Unit 8 B: Respiration
|
|
|
- Evelyn Allen
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit 8 B: Respiration Respiration: Respiration is a chemical reaction that happens in all living cells. It is the way that energy is released from glucose, for our cells to use to keep us functioning. Remember that respiration is not the same as breathing (which is properly called ventilation). Aerobic respiration: The glucose and oxygen react together in the cells to produce carbon dioxide and water. The reaction is called aerobic respiration because oxygen from the air is needed for it to work. Here is the word equation for aerobic respiration: glucose + oxygen carbon dioxide + water (+ energy) (Energy is released in the reaction. We show it in brackets in the equation because energy is not a substance.) Now we will look at how glucose and oxygen get to the cells so that respiration can take place and how we get rid of the carbon dioxide. Glucose from food to cells: Glucose is a type of carbohydrate, obtained through digestion of the food we eat. Digestion breaks food down into small molecules. These can be absorbed across the wall of the small intestine into the bloodstream. Glucose is carried round the body dissolved in blood plasma, the pale yellow liquid part of our blood. The dissolved glucose can diffuse into the cells of the body from the capillaries. Once in the cell glucose can be used in respiration. Oxygen from the air to cells: When we breathe in oxygen enters the small air sacs, called alveoli, in the lungs. Oxygen diffuses from there into the bloodstream. Oxygen is not carried in the plasma, but is carried by the red blood cells. These contain a red substance called haemoglobin, which joins onto oxygen and carries it around the body in the blood, then lets it go when necessary. Like glucose, oxygen can diffuse into cells from the capillaries. Red blood cells carry oxygen around the body. Carbon dioxide from cells to the air: The carbon dioxide produced during respiration diffuses out of the cells and into the blood plasma. The blood carries it to the lungs. It then diffuses across the walls of the alveoli and into the air, ready to be exhaled. 1
2 The respiratory system and ventilation: The respiratory system: The human respiratory system contains the organs that allow us to get the oxygen we need and to remove the waste carbon dioxide we don't need. It contains these parts: Lungs Tubes leading from the lungs to the mouth and nose Various structures in the chest that allow air to move in and out of the lungs. Ventilation: Movements of the ribs, rib muscles and diaphragm allow air into and out of the lungs. Take care - this is called breathing or ventilation, not respiration. When we breathe in, we inhale. When we breathe out, we exhale. Air passes between the lungs and the outside of the body through the windpipe, called the trachea. The trachea divides into two bronchi, with one bronchus for each lung. Each bronchus divides further in the lungs into smaller tubes called bronchioles. At the end of each bronchiole, there is a group of tiny air sacs. These air sacs have bulges called alveoli to increase their surface area. 2
3 Inhaled air and exhaled air: Gas Inhaled air (air entering lungs) Exhaled air (air leaving lungs) Oxygen 21% 17% Carbon dioxide 0.04% 4% Nitrogen 78% 78% Water vapour Varies Saturated Compared to the air we breathe in, the air we breathe out has: Less oxygen More carbon dioxide. The amount of nitrogen stays the same, but there is more water vapour in exhaled air. We can test for the presence of the extra carbon dioxide in exhaled air using limewater. If we exhale into limewater, it turns cloudy white. Gas exchange: We need to get oxygen from the air into the blood, and we need to remove waste carbon dioxide from the blood into the air. Moving gases like this is called gas exchange. The alveoli are adapted to make gas exchange in lungs happen easily and efficiently. Here are some features of the alveoli that allow this: They give the lungs a really big surface area They have moist, thin walls (just one cell thick) They have a lot of tiny blood vessels called capillaries. The gases move by diffusion from where they have a high concentration to where they have a low concentration: Oxygen diffuses from the air in the alveoli into the blood. Carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the air in the alveoli. 3
4 Some water vapour is also lost from the surface of the alveoli into the lungs - we can see this condensing when we breathe out on cold days. The circulatory system: The circulatory system is the body s transport system. Oxygen and nutrients including glucose travel around the body in the blood. Blood: Blood is a mixture of different types of cells in a liquid. Red blood cells carry oxygen from the lungs to the cells and take carbon dioxide back to the lungs. White blood cells help fight disease. Plasma is a straw coloured liquid that carries nutrients, as well as hormones which control your body, and antibodies which help fight disease. Platelets help blood to clot when you have a wound. Circulation of blood: Blood circulates around the body, pumped by the heart. It travels in a network of tubes called blood vessels. There are three main types: Arteries carry blood away from the heart. Veins carry blood back to the heart. Capillaries are tiny vessels that join arteries to veins. 4
5 Capillaries branch deep inside the body s tissues. Here substances such as oxygen, glucose and carbon dioxide can be exchanged between the blood and the cells. Pumping faster and harder: 1- The heart pumps blood to the lungs. Here, it picks up oxygen, and carbon dioxide leaves it. 2- Oxygenated blood goes back to the heart. 3- The heart pumps oxygenated blood around the body to organs such as the gut, the muscles and the brain. 4- Deep in the tissues oxygen, glucose and other nutrients pass from the blood to the cells for respiration. Waste material such as carbon dioxide passes from the cells to the blood to be carried away. 5- The deoxygenated blood travels back to the heart to be pumped back to the lungs again. If you run a race, your muscle cells are respiring fast so they need lots of oxygen and glucose. They are producing more carbon dioxide and water, as well as releasing lots of energy to win the race. To supply the cells, your heart pumps faster and harder, circulating the blood faster and you breathe faster too. What if you tried to sprint hard for an hour? Your lungs would not be able to pick up enough oxygen, and your heart would not be able to circulate the blood fast enough. Your muscle cells would run short of oxygen. When this happens you get cramp and feel exhausted. You have to stop! But if you jog slowly, your body can supply enough oxygen and glucose for a long time. 5
