Annelida and other worms
|
|
|
- Helena Kelly
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Phylum Annelida 1 Trochozoa (autapomorphie) Presence of the trochophore larval stage!! Porifera Placozoa Cnidaria Ctenophora Platyhelminthes Gastrotricha Gnathostomulida Cycliophora Rotifera Annelida Mollusca Sipuncula Nemertea Bryozoa Brachiopoda Phoronida Arthropoda Onychophora Tardigrada Nematomorpha Nematoda Priapulida Kinorhyncha Loricifera Echinodermata Hemichordata Chordata Trochophore larva Apical tuft Stomach Ciliary band Mouth Anus 3 Page 1
2 Animal innovations (symplesiomorphies) 1. Schizocoel, and metanephridia filtering coelomic fluid 2. Dorsal heart and pericardial cavity 1 2 Porifera Placozoa Cnidaria Ctenophora Platyhelminthes Gastrotricha Gnathostomulida Cycliophora Rotifera Annelida Mollusca Sipuncula Nemertea Bryozoa Brachiopoda Phoronida Arthropoda Onychophora Tardigrada Nematomorpha Nematoda Priapulida Kinorhyncha Loricifera Echinodermata Hemichordata Chordata Body cavities Schizocoelus Enterocoelus 5 Metanepridia Nephrostome Cilia Tubule Bladder Nephridiopore 6 Page 2
3 Extant Animalia ~1,300,000 species Parazoa (1.2%) Radiata (0.9%) Protostomia (3.9%) Platyzoa (2.2%) Platyhelminthes (1.9%) Others (0.3%) Lophotrochozoa (9.8%) Mollusca (8.5%) Annelida (0.9%) Others (0.5%) Ecdysozoa (82.0%) Crustecea (3.1%) Chelicerata (7.6%) Atelocerata (70.3%) Others (1.1%) Deuterostomia (4.0%) Chordata (3.5%) Others (0.4%) 7! Annelida (autapomorphies) Metamerisim of mesodermal structures Four bundles of setae formed from Beta-chitin! Porifera Placozoa Cnidaria Ctenophora Platyhelminthes Gastrotricha Gnathostomulida Cycliophora Rotifera Annelida Mollusca Sipuncula Nemertea Bryozoa Brachiopoda Phoronida Arthropoda Onychophora Tardigrada Nematomorpha Nematoda Priapulida Kinorhyncha Loricifera Echinodermata Hemichordata Chordata Annelid development 9 Page 3
4 Chitin O=C-CH 3 O=C-CH 3 NH CH 2 O H NH OH O O OH O OH O O CH 2 O H NH O=C-CH 3 CH 2 O H 10 beta-chitin sheets gama-chitin sheets 11 Annelid phylogeny Echiura Polychaeta Pognophora Clitellata!! Echiura (autapomorphies) Loss or fusion of segments Spoon shaped retractable proboscis 12 Page 4
5 Echiura - spoon worms Proboscis Gutter Setae Trunk Anus 13 Echiura spoon worms Seta sac Nephridium Nerve cord & Blood vessel Anal sac Gonad Proboscis Gutter Pharynx Intestine Anus 14 Annelid phylogeny Echiura Polychaeta Pognophora Clitellata!! Polychaeta (autapomorphies) Parapodia Absence of permanent gonads Gonads forming in septal walls Complex prostomium 15 Page 5
6 Nereis (Photo by: Dave Cowles, July 2005) 16 Nereid body wall Notopodium Longitudinal muscles Neuropodium Oblique muscles 17 Nereid body wall Setal bundle Notopodium Aciculum Acicular muscles Neuropodium Oblique muscles 18 Page 6
7 Nereid movement 19 Polychaete circulation Capillaries Dorsal vessel Dorsolateral Ventral vessel Midlateral Ventrolateral 20 Polychaete reproduction Epitoke segments Atoke segments 21 Page 7
8 Errant polychaetes Tentacle Palp Eye Cirrus 22 Feeding strategies Suspension feeders Setal nets Scan and trap Mucous nets Ciliary-mucous Tentacle/tube feet Deposit feeders Direct deposit feeders Select deposit feeders 23 Polychaete feeding and digestion (Suspension feeding) 24 Page 8
9 Chaetopterus Suspension feeding Mouth Ciliated groove Tentacle Wings (Aliform parapodium) Food cup Trunk parapodium Parapodium 25 Chaetopterus Suspension feeding Mouth Enlarged notopodium Fan parapodium Mucus bag with food 26 Polychaete feeding and digestion Suspension feeding (Photo by: Dave Cowles, July 2006) 27 Page 9
10 Polychaete feeding and digestion Deposit feeding Anus Mouth D. Schories 28 Annelid phylogeny Echiura Polychaeta Pogonophora Clitellata!! Pogonophora (autapomorphies) Loss of the gut Trophosome with symbionts First two segments enlarged Setal segments on opisthosoma 29 Pogonophorans 30 Page 10
11 Pogonophora Tentacles Cephalic lobe Glandular area Cilia and paired papillae Unpaired papilla Trunk Cilia and enlarged papillae Girdle of setae Papillae Opisthosoma 31 Pogonophora Tentacles Cephalic lobe Glandular area Setae Septa Opisthosoma 32 Chemosythesis CO 2 + 4H 2 S + O 2 [CH 2 O] n + 4S + 3H 2 O 33 Page 11
12 Annelid phylogeny Echiura Polychaeta Pogonophora Clitellata!! Clitellata (autapomorphies) Clitellum Gonads not metameric Hermaphrodite Eggs in a cocoon Direct development 34 Reproductive system Seminal vesicle Testis Seminal receptacle Sperm funnel Sperm duct Ovary Ovarian funnel 35 Cocoon formation 36 Page 12
13 Earthworm body wall Circular muscle Longitudinal muscle Coelom Seta 37 Earthworm locomotion Longitudinal contracted (setae out) Circular contracted (setae in) 38 Earthworm circulation Dorsosubneural vessel Dorsal vessel Ventral vessel Subneural vessel Aortic arches ( Hearts ) 39 Page 13
14 Earthworm circulation Intestinal vessel Dorsal vessel Nephridial vessel Ventral vessel Subneural vessel 40 Metanephridium Dorsal vessel Bladder Nephridiopore Nephrostome Ventral vessel 41 Nervous system Suprapharyngeal ganglion Lateral nerve Circumpharyngeal connectives Subpharyngeal ganglion Ventral nerve cord 42 Page 14
15 Nervous system Giant axon Ventral nerve cord 43 Leeches 44 Leech body wall Circular muscle Longitudinal muscle Dorsoventral muscle 45 Page 15
16 Leech body wall Dorsal sinus Dorsal vessel Ventral vessel Lateral sinus Nerve cord Ventral sinus 46 Leech locomotion 47 Hirudinida feeding and digestion Jaws Pharynx Esophagous 48 Page 16
17 Hirudinida feeding and digestion Crop Crop cecum Intestine Intestinal cecum Anus 49 Nemertea Nermertea 50 10:17 AM! Nemertea (autapomorphies) Combination of unique proboscis and rhynchocoel Lateral coelomic vessels Vascular plugs! Porifera Placozoa Cnidaria Ctenophora Platyhelminthes Gastrotricha Gnathostomulida Cycliophora Rotifera Annelida Mollusca Sipuncula Nemertea Bryozoa Brachiopoda Phoronida Arthropoda Onychophora Tardigrada Nematomorpha Nematoda Priapulida Kinorhyncha Loricifera Echinodermata Hemichordata Chordata Page 17
18 Nemertean worms Rhynchocoel Proboscis Dorsal vessel Intestine Anus Gonad 52 Proboscis 53 Organ systems Gonopore Gonad Gut Lateral coelomic vessels Lateral nerve cord 54 Page 18
19 Body wall Epidermis Dermis Proboscis Rhynchocoel Mesenchyme Circular muscle Longitudinal muscle 55 Protonephridia and lateral vessel Lateral coelomic vessel Coelomic fluid Cilia in terminal cell Protonephridia Collecting duct Nephridiopore 56 Pilidium larva Cilia tuft Muscle fiber Nerve fiber Muscle fiber Nerve ring Stomach Esophagus Mouth 57 Page 19
