BIOLOGY INTERACTIVE ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS BASED ON STANDARD PRACTICAL EXERCISES... Biology Part 1 LEARNING VERSION
|
|
|
- Donna Houston
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 INTERACTIVE ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS BASED ON STANDARD PRACTICAL EXERCISES... Biology Part 1 IN THIS ANSWERS ARE IMMEDIATELY AND VISIBLY MARKED, CORRECT ANSWERS ARE INDICATED ON REQUEST, AND END OF SECTION TOTALS AND PERCENTAGES SHOWN ON SCREEN. SOME OF THE MORE DIFFICULT QUESTIONS HAVE DROP DOWN HELP BOXES WHICH REVEAL INFORMATION WHEN THE CURSOR IS PASSED OVER THE QUESTION MARK. WHEN PRINTED OUT ONLY THE QUESTIONS SHOW, THEREFORE THIS CAN BE USED AS A PAPER VERSION FOR TESTS IF REQUIRED. The questions are of the Multiple Choice style, where the phrase Which ONE of the following... is implied, but is not always stated. So that students are reminded of the type of question that requires short written answers, which unfortunately cannot be automatically marked, each topic has one short passage with missing words, which must be identified in their correct sequence. NB The practical work presented should be familiar to students, either as demonstrations demonstration, or as an experiment they might have carried out themselves in the lab. The material is NOT presented as a practical guide, and while the methods followed safety guidelines, specific safety issues are NOT dealt with. Visit
2 Biology Part 1 2 of 12 CONTENTS The following practical topics have been selected according to exam question frequency to form the basis of revision and examination practice. FOR THE CORRECT FINAL TOTAL AND PERCENTAGE THE ENTER BUTTON AT THE BOTTOM LEFT OF EACH PAGE MUST BE CLICKED ON. Part 1 Diffusion and Osmosis Heart, Lungs & Smoking Part 2 Enzyme Reactions Respiration Fermentation Part 3 Leaf Structure and Function Photosynthesis Tropisms
3 Biology Part 1 Diffusion and Osmosis 3 of 12 Diffusion is very important in the transport of substances within and between the cells of organisms, and between organisms and their surroundings. Osmosis is a term used when discussing the special case of the diffusion of water. Practical - Thirteen small pieces of red litmus paper were carefully positioned at equal intervals along the length of a long glass tube with a rubber bung at one end. Cotton wool dipped in ammonia solution was introduced at the open end of the tube and sealed in with a rubber bung. The time it took for each piece of litmus paper to turn completely blue was recorded. Ammonia cotton wool plug Ammonia cotton wool plug Time in secs and mins for gas to reach pieces of red litmus paper Piece no. from left Time taken for each 4s 15s 55s 1m54s 3m38s 7m12s 12m14s piece to turn blue 1. Referring to the photographs of the diffusion tube, and the data obtained from it during the experiment set out in the table, which one of the following best matches your observations? A - The rate of diffusion of ammonia gas down the tube proceeds at a constant rate away from the cotton wool plug soaked in ammonia. B - The rate of diffusion of ammonia gas down the tube slows as the distance from the cotton wool plug increases. C - The rate of diffusion of ammonia gas down the tube increases as the distance away from the cotton wool plug increases. D - The rate of diffusion of ammonia gas is fastest in the middle of the tube as the particles have got up speed.
4 Biology Part 1 Diffusion and Osmosis 4 of Which one of the following correctly describes the direction of diffusion of particles? A - From regions of their higher concentration to regions of their lower concentratin. B - From regions of their lower concentration to regions of their higher concentration. C - From regions of higher temperature to regions of lower temperature. D - From regions of their lower pressure to regions of their higher pressure. HELP BOX PASS CURSOR OVER QUESTION MARK FOR HELP WITH QUESTION NUMBER 3? Only very small particles, much too small to be seen even under a microscope, move by diffusion. Coloured substances can be seen diffusing, but not the particles themselves. 3. Which one of the following occurs by diffusion in mammals? A - Movement of bile from the liver down the bile duct into the gut. B - Movement of food through the digestive tract. C - Movement of blood through the capillaries. D - Movement of oxygen from the blood to the tissues 4. Which one of the following occurs by diffusion in green plants? A - Movement of water into the leaves on a rainy day. B - Movement of sugars from the leaves to the roots. C - Movement of water from the roots to the leaves. D - Movement of oxygen from the soil into the roots.
5 Biology Part 1 Diffusion and Osmosis 5 of 12 Practical - Cylinders of tissue were cut from a potato with a cork borer and trimmed to exactly the same size. One cylinder was placed in each of 4 tubes containing one of the following sucrose solutions, 1 Molar (1 M), 0.75 M, 0.5 M, 0.25 M; and one in deionised water. 5. Which one of the following best explains why the cylinders of potato tissue in tubes A and B are floating? A - Osmosis has occurred in tubes A and B. B - The cylinders in tubes A and B are denser than the sucrose solutions. C - Tubes A and B contain the more concentrated (and dense) sucrose solutions. D - The cells in these potato cylinders are dead. 6. In which of the solutions in the pairs of tubes listed below will the cylinders of potato tissue increase in length and mass? A - Tubes A and B B - Tubes A and C C - Tubes B and D D - Tubes D and E 7. In which of the following pairs of tubes listed below will water move from the potato tissue into the surrounding fluid? A - Tubes A and B B - Tubes B and C C - Tubes C and D D - Tubes D and E
6 Biology Part 1 6 of 12 Diffusion and Osmosis HELP BOX PASS CURSOR OVER QUESTION MARK FOR HELP WITH QUESTION NUMBER 8? Capillary action is involved in the movement of fluids up inside narrow (capillary) tubing, but in this experiment it is not significant when compared to the other force involved. Practical - Some 1 M sucrose solution was coloured orange/red, and some deionised water was coloured blue. One beaker and a sealed length of visking tubing (a partially permeable membrane) were then filled with the orange/red 1M sucrose solution, and the other beaker and tubing filled with the blue deionised water. They were arranged as shown in Photo I, and then the two filled lengths of visking tubing were lowered into the liquids in the beakers and left for several minutes. PAGES 6-11 BLOCKED, GO TO PAGE 12 PHOTO 1 PHOTO 2 8. Which of the following best explains why the level of fluid has risen up inside the tube shown magnified on the left of Photo 2. A - Gravity has stopped the fluid rising up the same amount in the tube on the right. B - Water has left the solution inside the visking tubing by osmosis into the deionised water in the beaker. C - Capillary action results in the fluid moving up in the tube. D - Water has entered the visking tubing by osmosis from the beaker into the sucrose solution inside the tubing. 9. Why has the visking tubing on the right of Photo 2 become more flaccid (soft) than that on the left. A - Water has moved by osmosis from inside the visking tubing. B - Water has entered the solution inside the visking tubing by osmosis from the deionised water surrounding the tubing. C - Sucrose from the sucrose solution in the beaker has moved by diffusion into the the visking tubing. D - Gravity has caused the solution to seep out of the visking tubing on the right.
7 Biology Part 1 Diffusion and Osmosis 7 of 12 HELP BOX PASS CURSOR OVER QUESTION MARK FOR HELP WITH QUESTION NUMBER 10? Osmosis is the special case of the diffusion of water. In which water molecules diffuse from a high water concentration (pure water or a more dilute solution) to a lower water concentration (more concentrated solution) through a partially permeable membrane. 10. The following passage has four missing words. If you drink tap water, the contents of your stomach are and water passes by osmosis from the into the blood. If you swallow sea water the contents of your stomach are and water passes by osmosis from the into the stomach. PAGES 6-11 BLOCKED, GO TO PAGE 12 Which of the following has the correct missing words in the sequence as they should appear in the passage. A - concentrated - stomach - diluted - blood B - diluted - kidneys - concentrated - blood C - diluted - stomach - concentrated - kidneys D - diluted - stomach - concentrated - blood
8 Biology Part 1 The Heart, Lungs and Smoking 8 of 12 HELP BOX PASS CURSOR OVER QUESTION MARK FOR HELP WITH QUESTION NUMBER 11? Practical - The heart and lungs in humans are contained in the chest or thoracic cavity. The two lungs surround the heart, as shown in Photo 1 of a model thorax. The heart is a four chambered muscular pump, which by contracting and relaxing, pumps blood around the lungs, and the body. Photo 2 shows a model of a partially dissected heart showing some of the chambers in section, the valves and the major blood vessels entering and leaving the heart. Anatomical diagrams are labelled right and left as if you were looking at somebody in front of you, ie their right is on your left, and their left is on your right. 1 2 PAGES 6-11 BLOCKED, GO TO PAGE 12 PHOTO 1 PHOTO The large blood vessel shown blue and labelled 1 in Photo 1 carries blood into which chamber of the heart? A - Right Ventricle B - Left atrium C - Right atrium D - Left ventricle 12. Which chamber of the heart pumps blood into the large blood vessel shown red and labelled 2 in Photo 2? A - Right ventricle B - Left Ventricle C - Right atrium D - Left atrium
9 Biology Part 1 The Heart, Lungs and Smoking 9 of 12 HELP BOX PASS CURSOR OVER QUESTION MARK FOR HELP WITH QUESTION NUMBER 13? Blood passes through the heart twice on each complete circulation of the body. After entering the heart it goes to the lungs to get rid of carbon dioxide and pick up oxygen. From the lungs blood then returns to the heart and is pumped around the body. 13. The following passage has four missing words. The heart pumps the blood around the body. In its passage through the heart, the blood from the main veins of the body enters the atrium, from here it passes to the right ventricle, from where it is pumped to the. It returns to the atrium, passes to the left ventricle, and is then pumped around the. PAGES 6-11 BLOCKED, GO TO PAGE 12 Which of the following has the correct missing words in the sequence as they should appear in the passage. A - left - lungs - right - body. B - right - body - left - lungs. C - right - lungs - left - body. D - left - body - right - lungs.
10 Biology Part 1 The Heart, Lungs and Smoking 10 of 12 Practical - The lungs consist of millions of small air sacs or alveoli which give the lungs a huge surface area over which gas exchange occurs between the bloodstream and the air in the air sacs. The lungs are well supplied with blood vessels to carry oxygen away from and carbon dioxide to, the air sacs. In the photograph shown below the right lung of the model is shown in section, and the air tubes appear as circles as if cut across. 14. What is the name of the smaller tubes carrying air deep into each lung? A - Trachea. B - Bronchioles. C - Capillaries. D - Pulmonary tubes. PAGES 6-11 BLOCKED, GO TO PAGE What is the name of the large blood vessels shown blue that can be seen running through the left lung in the Photo? A - Pulmonary arteries. B - Pulmonary veins. C - Capillaries. D - Arterioles. 16. Which one of the following is a correct description of the movement of the ribs when breathing in? A - They move downwards and inwards decreasing the volume of the chest cavity. B - They move inwards keeping the volume of the chest cavity the same. C - They move sideways keeping the volume of the chest cavity the same. D - They move upwards and outwards increasing the volume of the chest cavity.
