SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
- Ruth Young
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 9.1 Using Figure 9.1, match the following: 1) Endomysium. 2) Fascicle. 3) The tissue that binds muscles into functional groups. 4) Perimysium. 5) Muscle fiber. 1
2 Figure 9.2 Using Figure 9.2, match the following: 6) I band. 7) H zone. 8) A band. 9) Z disc. 10) M line MATCHING. Choose the item in column 2 that best matches each item in column 1. Match the following: 11) The stimulus above which no stronger contraction can be elicited, because all motor units are firing in the muscle. 12) Continued sustained smooth contraction due to rapid stimulation. A) Tetanus B) Multiple motor unit summation C) Maximal stimulus 13) How a smooth increase in muscle force is produced. 2
3 Match the following: 14) A sarcomere is the distance between two. 15) The contains only the actin filaments. 16) The thicker filaments are the filaments. A) Z discs B) Myosin C) I band D) A band 17) Both actin and myosin are found in the. 18) The myosin filaments are located in the. Match the following: 19) Serves as the actual "trigger" for muscle contraction by removing the inhibition of the troponin molecules. 20) A neurotransmitter substance released at motor end plates by the axonal endings. 21) A metabolic pathway that provides for a large amount of ATP per glucose because oxygen is used. Products are water and carbon dioxide and ATP. A) Creatine phosphate B) Acetylcholine C) Acetylcholinesterase D) Aerobic respiration E) Calcium ions 22) Normally stored in the terminal cisternae. 23) Used to convert ADP to ATP by transfer of a high-energy phosphate group. A reserve high-energy compound. 24) Destroys ACh. TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 25) The force of muscle contraction is controlled by multiple motor unit summation or recruitment. 26) A nerve cell and all the muscle cells that it stimulates are referred to as a motor end plate. 27) Peristalsis is characteristic of smooth muscle. 28) A contraction in which the muscle does not shorten but its tension increases is called isometric. 3
4 29) During isometric contraction, the energy used appears as movement. 30) One of the important functions of skeletal muscle is production of heat. 31) Oxygen debt refers to the oxygen required to make creatine phosphate. 32) Although there are no sarcomeres, smooth muscle still possesses thick and thin filaments. 33) When a muscle fiber contracts, the I bands diminish in size, the H zones disappear, and the A bands move closer together but do not diminish in length. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 34) Which muscle cells have the greatest ability to regenerate? A) smooth B) no muscle can regenerate C) skeletal D) cardiac 35) Which of the following is not a usual result of exercise? A) increase in the efficiency of the circulatory system B) increase in the number of muscle cells C) increase in the number of myofibrils within the muscle cells D) increase in the efficiency of the respiratory system 36) In muscle contraction, calcium apparently acts to: A) increase the action potential transmitted along the sarcolemma. B) cause ATP to bind to actin. C) remove the blocking action of tropomyosin. D) release the inhibition on Z discs. 37) Calcium ions bind to the molecule in skeletal muscle cells. A) tropomyosin B) troponin C) actin D) myosin 38) Myoglobin: A) holds a reserve supply of oxygen in muscle cells. B) produces the end plate potential. C) is a protein involved in the direct phosphorylation of ADP. D) breaks down glycogen. 39) An elaborate network of membranes in skeletal muscle cells that functions in calcium storage is the: A) mitochondria. B) intermediate filament network. C) myofibrillar network. D) sarcoplasmic reticulum. 4
5 40) A sarcomere is: A) the nonfunctional unit of skeletal muscle. B) the wavy lines on the cell seen in the microscope. C) the area between two intercalated discs. D) the area between two Z discs. 41) Creatine phosphate functions in the muscle cell by: A) forming a temporary chemical compound with myosin. B) forming a chemical compound with actin. C) storing energy that will be transferred to ADP to resynthesize ATP as needed. D) inducing a conformational change in the myofilaments. 42) After nervous stimulation of the muscle cell has ceased, the calcium: A) is actively pumped into the extracellular fluid for storage until the next contraction. B) is chemically bound to the filaments. C) level in the cytoplasm drops. D) is destroyed by cholinesterase. 43) The major function of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in muscle contraction is to: A) provide a source of myosin for the contraction process. B) synthesize actin and myosin myofilaments. C) make and store phosphocreatine. D) regulate intracellular calcium concentration. 44) The striations of a skeletal muscle cell are produced, for the most part, by: A) the T tubules. B) the sarcoplasmic reticulum. C) a difference in the thickness of the sarcolemma. D) the arrangement of myofilaments. 45) Which of the following are composed of myosin? A) all myofilaments B) thick filaments C) Z discs D) thin filaments 46) During muscle contraction, myosin cross bridges attach to which active sites? A) actin filaments B) Z discs C) myosin filaments D) thick filaments 47) Which of the following surrounds the individual muscle cell? A) perimysium B) fascicle C) epimysium D) endomysium 48) Rigor mortis occurs because: A) the cells are dead. B) proteins are beginning to break down, thus preventing a flow of calcium ions. C) ATP is required to release the attached actin and myosin molecules. D) sodium ions leak out of the muscle. 49) The oxygen-binding protein found in muscle cells is: A) ATP. B) immunoglobin. C) hemoglobin. D) myoglobin. 5
6 50) The contractile units of skeletal muscles are: A) T tubules. B) mitochondria. C) myofibrils. D) microtubules. 51) One functional unit of a skeletal muscle is: A) a myofibril. B) a myofilament. C) a sarcomere. D) the sarcoplasmic reticulum. 52) The functional role of the T tubules is to: A) synthesize ATP to provide energy for muscle contraction. B) stabilize the G and F actin. C) hold cross bridges in place in a resting muscle. D) enhance cellular communication during muscle contraction. 53) The role of calcium ions in muscle contraction is to: A) act as a third messenger. B) reestablish glycogen stores. C) initiate the conversion of carbon dioxide to oxygen for storage. D) bind to regulatory sites on troponin, changing the configuration. 54) Athletes sometimes complain of oxygen debt, a condition that results when insufficient oxygen is available to completely break down pyruvic acid. As a result, the pyruvic acid is converted to: A) hydrochloric acid. B) stearic acid. C) lactic acid. D) a strong base. 55) In an isotonic contraction, the muscle: A) does not change in length but increases tension. B) changes in length and moves the "load." C) never converts pyruvate to lactate. D) rapidly resynthesizes creatine phosphate and ATP. 56) The muscle cell membrane is called a(n): A) sarcolemma. B) endomysium. C) epimysium. D) perimysium. 57) The giant protein titin maintains the organization of the assisting in muscle stretching. A) M line B) Z disc C) A band D) I band 58) An anaerobic metabolic pathway that results in the production of two net ATPs per glucose plus two pyruvic acid molecules is: A) the citric acid cycle. B) hydrolysis. C) glycolysis. D) the electron transport chain. 59) Muscle tone is: A) the condition of athletes after intensive training. B) the feeling of well-being following exercise. C) the ability of a muscle to efficiently cause skeletal movements. D) a state of sustained partial contraction. 6