6 Smoking : One serious smoking experiment: 1- Some of the disgusting grot that comes out of cigarettes can be observed by drawing the cigarette smoke through clean glass wool. 2- The results show the wool quickly get stained with horrible black ink. The thermometer shows a rapid increase in temperature as well. 3- One of the great unsolved mysteries of our time is why there are still so many people who take up smoking and destroy their lungs with disgusting black grot. Smoking destroys your lungs with three kinds of grot: 1- Nicotine: This is an addictive drug that makes the heart beat faster, narrows the arteries and so causes high blood pressure. This leads to heart disease. 2- Tar: This coats the lining of the lungs making them less able to take in oxygen. It also contains carcinogens which cause cancer. 3- Carbon monoxide: This is a poisonous gas which joins up with red blood cells, making them incapable of transporting oxygen around the body. Eight reasons not to start smoking: 6
7 Q1: 1- Complete the sentences: Food gives us the raw for making new cells. We need new cells so that we can and damage. Food also gives us the that we need for growing, and keeping. 2- Complete the table. What we use when we respire What we release when we respire 3- a)use the information in the table to complete the equation. Glucose + carbon dioxide + + ( ) b) Write the symbol equation for the reaction above. 7
8 c) Name the reactants and the products. What else is produced? Q2: Complete the following. is the body s transport system. It carries nutrients including and oxygen around the body to the cells and tissues. Here they are used for. Q3: Do an internet or library search on how people first found out about the human blood circulation. Try entering these names: Galen, Vesalius, Harvey, Ibn -Al- Nafis. Q4: Label the following parts of the diagram: Kidneys intestines heart cells in the body lungs Then match each of the following descriptions to the correct part. Blood collects digested food here: Blood drops off waste chemicals here: Blood collects oxygen and drops off carbon dioxide here: The heart keeps the blood moving round the body: Blood takes carbon dioxide and waste chemicals away from here: Blood drops off oxygen and food here: 8
9 Q5: Complete the following table: Arteries Capillaries Veins Carry blood from the heart Connect to Carry blood the heart Carry blood Carry both oxygenated and deoxygenated blood Carry blood Have valves to stop the back flow of blood Have a layer of Walls are very Thin layer of muscle muscle space inside Tiny vessels in close contact to space inside cells Blood flows at Pressure due to the action of the heart Low blood pressure and slow speed to allow exchange of materials Blood flows at pressure Q6: 1- Use the bold words around the diagram to complete the sentences. Small blood vessels called take substances to the cells in your body. Blood carries and to the cells. These substances pass into the. Waste and pass from the cells in to the. 2- The cells in your body need oxygen and glucose. 9
10 a) Complete the flow diagram. b) Why do the cells in your big toe need oxygen and glucose? Q7: The diagram below shows the blood circulation. Use arrows to show how blood circulates through the blood vessels and heart. (use red arrows to show oxygenated blood and blue arrows to show de-oxygenated blood) Q8: Sometimes your cells don t have enough oxygen to release all the energy that they need. But they can respire for a short time without oxygen. Respiration without oxygen is called anaerobic repiration. It releases less energy from glucose than aerobic respiration. The waste products of aerobic and anaerobic respiration are also different. Anaerobic respiration produces lactic acid, which is poisonous to cells. It is what makes your muscles sore when you do more exercise than usual. It can also give you cramp. 1- What does anaerobic respiration mean? 10
11 2- This is the word equation for aerobic respiration: glucose + oxygen carbon dioxide + water + energy This is the word equation for anaerobic respiration: glucose lactic acid + carbon dioxide + some energy Write down three differences between these equations. 3- Find out how you get rid of lactic acid. 4- Find out what oxygen debt is. Q 9: At sea level there is twice as much oxygen than at 6000m high on a mountain. People who climb mountains therefore need to take a supply of oxygen. The summit of Mount Everest is about 9000m above sea level. People who live at high altitudes breathe more quickly and more deeply than people who live at sea level. Also, their number of red blood cells is different. Altitude (m) Number of red blood cells per cm 3 of blood Sea level Look at the table. Use the information in the table to plot a bar chart. 11
12 2- What do the results show us about the relationship between altitude and the number of red blood cells? 3- Why do people who live at high altitudes breathe more quickly and more deeply? 4- The 1968 the Olympic Games were held in Mexico City, which is 2000m above sea level. How do you think this affected athletes from lowland countries? 5- Give a possible explanation why so many African runners are so successful in long distance and marathon races. Q10: Fire officer Allen has to use breathing apparatus to go into burning buildings. His breathing apparatus is connected to an oxygen tank on his back. 1- Complete the flow diagram with the followings: Alveoli blood fine tubes in lungs mouth Our lungs can be damaged by things that we breathe in. Dust, smoke from fires and cigarette smoke can all harm our lungs. 12
13 How well our lungs can take oxygen into our blood is called our lung function. The graph shows how cigarette smoke affects lung function. 2- How does the lung function of a smoker compare with that of a non- smoker? 3- What is the difference in lung function between a 65-year-old smoker and a 65-year-old who quit smoking at the age of 45? Q11: Look at the diagram to answer the following questions. 1- Complete these sentences: The gas moves from X to Y. The gas moves from V to W. 2- The wall around the alveolus is very thin. Why is it useful for the alveolus to have a very thin wall? Q12: Sometimes, patients in hospitals have to be fed by injecting liquid food directly into the blood vessels known as veins. This is called intravenous feeding. It happens when there is a problem with a person s digestive system. 1- Find out some other examples of when a person might need to be fed in this way. 13