11 Biology Part 1 The Heart, Lungs and Smoking 11 of 12 Practical - The following photos are of water and cotton wool taken from a smoking machine in which smoke from a lit cigarette was drawn through them to trap some of the components of cigarette smoke. 17. In which part of the lungs are these components of cigarette smoke most likely to accumulate? A - air sacs (alveoli) B - trachea C - bronchi D - bronchioles PAGES 6-11 BLOCKED, GO TO PAGE Which of the following components of cigarette smoke causes the addiction to smoking. A - smoke B - nicotine C - tars D - cancer causing chemicals 19. Which of the following diseases does NOT have smoking as a possible cause? A - bronchitis B - cancer C - influenza D - heart disease
12 Biology Part 1 Diffusion and Osmosis The Heart, Lungs and Smoking 12 of 12 SECTION TOTAL SECTION PERCENTAGE on T
13 INTERACTIVE ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS BASED ON STANDARD PRACTICAL EXERCISES... Biology Part 1 PRACTICE TEST VERSION IN THIS PRACTICE TEST VERSION NO MARKING OR ANSWERS ARE VISIBLE ON SCREEN, BUT TOTALS AND PERCENTAGES ARE SHOWN. NO HELP BOXES ARE AVAILABLE. ON THE PRINT-OUT THE STUDENT'S RESPONSES, MARKS, TOTALS AND PERCENTAGES ARE ALL VISIBLE, BUT CORRECT ANSWERS ARE NOT SHOWN. The questions are of the Multiple Choice style, where the phrase Which ONE of the following... is implied, but is not always stated. So that students are reminded of the type of question that requires short written answers, which unfortunately cannot be automatically marked, each topic has at least one short passage with missing words, which must be identified in their correct sequence. NB The practical work presented should be familiar to students, either as demonstrations or as procedures they might have carried out themselves in the lab. The material is NOT presented as a practical guide, and while the methods followed safety guidelines, specific safety issues are NOT dealt with. Visit
14 PRACTICE TEST VERSION Biology Part 1 2 of 12 CONTENTS The following practical topics have been selected according to exam question frequency to form the basis of revision and examination practice. FOR THE CORRECT FINAL TOTAL AND PERCENTAGE THE ENTER BUTTON AT THE BOTTOM LEFT OF EACH PAGE MUST BE CLICKED ON. Part 1 Diffusion and Osmosis Heart, Lungs & Smoking Part 2 Enzyme Reactions Respiration Fermentation Part 3 Leaf Structure and Function Photosynthesis Tropisms
15 Biology Part 1 Diffusion and Osmosis PRACTICE TEST VERSION 3 of 12 Diffusion is very important in the transport of substances within and between the cells of organisms, and between organisms and their surroundings. Osmosis is a term used when discussing the special case of the diffusion of water. Practical - Thirteen small pieces of red litmus paper were carefully positioned at equal intervals along the length of a long glass tube with a rubber bung at one end. Cotton wool dipped in ammonia solution was introduced at the open end of the tube and sealed in with a rubber bung. The time it took for each piece of litmus paper to turn completely blue was recorded. Ammonia cotton wool plug Ammonia cotton wool plug Time in secs and mins for gas to reach pieces of red litmus paper Piece no. from left Time taken for each 4s 15s 55s 1m54s 3m38s 7m12s 12m14s piece to turn blue 1. Referring to the photographs of the diffusion tube, and the data obtained from it during the experiment set out in the table, which one of the following best matches your observations? A - The rate of diffusion of ammonia gas down the tube proceeds at a constant rate away from the cotton wool plug soaked in ammonia. B - The rate of diffusion of ammonia gas down the tube slows as the distance from the cotton wool plug increases. C - The rate of diffusion of ammonia gas down the tube increases as the distance away from the cotton wool plug increases. D - The rate of diffusion of ammonia gas is fastest in the middle of the tube as the particles have got up speed.
16 Biology Part 1 Diffusion and Osmosis PRACTICE TEST VERSION 4 of Which one of the following correctly describes the direction of diffusion of particles? A - From regions of their higher concentration to regions of their lower concentratin. B - From regions of their lower concentration to regions of their higher concentration. C - From regions of higher temperature to regions of lower temperature. D - From regions of their lower pressure to regions of their higher pressure. HELP BOX PASS CURSOR OVER QUESTION MARK FOR HELP WITH QUESTION NUMBER 3? Only very small particles, much too small to be seen even under a microscope, move by diffusion. Coloured substances can be seen diffusing, but not the particles themselves. 3. Which one of the following occurs by diffusion in mammals? A - Movement of bile from the liver down the bile duct into the gut. B - Movement of food through the digestive tract. C - Movement of blood through the capillaries. D - Movement of oxygen from the blood to the tissues 4. Which one of the following occurs by diffusion in green plants? A - Movement of water into the leaves on a rainy day. B - Movement of sugars from the leaves to the roots. C - Movement of water from the roots to the leaves. D - Movement of oxygen from the soil into the roots.
17 Biology Part 1 Diffusion and Osmosis PRACTICE TEST VERSION 5 of 12 Practical - Cylinders of tissue were cut from a potato with a cork borer and trimmed to exactly the same size. One cylinder was placed in each of 4 tubes containing one of the following sucrose solutions, 1 Molar (1 M), 0.75 M, 0.5 M, 0.25 M; and one in deionised water. 5. Which one of the following best explains why the cylinders of potato tissue in tubes A and B are floating? A - Osmosis has occurred in tubes A and B. B - The cylinders in tubes A and B are denser than the sucrose solutions. C - Tubes A and B contain the more concentrated (and dense) solutions in the tubes. D - The cells in these potato cylinders are dead. 6. In which of the solutions in the pairs of tubes listed below will the cylinders of potato tissue increase in length and mass? A - Tubes A and B B - Tubes A and C C - Tubes B and D D - Tubes D and E 7. In which of the following pairs of tubes listed below will water move from the potato tissue into the surrounding fluid? A - Tubes A and B B - Tubes B and C C - Tubes C and D D - Tubes D and E
18 Biology Part 1 PRACTICE TEST VERSION 6 of 12 Diffusion and Osmosis HELP BOX PASS CURSOR OVER QUESTION MARK FOR HELP WITH QUESTION NUMBER 8? Capillary action is involved in the movement of fluids up inside narrow (capillary) tubing, but in this experiment it is not significant when compared to the other force involved. Practical - Some 1 M sucrose solution was coloured orange/red, and some deionised water was coloured blue. One beaker and a sealed length of visking tubing (a partially permeable membrane) were then filled with the orange/red 1M sucrose solution, and the other beaker and tubing filled with the blue deionised water. They were arranged as shown in Photo I, and then the two filled lengths of visking tubing were lowered into the liquids in the beakers and left for several minutes. PAGES 6-11 BLOCKED, GO TO PAGE 12 PHOTO 1 PHOTO 2 8. Which of the following best explains why the level of fluid has risen up inside the tube shown magnified on the left of Photo 2. A - Gravity has stopped the fluid rising up the same amount in the tube on the right. B - Water has left the solution inside the visking tubing by osmosis into the deionised water in the beaker. C - Capillary action results in the fluid moving up in the tube. D - Water has entered the visking tubing by osmosis from the beaker into the sucrose solution inside the tubing. 9. Why has the visking tubing on the right of Photo 2 become more flaccid (soft) than that on the left. A - Water has moved by osmosis from inside the visking tubing. B - Water has entered the solution inside the visking tubing by osmosis from the deionised water surrounding the tubing. C - Sucrose from the sucrose solution in the beaker has moved by diffusion into the the visking tubing. D - Gravity has caused the solution to seep out of the visking tubing on the right.
19 Biology Part 1 Diffusion and Osmosis PRACTICE TEST VERSION 7 of 12 HELP BOX PASS CURSOR OVER QUESTION MARK FOR HELP WITH QUESTION NUMBER 10? Osmosis is the special case of the diffusion of water. In which water molecules diffuse from a high water concentration (pure water or a more dilute solution) to a lower water concentration (more concentrated solution) through a partially permeable membrane. 10. The following passage has four missing words. If you drink tap water, the contents of your stomach are and water passes by osmosis from the into the blood. If you swallow sea water the contents of your stomach are and water passes by osmosis from the into the stomach. PAGES 6-11 BLOCKED, GO TO PAGE 12 Which of the following has the correct missing words in the sequence as they should appear in the passage. A - concentrated - stomach - diluted - blood B - diluted - kidneys - concentrated - blood C - diluted - stomach - concentrated - kidneys D - diluted - stomach - concentrated - blood
20 Biology Part 1 The Heart, Lungs and Smoking PRACTICE TEST VERSION 8 of 12 HELP BOX PASS CURSOR OVER QUESTION MARK FOR HELP WITH QUESTION NUMBER 11? Practical - The heart and lungs in humans are contained in the chest or thoracic cavity. The two lungs surround the heart, as shown in Photo 1 of a model. The heart is a four chambered muscular pump, which by contracting and relaxing, pumps blood around the lungs, and the body. Photo 2 shows a model of a partially dissected heart showing some of the chambers in section, the valves and the major blood vessels entering and leaving the heart. Anatomical diagrams are labelled right and left as if you were looking at somebody in front of you, ie their right is on your left, and their left is on your right. 1 2 PAGES 6-11 BLOCKED, GO TO PAGE 12 PHOTO 1 PHOTO The large blood vessel shown blue and labelled 1 in Photo 1 carries blood into which chamber of the heart? A - Right Ventricle B - Left atrium C - Right atrium D - Left ventricle 12. Which chamber of the heart pumps blood into the large blood vessel shown red and labelled 2 in Photo 2? A - Right ventricle B - Left Ventricle C - Right atrium D - Left atrium
21 Biology Part 1 The Heart, Lungs and Smoking PRACTICE TEST VERSION 9 of 12 HELP BOX PASS CURSOR OVER QUESTION MARK FOR HELP WITH QUESTION NUMBER 13? Blood passes through the heart twice on each complete circulation of the body. After entering the heart it goes to the lungs to get rid of carbon dioxide and pick up oxygen. From the lungs blood then returns to the heart and is pumped around the body. 13. The following passage has four missing words. The heart pumps the blood around the body. In its passage through the heart, the blood from the main veins of the body enters the atrium, from here it passes to the right ventricle, from where it is pumped to the. It returns to the atrium, passes to the left ventricle, and is then pumped around the. PAGES 6-11 BLOCKED, GO TO PAGE 12 Which of the following has the correct missing words in the sequence as they should appear in the passage. A - left - lungs - right - body. B - right - body - left - lungs. C - right - lungs - left - body. D - left - body - right - lungs.
22 Biology Part 1 The Heart, Lungs and Smoking PRACTICE TEST VERSION 10 of 12 Practical - The lungs consist of millions of small air sacs or alveoli which give the lungs a huge surface area over which gas exchange occurs between the bloodstream and the air in the air sacs. The lungs are well supplied with blood vessels to carry oxygen from and carbon dioxide to, the air sacs. In the photograph shown below the right lung of the model is shown in section, and the air tubes appear as circles as if cut across. 14. What is the name of the smaller tubes carrying air deep into each lung? A - Trachea. B - Bronchioles. C - Capillaries. D - Pulmonary tubes. PAGES 6-11 BLOCKED, GO TO PAGE What is the name of the large blood vessels shown blue that can be seen running through the left lung in the Photo? A - Pulmonary arteries. B - Pulmonary veins. C - Capillaries. D - Arterioles. 16. Which one of the following is a correct description of the movement of the ribs when breathing in? A - They move downwards and inwards decreasing the volume of the chest cavity. B - They move inwards keeping the volume of the chest cavity the same. C - They move sideways keeping the volume of the chest cavity the same. D - They move upwards and outwards increasing the volume of the chest cavity.
