S.A. Klein and G.F. Nellis Cambridge University Press, 2011
|
|
|
- Eustacia Miles
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 16-1 A flow nozzle is to be used to determine the mass flow rate of air through a 1.5 inch internal diameter pipe. The air in the line upstream of the meters is at 70 F and 95 psig. The barometric pressure = 14.7 psia. The diameter at the throat of the flow nozzle is 0.25 in. Assume that the flow nozzle operates isentropically. a.) Prepare a plot that relates the mass flow rate of the air in lb m /min to the absolute pressure at the nozzle throat in psia. b.) What is the maximum flow rate that can be measured by this nozzle in lb m /min?
2 16-2 For the Formula Car challenge, the air inlet to the engine is required to have a minimum area of 0.25 in 2. You are requested to evaluate the two inlet air design options shown below. Design A uses a converging nozzle with a throat area of 0.25 in 2. Design B uses a converging-diverging nozzle with a throat area of 0.25 in 2 and an exit area of in 2. The nozzle in both of these designs exhausts to the inlet plenum for a turbo charger. Assume that both nozzles operate isentropically. Air Inlet P atm =15psi Inlet Plenum Turbo Charger DESIGN A: A throat =0.25in 2 Air Inlet P atm =15psi Inlet Plenum Turbo Charger DESIGN B: A throat =0.25in 2 A exit =0.415in 2 a.) Compare the maximum air flow rates for the nozzles in Design A and Design B. Which nozzle provides the largest mass flow rate? b.) Prepare a plot of the mass flow rate for the converging nozzle in Design A as a function of the ratio of the plenum pressure to the inlet pressure. c.) Prepare a plot of the mass flow rate for the converging nozzle in Design B as a function of the ratio of the plenum pressure to the inlet pressure, assuming that flow in the diverging section of the nozzle is subsonic. d.) The turbocharger raises the pressure of the air from the pressure in the inlet plenum pressure to the pressure at which air is charged into the cylinders. Explain which nozzle (Design A or Design B) you would you recommend for this purpose any why.
3 16-3 A converging-diverging nozzle has the geometry shown in Figure 16P-3. Figure 16P-3 Nozzle Geometry a.) Assuming isentropic flow conditions otherwise, determine the lowest and highest pressures at the exit plane for which a shock wave is expected to develop within the diverging part of the nozzle b.) The pressure is at the exit of the nozzle is measured to be 400 kpa. Determine the velocity and temperature at the exit.
4 16-4 A rocket engine steady generates combustion gas at a pressure of 682 psia, as measured by a pressure sensor attached to the body of the motor as shown in Figure 16P-4. The combustion gas consists of 40% carbon dioxide and 60% water vapor (molar basis) at 1245 F. The nozzle has a throat diameter of 18 in and it discharges to the atmosphere with a barometric pressure of 14.5 psia. Experimental data verify that the performance of this system can be predicted by one-dimensional isentropic flow theory. Assuming ideal gas behavior, determine: a.) The required exit diameter of the nozzle in order for it to operate at design conditions. b.) The mass flow rate of gas out of the engine. c.) The thrust produced by the engine in lbf Figure 16P-4: Rocket engine
5 16-5 A converging-diverging and a converging nozzle are connected in a parallel flow arrangement, as shown in Figure 16P-5. The inlet air conditions for both nozzles are 300 K, 10 bar. The back pressure is varied from 10 bar to 1 bar. Both nozzles have the same minimum throat area = m 2. In addition, the cross-sectional area at the inlet of the converging nozzle and the exit area of the converging-diverging nozzle are both m 2. Figure 16P-5: Converging diverging and converging nozzles a.) Plot the mass flow rate though the converging nozzle as a function of back pressure for back pressures between 10 bar and 1 bar. b.) Plot the mass flow rate though the converging-diverging nozzle as a function of back pressure for back pressures between 10 bar and 1 bar.
6 16.6 An engineer is studying the leakage that occurs from a labyrinth seal in a super-critical carbon dioxide Brayton cycle. He has decided to model the leakage that occurs through the seal as a nozzle, in order to determine a limit on leakage rate and the temperature that may be experienced at the seal. Carbon dioxide enters the seal at 55 C and 75 bar. The exit area is estimated to be 4.5E-6 m 2. Assume that the process can be modeled as isentropic process and that choked flow occurs at the seal exit. a.) Calculate the leakage rate and the pressure and temperature at the seal exit assuming carbon dioxide can be modeled as an ideal gas. b.) The inlet pressure is above the critical pressure. Repeat part a, but do not assume that carbon dioxide obeys the ideal gas law.
7 16.7 A nozzle is used to determine the mass flow rate of methane (CH 4 ) as it flows through a pipeline. The stagnation conditions of the methane are 30 C, 10 bar. The exit diameter of the nozzle is 5.0 cm. The pressure downstream of the nozzle is 9 bar. The nozzle is adiabatic and, except for a normal shock (if one is present) the flow may be assumed to be reversible. a.) If a converging nozzle is used to make this measurement, what is the mass flow rate of methane? b.) If a converging-diverging nozzle with a throat diameter of 3.5 cm and an exit diameter of 5.0 cm is used to make this measurement, what is the mass flow rate of methane?
8 16-8 Air is flowing through a CD nozzle for which the cross-sectional area as a function of position is shown in Table 16P-8. The pressure at the inlet plenum is 550 kpa and the temperature is 42 C. A shock is observed to occur at position 8. Table 16P.8: Area at various cross-sectional areas in a nozzle Position Area (cm 2 ) 0 (inlet) (exit plane) 54 a) Determine the mass flow rate of air through this nozzle. b) Determine the pressures just upstream and just downstream of the shock wave, assuming the nozzle behaves isentropically. c) Determine the temperature, pressure and velocity of air at the nozzle exit plane.
9 16-9 A gas cylinder having a volume of 0.24 m 3 contains air at 20ºC, 24 bar. The cylinder is equipped with a valve. The valve is opened and the air is rapidly vented to the atmosphere at kpa through a valve with an exit diameter of cm. It is not clear how much thermal interaction there is between the air remaining in the cylinder and the cylinder walls. At one extreme, the venting process can be considered to be adiabatic. At the other extreme, the heat transfer coefficient between the air and the cylinder walls may be high so that the air remains at 20 C throughout the venting process. The valve can be modeled as a converging nozzle, which may or may not be choked, depending on the pressure in the cylinder. Assume air to behave as an ideal gas. a.) Assuming that the venting process is adiabatic, calculate and plot the pressure in the tank as a function of time. How much time is needed to reduce the pressure to 110 kpa? b.) Repeat part a, but assume the venting process is isothermal at 20 C.
10 16-10 Hydrogen has been proposed as a fuel for vehicles. This problem is concerned with the time it will take to fill the tank in the vehicle with high pressure hydrogen. The tank is a carbon-fiber reinforced shell with a volume of 150 liters. The filling stations supplies compressed hydrogen at 400 bar and 25 C. A vehicle enters a filling station with its hydrogen fuel tank at 25 C and 20 bar and the tank is filled to a pressure of 375 bar through a converging nozzle that has an exit diameter of 1 mm. (The nozzle is also used for measuring the mass flow rate.) In the actual filling process, the flow through the nozzle will initially be choked and at a later time, as the pressure in the tank increases, the flow at nozzle exit will be subsonic. Assume ideal gas behavior in your analysis. a.) Prepare a plot of the pressure in the tank as a function of time assuming that choked flow always occurs in the nozzle during the filling process. Based on your plot, determine the time required to fill the tank to 375 bar and the mass of hydrogen delivered. b.) Repeat the calculations for part a, but in this case, account for subsonic flow when it occurs. Compare the time and mass of hydrogen delivered to the tank with the results from part a.