7 60) The sliding filament model of contraction involves: A) the shortening of thick filaments so that thin filaments slide past. B) the Z discs sliding over the myofilaments. C) actin and myosin shortening but not sliding past each other. D) actin and myosin sliding past each other but not shortening. 61) The first thing that stops a contraction after the nerve stops sending ACh is: A) calcium ions return to the terminal cisternae. B) the action potential stops going down the T tubule. C) acetylcholinesterase destroys the ACh, and they are removed from the membrane receptors. D) the tropomyosin blocks the myosin. 62) Theoretically, if a muscle were stretched to the point where thick and thin filaments no longer overlapped: A) ATP consumption would increase since the sarcomere is "trying" to contract. B) cross bridge attachment would be optimum because of all the free binding sites on actin. C) no muscle tension could be generated. D) maximum force production would result since the muscle has a maximum range of travel. 63) An individual has just ingested a chemical that binds irreversibly to the ACh receptors in the sarcolemma. By itself it does not alter membrane potential, yet prevents normal neurotransmitter binding. Ignoring the effects on any other system, the consequence to skeletal muscle would be: A) irreversible contraction as soon as the first nervous stimulation reached the sarcolemma. B) no contraction at all by nervous mechanisms. C) contraction if stimulated by an external electrode. D) no contraction at all by nervous mechanisms, but contraction if stimulated by an external electrode. SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 64) Only muscle cells are multinucleated. 65) The end of the muscle that moves when a muscle contracts is called the. 66) In the synaptic cleft of a neuromuscular junction, is always present. 67) The time in which cross bridges are active is called the period of. 68) Only muscle cells branch. 69) A smooth, sustained contraction is called. 70) Define muscle fatigue. 71) Briefly, what causes rigor mortis? 72) What ultimately stops a muscle contraction? 73) Briefly explain where the energy comes from in a one-minute sustained muscle contraction. 7
8 ESSAY. Write your answer in the space provided or on a separate sheet of paper. 74) Gary was injured in an automobile accident that severed the motor neurons innervating his quadriceps. Even though he has had extensive physical therapy, he is still suffering muscle atrophy. Why is the therapy not working? 75) Aaron arrived at the hospital with the following symptoms: drooping eyelids; fatigue and weakness of his muscles; and difficulty talking, breathing, and swallowing. What was his diagnosis? 76) Lynn has been waking up each night with intense pain in her calves. She does not feel that it is serious enough to seek medical attention but would like to know what is causing the pain. What would you tell her concerning this problem? She has been playing tennis all summer for several hours each day. Could this have anything to do with the night pain? 77) After removal of an elbow cast, Lauren noticed her arm was immovable. What happened to her arm? 78) When a geriatric client is admitted to the rehabilitation unit, an important nursing measure is to prevent the loss of muscle mass. What is the term used for loss of muscle mass and how can the patient prevent it? 79) The nurse encourages the patient to do his own activities of daily living such as bathing, feeding, dressing and toileting activities. How do these activities promote physical conditioning? 80) A patient is admitted for electroconvulsive treatment (ECT). The physician orders the neuromuscular blocking agent metocurine iodide (metubine) to reduce trauma by relaxing skeletal muscles. Explain the process of muscle contraction and how a neuromuscular blocking agent such as metubine would interfere with muscle contraction. 8
9 Answer Key Testname: 9-MUSCLE-TISSUE-CONTR.TST SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 1) B 2) D 3) A 4) E 5) C 6) C 7) B 8) D 9) A 10) E MATCHING. Choose the item in column 2 that best matches each item in column 1. 11) C 12) A 13) B 14) A 15) C 16) B 17) D 18) D 19) E 20) B 21) D 22) E 23) A 24) C TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 25) TRUE 26) FALSE 27) TRUE 28) TRUE 29) FALSE 30) TRUE 31) FALSE 32) TRUE 33) TRUE MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 34) A 35) B 36) C 37) B 38) A 39) D 40) D 1
10 Answer Key Testname: 9-MUSCLE-TISSUE-CONTR.TST 41) C 42) C 43) D 44) D 45) B 46) A 47) D 48) C 49) D 50) C 51) C 52) D 53) D 54) C 55) B 56) A 57) C 58) C 59) D 60) D 61) C 62) C 63) D SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 64) skeletal 65) insertion 66) acetylcholinesterase 67) contraction 68) cardiac 69) tetanus 70) Fatigue occurs when ATP production fails to keep pace with ATP use even though the muscle still receives stimuli. 71) Following the death of an individual, ATP is rapidly consumed and cannot be replaced. Because cross bridge detachment and calcium active transport is ATP driven, calcium leakage from the sarcoplasmic reticulum causes attachment of cross bridges, and lack of ATP prevents detachments. 72) The ultimate switch is the enzyme acetylcholinesterase. When the neuron stops releasing ACh, the muscle would not stop contracting if the acetylcholinesterase did not split the ACh into its two components, acetyl and choline, making them release their binding sites. 73) 1. The first 4-6 seconds of energy come from stored ATP in the muscle cell seconds of energy come from the transfer of creatine phosphate and ADP (which come from the first few seconds of burn) to form additional ATP seconds of energy come from glycolysis which by now has begun full production of ATP from glucose. ESSAY. Write your answer in the space provided or on a separate sheet of paper. 74) In denervation atrophy, fibrous connective tissue replaces the muscle tissue that was lost. When atrophy is complete, fibrous tissue cannot be reversed to muscle tissue. 75) Aaron probably has myasthenia gravis (an autoimmune disease), which involves a shortage of ACh receptors at the neuromuscular junction. 2
11 Answer Key Testname: 9-MUSCLE-TISSUE-CONTR.TST 76) This is due to sustained spasm, or tetanic contraction, of the gastrocnemius muscle. The causes could be low blood sugar, electrolyte depletion (particularly sodium and calcium), dehydration, or irritability of the spinal cord neurons. The fact that Lynn has been playing tennis for several hours each day may have caused an electrolyte depletion. She should increase her intake of calcium. 77) Two things have occurred to Lauren while she was convalescing from her injury. First, the immobilization of the arm caused some muscle mass to atrophy. Second, the loss of muscle was replaced with tough connective tissue that locked her arm in place. With therapy the tissue can be stretched or torn enough to return the full range of motion. 78) Disuse atrophy is degeneration and loss of muscle mass. The size, shape, tone, and strength of muscles (including the heart) are maintained with mild exercise and increased with strenuous exercise. Promoting exercise to maintain a patient's muscle tone, joint mobility, and cardiovascular function is an important nursing function. 79) These activities are isotonic exercises in which muscle tension is constant and then shortens to produce muscle contraction and movement. Because the muscles contract, the shape, size, and strength of the muscles are maintained as well as joint mobility. 80) Muscle contraction begins with a stimulus to the nerve. When the impulse reaches the neuromuscular junction, depolarization occurs, resulting in an influx of calcium ions from the extracellular fluid into the terminals, which then release a neurotransmitter, acetylcholine (Ach), into the cleft. The Ach combines with receptor sites on the post junctional muscle cell membrane, depolarizing it and facilitating the entry of sodium. Neuromuscular blocking agents act at the motor end plate by competing with the Ach for the receptor sites, or by blocking depolarization. 3
NOTES: The Muscular System (Ch 6, part 1)
 NOTES: The Muscular System (Ch 6, part 1) The muscular system consists of three types of muscle tissue: Skeletal Smooth Cardiac STRUCTURE OF A SKELETAL MUSCLE: *Individual muscles are the organs of the
NOTES: The Muscular System (Ch 6, part 1) The muscular system consists of three types of muscle tissue: Skeletal Smooth Cardiac STRUCTURE OF A SKELETAL MUSCLE: *Individual muscles are the organs of the
1. A.- 2. B.- 3. C.- 4. D.- 5. E.- Anatomy & Physiology 2A Name: FALL 2015 (Take Home) MINI-EXAM #4. Figure 11.2
 Anatomy & Physiology 2A Name: FALL 2015 (Take Home) MINI-EXAM #4 _ Figure 11.2 Using Figure 11.2: Completely define and describe letters A-E in the spaces provided below: 1. A.- 2. B.- 3. C.- 4. D.- 5.
