P;\Honeywell-SYR\444576 2008 Capping\09 Reports\9.1 Capping and Dredge Area & Depth IDS\Appendices\Appendix
DRAFT ONONDAGA LAKE CAPPING, DREDGING AND HABITAT INTERMEDIATE DESIGN E.2 CAP SETTLEMENT RA D AND OUTBOARD Parsons P;\Honeywell-SYR\444576 2008 Capping\09 Reports\9.1 Capping and Dredge Area & Depth IDS\Appendices\Appendix
Cyclic loading of shallow offshore foundations on sand
 Cyclic loading of shallow offshore foundations on sand B.W. Byrne, G.T. Houlsby & C.M. Martin Department of Engineering Science, The University of Oxford, United Kingdom ABSTRACT: A significant challenge
Cyclic loading of shallow offshore foundations on sand B.W. Byrne, G.T. Houlsby & C.M. Martin Department of Engineering Science, The University of Oxford, United Kingdom ABSTRACT: A significant challenge
OP CHECKLIST FOR 1D CONSOLIDATION LABORATORY TEST
 Page 1 of 5 WORK INSTRUCTIONS FOR ENGINEERS NHB Compiled by : LSS Checked by : GSS Approved by : OP-3-31. CHECKLIST FOR 1D CONSOLIDATION LABORATORY TEST Page 2 of 5 31.0 CHECKLIST ITEMS *(refer to respective
Page 1 of 5 WORK INSTRUCTIONS FOR ENGINEERS NHB Compiled by : LSS Checked by : GSS Approved by : OP-3-31. CHECKLIST FOR 1D CONSOLIDATION LABORATORY TEST Page 2 of 5 31.0 CHECKLIST ITEMS *(refer to respective
Response Analysis of a Suction Pile Under the Influence of Mooring Tension
 Volume 1, Issue 1, pp. 4-8, 017. ISSN (Online): 456-7361 Response Analysis of a Suction Pile Under the Influence of Mooring Tension Ezenwankwo J. U. 1, Azubike N. D., Awuchi C. G. 3 1, 3 School of Engineering
Volume 1, Issue 1, pp. 4-8, 017. ISSN (Online): 456-7361 Response Analysis of a Suction Pile Under the Influence of Mooring Tension Ezenwankwo J. U. 1, Azubike N. D., Awuchi C. G. 3 1, 3 School of Engineering
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF ELASTIC BEHAVIOR OF SUCTION CAISSON. A Dissertation YUZE ZHANG
 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF ELASTIC BEHAVIOR OF SUCTION CAISSON A Dissertation by YUZE ZHANG Submitted to the Office of Graduate and Professional Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF ELASTIC BEHAVIOR OF SUCTION CAISSON A Dissertation by YUZE ZHANG Submitted to the Office of Graduate and Professional Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of
GEOTECHNICAL PERFORMANCE OF SPUDCAN FOUNDATIONS
 Guidance Notes on Geotechnical Performance of Spudcan Foundations GUIDANCE NOTES ON GEOTECHNICAL PERFORMANCE OF SPUDCAN FOUNDATIONS JANUARY 2017 (Updated March 2018 see next page) American Bureau of Shipping
Guidance Notes on Geotechnical Performance of Spudcan Foundations GUIDANCE NOTES ON GEOTECHNICAL PERFORMANCE OF SPUDCAN FOUNDATIONS JANUARY 2017 (Updated March 2018 see next page) American Bureau of Shipping
Influence of effective stress on swelling pressure of expansive soils
 ES Web of Conferences 9, 06 (06) DOI: 0.0/ esconf/060906 E-UNSAT 06 Influence of effective stress on swelling pressure of expansive soils,a Wiebke Baille, Linzhi Lang, Snehasis Tripathy and Tom Schanz
ES Web of Conferences 9, 06 (06) DOI: 0.0/ esconf/060906 E-UNSAT 06 Influence of effective stress on swelling pressure of expansive soils,a Wiebke Baille, Linzhi Lang, Snehasis Tripathy and Tom Schanz
Example 4 - Airbag. Summary
 Example 4 - Airbag Summary This example deals with the deployment of a chambered airbag modeled by monitored volumes using communications. The airbag is initially folded along four fold lines. The fabric
Example 4 - Airbag Summary This example deals with the deployment of a chambered airbag modeled by monitored volumes using communications. The airbag is initially folded along four fold lines. The fabric
Hardware Triaxial and Consolidation Testing Systems Pressure Measurement and Control
 25 GDS Helpsheet Hardware Triaxial and Consolidation Testing Systems Pressure Measurement and Control World Leaders in Computer Controlled Testing Systems for Geotechnical Engineers and Geologists 1. Digital