14 2- Intravenous feeding has to provide a balance of nutrients. a) What do you think intravenous food contains? b) Why does the intravenous fluid contain only soluble foods? c) What parts of the intravenous food provide a patient with energy? 3- Doctors can use the intravenous feeding method to get other things into the patient s body. Write down one example. Q13: List the parts of the blood. Underline the part that carries oxygen, and in another colour the part that carries glucose. Q14: Mrs Daniel, the science teacher, set up three gas jars and timed how long it took for each candle to go out. The diagram shows us what she did. 1- For each gas jar, write down the percentage of oxygen in the air. 2- Predict the order that the candle go out. Explain your prediction. 3- What should Mrs Daniel do to make this experiment a fair test? 14
15 4- Mrs Daniel did a similar experiment again using inhaled air. This time, she grew a small pot of cress plants in the jar under a lamp for one week, before putting the burning candle in the jar (carefully, so as not to let the gases in the jar escape). The candle burnt for longer. Find out why this happened. Activity: Using a respirometer This is a diagram of apparatus that you can use to measure the rate of respiration. It is used to measure the amount of oxygen removed or carbon dioxide added to the air in the test tube. The maggots take in oxygen and give out carbon dioxide. Any carbon dioxide in the test tube is absorbed by the soda lime. So as oxygen is taken out of the air in the test tube and carbon dioxide is added, the coloured liquid moves towards the maggots. You can use the scale to measure how much the liquid moves. Planning your investigation Your task is to plan an investigation to find out the effect of temperature on the volume of oxygen and carbon dioxide exchanged by the maggots. For your plan, you must do the following: 1- Decide on a heading for your investigation. The heading might start like this: The effect of temperature on the Make a prediction. We normally make a prediction about what will happen and we say why we think it will happen. Fanoulla; As it gets hotter, the air will expand and the coloured liquid will move away from the test tube. Christopher: As it gets hotter, the maggots become more active and they take up more oxygen. This causes the coloured liquid to move towards the test tube. Maliwan: 15
16 As it gets hotter, the maggots produce more carbon dioxide. This pushes the coloured liquid away from the test tube. a) Discuss Fanoulla s, Christopher s and Maliwan s ideas with other pupils. b) Write down your prediction. 3- Decide the temperatures that you will use. Ideally you need a range of at least five temperatures (ranging from 0 C to 40 C). 4- Decide how you will measure the temperature. (Whether you will use a temperature sensor or a thermometer). 5- How you will keep each experiment at a constant temperature. You could use: Ice Hot water from a kettle A Bunsen burner to heat water An electronic water bath 6- The number of times that you will repeat each experiment, and why. 7- What things (factors) you will keep the same and how you will make this a fair test. You could consider: The number of maggots The kind of maggots (species, size, age) The glassware The time it is left before taking a reading 8- What safety precautions you will take. When we handle living material, we always wash our hands and wipe the bench with disinfectant. Remember, you will be handling glassware, hot water and living things. 9- What results you will take from the experiment. You will need to produce a table for your results. In this experiment, you will be measuring: Different temperatures The volume of oxygen taken up by maggots, or The volume of carbon dioxide released by the maggots 16
17 17
The Breathing System
 The Breathing System Learning Intentions 1. Students should Know how Breathing happens 2. Name and know the functions of the Breathing System 3. Know how the organs work and how they work with other systems
The Breathing System Learning Intentions 1. Students should Know how Breathing happens 2. Name and know the functions of the Breathing System 3. Know how the organs work and how they work with other systems
A breath of fresh air
 A breath of fresh air BIG IDEAS You are learning to: Describe the structure of the lungs Explain how the lungs clean themselves Interpret patterns in data Where are the lungs and what do they do? The lungs
A breath of fresh air BIG IDEAS You are learning to: Describe the structure of the lungs Explain how the lungs clean themselves Interpret patterns in data Where are the lungs and what do they do? The lungs
Monday, ! Today: Respiratory system! 5/20/14! Transport of Blood! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing!
 Monday, 5.19.14! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing! Transport of Blood! What is transported! Nutrients! Oxygen! Carbon Dioxide! Hormones! Antibodies! What it is/does!
Monday, 5.19.14! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing! Transport of Blood! What is transported! Nutrients! Oxygen! Carbon Dioxide! Hormones! Antibodies! What it is/does!
OB11 Carry out qualitative tests to compare the carbon dioxide levels of inhaled and exhaled air
 Biology: 5. Respiration and Breathing Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier OB9 Syllabus Describe the process of aerobic respiration
Biology: 5. Respiration and Breathing Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier OB9 Syllabus Describe the process of aerobic respiration
The diagram shows an alveolus next to a blood capillary in a lung. (a) (i) Draw a ring around the correct answer to complete the sentence. diffusion.
 BREATHING / GAS EXCHANGE. NAME. Q.Gas exchange takes place in the lungs. The diagram shows an alveolus next to a blood capillary in a lung. The arrows show the movement of two gases, A and B. (a) (i) Draw
BREATHING / GAS EXCHANGE. NAME. Q.Gas exchange takes place in the lungs. The diagram shows an alveolus next to a blood capillary in a lung. The arrows show the movement of two gases, A and B. (a) (i) Draw
practices makes perfect
 Human Respiratory system Chapter 1: Respiration PMR 03, 08 1. The human respiratory system consists of: a... b... c.. d... e. Our body has.. lungs (right & left). f. Each lung consists of the, and alveoli.
Human Respiratory system Chapter 1: Respiration PMR 03, 08 1. The human respiratory system consists of: a... b... c.. d... e. Our body has.. lungs (right & left). f. Each lung consists of the, and alveoli.