20 Sipuncula Allen Collins University of California Museum of Paleontology 58! Sipuncula (autapomorphies) Introvert with central disc surrunded by tentacles J shaped coiled gut Compensation sacs Unpaired nongaglionic nerve cord! Porifera Placozoa Cnidaria Ctenophora Platyhelminthes Gastrotricha Gnathostomulida Cycliophora Rotifera Annelida Mollusca Sipuncula Nemertea Bryozoa Brachiopoda Phoronida Arthropoda Onychophora Tardigrada Nematomorpha Nematoda Priapulida Kinorhyncha Loricifera Echinodermata Hemichordata Chordata Sipuncula Tentacles Introvert Trunk 60 Page 20
21 Sipuncula Compensation sac Metanephridia Ventral nerve cord Tentacles Mouth Retractor muscle Rectum Ascending intestine Descending intestine 61 Urns Mucous with coelomic debris Cilia Urn 62 Page 21
Annelida and other worms
 Phylum Annelida 1 Trochozoa (autapomorphie) Presence of the trochophore larval stage Porifera Placozoa Cnidaria Ctenophora Platyhelminthes Gastrotricha Gnathostomulida Cycliophora Rotifera Annelida Mollusca
Phylum Annelida 1 Trochozoa (autapomorphie) Presence of the trochophore larval stage Porifera Placozoa Cnidaria Ctenophora Platyhelminthes Gastrotricha Gnathostomulida Cycliophora Rotifera Annelida Mollusca
Mollusca. BIO2135 Animal Form & Function. Page 1. Phylum Mollusca. Lophotrochozoa. Trochozoans. BIO2135 Animal Form and Function 1 10:29 AM
 Phylum Mollusca 1 10:29 AM Lophotrochozoa Either presence of a U shaped gut and lophophore or Trochophore larval stage Porifera Placozoa Cnidaria Ctenophora Platyhelminthes Gastrotricha Gnathostomulida
Phylum Mollusca 1 10:29 AM Lophotrochozoa Either presence of a U shaped gut and lophophore or Trochophore larval stage Porifera Placozoa Cnidaria Ctenophora Platyhelminthes Gastrotricha Gnathostomulida
Hemichordates and Invert chordates
 Hemichordates and Invertebrate chordates 1 Animal innovations (Symplesiomorphies) Pharyngeal gill slits Dorsal hollow nerve cord Porifera Placozoa Cnidaria Ctenophora Platyhelminthes Gastrotricha Gnathostomulida
Hemichordates and Invertebrate chordates 1 Animal innovations (Symplesiomorphies) Pharyngeal gill slits Dorsal hollow nerve cord Porifera Placozoa Cnidaria Ctenophora Platyhelminthes Gastrotricha Gnathostomulida
"Protochordates" BIO3334 Invertebrate Zoology. Page 1. Hemichordates and Invertebrate chordates. Protochordate taxa 2 8:30 AM
 Hemichordates and Invertebrate chordates 1 Protochordate taxa Phylum. Hemichordata Class. Enteropneusta Class. Pterobranchia Phylum. Chordata Subphylum. Urochordata Subphylum. Cephalochordata Subphylum.
Hemichordates and Invertebrate chordates 1 Protochordate taxa Phylum. Hemichordata Class. Enteropneusta Class. Pterobranchia Phylum. Chordata Subphylum. Urochordata Subphylum. Cephalochordata Subphylum.
Each unit contains components of most organ systems. Increased burrowing efficiency by permitting movement of segments
 CHAPTER 17 Annelids Characteristics of the Phylum Annelida Diversity Exhibit segmentation or Bodies composed of units Each unit contains components of most organ systems Increased burrowing efficiency
CHAPTER 17 Annelids Characteristics of the Phylum Annelida Diversity Exhibit segmentation or Bodies composed of units Each unit contains components of most organ systems Increased burrowing efficiency
Lumbricus terrestris - preserved specimens for dissection
 Lumbricus terrestris - preserved specimens for dissection External Anatomy: Prostomium (observe under dissecting microscope for external sensory organs), peristomium, clitellum, setae (dissecting microscope),
Lumbricus terrestris - preserved specimens for dissection External Anatomy: Prostomium (observe under dissecting microscope for external sensory organs), peristomium, clitellum, setae (dissecting microscope),
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. CHAPTER 17. Annelids 17-1
 CHAPTER 17 Annelids 17-1 Characteristics of the Phylum Annelida Diversity Exhibit segmentation or metamerism Bodies composed of repeated units Each unit contains components of most MAJOR organ systems
CHAPTER 17 Annelids 17-1 Characteristics of the Phylum Annelida Diversity Exhibit segmentation or metamerism Bodies composed of repeated units Each unit contains components of most MAJOR organ systems
ZOOLOGY SEGMENTED WORMS (Phylum Annelida)
 ZOOLOGY SEGMENTED WORMS (Phylum Annelida) I. Compared and Contrasted to Phylum Mollusca. A. They are like the molluscs in that they 1. are eucoelomate animals. 2. have specialized sense organs. 3. have
ZOOLOGY SEGMENTED WORMS (Phylum Annelida) I. Compared and Contrasted to Phylum Mollusca. A. They are like the molluscs in that they 1. are eucoelomate animals. 2. have specialized sense organs. 3. have
CHAPTER 11 STUDY GUIDE 11.1 Dividing Up the Body A. A spacious, fluid-filled coelom provides an efficient hydrostatic skeleton. B. When septa divided
 CHAPTER 11 STUDY GUIDE 11.1 Dividing Up the Body A. A spacious, fluid-filled coelom provides an efficient hydrostatic skeleton. B. When septa divided this coelom into a series of compartments, metamerism
CHAPTER 11 STUDY GUIDE 11.1 Dividing Up the Body A. A spacious, fluid-filled coelom provides an efficient hydrostatic skeleton. B. When septa divided this coelom into a series of compartments, metamerism
BIO 221 Invertebrate Zoology I Spring 2010
 BIO 221 Invertebrate Zoology I Spring 2010 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 14 Invertebrate Classification Note: we now have some additional characteristics
BIO 221 Invertebrate Zoology I Spring 2010 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 14 Invertebrate Classification Note: we now have some additional characteristics
Chapter 10: Mollusca
 Chapter 10: Mollusca Latin: soft 90,000 living spp. 70,000 fossil spp. marine fresh water terrestrial chitons snails nudibranchs clams oysters nautiluses tusk shells slugs sea butterflies mussels squids/cuttlefish
Chapter 10: Mollusca Latin: soft 90,000 living spp. 70,000 fossil spp. marine fresh water terrestrial chitons snails nudibranchs clams oysters nautiluses tusk shells slugs sea butterflies mussels squids/cuttlefish
Chapter 35. Table of Contents. Section 1 Mollusca. Section 2 Annelida. Mollusks and Annelids
 Mollusks and Annelids Table of Contents Section 1 Mollusca Section 2 Annelida Section 1 Mollusca Objectives Describe the key characteristics of mollusks. Describe the body plan of mollusks. Name the characteristics
Mollusks and Annelids Table of Contents Section 1 Mollusca Section 2 Annelida Section 1 Mollusca Objectives Describe the key characteristics of mollusks. Describe the body plan of mollusks. Name the characteristics
Chapter 5 Marine Protozoans and Invertebrates
 Chapter 5 Marine Protozoans and Invertebrates I. The Protozoans A. Kindgom Protista a catch-all category B. Characteristics 1. Mode of nutrition 2. Single-celled or multicellular? 3. Cell structure 4.