25 GDS Helpsheet Hardware Triaxial and Consolidation Testing Systems Pressure Measurement and Control World Leaders in Computer Controlled Testing Systems for Geotechnical Engineers and Geologists 1. Digital
SUMMARY OF SUBSURFACE STRATIGRAPHY AND MATERIAL PROPERTIES
 Page 1 of 101 Written by: Ming Zhu Date: 08/20/2008 Reviewed by: R. Kulasingam/J. Beech Date: 08/20/2008 SUMMARY OF SUBSURFACE STRATIGRAPHY AND MATERIAL PROPERTIES 1. INTRODUCTION This Summary of Subsurface
Page 1 of 101 Written by: Ming Zhu Date: 08/20/2008 Reviewed by: R. Kulasingam/J. Beech Date: 08/20/2008 SUMMARY OF SUBSURFACE STRATIGRAPHY AND MATERIAL PROPERTIES 1. INTRODUCTION This Summary of Subsurface
Experimental Determination of Temperature and Pressure Profile of Oil Film of Elliptical Journal Bearing
 International Journal of Advanced Mechanical Engineering. ISSN 2250-3234 Volume 4, Number 5 (2014), pp. 469-474 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Experimental Determination of Temperature
International Journal of Advanced Mechanical Engineering. ISSN 2250-3234 Volume 4, Number 5 (2014), pp. 469-474 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Experimental Determination of Temperature
UNIAXIAL BEHAVIOUR OF SUCTION CAISSONS IN SOFT DEPOSITS IN DEEPWATER
 UNIAXIAL BEHAVIOUR OF SUCTION CAISSONS IN SOFT DEPOSITS IN DEEPWATER by Wen CHEN B. Eng. (in Civil), M.Sc. (in Geotech.) A thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy at School of Civil and
UNIAXIAL BEHAVIOUR OF SUCTION CAISSONS IN SOFT DEPOSITS IN DEEPWATER by Wen CHEN B. Eng. (in Civil), M.Sc. (in Geotech.) A thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy at School of Civil and
Experimental Investigations of the Cyclic Response of Suction Caissons in Sand B.W. Byrne and G.T. Houlsby
 OTC 12194 Experimental Investigations of the Cyclic Response of Suction Caissons in Sand B.W. Byrne and G.T. Houlsby Copyright 2, Offshore Technology Conference This paper was prepared for presentation
OTC 12194 Experimental Investigations of the Cyclic Response of Suction Caissons in Sand B.W. Byrne and G.T. Houlsby Copyright 2, Offshore Technology Conference This paper was prepared for presentation
City, University of London Institutional Repository
 City Research Online City, University of London Institutional Repository Citation: Gorasia, R. J., McNamara, A. M. & Rettura, D. (212). Reducing driving forces for pressed-in. Proceedings of the Institution
City Research Online City, University of London Institutional Repository Citation: Gorasia, R. J., McNamara, A. M. & Rettura, D. (212). Reducing driving forces for pressed-in. Proceedings of the Institution
Module 7 Lecture 1. Swelling and Collapse Behavior
 Swelling and Collapse Behavior Module 7 Lecture 1 Collapse and swelling phenomena occur in unsaturated soils during the saturation process. The compacted unsaturated soils, on the dry of optimum, have
Swelling and Collapse Behavior Module 7 Lecture 1 Collapse and swelling phenomena occur in unsaturated soils during the saturation process. The compacted unsaturated soils, on the dry of optimum, have
OMAE INVESTIGATING NOVEL FOUNDATIONS FOR OFFSHORE WINDPOWER GENERATION
 Proceedings of OMAE 2 21 st International Conference on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering June 23-28, 22 Oslo, Norway OMAE22-28423 INVESTIGATING NOVEL FOUNDATIONS FOR OFFSHORE WINDPOWER GENERATION
Proceedings of OMAE 2 21 st International Conference on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering June 23-28, 22 Oslo, Norway OMAE22-28423 INVESTIGATING NOVEL FOUNDATIONS FOR OFFSHORE WINDPOWER GENERATION
Saturated-Unsaturated Consolidation
 Introduction Saturated-Unsaturated Consolidation This example looks at the volume change behavior of a saturated-unsaturated column under loading, wetting and drying conditions. Feature Highlights GeoStudio