23 Biology Part 1 The Heart, Lungs and Smoking PRACTICE TEST VERSION 11 of 12 Practical - The following photos are of water and cotton wool taken from a smoking machine in which smoke from a lit cigarette was drawn through them to trap some of the components of cigarette smoke. 17. In which part of the lungs are these components of cigarette smoke most likely to accumulate? A - air sacs (alveoli) B - trachea C - bronchi D - bronchioles PAGES 6-11 BLOCKED, GO TO PAGE Which of the following components of cigarette smoke causes the addiction to smoking. A - smoke B - nicotine C - tars D - cancer causing chemicals 19. Which of the following diseases does NOT have smoking as a possible cause? A - bronchitis B - cancer C - influenza D - heart disease
24 Biology Part 1 Diffusion and Osmosis The Heart, Lungs and Smoking PRACTICE TEST VERSION 12 of 12 SECTION TOTAL 0/19 SECTION PERCENTAGE 0% on T
25 INTERACTIVE ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS BASED ON STANDARD PRACTICAL EXERCISES FOR REVISION AND EXAMINATION PRACTICE Biology Part 1 TEST VERSION IN THIS TEST VERSION NO MARKING, ANSWERS OR TOTALS ARE VISIBLE ON SCREEN. ON THE PRINT-OUT STUDENT'S RESPONSES, TOTALS AND PERCENTAGES ARE VISIBLE BUT NO CORRECT ANSWERS ARE INDICATED. NO HELP BOXES ARE PROVIDED. THE ANSWER SEQUENCE IN THIS TEST VERSION IS ONLY AVAILABLE BY WORKING OUT THE CORRECT ANSWER THROUGH UNDERSTANDING. The questions are of the Multiple Choice style, where the phrase Which ONE of the following... is implied, but is not always stated. So that students are reminded of the type of question that requires short written answers, which unfortunately cannot be automatically marked, each topic has at least one short passage with missing words, which must be identified in their correct sequence. NB The practical work presented should be familiar to students, either as demonstrations or as procedures they might have carried out themselves in the lab. The material is NOT presented as a practical guide, and while the methods followed safety guidelines, specific safety issues are NOT dealt with. Visit
26 TEST VERSION Biology Part 1 2 of 12 CONTENTS The following practical topics have been selected according to exam question frequency to form the basis of revision and examination practice. FOR THE CORRECT FINAL TOTAL AND PERCENTAGE THE ENTER BUTTON AT THE BOTTOM LEFT OF EACH PAGE MUST BE CLICKED ON. Part 1 Diffusion and Osmosis Heart, Lungs & Smoking Part 2 Enzyme Reactions Respiration Fermentation Part 3 Leaf Structure and Function Photosynthesis Tropisms
27 Biology Part 1 Diffusion and Osmosis TEST VERSION 3 of 12 Diffusion is very important in the transport of substances within and between the cells of organisms, and between organisms and their surroundings. Osmosis is a term used when discussing the special case of the diffusion of water. Practical - Thirteen small pieces of red litmus paper were carefully positioned at equal intervals along the length of a long glass tube with a rubber bung at one end. Cotton wool dipped in ammonia solution was introduced at the open end of the tube and sealed in with a rubber bung. The time it took for each piece of litmus paper to turn completely blue was recorded. Ammonia cotton wool plug Ammonia cotton wool plug Time in secs and mins for gas to reach pieces of red litmus paper Piece no. from left Time taken for each 4s 15s 55s 1m54s 3m38s 7m12s 12m14s piece to turn blue 1. Referring to the photographs of the diffusion tube, and the data obtained from it during the experiment set out in the table, which one of the following best matches your observations? A - The rate of diffusion of ammonia gas down the tube proceeds at a constant rate away from the cotton wool plug soaked in ammonia. B - The rate of diffusion of ammonia gas down the tube slows as the distance from the cotton wool plug increases. C - The rate of diffusion of ammonia gas down the tube increases as the distance away from the cotton wool plug increases. D - The rate of diffusion of ammonia gas is fastest in the middle of the tube as the particles have got up speed.
28 Biology Part 1 Diffusion and Osmosis TEST VERSION 4 of Which one of the following correctly describes the direction of diffusion of particles? A - From regions of their higher concentration to regions of their lower concentratin. B - From regions of their lower concentration to regions of their higher concentration. C - From regions of higher temperature to regions of lower temperature. D - From regions of their lower pressure to regions of their higher pressure. HELP BOX PASS CURSOR OVER QUESTION MARK FOR HELP WITH QUESTION NUMBER 3? Only very small particles, much too small to be seen even under a microscope, move by diffusion. Coloured substances can be seen diffusing, but not the particles themselves. 3. Which one of the following occurs by diffusion in mammals? A - Movement of bile from the liver down the bile duct into the gut. B - Movement of food through the digestive tract. C - Movement of blood through the capillaries. D - Movement of oxygen from the blood to the tissues 4. Which one of the following occurs by diffusion in green plants? A - Movement of water into the leaves on a rainy day. B - Movement of sugars from the leaves to the roots. C - Movement of water from the roots to the leaves. D - Movement of oxygen from the soil into the roots.
29 Biology Part 1 Diffusion and Osmosis TEST VERSION 5 of 12 Practical - Cylinders of tissue were cut from a potato with a cork borer and trimmed to exactly the same size. One cylinder was placed in each of 4 tubes containing one of the following sucrose solutions, 1 Molar (1 M), 0.75 M, 0.5 M, 0.25 M; and one in deionised water. 5. Which one of the following best explains why the cylinders of potato tissue in tubes A and B are floating? A - Osmosis has occurred in tubes A and B. B - The cylinders in tubes A and B are denser than the sucrose solutions. C - Tubes A and B contain the more concentrated (and dense) sucrose solutions in the tubes. D - The cells in these potato cylinders are dead. 6. In which of the solutions in the pairs of tubes listed below will the cylinders of potato tissue increase in length and mass? A - Tubes D and E B - Tubes A and C C - Tubes B and D D - Tubes A and B 7. In which of the following pairs of tubes listed below will water move from the potato tissue into the surrounding fluid? A - Tubes D and E B - Tubes B and C C - Tubes C and D D - Tubes A and B
30 Biology Part 1 TEST VERSION 6 of 12 Diffusion and Osmosis HELP BOX PASS CURSOR OVER QUESTION MARK FOR HELP WITH QUESTION NUMBER 8? Capillary action is involved in the movement of fluids up inside narrow (capillary) tubing, but in this experiment it is not significant when compared to the other force involved. Practical - Some 1 M sucrose solution was coloured orange/red, and some deionised water was coloured blue. One beaker and a sealed length of visking tubing (a partially permeable membrane) were then filled with the orange/red 1M sucrose solution, and the other beaker and tubing filled with the blue deionised water. They were arranged as shown in Photo I, and then the two filled lengths of visking tubing were lowered into the liquids in the beakers and left for several minutes. PAGES 6-11 BLOCKED, GO TO PAGE 12 PHOTO 1 PHOTO 2 8. Which of the following best explains why the level of fluid has risen up inside the tube shown magnified on the left of Photo 2. A - Gravity has stopped the fluid rising up the same amount in the tube on the right. B - Water has left the solution inside the visking tubing by osmosis into the deionised water in the beaker. C - Capillary action results in the fluid moving up in the tube. D - Water has entered the visking tubing by osmosis from the beaker into the sucrose solution inside the tubing. 9. Why has the visking tubing on the right of Photo 2 become more flaccid (soft) than that on the left. A - Water has moved by osmosis from inside the visking tubing. B - Water has entered the solution inside the visking tubing by osmosis from the deionised water surrounding the tubing. C - Sucrose from the sucrose solution in the beaker has moved by diffusion into the the visking tubing. D - Gravity has caused the solution to seep out of the visking tubing on the right.
31 Biology Part 1 Diffusion and Osmosis TEST VERSION 7 of 12 HELP BOX PASS CURSOR OVER QUESTION MARK FOR HELP WITH QUESTION NUMBER 10? Osmosis is the special case of the diffusion of water. In which water molecules diffuse from a high water concentration (pure water or a more dilute solution) to a lower water concentration (more concentrated solution) through a partially permeable membrane. 10. The following passage has four missing words. If you drink tap water, the contents of your stomach are and water passes by osmosis from the into the blood. If you swallow sea water the contents of your stomach are and water passes by osmosis from the into the stomach. PAGES 6-11 BLOCKED, GO TO PAGE 12 Which of the following has the correct missing words in the sequence as they should appear in the passage. A - concentrated - stomach - diluted - blood B - diluted - kidneys - concentrated - blood C - diluted - stomach - concentrated - kidneys D - diluted - stomach - concentrated - blood
32 Biology Part 1 The Heart, Lungs and Smoking TEST VERSION 8 of 12 HELP BOX PASS CURSOR OVER QUESTION MARK FOR HELP WITH QUESTION NUMBER 11? Practical - The heart and lungs in humans are contained in the chest or thoracic cavity. The two lungs surround the heart, as shown in Photo 1 of a model. The heart is a four chambered muscular pump, which by contracting and relaxing, pumps blood around the lungs, and the body. Photo 2 shows a model of a partially dissected heart showing some of the chambers in section, the valves and the major blood vessels entering and leaving the heart. Anatomical diagrams are labelled right and left as if you were looking at somebody in front of you, ie their right is on your left, and their left is on your right. 1 2 PAGES 6-11 BLOCKED, GO TO PAGE 12 PHOTO 1 PHOTO The large blood vessel shown blue and labelled 1 in Photo 1 carries blood into which chamber of the heart? A - Right Ventricle B - Right atrium C - Left atrium D - Left ventricle 12. Which chamber of the heart pumps blood into the large blood vessel shown red and labelled 2 in Photo 2? A - Right ventricle B - Right atrium C - Left Ventricle D - Left atrium
33 Biology Part 1 The Heart, Lungs and Smoking TEST VERSION 9 of 12 HELP BOX PASS CURSOR OVER QUESTION MARK FOR HELP WITH QUESTION NUMBER 13? Blood passes through the heart twice on each complete circulation of the body. After entering the heart it goes to the lungs to get rid of carbon dioxide and pick up oxygen. From the lungs blood then returns to the heart and is pumped around the body. 13. The following passage has four missing words. The heart pumps the blood around the body. In its passage through the heart, the blood from the main veins of the body enters the atrium, from here it passes to the right ventricle, from where it is pumped to the. It returns to the atrium, passes to the left ventricle, and is then pumped around the. PAGES 6-11 BLOCKED, GO TO PAGE 12 Which of the following has the correct missing words in the sequence as they should appear in the passage. A - left - lungs - right - body. B - right - body - left - lungs. C - right - lungs - left - body. D - left - body - right - lungs.
34 Biology Part 1 The Heart, Lungs and Smoking TEST VERSION 10 of 12 Practical - The lungs consist of millions of small air sacs or alveoli which give the lungs a huge surface area over which gas exchange occurs between the bloodstream and the air in the air sacs. The lungs are well supplied with blood vessels to carry oxygen from and carbon dioxide to, the air sacs. In the photograph shown below the right lung of the model is shown in section, and the air tubes appear as circles as if cut across. 14. What is the name of the smaller tubes carrying air deep into each lung? A - Bronchioles B - Trachea C - Capillaries D - Pulmonary tubes PAGES 6-11 BLOCKED, GO TO PAGE What is the name of the large blood vessels shown blue that can be seen running through the left lung in the Photo? A - Pulmonary veins. B - Pulmonary arteries. C - Capillaries. D - Arterioles. 16. Which one of the following is a correct description of the movement of the ribs when breathing in? A - They move downwards and inwards decreasing the volume of the chest cavity. B - They move inwards keeping the volume of the chest cavity the same. C - They move sideways keeping the volume of the chest cavity the same. D - They move upwards and outwards increasing the volume of the chest cavity.