Chapter 5 Marine Protozoans and Invertebrates I. The Protozoans A. Kindgom Protista a catch-all category B. Characteristics 1. Mode of nutrition 2. Single-celled or multicellular? 3. Cell structure 4.
Coelomate Worms: Sipunculans, Pogonophorans, Echiurans and Vestimenifera
 Coelomate Worms Coelomate Worms: Sipunculans, Pogonophorans, Echiurans and Vestimenifera Ectoderm Mesoderm Dt Endoderm Coelom Often dismissed as minor or lesser Comprise less than 600 species total Never
Coelomate Worms Coelomate Worms: Sipunculans, Pogonophorans, Echiurans and Vestimenifera Ectoderm Mesoderm Dt Endoderm Coelom Often dismissed as minor or lesser Comprise less than 600 species total Never
Chapter 12 Part 2. The Worms Platyhelminthes, Nematoda & Annelida
 Chapter 12 Part 2 The Worms Platyhelminthes, Nematoda & Annelida Phylum: Platyhelminthes Examples: Flatworms, Planaria sp., tapeworms and blood flukes Acoelomate, Invertebrate, Simplest critter w/ bilateral
Chapter 12 Part 2 The Worms Platyhelminthes, Nematoda & Annelida Phylum: Platyhelminthes Examples: Flatworms, Planaria sp., tapeworms and blood flukes Acoelomate, Invertebrate, Simplest critter w/ bilateral
Phylum Platyhelminthes. You will need: five colours of pencil crayon or pen (preferably blue, green, red, orange and purple)
 Phylum Platyhelminthes You will need: five colours of pencil crayon or pen (preferably blue, green, red, orange and purple) Phylum Platyhelminthes bilaterally symmetrical have all 3 embryonic germ layers:
Phylum Platyhelminthes You will need: five colours of pencil crayon or pen (preferably blue, green, red, orange and purple) Phylum Platyhelminthes bilaterally symmetrical have all 3 embryonic germ layers:
Biology 222 Invertebrate Zoology II
 Biology 222 Invertebrate Zoology II Fall 2004 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University Lecture 12 Annelid Systematics Three primary groups a. Class Polychaeta b. Class Oligochaeta c. Class Hirudinida
Biology 222 Invertebrate Zoology II Fall 2004 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University Lecture 12 Annelid Systematics Three primary groups a. Class Polychaeta b. Class Oligochaeta c. Class Hirudinida
Z202-Unit 9/10 Chapter 22 Chaetognaths, Echinoderms & Hemichordates
 Z202-Unit 9/10 Chapter 22 Chaetognaths, Echinoderms & Hemichordates I. Diversity A. Evolutionary Diversity - Cambrian Explosion (535 to 530 mya) radiation in diversity seen in fossil record other explosions
Z202-Unit 9/10 Chapter 22 Chaetognaths, Echinoderms & Hemichordates I. Diversity A. Evolutionary Diversity - Cambrian Explosion (535 to 530 mya) radiation in diversity seen in fossil record other explosions
ANNELID LAB. Phylum Annelida
 ANNELID LAB Phylum Annelida Class Oligochaeta 1. Lumbricus terrestris preserved specimen for dissection 2. Lumbricus terrestris cross section slides 3. Lumbricus terrestris longitudinal, whole animal slides
ANNELID LAB Phylum Annelida Class Oligochaeta 1. Lumbricus terrestris preserved specimen for dissection 2. Lumbricus terrestris cross section slides 3. Lumbricus terrestris longitudinal, whole animal slides
Figure 32.8 Animal phylogeny based on sequencing of SSU-rRNA
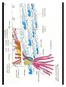 Figure 32.8 Animal phylogeny based on sequencing of SSU-rRNA Polychaetes Representative Annelids Oligochaetes Marine worms Hirudineans Terrestrial & aquatic Leeches - Aquatic & terrestrial Annelid Circulatory,
Figure 32.8 Animal phylogeny based on sequencing of SSU-rRNA Polychaetes Representative Annelids Oligochaetes Marine worms Hirudineans Terrestrial & aquatic Leeches - Aquatic & terrestrial Annelid Circulatory,
Phylum: Porifera (sponges)
 Phylum: Porifera (sponges) (8,761 known species) General Description: Simplest animals, multicellular No organs or body systems Skeleton composed of spongin (soft) and spicules (hard) Symmetry: Asymmetrical
Phylum: Porifera (sponges) (8,761 known species) General Description: Simplest animals, multicellular No organs or body systems Skeleton composed of spongin (soft) and spicules (hard) Symmetry: Asymmetrical
The Animal Kingdom. Animal Kingdom. Characteristics of All Animals. Major Characteristics Used To Classify Animals
 The Animal Kingdom Animal Kingdom Phylums: 1. Sponges 2. Cnidaria Jelly Fish, Hydra 3. Flatworms Flukes, Tapeworms 4. Roundworms- Hookworms 5. Segmented Worms- Earthworms 6. Rotifera- Rotifers 7. Mullusca
The Animal Kingdom Animal Kingdom Phylums: 1. Sponges 2. Cnidaria Jelly Fish, Hydra 3. Flatworms Flukes, Tapeworms 4. Roundworms- Hookworms 5. Segmented Worms- Earthworms 6. Rotifera- Rotifers 7. Mullusca
Mollusks and Annelids. Chapter 23+
 Mollusks and Annelids Chapter 23+ 1 Annelids and Mollusks Coelomates Trochophore larvae Bilateral symmetry More complex organ systems 2 Moving On Up 3 Coelom Coelomates Evolutionary milestone True body
Mollusks and Annelids Chapter 23+ 1 Annelids and Mollusks Coelomates Trochophore larvae Bilateral symmetry More complex organ systems 2 Moving On Up 3 Coelom Coelomates Evolutionary milestone True body
BIO 221 Invertebrate Zoology I Spring Cycloneuralia Characters. Pseudo- coelomates (Ecdysozoa): Lecture 19
 BIO 221 Invertebrate Zoology I Spring 2010 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 19 Cycloneuralia Characters 18(2): Ambiguous spiral cleavage. 92: Terminal mouth
BIO 221 Invertebrate Zoology I Spring 2010 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 19 Cycloneuralia Characters 18(2): Ambiguous spiral cleavage. 92: Terminal mouth
Invertebrates. Sponges: Porifera pore bearer 10/3/13
 Animals without backbones We ll cover characteristics of major phyla and some to class level (KPCOFGS) We ll also cover some natural history Refer to your notes that I posted on-line! Invertebrates Levels
Animals without backbones We ll cover characteristics of major phyla and some to class level (KPCOFGS) We ll also cover some natural history Refer to your notes that I posted on-line! Invertebrates Levels
What is an animal? 10/22/17. Bio 242 Laboratory Module 2
 Bio 242 Laboratory Module 2 Theme: Evolution shapes the flow and pattern of information through phylogenetic lineages, evident in the linkage between form and function Objectives -we will track the effects