Anatomy & Physiology 2A Name: FALL 2015 (Take Home) MINI-EXAM #4 _ Figure 11.2 Using Figure 11.2: Completely define and describe letters A-E in the spaces provided below: 1. A.- 2. B.- 3. C.- 4. D.- 5.
The Muscular System. Biology 105 Lecture 12 Chapter 6
 The Muscular System Biology 105 Lecture 12 Chapter 6 Outline I. Characteristics of muscles II. Three types of muscles III. Functions of muscles IV. Structure of skeletal muscles V. Mechanics of muscle
The Muscular System Biology 105 Lecture 12 Chapter 6 Outline I. Characteristics of muscles II. Three types of muscles III. Functions of muscles IV. Structure of skeletal muscles V. Mechanics of muscle
Composition of Skeletal Muscle. Unit 6 Muscular System. 8.2 Structure of Skeletal Muscle. Functions of the Muscular System 12/7/2009
 Unit 6 Muscular System Mrs. Michaelsen Chetek High School Composition of Skeletal Muscle A. Skeletal muscle is an composed of several tissue types. 1. muscle tissue 2. tissue 3. vessels 4. tissues http://www.eicsd.k12.ny.us/schools/ems/sjf/spring2006/kelly-
Unit 6 Muscular System Mrs. Michaelsen Chetek High School Composition of Skeletal Muscle A. Skeletal muscle is an composed of several tissue types. 1. muscle tissue 2. tissue 3. vessels 4. tissues http://www.eicsd.k12.ny.us/schools/ems/sjf/spring2006/kelly-
KeyPoint Muscle Physiology
 KeyPoint Muscle Physiology Muscle, what it s for and how it works, with mention of skeleton and adipose tissue BAB L7 Food Animal Biotechnology 3 types of muscle Skeletal. Striated, tubular, multinucleated
KeyPoint Muscle Physiology Muscle, what it s for and how it works, with mention of skeleton and adipose tissue BAB L7 Food Animal Biotechnology 3 types of muscle Skeletal. Striated, tubular, multinucleated
*The plasma membrane of a muscle fiber
 Skeletal Muscle Contraction: Histology: Sarcolemma: *The plasma membrane of a muscle fiber -T- tubules - Terminal Cisternae - Sarcoplasmic Reticulum *Transverse tubules- tube like invaginations or inward
Skeletal Muscle Contraction: Histology: Sarcolemma: *The plasma membrane of a muscle fiber -T- tubules - Terminal Cisternae - Sarcoplasmic Reticulum *Transverse tubules- tube like invaginations or inward
Meat proteins. Levels of complexity. Levels of complexity Myofibrils C, H, O, N. Amino acids. Myofibrils. Muscle fiber.
 Meat proteins Levels of complexity C, H, O, N Amino acids Actin Myosin Thin filaments Thick filaments Myofibrils Levels of complexity Myofibrils Muscle fiber Primary bundle Secondary bundle Muscle Changes
Meat proteins Levels of complexity C, H, O, N Amino acids Actin Myosin Thin filaments Thick filaments Myofibrils Levels of complexity Myofibrils Muscle fiber Primary bundle Secondary bundle Muscle Changes
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 September 1, 2017 Mechanisms of Skeletal Muscle Contraction
 NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 September 1, 2017 Mechanisms of Skeletal Muscle Contraction Anatomy of Skeletal Muscle Fibers Most skeletal muscle fibers extend the entire length of a muscle, and are
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 September 1, 2017 Mechanisms of Skeletal Muscle Contraction Anatomy of Skeletal Muscle Fibers Most skeletal muscle fibers extend the entire length of a muscle, and are
Muscular System Functions
 BMI 04 Skeletal Muscle & Force Generator J F Grosset BMI 04 2014 J F GROSSET 1 Muscular System Functions Body movement (Locomotion) Maintenance of posture Respiration Diaphragm and intercostal contractions
BMI 04 Skeletal Muscle & Force Generator J F Grosset BMI 04 2014 J F GROSSET 1 Muscular System Functions Body movement (Locomotion) Maintenance of posture Respiration Diaphragm and intercostal contractions
Unit Five The Muscular System
 Unit Five The Muscular System I. Introduction A. Definition: the muscular system is composed of all the muscles of the body including the movements of the total body, as well as movements the body. B.
Unit Five The Muscular System I. Introduction A. Definition: the muscular system is composed of all the muscles of the body including the movements of the total body, as well as movements the body. B.
Catabolism in Skeletal Muscle The Phosphagen System
 Catabolism in Skeletal Muscle The Phosphagen System Overview of ATP Regeneration Anaerobic vs Aerobic Metabolism Creatine Kinase Reaction Adenylate Kinase Reaction Purine Nucleotide Cycle Creatine Phosphate
Catabolism in Skeletal Muscle The Phosphagen System Overview of ATP Regeneration Anaerobic vs Aerobic Metabolism Creatine Kinase Reaction Adenylate Kinase Reaction Purine Nucleotide Cycle Creatine Phosphate
The process that involves air entering and exiting the lungs is called VENTILATION
 Bio 067: Review sections 10-12 Respiration, skeletal, muscular Functions of the respiratory system: The process that involves air entering and exiting the lungs is called VENTILATION Involves: Inhalation
Bio 067: Review sections 10-12 Respiration, skeletal, muscular Functions of the respiratory system: The process that involves air entering and exiting the lungs is called VENTILATION Involves: Inhalation
ANSC/FSTC 607 Physiology & Biochemistry of Muscle as a Food Muscle Ultrastructure
 Muscle ultrastructure ANSC/FSTC 607 Physiology & Biochemistry of Muscle as a Food Muscle Ultrastructure I. Sarcomeres A. Sarcomeres are the functional units of myofibrils. B. Resting length is 2-3 µm (from
Muscle ultrastructure ANSC/FSTC 607 Physiology & Biochemistry of Muscle as a Food Muscle Ultrastructure I. Sarcomeres A. Sarcomeres are the functional units of myofibrils. B. Resting length is 2-3 µm (from
CHAPTER XVI PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY. Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer.