35 Biology Part 1 The Heart, Lungs and Smoking TEST VERSION 11 of 12 Practical - The following photos are of water and cotton wool taken from a smoking machine in which smoke from a lit cigarette was drawn through them to trap some of the components of cigarette smoke. 17. In which part of the lungs are these components of cigarette smoke most likely to accumulate? A - trachea B - air sacs (alveoli) C - bronchi D - bronchioles PAGES 6-11 BLOCKED, GO TO PAGE Which of the following components of cigarette smoke causes the addiction to smoking. A - nicotine B - smoke C - tars D - cancer causing chemicals 19. Which of the following diseases does NOT have smoking as a possible cause? A - bronchitis B - cancer C - influenza D - heart disease
36 Biology Part 1 Diffusion and Osmosis The Heart, Lungs and Smoking TEST VERSION 12 of 12 SECTION TOTAL 0/19 SECTION PERCENTAGE 0% on T
37 INTERACTIVE ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS BASED ON STANDARD PRACTICAL EXERCISES... Biology Part 2 IN THIS ANSWERS ARE IMMEDIATELY AND VISIBLY MARKED, CORRECT ANSWERS ARE INDICATED ON REQUEST, AND END OF SECTION TOTALS AND PERCENTAGES SHOWN ON SCREEN. SOME OF THE MORE DIFFICULT QUESTIONS HAVE DROP DOWN HELP BOXES WHICH REVEAL INFORMATION WHEN THE CURSOR IS PASSED OVER THE QUESTION MARK. WHEN PRINTED OUT ONLY THE QUESTIONS SHOW, THEREFORE THIS CAN BE USED AS A PAPER VERSION FOR TESTS IF REQUIRED. The questions are of the Multiple Choice style, where the phrase Which ONE of the following... is implied, but is not always stated. So that students are reminded of the type of question that requires short written answers, which unfortunately cannot be automatically marked, each topic has one short passage with missing words, which must be identified in their correct sequence. NB The practical work presented should be familiar to students, either as demonstrations or as procedures they might have carried out themselves in the lab. The material is NOT presented as a practical guide, and while the methods followed safety guidelines, specific safety issues are NOT dealt with. Visit
38 Biology Part 2 2 of 14 CONTENTS The following practical topics have been selected according to exam question frequency to form the basis of revision and examination practice. Part 1 Diffusion and Osmosis Heart, Lungs & Smoking Part 2 Enzyme Reactions Respiration Fermentation Part 3 Leaf Structure and Function Photosynthesis Tropisms
39 Biology Part 2 Enzyme Reactions 3 of 14 Enzymes catalyse (speed up) all the chemical reactions necessary for life. Practical - The enzyme amylase catalyses the breakdown of starch into a sugar (maltose). The presence of starch is shown by testing with iodine solution. As the amount of starch decreases, the colour of the reaction with iodine solution goes from blue black to a lighter blue colour, until there is no change from the original iodine colour. PHOTO 1 shows a tile with spots of iodine solution at the start of an experiment investigating the effects of amylase on a starch solution. PHOTO 2 shows the same tile at the end of the experiment. PHOTO 1 Tile with spots of iodine solution at start of experiment. PHOTO 2 Tile with iodine solution after samples from an amylase - starch mixture have been added. The first spot (top left) was taken immediately the amylase was added to the starch, and then samples were taken at 30 sec intervals 1. In the experiment described above, and using the results shown in Photo 2, how long did it take for the starch to be broken down by amylase into sugar? A - more than 5 minutes B - less than a minute C - more than 4 minutes D - more than 2 minutes 2. If in the experiment none of the spots of iodine solution changed colour, which one of the following would be the best explanation? A - The enzyme amylase was not working. B - All of the starch had been broken down immediately. C - No sugars had been produced. D - There was too much starch present for the enzyme to break down.
40 Biology Part 2 Enzyme Reactions 4 of 14 HELP BOX PASS CURSOR OVER QUESTION MARK FOR HELP WITH QUESTION NUMBER 4? Practical - The production of sugar from the breakdown of starch can be tested for with the Benedict s Test. Benedict s solution is clear blue, and when boiled with samples from a starch/amylase mixture gives a precipitate with a range of colours from green to red depending on the amount of sugar present. A precipitate is a suspension of tiny particles of an insoluble substance produced in a reaction (in this case the Benedict s Test) In the photograph above of the Benedict s Test, which tube contains the greatest amount of sugar? A - Tube 3 B - Tube 1 C - Tube 4 D - Tube 2 Practical - If the tubes shown above were allowed to stand for some time, gradually the colour would appear to fade at the top and get darker at the bottom of the tubes. Depending on your screen, you may be able to see that the process has already started. 4. Which one of the following is the best explanation of the above observation? A - There are more sugars at the bottom than at the top of the solution in the tubes. B - The colour is oxidised by the air at the surface of the solution. C - The enzyme is continuing its action on the starch. D - The colour is caused by a precipitate which gradually sinks to the bottom if the tubes are left to stand.
41 Biology Part 2 Enzyme Reactions 5 of 14 HELP BOX PASS CURSOR OVER QUESTION MARK FOR HELP WITH QUESTION NUMBER 5? Enzymes work best at a certain ph (acidity/alkalinity). The saliva is typically slightly alkaline, but the stomach contents are strongly acidic. 5. Which of the following could best explain why protease enzymes digest proteins in the stomach, but amylase in your saliva does not carry on working on starch in the stomach for very long? A - The enzyme amylase is killed when the food is chewed. B - The enzyme amylase is neutralised by the acid in the stomach. C - All the starch is digested in the mouth. D - The amylase is broken down by the acid in the stomach but the protease is not. 6. The following passage has four missing words. Amylase speeds up the breakdown of to sugars, lipase speeds up the breakdown of fats to fatty acids and, and proteases speed up the breakdown of to. In the body, each type of enzyme works fastest at a particular ph, for example amylase works best at a ph around neutral. Which of the following has the correct missing words in the sequence as they should appear in the passage. A - fats - glycerol - starch - amino acids B - starch - glycerol - proteins - amino acids C - starch - amino acids - proteins - glycerol D - starch - glycerol - amino acids - proteins
42 Biology Part 2 Respiration 6 of 14 Practical - Five tubes were set up containing hydrogen carbonate indicator solution, which is red when neutral (in equilibrium with the CO 2 in the air), yellow when acidic (lower ph), and cherry red and then purple when alkaline (higher ph). Four tubes were set up containing various combinations of well washed pondweed and/or water snails, along with a tube of indicator solution only, as shown in the photograph below. HELP BOX PASS CURSOR OVER QUESTION MARK FOR HELP WITH QUESTION NUMBER 7? If carbon dioxide is added to the indicator solution it becomes more acid (lower ph), and if carbon dioxide is removed from the indicator solution it becomes more alkaline (higher ph). Tube contents A - indicator solution B - indicator solution plus pondweed C - indicator solution plus pond snail D - indicator solution plus pondweed and pond snail E - indicator solution & pondweed in tube covered in silver foil At the start of the experiment the indicator solution in all the tubes was a red colour. The photograph shows the tubes at the end of the experiment, during which they were all tightly sealed with rubber bungs. As screen colours can vary the results are also given below: A - Red B - Deeper red/purple C - Yellow D - Red E - Yellow 7. Which of the following is the correct identification and explanation of the tube that is the control for this experiment? A - Tube C because the pond snail is found in two other tubes. B - Tube B because the pondweed is found in three other tubes. C - Tube A because it demonstrates that the indicator solution does not change colour on its own. D - Tube E because it eliminates light from the experiment.
43 Biology Part 2 Respiration 7 of What does tube E demonstrate? A - Light is necessary for photosynthesis. B - Plants increase the acidity (decrease the ph) of the surrounding indicator solution in the absence of light. C - Plants decrease the acidity (raise the ph) of the surrounding indicator solution in the absence of light. D - Light is not necessary for the indicator solution to change colour. PAGES 7-13 BLOCKED, GO TO PAGE Which of the following is the correct identification and explanation of why one of the tubes has the lowest oxygen concentration? A - Tube E because no photosynthesis is taking place there. B - Tube D because both plant and animal are respiring together. C - Tube B because photosynthesis is using up oxygen faster than respiration. D - Tube C because animal respiration is faster than plant respiration and no photosynthesis is taking place. 10. Which of the following correctly explains why there was no change in colour in tube D? A - The presence of the snail prevents the indicator solution from working. B - The presence of the pondweed prevents the indicator solution from working. C - The snail s exchange of gases is balanced by those of the pondweed. D - The indicator solution has poisoned the snail.
44 Biology Part 2 Respiration 8 of 14 HELP BOX PASS CURSOR OVER QUESTION MARK FOR HELP WITH QUESTION NUMBER 11 & 12? Animals and plants respire all the time. In the light green plants carry out photosynthesis during which carbon dioxide is taken in and oxygen is given out. In the light photosynthesis produces more oxygen than respiration uses. 11. In which of the tubes containing pondweed is plant respiration occurring? A - None of them B - D C - E D - All of them PAGES 7-13 BLOCKED, GO TO PAGE The following passage has four missing words. Animals only carry out respiration so always take in oxygen and give out carbon dioxide. Plants carry out at all times, but also carry out in the light. Above a certain light intensity photosynthesis proceeds at a faster rate than plant respiration. Therefore in the dark, plants usually take in and give out, but in the light this is reversed. Which of the following has the correct missing words in the sequence they should appear in the passage. A - respiration - photosynthesis - oxygen - carbon dioxide B - photosynthesis - respiration - oxygen - carbon dioxide C - respiration - photosynthesis - carbon dioxide - oxygen D - photosynthesis - respiration - carbon dioxide - oxygen
45 Biology Part 2 Fermentation 9 of 14 Yeast cells produce enzymes which break down sugar into alcohol and carbon dioxide, in a process known as fermentation. This process is made use of in the brewing and baking industries. Practical - The apparatus was set up as shown. The boiling tube had a mixture of yeast and sugar solution added, after which a pre-stretched balloon was attached tightly to the top. The tube was then placed in a beaker-waterbath at 40 o C. After about 15 minutes the balloon became inflated as shown below. PAGES 7-13 BLOCKED, GO TO PAGE Which of the following is the best explanation of the balloon becoming inflated in this experiment? A - Air in the tube is expanding because the water surrounding it is at 40 o C. B - A gas is being produced by the yeast in the sugar solution. C - Alcohol vapour is being produced. D - The mixture has foamed up and filled the balloon.
46 Biology Part 2 Fermentation 10 of 14 Practical - The production of a gas as a result of yeast reacting with a sugar solution can be MEASURED by counting the bubbles of gas as they are pushed out into the water in tube X shown below. Using the apparatus shown, the number of bubbles produced in 30 seconds was counted. The counting was repeated three times and recorded in the table shown below. Yeast / sugar mixture at 40 o C Tube X 30 sec Period No. of bubbles First period 12 Second period 16 Third period 17 HELP BOX PASS CURSOR OVER QUESTION MARK FOR HELP WITH QUESTION NUMBER 14? To obtain the average or mean of a set of figures, add them all up and divide by the number of results, in this case 3. PAGES 7-13 BLOCKED, GO TO PAGE Which of the following figures represents the average of the number of bubbles produced in a 30 second period? A - 15 B - 14 C - 13 D Which of the following changes in conditions of the experiment would NOT result in an increase in the rate of bubbling? A - An increase in the amount of sugar. B - An increase in temperature. C - An increase in the amount of light. D - An increase in the amount of yeast.
47 Biology Part 2 Fermentation 11 of 14 HELP BOX PASS CURSOR OVER QUESTION MARK FOR HELP WITH QUESTION NUMBER 16? Enzymes are permanently damaged (denatured) at 100 o C (see Enzymes sub-section). 16. After heating a sample of the yeast/sugar solution mixture to 100 oc, it was cooled to 40 o C and more sugar solution added. Which of the following is the best description of what you would expect to occur. A - The rate of reaction would be the same as it was before at 40 o C. B - No reaction would occur. C - The rate of reaction would be much slower than it was before at 40 o C. D - The rate of reaction would be much faster than it was before at 40 o C. PAGES 7-13 BLOCKED, GO TO PAGE After cooling a sample of the yeast/sugar solution mixture to 0 oc, it was re-warmed to 40 o C and more sugar solution added. Which of the following is the best description of what you would expect to occur. A - The rate of reaction would return towards what it was previously at 40 oc. as the mixture was rewarmed. B - No reaction would occur. C - The rate of reaction would be much slower than it was before at 40 oc. D - The rate of reaction would be much faster than it was before at 40 o C.
48 Biology Part 2 Fermentation 12 of 14 Practical - The previous experiment was set up again with the test tube through which the gas is bubbling now filled with LIME WATER. Observe the result and answer the following questions. Gas bubbling through water in tube on right Gas bubbling through lime water in tube on right PAGES 7-13 BLOCKED, GO TO PAGE 14 Another tube of lime water was stood near by, open to the air, and did NOT go cloudy over the same period. 18. Which of the following best explains the results? A - The gas produced by yeast contains impurities that cloud the lime water. B - Air causes lime water to go milky at the same rate as yeast respiration. C - Lime water goes milky in contact with glass. D - The gas produced by yeast is carbon dioxide which turns limewater milky.