Quiz #1 Thermodynamics Spring, 2018 Closed Book, Open Appendices, Closed Notes, CLOSED CALCULATORS
 Quiz #1 Closed Book, Open Appendices, Closed Notes, CLOSED CALCULATORS An astronaut has a mass of 161 lbm on the surface of the earth. Calculate his weight (in lbf) on planet Rigel 4 where g = 20.0 ft/s
Quiz #1 Closed Book, Open Appendices, Closed Notes, CLOSED CALCULATORS An astronaut has a mass of 161 lbm on the surface of the earth. Calculate his weight (in lbf) on planet Rigel 4 where g = 20.0 ft/s
Enter your parameter set number (1-27)
 1- Helium balloons fly and balloons with air sink. Assume that we want to get a balloon that is just floating in the air, neither rising nor falling, when a small weight is placed hanging in the balloon.
1- Helium balloons fly and balloons with air sink. Assume that we want to get a balloon that is just floating in the air, neither rising nor falling, when a small weight is placed hanging in the balloon.
Cover Page for Lab Report Group Portion. Compressible Flow in a Converging-Diverging Nozzle
 Cover Page for Lab Report Group Portion Compressible Flow in a Converging-Diverging Nozzle Prepared by Professor J. M. Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revision: Prof. Steve Lynch, 14 February 2017
Cover Page for Lab Report Group Portion Compressible Flow in a Converging-Diverging Nozzle Prepared by Professor J. M. Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revision: Prof. Steve Lynch, 14 February 2017
ASSIGNMENT 2 CHE 3473
 DUE: May 23 ASSIGNMENT 2 CHE 3473 #Problem 1: 3.3 #Problem 2: 3.4 #Problem 3: 3.5 #Problem 4: 3.6 #Problem 5: 3.7 #Problem 6: 3.8 #Problem 7: 3.11 #Problem 8: 3.15 #Problem 9: 3.22 #Problem 10: 3.32 #Problem
DUE: May 23 ASSIGNMENT 2 CHE 3473 #Problem 1: 3.3 #Problem 2: 3.4 #Problem 3: 3.5 #Problem 4: 3.6 #Problem 5: 3.7 #Problem 6: 3.8 #Problem 7: 3.11 #Problem 8: 3.15 #Problem 9: 3.22 #Problem 10: 3.32 #Problem
ASSIGNMENT 2 CHE 3473
 DUE: May 21 ASSIGNMENT 2 CHE 3473 #Problem 1 Read Chapter 3. ALL OF IT. Time yourself and report the time. #Problem 2: 3.2 #Problem 3: 3.3 #Problem 4: 3.5 #Problem 5: 3.6 #Problem 6: 3.7 #Problem 7: 3.8
DUE: May 21 ASSIGNMENT 2 CHE 3473 #Problem 1 Read Chapter 3. ALL OF IT. Time yourself and report the time. #Problem 2: 3.2 #Problem 3: 3.3 #Problem 4: 3.5 #Problem 5: 3.6 #Problem 6: 3.7 #Problem 7: 3.8
Applied Fluid Mechanics
 Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
****** * EX * ****** DWN W.W.POWELL CALCULATION OF FLOW LOSSES IN INLET CHK D.PAPA AND DISCHARGE HEADERS ASSOCIATED WITH
 BC ****** * EX * ****** DWN W.W.POWELL 4-17-75 CALCULATION OF FLOW LOSSES IN INLET CHK D.PAPA 4-17-75 AND DISCHARGE HEADERS ASSOCIATED WITH APPR APPR SAFETY RELIEF VALVES SIZE REV APPR A 02.0175.128 L
BC ****** * EX * ****** DWN W.W.POWELL 4-17-75 CALCULATION OF FLOW LOSSES IN INLET CHK D.PAPA 4-17-75 AND DISCHARGE HEADERS ASSOCIATED WITH APPR APPR SAFETY RELIEF VALVES SIZE REV APPR A 02.0175.128 L
Cover Page for Lab Report Group Portion. Compressible Flow in a Converging-Diverging Nozzle
 Cover Page for Lab Report Group Portion Compressible Flow in a Converging-Diverging Nozzle Prepared by Professor J. M. Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revision: 13 January 2012 Name 1: Name 2: Name
Cover Page for Lab Report Group Portion Compressible Flow in a Converging-Diverging Nozzle Prepared by Professor J. M. Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revision: 13 January 2012 Name 1: Name 2: Name
Device Description. Operating Information. CP Q (eq. 1) GT. Technical Bulletin TB-0607-CFP Hawkeye Industries Critical Flow Prover
 A compressible fluid traveling at subsonic velocity through a duct of constant cross section will increase velocity when passing through a region of reduced cross-sectional area (in this case, an orifice)
A compressible fluid traveling at subsonic velocity through a duct of constant cross section will increase velocity when passing through a region of reduced cross-sectional area (in this case, an orifice)
Please welcome for any correction or misprint in the entire manuscript and your valuable suggestions kindly mail us
 Problems of Practices Of Basic and Applied Thermodynamics First Law of Thermodynamics Prepared By Brij Bhooshan Asst. Professor B. S. A. College of Engg. And Technology Mathura, Uttar Pradesh, (India)
Problems of Practices Of Basic and Applied Thermodynamics First Law of Thermodynamics Prepared By Brij Bhooshan Asst. Professor B. S. A. College of Engg. And Technology Mathura, Uttar Pradesh, (India)
CHEMISTRY - CLUTCH CH.5 - GASES.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: UNITS OF PRESSURE Pressure is defined as the force exerted per unit of surface area. Pressure = Force Area The SI unit for Pressure is the, which has the units of. The SI
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: UNITS OF PRESSURE Pressure is defined as the force exerted per unit of surface area. Pressure = Force Area The SI unit for Pressure is the, which has the units of. The SI
Constant-Volume Process
 Constant-Volume Process A constant-volume process is called an isochoric process. Consider the gas in a closed, rigid container. Warming the gas with a flame will raise its pressure without changing its
Constant-Volume Process A constant-volume process is called an isochoric process. Consider the gas in a closed, rigid container. Warming the gas with a flame will raise its pressure without changing its
Lab # 03: Visualization of Shock Waves by using Schlieren Technique
 AerE545 Lab # 03: Visualization of Shock Waves by using Schlieren Technique Objectives: 1. To get hands-on experiences about Schlieren technique for flow visualization. 2. To learn how to do the optics
AerE545 Lab # 03: Visualization of Shock Waves by using Schlieren Technique Objectives: 1. To get hands-on experiences about Schlieren technique for flow visualization. 2. To learn how to do the optics
Application Worksheet
 Application Worksheet All dimensions are nominal. Dimensions in [ ] are in millimeters. Service Conditions Medium Through Valve: Required C v : Temperature Maximum: Minimum: Normal: Flow Maximum: Minimum:
Application Worksheet All dimensions are nominal. Dimensions in [ ] are in millimeters. Service Conditions Medium Through Valve: Required C v : Temperature Maximum: Minimum: Normal: Flow Maximum: Minimum:
Tutorial. BOSfluids. Relief valve
 Tutorial Relief valve The Relief valve tutorial describes the theory and modeling process of a pressure relief valve or safety valve. It covers the algorithm BOSfluids uses to model the valve and a worked
Tutorial Relief valve The Relief valve tutorial describes the theory and modeling process of a pressure relief valve or safety valve. It covers the algorithm BOSfluids uses to model the valve and a worked
Gas Turbine Performance Analysis
 Gas Turbine Performance Analysis Gas turbines may seem too complicated or overwhelming at first glance, but for regular field monitoring on a relative basis, it is not all that difficult. A regular check