Introduction Saturated-Unsaturated Consolidation This example looks at the volume change behavior of a saturated-unsaturated column under loading, wetting and drying conditions. Feature Highlights GeoStudio
Analysis of Shear Lag in Steel Angle Connectors
 University of New Hampshire University of New Hampshire Scholars' Repository Honors Theses and Capstones Student Scholarship Spring 2013 Analysis of Shear Lag in Steel Angle Connectors Benjamin Sawyer
University of New Hampshire University of New Hampshire Scholars' Repository Honors Theses and Capstones Student Scholarship Spring 2013 Analysis of Shear Lag in Steel Angle Connectors Benjamin Sawyer
SOIL IMPROVEMENT BY VACUUM PRELOADING FOR A POWER PLANT PROJECT IN VIETNAM
 18 th Southeast Asian Geotechnical & Inaugural AGSSEA Conference 29-31 May 213, Singapore Leung, Goh & Shen (eds) SOIL IMPROVEMENT BY VACUUM PRELOADING FOR A POWER PLANT PROJECT IN VIETNAM GOUW TJIE-LIONG
18 th Southeast Asian Geotechnical & Inaugural AGSSEA Conference 29-31 May 213, Singapore Leung, Goh & Shen (eds) SOIL IMPROVEMENT BY VACUUM PRELOADING FOR A POWER PLANT PROJECT IN VIETNAM GOUW TJIE-LIONG
PUBLISHED PROJECT REPORT PPR850. Optimisation of water flow depth for SCRIM. S Brittain, P Sanders and H Viner
 PUBLISHED PROJECT REPORT PPR850 Optimisation of water flow depth for SCRIM S Brittain, P Sanders and H Viner Report details Report prepared for: Project/customer reference: Copyright: Highways England,
PUBLISHED PROJECT REPORT PPR850 Optimisation of water flow depth for SCRIM S Brittain, P Sanders and H Viner Report details Report prepared for: Project/customer reference: Copyright: Highways England,
Wave Force Characteristics for Structural Members of Hybrid Marine Structure
 Wave Force Characteristics for Structural Members of Hybrid Marine Structure Youn-JuJeong Research Fellow, Structural Engineering Research Institute, Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology,
Wave Force Characteristics for Structural Members of Hybrid Marine Structure Youn-JuJeong Research Fellow, Structural Engineering Research Institute, Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology,
Numerical Fluid Analysis of a Variable Geometry Compressor for Use in a Turbocharger
 Special Issue Turbocharging Technologies 15 Research Report Numerical Fluid Analysis of a Variable Geometry Compressor for Use in a Turbocharger Yuji Iwakiri, Hiroshi Uchida Abstract A numerical fluid
Special Issue Turbocharging Technologies 15 Research Report Numerical Fluid Analysis of a Variable Geometry Compressor for Use in a Turbocharger Yuji Iwakiri, Hiroshi Uchida Abstract A numerical fluid
MODELLING OF FUME EXTRACTORS C. R.
 LD8 19th International Symposium of Ballistics, 7 11 May 21, Interlaken, Switzerland MODELLING OF FUME EXTRACTORS C. R. Woodley WS4 Guns and Warheads Department, Defence Evaluation and Research Agency,
LD8 19th International Symposium of Ballistics, 7 11 May 21, Interlaken, Switzerland MODELLING OF FUME EXTRACTORS C. R. Woodley WS4 Guns and Warheads Department, Defence Evaluation and Research Agency,
Mat-Supported Jack-Up Foundation On Soft Clay Overturning Storm Stability
 Mat-Supported Jack-Up Foundation On Soft Clay Overturning Storm Stability W.P. Stewart, with support from various companies and consultants. Stewart Technology Associates Abstract The Maleo Producer is
Mat-Supported Jack-Up Foundation On Soft Clay Overturning Storm Stability W.P. Stewart, with support from various companies and consultants. Stewart Technology Associates Abstract The Maleo Producer is
Autodesk Moldflow Communicator Process settings
 Autodesk Moldflow Communicator 212 Process settings Revision 1, 3 March 211. Contents Chapter 1 Process settings....................................... 1 Profiles.................................................