49 Biology Part 2 Fermentation 13 of 14 HELP BOX PASS CURSOR OVER QUESTION MARK FOR HELP WITH QUESTION NUMBER 19? Aerobic means in the presence of oxygen, and anaerobic means in the absence of oxygen. 19. The following passage has four missing words. Yeast is a single celled organism that occurs naturally, decomposing dead organic matter, e.g. fruit. It is capable of breaking down and absorbing sugars from its surroundings and using them to release. This process is respiration. In the presence of, yeast can carry out aerobic respiration to produce carbon dioxide and. In the absence of oxygen, yeast respires anaerobically and produces carbon dioxide and, this process can also be called fermentation. PAGES 7-13 BLOCKED, GO TO PAGE 14 Which of the following has the correct missing words in the sequence as they should appear in the passage. A - water - oxygen - alcohol - energy B - oxygen - energy - water - alcohol C - energy - water - alcohol - oxygen D - energy - oxygen - water - alcohol
50 Biology Part 2 Enzymes 14 of 14 Respiration Fermentation SECTION TOTAL SECTION PERCENTAGE Section Total =
51 INTERACTIVE ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS BASED ON STANDARD PRACTICAL EXERCISES... Biology Part 2 PRACTICE TEST VERSION IN THIS PRACTICE TEST VERSION NO MARKING OR ANSWERS ARE VISIBLE ON SCREEN, BUT TOTALS AND PERCENTAGES ARE SHOWN. HELP BOXES ARE NOT AVAILABLE. ON THE PRINT-OUT THE STUDENT'S RESPONSES, MARKS, TOTALS AND PERCENTAGES ARE ALL VISIBLE, BUT CORRECT ANSWERS ARE NOT SHOWN. The questions are of the Multiple Choice style, where the phrase Which ONE of the following... is implied, but is not always stated. So that students are reminded of the type of question that requires short written answers, which unfortunately cannot be automatically marked, each topic has at least one short passage with missing words, which must be identified in their correct sequence. NB The practical work presented should be familiar to students, either as demonstrations or as procedures they might have carried out themselves in the lab. The material is NOT presented as a practical guide, and while the methods followed safety guidelines, specific safety issues are NOT dealt with. Visit
52 Biology Part 2 PRACTICE TEST VERSION 2 of 14 CONTENTS The following practical topics have been selected according to exam question frequency to form the basis of revision and examination practice. Part 1 Diffusion and Osmosis Heart, Lungs & Smoking Part 2 Enzyme Reactions Respiration Fermentation Part 3 Leaf Structure and Function Photosynthesis Tropisms
53 INTERACTIVE ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS BASED ON STANDARD PRACTICAL EXERCISES... Biology Part 2 TEST VERSION IN THIS TEST VERSION NO MARKING, ANSWERS OR TOTALS ARE VISIBLE ON SCREEN. ON THE PRINT-OUT THE STUDENTS RESPONSES, TOTALS AND PERCENTAGES ARE SEEN BUT NO CORRECT ANSWERS ARE INDICATED. NO HELP BOXES ARE PROVIDED. THE ANSWER SEQUENCE IN THIS TEST VERSION IS UNIQUE AND ONLY AVAILABLE BY WORKING OUT THE CORRECT ANSWER THROUGH UNDERSTANDING. The questions are of the Multiple Choice style, where the phrase Which ONE of the following... is implied, but is not always stated. So that students are reminded of the type of question that requires short written answers, which unfortunately cannot be automatically marked, each topic has at least one short passage with missing words, which must be identified in their correct sequence. NB The practical work presented should be familiar to students, either as demonstrations or as procedures they might have carried out themselves in the lab. The material is NOT presented as a practical guide, and while the methods followed safety guidelines, specific safety issues are NOT dealt with. Visit
54 Biology Part 2 TEST VERSION 2 of 14 CONTENTS The following practical topics have been selected according to exam question frequency to form the basis of revision and examination practice. Part 1 Diffusion and Osmosis Heart, Lungs & Smoking Part 2 Enzyme Reactions Respiration Fermentation Part 3 Leaf Structure and Function Photosynthesis Tropisms
55 INTERACTIVE ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS BASED ON STANDARD PRACTICAL EXERCISES... Biology Part 3 IN THIS ANSWERS ARE IMMEDIATELY AND VISIBLY MARKED, CORRECT ANSWERS ARE INDICATED ON REQUEST, AND END OF SECTION TOTALS AND PERCENTAGES SHOWN ON SCREEN. SOME OF THE MORE DIFFICULT QUESTIONS HAVE DROP DOWN HELP BOXES WHICH REVEAL INFORMATION WHEN THE CURSOR IS PASSED OVER THE QUESTION MARK. WHEN PRINTED OUT ONLY THE QUESTIONS SHOW, THEREFORE THIS CAN BE USED AS A PAPER VERSION FOR TESTS IF REQUIRED. The questions are of the Multiple Choice style, where the phrase Which ONE of the following... is implied, but is not always stated. So that students are reminded of the type of question that requires short written answers, which unfortunately cannot be automatically marked, each topic has one short passage with missing words, which must be identified in their correct sequence. NB The practical work presented should be familiar to students, either as demonstrations or as procedures they might have carried out themselves in the lab. The material is NOT presented as a practical guide, and while the methods followed safety guidelines, specific safety issues are NOT dealt with. Visit
56 Biology Part 3 2 of 13 CONTENTS The following practical topics have been selected according to exam question frequency to form the basis of revision and examination practice. Part 1 Diffusion and Osmosis Heart, Lungs & Smoking Part 2 Enzyme Reactions Respiration Fermentation Part 3 Leaf Structure and Function Photosynthesis Tropisms
57 Biology Part 3 Leaf Structure and Function 3 of 13 There are two main groups of flowering plants with respect to leaf structure. Those with grass-like leaves, and those with broader flatter leaves. Despite the slight differences in their structure the leaves all function in the same way. All the questions here relate to the broader flatter leaves. Practical - If a leaf is cut across in a thin section (transverse section) mounted on a slide and viewed under a microscope, its internal structure can be seen. This is shown in the photograph and drawing below: HELP BOX PASS CURSOR OVER QUESTION MARK FOR HELP WITH QUESTION NUMBER 1? Photosynthesis requires light, chlorophyll, carbon dioxide and water. Only some cells are drawn in detail 1. Which of the following features of this type of leaf does NOT make it more efficient at carrying out photosynthesis? A - Many chloroplasts in the upper most layers of palisade cells. B - Waterproof waxy cuticle or surface film. C - Large surface area when compared to its volume ie relatively thin. D - Holes in the leaf for the exchange of gases with its surroundings. 2. Which of the following statements about the exchanges between a leaf and the surrounding air is NOT correct? A - In the dark water vapour enters the leaf. B - In the light oxygen leaves the leaf. C - In the dark carbon dioxide leaves the leaf. D - In the light carbon dioxide enters the leaf.
58 Biology Part 3 Leaf Structure and Function 4 of 13 Practical - A woody shoot with leaves was set up as shown in the photograph. The water in the flask was covered by a layer of oil. The initial reading of the balance was noted, and then a series of readings was taken over a period of time, these are shown in the table. Mass in g at 30 min intervals Which of the following is the best explanation of why the balance recorded a loss of mass over the period of time shown in the table? A - The shoot was taking water up from the flask. B - The water in the flask was evaporating. C - The shoot was using up its stores of starch. D - The leaves were losing water vapour to the air. 4. Which of the following, in comparison to the above experiment, would you expect to occur if the experiment was repeated with a fan blowing a stream of air over the leaves of the shoot? A - There would be a loss of mass at a slower rate. B - There would be a smaller loss of mass. C - There would be the same loss of mass. D - There would be a greater loss of mass.
59 Biology Part 3 Leaf Structure and Function 5 of 13 HELP BOX PASS CURSOR OVER QUESTION MARK FOR HELP WITH QUESTION NUMBER 5? Most leaves have more stomata (small holes) on the lower surface. Some eg Laurel have none on the upper surface at all. 5. Which one of the following would occur if the experiment was repeated with the lower surfaces of the leaves covered with vaseline? A - There would be a greater loss of mass. B - There would be the same loss of mass. C - There would be a smaller loss of mass. D - There would be a gain of mass due to the vaseline. 6. The following passage has four missing words. The leaf is adapted for efficient photosynthesis. It has a large surface area, cells containing arranged in a way to maximise the absorbtion of, and stomata to allow the uptake of, and the release of. Which of the following has the correct missing words in the sequence as they should appear in the passage. A - chloroplasts - carbon dioxide - light - water vapour B - chloroplasts - light - water vapour - carbon dioxide C - chloroplasts - water vapour - light - carbon dioxide D - chloroplasts - light - carbon dioxide - water vapour
60 Biology Part 3 Photosynthesis 6 of 13 HELP BOX PASS CURSOR OVER QUESTION MARK FOR HELP WITH QUESTION NUMBER 8? Practical - The apparatus was set up as shown in the photograph and the drawing. The pondweed had been kept in a container of pond water in bright light at room temperature for a period of 3 hours before being placed in the apparatus. The water in the beaker and tube had been enriched with hydrogen carbonate solution. After a few minutes bubbles of gas were seen coming from the leaves and cut stem of the plant and collecting over the water in the tube above the glass funnel. Hydrogen carbonate solution is a source of hydrogen carbonate ions which is the form in which aquatic green plants absorb their carbon dioxide. 7. Which of the following best explains why the pond weed was kept in bright light for a period of 3 hours before being placed in the apparatus? A - To make sure photosynthesis was happening at a fast rate. B - To make sure that the pond weed was pointing to the light. C - To stop respiration from interfering with the experiment. D - To warm the water to an optimum temperature. PAGES 6-12 BLOCKED, GO TO PAGE Which of the following best explains why the water in the apparatus had hydrogen carbonate solution added? A - To make sure the pond weed continued to grow. B - To sterilise the apparatus. C - To ensure respiration did not interfere with the experiment. D - To increase the carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. 9. Which one of the following gases was being collected in the tube? A - Oxygen B - Nitrogen C - Carbon dioxide D - Carbon monoxide
61 Biology Part 3 Photosynthesis 7 of 13 Practical - Glucose, one of the products of photosynthesis, is converted into starch and stored in the cells of the leaf. A leaf can be tested for the presence of starch by the procedure illustrated below. Leaves boiled in water to break down cell membranes Leaves boiled in tubes of alcohol in a hot waterbath to release chlorophyll from leaves (with Bunsen burner turned off). Leaves soaked in iodine solution to test for the presence of starch which produces a darker brown/blue-black colour PAGES 6-12 BLOCKED, GO TO PAGE In the above procedure which of the following best describes why it is necessary to remove the chlorophyll from the leaves. A - The chlorophyll would colour the starch green. B - The chlorophyll would react with the iodine solution. C - To stop photosynthesis from continuing. D - The chlorophyll would mask the colouration of starch by the iodine solution.
62 Biology Part 3 Photosynthesis 8 of 13 Practical - Variegated leaves have a patchy green and white pattern. When a variegated leaf is tested for the presence of starch, the distribution of the starch is the same as that of the green area, as shown in the photographs. PAGES 6-12 BLOCKED, GO TO PAGE Which of the following is the best explanation of why the two patterns are so similar? A - The white area is producing sugars not starch. B - The green area is the only area with living cells. C - The green area is the only one where photosynthesis was occurring. D - The white area is using up starch in respiration.
63 Biology Part 3 Photosynthesis 9 of 13 Practical - A plant was kept in the dark for 48 hours so that it used up all its stores of starch (de-starched). A silver foil stencil was attached to one of the leaves, which was then exposed to a bright light (PHOTO 1) for some hours. The leaf was then removed from the plant (PHOTO 2) and tested for the presence of starch, as described for a previous question. When the leaf was placed in iodine solution the result was as shown in PHOTO 3. PHOTO 1 PHOTO 2 PHOTO 3 PAGES 6-12 BLOCKED, GO TO PAGE Which of the following statements best explains why the pattern of the stencil shown in photo 3 was the same as that of the starch in the leaf? A - The stencil marked the leaf. B - Starch was only produced where the light could reach the leaf. C - The leaf used up less starch in the light. D - The leaf only carried out respiration in the dark areas. 13. Which of the following statements is the best explanation of why the plant had to be de-starched at the start of the experiment? A - Photosynthesis would not take place if starch was present. B - To stop respiration taking place. C - So that only starch newly produced during the experiment could be detected. D - So it did not stop light reaching the chlorophyll.