Gas Turbine Performance Analysis Gas turbines may seem too complicated or overwhelming at first glance, but for regular field monitoring on a relative basis, it is not all that difficult. A regular check
CALCULATING THE SPEED OF SOUND IN NATURAL GAS USING AGA REPORT NO Walnut Lake Rd th Street Houston TX Garner, IA 50438
 CALCULATING THE SPEED OF SOUND IN NATURAL GAS USING AGA REPORT NO. 10 Jerry Paul Smith Joel Clancy JPS Measurement Consultants, Inc Colorado Engineering Experiment Station, Inc (CEESI) 13002 Walnut Lake
CALCULATING THE SPEED OF SOUND IN NATURAL GAS USING AGA REPORT NO. 10 Jerry Paul Smith Joel Clancy JPS Measurement Consultants, Inc Colorado Engineering Experiment Station, Inc (CEESI) 13002 Walnut Lake
CHAPTER 31 IDEAL GAS LAWS
 CHAPTER 31 IDEAL GAS LAWS EXERCISE 144, Page 317 1. The pressure of a mass of gas is increased from 150 kpa to 750 kpa at constant temperature. Determine the final volume of the gas, if its initial volume
CHAPTER 31 IDEAL GAS LAWS EXERCISE 144, Page 317 1. The pressure of a mass of gas is increased from 150 kpa to 750 kpa at constant temperature. Determine the final volume of the gas, if its initial volume
DEVELOPMENT OF HIGH ALTITUDE TEST FACILITY FOR COLD JET SIMULATION
 DEVELOPMENT OF HIGH ALTITUDE TEST FACILITY FOR COLD JET SIMULATION Aldin Justin 1, Robin James, Shruti Panicker 2,A.N.Subash,Saravana Kumar 1 Assistant Professor,Karunya University, aldinjustin@karunya.edu
DEVELOPMENT OF HIGH ALTITUDE TEST FACILITY FOR COLD JET SIMULATION Aldin Justin 1, Robin James, Shruti Panicker 2,A.N.Subash,Saravana Kumar 1 Assistant Professor,Karunya University, aldinjustin@karunya.edu
Chapter 13 Gases, Vapors, Liquids, and Solids
 Chapter 13 Gases, Vapors, Liquids, and Solids Property is meaning any measurable characteristic of a substance, such as pressure, volume, or temperature, or a characteristic that can be calculated or deduced,
Chapter 13 Gases, Vapors, Liquids, and Solids Property is meaning any measurable characteristic of a substance, such as pressure, volume, or temperature, or a characteristic that can be calculated or deduced,
MEASUREMENT OF GAS DISCHARGE COEFFICIENT
 MEASUREMENT OF GAS DISCHARGE COEFFICIENT Ilona Pasková, Ondřej Novák, Václav Koza RWE GasNet, ilona.paskova@rwe.cz ICT Prague, Department of gas, coke and air protection, ondrej.novak@vscht.cz, vaclav.koza@vscht.cz
MEASUREMENT OF GAS DISCHARGE COEFFICIENT Ilona Pasková, Ondřej Novák, Václav Koza RWE GasNet, ilona.paskova@rwe.cz ICT Prague, Department of gas, coke and air protection, ondrej.novak@vscht.cz, vaclav.koza@vscht.cz
THE IMPLEMENTATION OF TOROIDAL THROAT VENTURI NOZZLES TO MAXIMIZE PRECISION IN GAS FLOW TRANSFER STANDARD APPLICATIONS
 Presented 2005 JUNE FLOMEKO Peebles, SCOTLAND THE IMPLEMENTATION OF TOROIDAL THROAT VENTURI NOZZLES TO MAXIMIZE PRECISION IN GAS FLOW TRANSFER STANDARD APPLICATIONS Pierre Delajoud, Martin Girard, Michael
Presented 2005 JUNE FLOMEKO Peebles, SCOTLAND THE IMPLEMENTATION OF TOROIDAL THROAT VENTURI NOZZLES TO MAXIMIZE PRECISION IN GAS FLOW TRANSFER STANDARD APPLICATIONS Pierre Delajoud, Martin Girard, Michael
Case 12 Multistage Centrifugal Refrigeration System Halocarbon Refrigerant
 Case 12 Multistage Centrifugal Refrigeration System Halocarbon Refrigerant Copy Right By: Thomas T.S. Wan 温 ) April 15, 2011 All Rights Reserved Case Background: This case is to show how to achieve the
Case 12 Multistage Centrifugal Refrigeration System Halocarbon Refrigerant Copy Right By: Thomas T.S. Wan 温 ) April 15, 2011 All Rights Reserved Case Background: This case is to show how to achieve the
Micro Channel Recuperator for a Reverse Brayton Cycle Cryocooler
 Micro Channel Recuperator for a Reverse Brayton Cycle Cryocooler C. Becnel, J. Lagrone, and K. Kelly Mezzo Technologies Baton Rouge, LA USA 70806 ABSTRACT The Missile Defense Agency has supported a research
Micro Channel Recuperator for a Reverse Brayton Cycle Cryocooler C. Becnel, J. Lagrone, and K. Kelly Mezzo Technologies Baton Rouge, LA USA 70806 ABSTRACT The Missile Defense Agency has supported a research
Rupture Disc Sizing for Micro Motion Coriolis Sensors
 Rupture Disc Sizing for Micro Motion Coriolis Sensors www.emerson.com/micromotion Rupture Disc Sizing White Paper 1 Introduction Emerson s Micro Motion Coriolis flow meters are widely used in many industries
Rupture Disc Sizing for Micro Motion Coriolis Sensors www.emerson.com/micromotion Rupture Disc Sizing White Paper 1 Introduction Emerson s Micro Motion Coriolis flow meters are widely used in many industries
Name Chemistry Pre-AP
 Name Chemistry Pre-AP Notes: Gas Laws and Gas Stoichiometry Period Part 1: The Nature of Gases and The Gas Laws I. Nature of Gases A. Kinetic-Molecular Theory The - theory was developed to account for
Name Chemistry Pre-AP Notes: Gas Laws and Gas Stoichiometry Period Part 1: The Nature of Gases and The Gas Laws I. Nature of Gases A. Kinetic-Molecular Theory The - theory was developed to account for
Process Nature of Process
 AP Physics Free Response Practice Thermodynamics 1983B4. The pv-diagram above represents the states of an ideal gas during one cycle of operation of a reversible heat engine. The cycle consists of the
AP Physics Free Response Practice Thermodynamics 1983B4. The pv-diagram above represents the states of an ideal gas during one cycle of operation of a reversible heat engine. The cycle consists of the
CERTIFICATES OF COMPETENCY IN THE MERCHANT NAVY MARINE ENGINEER OFFICER
 CERTIFICATES OF COMPETENCY IN THE MERCHANT NAVY MARINE ENGINEER OFFICER EXAMINATIONS ADMINISTERED BY THE SCOTTISH QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY ON BEHALF OF THE MARITIME AND COASTGUARD AGENCY STCW 95 CHIEF
CERTIFICATES OF COMPETENCY IN THE MERCHANT NAVY MARINE ENGINEER OFFICER EXAMINATIONS ADMINISTERED BY THE SCOTTISH QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY ON BEHALF OF THE MARITIME AND COASTGUARD AGENCY STCW 95 CHIEF
NORDCALC Introduction... 2 Registration... 2 Flow Calculations tab Torque Calculation & Actuator Mounting Data tab... 21
 NORDCALC User Guide Table of Contents NORDCALC Introduction... 2 Registration... 2 Flow Calculations tab... 5 Calculating the gas flow rate for gaseous medium... 6 Calculating the pressure drop for gaseous
NORDCALC User Guide Table of Contents NORDCALC Introduction... 2 Registration... 2 Flow Calculations tab... 5 Calculating the gas flow rate for gaseous medium... 6 Calculating the pressure drop for gaseous
Chemistry HP Unit 6 Gases. Learning Targets (Your exam at the end of Unit 6 will assess the following:) 6. Gases
 Chemistry HP Unit 6 Gases Learning Targets (Your exam at the end of Unit 6 will assess the following:) 6. Gases 6-1. Define pressure using a mathematical equation. 6-2. Perform calculations involving pressure,
Chemistry HP Unit 6 Gases Learning Targets (Your exam at the end of Unit 6 will assess the following:) 6. Gases 6-1. Define pressure using a mathematical equation. 6-2. Perform calculations involving pressure,
Name: Class: Date: SHORT ANSWER Answer the following questions in the space provided.
