ECG-Heart Rate Compact Trainer An Awareness Control Stress-Reduction Program Computer-aided Guided Breathing Relaxation Exercises
|
|
|
- Anna Christiana Bradford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ECG-Heart Rate Compact Trainer An Awareness Control Stress-Reduction Program Computer-aided Guided Breathing Relaxation Exercises PhysioData 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 1/49
2 CONTENTS: Organization of this manual: This manual provides basic instruction on the signals and training tasks used in these applications. It also does provide examples of how to train signals using the screens and exercises. SIGNAL BASICS OVERVIEW OF PROGRAMS...3 GETTING A GOOD SIGNAL...3 CHECK SIGNALS:...3 SIGNALS TESTS EMG AND ECG...3 HOW TO TRAIN. UPPER THORACIC MUSCLE TENSION...3 HEART PULSE [ELECTROCARDIOGRAM, ECG]...3 HEART RATE AND BREATHING WAVES...3 BREATHING PACERS AND RESONANT FREQUENCY...3 CARDIO-RESPIRATORY SYNCHRONY...3 INCREASE THE MINIMUM-MAXIMUM HEART RATE WAVES...3 INCREASE THE AVERAGE HEART RATE WAVES:...3 WATCH THE SPECTRAL HRV WAVES...3 BOOST THE LF WAVES...3 LOWER THE VLF WAVES...3 RESONANT BREATHING FREQUENCY ANALYSIS FIND YOUR OPTIMAL BREATH...3 OPTIMAL BREATHING REPORT...3 APPENDICES APPENDIX: FINE-TUNING SIGNALS...3 APPENDIX: PRO SERIES ADVANCED TRAINING DISPLAYS:...3 APPENDIX: ABOUT HRV & HR FEEDBACK...3 APPENDIX: ADDITIONAL EXERCISES...3 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 2/49
3 "Heart Wave Fitness A Personal Stress Management Aid Welcome to Heart Wave Fitness Personal Awareness Training: Heart Wave Fitness is a unique educational application. It is a tool to train you in self-awareness and deep relaxation. What you learn from Heart Wave Fitness Trainer is a kind of double-awareness, a better awareness of things in your daily life that trigger arousal and relaxation, and a companion awareness of how your body responds to these situations. This is entirely consistent with a recent set of discoveries in mind-body medicine in stress management, called mindfulness. Mindfulness deals with stress reactivity by emphasizing body awareness and self-appraisal of eminent threat. Our Heart Wave Fitness Trainer programs focus on the same self-education areas, and directly extends mindfulness to real-time mind-body awareness, a well-documented field in biofeedback and applied psychophysiology. The exercises presented here are a form of mind-body awareness, and are great fun to learn. Once learned, most users report a new awareness of small bodily changes that may trigger a stress response, and feel more confident to cope with and recover from everyday stressors. You may use these programs as they are. Some wish to combine these exercises with advanced meditation, creativity and breathing techniques. If you seek additional training outside the scope of this little training device, we recommend that you first learn these techniques from experts in the field, as these are not a part of a basic educational stress management device. Note: This device does not shock nor inject current into the body. It is purely passive. Our ECG is an educational device. The way we place our electrodes is different from that used by medical devices, and will give a signal signature that is different from those used by medical devices. 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 3/49
4 OVERVIEW OF PROGRAMS We include two kinds of programs. Self-Trainer Series: The first is for laypeople who want to use physiology-guided exercises to improve breathing-relaxation and stress management skills. The self-trainer program guides you through stages of exercises. EMG training. Breathing Training. HR Wave Training. HR and Breathing Wave Co-Training,. LF Boost Training. VLF Reduction Training Screens. Pro-Trainer Series: The second set of programs, the Pro series, is provided for use by stress management coaches, and related professionals who can use them educationally to coach clients to maximize health or reduce stress. INSTALLATION: Insert the CD. Double click on the SmartHeart.exe file. Follow instructions. Finish. Restart your computer. HEART WAVE FITNESS TRAINER PROGRAMS The Installation Disk inserts the following programs into the Select Application menu: Heart Wave Fitness Trainer A very basic guide for the educated layman. It includes feedback sounds, one for each signal, that are enabled by pressing the Speaker icon on the side menu. Heart Wave Pro : -Optimal Breath [-ResFreq] This program guides you through a series of structured, paced