64 Biology Part 3 Photosynthesis 10 of 13 HELP BOX PASS CURSOR OVER QUESTION MARK FOR HELP WITH QUESTION NUMBER 14? Photosynthesis produces simple sugars, of which glucose is an example. Many molecules of glucose combine chemically to produce starch. 14. The following passage has four missing words. Photosynthesis is a process by which light energy trapped by in the leaves of a plant, water and, are involved in a series of enzyme controlled reactions to produce and. The simple sugar is then converted into insoluble starch and stored in the leaf cells. PAGES 6-12 BLOCKED, GO TO PAGE 13 Which of the following has the correct missing words in the sequence as they should appear in the passage. A - chlorophyll - nitrogen - carbon dioxide - oxygen B - chlorophyll - carbon dioxide - glucose - oxygen C - haemoglobin - air - glucose - oxygen D - cells - chlorophyll - oxygen - carbon dioxide
65 Biology Part 3 11 of 13 Tropisms Practical - The shoots of green plants, if they do not receive light evenly from all around, grow towards the direction from which the light is coming. This response is known as phototropism, and a similar response of roots to gravity is known as geotropism. Two dishes of cress seeds were sown on damp cotton wool. One dish was placed in a box with a black lining and a hole at one end, at which a bright light was shone. The other dish of seeds was grown surrounded by light. The results, after the seeds had germinated, are shown in the photographs. PAGES Why BLOCKED, was the lining of GO the box TOpainted PAGEblack? 13 A - To stop the internal reflection of light entering via the hole in the box. B - To mimic the conditions of night time. C - To stop the leaves growing on one side. D - To make sure the plant knew which end the hole was. 16. What is the advantage to the plant of its shoots growing towards light? A - To avoid leaf eating pests that prefer the dark. B - To increase the uptake of carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. C - To increase the release of oxygen produced by photosynthesis from the leaves. D - To increase the absorption of light for photosynthesis. 17. How do plant shoots manage to grow towards light coming from one direction only? A - The stem grows more on the dark side. B - The stem grows less on the dark side. C - The stem contracts on the light side. D - The light destroys cells on the light side making it shorter.
66 Biology Part 3 Tropisms 12 of 13 HELP BOX PASS CURSOR OVER QUESTION MARK FOR HELP WITH QUESTION NUMBER 18? Practical - A Broad Bean seed was germinated and pinned with its young shoot and root positioned horizontally and then placed in the dark. After several days the result was as shown in the photograph. A stimulus is something in the environment to which a living organism responds, typically by growing towards or away from it. 18. What is the stimulus to which the shoot and the root of the seedling are responding? A - Light. B - Gravity. C - Water. D - Air. PAGES 6-12 BLOCKED, GO TO PAGE The following passage has four missing words. The advantages to the plant of these responses by the root and the shoot are that they make sure that the grows into the soil for anchorage, water and nutrients; and that the grows to reach the light for photosynthesis. Which of the following has the correct missing words in the sequence as they should appear in the passage. A - root - down - leaves - up B - embryo - down - shoot - up C - root - down - shoot - up D - seed - down - shoot -up
Multicellular Organisms. Sub-Topic 2.7 Animal Transport & Exchange Systems
 Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.7 Animal Transport & Exchange Systems On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: Rings of cartilage keep the main airways open Oxygen and carbon dioxide
Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.7 Animal Transport & Exchange Systems On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: Rings of cartilage keep the main airways open Oxygen and carbon dioxide
Monday, ! Today: Respiratory system! 5/20/14! Transport of Blood! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing!
 Monday, 5.19.14! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing! Transport of Blood! What is transported! Nutrients! Oxygen! Carbon Dioxide! Hormones! Antibodies! What it is/does!
Monday, 5.19.14! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing! Transport of Blood! What is transported! Nutrients! Oxygen! Carbon Dioxide! Hormones! Antibodies! What it is/does!
08 Respiration. #79 Respiration realeases energy from food
 08 Respiration #79 Respiration realeases energy from food Respiration is the chemical reactions that break down nutrient molecules in living cells to release energy. In humans, our cells need energy (ATP)
08 Respiration #79 Respiration realeases energy from food Respiration is the chemical reactions that break down nutrient molecules in living cells to release energy. In humans, our cells need energy (ATP)
The Breathing System
 The Breathing System Learning Intentions 1. Students should Know how Breathing happens 2. Name and know the functions of the Breathing System 3. Know how the organs work and how they work with other systems
The Breathing System Learning Intentions 1. Students should Know how Breathing happens 2. Name and know the functions of the Breathing System 3. Know how the organs work and how they work with other systems
Explain how the structure of the gas exchange system of an insect ensures that there is a large surface area for gas exchange.
 1 Gas exchange takes place by diffusion. surfacearea differenceinconcentration diffusion lengthof diffusionpath a The diagram shows part of an insect tracheal system. i Explain how the structure of the
1 Gas exchange takes place by diffusion. surfacearea differenceinconcentration diffusion lengthof diffusionpath a The diagram shows part of an insect tracheal system. i Explain how the structure of the
practices makes perfect
 Human Respiratory system Chapter 1: Respiration PMR 03, 08 1. The human respiratory system consists of: a... b... c.. d... e. Our body has.. lungs (right & left). f. Each lung consists of the, and alveoli.
Human Respiratory system Chapter 1: Respiration PMR 03, 08 1. The human respiratory system consists of: a... b... c.. d... e. Our body has.. lungs (right & left). f. Each lung consists of the, and alveoli.
Directions: The following two questions refer to the diagram below, which shows a group of cells from the respiratory tract.
 Topic 7 Gas exchange in humans Directions: The following two questions refer to the diagram below, which shows a group of cells from the respiratory tract. X Y 1. What is the function of structure X? A.
Topic 7 Gas exchange in humans Directions: The following two questions refer to the diagram below, which shows a group of cells from the respiratory tract. X Y 1. What is the function of structure X? A.
Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class
 I. Name the following : Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class 1. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. 2. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous
I. Name the following : Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class 1. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. 2. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous
The Human Body. Everyone Needs Healthy Systems. Blood Vessels
 The Human Body Everyone Needs Healthy Systems There are several systems that make up the human body. Although their functions differ, they all work together to keep your body running smoothly. Some of
The Human Body Everyone Needs Healthy Systems There are several systems that make up the human body. Although their functions differ, they all work together to keep your body running smoothly. Some of
OB11 Carry out qualitative tests to compare the carbon dioxide levels of inhaled and exhaled air
 Biology: 5. Respiration and Breathing Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier OB9 Syllabus Describe the process of aerobic respiration
Biology: 5. Respiration and Breathing Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier OB9 Syllabus Describe the process of aerobic respiration
Glucose + Oxygen Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy C6H12O CO2 + 6H20 + energy
 Cell Respiration - A food oxidization process in body cells to produce energy - Occurs (happens) in animal cells and plant cells Notes : Metabolic Reactions in Gaseous Exchange CELL RESPIRATION Photosynthesis
Cell Respiration - A food oxidization process in body cells to produce energy - Occurs (happens) in animal cells and plant cells Notes : Metabolic Reactions in Gaseous Exchange CELL RESPIRATION Photosynthesis
Human gas exchange. Question Paper. Save My Exams! The Home of Revision. Cambridge International Examinations. 56 minutes. Time Allowed: Score: /46
 Human gas exchange Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International Examinations Respiration Human gas exchange Question Paper Time llowed: 56 minutes
Human gas exchange Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International Examinations Respiration Human gas exchange Question Paper Time llowed: 56 minutes
A breath of fresh air
 A breath of fresh air BIG IDEAS You are learning to: Describe the structure of the lungs Explain how the lungs clean themselves Interpret patterns in data Where are the lungs and what do they do? The lungs
A breath of fresh air BIG IDEAS You are learning to: Describe the structure of the lungs Explain how the lungs clean themselves Interpret patterns in data Where are the lungs and what do they do? The lungs
Transport in cells. Specification coverage
 3 Transport in cells T F A R What does smelling your best friend s deodorant have in common with making a cup of tea? One thing is that they both involve the movement of particles. Particles spread out
3 Transport in cells T F A R What does smelling your best friend s deodorant have in common with making a cup of tea? One thing is that they both involve the movement of particles. Particles spread out
1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives
 1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives To understand the functions of the circulatory system. To be able to identify the differences between veins, arteries
1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives To understand the functions of the circulatory system. To be able to identify the differences between veins, arteries
The Respiratory System
 Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
SCIENCE- NOTES. Q1. Draw the diagram of human respiratory system and explain the function of the following parts:
 SCIENCE- NOTES NAME: RESPIRATION IN ORGANISMS STD.VII DIV: Q1. Draw the diagram of human respiratory system and explain the function of the following parts: i. Nasal cavity ii. Trachea iii. Lungs iv. Bronchioles
SCIENCE- NOTES NAME: RESPIRATION IN ORGANISMS STD.VII DIV: Q1. Draw the diagram of human respiratory system and explain the function of the following parts: i. Nasal cavity ii. Trachea iii. Lungs iv. Bronchioles
Structures of the Respiratory System include:
 Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System include: ü Oral Cavity ü Nasal Cavity ü Pharynx ü Epiglottis ü Larynx ü Trachea ü Diaphragm ü Lung ü Bronchus ü Bronchioles ü Alveolus ü Pulmonary
A.M. WEDNESDAY, 7 January hour
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4471/02 W15-4471-02 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE/BIOLOGY BIOLOGY 2 HIGHER TIER A.M. WEDNESDAY, 7 January 2015 1 hour For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4471/02 W15-4471-02 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE/BIOLOGY BIOLOGY 2 HIGHER TIER A.M. WEDNESDAY, 7 January 2015 1 hour For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system. Objective sheet 3 Notes
 1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
Chapter 1: Respiration
 Chapter 1: Respiration Respiration Human Breathing Mechanism Transport of oxygen Importance of a healthy respiratory system Respiratory system lungs inhalation exhalation Diffusion of oxygen by blood Transport
Chapter 1: Respiration Respiration Human Breathing Mechanism Transport of oxygen Importance of a healthy respiratory system Respiratory system lungs inhalation exhalation Diffusion of oxygen by blood Transport
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System
 Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Unit 8 B: Respiration
 Unit 8 B: Respiration Respiration: Respiration is a chemical reaction that happens in all living cells. It is the way that energy is released from glucose, for our cells to use to keep us functioning.
Unit 8 B: Respiration Respiration: Respiration is a chemical reaction that happens in all living cells. It is the way that energy is released from glucose, for our cells to use to keep us functioning.
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE 24 SEPTEMBER 2014 Lesson Description
 REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE 24 SEPTEMBER 2014 Lesson Description In this lesson, we revise: Gaseous Exchange in Plants & Animals Gaseous Exchange in Humans Excretion in Humans Focus on the Kidney Gaseous
REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE 24 SEPTEMBER 2014 Lesson Description In this lesson, we revise: Gaseous Exchange in Plants & Animals Gaseous Exchange in Humans Excretion in Humans Focus on the Kidney Gaseous
Respiration. The ins and outs
 Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
Respiration The ins and outs Functions 1. To bring O 2 into the body and transfer it to the blood stream 2. To remove CO 2 Circulation and respiration work together to achieve these functions Why Do We
Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration)
 Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration) 1 Question 1 Why do organisms need food? Organisms need food for obtaining energy to perform the vital functions. Question 2 What is a respiratory substrate?
Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration) 1 Question 1 Why do organisms need food? Organisms need food for obtaining energy to perform the vital functions. Question 2 What is a respiratory substrate?
The bar chart shows the amount of water lost from the body of a student on two different days.
 RESPIRATION (2nd PART) Q1. The bar chart shows the amount of water lost from the body of a student on two different days. The student ate the same amount of food and drank the same amount of liquid on
RESPIRATION (2nd PART) Q1. The bar chart shows the amount of water lost from the body of a student on two different days. The student ate the same amount of food and drank the same amount of liquid on
You Might Also Like. I look forward helping you focus your instruction while saving tons of time. Kesler Science Station Lab Activities 40%+ Savings!