Bio 242 Laboratory Module 2 Theme: Evolution shapes the flow and pattern of information through phylogenetic lineages, evident in the linkage between form and function Objectives -we will track the effects
Platyzoans Phylum Platyhelminthes
 PROTOSTOMES Micrognathozoa Rotifera Cycliophora Platyhelminthes Brachiopoda Bryozoa Annelida Mollusca Nemertea Loricifera Kinorhyncha Nematoda Tardigrada Arthropoda Onychophora Chaetognatha Echinodermata
PROTOSTOMES Micrognathozoa Rotifera Cycliophora Platyhelminthes Brachiopoda Bryozoa Annelida Mollusca Nemertea Loricifera Kinorhyncha Nematoda Tardigrada Arthropoda Onychophora Chaetognatha Echinodermata
Characteristics of Animals pp Topic 7: Animal Diversity Ch Symmetry pp Characteristics of Animals
 Topic 7: Animal Diversity Ch. 32-34 Characteristics of Animals pp.704-705 Animals: Are eukaryotic Are multicellular Are ingestive heterotrophs Have no cell walls Most are motile Most have tissues organized
Topic 7: Animal Diversity Ch. 32-34 Characteristics of Animals pp.704-705 Animals: Are eukaryotic Are multicellular Are ingestive heterotrophs Have no cell walls Most are motile Most have tissues organized
Chapter 28 Mollusks & Annelids. BIOLOGY II Miss. Loulousis
 Chapter 28 Mollusks & Annelids BIOLOGY II Miss. Loulousis Mollusks have a true coelom Snails, slugs, oysters, clams, scallops, octopuses, and squids are all mollusks Annelid earthworm next section Mollusks
Chapter 28 Mollusks & Annelids BIOLOGY II Miss. Loulousis Mollusks have a true coelom Snails, slugs, oysters, clams, scallops, octopuses, and squids are all mollusks Annelid earthworm next section Mollusks
An Overview of Animal Diversity
 Fig. 32-1 An Overview of Animal Diversity Multicellular Nutrition mode: Heterotrophic (ingestion) Cell structure & specialization Tissues develop from embryonic layers Nervous & Muscle (unique) Lack cell
Fig. 32-1 An Overview of Animal Diversity Multicellular Nutrition mode: Heterotrophic (ingestion) Cell structure & specialization Tissues develop from embryonic layers Nervous & Muscle (unique) Lack cell
Worm Essential Questions
 1. What are the four major phyla of marine worms? (in order from least to most complex) Worm Essential Questions Marine Biology Platyhelminthes - flatworms Nemertea ribbon worms or proboscis worms Nematoda
1. What are the four major phyla of marine worms? (in order from least to most complex) Worm Essential Questions Marine Biology Platyhelminthes - flatworms Nemertea ribbon worms or proboscis worms Nematoda
Mollusks and Annelids
 Mollusks and Annelids Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The mollusks are a diverse group (85,000 described species) of mostly marine species. They have a variety of forms, ranging from large predatory squid and octopus,
Mollusks and Annelids Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The mollusks are a diverse group (85,000 described species) of mostly marine species. They have a variety of forms, ranging from large predatory squid and octopus,
 Kingdom: Animalia Phylum:Mollusca Classes: Bivalva, Gastropoda, Cephalopoda http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0a7j5prl8hc&feature=related http://www2.beavercreek.k12.oh.us/videos/45/pgr45_700k.asf What is
Kingdom: Animalia Phylum:Mollusca Classes: Bivalva, Gastropoda, Cephalopoda http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0a7j5prl8hc&feature=related http://www2.beavercreek.k12.oh.us/videos/45/pgr45_700k.asf What is
The Animal Kingdom: The Deuterostomes. Deuterostomes. Phylum Echinodermata 4/23/2012. Chapter 31. (bilateral ciliated larvae)
 Porifera Porifera Cnidaria Cnidaria Ctenophora Ctenophora Platyhelminthes Platyhelminthes Nemerteans Nemerteans Nematoda Nematoda Rotifera Rotifera Tardigrada Tardigrada Onychophora Onychophora Arthropoda
Porifera Porifera Cnidaria Cnidaria Ctenophora Ctenophora Platyhelminthes Platyhelminthes Nemerteans Nemerteans Nematoda Nematoda Rotifera Rotifera Tardigrada Tardigrada Onychophora Onychophora Arthropoda
Sinauer Associates, Inc., Publishers Sunderland, Massachusetts 01375
 Invertebrates SECOND EDITION Richard C. Brusca Director of Conservation and Science, Arizona-Sonora Desert Museum Gary J. Brusca Late, Professor of Zoology, Humboldt State University with illustrations
Invertebrates SECOND EDITION Richard C. Brusca Director of Conservation and Science, Arizona-Sonora Desert Museum Gary J. Brusca Late, Professor of Zoology, Humboldt State University with illustrations
What Is an Annelid? Annelids are worms with segmented bodies. They have a true coelom that is lined with tissue derived from mesoderm.
 What Is an Annelid? What Is an Annelid? Phylum: Annelidae Annelids are worms with segmented bodies. They have a true coelom that is lined with tissue derived from mesoderm. Three Germ Layers of an Annelid
What Is an Annelid? What Is an Annelid? Phylum: Annelidae Annelids are worms with segmented bodies. They have a true coelom that is lined with tissue derived from mesoderm. Three Germ Layers of an Annelid
Requirements for Animal Life. Phylum Bryozoa. Colonial Bryozoans. A lophophore is a structure used for:
 Requirements for Animal Life Animal phylogeny based on sequencing of SSU-rRNA The demands of 3 unique environments Marine, freshwater, terrestrial Gas exchange Nutrition Distribution and transport Disposal
Requirements for Animal Life Animal phylogeny based on sequencing of SSU-rRNA The demands of 3 unique environments Marine, freshwater, terrestrial Gas exchange Nutrition Distribution and transport Disposal
A. Porifera (sponges): B. Cnidaria (jellies, hydra, sea anemones, and corals):
 Invertebrates Notes A. Porifera (sponges): Porifera literally means. Most sponges are. They are that collect food particles from the water as they pass through flagellated cells called. These cells then
Invertebrates Notes A. Porifera (sponges): Porifera literally means. Most sponges are. They are that collect food particles from the water as they pass through flagellated cells called. These cells then
What is an animal? Mul.cellular heterotrophs: feed by inges&on. How does this differ from plants, fungi, pro.sts?