Autodesk Moldflow Communicator 212 Process settings Revision 1, 3 March 211. Contents Chapter 1 Process settings....................................... 1 Profiles.................................................
Flow transients in multiphase pipelines
 Flow transients in multiphase pipelines David Wiszniewski School of Mechanical Engineering, University of Western Australia Prof. Ole Jørgen Nydal Multiphase Flow Laboratory, Norwegian University of Science
Flow transients in multiphase pipelines David Wiszniewski School of Mechanical Engineering, University of Western Australia Prof. Ole Jørgen Nydal Multiphase Flow Laboratory, Norwegian University of Science
Cubzac-les-Ponts Experimental Embankments on Soft Clay
 Cubzac-les-Ponts Experimental Embankments on Soft Clay GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. www.geo-slope.com 1, 7 - th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada TP T Main: +1 3 9 Fax: +1 3 39 Introduction In the 197 s, a series
Cubzac-les-Ponts Experimental Embankments on Soft Clay GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. www.geo-slope.com 1, 7 - th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada TP T Main: +1 3 9 Fax: +1 3 39 Introduction In the 197 s, a series
A comparison of NACA 0012 and NACA 0021 self-noise at low Reynolds number
 A comparison of NACA 12 and NACA 21 self-noise at low Reynolds number A. Laratro, M. Arjomandi, B. Cazzolato, R. Kelso Abstract The self-noise of NACA 12 and NACA 21 airfoils are recorded at a Reynolds
A comparison of NACA 12 and NACA 21 self-noise at low Reynolds number A. Laratro, M. Arjomandi, B. Cazzolato, R. Kelso Abstract The self-noise of NACA 12 and NACA 21 airfoils are recorded at a Reynolds
Gas Gathering System Modeling The Pipeline Pressure Loss Match
 PETROLEUM SOCIETY CANADIAN INSTITUTE OF MINING, METALLURGY & PETROLEUM PAPER 2005-230 Gas Gathering System Modeling The Pipeline Pressure Loss Match R.G. MCNEIL, P.ENG. Fekete Associates Inc. D.R. LILLICO,
PETROLEUM SOCIETY CANADIAN INSTITUTE OF MINING, METALLURGY & PETROLEUM PAPER 2005-230 Gas Gathering System Modeling The Pipeline Pressure Loss Match R.G. MCNEIL, P.ENG. Fekete Associates Inc. D.R. LILLICO,
CONSIDERATION OF DENSITY VARIATIONS IN THE DESIGN OF A VENTILATION SYSTEM FOR ROAD TUNNELS
 - 56 - CONSIDERATION OF DENSITY VARIATIONS IN THE DESIGN OF A VENTILATION SYSTEM FOR ROAD TUNNELS Gloth O., Rudolf A. ILF Consulting Engineers Zürich, Switzerland ABSTRACT This article investigates the
- 56 - CONSIDERATION OF DENSITY VARIATIONS IN THE DESIGN OF A VENTILATION SYSTEM FOR ROAD TUNNELS Gloth O., Rudolf A. ILF Consulting Engineers Zürich, Switzerland ABSTRACT This article investigates the
Critical Pool Level and Stability of Slopes in Granular Soils
 TECHNICAL NOTES Critical Pool Level and Stability of Slopes in Granular Soils Radoslaw L. Michalowski, F.ASCE 1 Abstract: The influence of pore-water pressure and the pool water pressure on stability of
TECHNICAL NOTES Critical Pool Level and Stability of Slopes in Granular Soils Radoslaw L. Michalowski, F.ASCE 1 Abstract: The influence of pore-water pressure and the pool water pressure on stability of
I.CHEM.E. SYMPOSIUM SERIES NO. 97 BUOYANCY-DRIVEN NATURAL VENTILATION OP ENCLOSED SPACES
 BUOYANCY-DRIVEN NATURAL VENTILATION OP ENCLOSED SPACES M. R. Marshall* and P. L. Stewart-Darling* A simple mathematical model for the buoyancy driven ventilation of an enclosed space, using a two-pipe