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 4
 Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 4 64 minutes 64 marks Page of 0 Q. (a) The table shows an athlete s breathing rate after the end of a race. Use the information shown in the table to draw a line
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 4 64 minutes 64 marks Page of 0 Q. (a) The table shows an athlete s breathing rate after the end of a race. Use the information shown in the table to draw a line
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System
 Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Supporting inquiry based teaching and learning. Respiration. Student Name: Class:
 Supporting inquiry based teaching and learning Respiration Student Name: Class: Teacher Name: School: Question 1 a) Respiration is the process that the swimmer uses to release energy from the digested
Supporting inquiry based teaching and learning Respiration Student Name: Class: Teacher Name: School: Question 1 a) Respiration is the process that the swimmer uses to release energy from the digested
08 Respiration. #79 Respiration realeases energy from food
 08 Respiration #79 Respiration realeases energy from food Respiration is the chemical reactions that break down nutrient molecules in living cells to release energy. In humans, our cells need energy (ATP)
08 Respiration #79 Respiration realeases energy from food Respiration is the chemical reactions that break down nutrient molecules in living cells to release energy. In humans, our cells need energy (ATP)
Chapter 1: Respiration
 Chapter 1: Respiration Respiration Human Breathing Mechanism Transport of oxygen Importance of a healthy respiratory system Respiratory system lungs inhalation exhalation Diffusion of oxygen by blood Transport
Chapter 1: Respiration Respiration Human Breathing Mechanism Transport of oxygen Importance of a healthy respiratory system Respiratory system lungs inhalation exhalation Diffusion of oxygen by blood Transport
Video. Respiration System. You will use 3 pages of your journal for this lesson. 1. One page for hand written notes onto a journal page
 Respiratory System Video Respiration System You will use 3 pages of your journal for this lesson. 1. One page for hand written notes onto a journal page 2. 2 nd page for diagram 3. 3 rd page for chart
Respiratory System Video Respiration System You will use 3 pages of your journal for this lesson. 1. One page for hand written notes onto a journal page 2. 2 nd page for diagram 3. 3 rd page for chart
Human gas exchange. Question Paper. Save My Exams! The Home of Revision. Cambridge International Examinations. 56 minutes. Time Allowed: Score: /46
 Human gas exchange Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International Examinations Respiration Human gas exchange Question Paper Time llowed: 56 minutes
Human gas exchange Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International Examinations Respiration Human gas exchange Question Paper Time llowed: 56 minutes
Multicellular Organisms. Sub-Topic 2.7 Animal Transport & Exchange Systems
 Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.7 Animal Transport & Exchange Systems On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: Rings of cartilage keep the main airways open Oxygen and carbon dioxide
Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.7 Animal Transport & Exchange Systems On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: Rings of cartilage keep the main airways open Oxygen and carbon dioxide
Glucose + Oxygen Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy C6H12O CO2 + 6H20 + energy
 Cell Respiration - A food oxidization process in body cells to produce energy - Occurs (happens) in animal cells and plant cells Notes : Metabolic Reactions in Gaseous Exchange CELL RESPIRATION Photosynthesis
Cell Respiration - A food oxidization process in body cells to produce energy - Occurs (happens) in animal cells and plant cells Notes : Metabolic Reactions in Gaseous Exchange CELL RESPIRATION Photosynthesis
1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives
 1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives To understand the functions of the circulatory system. To be able to identify the differences between veins, arteries
1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives To understand the functions of the circulatory system. To be able to identify the differences between veins, arteries
Lesson 6 Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift PS 2.2 a,e PS 3.1i
 Table of Contents Letter to the Student...................................... 5 Letter to the Family....................................... 6 New York State Performance Standards Correlation Chart.......
Table of Contents Letter to the Student...................................... 5 Letter to the Family....................................... 6 New York State Performance Standards Correlation Chart.......
The bar chart shows the amount of water lost from the body of a student on two different days.
 RESPIRATION (2nd PART) Q1. The bar chart shows the amount of water lost from the body of a student on two different days. The student ate the same amount of food and drank the same amount of liquid on
RESPIRATION (2nd PART) Q1. The bar chart shows the amount of water lost from the body of a student on two different days. The student ate the same amount of food and drank the same amount of liquid on
It is a product of proteins broken down in the mammal. It is exchanged for oxygen which is taken into the blood.
 5 The table shows the approximate composition of air breathed out by a mammal. Where does the nitrogen in the air breathed out come from? It is a product of proteins broken down in the mammal. It is a
5 The table shows the approximate composition of air breathed out by a mammal. Where does the nitrogen in the air breathed out come from? It is a product of proteins broken down in the mammal. It is a
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION
 SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION WHEN WE BREATHE, WHAT DO WE BREATHE IN? O2, N2, CO2, O3, NO2 (gas fumes), CO, pollutant, fragrants, toxins, etc. WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF BREATHING IN? WHAT DOES OUR BODY WANT? O2 WHY?
SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION WHEN WE BREATHE, WHAT DO WE BREATHE IN? O2, N2, CO2, O3, NO2 (gas fumes), CO, pollutant, fragrants, toxins, etc. WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF BREATHING IN? WHAT DOES OUR BODY WANT? O2 WHY?
The Human Body. Everyone Needs Healthy Systems. Blood Vessels
 The Human Body Everyone Needs Healthy Systems There are several systems that make up the human body. Although their functions differ, they all work together to keep your body running smoothly. Some of
The Human Body Everyone Needs Healthy Systems There are several systems that make up the human body. Although their functions differ, they all work together to keep your body running smoothly. Some of
Structures of the Respiratory System include:
 Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
RESPIRATION AND EXCRETION
 CHAPTER 13 RESPIRATION AND EXCRETION SECTION 13 1 The Respiratory System (pages 430-438) This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Introduction
CHAPTER 13 RESPIRATION AND EXCRETION SECTION 13 1 The Respiratory System (pages 430-438) This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Introduction
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system. Objective sheet 3 Notes
 1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
The Respiratory System
 Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Parts of the Respiratory System The RS can be divided into two parts: 1. Respiratory Tract, (path that air follows). Nasal passage Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi,
PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Parts of the Respiratory System The RS can be divided into two parts: 1. Respiratory Tract, (path that air follows). Nasal passage Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi,
SCIENCE- NOTES. Q1. Draw the diagram of human respiratory system and explain the function of the following parts:
 SCIENCE- NOTES NAME: RESPIRATION IN ORGANISMS STD.VII DIV: Q1. Draw the diagram of human respiratory system and explain the function of the following parts: i. Nasal cavity ii. Trachea iii. Lungs iv. Bronchioles
SCIENCE- NOTES NAME: RESPIRATION IN ORGANISMS STD.VII DIV: Q1. Draw the diagram of human respiratory system and explain the function of the following parts: i. Nasal cavity ii. Trachea iii. Lungs iv. Bronchioles
Directions: The following two questions refer to the diagram below, which shows a group of cells from the respiratory tract.
 Topic 7 Gas exchange in humans Directions: The following two questions refer to the diagram below, which shows a group of cells from the respiratory tract. X Y 1. What is the function of structure X? A.
Topic 7 Gas exchange in humans Directions: The following two questions refer to the diagram below, which shows a group of cells from the respiratory tract. X Y 1. What is the function of structure X? A.