 What is an animal? Mul.cellular heterotrophs: feed by inges&on. How does this differ from plants, fungi, pro.sts? What is an animal? Carbohydrates stored as glycogen Polysaccharide of glucose (no, you
What is an animal? Mul.cellular heterotrophs: feed by inges&on. How does this differ from plants, fungi, pro.sts? What is an animal? Carbohydrates stored as glycogen Polysaccharide of glucose (no, you
BIO 221 Invertebrate Zoology I Spring Larval Development. Larval Development. Lecture 18
 BIO 221 Invertebrate Zoology I Spring 2010 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 18 Larval Development 1. Often presented as a progression of stages a. Representative
BIO 221 Invertebrate Zoology I Spring 2010 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 18 Larval Development 1. Often presented as a progression of stages a. Representative
Mollusks and Annelids *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m45526 1 Mollusks and Annelids * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
OpenStax-CNX module: m45526 1 Mollusks and Annelids * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
CHAPTER 22. Echinoderms 22-1
 CHAPTER 22 Echinoderms 22-1 Phylum Echinodermata: Diversity and Characteristics Characteristics All members have a calcareous skeleton Spiny endoskeleton consists of plates Unique water-vascular system
CHAPTER 22 Echinoderms 22-1 Phylum Echinodermata: Diversity and Characteristics Characteristics All members have a calcareous skeleton Spiny endoskeleton consists of plates Unique water-vascular system
Animal Evolution. II. Overview of Animal Phylogeny A. Parazoan 1. Lack tissue 2. Animals with tissue are classified eumetazoa 3.
 Animal Evolution I. Animal Characteristics A. Most animals share the following characteristics: 1. Multi-cellular 2. Eukaryotic 3. Heterotrophy a. Ingestion b. Carbohydrates stored as glycogen 4. No cell
Animal Evolution I. Animal Characteristics A. Most animals share the following characteristics: 1. Multi-cellular 2. Eukaryotic 3. Heterotrophy a. Ingestion b. Carbohydrates stored as glycogen 4. No cell
BIOLOGY. An Introduction to Invertebrates CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 33 An Introduction to Invertebrates Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Deuterostomia Metazoa Eumetazoa
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 33 An Introduction to Invertebrates Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Deuterostomia Metazoa Eumetazoa
Class XI Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Biology
 Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Question 1: What are the difficulties that you would face in classification of animals, if common fundamental features are not taken into account? For the classification of living
Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Question 1: What are the difficulties that you would face in classification of animals, if common fundamental features are not taken into account? For the classification of living
Annelid Segmentation:
 Phylum Annelida Note: These links do not work. Use the links within the outline to access the mages in the popup windows. This text is the same as the scrolling text in the popup windows.. What is an annelid?
Phylum Annelida Note: These links do not work. Use the links within the outline to access the mages in the popup windows. This text is the same as the scrolling text in the popup windows.. What is an annelid?
Chordates 1. Biology 2
 Chordates 1 Biology 2 Kingdom Animals Eukaryotic Multicellular - Many cell types Heterotrophic Feed by ingestion No cell walls Diploid life cycle Phylogenetic Tree Deuterostome Bilateral Symmetry 3 tissues
Chordates 1 Biology 2 Kingdom Animals Eukaryotic Multicellular - Many cell types Heterotrophic Feed by ingestion No cell walls Diploid life cycle Phylogenetic Tree Deuterostome Bilateral Symmetry 3 tissues
Class XI Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Biology
 Class XI Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Biology Question 1: What are the difficulties that you would face in classification of animals, if common fundamental features are not taken into account? For the classification
Class XI Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Biology Question 1: What are the difficulties that you would face in classification of animals, if common fundamental features are not taken into account? For the classification
Classification. Phylum Chordata
 AP Biology Chapter 23 Exercise #17: Chordates: Urochordata & Cephalochordata Lab Guide Chordates show remarkable diversity. Most are vertebrates. All animals that belong to this phylum MUST, at some point
AP Biology Chapter 23 Exercise #17: Chordates: Urochordata & Cephalochordata Lab Guide Chordates show remarkable diversity. Most are vertebrates. All animals that belong to this phylum MUST, at some point
Topic Page: Annelida. Annelid Charact erist ics.
 Topic Page: Annelida Definition: annelid from Philip's Encyclopedia Any member of the Annelida phylum of segmented worms. All have encircling grooves usually corresponding to internal partitions of the
Topic Page: Annelida Definition: annelid from Philip's Encyclopedia Any member of the Annelida phylum of segmented worms. All have encircling grooves usually corresponding to internal partitions of the
Major groups of animals. I. Phylum Porifera. RADIATA II. Phylum Cnidaria. A. Class Hydrozoa. B. Class Anthozoa. C. Class Cubozoa. D.