 CHAPTER 11 REVIEW Gases SECTION 1 SHORT ANSWER Answer the following questions in the space provided. 1. Pressure =. For a constant force, when the surface area is tripled the pressure is (a) doubled. (b)
CHAPTER 11 REVIEW Gases SECTION 1 SHORT ANSWER Answer the following questions in the space provided. 1. Pressure =. For a constant force, when the surface area is tripled the pressure is (a) doubled. (b)
Investigation on Divergent Exit Curvature Effect on Nozzle Pressure Ratio of Supersonic Convergent Divergent Nozzle
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Investigation on Divergent Exit Curvature Effect on Nozzle Pressure Ratio of Supersonic Convergent Divergent Nozzle Shyamshankar.M.B*, Sankar.V** *(Department of Aeronautical
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Investigation on Divergent Exit Curvature Effect on Nozzle Pressure Ratio of Supersonic Convergent Divergent Nozzle Shyamshankar.M.B*, Sankar.V** *(Department of Aeronautical
Test Report # Rev 0. Adiabatic Compression With Constant Bleed Valve
 Test Report # 30016558 Rev 0 Adiabatic Compression With Constant Bleed Valve Scope: This test report contains test data on the effects of adiabatic compression in nitrogen service on AP3600 diaphragm valves,
Test Report # 30016558 Rev 0 Adiabatic Compression With Constant Bleed Valve Scope: This test report contains test data on the effects of adiabatic compression in nitrogen service on AP3600 diaphragm valves,
Boyle s Law Practice
 Boyle s Law Practice Boyle s Law is an indirect relationship. Most of these problems can be done in your head without showing your work. 1. Herman has 30.0 L of helium gas trapped in a cylinder by a piston.
Boyle s Law Practice Boyle s Law is an indirect relationship. Most of these problems can be done in your head without showing your work. 1. Herman has 30.0 L of helium gas trapped in a cylinder by a piston.
Single & Headered Relief Vent Piping Analysis
 Single & Headered Relief Vent Piping Analysis Todd Jekel, Ph.D., P.E. Industrial Refrigeration Consortium 2005 Research & Technology Forum January 21, 2005 Madison, WI 1 Purpose Vent piping requirements
Single & Headered Relief Vent Piping Analysis Todd Jekel, Ph.D., P.E. Industrial Refrigeration Consortium 2005 Research & Technology Forum January 21, 2005 Madison, WI 1 Purpose Vent piping requirements
Impact of imperfect sealing on the flow measurement of natural gas by orifice plates
 Impact of imperfect sealing on the flow measurement of natural gas by orifice plates Rubens Silva Telles 1, Kazuto Kawakita 2 1 IPT Instituto de Pesquisas Tecnológicas, São Paulo, Brazil, rtelles@ipt.br
Impact of imperfect sealing on the flow measurement of natural gas by orifice plates Rubens Silva Telles 1, Kazuto Kawakita 2 1 IPT Instituto de Pesquisas Tecnológicas, São Paulo, Brazil, rtelles@ipt.br
Write important assumptions used in derivation of Bernoulli s equation. Apart from an airplane wing, give an example based on Bernoulli s principle
 HW#3 Sum07 #1. Answer in 4 to 5 lines in the space provided for each question: (a) A tank partially filled with water has a balloon well below the free surface and anchored to the bottom by a string. The
HW#3 Sum07 #1. Answer in 4 to 5 lines in the space provided for each question: (a) A tank partially filled with water has a balloon well below the free surface and anchored to the bottom by a string. The
UNIT 10 - GASES. Notes & Worksheets - Honors
 Ideal Gas Equation 1 WKSHT 1.) What is the pressure exerted by 2.0 moles of an ideal gas when it occupies a volume of 12.0 L at 373 K? 2.) A flashbulb of volume 2.6 cm 3 contains O 2 gas at a pressure
Ideal Gas Equation 1 WKSHT 1.) What is the pressure exerted by 2.0 moles of an ideal gas when it occupies a volume of 12.0 L at 373 K? 2.) A flashbulb of volume 2.6 cm 3 contains O 2 gas at a pressure
PHYS 102 Quiz Problems Chapter 19 : Kinetic Theory of Gases Dr. M. F. Al-Kuhaili
 PHYS 102 Quiz Problems Chapter 19 : Kinetic Theory of Gases Dr. M. F. Al-Kuhaili 1. (TERM 001) Two moles of an ideal gas initially at 300 K and 0.40 atm are compressed isothermally to 1.2 atm. (a) Find
PHYS 102 Quiz Problems Chapter 19 : Kinetic Theory of Gases Dr. M. F. Al-Kuhaili 1. (TERM 001) Two moles of an ideal gas initially at 300 K and 0.40 atm are compressed isothermally to 1.2 atm. (a) Find
Chapter 3 EXPERIMENTAL: EQUIPMENT, SET-UP, AND PROCEDURE
 Chapter 3 EXPERIMENTAL: EQUIPMENT, SET-UP, AND PROCEDURE 72 3.0 Introduction The experimental work was carried out in three stages. First stage: a laboratory scale single nozzle horizontal jet ejector
Chapter 3 EXPERIMENTAL: EQUIPMENT, SET-UP, AND PROCEDURE 72 3.0 Introduction The experimental work was carried out in three stages. First stage: a laboratory scale single nozzle horizontal jet ejector
To convert to millimeters of mercury, we derive a unit factor related to the equivalent relationship 29.9 in. Hg = 760 mm Hg.