BUOYANCY-DRIVEN NATURAL VENTILATION OP ENCLOSED SPACES M. R. Marshall* and P. L. Stewart-Darling* A simple mathematical model for the buoyancy driven ventilation of an enclosed space, using a two-pipe
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF WIND PRESSURES ON IRREGULAR- PLAN SHAPE BUILDINGS
 BBAA VI International Colloquium on: Bluff Bodies Aerodynamics & Applications Milano, Italy, July, 2-24 8 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF WIND PRESSURES ON IRREGULAR- PLAN SHAPE BUILDINGS J. A. Amin and A. K. Ahuja
BBAA VI International Colloquium on: Bluff Bodies Aerodynamics & Applications Milano, Italy, July, 2-24 8 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF WIND PRESSURES ON IRREGULAR- PLAN SHAPE BUILDINGS J. A. Amin and A. K. Ahuja
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON THE HYDRODYNAMIC BEHAVIORS OF TWO CONCENTRIC CYLINDERS
 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON THE HYDRODYNAMIC BEHAVIORS OF TWO CONCENTRIC CYLINDERS *Jeong-Rok Kim 1), Hyeok-Jun Koh ), Won-Sun Ruy 3) and Il-Hyoung Cho ) 1), 3), ) Department of Ocean System Engineering, Jeju
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON THE HYDRODYNAMIC BEHAVIORS OF TWO CONCENTRIC CYLINDERS *Jeong-Rok Kim 1), Hyeok-Jun Koh ), Won-Sun Ruy 3) and Il-Hyoung Cho ) 1), 3), ) Department of Ocean System Engineering, Jeju
THE USE OF SPIN FIN PILES IN MASSACHUSETTS
 THE USE OF SPIN FIN PILES IN MASSACHUSETTS Les R. Chernauskas, P.E., Geosciences Testing and Research, Inc., North Chelmsford, MA Leo J. Hart, Geosciences Testing and Research, Inc., North Chelmsford,
THE USE OF SPIN FIN PILES IN MASSACHUSETTS Les R. Chernauskas, P.E., Geosciences Testing and Research, Inc., North Chelmsford, MA Leo J. Hart, Geosciences Testing and Research, Inc., North Chelmsford,
SEMI-SPAN TESTING IN WIND TUNNELS
 25 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES SEMI-SPAN TESTING IN WIND TUNNELS S. Eder, K. Hufnagel, C. Tropea Chair of Fluid Mechanics and Aerodynamics, Darmstadt University of Technology
25 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES SEMI-SPAN TESTING IN WIND TUNNELS S. Eder, K. Hufnagel, C. Tropea Chair of Fluid Mechanics and Aerodynamics, Darmstadt University of Technology
m v = 1.04 x 10-4 m 2 /kn, C v = 1.29 x 10-2 cm 2 /min
 2.10 Problems Example 2.1: Design of Shallow Foundation in Saturated Clay Design a square footing to support a column load of 667 kn. The base of the footing will be located 1 m below the ground level
2.10 Problems Example 2.1: Design of Shallow Foundation in Saturated Clay Design a square footing to support a column load of 667 kn. The base of the footing will be located 1 m below the ground level
382. Fellenius, B.H. and Terceros, M.H., Information on the single pile, static loading tests at B.E.S.T. Proceedings of the 3rd Bolivian
 382. Fellenius, B.H. and Terceros, M.H., 2017. Information on the single pile, static loading tests at B.E.S.T. Proceedings of the 3rd Bolivian International Conference on Deep Foundations, Santa Cruz
382. Fellenius, B.H. and Terceros, M.H., 2017. Information on the single pile, static loading tests at B.E.S.T. Proceedings of the 3rd Bolivian International Conference on Deep Foundations, Santa Cruz
Lateral Load Analysis Considering Soil-Structure Interaction. ANDREW DAUMUELLER, PE, Ph.D.