 Major groups of animals I. Phylum Porifera A. no true tissues B. cell types 1. pinacocytes (pinacoderm - incipient tissue) 2. archaeocytes - in mesohyl 3. choanocytes C. Body forms 1. Asconoid a) water
Major groups of animals I. Phylum Porifera A. no true tissues B. cell types 1. pinacocytes (pinacoderm - incipient tissue) 2. archaeocytes - in mesohyl 3. choanocytes C. Body forms 1. Asconoid a) water
Phylum Platyhelminthes Phylum Nematoda Phylum Mollusca. By: Jerzylin, Beata & Jennifer
 Phylum Platyhelminthes Phylum Nematoda Phylum Mollusca By: Jerzylin, Beata & Jennifer Phylum Platyhelminthes Common Characteristics: Triploblastic Bilateral Symmetry Protostome No true stomach structure
Phylum Platyhelminthes Phylum Nematoda Phylum Mollusca By: Jerzylin, Beata & Jennifer Phylum Platyhelminthes Common Characteristics: Triploblastic Bilateral Symmetry Protostome No true stomach structure
Chapter 23: The Animal Kingdom
 Chapter 23: The Animal Kingdom Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 23-1 What is an animal? 23-2 Eukaryotic Multicellular
Chapter 23: The Animal Kingdom Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 23-1 What is an animal? 23-2 Eukaryotic Multicellular
a. Kingdom: b. Phylum: c. Class: d. Order: e. Family: f. Genus: g. Species:
 Pre-lab Discussion: The earthworm belongs to a group of animals called annelids (segmented worms). The body of an annelid is usually divided internally and externally into well-defined segments, which
Pre-lab Discussion: The earthworm belongs to a group of animals called annelids (segmented worms). The body of an annelid is usually divided internally and externally into well-defined segments, which
The Animals: Kingdom Animalia
 The Animals: Kingdom Animalia Kingdom Animalia (Animals) What is an Animal? Zoology- The study of Animals General Characteristics of 1. Animals are multicellular and eukaryotic. Animals 2. Animals consume
The Animals: Kingdom Animalia Kingdom Animalia (Animals) What is an Animal? Zoology- The study of Animals General Characteristics of 1. Animals are multicellular and eukaryotic. Animals 2. Animals consume
Phylum Mollusca Snails, slugs, oysters, clams, octopuses, and squids
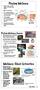 Phylum Mollusca Snails, slugs, oysters, clams, octopuses, and squids Nephridium Most are marine Visceral mass Soft-bodied animals, but most are protected by a hard shell Coelom Digestive tract Gonads Shell
Phylum Mollusca Snails, slugs, oysters, clams, octopuses, and squids Nephridium Most are marine Visceral mass Soft-bodied animals, but most are protected by a hard shell Coelom Digestive tract Gonads Shell
Internal Anatomy of Fish
 Internal Anatomy of Fish The Systems of a Fish Skeletal System Muscular System Respiratory System Digestive System Circulatory System Nervous System Reproductive System Special Organs Skeletal System
Internal Anatomy of Fish The Systems of a Fish Skeletal System Muscular System Respiratory System Digestive System Circulatory System Nervous System Reproductive System Special Organs Skeletal System
Symmetry. Asymmetrical- no shape. Radial- same in half when cut any angle. Bilateral- having a distinct right and left side
 Symmetry Asymmetrical- no shape Radial- same in half when cut any angle Bilateral- having a distinct right and left side Invertebrates 95% of Animals No Backbone The simplest animals and they do not have
Symmetry Asymmetrical- no shape Radial- same in half when cut any angle Bilateral- having a distinct right and left side Invertebrates 95% of Animals No Backbone The simplest animals and they do not have
Unit 18.2: Mollusks and Annelids
 Unit 18.2: Mollusks and Annelids Lesson Objectives Describe invertebrates in the phylum Mollusca. Summarize the characteristics of annelids. Vocabulary Annelida deposit feeder gills heart mantle Mollusca
Unit 18.2: Mollusks and Annelids Lesson Objectives Describe invertebrates in the phylum Mollusca. Summarize the characteristics of annelids. Vocabulary Annelida deposit feeder gills heart mantle Mollusca
27-4 Mollusks. Slide 1 of 43. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 1 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What Is a Mollusk? Mollusks are soft-bodied animals that usually have an internal or external shell. Mollusks include snails, slugs, clams, squids, octopi... They are group together
1 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What Is a Mollusk? Mollusks are soft-bodied animals that usually have an internal or external shell. Mollusks include snails, slugs, clams, squids, octopi... They are group together
Major groups of animals. I. Phylum Porifera. RADIATA II. Phylum Cnidaria. A. Class Hydrozoa. B. Class Anthozoa. C. Class Cubozoa. D.
 Major groups of animals I. Phylum Porifera A. no true tissues B. cell types 1. pinacocytes (pinacoderm - incipient tissue) 2. archaeocytes - in mesohyl 3. choanocytes C. Body forms 1. Asconoid a) water
Major groups of animals I. Phylum Porifera A. no true tissues B. cell types 1. pinacocytes (pinacoderm - incipient tissue) 2. archaeocytes - in mesohyl 3. choanocytes C. Body forms 1. Asconoid a) water
deuterostomes eucoelomates pseudocoelomates acoelomate
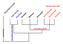 deuterostomes Mollusca Arthropoda Echinodermata Hemichordata Chordata eucoelomates Annelida Rotifera Platyhelminthes Nematoda acoelomate pseudocoelomates Phylum Hemichordata Share characteristics with
deuterostomes Mollusca Arthropoda Echinodermata Hemichordata Chordata eucoelomates Annelida Rotifera Platyhelminthes Nematoda acoelomate pseudocoelomates Phylum Hemichordata Share characteristics with
Mollusks are soft bodied animals that have an internal or external shell, a similar body plan consisting of four basic parts: a foot, mantle, shell,
 Mollusca Mollusks are soft bodied animals that have an internal or external shell, a similar body plan consisting of four basic parts: a foot, mantle, shell, and visceral mass. Mollusks also possess a
Mollusca Mollusks are soft bodied animals that have an internal or external shell, a similar body plan consisting of four basic parts: a foot, mantle, shell, and visceral mass. Mollusks also possess a
Invertebrates. Sponges: Porifera pore bearer 10/8/09
 Animals without backbones We ll cover characteristics of major phyla and some to class level (KPCOFGS) We ll also cover some natural history Refer to your notes that I posted on-line! Invertebrates Levels
Animals without backbones We ll cover characteristics of major phyla and some to class level (KPCOFGS) We ll also cover some natural history Refer to your notes that I posted on-line! Invertebrates Levels
Name Date Period. Mollusk Review TORSION HEMOLYMPH SESSILE TROCHOPHORE ADDUCTOR KIDNEY HEMOCOEL MANTLE CHROMATOPHORES VISCERAL MASS
 Name Date Period Mollusk Review MOLLUSK VOCABULARY: Match the word with its definition. TORSION HEMOLYMPH SESSILE TROCHOPHORE ADDUCTOR KIDNEY HEMOCOEL MANTLE CHROMATOPHORES VISCERAL MASS Free-swimming
Name Date Period Mollusk Review MOLLUSK VOCABULARY: Match the word with its definition. TORSION HEMOLYMPH SESSILE TROCHOPHORE ADDUCTOR KIDNEY HEMOCOEL MANTLE CHROMATOPHORES VISCERAL MASS Free-swimming
Protostomes vs Deuterostomes. Phylum Mollusca
 Protostomes vs Deuterostomes Animals that have a true coelom and complete digestive system can be divided into two main groups. This division is based on the way their embryos develop and the way in which
Protostomes vs Deuterostomes Animals that have a true coelom and complete digestive system can be divided into two main groups. This division is based on the way their embryos develop and the way in which
Kingdom Animalia part 2.notebook. April 08, The fun continues... Kingdom Animalia
 The fun continues....... Kingdom Animalia 1 2 Joint legged animals (arthropoda) found from the bottom of the ocean to high above the Earth's surface included insects, arachnid, and crustacean hard external
The fun continues....... Kingdom Animalia 1 2 Joint legged animals (arthropoda) found from the bottom of the ocean to high above the Earth's surface included insects, arachnid, and crustacean hard external
Animal Diversity. Kingdom Animalia
 7ch11 Animal Diversity Kingdom Animalia Animal Characteristics 1. animals are eukaryotes and are multicellular 2. cells are specialized for different functions (vision,digestion,reproduction) 3. protein,
7ch11 Animal Diversity Kingdom Animalia Animal Characteristics 1. animals are eukaryotes and are multicellular 2. cells are specialized for different functions (vision,digestion,reproduction) 3. protein,
 http://bio.fsu.edu/~bsc2011l/ Click on Course Documents, then Lab Review & select phyla of choice This presentation is also available: Click on Lab Review, then Spring 2005 Midterm Practical Review Practical
http://bio.fsu.edu/~bsc2011l/ Click on Course Documents, then Lab Review & select phyla of choice This presentation is also available: Click on Lab Review, then Spring 2005 Midterm Practical Review Practical
Protostome: Embryonic blastopore becomes mouth
 Classical hypothesis Molecular hypothesis Adoutte 2000 PNAS Protostome: Embryonic blastopore becomes mouth Schizocoelous development (typical of the protostome coelomates) 1 Deuterostome: Embryonic blastopore
Classical hypothesis Molecular hypothesis Adoutte 2000 PNAS Protostome: Embryonic blastopore becomes mouth Schizocoelous development (typical of the protostome coelomates) 1 Deuterostome: Embryonic blastopore
Title: May 31 2:42 PM (1 of 23) Phylum Mollusca
 Title: May 31 2:42 PM (1 of 23) Phylum Mollusca Title: May 31 3:25 PM (2 of 23) often referred to as mollusks second largest phylum has 7 classes only looking at 4 bilateral symmetry, true body cavity
Title: May 31 2:42 PM (1 of 23) Phylum Mollusca Title: May 31 3:25 PM (2 of 23) often referred to as mollusks second largest phylum has 7 classes only looking at 4 bilateral symmetry, true body cavity
Phylum Mollusca. Includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids.
 Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids. Bivalves Nautilus Characteristics Soft-bodied invertebrate Covered with protective mantle that may or may
Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids. Bivalves Nautilus Characteristics Soft-bodied invertebrate Covered with protective mantle that may or may
Chapter Outline CHAPTER 30 THE PROTOSTOMES
 CHAPTER 30 THE PROTOSTOMES Chapter Outline 30.1 A Coelom A. Protostome Organization 1. Protostomes are bilaterally symmetrical, have three germ layers, the organ level of organization, the tube-within-a-tube
CHAPTER 30 THE PROTOSTOMES Chapter Outline 30.1 A Coelom A. Protostome Organization 1. Protostomes are bilaterally symmetrical, have three germ layers, the organ level of organization, the tube-within-a-tube
ANIMAL KINGDOM CHAPTER 4 14 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 14 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 4 ANIMAL KINGDOM MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. In some animal groups, the body is found divided into compartments with at least some organs/ organ repeated. This characteristic
14 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 4 ANIMAL KINGDOM MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. In some animal groups, the body is found divided into compartments with at least some organs/ organ repeated. This characteristic
Perch Dissection Lab
 Name: Block: Due Date: Perch Dissection Lab Background The fish in the class Osteichthyes have bony skeletons. There are three groups of the bony fish: ray-finned, lobe-finned, and the lungfish. The perch
Name: Block: Due Date: Perch Dissection Lab Background The fish in the class Osteichthyes have bony skeletons. There are three groups of the bony fish: ray-finned, lobe-finned, and the lungfish. The perch
Chapter 33 - Protostome Animals
 Chapter 33 - Protostome Animals Learning Objectives: Students should be able to... Describe the major characteristics that differentiate the Ecdysozoa and the Lophotrochozoa. List and describe the basic
Chapter 33 - Protostome Animals Learning Objectives: Students should be able to... Describe the major characteristics that differentiate the Ecdysozoa and the Lophotrochozoa. List and describe the basic
1. Animals are (diploid) with tissues arranged into organs and organ systems. 3. Animals require for aerobic respiration.
 Chapter 25 Animals: The Invertebrates I. Overview of the Animal Kingdom A. General Characteristics of Animals 1. Animals are (diploid) with tissues arranged into organs and organ systems. 2. Animals are.
Chapter 25 Animals: The Invertebrates I. Overview of the Animal Kingdom A. General Characteristics of Animals 1. Animals are (diploid) with tissues arranged into organs and organ systems. 2. Animals are.
Biol Echinoderms & Chordates. But first a few words about Development
 Biol 1309 Echinoderms & Chordates 1 But first a few words about Development Blastula- zygote first develops into a hollow ball of cells Deuterostome - mouth second Protostome - mouth first Cleavage - describes
Biol 1309 Echinoderms & Chordates 1 But first a few words about Development Blastula- zygote first develops into a hollow ball of cells Deuterostome - mouth second Protostome - mouth first Cleavage - describes
Overview of Invertebrates
 Overview of Invertebrates General Features of Animals Heterotrophic Multicellular (eukaryotic) Cells lack rigid cell walls Cells are usually quite flexible. Cells (except sponges) are organized into structural
Overview of Invertebrates General Features of Animals Heterotrophic Multicellular (eukaryotic) Cells lack rigid cell walls Cells are usually quite flexible. Cells (except sponges) are organized into structural
I. Evolutionary Perspective. Chapter 12. II. Molluscan Characteristics. A. Regions of Molluscan Body 11/2/10
 I. Evolutionary Perspective Chapter 12 Molluscan Success Some of the world s best predators Large brains Complex sensory structures Rapid locomotion Grasping tentacles Tearing mouthparts Have been around
I. Evolutionary Perspective Chapter 12 Molluscan Success Some of the world s best predators Large brains Complex sensory structures Rapid locomotion Grasping tentacles Tearing mouthparts Have been around
Kingdom Animalia. Eukaryotic Multicellular Heterotrophs Lack Cell Walls
 Kingdom Animalia Eukaryotic Multicellular Heterotrophs Lack Cell Walls Must do: Feed, Respiration, Circulation, Excretion, Response, Movement, and Reproduction Symmetry Asymmetrical- no shape Radial- same
Kingdom Animalia Eukaryotic Multicellular Heterotrophs Lack Cell Walls Must do: Feed, Respiration, Circulation, Excretion, Response, Movement, and Reproduction Symmetry Asymmetrical- no shape Radial- same
 Echinoderms Name Means: Echino- Spiny Derm- Skin About 7,000 species No Head! No Brain! No ventral, dorsal, posterior, or anterior sides! Do have oral (mouth) and aboral sides. Symmetry: Larvae are
Echinoderms Name Means: Echino- Spiny Derm- Skin About 7,000 species No Head! No Brain! No ventral, dorsal, posterior, or anterior sides! Do have oral (mouth) and aboral sides. Symmetry: Larvae are
Kingdom Animalia Subkingdom Eumetazoa Bilateria Phylum Mollusca
 Kingdom Animalia Subkingdom Eumetazoa Bilateria Phylum Mollusca Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A Illustrations 2014 Cengage Learning unless otherwise noted Phylum Mollusca Molluscs (mollis = soft)
Kingdom Animalia Subkingdom Eumetazoa Bilateria Phylum Mollusca Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A Illustrations 2014 Cengage Learning unless otherwise noted Phylum Mollusca Molluscs (mollis = soft)
Characteris*c s of Living Things 1. Chemical Uniqueness: Molecular Organization
 Characteris*c s of Living Things 1. Chemical Uniqueness: Molecular Organization 2. Hierarchical Organization: macromolecules - > Cells - >Organs - >Organ systems 3. Reproduction 4. Genetic Programs 5.
Characteris*c s of Living Things 1. Chemical Uniqueness: Molecular Organization 2. Hierarchical Organization: macromolecules - > Cells - >Organs - >Organ systems 3. Reproduction 4. Genetic Programs 5.
CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) CHAPTER-04 ANIMAL KINGDOM
 CBSE Quick Revision Notes (-11 Biology) CHAPTER-04 ANIMAL KINGDOM Millions of species of animals have been described and it becomes more necessary to classify them to assign a systematic position. Animals
CBSE Quick Revision Notes (-11 Biology) CHAPTER-04 ANIMAL KINGDOM Millions of species of animals have been described and it becomes more necessary to classify them to assign a systematic position. Animals
Phylum Mollusca Classes
 Lecture Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Classes Aculifera with spicules Aplacophora - mollusks without shells Polyplacophora ( Amphineura) chiton, eight plates, intertidal Conchifera with shells Monoplacophora
Lecture Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Classes Aculifera with spicules Aplacophora - mollusks without shells Polyplacophora ( Amphineura) chiton, eight plates, intertidal Conchifera with shells Monoplacophora
ADVANCED INVERTEBRATES HAVE COMPLEX BODIES AND INTERNAL SYSTEMS
 ADVANCED INVERTEBRATES HAVE COMPLEX BODIES AND INTERNAL SYSTEMS Arthropoda Most successful phylum on Earth Exoskeleton chitin Striated muscle Articulation Crayfish, lobsters, shrimp, crabs Echinodermata
ADVANCED INVERTEBRATES HAVE COMPLEX BODIES AND INTERNAL SYSTEMS Arthropoda Most successful phylum on Earth Exoskeleton chitin Striated muscle Articulation Crayfish, lobsters, shrimp, crabs Echinodermata
 http://bio.fsu.edu/~bsc2011l/ Click on Course Documents, then Lab Documents Look at each lab (1 or more phyla) and the images posted. This presentation is also available: Click on Course Documents, then
http://bio.fsu.edu/~bsc2011l/ Click on Course Documents, then Lab Documents Look at each lab (1 or more phyla) and the images posted. This presentation is also available: Click on Course Documents, then
Animal Evolution: Chordate and Vertebrate Evolution and Diversity (Learning Outline)
 Animal Evolution: Chordate and Vertebrate Evolution and Diversity (Learning Outline) 1. Distinguishing features of the phylum Chordata and representative organisms. 2. Highlights of evolutionary steps
Animal Evolution: Chordate and Vertebrate Evolution and Diversity (Learning Outline) 1. Distinguishing features of the phylum Chordata and representative organisms. 2. Highlights of evolutionary steps
ANIMAL FORM AND FUNCTION CEPHALOPODS (PHYLUM MOLLUSCA)
 ANIMAL FORM AND FUNCTION CEPHALOPODS (PHYLUM MOLLUSCA) As part of our continued exploration of the animal kingdom today we will perform a dissection of a squid, which is a member of the Class Cephalopoda
ANIMAL FORM AND FUNCTION CEPHALOPODS (PHYLUM MOLLUSCA) As part of our continued exploration of the animal kingdom today we will perform a dissection of a squid, which is a member of the Class Cephalopoda
Course: Biology 211 Iowa State University
 Leader: Elizabeth Supplemental Instruction Course: Biology 211 Iowa State University Instructor: Dr. Deitloff Date: 2/27/14 Exam 2: Chapters 31 through 34 and information from guest lecturer 50 questions
Leader: Elizabeth Supplemental Instruction Course: Biology 211 Iowa State University Instructor: Dr. Deitloff Date: 2/27/14 Exam 2: Chapters 31 through 34 and information from guest lecturer 50 questions
REMEMBER: Look over your classification and taxonomy notes from AS2!
 Kingdom Animalia REMEMBER: Look over your classification and taxonomy notes from AS2! Kingdom Animalia Features Eukaryotic cells lacking cell walls They have an internal cavity termed an enteron in which
Kingdom Animalia REMEMBER: Look over your classification and taxonomy notes from AS2! Kingdom Animalia Features Eukaryotic cells lacking cell walls They have an internal cavity termed an enteron in which
Phyllum: Annelida BODY SURFACE. cuticle epidermis
 Phyllum: Annelida from mm to about 3 meters (most species from 2 to 10 mm) prostomium - head prior to the oral opening pygidium - abdominal segment of links between prostomiem and pygidiem BODY SURFACE
Phyllum: Annelida from mm to about 3 meters (most species from 2 to 10 mm) prostomium - head prior to the oral opening pygidium - abdominal segment of links between prostomiem and pygidiem BODY SURFACE
Molluscs. Chapter 16
 Molluscs Chapter 16 Phylum Mollusca Phylum Mollusca includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids. Phylum Mollusca Molluscs have a mesoderm lined body cavity a coelom. They are
Molluscs Chapter 16 Phylum Mollusca Phylum Mollusca includes snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids. Phylum Mollusca Molluscs have a mesoderm lined body cavity a coelom. They are
PHYLUM: PLATHYHELMINTHES
 PHYLUM: PLATHYHELMINTHES FLATWORMS Free living (living independently i.e. not attached) Bilaterally symmetrical with a definite front and back, and with left and right sides. Mobile creeping animals. Concentration
PHYLUM: PLATHYHELMINTHES FLATWORMS Free living (living independently i.e. not attached) Bilaterally symmetrical with a definite front and back, and with left and right sides. Mobile creeping animals. Concentration
Body Plan of the Chordates. Notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal gill slits, blocks of muscle, post-anal tail
 Chordata The Major Groups Invertebrate Chordates Fishes Class: Agnatha Class Condrichthyes Class Osteichthyes Class: Amphibia Class: Reptilia Class: Aves Class: Mammalia Body Plan of the Chordates Notochord,
Chordata The Major Groups Invertebrate Chordates Fishes Class: Agnatha Class Condrichthyes Class Osteichthyes Class: Amphibia Class: Reptilia Class: Aves Class: Mammalia Body Plan of the Chordates Notochord,
What do animals do to survive?
 What do animals do to survive? Section 26-1 All Animals have are carry out Eukaryotic cells with Heterotrophs Essential functions such as No cell walls Feeding Respiration Circulation Excretion Response
What do animals do to survive? Section 26-1 All Animals have are carry out Eukaryotic cells with Heterotrophs Essential functions such as No cell walls Feeding Respiration Circulation Excretion Response
2 Mollusks and Annelid Worms
 CHAPTER 15 2 Mollusks and Annelid Worms SECTION Invertebrates BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the four features of mollusks? What are
CHAPTER 15 2 Mollusks and Annelid Worms SECTION Invertebrates BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the four features of mollusks? What are
Biology. Slide 1 of 43. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 43 2 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What are the defining features of mollusks? 3 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What Is a Mollusk? Mollusks are soft-bodied animals that usually have an internal or external
Biology 1 of 43 2 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What are the defining features of mollusks? 3 of 43 What Is a Mollusk? What Is a Mollusk? Mollusks are soft-bodied animals that usually have an internal or external
General Characters of Trematodes
 Parasitology Department General Characters of Trematodes By Hala Elwakil, MD Intended Learning Outcomes By the end of this lecture, the student will be able to know: 1. General morphology of trematodes
Parasitology Department General Characters of Trematodes By Hala Elwakil, MD Intended Learning Outcomes By the end of this lecture, the student will be able to know: 1. General morphology of trematodes