 Thanks Connect Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over
Thanks Connect Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over
REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE & EXCRETION 11 SEPTEMBER 2013
 REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE & EXCRETION 11 SEPTEMBER 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Revise gaseous exchange in different animals and examine the structure of the kidney Key Concepts Important
REVISION: GASEOUS EXCHANGE & EXCRETION 11 SEPTEMBER 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Revise gaseous exchange in different animals and examine the structure of the kidney Key Concepts Important
Video. Respiration System. You will use 3 pages of your journal for this lesson. 1. One page for hand written notes onto a journal page
 Respiratory System Video Respiration System You will use 3 pages of your journal for this lesson. 1. One page for hand written notes onto a journal page 2. 2 nd page for diagram 3. 3 rd page for chart
Respiratory System Video Respiration System You will use 3 pages of your journal for this lesson. 1. One page for hand written notes onto a journal page 2. 2 nd page for diagram 3. 3 rd page for chart
PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Parts of the Respiratory System The RS can be divided into two parts: 1. Respiratory Tract, (path that air follows). Nasal passage Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi,
PARTS AND STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Parts of the Respiratory System The RS can be divided into two parts: 1. Respiratory Tract, (path that air follows). Nasal passage Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi,
A.M. WEDNESDAY, 7 January hour
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4471/01 W15-4471-01 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE/BIOLOGY BIOLOGY 2 FOUNDATION TIER A.M. WEDNESDAY, 7 January 2015 1 hour For s use Question Maximum Mark
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4471/01 W15-4471-01 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE/BIOLOGY BIOLOGY 2 FOUNDATION TIER A.M. WEDNESDAY, 7 January 2015 1 hour For s use Question Maximum Mark
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 4
 Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 4 64 minutes 64 marks Page of 0 Q. (a) The table shows an athlete s breathing rate after the end of a race. Use the information shown in the table to draw a line
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 4 64 minutes 64 marks Page of 0 Q. (a) The table shows an athlete s breathing rate after the end of a race. Use the information shown in the table to draw a line
Lesson 6 Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift PS 2.2 a,e PS 3.1i
 Table of Contents Letter to the Student...................................... 5 Letter to the Family....................................... 6 New York State Performance Standards Correlation Chart.......
Table of Contents Letter to the Student...................................... 5 Letter to the Family....................................... 6 New York State Performance Standards Correlation Chart.......
It is a product of proteins broken down in the mammal. It is exchanged for oxygen which is taken into the blood.
 5 The table shows the approximate composition of air breathed out by a mammal. Where does the nitrogen in the air breathed out come from? It is a product of proteins broken down in the mammal. It is a
5 The table shows the approximate composition of air breathed out by a mammal. Where does the nitrogen in the air breathed out come from? It is a product of proteins broken down in the mammal. It is a
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at gaseous exchange in humans in terms of o Ventilation o Inspiration o Expiration o Transport of gases o Homeostatic
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at gaseous exchange in humans in terms of o Ventilation o Inspiration o Expiration o Transport of gases o Homeostatic
RESPIRATION AND EXCRETION
 CHAPTER 13 RESPIRATION AND EXCRETION SECTION 13 1 The Respiratory System (pages 430-438) This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Introduction
CHAPTER 13 RESPIRATION AND EXCRETION SECTION 13 1 The Respiratory System (pages 430-438) This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Introduction
COMBINED SCIENCE 0653/6 CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/6
 Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Name International General Certificate of Secondary Education UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE LOCAL EXAMINATIONS SYNDICATE COMBINED SCIENCE 0653/6 CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES
Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Name International General Certificate of Secondary Education UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE LOCAL EXAMINATIONS SYNDICATE COMBINED SCIENCE 0653/6 CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
EXPERIMENTING The Respiratory and Circulatory Systems CLIL Course University of Nottingham STUDENT S WORKSHEETS
 EXPERIMENTING The Respiratory and Circulatory Systems CLIL Course University of Nottingham STUDENT S WORKSHEETS M. Antònia Berga Sabaté January March 2009 Worksheet 1 You breathe to take air into your
EXPERIMENTING The Respiratory and Circulatory Systems CLIL Course University of Nottingham STUDENT S WORKSHEETS M. Antònia Berga Sabaté January March 2009 Worksheet 1 You breathe to take air into your
Respiratory System Homework
 Respiratory System Homework The R S is the body s breathing equipment. Similar to the D system, it takes S from outside the body (G, particularly O ), circulates them through the body to C and T, then
Respiratory System Homework The R S is the body s breathing equipment. Similar to the D system, it takes S from outside the body (G, particularly O ), circulates them through the body to C and T, then
Name period date assigned date due date returned
 Name period date assigned date due date returned procedure 1. Take one balloon and stretch it out 2. Take one deep breath and blow into the balloon until you cannot breath out anymore. Do Not Take A Second
Name period date assigned date due date returned procedure 1. Take one balloon and stretch it out 2. Take one deep breath and blow into the balloon until you cannot breath out anymore. Do Not Take A Second
INTERNATIONAL TURKISH HOPE SCHOOL
 INTERNATIONAL TURKISH HOPE SCHOOL 2014 2015 ACADEMIC YEAR CHITTAGONG SENIOR SECTION RESPIRATION and GAS EXCHANGE CLASS IX and X Name :... Date :... SYLLABUS CONTENT Section 2: Structures and functions
INTERNATIONAL TURKISH HOPE SCHOOL 2014 2015 ACADEMIC YEAR CHITTAGONG SENIOR SECTION RESPIRATION and GAS EXCHANGE CLASS IX and X Name :... Date :... SYLLABUS CONTENT Section 2: Structures and functions
Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42. Gas Exchange pp Gas Exchange. Gas Exchange in Fish pp Gas Exchange in Fish
 Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42 Fig. 42.24 Gas Exchange pp.979-989 Gas exchange involves the uptake of oxygen and the discharge of carbon dioxide (i.e. respiration or breathing). It is necessary for cellular
Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42 Fig. 42.24 Gas Exchange pp.979-989 Gas exchange involves the uptake of oxygen and the discharge of carbon dioxide (i.e. respiration or breathing). It is necessary for cellular
SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION
 SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION WHEN WE BREATHE, WHAT DO WE BREATHE IN? O2, N2, CO2, O3, NO2 (gas fumes), CO, pollutant, fragrants, toxins, etc. WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF BREATHING IN? WHAT DOES OUR BODY WANT? O2 WHY?
SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION WHEN WE BREATHE, WHAT DO WE BREATHE IN? O2, N2, CO2, O3, NO2 (gas fumes), CO, pollutant, fragrants, toxins, etc. WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF BREATHING IN? WHAT DOES OUR BODY WANT? O2 WHY?
Human Biology Respiratory System
 Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
Hyndland Secondary School Biology Department
 Hyndland Secondary School Biology Department Body in Action Homework and Question Booklet 1 Body in Action (a) Movement... 2 Skeleton... 2 Joints... 3 Body in Action (b) The need for Energy... 5 Heart...
Hyndland Secondary School Biology Department Body in Action Homework and Question Booklet 1 Body in Action (a) Movement... 2 Skeleton... 2 Joints... 3 Body in Action (b) The need for Energy... 5 Heart...
--- Respiration in Organisms. Lesson at a Glance
 --- Respiration in Organisms Lesson at a Glance. Respiration is essential for survival of every living organism whether it is an animal or a plant. It is a process by which living organisms produce energy
--- Respiration in Organisms Lesson at a Glance. Respiration is essential for survival of every living organism whether it is an animal or a plant. It is a process by which living organisms produce energy
Respiration. The resspiratory system
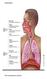 Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
Pop Quiz. What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach?
 Pop Quiz What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach? Respiratory System Review Cellular respiration: obtain glucose and oxygen, get
Pop Quiz What produces mucus, HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach? List a water soluable vitamin What is a ruminant stomach? Respiratory System Review Cellular respiration: obtain glucose and oxygen, get
Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment
 Name: Date: Mark: / 45 Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following
Name: Date: Mark: / 45 Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following
The diagram shows an alveolus next to a blood capillary in a lung. (a) (i) Draw a ring around the correct answer to complete the sentence. diffusion.
 BREATHING / GAS EXCHANGE. NAME. Q.Gas exchange takes place in the lungs. The diagram shows an alveolus next to a blood capillary in a lung. The arrows show the movement of two gases, A and B. (a) (i) Draw
BREATHING / GAS EXCHANGE. NAME. Q.Gas exchange takes place in the lungs. The diagram shows an alveolus next to a blood capillary in a lung. The arrows show the movement of two gases, A and B. (a) (i) Draw
Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system
 Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system 1. Name the following : i. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. ii. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous rings.
Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system 1. Name the following : i. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. ii. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous rings.
25/4/2016. Physiology #01 Respiratory system Nayef Garaibeh Rawan Alwaten
 25/4/2016 Physiology #01 Respiratory system Nayef Garaibeh Rawan Alwaten Respiratory System Introduction: - We breath while we are sleeping, talking, working and resting. - Respiratory diseases are abundant
25/4/2016 Physiology #01 Respiratory system Nayef Garaibeh Rawan Alwaten Respiratory System Introduction: - We breath while we are sleeping, talking, working and resting. - Respiratory diseases are abundant
The physiological functions of respiration and circulation. Mechanics. exercise 7. Respiratory Volumes. Objectives
 exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
Frog Dissection. PreLab: 1. Where do frogs get their energy? Draw a simple food chain to illustrate.
 Name Date Frog Dissection Class # PreLab: Amphibian Reading As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but they must return to water to reproduce. Eggs are laid
Name Date Frog Dissection Class # PreLab: Amphibian Reading As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but they must return to water to reproduce. Eggs are laid
Lesson: What a Gas! Human Respiration 7 th Grade Life Science November 30 th -31 st. Rationale/Goal:
 Lesson: What a Gas! Teacher: Unit Theme/Course: Date: Timing: Kaylan Duthie Human Respiration 7 th Grade Life Science November 30 th -31 st 1.5 days Rationale/Goal: Students will draw upon a previous lab
Lesson: What a Gas! Teacher: Unit Theme/Course: Date: Timing: Kaylan Duthie Human Respiration 7 th Grade Life Science November 30 th -31 st 1.5 days Rationale/Goal: Students will draw upon a previous lab
Introduction. Respiration. Chapter 10. Objectives. Objectives. The Respiratory System
 Introduction Respiration Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body Plays a role in the regulation of acidbase balance during exercise Objectives
Introduction Respiration Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body Plays a role in the regulation of acidbase balance during exercise Objectives
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system
 CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
Gas Exchange ACTIVITY OVERVIEW SUMMARY KEY CONCEPTS AND PROCESS SKILLS KEY VOCABULARY. Teacher s Guide B-75 L A B O R ATO R Y
 Gas Exchange 17 40- to 2 50-minute sessions ACTIVITY OVERVIEW L A B O R ATO R Y SUMMARY This activity explores the role of the respiratory system in the regulation of gases in the blood. Students investigate
Gas Exchange 17 40- to 2 50-minute sessions ACTIVITY OVERVIEW L A B O R ATO R Y SUMMARY This activity explores the role of the respiratory system in the regulation of gases in the blood. Students investigate
Sc ienc e 9-Biology Work sheet 8-2 A Single Breat h & Tak ing Care
 Unit 2 Your Living Body Sc ienc e 9-Biology Work sheet 8-2 A Single Breat h & Tak ing Care Name No pen or pencil No Textbook 20 Due Date Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Read pages 159-167
Unit 2 Your Living Body Sc ienc e 9-Biology Work sheet 8-2 A Single Breat h & Tak ing Care Name No pen or pencil No Textbook 20 Due Date Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Read pages 159-167
The Respiratory System
 Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, complete the flowchart
Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, complete the flowchart
Breathing: The normal rate is about 14 to 20 times a minute. Taking in of air is called Inspiration and the forcing out of air is called Expiration.
 Biology 12 Respiration Divisions of Respiration Breathing: entrance and exit of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration: exchange of gases(o2 and CO2) between air (in alveoli) and blood Internal
Biology 12 Respiration Divisions of Respiration Breathing: entrance and exit of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration: exchange of gases(o2 and CO2) between air (in alveoli) and blood Internal
Use scientific principles to explain how the sprayer works. You may use diagrams to support your answer.