 Lateral Load Analysis Considering Soil-Structure Interaction ANDREW DAUMUELLER, PE, Ph.D. Overview Introduction Methods commonly used to account for soil-structure interaction for static loads Depth to
Lateral Load Analysis Considering Soil-Structure Interaction ANDREW DAUMUELLER, PE, Ph.D. Overview Introduction Methods commonly used to account for soil-structure interaction for static loads Depth to
ARA PROJECT Prepared by: Peter T. Dzwilewski Applied Research Associates, Inc Shaffer Parkway Littleton, Colorado 80127
 ARA PROJECT 001974 WATER SHOCK PREDICTION FOR EXPLOSIVE REMOVAL OF OFFSHORE STRUCTURES: UNDERWATER CALCULATOR (UWC) VERSION 2.0 UPDATE BASED UPON FIELD DATA Prepared by: Peter T. Dzwilewski Applied Research
ARA PROJECT 001974 WATER SHOCK PREDICTION FOR EXPLOSIVE REMOVAL OF OFFSHORE STRUCTURES: UNDERWATER CALCULATOR (UWC) VERSION 2.0 UPDATE BASED UPON FIELD DATA Prepared by: Peter T. Dzwilewski Applied Research
Figure 1 Schematic of opposing air bearing concept
 Theoretical Analysis of Opposing Air Bearing Concept This concept utilizes air bearings to constrain five degrees of freedom of the optic as shown in the figure below. Three pairs of inherently compensated
Theoretical Analysis of Opposing Air Bearing Concept This concept utilizes air bearings to constrain five degrees of freedom of the optic as shown in the figure below. Three pairs of inherently compensated
Field Testing of Suction Caissons at Bothkennar and Luce Bay
 Field Testing of Suction Caissons at Bothkennar and Luce Bay by G.T. Houlsby, R.B. Kelly, J. Huxtable and B.W. Byrne Report No. OUEL 2276/5 University of Oxford Department of Engineering Science Parks
Field Testing of Suction Caissons at Bothkennar and Luce Bay by G.T. Houlsby, R.B. Kelly, J. Huxtable and B.W. Byrne Report No. OUEL 2276/5 University of Oxford Department of Engineering Science Parks
AERODYNAMICS I LECTURE 7 SELECTED TOPICS IN THE LOW-SPEED AERODYNAMICS
 LECTURE 7 SELECTED TOPICS IN THE LOW-SPEED AERODYNAMICS The sources of a graphical material used in this lecture are: [UA] D. McLean, Understanding Aerodynamics. Arguing from the Real Physics. Wiley, 2013.
LECTURE 7 SELECTED TOPICS IN THE LOW-SPEED AERODYNAMICS The sources of a graphical material used in this lecture are: [UA] D. McLean, Understanding Aerodynamics. Arguing from the Real Physics. Wiley, 2013.
PRESSURE DISTRIBUTION OF SMALL WIND TURBINE BLADE WITH WINGLETS ON ROTATING CONDITION USING WIND TUNNEL
 International Journal of Mechanical and Production Engineering Research and Development (IJMPERD ) ISSN 2249-6890 Vol.2, Issue 2 June 2012 1-10 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd., PRESSURE DISTRIBUTION OF SMALL WIND TURBINE
International Journal of Mechanical and Production Engineering Research and Development (IJMPERD ) ISSN 2249-6890 Vol.2, Issue 2 June 2012 1-10 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd., PRESSURE DISTRIBUTION OF SMALL WIND TURBINE
Presented to the International Technical Rescue Symposium, November Abstract
 Presented to the International Technical Rescue Symposium, November 21 Presented by: Chuck Weber, PMI Quality Manager Abstract This paper presents the results of 162 individual drop tests performed at
Presented to the International Technical Rescue Symposium, November 21 Presented by: Chuck Weber, PMI Quality Manager Abstract This paper presents the results of 162 individual drop tests performed at
A Review of the Bed Roughness Variable in MIKE 21 FLOW MODEL FM, Hydrodynamic (HD) and Sediment Transport (ST) modules
 A Review of the Bed Roughness Variable in MIKE 1 FLOW MODEL FM, Hydrodynamic (HD) and Sediment Transport (ST) modules by David Lambkin, University of Southampton, UK 1 Bed roughness is considered a primary
A Review of the Bed Roughness Variable in MIKE 1 FLOW MODEL FM, Hydrodynamic (HD) and Sediment Transport (ST) modules by David Lambkin, University of Southampton, UK 1 Bed roughness is considered a primary
Wind Directional Effect on a Single Storey House Using Educational Wind Tunnel
 Wind Directional Effect on a Single Storey House Using Educational Wind Tunnel S S Zaini 1, N Rossli 1, T A Majid 1, S N C Deraman 1 and N A Razak 2 1 Disaster Research Nexus, School of Civil Engineering,
Wind Directional Effect on a Single Storey House Using Educational Wind Tunnel S S Zaini 1, N Rossli 1, T A Majid 1, S N C Deraman 1 and N A Razak 2 1 Disaster Research Nexus, School of Civil Engineering,
Pressure Plate Drying and Wetting
 1 Introduction Pressure Plate Drying and Wetting This air flow example illustrates how the process of axis translation, which is used in pressure plates to measure the water content function, can be modeled.