 CHAPTER XVI PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. Muscle Cell Metabolism Muscle Cells Provide ATP to Drive the Crossbridge Cycle The sources of ATP: Available ATP in the
CHAPTER XVI PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. Muscle Cell Metabolism Muscle Cells Provide ATP to Drive the Crossbridge Cycle The sources of ATP: Available ATP in the
ARE YOU A SLOW- OR A FAST-TWITCH RUNNER?
 ARE YOU A SLOW- OR A FAST-TWITCH RUNNER? How can we individualize our training towards our different goals based on our muscular makeup? In this article you will learn how to decide if you are a Fast-twitch,
ARE YOU A SLOW- OR A FAST-TWITCH RUNNER? How can we individualize our training towards our different goals based on our muscular makeup? In this article you will learn how to decide if you are a Fast-twitch,
Nelson Pages
 Nelson Pages 280 309 Biology 20 Unit D: Respiratory and Motor Systems Earth s atmosphere is about: 78 % N2 21 % O2 1 % remaining gases Aerobic organisms require O 2 for cellular respiration Breathing (ventilation).
Nelson Pages 280 309 Biology 20 Unit D: Respiratory and Motor Systems Earth s atmosphere is about: 78 % N2 21 % O2 1 % remaining gases Aerobic organisms require O 2 for cellular respiration Breathing (ventilation).
Muscular Factors Muscular Factors
 2014 IDEA World Fitness Convention Running Secrets to Success: Skills and Drills for Trainers Jason Karp, Ph.D. Run-Fit.com 2011 IDEA Personal Trainer of the Year Cardiovascular Factors Cardiac output
2014 IDEA World Fitness Convention Running Secrets to Success: Skills and Drills for Trainers Jason Karp, Ph.D. Run-Fit.com 2011 IDEA Personal Trainer of the Year Cardiovascular Factors Cardiac output
Breathing: The normal rate is about 14 to 20 times a minute. Taking in of air is called Inspiration and the forcing out of air is called Expiration.
 Biology 12 Respiration Divisions of Respiration Breathing: entrance and exit of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration: exchange of gases(o2 and CO2) between air (in alveoli) and blood Internal
Biology 12 Respiration Divisions of Respiration Breathing: entrance and exit of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration: exchange of gases(o2 and CO2) between air (in alveoli) and blood Internal
I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface:
 I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface: Common characteristics of respiratory surfaces: a) Moist: allows for the RAPID diffusion of dissolved gasses across its surface. Whereas the respiratory
I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface: Common characteristics of respiratory surfaces: a) Moist: allows for the RAPID diffusion of dissolved gasses across its surface. Whereas the respiratory
How Animals Survive (Circulation and Gas Exchange)
 How Animals Survive (Circulation and Gas Exchange) by Flourence Octaviano on February 16, 2018 lesson duration of 30 minutes under Earth and Life Science generated on February 16, 2018 at 12:45 am Tags:
How Animals Survive (Circulation and Gas Exchange) by Flourence Octaviano on February 16, 2018 lesson duration of 30 minutes under Earth and Life Science generated on February 16, 2018 at 12:45 am Tags:
The diagram shows an alveolus next to a blood capillary in a lung. (a) (i) Draw a ring around the correct answer to complete the sentence. diffusion.
 BREATHING / GAS EXCHANGE. NAME. Q.Gas exchange takes place in the lungs. The diagram shows an alveolus next to a blood capillary in a lung. The arrows show the movement of two gases, A and B. (a) (i) Draw
BREATHING / GAS EXCHANGE. NAME. Q.Gas exchange takes place in the lungs. The diagram shows an alveolus next to a blood capillary in a lung. The arrows show the movement of two gases, A and B. (a) (i) Draw
Recitation question # 05
 Recitation and Lab # 05 The goal of this recitations / labs is to review material related to the CV and respiratory lectures for the second test of this course. Info required to answer this recitation
Recitation and Lab # 05 The goal of this recitations / labs is to review material related to the CV and respiratory lectures for the second test of this course. Info required to answer this recitation
EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT CREATINE
 [@charlotteclarkeuk] EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT CREATINE T here s are a lot of myths and misconceptions surrounding creatine. Some sources question its safety, suggesting that creatine may cause
[@charlotteclarkeuk] EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT CREATINE T here s are a lot of myths and misconceptions surrounding creatine. Some sources question its safety, suggesting that creatine may cause
Monday, ! Today: Respiratory system! 5/20/14! Transport of Blood! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing!
 Monday, 5.19.14! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing! Transport of Blood! What is transported! Nutrients! Oxygen! Carbon Dioxide! Hormones! Antibodies! What it is/does!
Monday, 5.19.14! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing! Transport of Blood! What is transported! Nutrients! Oxygen! Carbon Dioxide! Hormones! Antibodies! What it is/does!
RESPIRATORY REGULATION DURING EXERCISE
 RESPIRATORY REGULATION DURING EXERCISE Respiration Respiration delivery of oxygen to and removal of carbon dioxide from the tissue External respiration ventilation and exchange of gases in the lung Internal
RESPIRATORY REGULATION DURING EXERCISE Respiration Respiration delivery of oxygen to and removal of carbon dioxide from the tissue External respiration ventilation and exchange of gases in the lung Internal
Dietary supplements and nutrition in sports and exercices performance
 Dietary supplements and nutrition in sports and exercices performance Nutrition for endurance sports The most likely contributors to fatigue during an endurance exercise are dehydration and carbohydrates
Dietary supplements and nutrition in sports and exercices performance Nutrition for endurance sports The most likely contributors to fatigue during an endurance exercise are dehydration and carbohydrates
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 4
 Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 4 64 minutes 64 marks Page of 0 Q. (a) The table shows an athlete s breathing rate after the end of a race. Use the information shown in the table to draw a line
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 4 64 minutes 64 marks Page of 0 Q. (a) The table shows an athlete s breathing rate after the end of a race. Use the information shown in the table to draw a line
#10 Work Physiology. By : Dewi Hardiningtyas, ST., MT., MBA. Industrial Engineering Dept. University of Brawijaya
 #10 Work Physiology By : Dewi Hardiningtyas, ST., MT., MBA. Industrial Engineering Dept. University of Brawijaya This topic is a discussion of the energy side of using muscles rather than the mechanics/force
#10 Work Physiology By : Dewi Hardiningtyas, ST., MT., MBA. Industrial Engineering Dept. University of Brawijaya This topic is a discussion of the energy side of using muscles rather than the mechanics/force
HCO - 3 H 2 CO 3 CO 2 + H H H + Breathing rate is regulated by blood ph and C02. CO2 and Bicarbonate act as a ph Buffer in the blood
 Breathing rate is regulated by blood ph and C02 breathing reduces plasma [CO2]; plasma [CO2] increases breathing. When C02 levels are high, breating rate increases to blow off C02 In low C02 conditions,
Breathing rate is regulated by blood ph and C02 breathing reduces plasma [CO2]; plasma [CO2] increases breathing. When C02 levels are high, breating rate increases to blow off C02 In low C02 conditions,
2) During exhalation Air is cooled due to condensation and loses its moisture, depositing it on lining in trachea and nose
 Section 10: The Respiratory System A. Functions of the respiratory system: The organs of the respiratory system make sure oxygen enters the body and carbon dioxide leaves the body. 2 stages: Inhalation
Section 10: The Respiratory System A. Functions of the respiratory system: The organs of the respiratory system make sure oxygen enters the body and carbon dioxide leaves the body. 2 stages: Inhalation
Human Biology Respiratory System
 Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
Use scientific principles to explain how the sprayer works. You may use diagrams to support your answer.