breathing exercises. The purpose is to discover the optimum breathing rate to trigger a balanced heart rate rhythm. This test was developed by a University research team and remains experimental. Try it for fun! Heart Wave Pro - Fitness Coach This application as a variety of training screens. It includes advanced screens used by stress management specialists. It is intended for use by experts. Laymen may explore these screens. It is best to master the exercises in the Heart Wave Fitness Trainer first. Heart Wave Signals :TUTORIAL This is a technical guide to different signals extracted from Heart Rate and Chest EMG. It is provided for those who are interested in the technical aspects of this physiology. 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 4/49
5 INTRODUCTION CARDIO-RESPIRATORY SYNCHRONY When breathing exercises are effective, they place the body into balanced Cardio-Respiratory Synchrony. CRS is also called Respiratory Sinus Arrhythmia (RSA) There are all sorts of breathing techniques in today's culture. Some are better than others in achieving CRS. They all stem from ancient meditation practices to modernized versions with ritualized, extended breathing routines. But is there an optimum breathing technique? Yes, but you need science to guide you. Our Heart Wave detector can indicate precisely how different breathing techniques affect your nervous system, especially the breath-heart wave connection. Using information presented to you about your own breathing and heart rhythms, you can use that information to find the breathing technique which is best for you. This scientific approach is sometimes called effortless breathing. It is based on decades of biomedical and learning research. Here are some facts as background: The heart does not beat at a constant rate. It goes up with stress or exertion, and down with rest or relaxation. This is classic stress-relaxation theory. A HR of 120 beats per minute is high, and 60 bpm is low. The rate of the heart varies or cycles with easy breathing. It only varies by 5 to 15 beats, per breath. In fact this kind of breath-wave HR change is healthy. This is a special form of physiological 'variability,' called heart rate variability. Breath-wave HR cycles are not linked to stress-relaxation, but to breathing itself. Heart rate increases when breathing in and decreases when breathing out. This is called Heart-Rate Variability or HRV. EXAMPLE: This graph shows the ideal heart rate variability. This is your goal for training- a perfectly symmetrical sine wave! TECHNICAL: The degree of fluctuation in heart rate is controlled by several factors, including regular impulses from the baroreceptors (pressure sensors) in the main arteries. Heart rate normally has a lot of variability. Loss of this variability is uniformly associated with a negative effect on health. Interestingly it is as good a predictor of the effects of heart problems (and possible death 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 5/49
6 from heart problems) as are the traditional psychosocial and health risk factors for heart problems (smoking, diet, exercise etc). HRV and HEALTH: Heart-rate variability is decreased in heart disease, chronic fatigue syndrome, diabetic autonomic neuropathy, panic and phobias, generalized anxiety, major depression, anorexia, irritable bowel syndrome, fibromyalgia and other pain disorders, aging and stress. HRV and EXERCISE: Heart-rate variability is increased with exercise. o Heart rate variability change with breathing is also used as an index of vagal tone. (vagal tone is an indication of the health of the vagus nerve which influences heart, breathing and gut function). So, to be clear, Cardio-Respiratory Synchrony feedback is boosting the synchrony between breathing and the heart rate wave. HRV FEEDBACK: This kind of biofeedback is a new form of stress-reduction. Like earlier kinds of stress management, this kind of relaxed-breathing feedback should be useful in a variety of disorders where it is reasonable to assume that loss of homeostasis in the autonomic system is contributing to symptoms. HOW WE PICK UP HEART RATE AND BREATHING: 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 6/49