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Learning Outcomes Identify the following structures in the lungs: windpipe, bronchus, bronchioles and air sacs State the function of the air sacs State the path oxygen takes when
The Respiratory System Learning Outcomes Identify the following structures in the lungs: windpipe, bronchus, bronchioles and air sacs State the function of the air sacs State the path oxygen takes when
Gas Exchange ACTIVITY OVERVIEW SUMMARY KEY CONCEPTS AND PROCESS SKILLS KEY VOCABULARY. Teacher s Guide B-75 L A B O R ATO R Y
 Gas Exchange 17 40- to 2 50-minute sessions ACTIVITY OVERVIEW L A B O R ATO R Y SUMMARY This activity explores the role of the respiratory system in the regulation of gases in the blood. Students investigate
Gas Exchange 17 40- to 2 50-minute sessions ACTIVITY OVERVIEW L A B O R ATO R Y SUMMARY This activity explores the role of the respiratory system in the regulation of gases in the blood. Students investigate
Sc ienc e 9-Biology Work sheet 8-2 A Single Breat h & Tak ing Care
 Unit 2 Your Living Body Sc ienc e 9-Biology Work sheet 8-2 A Single Breat h & Tak ing Care Name No pen or pencil No Textbook 20 Due Date Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Read pages 159-167
Unit 2 Your Living Body Sc ienc e 9-Biology Work sheet 8-2 A Single Breat h & Tak ing Care Name No pen or pencil No Textbook 20 Due Date Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Read pages 159-167
The table shows the effect of exercise on the action of one person s heart. Heart rate in beats per minute
 ## (a) The table shows the effect of exercise on the action of one person s heart. At rest During exercise Heart rate in beats per minute 7 165 Volume of blood leaving the heart in each beat in cm 3 Heart
## (a) The table shows the effect of exercise on the action of one person s heart. At rest During exercise Heart rate in beats per minute 7 165 Volume of blood leaving the heart in each beat in cm 3 Heart
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at gaseous exchange in humans in terms of o Ventilation o Inspiration o Expiration o Transport of gases o Homeostatic
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at gaseous exchange in humans in terms of o Ventilation o Inspiration o Expiration o Transport of gases o Homeostatic
1. Harry investigated the effects of fizzy cola drink on his heart rate.
 1. Harry investigated the effects of fizzy cola drink on his heart rate. First he measured his heart rate every minute for 5 minutes when sitting down. Then he drank some cola. He continued to measure
1. Harry investigated the effects of fizzy cola drink on his heart rate. First he measured his heart rate every minute for 5 minutes when sitting down. Then he drank some cola. He continued to measure
Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class
 I. Name the following : Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class 1. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. 2. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous
I. Name the following : Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class 1. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. 2. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous
Transport in cells. Specification coverage
 3 Transport in cells T F A R What does smelling your best friend s deodorant have in common with making a cup of tea? One thing is that they both involve the movement of particles. Particles spread out
3 Transport in cells T F A R What does smelling your best friend s deodorant have in common with making a cup of tea? One thing is that they both involve the movement of particles. Particles spread out
Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired
 Chapter 6 Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired This chapter covers: the structure of the human gas exchange system the mechanism of breathing gas exchange in the alveoli the concept
Chapter 6 Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired This chapter covers: the structure of the human gas exchange system the mechanism of breathing gas exchange in the alveoli the concept
Respiration. The ins and outs
 Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
Human Biology Respiratory System
 Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
Hyndland Secondary School Biology Department
 Hyndland Secondary School Biology Department Body in Action Homework and Question Booklet 1 Body in Action (a) Movement... 2 Skeleton... 2 Joints... 3 Body in Action (b) The need for Energy... 5 Heart...
Hyndland Secondary School Biology Department Body in Action Homework and Question Booklet 1 Body in Action (a) Movement... 2 Skeleton... 2 Joints... 3 Body in Action (b) The need for Energy... 5 Heart...
REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE 24 SEPTEMBER 2014 Lesson Description
 REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE 24 SEPTEMBER 2014 Lesson Description In this lesson, we revise: Gaseous Exchange in Plants & Animals Gaseous Exchange in Humans Excretion in Humans Focus on the Kidney Gaseous
REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE 24 SEPTEMBER 2014 Lesson Description In this lesson, we revise: Gaseous Exchange in Plants & Animals Gaseous Exchange in Humans Excretion in Humans Focus on the Kidney Gaseous
You Might Also Like. I look forward helping you focus your instruction while saving tons of time. Kesler Science Station Lab Activities 40%+ Savings!
 Thanks Connect Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over
Thanks Connect Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over
Components: Reader with DIGI MATERIAL cross-platform application (ios, Android, Windows, MacOSX) CLIL READERS. Level headwords.
 CirculatorySystem _6 cover.qxp_circulatorysystem _6 cover.qxp 21/9/16 6:56 PM Page 1 Level 6 Components: Reader with DIGI MATERIAL cross-platform application (ios, Android, Windows, MacOSX) Level 1 300
CirculatorySystem _6 cover.qxp_circulatorysystem _6 cover.qxp 21/9/16 6:56 PM Page 1 Level 6 Components: Reader with DIGI MATERIAL cross-platform application (ios, Android, Windows, MacOSX) Level 1 300
The Respiratory System
 Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, complete the flowchart
Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, complete the flowchart
What is breathing an respiration?