 Example Exercise 11.1 Gas Pressure Conversion Meteorologists state that a falling barometer indicates an approaching storm. Given a barometric pressure of 27.5 in. Hg, express the pressure in each of the
Example Exercise 11.1 Gas Pressure Conversion Meteorologists state that a falling barometer indicates an approaching storm. Given a barometric pressure of 27.5 in. Hg, express the pressure in each of the
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF A COLD GAS PROPULSION SYSTEM FOR STABILIZATION
 DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF A COLD GAS PROPULSION SYSTEM FOR STABILIZATION AND MANEUVERABILITY OF A HIGH ALTITUDE RESEARCH BALLOON COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & APPLIED SCIENCES SENIOR DESIGN THESIS GREGORY A. NEFF
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF A COLD GAS PROPULSION SYSTEM FOR STABILIZATION AND MANEUVERABILITY OF A HIGH ALTITUDE RESEARCH BALLOON COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & APPLIED SCIENCES SENIOR DESIGN THESIS GREGORY A. NEFF
ASHRAE made significant changes in 2001 to the calculations. Fundamentals of Safety Relief Systems
 2008, American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers, Inc. (www.ashrae.org). Published in ASHRAE Journal, Vol. 50, February 2008. This posting is by permission of ASHRAE. Additional
2008, American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers, Inc. (www.ashrae.org). Published in ASHRAE Journal, Vol. 50, February 2008. This posting is by permission of ASHRAE. Additional
Development of Gasdynamic Probe for Total Temperature Measurement in gases
 ASET 20- National Conference on Emerging Trends in Propulsion Technology Development of Gasdynamic Probe for Total Temperature Measurement in gases K Sathiyamoorthy, Souren Misra 2, Srinivas J, Baskaran
ASET 20- National Conference on Emerging Trends in Propulsion Technology Development of Gasdynamic Probe for Total Temperature Measurement in gases K Sathiyamoorthy, Souren Misra 2, Srinivas J, Baskaran
4. Using the kinetic molecular theory, explain why a gas can be easily compressed, while a liquid and a solid cannot?
 Name Period HW 1 Worksheet (Goals 1-4) - Kinetic Molecular Theory 1. Describe how gases, liquids, and solids compare using the following table. Solids Liquids Gases Volume (definite or indefinite) Molecular
Name Period HW 1 Worksheet (Goals 1-4) - Kinetic Molecular Theory 1. Describe how gases, liquids, and solids compare using the following table. Solids Liquids Gases Volume (definite or indefinite) Molecular
CRYOGENICS LIQUID NITROGEN AS A NON- POLLUTING FUEL
 CRYOGENICS LIQUID NITROGEN AS A NON- POLLUTING FUEL 1 INTRODUCTION: In 1997, the University of North Texas (UNT) and University of Washington (UW) independently developed liquid nitrogen powered vehicles
CRYOGENICS LIQUID NITROGEN AS A NON- POLLUTING FUEL 1 INTRODUCTION: In 1997, the University of North Texas (UNT) and University of Washington (UW) independently developed liquid nitrogen powered vehicles
CHEM 3351 Physical Chemistry I, Fall 2017
 CHEM 3351 Physical Chemistry I, Fall 2017 Problem set 1 Due 9/15/2017 (Friday) 1. An automobile tire was inflated to a pressure of 24 lb in -2 (1.00 atm = 14.7 lb in -2 ) on a winter s day when the temperature
CHEM 3351 Physical Chemistry I, Fall 2017 Problem set 1 Due 9/15/2017 (Friday) 1. An automobile tire was inflated to a pressure of 24 lb in -2 (1.00 atm = 14.7 lb in -2 ) on a winter s day when the temperature
Kinetic Molecular Theory imaginary Assumptions of Kinetic Molecular Theory: Problems with KMT:
 AP Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block Kinetic Molecular Theory Explains properties of gases, liquids, and solids in terms of energy using an ideal gas, an imaginary which fits all the assumptions of kinetic
AP Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block Kinetic Molecular Theory Explains properties of gases, liquids, and solids in terms of energy using an ideal gas, an imaginary which fits all the assumptions of kinetic
Compiled by: B Beard. Approved by: SH Carstens. Description of requirements and procedures for compact provers to be used as verification standards.
 1. Scope Description of requirements and procedures for compact provers to be used as verification standards. 2. Reference documents Trade Metrology Act SANS1698 3. Policy A. BASIC REQUIREMENTS Compact
1. Scope Description of requirements and procedures for compact provers to be used as verification standards. 2. Reference documents Trade Metrology Act SANS1698 3. Policy A. BASIC REQUIREMENTS Compact
Example: Calculate the density of methane at 50 psig and 32 ⁰F. H.W. In previous example calculate the density of methane in gm/m 3.
 Gas density Because the density of a substance is defined as mass per unit volume, the density of gas (ρ g ), at given temperature and pressure can be derived as follows: If P in psia, T in ⁰R and R =
Gas density Because the density of a substance is defined as mass per unit volume, the density of gas (ρ g ), at given temperature and pressure can be derived as follows: If P in psia, T in ⁰R and R =
Design Review Agenda
 Design Review Agenda 1) Introduction, Motivation, and Previous Work a. Previous Work and Accomplishments i. Platform Launches ii. Successful Test Firings 2) More In-Depth Design Overview of the Existing
Design Review Agenda 1) Introduction, Motivation, and Previous Work a. Previous Work and Accomplishments i. Platform Launches ii. Successful Test Firings 2) More In-Depth Design Overview of the Existing
MEASURING A DISCHARGE COEFFICIENT OF AN ORIFICE FOR AN UNSTEADY COMPRESSIBLE FLOW
 MEASURING A DISCHARGE COEFFICIENT OF AN ORIFICE FOR AN UNSTEADY COMPRESSIBLE FLOW Ondřej Novák, Václav Koza ICT Prague, Department of Gas, Coke and Air Protection, ondrej.novak@vscht.cz There are many
MEASURING A DISCHARGE COEFFICIENT OF AN ORIFICE FOR AN UNSTEADY COMPRESSIBLE FLOW Ondřej Novák, Václav Koza ICT Prague, Department of Gas, Coke and Air Protection, ondrej.novak@vscht.cz There are many
Research and optimization of intake restrictor for Formula SAE car engine
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 4, Issue 4, April 2014 1 Research and optimization of intake restrictor for Formula SAE car engine Pranav Anil Shinde Mechanical Engineering,
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 4, Issue 4, April 2014 1 Research and optimization of intake restrictor for Formula SAE car engine Pranav Anil Shinde Mechanical Engineering,
Name Hour. The Behavior of Gases. Practice B
 Name Hour The Behavior of Gases Practice B B 1 Objective 1: Apply Boyle s Law, Charles s Law, and Gay-Lussac s Law to solve problems involving pressure and volume and temperature. 1. A high-altitude balloon
Name Hour The Behavior of Gases Practice B B 1 Objective 1: Apply Boyle s Law, Charles s Law, and Gay-Lussac s Law to solve problems involving pressure and volume and temperature. 1. A high-altitude balloon
hydro-pac, inc. Low-Pressure Gas Compressors 1500 to 6000 PSI
 hydro-pac, inc. LX-SERIES Low-Pressure Gas Compressors 1500 to 6000 PSI hydro-pac, inc. LX-SERIES Features Hydro-Pac LX-SERIES Gas Compressors feature: Oil-free non lubricated gas pistons and cylinders
hydro-pac, inc. LX-SERIES Low-Pressure Gas Compressors 1500 to 6000 PSI hydro-pac, inc. LX-SERIES Features Hydro-Pac LX-SERIES Gas Compressors feature: Oil-free non lubricated gas pistons and cylinders
Experimental Analysis on Vortex Tube Refrigerator Using Different Conical Valve Angles
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 7-067X, p-issn: 7-00X, www.ijerd.com Volume 3, Issue 4 (August ), PP. 33-39 Experimental Analysis on Vortex Tube Refrigerator Using
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 7-067X, p-issn: 7-00X, www.ijerd.com Volume 3, Issue 4 (August ), PP. 33-39 Experimental Analysis on Vortex Tube Refrigerator Using
Lab 1c Isentropic Blow-down Process and Discharge Coefficient