 4.3 Marking Key This guide includes sample answers, task-specific observable elements, (Appendices 1 and 2), descriptive evaluation rubrics for each competency (Appendices 3 and 4), and non-descriptive
4.3 Marking Key This guide includes sample answers, task-specific observable elements, (Appendices 1 and 2), descriptive evaluation rubrics for each competency (Appendices 3 and 4), and non-descriptive
Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System
 Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System Animals require a continuous supply of oxygen (O 2 ) for cellular respiration, and they must expel carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), the waste product of this
Lesson 9.1: The Importance of an Organ Delivery System Animals require a continuous supply of oxygen (O 2 ) for cellular respiration, and they must expel carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), the waste product of this
Then the partial pressure of oxygen is x 760 = 160 mm Hg
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: the uptake of molecular oxygen (O2) from the environment and the discharge of
1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: the uptake of molecular oxygen (O2) from the environment and the discharge of
Show Me Hand In. Correct and Hand In Again By. Read pages of SP to help you answer the following questions: 1. Name 4 gases contained in air:,
 Name 20 Due Date Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Read pages 151-157 of SP to help you answer the following questions: 1. Name 4 gases contained in air:, and. 2. What are two types of solid
Name 20 Due Date Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Read pages 151-157 of SP to help you answer the following questions: 1. Name 4 gases contained in air:, and. 2. What are two types of solid
How Animals Survive (Circulation and Gas Exchange)
 How Animals Survive (Circulation and Gas Exchange) by Flourence Octaviano on February 16, 2018 lesson duration of 30 minutes under Earth and Life Science generated on February 16, 2018 at 12:45 am Tags:
How Animals Survive (Circulation and Gas Exchange) by Flourence Octaviano on February 16, 2018 lesson duration of 30 minutes under Earth and Life Science generated on February 16, 2018 at 12:45 am Tags:
The equation describes anaerobic respiration in muscle cells. How can you tell from the equation that this process is anaerobic?
 Respiration. Name.. Q.Anaerobic respiration happens in muscle cells and yeast cells. The equation describes anaerobic respiration in muscle cells. glucose lactic acid (a) How can you tell from the equation
Respiration. Name.. Q.Anaerobic respiration happens in muscle cells and yeast cells. The equation describes anaerobic respiration in muscle cells. glucose lactic acid (a) How can you tell from the equation
The Respiratory System. Medical Terminology
 The Respiratory System Medical Terminology The respiratory system is where gas exchange occurs via respiration; inhalation/exhalation. pick up oxygen from inhaled air expels carbon dioxide and water sinus
The Respiratory System Medical Terminology The respiratory system is where gas exchange occurs via respiration; inhalation/exhalation. pick up oxygen from inhaled air expels carbon dioxide and water sinus
Respiration. Chapter 33
 Respiration Chapter 33 Learning Objectives: Understand the basis of gas exchange and factors that influence diffusion of gases in and out of tissues Compare and contrast different respiratory systems among
Respiration Chapter 33 Learning Objectives: Understand the basis of gas exchange and factors that influence diffusion of gases in and out of tissues Compare and contrast different respiratory systems among
Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired
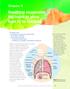 Chapter 6 Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired This chapter covers: the structure of the human gas exchange system the mechanism of breathing gas exchange in the alveoli the concept
Chapter 6 Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired This chapter covers: the structure of the human gas exchange system the mechanism of breathing gas exchange in the alveoli the concept
CHAPTER 3: The cardio-respiratory system
 : The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
: The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
system. and then into the tissues. Diffusion of wastes such as Carbon Dioxide from tissues into blood and out of blood into the lungs.
 Respiratory System 1.Exchange Why do of we gases breathe? into the Think blood of all and the tissues. reasons Diffusion why we of Oxygen need a respiratory into blood from the lungs system. and then into
Respiratory System 1.Exchange Why do of we gases breathe? into the Think blood of all and the tissues. reasons Diffusion why we of Oxygen need a respiratory into blood from the lungs system. and then into
Experiment 18 Properties of Gases
 Experiment 18 Properties of Gases E18-1 E18-2 The Task In this experiment you will investigate some of the properties of gases, i.e. how gases flow, their phase changes and chemical reactivity. Skills
Experiment 18 Properties of Gases E18-1 E18-2 The Task In this experiment you will investigate some of the properties of gases, i.e. how gases flow, their phase changes and chemical reactivity. Skills
Respiration - Human 1
 Respiration - Human 1 At the end of the lectures on respiration you should be able to, 1. Describe events in the respiratory processes 2. Discuss the mechanism of lung ventilation in human 3. Discuss the
Respiration - Human 1 At the end of the lectures on respiration you should be able to, 1. Describe events in the respiratory processes 2. Discuss the mechanism of lung ventilation in human 3. Discuss the
Chapter 16 Respiratory System
 Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation
 Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing and the first step in the respiratory process. Pulmonary ventilation brings in air with a new supply
Respiratory Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing and the first step in the respiratory process. Pulmonary ventilation brings in air with a new supply
Gaseous exchange. Grade 11
 z Gaseous exchange Grade 11 z Terminology 1. Breathing 2. Gaseous exchange 3. Diffusion 4. Spongy mesophyll cells 5. Tracheae 6. Gills 7. Alveoli 8. Larynx 9. Diaphragm 10. Endothelium 1. Pleura 2. Squamous
z Gaseous exchange Grade 11 z Terminology 1. Breathing 2. Gaseous exchange 3. Diffusion 4. Spongy mesophyll cells 5. Tracheae 6. Gills 7. Alveoli 8. Larynx 9. Diaphragm 10. Endothelium 1. Pleura 2. Squamous
Frog Dissection. External Observation
 Frog Dissection External Observation Use the diagram below to locate and identify the external features of the head. Find the mouth, external nares, tympani (ear drum), eyes, and nictitating membranes
Frog Dissection External Observation Use the diagram below to locate and identify the external features of the head. Find the mouth, external nares, tympani (ear drum), eyes, and nictitating membranes
General Certificate of Secondary Education
 General Certificate of Secondary Education 2011 2012 Science: Double Award (Modular) Living Organisms and the Processes of Life End of Module Test Higher Tier A [GDA02] MONDAY 27 FEBRUARY 2012 9.0 am 10.15
General Certificate of Secondary Education 2011 2012 Science: Double Award (Modular) Living Organisms and the Processes of Life End of Module Test Higher Tier A [GDA02] MONDAY 27 FEBRUARY 2012 9.0 am 10.15
Outline - Respiratory System. Function of the respiratory system Parts of the respiratory system Mechanics of breathing Regulation of breathing
 Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
Chapter 22 Gas Exchange
 Chapter 22 Gas Exchange PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction: Surviving in Thin Air
Chapter 22 Gas Exchange PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction: Surviving in Thin Air
 Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
Living with. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease COPD. Breathing and Relaxation
 Living with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease COPD Breathing and Relaxation Anatomy and Physiology of COPD Breathing Techniques Positions to Reduce Shortness of Breath Relaxation Exercise Breathing
Living with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease COPD Breathing and Relaxation Anatomy and Physiology of COPD Breathing Techniques Positions to Reduce Shortness of Breath Relaxation Exercise Breathing
Supporting inquiry based teaching and learning. Respiration. Student Name: Class:
 Supporting inquiry based teaching and learning Respiration Student Name: Class: Teacher Name: School: Question 1 a) Respiration is the process that the swimmer uses to release energy from the digested
Supporting inquiry based teaching and learning Respiration Student Name: Class: Teacher Name: School: Question 1 a) Respiration is the process that the swimmer uses to release energy from the digested
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Learning Outcomes Identify the following structures in the lungs: windpipe, bronchus, bronchioles and air sacs State the function of the air sacs State the path oxygen takes when
The Respiratory System Learning Outcomes Identify the following structures in the lungs: windpipe, bronchus, bronchioles and air sacs State the function of the air sacs State the path oxygen takes when
Respiratory System Review
 KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
Then the partial pressure of oxygen is. b) Gases will diffuse down a pressure gradient across a respiratory surface if it is: i) permeable ii) moist
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: Relies on the diffusion of gases down pressure gradients. At sea level, atmosphere
1 AP Biology March 2008 Respiration Chapter 42 Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces. 1) Gas exchange: Relies on the diffusion of gases down pressure gradients. At sea level, atmosphere
(Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System
 (Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System I. (Slide 2) The Respiratory Tract A) Major structures and regions of the respiratory Tract/Route INTO body 1) nose 2) nasal cavity 3) pharynx 4) glottis 5)
(Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Respiratory System I. (Slide 2) The Respiratory Tract A) Major structures and regions of the respiratory Tract/Route INTO body 1) nose 2) nasal cavity 3) pharynx 4) glottis 5)
What is breathing an respiration?
 LE SSON 15 What is breathing an respiration? You need energy to live. So do birds, trees, and bacteria. All living things need energy to carry out the life processes. And, there can be no life without
LE SSON 15 What is breathing an respiration? You need energy to live. So do birds, trees, and bacteria. All living things need energy to carry out the life processes. And, there can be no life without
2.1.1 List the principal structures of the
 physiology 2.1.1 List the principal structures of the The principle structures of the respiratory are: Nose/Mouth used for inhalation of oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide rich air Pharynx -
physiology 2.1.1 List the principal structures of the The principle structures of the respiratory are: Nose/Mouth used for inhalation of oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide rich air Pharynx -
Lung Volumes and Capacities
 Lung Volumes and Capacities Normally the volume of air entering the lungs during a single inspiration is approximately equal to the volume leaving on the subsequent expiration and is called the tidal volume.
Lung Volumes and Capacities Normally the volume of air entering the lungs during a single inspiration is approximately equal to the volume leaving on the subsequent expiration and is called the tidal volume.
(A) The partial pressure in the lungs is higher than in the blood, and oxygen diffuses out of the lungs passively.
 DAT Biology - Problem Drill 12: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement about the partial pressure of oxygen inside the lungs is correct? Question #01 (A) The partial pressure in
DAT Biology - Problem Drill 12: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement about the partial pressure of oxygen inside the lungs is correct? Question #01 (A) The partial pressure in
Circulatory And Respiration
 Circulatory And Respiration Composition Of Blood Blood Heart 200mmHg 120mmHg Aorta Artery Arteriole 50mmHg Capillary Bed Venule Vein Vena Cava Heart Differences Between Arteries and Veins Veins transport
Circulatory And Respiration Composition Of Blood Blood Heart 200mmHg 120mmHg Aorta Artery Arteriole 50mmHg Capillary Bed Venule Vein Vena Cava Heart Differences Between Arteries and Veins Veins transport
Gas Exchange in Animals. Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2. Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial
 Gas Exchange in Animals Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2 Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial Respiratory surface! skin, gills, lungs Circulatory System O2/CO2
Gas Exchange in Animals Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2 Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial Respiratory surface! skin, gills, lungs Circulatory System O2/CO2
Anatomy and Physiology Part 11: Of Blood and Breath by: Les Sellnow
 Anatomy and Physiology Part 11: Of Blood and Breath by: Les Sellnow There are few similarities between horses and automobiles, but in a manner of speaking, the horse's circulatory and respiratory systems
Anatomy and Physiology Part 11: Of Blood and Breath by: Les Sellnow There are few similarities between horses and automobiles, but in a manner of speaking, the horse's circulatory and respiratory systems
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System (pages 112 120) Respiratory System Functions (pages 113 114) Key Concept: The respiratory system moves oxygen from the outside environment into the body. It also removes carbon dioxide
The Respiratory System (pages 112 120) Respiratory System Functions (pages 113 114) Key Concept: The respiratory system moves oxygen from the outside environment into the body. It also removes carbon dioxide
Section Two Diffusion of gases
 Section Two Diffusion of gases Lecture 5: Partial pressure and the composition of gasses in air. Factors affecting diffusion of gases. Ventilation perfusion ratio effect on alveolar gas concentration.
Section Two Diffusion of gases Lecture 5: Partial pressure and the composition of gasses in air. Factors affecting diffusion of gases. Ventilation perfusion ratio effect on alveolar gas concentration.