 LE SSON 15 What is breathing an respiration? You need energy to live. So do birds, trees, and bacteria. All living things need energy to carry out the life processes. And, there can be no life without
LE SSON 15 What is breathing an respiration? You need energy to live. So do birds, trees, and bacteria. All living things need energy to carry out the life processes. And, there can be no life without
Respiration. Chapter 33
 Respiration Chapter 33 Learning Objectives: Understand the basis of gas exchange and factors that influence diffusion of gases in and out of tissues Compare and contrast different respiratory systems among
Respiration Chapter 33 Learning Objectives: Understand the basis of gas exchange and factors that influence diffusion of gases in and out of tissues Compare and contrast different respiratory systems among
Respiratory System Homework
 Respiratory System Homework The R S is the body s breathing equipment. Similar to the D system, it takes S from outside the body (G, particularly O ), circulates them through the body to C and T, then
Respiratory System Homework The R S is the body s breathing equipment. Similar to the D system, it takes S from outside the body (G, particularly O ), circulates them through the body to C and T, then
Part 3: Simulation Cards Reader s Page
 Reader s Page Make 1 copy for Reader. Instructions will be on the front, questions on the back. As an option, the simulation may be frozen and a discussion of information on back of card undertaken. Students
Reader s Page Make 1 copy for Reader. Instructions will be on the front, questions on the back. As an option, the simulation may be frozen and a discussion of information on back of card undertaken. Students
Page 1. Chapter 33: Respiration O 2 CO 2
 Chapter 33: Respiration O 2 CO 2 Features of Respiratory Systems: 1) Moist surface (to dissolve gas) 2) Thin cells lining surface 3) Large surface area contacting environment Facilitate Diffusion Methods
Chapter 33: Respiration O 2 CO 2 Features of Respiratory Systems: 1) Moist surface (to dissolve gas) 2) Thin cells lining surface 3) Large surface area contacting environment Facilitate Diffusion Methods
Name period date assigned date due date returned
 Name period date assigned date due date returned procedure 1. Take one balloon and stretch it out 2. Take one deep breath and blow into the balloon until you cannot breath out anymore. Do Not Take A Second
Name period date assigned date due date returned procedure 1. Take one balloon and stretch it out 2. Take one deep breath and blow into the balloon until you cannot breath out anymore. Do Not Take A Second
Pop Quiz. What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach?
 Pop Quiz What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach? Respiratory System Review Cellular respiration: obtain glucose and oxygen, get
Pop Quiz What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach? Respiratory System Review Cellular respiration: obtain glucose and oxygen, get
The Respiratory System
 Name Date Class The Respiratory System (pages 564-572) Respiratory System Functions (pages 565-566) Key Concept: The respiratory system moves oxygen from the outside environment into the body. It also
Name Date Class The Respiratory System (pages 564-572) Respiratory System Functions (pages 565-566) Key Concept: The respiratory system moves oxygen from the outside environment into the body. It also
Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration)
 Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration) 1 Question 1 Why do organisms need food? Organisms need food for obtaining energy to perform the vital functions. Question 2 What is a respiratory substrate?
Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration) 1 Question 1 Why do organisms need food? Organisms need food for obtaining energy to perform the vital functions. Question 2 What is a respiratory substrate?
EXPERIMENTING The Respiratory and Circulatory Systems CLIL Course University of Nottingham STUDENT S WORKSHEETS
 EXPERIMENTING The Respiratory and Circulatory Systems CLIL Course University of Nottingham STUDENT S WORKSHEETS M. Antònia Berga Sabaté January March 2009 Worksheet 1 You breathe to take air into your
EXPERIMENTING The Respiratory and Circulatory Systems CLIL Course University of Nottingham STUDENT S WORKSHEETS M. Antònia Berga Sabaté January March 2009 Worksheet 1 You breathe to take air into your
Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment
 Name: Date: Mark: / 45 Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following
Name: Date: Mark: / 45 Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following
Circulation and Gas Exchange Chapter 42
 Circulation and Gas Exchange Chapter 42 Circulatory systems link exchange surfaces with cells throughout the body Diffusion is only efficient over small distances In small and/or thin animals, cells can
Circulation and Gas Exchange Chapter 42 Circulatory systems link exchange surfaces with cells throughout the body Diffusion is only efficient over small distances In small and/or thin animals, cells can
Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42. Gas Exchange pp Gas Exchange. Gas Exchange in Fish pp Gas Exchange in Fish
 Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42 Fig. 42.24 Gas Exchange pp.979-989 Gas exchange involves the uptake of oxygen and the discharge of carbon dioxide (i.e. respiration or breathing). It is necessary for cellular
Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42 Fig. 42.24 Gas Exchange pp.979-989 Gas exchange involves the uptake of oxygen and the discharge of carbon dioxide (i.e. respiration or breathing). It is necessary for cellular
 Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface:
 I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface: Common characteristics of respiratory surfaces: a) Moist: allows for the RAPID diffusion of dissolved gasses across its surface. Whereas the respiratory
I. Gas Exchange Respiratory Surfaces Respiratory Surface: Common characteristics of respiratory surfaces: a) Moist: allows for the RAPID diffusion of dissolved gasses across its surface. Whereas the respiratory
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System (pages 112 120) Respiratory System Functions (pages 113 114) Key Concept: The respiratory system moves oxygen from the outside environment into the body. It also removes carbon dioxide
The Respiratory System (pages 112 120) Respiratory System Functions (pages 113 114) Key Concept: The respiratory system moves oxygen from the outside environment into the body. It also removes carbon dioxide
Respiration in Organisms MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS NCERT
 10 Respiration in Organisms MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Sometimes when we do heavy exercise, anaerobic respiration takes place in our muscle cells. What is produced during this process? alcohol and lactic
10 Respiration in Organisms MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Sometimes when we do heavy exercise, anaerobic respiration takes place in our muscle cells. What is produced during this process? alcohol and lactic
REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE & EXCRETION 11 SEPTEMBER 2013
 REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE & EXCRETION 11 SEPTEMBER 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Revise gaseous exchange in different animals and examine the structure of the kidney Key Concepts Important
REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE & EXCRETION 11 SEPTEMBER 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Revise gaseous exchange in different animals and examine the structure of the kidney Key Concepts Important
The Respiratory System. Medical Terminology
 The Respiratory System Medical Terminology The respiratory system is where gas exchange occurs via respiration; inhalation/exhalation. pick up oxygen from inhaled air expels carbon dioxide and water sinus
The Respiratory System Medical Terminology The respiratory system is where gas exchange occurs via respiration; inhalation/exhalation. pick up oxygen from inhaled air expels carbon dioxide and water sinus
Use scientific principles to explain how the sprayer works. You may use diagrams to support your answer.