 058:080 Experimental Engineering Lab 1c Isentropic Blow-down Process and Discharge Coefficient OBJECTIVES - To study the transient discharge of a rigid pressurized tank; To determine the discharge coefficients
058:080 Experimental Engineering Lab 1c Isentropic Blow-down Process and Discharge Coefficient OBJECTIVES - To study the transient discharge of a rigid pressurized tank; To determine the discharge coefficients
THEORETICAL EVALUATION OF FLOW THROUGH CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSOR STAGE
 THEORETICAL EVALUATION OF FLOW THROUGH CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSOR STAGE S.Ramamurthy 1, R.Rajendran 1, R. S. Dileep Kumar 2 1 Scientist, Propulsion Division, National Aerospace Laboratories, Bangalore-560017,ramamurthy_srm@yahoo.com
THEORETICAL EVALUATION OF FLOW THROUGH CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSOR STAGE S.Ramamurthy 1, R.Rajendran 1, R. S. Dileep Kumar 2 1 Scientist, Propulsion Division, National Aerospace Laboratories, Bangalore-560017,ramamurthy_srm@yahoo.com
The Estimation Of Compressor Performance Using A Theoretical Analysis Of The Gas Flow Through the Muffler Combined With Valve Motion
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering The Estimation Of Compressor Performance Using A Theoretical Analysis Of The Gas Flow Through
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering The Estimation Of Compressor Performance Using A Theoretical Analysis Of The Gas Flow Through
Pressure Control. where: p is the pressure F is the normal component of the force A is the area
 Pressure Control First of all, what is pressure, the property we want to control? From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Pressure is the application of force to a surface, and the concentration of that
Pressure Control First of all, what is pressure, the property we want to control? From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Pressure is the application of force to a surface, and the concentration of that
The University of Hong Kong Department of Physics Experimental Physics Laboratory
 The University of Hong Kong Department of Physics Experimental Physics Laboratory PHYS2260 Heat and Waves 2260-1 LABORATORY MANUAL Experiment 1: Adiabatic Gas Law Part A. Ideal Gas Law Equipment Required:
The University of Hong Kong Department of Physics Experimental Physics Laboratory PHYS2260 Heat and Waves 2260-1 LABORATORY MANUAL Experiment 1: Adiabatic Gas Law Part A. Ideal Gas Law Equipment Required:
You should be able to: Describe Equipment Barometer Manometer. 5.1 Pressure Read and outline 5.1 Define Barometer
 A P CHEMISTRY - Unit 5: Gases Unit 5: Gases Gases are distinguished from other forms of matter, not only by their power of indefinite expansion so as to fill any vessel, however large, and by the great
A P CHEMISTRY - Unit 5: Gases Unit 5: Gases Gases are distinguished from other forms of matter, not only by their power of indefinite expansion so as to fill any vessel, however large, and by the great
Ch. 14 The Behavior of Gases
 Ch. 14 The Behavior of Gases 14.1 PROPERTIES OF GASES Compressibility Compressibility: a measure of how much the volume of matter decreases under pressure Gases are easily compressed because of the spaces
Ch. 14 The Behavior of Gases 14.1 PROPERTIES OF GASES Compressibility Compressibility: a measure of how much the volume of matter decreases under pressure Gases are easily compressed because of the spaces
CP Chapter 13/14 Notes The Property of Gases Kinetic Molecular Theory
 CP Chapter 13/14 Notes The Property of Gases Kinetic Molecular Theory Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases The word kinetic refers to. Kinetic energy is the an object has because of its motion. Kinetic Molecular
CP Chapter 13/14 Notes The Property of Gases Kinetic Molecular Theory Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases The word kinetic refers to. Kinetic energy is the an object has because of its motion. Kinetic Molecular
An Impeller Blade Analysis of Centrifugal Gas Compressor Using CFD
 An Impeller Blade Analysis of Centrifugal Gas Compressor Using CFD Vivek V. Kulkarni Department of Mechanical Engineering KLS Gogte Institute of Technology, Belagavi, Karnataka Dr. Anil T.R. Department
An Impeller Blade Analysis of Centrifugal Gas Compressor Using CFD Vivek V. Kulkarni Department of Mechanical Engineering KLS Gogte Institute of Technology, Belagavi, Karnataka Dr. Anil T.R. Department
Pressure Measurement
 Pressure Measurement Manometers Sensors, Transducers Ashish J. Modi Lecturer, Dept. of Mech.Engg., Shri S.V.M. inst. Of Technology, Bharuch Pressure Pressure is a force per unit area exerted by a fluid
Pressure Measurement Manometers Sensors, Transducers Ashish J. Modi Lecturer, Dept. of Mech.Engg., Shri S.V.M. inst. Of Technology, Bharuch Pressure Pressure is a force per unit area exerted by a fluid
A & AE 520 Background Information, Adapted from AAE334L, last revised 10-Feb-14 Page 1 1. SUPERSONIC WIND TUNNEL
 A & AE 50 Background Information, Adapted from AAE334L, last revised 10-Feb-14 Page 1 1.1 BACKGROUND 1. SUPERSONIC WIND TUNNEL 1.1.1 Objectives: This handout is adapted from the one once used in AAE334L
A & AE 50 Background Information, Adapted from AAE334L, last revised 10-Feb-14 Page 1 1.1 BACKGROUND 1. SUPERSONIC WIND TUNNEL 1.1.1 Objectives: This handout is adapted from the one once used in AAE334L
AE3610 Experiments in Fluid and Solid Mechanics OPTICAL/PRESSURE MEASUREMENTS IN SUPERSONIC FLOW
 AE3610 Experiments in Fluid and Solid Mechanics OPTICAL/PRESSURE MEASUREMENTS IN SUPERSONIC FLOW Objective This lab covers the use of taps, probes and transducers for measurement of static and stagnation
AE3610 Experiments in Fluid and Solid Mechanics OPTICAL/PRESSURE MEASUREMENTS IN SUPERSONIC FLOW Objective This lab covers the use of taps, probes and transducers for measurement of static and stagnation
Kinetic Molecular Theory
 Kinetic Molecular Theory Name Period Unit 7 HW 1 Worksheet (Goals 1 & 2) 1. Describe how gases, liquids, and solids compare using the following table. Volume (definite or indefinite) Molecular Motion (high,
Kinetic Molecular Theory Name Period Unit 7 HW 1 Worksheet (Goals 1 & 2) 1. Describe how gases, liquids, and solids compare using the following table. Volume (definite or indefinite) Molecular Motion (high,
Methods of Rating Flow
 Methods of Rating Flow What engineers need to know when using CV as a measurement of flow in pneumatic applications In the pneumatic industry, CV is one standard for expressing the flow capacity of devices
Methods of Rating Flow What engineers need to know when using CV as a measurement of flow in pneumatic applications In the pneumatic industry, CV is one standard for expressing the flow capacity of devices
HW-1: Due by 5:00 pm EDT on Wednesday 13 June 2018 to GradeScope.
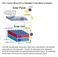 HW-1: Due by 5:00 pm EDT on Wednesday 13 June 2018 to GradeScope. The solar cell/solar panel shown above depict how a semiconductor can transform solar power into electrical power. Consider the solar panel
HW-1: Due by 5:00 pm EDT on Wednesday 13 June 2018 to GradeScope. The solar cell/solar panel shown above depict how a semiconductor can transform solar power into electrical power. Consider the solar panel
ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS
 ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS Unit-1 [8 hrs] Introduction To Thermodynamics: Basic concepts of Thermodynamics, Closed & Open Systems, Forms of energy, Properties of a system, State and Equilibrium, Processes and
ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS Unit-1 [8 hrs] Introduction To Thermodynamics: Basic concepts of Thermodynamics, Closed & Open Systems, Forms of energy, Properties of a system, State and Equilibrium, Processes and
Pressure of the atmosphere varies with elevation and weather conditions. Barometer- device used to measure atmospheric pressure.