 4.3 Marking Key This guide includes sample answers, task-specific observable elements, (Appendices 1 and 2), descriptive evaluation rubrics for each competency (Appendices 3 and 4), and non-descriptive
4.3 Marking Key This guide includes sample answers, task-specific observable elements, (Appendices 1 and 2), descriptive evaluation rubrics for each competency (Appendices 3 and 4), and non-descriptive
P215 Respiratory System, Part 2
 P15 Respiratory System, Part Gas Exchange Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide constant need for oxygen constant production of carbon dioxide exchange (and movement) lung alveoli pulmonary arteries pulmonary capillaries
P15 Respiratory System, Part Gas Exchange Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide constant need for oxygen constant production of carbon dioxide exchange (and movement) lung alveoli pulmonary arteries pulmonary capillaries
Physiology of Respiration
 Physiology of Respiration External Respiration = pulmonary ventilation breathing involves 2 processes: inspiration expiration Inspiration an active process involves contraction of diaphragm innervated
Physiology of Respiration External Respiration = pulmonary ventilation breathing involves 2 processes: inspiration expiration Inspiration an active process involves contraction of diaphragm innervated
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Atmosphere Tissue cell External respiration Alveoli of lungs 1 Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Atmosphere Tissue cell External respiration Alveoli of lungs 1 Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
Pop Quiz. What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach?
 Pop Quiz What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach? Respiratory System Review Cellular respiration: obtain glucose and oxygen, get
Pop Quiz What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach? Respiratory System Review Cellular respiration: obtain glucose and oxygen, get
CHAPTER 26 PERFORMANCE ENHANCEMENT
 PERFORMANCE ENHANCEMENT Text between pages 164 and 170 answers to questions on page 170 of the text book. 1) a) How does dehydration affect heart rate, body temperature and exercise performance? 3 marks
PERFORMANCE ENHANCEMENT Text between pages 164 and 170 answers to questions on page 170 of the text book. 1) a) How does dehydration affect heart rate, body temperature and exercise performance? 3 marks
- How do the carotid bodies sense arterial blood gases? o The carotid bodies weigh 25mg, yet they have their own artery. This means that they have
 - How do the carotid bodies sense arterial blood gases? o The carotid bodies weigh 25mg, yet they have their own artery. This means that they have the highest blood flow of all organs, which makes them
- How do the carotid bodies sense arterial blood gases? o The carotid bodies weigh 25mg, yet they have their own artery. This means that they have the highest blood flow of all organs, which makes them
NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY. Androgenic-Anabolic Alternatives. A Thesis Submitted to the. University Honors Program. In Partial Fulfillment o f the
 NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY Androgenic-Anabolic Alternatives A Thesis Submitted to the University Honors Program In Partial Fulfillment o f the Requirements o f the Baccalaureate Degree With Upper D ivision
NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY Androgenic-Anabolic Alternatives A Thesis Submitted to the University Honors Program In Partial Fulfillment o f the Requirements o f the Baccalaureate Degree With Upper D ivision
Copyright Strengthworks International Publishing. All rights are reserved. Updated egor 1: GUIDE
 Copyright 2016. Strengthworks International Publishing. All rights are reserved. Updated 01.04.17 THE V-TAPER SOLUTION SUPPLEMENT GUIDE Category 1 Primary Goal Muscle Gain Based on your measurements your
Copyright 2016. Strengthworks International Publishing. All rights are reserved. Updated 01.04.17 THE V-TAPER SOLUTION SUPPLEMENT GUIDE Category 1 Primary Goal Muscle Gain Based on your measurements your
Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration)
 Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration) 1 Question 1 Why do organisms need food? Organisms need food for obtaining energy to perform the vital functions. Question 2 What is a respiratory substrate?
Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration) 1 Question 1 Why do organisms need food? Organisms need food for obtaining energy to perform the vital functions. Question 2 What is a respiratory substrate?
Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 3
 Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 3 1. The pressure of a gas: a. is inversely proportional to its volume b. is unaffected by temperature changes c. is directly proportional to its volume d. does not
Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 3 1. The pressure of a gas: a. is inversely proportional to its volume b. is unaffected by temperature changes c. is directly proportional to its volume d. does not
Fatigue Determines Endurance Performance: The Training Application
 Fatigue Determines Endurance Performance: The Training Application USTFCCCA Endurance Symposium 2015 Don t let fatigue make a coward out of you. Steve Prefontaine Runner Outline Of San Antonio Fatigue
Fatigue Determines Endurance Performance: The Training Application USTFCCCA Endurance Symposium 2015 Don t let fatigue make a coward out of you. Steve Prefontaine Runner Outline Of San Antonio Fatigue
Structures of the Respiratory System include:
 Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems
 alveoli gills Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? respiration for respiration Need O 2 in for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need CO 2
alveoli gills Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? respiration for respiration Need O 2 in for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need CO 2
Lung Volumes and Capacities
 Lung Volumes and Capacities Normally the volume of air entering the lungs during a single inspiration is approximately equal to the volume leaving on the subsequent expiration and is called the tidal volume.
Lung Volumes and Capacities Normally the volume of air entering the lungs during a single inspiration is approximately equal to the volume leaving on the subsequent expiration and is called the tidal volume.
ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE G622 APPLIED SCIENCE
 ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE APPLIED SCIENCE Unit 3: Monitoring the activity of the human body TUESDAY 5 JUNE 2007 G622 Afternoon *CUP/T21601* Additional materials: Electronic calculator Ruler (cm/mm) Time:
ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE APPLIED SCIENCE Unit 3: Monitoring the activity of the human body TUESDAY 5 JUNE 2007 G622 Afternoon *CUP/T21601* Additional materials: Electronic calculator Ruler (cm/mm) Time:
Vector Rope Trainer Cardiovascular Program Fitness Level: GENERAL
 Cardiovascular Program Fitness Level: GENERAL These are exercise options. Mix and match as preferred during each workout session. Frequency: Two to three days per week Start with 3 minutes of light pace
Cardiovascular Program Fitness Level: GENERAL These are exercise options. Mix and match as preferred during each workout session. Frequency: Two to three days per week Start with 3 minutes of light pace
08 Respiration. #79 Respiration realeases energy from food
 08 Respiration #79 Respiration realeases energy from food Respiration is the chemical reactions that break down nutrient molecules in living cells to release energy. In humans, our cells need energy (ATP)
08 Respiration #79 Respiration realeases energy from food Respiration is the chemical reactions that break down nutrient molecules in living cells to release energy. In humans, our cells need energy (ATP)
Section 01: The Pulmonary System
 Section 01: The Pulmonary System Chapter 12 Pulmonary Structure and Function Chapter 13 Gas Exchange and Transport Chapter 14 Dynamics of Pulmonary Ventilation HPHE 6710 Exercise Physiology II Dr. Cheatham
Section 01: The Pulmonary System Chapter 12 Pulmonary Structure and Function Chapter 13 Gas Exchange and Transport Chapter 14 Dynamics of Pulmonary Ventilation HPHE 6710 Exercise Physiology II Dr. Cheatham
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange elephant seals gills AP Biology
 alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange O 2 & CO 2 exchange exchange between environment & cells provides O 2 for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange O 2 & CO 2 exchange exchange between environment & cells provides O 2 for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high
AP Biology. Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems. Gas exchange. Why do we need a respiratory system? Optimizing gas exchange. Gas exchange in many forms
 alveoli Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems gills elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? Need O 2 in food respiration for respiration for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need
alveoli Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems gills elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? Need O 2 in food respiration for respiration for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need
Respiration. Figure 22: Schematic representation of the respiratory system
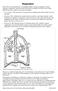 Respiration One of the seven characteristics of something which is living is respiration. Strictly speaking, respiration is the process that takes place at cellular level and is one of three different
Respiration One of the seven characteristics of something which is living is respiration. Strictly speaking, respiration is the process that takes place at cellular level and is one of three different
Exercise & Cellular Respiration
 Exercise & Cellular Respiration Name: Block: Background Information. Cellular respiration (see chemical reaction below) is a chemical reaction that occurs in your cells to create energy; when you are exercising
Exercise & Cellular Respiration Name: Block: Background Information. Cellular respiration (see chemical reaction below) is a chemical reaction that occurs in your cells to create energy; when you are exercising
Gases and Respiration. Respiration Overview I
 Respiration Overview I Respiration Overview II Gas Laws Equation of State: PV = nrt Same volumes of different gases have same # of molecules BTPS: body temp, atmospheric pressure, saturated ATPS: ambient
Respiration Overview I Respiration Overview II Gas Laws Equation of State: PV = nrt Same volumes of different gases have same # of molecules BTPS: body temp, atmospheric pressure, saturated ATPS: ambient
What needs to be done to support muscle building in horses? Engage in effective
 marstall feeding knowledge Helping your horse build muscles What needs to be done to support muscle building in horses? Engage in effective training, aid your horse with proper feeding, train up and watch
marstall feeding knowledge Helping your horse build muscles What needs to be done to support muscle building in horses? Engage in effective training, aid your horse with proper feeding, train up and watch
system. and then into the tissues. Diffusion of wastes such as Carbon Dioxide from tissues into blood and out of blood into the lungs.
 Respiratory System 1.Exchange Why do of we gases breathe? into the Think blood of all and the tissues. reasons Diffusion why we of Oxygen need a respiratory into blood from the lungs system. and then into
Respiratory System 1.Exchange Why do of we gases breathe? into the Think blood of all and the tissues. reasons Diffusion why we of Oxygen need a respiratory into blood from the lungs system. and then into
Unpacking Interval. Lisa A. Workman
 Unpacking Interval Training Lisa A. Workman Sunday, September 24, 2017 Overview History Exercise Physiology 101 The Three Energy Systems Training Continuum Types of Intervals Benefits History Joe Binks
Unpacking Interval Training Lisa A. Workman Sunday, September 24, 2017 Overview History Exercise Physiology 101 The Three Energy Systems Training Continuum Types of Intervals Benefits History Joe Binks
AP Biology. Chapter 42. Gas Exchange. Optimizing gas exchange. Gas exchange. Gas exchange in many forms. Evolution of gas exchange structures
 alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange & C exchange exchange between environment & cells provides for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high surface area
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange & C exchange exchange between environment & cells provides for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high surface area
Chapter 17 The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and Regulation of Breathing
 Chapter 17 The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and Regulation of Breathing Overview of Pulmonary Circulation o Diffusion of Gases o Exchange of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide o Transport of Gases in the Blood
Chapter 17 The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and Regulation of Breathing Overview of Pulmonary Circulation o Diffusion of Gases o Exchange of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide o Transport of Gases in the Blood
Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System
 Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System Animals require a continuous supply of oxygen (O 2 ) for cellular respiration, and they must expel carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), the waste product of this
Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System Animals require a continuous supply of oxygen (O 2 ) for cellular respiration, and they must expel carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), the waste product of this
Exercise 1/Microscopy Dr. Marvin E. Holtz Human Anatomy and Physiology Lab I
 Exercise 1/Microscopy Parts of the Microscope (page 1) Each student will locate, identify and familiarize themselves with all of the parts and associated functions for each microscope part listed in the
Exercise 1/Microscopy Parts of the Microscope (page 1) Each student will locate, identify and familiarize themselves with all of the parts and associated functions for each microscope part listed in the
(Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System
 (Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System I. (Slide 2) The Respiratory Tract A) Major structures and regions of the respiratory Tract/Route INTO body 1) nose 2) nasal cavity 3) pharynx 4) glottis 5)
(Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System I. (Slide 2) The Respiratory Tract A) Major structures and regions of the respiratory Tract/Route INTO body 1) nose 2) nasal cavity 3) pharynx 4) glottis 5)
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System
 Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Ergogenic Aids 1. Ergogenic Aids. Caffeine
 Ergogenic Aids 1 Dr David Jenkins School of Human Movement Studies The University of Queensland Ergogenic Aids drug derived from a number of plants 2004 removed from WADA Prohibited List possible mechanisms
Ergogenic Aids 1 Dr David Jenkins School of Human Movement Studies The University of Queensland Ergogenic Aids drug derived from a number of plants 2004 removed from WADA Prohibited List possible mechanisms