 4.3 Marking Key This guide includes sample answers, task-specific observable elements, (Appendices 1 and 2), descriptive evaluation rubrics for each competency (Appendices 3 and 4), and non-descriptive
4.3 Marking Key This guide includes sample answers, task-specific observable elements, (Appendices 1 and 2), descriptive evaluation rubrics for each competency (Appendices 3 and 4), and non-descriptive
--- Respiration in Organisms. Lesson at a Glance
 --- Respiration in Organisms Lesson at a Glance. Respiration is essential for survival of every living organism whether it is an animal or a plant. It is a process by which living organisms produce energy
--- Respiration in Organisms Lesson at a Glance. Respiration is essential for survival of every living organism whether it is an animal or a plant. It is a process by which living organisms produce energy
CHAPTER 5 : THE AIR AROUND US
 CHAPTER 5 : THE AIR AROUND US The Composition of Air Air is a mixture consist of Nitrogen 78% Oxygen 21% Carbon dioxide 0.03% Inert gases 0.97% Water vapour Microorganism Dust The percentage of the constituents
CHAPTER 5 : THE AIR AROUND US The Composition of Air Air is a mixture consist of Nitrogen 78% Oxygen 21% Carbon dioxide 0.03% Inert gases 0.97% Water vapour Microorganism Dust The percentage of the constituents
Gas Exchange in Animals. Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2. Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial
 Gas Exchange in Animals Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2 Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial Respiratory surface! skin, gills, lungs Circulatory System O2/CO2
Gas Exchange in Animals Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2 Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial Respiratory surface! skin, gills, lungs Circulatory System O2/CO2
Chapter 16 Respiratory System
 Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System
 Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System Animals require a continuous supply of oxygen (O 2 ) for cellular respiration, and they must expel carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), the waste product of this
Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System Animals require a continuous supply of oxygen (O 2 ) for cellular respiration, and they must expel carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), the waste product of this
The equation describes anaerobic respiration in muscle cells. How can you tell from the equation that this process is anaerobic?
 Respiration. Name.. Q.Anaerobic respiration happens in muscle cells and yeast cells. The equation describes anaerobic respiration in muscle cells. glucose lactic acid (a) How can you tell from the equation
Respiration. Name.. Q.Anaerobic respiration happens in muscle cells and yeast cells. The equation describes anaerobic respiration in muscle cells. glucose lactic acid (a) How can you tell from the equation
UNIFYING CONCEPTS OF ANIMAL CIRCULATION
 UNIFYING CONCEPTS OF ANIMAL CIRCULATION Every organism must exchange materials with its environment, relying upon diffusion, the spontaneous movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to
UNIFYING CONCEPTS OF ANIMAL CIRCULATION Every organism must exchange materials with its environment, relying upon diffusion, the spontaneous movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to
3.6. The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Whether you are aware of it or not, you breathe in and out 15 times each minute on average. This rate increases automatically if your physical activity increases. With normal breathing,
The Respiratory System Whether you are aware of it or not, you breathe in and out 15 times each minute on average. This rate increases automatically if your physical activity increases. With normal breathing,
Chapter 22 Gas Exchange
 Chapter 22 Gas Exchange PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction: Surviving in Thin Air
Chapter 22 Gas Exchange PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction: Surviving in Thin Air
Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems
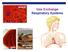 alveoli gills Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? respiration for respiration Need O 2 in for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need CO 2
alveoli gills Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? respiration for respiration Need O 2 in for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need CO 2
Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system
 Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system 1. Name the following : i. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. ii. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous rings.
Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system 1. Name the following : i. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. ii. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous rings.
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
Standard: Knows the general structure and functions of cells in organisms
 DESCRIPTION During an average lifetime, enough air passes through our lungs to fill a football stadium. Examines the complex process of respiration, beginning with the air's entrance into the nose. Explores
DESCRIPTION During an average lifetime, enough air passes through our lungs to fill a football stadium. Examines the complex process of respiration, beginning with the air's entrance into the nose. Explores
Gaseous exchange. Grade 11
 z Gaseous exchange Grade 11 z Terminology 1. Breathing 2. Gaseous exchange 3. Diffusion 4. Spongy mesophyll cells 5. Tracheae 6. Gills 7. Alveoli 8. Larynx 9. Diaphragm 10. Endothelium 1. Pleura 2. Squamous
z Gaseous exchange Grade 11 z Terminology 1. Breathing 2. Gaseous exchange 3. Diffusion 4. Spongy mesophyll cells 5. Tracheae 6. Gills 7. Alveoli 8. Larynx 9. Diaphragm 10. Endothelium 1. Pleura 2. Squamous
Q1. Which activity is most likely to use aerobic respiration for energy?
 Q1. Which activity is most likely to use aerobic respiration for energy? 10 km cross country run Vault in gymnastics Shot put Jumping to block a shot in basketball (Total 1 mark) Q. All of the following
Q1. Which activity is most likely to use aerobic respiration for energy? 10 km cross country run Vault in gymnastics Shot put Jumping to block a shot in basketball (Total 1 mark) Q. All of the following
system. and then into the tissues. Diffusion of wastes such as Carbon Dioxide from tissues into blood and out of blood into the lungs.
 Respiratory System 1.Exchange Why do of we gases breathe? into the Think blood of all and the tissues. reasons Diffusion why we of Oxygen need a respiratory into blood from the lungs system. and then into
Respiratory System 1.Exchange Why do of we gases breathe? into the Think blood of all and the tissues. reasons Diffusion why we of Oxygen need a respiratory into blood from the lungs system. and then into
Clinical Respiratory System Quiz
 Quiz Description Clinical Respiratory System Quiz Q.1) Q.2) Q.3) Q.4) Q.5) Q.6) What is NOT true about Asthma? It can be triggered by air temperature and allergens. It is the inflammation of the throat.
Quiz Description Clinical Respiratory System Quiz Q.1) Q.2) Q.3) Q.4) Q.5) Q.6) What is NOT true about Asthma? It can be triggered by air temperature and allergens. It is the inflammation of the throat.
Explain how the structure of the gas exchange system of an insect ensures that there is a large surface area for gas exchange.