 Chapter 12 Section 1 Pressure A gas exerts pressure on its surroundings. Blow up a balloon. The gas we are most familiar with is the atmosphere, a mixture of mostly elemental nitrogen and oxygen. Pressure
Chapter 12 Section 1 Pressure A gas exerts pressure on its surroundings. Blow up a balloon. The gas we are most familiar with is the atmosphere, a mixture of mostly elemental nitrogen and oxygen. Pressure
Gases NO CALCULATORS MAY BE USED FOR THESE QUESTIONS
 NO CALCULATORS MAY BE USED FOR THESE QUESTIONS Questions 1-3 refer to the following gases at 0 C and 1 atm. (A) Ar (B) NO 2 (C) Xe (D) H 2 (E) N 2 1. Has an average atomic or molecular speed closest to
NO CALCULATORS MAY BE USED FOR THESE QUESTIONS Questions 1-3 refer to the following gases at 0 C and 1 atm. (A) Ar (B) NO 2 (C) Xe (D) H 2 (E) N 2 1. Has an average atomic or molecular speed closest to
University of Cincinnati
 Mapping the Design Space of a Recuperated, Recompression, Precompression Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Power Cycle with Intercooling, Improved Regeneration, and Reheat Andrew Schroder Mark Turner University
Mapping the Design Space of a Recuperated, Recompression, Precompression Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Power Cycle with Intercooling, Improved Regeneration, and Reheat Andrew Schroder Mark Turner University
CHM 111 Unit 5 Sample Questions
 Name: Class: Date: As you work these problems, consider and explain: A. What type of question is it? B. How do you know what type of question it is? C. What information are you looking for? D. What information
Name: Class: Date: As you work these problems, consider and explain: A. What type of question is it? B. How do you know what type of question it is? C. What information are you looking for? D. What information
Fundamentals of Turboexpanders Basic Theory and Design
 Fundamentals of Turboexpanders Basic Theory and Design Edited Date: September 16, 2015 Presented By: Mr. James Simms Simms Machinery International, Inc. 2357 A Street Santa Maria, CA 93455 U.S.A. About
Fundamentals of Turboexpanders Basic Theory and Design Edited Date: September 16, 2015 Presented By: Mr. James Simms Simms Machinery International, Inc. 2357 A Street Santa Maria, CA 93455 U.S.A. About
Control Valve Sizing. Sizing & Selection 3 P 1. P 2 (Outlet Pressure) P V P VC. CONTENTS Introduction Nomenclature Calculating C v
 Sizing & Selection 3 Control Valve Sizing CONTENTS Introduction 3-1 Nomenclature 3-1 Calculating for Liquids 3-3 Liquid Sizing Examples 3-7 Calculating for Gases 3-10 Gas Sizing Examples 3-13 Calculating
Sizing & Selection 3 Control Valve Sizing CONTENTS Introduction 3-1 Nomenclature 3-1 Calculating for Liquids 3-3 Liquid Sizing Examples 3-7 Calculating for Gases 3-10 Gas Sizing Examples 3-13 Calculating
Problems of Chapter 3
 Problems of Chapter 3 Section 3.1 Molecular Model of an Ideal Gas 3. A sealed cubical container 20 cm on a side contains three times Avogadro s number of molecules at a temperature of 20 C. Find the force
Problems of Chapter 3 Section 3.1 Molecular Model of an Ideal Gas 3. A sealed cubical container 20 cm on a side contains three times Avogadro s number of molecules at a temperature of 20 C. Find the force
SIMULATIONS OF HYDROGEN RELEASES FROM A STORAGE TANKS: DISPERSION AND CONSEQUENCES OF IGNITION
 SIMULATIONS OF HYDROGEN RELEASES FROM A STORAGE TANKS: DISPERSION AND CONSEQUENCES OF IGNITION Angers, B. 1, Hourri, A. 1, Bénard, P. 1, Tessier, P. 2 and Perrin, J. 3 1 Hydrogen Research Institute, Université
SIMULATIONS OF HYDROGEN RELEASES FROM A STORAGE TANKS: DISPERSION AND CONSEQUENCES OF IGNITION Angers, B. 1, Hourri, A. 1, Bénard, P. 1, Tessier, P. 2 and Perrin, J. 3 1 Hydrogen Research Institute, Université
2. Calculate the ratio of diffusion rates for carbon monoxide (CO) and carbon dioxide (CO2). υa = MB = 44 = 1.25
 Gas laws worksheet (2-08) (modified 3/17) Answer key Graham s Law 1. Calculate the ratio of effusion rates for nitrogen (N2) and neon (Ne). υa = MB = 20 = 0.845 υb MA 28 2. Calculate the ratio of diffusion
Gas laws worksheet (2-08) (modified 3/17) Answer key Graham s Law 1. Calculate the ratio of effusion rates for nitrogen (N2) and neon (Ne). υa = MB = 20 = 0.845 υb MA 28 2. Calculate the ratio of diffusion
Dean Pump Self-Priming Chemical Process Pumps
 Bulletin C 1.2.34.7 Dean Pump Self-Priming Chemical Process Pumps php Series HEAD CAPACITY RANGE CHARTS php Self Primer - 2 Pole 3500 RPM 500 CAPACITY M 3 /HR 2900 RPM 50 HERTZ 25 50 75 125 150 400 TOTAL
Bulletin C 1.2.34.7 Dean Pump Self-Priming Chemical Process Pumps php Series HEAD CAPACITY RANGE CHARTS php Self Primer - 2 Pole 3500 RPM 500 CAPACITY M 3 /HR 2900 RPM 50 HERTZ 25 50 75 125 150 400 TOTAL
Honors Chemistry Unit 7 Gas Laws Notes
 Honors Chemistry Unit 7 Gas Laws Notes Kinetic Molecular Theory 1. List the five assumptions: Assumption Description Extra Info 1 Basically means: the particles themselves have compared to the space between
Honors Chemistry Unit 7 Gas Laws Notes Kinetic Molecular Theory 1. List the five assumptions: Assumption Description Extra Info 1 Basically means: the particles themselves have compared to the space between
NOTES: Behavior of Gases
 NOTES: Behavior of Gases Properties of Gases Gases have weight Gases take up space Gases exert pressure Gases fill their containers Gases are mostly empty space The molecules in a gas are separate, very
NOTES: Behavior of Gases Properties of Gases Gases have weight Gases take up space Gases exert pressure Gases fill their containers Gases are mostly empty space The molecules in a gas are separate, very
Pilot Operated Safety Relief Valves For Liquified Gas Carriers
 Pilot Operated Safety Relief Valves For Liquified Gas Carriers LUCET Features and dvantages High seat tightness - s the force that holds the disc on the nozzle increases with the pressure, the valve remains
Pilot Operated Safety Relief Valves For Liquified Gas Carriers LUCET Features and dvantages High seat tightness - s the force that holds the disc on the nozzle increases with the pressure, the valve remains
Chapter 14 Practice Problems
 Chapter 14 Practice Problems In problems that require the atomic masses (atomic weights) of atomic hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon, we will use the rounded values, 1, 16, 14, and 12, respectively.
Chapter 14 Practice Problems In problems that require the atomic masses (atomic weights) of atomic hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon, we will use the rounded values, 1, 16, 14, and 12, respectively.