1 Introduction Pressure Plate Drying and Wetting This air flow example illustrates how the process of axis translation, which is used in pressure plates to measure the water content function, can be modeled.
Pore-Air Entrapment during Infiltration
 Pore-Air Entrapment during Infiltration GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. www.geo-slope.com 1200, 700-6th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada T2P 0T8 Main: +1 403 269 2002 Fax: +1 888 463 2239 Introduction Infiltration
Pore-Air Entrapment during Infiltration GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. www.geo-slope.com 1200, 700-6th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada T2P 0T8 Main: +1 403 269 2002 Fax: +1 888 463 2239 Introduction Infiltration
The effect of back spin on a table tennis ball moving in a viscous fluid.
 How can planes fly? The phenomenon of lift can be produced in an ideal (non-viscous) fluid by the addition of a free vortex (circulation) around a cylinder in a rectilinear flow stream. This is known as
How can planes fly? The phenomenon of lift can be produced in an ideal (non-viscous) fluid by the addition of a free vortex (circulation) around a cylinder in a rectilinear flow stream. This is known as
INTERACTION BETWEEN WIND-DRIVEN AND BUOYANCY-DRIVEN NATURAL VENTILATION Bo Wang, Foster and Partners, London, UK
 INTERACTION BETWEEN WIND-DRIVEN AND BUOYANCY-DRIVEN NATURAL VENTILATION Bo Wang, Foster and Partners, London, UK ABSTRACT Ventilation stacks are becoming increasingly common in the design of naturally
INTERACTION BETWEEN WIND-DRIVEN AND BUOYANCY-DRIVEN NATURAL VENTILATION Bo Wang, Foster and Partners, London, UK ABSTRACT Ventilation stacks are becoming increasingly common in the design of naturally
Results and Discussion for Steady Measurements
 Chapter 5 Results and Discussion for Steady Measurements 5.1 Steady Skin-Friction Measurements 5.1.1 Data Acquisition and Reduction A Labview software program was developed for the acquisition of the steady
Chapter 5 Results and Discussion for Steady Measurements 5.1 Steady Skin-Friction Measurements 5.1.1 Data Acquisition and Reduction A Labview software program was developed for the acquisition of the steady
Development of Data Acquisition System for Consolidated Undrained Triaxial Test
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Development of Data Acquisition System for Consolidated Undrained Triaxial Test To cite this article: L M Lee et al 2016 IOP Conf.
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Development of Data Acquisition System for Consolidated Undrained Triaxial Test To cite this article: L M Lee et al 2016 IOP Conf.
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING Volume 1, No 4, 2010
 Effect of geometric dimensions on the transmission coefficient of floating breakwaters Mohammad Hosein Tadayon, Khosro Bargi 2, Hesam Sharifian, S. Reza Hoseini - Ph.D student, Department of Civil Engineering,
Effect of geometric dimensions on the transmission coefficient of floating breakwaters Mohammad Hosein Tadayon, Khosro Bargi 2, Hesam Sharifian, S. Reza Hoseini - Ph.D student, Department of Civil Engineering,
RESOURCE DECREASE BY LARGE SCALE WIND FARMING
 ECN-RX--4-14 RESOURCE DECREASE BY LARGE SCALE WIND FARMING G.P. Corten A.J. Brand This paper has been presented at the European Wind Energy Conference, London, -5 November, 4 NOVEMBER 4 Resource Decrease
ECN-RX--4-14 RESOURCE DECREASE BY LARGE SCALE WIND FARMING G.P. Corten A.J. Brand This paper has been presented at the European Wind Energy Conference, London, -5 November, 4 NOVEMBER 4 Resource Decrease
An integrated three-dimensional model of wave-induced pore pressure and effective stresses in a porous seabed: II. Breaking waves