4/18/2012. Northern Fur Seal Three Foraging Patterns. Thermocline. Diving Physiology and Behavior
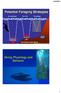 Northern Fur Seal Three Foraging Patterns Thermocline Diving Physiology and Behavior 1 Fundamental Constraint on Foraging Behavior Return to Surface to Breathe 2 Studies of Dive Behavior Dive depths from
Northern Fur Seal Three Foraging Patterns Thermocline Diving Physiology and Behavior 1 Fundamental Constraint on Foraging Behavior Return to Surface to Breathe 2 Studies of Dive Behavior Dive depths from
CHAPTER 3: The cardio-respiratory system
 : The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
: The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
The table shows the effect of exercise on the action of one person s heart. Heart rate in beats per minute
 ## (a) The table shows the effect of exercise on the action of one person s heart. At rest During exercise Heart rate in beats per minute 7 165 Volume of blood leaving the heart in each beat in cm 3 Heart
## (a) The table shows the effect of exercise on the action of one person s heart. At rest During exercise Heart rate in beats per minute 7 165 Volume of blood leaving the heart in each beat in cm 3 Heart
Section Three Gas transport
 Section Three Gas transport Lecture 6: Oxygen transport in blood. Carbon dioxide in blood. Objectives: i. To describe the carriage of O2 in blood. ii. iii. iv. To explain the oxyhemoglobin dissociation
Section Three Gas transport Lecture 6: Oxygen transport in blood. Carbon dioxide in blood. Objectives: i. To describe the carriage of O2 in blood. ii. iii. iv. To explain the oxyhemoglobin dissociation
Page 1. Chapter 33: Respiration O 2 CO 2
 Chapter 33: Respiration O 2 CO 2 Features of Respiratory Systems: 1) Moist surface (to dissolve gas) 2) Thin cells lining surface 3) Large surface area contacting environment Facilitate Diffusion Methods
Chapter 33: Respiration O 2 CO 2 Features of Respiratory Systems: 1) Moist surface (to dissolve gas) 2) Thin cells lining surface 3) Large surface area contacting environment Facilitate Diffusion Methods
Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation
 Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing and the first step in the respiratory process. Pulmonary ventilation brings in air with a new supply
Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing and the first step in the respiratory process. Pulmonary ventilation brings in air with a new supply
Essential Skills Course Acute Care Module. Respiratory Day 2 (Arterial Blood Gases) Pre course Workbook
 Essential Skills Course Acute Care Module Respiratory Day 2 (Arterial Blood Gases) Pre course Workbook Acknowledgements This pre course workbook has been complied and updated with reference to the original
Essential Skills Course Acute Care Module Respiratory Day 2 (Arterial Blood Gases) Pre course Workbook Acknowledgements This pre course workbook has been complied and updated with reference to the original
Pco2 *20times = 0.6, 2.4, so the co2 carried in the arterial blood in dissolved form is more than the o2 because of its solubility.
 Physiology, sheet #9 Oxygen, is first dissolved in the plasma and the cytosol of the rbc, we have around blood constitutes 7% of our body weight, oxygen, in the capillaries is present in the rbc s and
Physiology, sheet #9 Oxygen, is first dissolved in the plasma and the cytosol of the rbc, we have around blood constitutes 7% of our body weight, oxygen, in the capillaries is present in the rbc s and
Rapid Recovery Hyperbarics 9439 Archibald Ave. Suite 104 Rancho Cucamonga CA,
 Hyperbaric Oxygen Exposure Reduces Age- Related Decrease in Oxidative Capacity of the Tibialis Anterior Muscle in Mice Takahiro Nishizaka,1 Fumiko Nagatomo,2 Hidemi Fujino,3 Tomoko Nomura,4 Tomohiko Sano,4
Hyperbaric Oxygen Exposure Reduces Age- Related Decrease in Oxidative Capacity of the Tibialis Anterior Muscle in Mice Takahiro Nishizaka,1 Fumiko Nagatomo,2 Hidemi Fujino,3 Tomoko Nomura,4 Tomohiko Sano,4
Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY
 Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Respiration External respiration ventilation gas exchange Internal respiration cellular respiration gas exchange Respiratory Cycle Inspiration
Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Respiration External respiration ventilation gas exchange Internal respiration cellular respiration gas exchange Respiratory Cycle Inspiration
Runners! Workshop. How To Become Your Fastest And Strongest Runner From Beginner, To 5K, To Ultra Marathons
 Runners! Workshop How To Become Your Fastest And Strongest Runner From Beginner, To 5K, To Ultra Marathons Dr. Maria Sundberg Senior Trainer, FitEverywhere Why Do YOU Run? Recreation? To lose weight? To
Runners! Workshop How To Become Your Fastest And Strongest Runner From Beginner, To 5K, To Ultra Marathons Dr. Maria Sundberg Senior Trainer, FitEverywhere Why Do YOU Run? Recreation? To lose weight? To
Alveolus and Respiratory Membrane
 Alveolus and Respiratory Membrane thin membrane where gas exchange occurs in the lungs, simple squamous epithelium (Squamous cells have the appearance of thin, flat plates. They fit closely together in
Alveolus and Respiratory Membrane thin membrane where gas exchange occurs in the lungs, simple squamous epithelium (Squamous cells have the appearance of thin, flat plates. They fit closely together in
Chapter 16 Respiratory System
 Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Anatomy and Physiology Part 11: Of Blood and Breath by: Les Sellnow
 Anatomy and Physiology Part 11: Of Blood and Breath by: Les Sellnow There are few similarities between horses and automobiles, but in a manner of speaking, the horse's circulatory and respiratory systems
Anatomy and Physiology Part 11: Of Blood and Breath by: Les Sellnow There are few similarities between horses and automobiles, but in a manner of speaking, the horse's circulatory and respiratory systems
Gas exchange. Tissue cells CO2 CO 2 O 2. Pulmonary capillary. Tissue capillaries
 Gas exchange Pulmonary gas exchange Tissue gas exchange CO 2 O 2 O 2 Tissue cells CO2 CO 2 Pulmonary capillary O 2 O 2 CO 2 Tissue capillaries Physical principles of gas exchange Diffusion: continuous
Gas exchange Pulmonary gas exchange Tissue gas exchange CO 2 O 2 O 2 Tissue cells CO2 CO 2 Pulmonary capillary O 2 O 2 CO 2 Tissue capillaries Physical principles of gas exchange Diffusion: continuous
Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment
 Name: Date: Mark: / 45 Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following
Name: Date: Mark: / 45 Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following
LACTATE TRANSPORTERS How do these fit into Competition and Training? By Dr. Bob Treffene INTRODUCTION The human muscle has a very complicated taxi
 LACTATE TRANSPORTERS How do these fit into Competition and Training? By Dr. Bob Treffene INTRODUCTION The human muscle has a very complicated taxi system for transporting various things from one part to
LACTATE TRANSPORTERS How do these fit into Competition and Training? By Dr. Bob Treffene INTRODUCTION The human muscle has a very complicated taxi system for transporting various things from one part to
Physiology and Training for Peak Performance Tom Vandenbogaerde, Australian Institute of Sport
 Physiology and Training for Peak Performance Tom Vandenbogaerde, Australian Institute of Sport Presentation Overview: ~50 min: Snapshot of Training Week, discuss anticipated physiological adaptations ~20
Physiology and Training for Peak Performance Tom Vandenbogaerde, Australian Institute of Sport Presentation Overview: ~50 min: Snapshot of Training Week, discuss anticipated physiological adaptations ~20
Energy Metabolism. Symptoms of Tying-up
 TYING-UP IN HORSES Research Leads to Dietary and Exercise Management Strategies by Stephanie J. Valberg, D.V.M., Ph.D., College of Veterinary Medicine, University of Minnesota, St. Paul, Minnesota Tying-up,
TYING-UP IN HORSES Research Leads to Dietary and Exercise Management Strategies by Stephanie J. Valberg, D.V.M., Ph.D., College of Veterinary Medicine, University of Minnesota, St. Paul, Minnesota Tying-up,
Neuroanatomy of a Kick
 Victor Da Costa Introduction A kick is a staple fighting technique that is included in many martial arts. A kick may vary in appearance from a straightforward front kick to a complicated jump spin heel
Victor Da Costa Introduction A kick is a staple fighting technique that is included in many martial arts. A kick may vary in appearance from a straightforward front kick to a complicated jump spin heel
SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION
 SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION WHEN WE BREATHE, WHAT DO WE BREATHE IN? O2, N2, CO2, O3, NO2 (gas fumes), CO, pollutant, fragrants, toxins, etc. WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF BREATHING IN? WHAT DOES OUR BODY WANT? O2 WHY?
SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION WHEN WE BREATHE, WHAT DO WE BREATHE IN? O2, N2, CO2, O3, NO2 (gas fumes), CO, pollutant, fragrants, toxins, etc. WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF BREATHING IN? WHAT DOES OUR BODY WANT? O2 WHY?
Researcher 2018;10(1) Study of the shuttle movement of blood lactate in athletes. Dr.
 Study of the shuttle movement of blood lactate in athletes Dr. Nawaf Alshammari Associate professor, Ph.D. College of Basiuwaitc education, Kuwait. dr.nawaf_@hotmail.com Abstract: The bioenergy study is
Study of the shuttle movement of blood lactate in athletes Dr. Nawaf Alshammari Associate professor, Ph.D. College of Basiuwaitc education, Kuwait. dr.nawaf_@hotmail.com Abstract: The bioenergy study is
Gas Exchange in Animals. Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2. Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial
 Gas Exchange in Animals Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2 Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial Respiratory surface! skin, gills, lungs Circulatory System O2/CO2
Gas Exchange in Animals Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2 Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial Respiratory surface! skin, gills, lungs Circulatory System O2/CO2
Introduction to Biological Science - BIOL Gas Exchange
 Gas Exchange A. Influence of concentration gradient on gas diffusion rate 1. You have two tubes of permeable membrane. a. Add an arrow to illustrate concurrent fluid flow in Tubes A and B. Tube A Tube
Gas Exchange A. Influence of concentration gradient on gas diffusion rate 1. You have two tubes of permeable membrane. a. Add an arrow to illustrate concurrent fluid flow in Tubes A and B. Tube A Tube
Qualification title: Level 3 Advanced Technical Diploma in Sport and Physical Activity (Sports Coaching) (540)
 Qualification title: 4827-31 Level 3 Advanced Technical Diploma in Sport and Physical Activity (Sports Coaching) (540) Test title: External test Version: Sample for submission Base mark: 80 Proposed grading
Qualification title: 4827-31 Level 3 Advanced Technical Diploma in Sport and Physical Activity (Sports Coaching) (540) Test title: External test Version: Sample for submission Base mark: 80 Proposed grading
Hyndland Secondary School Biology Department
 Hyndland Secondary School Biology Department Body in Action Homework and Question Booklet 1 Body in Action (a) Movement... 2 Skeleton... 2 Joints... 3 Body in Action (b) The need for Energy... 5 Heart...
Hyndland Secondary School Biology Department Body in Action Homework and Question Booklet 1 Body in Action (a) Movement... 2 Skeleton... 2 Joints... 3 Body in Action (b) The need for Energy... 5 Heart...
A Patient s Guide to Lateral Epicondylitis (Tennis Elbow) William T. Grant, MD
 A Patient s Guide to Lateral Epicondylitis (Tennis Elbow) Dr. Grant is a talented orthopedic surgeon with more than 30 years of experience helping people return to their quality of life. He and GM Pugh,
A Patient s Guide to Lateral Epicondylitis (Tennis Elbow) Dr. Grant is a talented orthopedic surgeon with more than 30 years of experience helping people return to their quality of life. He and GM Pugh,
Circulation and Gas Exchange Chapter 42
 Circulation and Gas Exchange Chapter 42 Circulatory systems link exchange surfaces with cells throughout the body Diffusion is only efficient over small distances In small and/or thin animals, cells can
Circulation and Gas Exchange Chapter 42 Circulatory systems link exchange surfaces with cells throughout the body Diffusion is only efficient over small distances In small and/or thin animals, cells can
Some major points on the Effects of Hypoxia
 Some major points on the Effects of Hypoxia Source: Kings College London http://www.kcl.ac.uk/teares/gktvc/vc/dental/year1/lectures/rbmsmajorpoints/effectsofhypoxia.htm Cells obtain their energy from oxygen.
Some major points on the Effects of Hypoxia Source: Kings College London http://www.kcl.ac.uk/teares/gktvc/vc/dental/year1/lectures/rbmsmajorpoints/effectsofhypoxia.htm Cells obtain their energy from oxygen.
Life 24 - Blood and Circulation Raven & Johnson Ch 52 & 53 (parts)
 1 Life 24 - Blood and Circulation Raven & Johnson Ch 52 & 53 (parts) Objectives 1: Understand the importance of oxygen carrier molecules in respiration 2: Describe the characteristics and locations of
1 Life 24 - Blood and Circulation Raven & Johnson Ch 52 & 53 (parts) Objectives 1: Understand the importance of oxygen carrier molecules in respiration 2: Describe the characteristics and locations of
Energy Systems and Growth
 Energy Systems and Growth Understanding Energy Systems and Growth Understanding how your body produces energy is vital to understanding why you train in certain ways to enhance your energy systems and
Energy Systems and Growth Understanding Energy Systems and Growth Understanding how your body produces energy is vital to understanding why you train in certain ways to enhance your energy systems and
Respiratory system & exercise. Dr. Rehab F Gwada
 Respiratory system & exercise Dr. Rehab F Gwada Objectives of lecture Outline the major anatomical components & important functions of the respiratory system. Describe the mechanics of ventilation. List
Respiratory system & exercise Dr. Rehab F Gwada Objectives of lecture Outline the major anatomical components & important functions of the respiratory system. Describe the mechanics of ventilation. List
2.1.1 List the principal structures of the
 physiology 2.1.1 List the principal structures of the The principle structures of the respiratory are: Nose/Mouth used for inhalation of oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide rich air Pharynx -
physiology 2.1.1 List the principal structures of the The principle structures of the respiratory are: Nose/Mouth used for inhalation of oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide rich air Pharynx -
Exam Key. NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 Exam # 2 October 28, 2016 Total POINTS: % of grade in class
 NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 Exam # 2 October 28, 2016 Total POINTS: 100 20% of grade in class 1) An arterial blood sample for a patient at sea level is obtained, and the following physiological values
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 Exam # 2 October 28, 2016 Total POINTS: 100 20% of grade in class 1) An arterial blood sample for a patient at sea level is obtained, and the following physiological values