Figure Vapor-liquid equilibrium for a binary mixture. The dashed lines show the equilibrium compositions.
 Another way to view this problem is to say that the final volume contains V m 3 of alcohol at 5.93 kpa and 20 C V m 3 of air at 94.07 kpa and 20 C V m 3 of air plus alcohol at 100 kpa and 20 C Thus, the
Another way to view this problem is to say that the final volume contains V m 3 of alcohol at 5.93 kpa and 20 C V m 3 of air at 94.07 kpa and 20 C V m 3 of air plus alcohol at 100 kpa and 20 C Thus, the
AIR DRIVEN. Gas Boosters & SYSTEMS. Accepting VISA, MasterCard and American Express
 AIR DRIVEN Gas Boosters & SYSTEMS Accepting VISA, MasterCard and American Express Gas Boosters AIR DRIVEN FROM 30 PSI TO 21,750 PSI MAXIMATOR Maximator gas boosters are an excellent alternative to high
AIR DRIVEN Gas Boosters & SYSTEMS Accepting VISA, MasterCard and American Express Gas Boosters AIR DRIVEN FROM 30 PSI TO 21,750 PSI MAXIMATOR Maximator gas boosters are an excellent alternative to high
TUTORIAL. NPSHA for those who hate that stuffy word. by Jacques Chaurette p. eng. copyright 2006
 TUTORIAL NPSHA for those who hate that stuffy word by Jacques Chaurette p. eng. www.lightmypump.com copyright 2006 page.2 NPSHA for those who hate that stuffy word This article follows the same approach
TUTORIAL NPSHA for those who hate that stuffy word by Jacques Chaurette p. eng. www.lightmypump.com copyright 2006 page.2 NPSHA for those who hate that stuffy word This article follows the same approach
PERFORMANCE OF NEEDLE VALVES
 Br. J. Anaesth. (1986), 58, 919-924 PERFORMANCE OF NEEDLE VALVES P. HUTTON AND R. W. BOADEN The use of needle valves to control theflowof gas in anaesthetic breathing systems is almost universal. We became
Br. J. Anaesth. (1986), 58, 919-924 PERFORMANCE OF NEEDLE VALVES P. HUTTON AND R. W. BOADEN The use of needle valves to control theflowof gas in anaesthetic breathing systems is almost universal. We became
Bottle Rockets. The bottle rocket, like the squid, uses water as the driving agent and compressed air instead of heat to provide the energy.
 Bottle Rockets Problem/Purpose: To create a bottle rocket that will fly straight and will stay in the air for as long as possible. Background Information: A squid propels itself by filling its body with
Bottle Rockets Problem/Purpose: To create a bottle rocket that will fly straight and will stay in the air for as long as possible. Background Information: A squid propels itself by filling its body with
Part 6: Critical flow orifices
 Provläsningsexemplar / Preview INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 6145-6 Third edition 2017-07 Gas analysis Preparation of calibration gas mixtures using dynamic methods Part 6: Critical flow orifices Analyse
Provläsningsexemplar / Preview INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 6145-6 Third edition 2017-07 Gas analysis Preparation of calibration gas mixtures using dynamic methods Part 6: Critical flow orifices Analyse
THE INNER WORKINGS OF A SIPHON Jacques Chaurette p. eng. January 2003
 THE INNER WORKINGS OF A SIPHON Jacques Chaurette p. eng. www.lightmypump.com January 2003 Synopsis The objective of this article is to explain how a siphon works. The difference between low pressure, atmospheric
THE INNER WORKINGS OF A SIPHON Jacques Chaurette p. eng. www.lightmypump.com January 2003 Synopsis The objective of this article is to explain how a siphon works. The difference between low pressure, atmospheric
Advanced Management of Compressed Air Systems Pre-Workshop Assignment
 Advanced Management of Compressed Air Systems Page 1 In order to ensure that the Compressed Air Challenge Level II Training is most useful to you, it will be important for you to bring information about
Advanced Management of Compressed Air Systems Page 1 In order to ensure that the Compressed Air Challenge Level II Training is most useful to you, it will be important for you to bring information about
CVEN 311 Fluid Dynamics Fall Semester 2011 Dr. Kelly Brumbelow, Texas A&M University. Final Exam
 CVEN 311 Fluid Dynamics Fall Semester 2011 Dr. Kelly Brumbelow, Texas A&M University Final Exam 8 pages, front & back, not including reference sheets; 21 questions An excerpt from the NCEES Fundamentals
CVEN 311 Fluid Dynamics Fall Semester 2011 Dr. Kelly Brumbelow, Texas A&M University Final Exam 8 pages, front & back, not including reference sheets; 21 questions An excerpt from the NCEES Fundamentals
Simulations of hydrogen releases from high pressure storage systems
 Simulations of hydrogen releases from high pressure storage systems Benjamin Angers a, Pierre Bénard a, Ahmed Hourri a, Pascal Tessier b and Jérôme Perrin c a Institut de recherche sur l hydrogène, Université
Simulations of hydrogen releases from high pressure storage systems Benjamin Angers a, Pierre Bénard a, Ahmed Hourri a, Pascal Tessier b and Jérôme Perrin c a Institut de recherche sur l hydrogène, Université
Chapter 13 Gases. H. Cannon, C. Clapper and T. Guillot Klein High School. Pressure/Temperature Conversions
 Chapter 13 Gases Pressure/Temperature Conversions Convert the following: 1. 3.50 atm = kpa 2. 123 atm = mmhg 3. 970.0 mmhg = torr 4. 870.0 torr = kpa 5. 250.0 kpa = atm 6. 205.0 mmhg = kpa 7. 12.4 atm
Chapter 13 Gases Pressure/Temperature Conversions Convert the following: 1. 3.50 atm = kpa 2. 123 atm = mmhg 3. 970.0 mmhg = torr 4. 870.0 torr = kpa 5. 250.0 kpa = atm 6. 205.0 mmhg = kpa 7. 12.4 atm
Proper Pump Installation Practices
 Proper Pump Installation Practices 80-779, Rev. 10/08 There is a Reason Every Unit Comes With This Bright Orange Tag! Proper Alignment and Coupling Installation Do Not Drive Coupling Onto Shaft Pump Alignment
Proper Pump Installation Practices 80-779, Rev. 10/08 There is a Reason Every Unit Comes With This Bright Orange Tag! Proper Alignment and Coupling Installation Do Not Drive Coupling Onto Shaft Pump Alignment
2. Convert these pressures to atm: 1 atm! Or to mm Hg, 760 mm Hg! 760 mm Hg! 1 atm. 800 mm Hg 380 mm Hg 0.75 atm 0.25 atm
 Chemistry L 3, Gas laws: Chapter 12: Name! Page 1 pg. 326-355 and Notes: Keep your Forces handout. We will not use kilopascals for pressure on worksheets or tests. Show your work on all worksheets!! Temperature
Chemistry L 3, Gas laws: Chapter 12: Name! Page 1 pg. 326-355 and Notes: Keep your Forces handout. We will not use kilopascals for pressure on worksheets or tests. Show your work on all worksheets!! Temperature
Behavior of Gases. Gases are mostly The molecules in a gas are separate, very small and very
 Properties of Gases Gases have Gases Gases exert Gases fill their containers Behavior of Gases Gases are mostly The molecules in a gas are separate, very small and very Kinetic Theory of Matter: Gas molecules
Properties of Gases Gases have Gases Gases exert Gases fill their containers Behavior of Gases Gases are mostly The molecules in a gas are separate, very small and very Kinetic Theory of Matter: Gas molecules