 1 Gas exchange takes place by diffusion. surfacearea differenceinconcentration diffusion lengthof diffusionpath a The diagram shows part of an insect tracheal system. i Explain how the structure of the
1 Gas exchange takes place by diffusion. surfacearea differenceinconcentration diffusion lengthof diffusionpath a The diagram shows part of an insect tracheal system. i Explain how the structure of the
Outline - Respiratory System. Function of the respiratory system Parts of the respiratory system Mechanics of breathing Regulation of breathing
 Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
The physiological functions of respiration and circulation. Mechanics. exercise 7. Respiratory Volumes. Objectives
 exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
AP Biology. Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems. Gas exchange. Why do we need a respiratory system? Optimizing gas exchange. Gas exchange in many forms
 alveoli Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems gills elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? Need O 2 in food respiration for respiration for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need
alveoli Gas Exchange Respiratory Systems gills elephant seals 2008-2009 Why do we need a respiratory system? Need O 2 in food respiration for respiration for aerobic cellular respiration make ATP Need
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange elephant seals gills AP Biology
 alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange O 2 & CO 2 exchange exchange between environment & cells provides O 2 for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange O 2 & CO 2 exchange exchange between environment & cells provides O 2 for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high
PMT. Smaller species of annelid do not have gills. Explain why these small worms do not need gills to obtain sufficient oxygen
 1. There are many different species of annelid worm. Some are very small, only a few millimetres in length. Others, such as lugworms, are much larger. The drawing shows a lugworm and part of one of its
1. There are many different species of annelid worm. Some are very small, only a few millimetres in length. Others, such as lugworms, are much larger. The drawing shows a lugworm and part of one of its
Lab: The Effect of Exercise on Cellular Respiration
 Lab: The Effect of Exercise on Cellular Respiration Purpose: To analyze the effect the exercise has on breathing rate, heart rate, and carbon dioxide production Background Information: Cellular respiration
Lab: The Effect of Exercise on Cellular Respiration Purpose: To analyze the effect the exercise has on breathing rate, heart rate, and carbon dioxide production Background Information: Cellular respiration
A.M. WEDNESDAY, 7 January hour
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4471/02 W15-4471-02 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE/BIOLOGY BIOLOGY 2 HIGHER TIER A.M. WEDNESDAY, 7 January 2015 1 hour For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4471/02 W15-4471-02 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE/BIOLOGY BIOLOGY 2 HIGHER TIER A.M. WEDNESDAY, 7 January 2015 1 hour For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark
ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE G622 APPLIED SCIENCE
 ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE APPLIED SCIENCE Unit 3: Monitoring the activity of the human body TUESDAY 5 JUNE 2007 G622 Afternoon *CUP/T21601* Additional materials: Electronic calculator Ruler (cm/mm) Time:
ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE APPLIED SCIENCE Unit 3: Monitoring the activity of the human body TUESDAY 5 JUNE 2007 G622 Afternoon *CUP/T21601* Additional materials: Electronic calculator Ruler (cm/mm) Time:
Then the partial pressure of oxygen is x 760 = 160 mm Hg
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: the uptake of molecular oxygen (O2) from the environment and the discharge of
1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: the uptake of molecular oxygen (O2) from the environment and the discharge of
Then the partial pressure of oxygen is. b) Gases will diffuse down a pressure gradient across a respiratory surface if it is: i) permeable ii) moist
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: Relies on the diffusion of gases down pressure gradients. At sea level, atmosphere
1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: Relies on the diffusion of gases down pressure gradients. At sea level, atmosphere
The Respiratory System
 Science Unit: Lesson 4: Human Anatomy How Do We Move? The Respiratory System School year: 2007/2008 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Henderson Annex Elementary School, Vancouver
Science Unit: Lesson 4: Human Anatomy How Do We Move? The Respiratory System School year: 2007/2008 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Henderson Annex Elementary School, Vancouver
Respiratory System Review
 KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
AP Biology. Chapter 42. Gas Exchange. Optimizing gas exchange. Gas exchange. Gas exchange in many forms. Evolution of gas exchange structures
 alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange & C exchange exchange between environment & cells provides for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high surface area
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange & C exchange exchange between environment & cells provides for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high surface area
year 6 REVISION End of Year
 year 6 REVISION End of Year The Science Department This Revision Guide can be utilised at home or on your ipad. This electronic book has been made as an additional aid in the revision process. The material
year 6 REVISION End of Year The Science Department This Revision Guide can be utilised at home or on your ipad. This electronic book has been made as an additional aid in the revision process. The material
BIOLOGY INTERACTIVE ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS BASED ON STANDARD PRACTICAL EXERCISES... Biology Part 1 LEARNING VERSION
 INTERACTIVE ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS BASED ON STANDARD PRACTICAL EXERCISES... Biology Part 1 IN THIS ANSWERS ARE IMMEDIATELY AND VISIBLY MARKED, CORRECT ANSWERS ARE INDICATED ON REQUEST, AND END OF SECTION
INTERACTIVE ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS BASED ON STANDARD PRACTICAL EXERCISES... Biology Part 1 IN THIS ANSWERS ARE IMMEDIATELY AND VISIBLY MARKED, CORRECT ANSWERS ARE INDICATED ON REQUEST, AND END OF SECTION
3.3.2 Gas Exchange SPECIFICATION
 alevelbiology.co.uk 3.3.2 Gas Exchange SPECIFICATION Adaptations of gas exchange surfaces, shown by gas exchange: Across the body surface of a single-celled organism In the tracheal system of an insect
alevelbiology.co.uk 3.3.2 Gas Exchange SPECIFICATION Adaptations of gas exchange surfaces, shown by gas exchange: Across the body surface of a single-celled organism In the tracheal system of an insect
Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange
 Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange Session Objectives. What you will cover Basic anatomy of the lung including airways Breathing movements Lung volumes and capacities Compliance and Resistance in
Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange Session Objectives. What you will cover Basic anatomy of the lung including airways Breathing movements Lung volumes and capacities Compliance and Resistance in