 An integrated three-dimensional model of wave-induced pore pressure and effective stresses in a porous seabed: II. Breaking waves Author Jeng, D., Zhang, Hong Published 2005 Journal Title Ocean Engineering
An integrated three-dimensional model of wave-induced pore pressure and effective stresses in a porous seabed: II. Breaking waves Author Jeng, D., Zhang, Hong Published 2005 Journal Title Ocean Engineering
AIRFLOW GENERATION IN A TUNNEL USING A SACCARDO VENTILATION SYSTEM AGAINST THE BUOYANCY EFFECT PRODUCED BY A FIRE
 - 247 - AIRFLOW GENERATION IN A TUNNEL USING A SACCARDO VENTILATION SYSTEM AGAINST THE BUOYANCY EFFECT PRODUCED BY A FIRE J D Castro a, C W Pope a and R D Matthews b a Mott MacDonald Ltd, St Anne House,
- 247 - AIRFLOW GENERATION IN A TUNNEL USING A SACCARDO VENTILATION SYSTEM AGAINST THE BUOYANCY EFFECT PRODUCED BY A FIRE J D Castro a, C W Pope a and R D Matthews b a Mott MacDonald Ltd, St Anne House,
TACKLING JACK-UP RIG NO-GO LOCATIONS. Prakasha Kuppalli ABSTRACT
 TACKLING JACK-UP RIG NO-GO LOCATIONS Prakasha Kuppalli ABSTRACT Jack-up rigs are deployed for drilling and work-over (maintenance) of offshore oil and gas wells for producing hydrocarbons. Rigs drill through
TACKLING JACK-UP RIG NO-GO LOCATIONS Prakasha Kuppalli ABSTRACT Jack-up rigs are deployed for drilling and work-over (maintenance) of offshore oil and gas wells for producing hydrocarbons. Rigs drill through
ESTIMATION OF LATERAL SPREAD OF A CAISSON TYPE QUAY CAUSED BY BACK FILL LIQUEFACTION
 ESTIMATION OF LATERAL SPREAD OF A CAISSON TYPE QUAY CAUSED BY BACK FILL LIQUEFACTION Kunio MIZUMOTO 1, Tetsuya TSURUMI 2, Hidekatsu NAKAJIMA 3 And Susumu OKADA 4 SUMMARY It is said on the lateral spread
ESTIMATION OF LATERAL SPREAD OF A CAISSON TYPE QUAY CAUSED BY BACK FILL LIQUEFACTION Kunio MIZUMOTO 1, Tetsuya TSURUMI 2, Hidekatsu NAKAJIMA 3 And Susumu OKADA 4 SUMMARY It is said on the lateral spread
Journal of Applied Fluid Transients, Vol 1-1, April 2014 (3-1)
 Modeling and Field Verification Study of Air Slam Conditions on kalanit Pipeline System By Yiftach Brunner & Sathish Kumar ir valves are integral part of long water transmission mains and are essential
Modeling and Field Verification Study of Air Slam Conditions on kalanit Pipeline System By Yiftach Brunner & Sathish Kumar ir valves are integral part of long water transmission mains and are essential
A STUDY OF THE LOSSES AND INTERACTIONS BETWEEN ONE OR MORE BOW THRUSTERS AND A CATAMARAN HULL
 A STUDY OF THE LOSSES AND INTERACTIONS BETWEEN ONE OR MORE BOW THRUSTERS AND A CATAMARAN HULL L Boddy and T Clarke, Austal Ships, Australia SUMMARY CFD analysis has been conducted on a 100m catamaran hull
A STUDY OF THE LOSSES AND INTERACTIONS BETWEEN ONE OR MORE BOW THRUSTERS AND A CATAMARAN HULL L Boddy and T Clarke, Austal Ships, Australia SUMMARY CFD analysis has been conducted on a 100m catamaran hull
Paper 2.2. Operation of Ultrasonic Flow Meters at Conditions Different Than Their Calibration
 Paper 2.2 Operation of Ultrasonic Flow Meters at Conditions Different Than Their Calibration Mr William Freund, Daniel Measurement and Control Mr Klaus Zanker, Daniel Measurement and Control Mr Dale Goodson,
Paper 2.2 Operation of Ultrasonic Flow Meters at Conditions Different Than Their Calibration Mr William Freund, Daniel Measurement and Control Mr Klaus Zanker, Daniel Measurement and Control Mr Dale Goodson,
Ermenek Dam and HEPP: Spillway Test & 3D Numeric-Hydraulic Analysis of Jet Collision
 Ermenek Dam and HEPP: Spillway Test & 3D Numeric-Hydraulic Analysis of Jet Collision J.Linortner & R.Faber Pöyry Energy GmbH, Turkey-Austria E.Üzücek & T.Dinçergök General Directorate of State Hydraulic
Ermenek Dam and HEPP: Spillway Test & 3D Numeric-Hydraulic Analysis of Jet Collision J.Linortner & R.Faber Pöyry Energy GmbH, Turkey-Austria E.Üzücek & T.Dinçergök General Directorate of State Hydraulic