7 BREATHING DETECTION: This program uses muscle activity detection from the arm and chest to measure your breathing waves. The muscles of respiration, shown above, trigger together to expand the chest during an inhale and release the muscles during exhale. When you learn to deeply relax, your arms are calm and quiet your breathing is slow and regular. So the only relaxed muscles that move are the breathing muscles. HEART RATE VARIABILITY DETECTION: We also measure the electrical pulse from heart muscle, the electrocardiogram. We use that pulse to find Heart Rate, the number of beats per minute. TECHNICAL : A hidden software loop detects HRV for Heart Rates. This software loop abstracts information from the heart rhythm from inside the cardiovascular control system [see above]. This rhythm is associated with brain centers that constantly regulate and adjust our unconsiuos nervous sytem. It gives a clear picture of our background sympathetic [arousal] and parasympathetic [relaxation] responses. Breathing training, when done properly, brings these opposing arousal-relaxation responses into balance and can prompt a strong biological response of deeper relaxation and stress resilience. 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 7/49
8 GETTING A GOOD SIGNAL Hook up is easy. Attach the wrist-bands. Wet the wrists with alcohol, wet the device sensors disks with alcohol, keep the surfaces moist, and insert the sensors under the wrist bands. Here are the instructions in detail: Slip the elastic Wrist Bands below the wrist-joint. Using an alcohol wipe, clean the skin below the wrists. The goal is to wipe away any dead skin or lotion to allow good contact between the gel-free electrodes and the skin. Leave the alcohol to keep the skin moist. Insert the black sensor box, electrodes down, on one wrist. Make sure the skin is moist. Do the same for the second wrist. Allow several seconds for the sensors to stabilize. NOTE: The 'interference' Signal may remain high until the amplifiers stabilize 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 8/49
9 CHECK SIGNALS People s skin varies. If you have dry skin for example it will require more preparation to get a good signal. Dry climates, high altitude and air conditioning can also lead to dry skin. Likewise voltage leaks form motors and other electronics can generate signals thart interfere with a clean signal. The only way to know if you have a good connection is to watch the two check signal monitors, Sensor Contact and Interference. SIGNAL INTEGRITY CHECKS Sensor Contact Test: This signal continuously monitors the sensor connection. Sensor Test assures you that the sensors are indeed detecting the signal from the sensor source. If you get a high reading, check the sensor contact with the skin. It may have moved or dried out. Interference Test: Even a good sensor can produce a noisy signal - if you are monitoring the signal in an electrically noisy environment. The Interference Test continuously monitors ECG and EMG signals and tells you when interference is so high it will degrade the signal. This means that you will always know if the heart rate is 'true' and can immediately check if outside interference is corrupting your data. 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 9/49
10 There is a third way of knowing you have a good signal: look for a 60 Hz spike in the graph, FFT-EMG. This graph separates all the frequencies in an EMG signal, like a graphics equalizer displays. If you see a 60 Hz spike, you have interference from line voltage,. Check your contacts and try another location. EXAMPLE: Raw EMG WAVE on top graph: It looks normal. EMG 60 Hz SPIKE: Note the 60 Hz spike in the second graph.. Sensor Contact Test: Here the basic sensor contact is good. Interference Test: The Interference is very high. Even a good sensor can produce a noisy signal - if you are monitoring the signal in an electrically noisy environment. What caused this interference? A dry electrode! The electrodes were placed below the wrists without premoistening with alcohol.this example also demonstrates how robust our EMG detection signal is. Even with a large interference response, the basic EMG signal [top graph] is still maintained. KEY POINT: Once properly moistened it may take several seconds to absorb into the skin enough to bring the Interference signal down. 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 10/49
11 SIGNALS TESTS EMG and ECG Raw EMG muscle signals should look smooth and centered: When relaxed, you see regular spikes followed by a quiet period. The spikes come from electrical pulses generated by heart muscle, one big spike per beat. Heart Rate pulses are expected in the raw EMG signal. This is not a mistake. The spikes indicate a good signal. Large excursions above zero indicate movement, poor connection. INSPECT THE SPECTRAL EMG BANDS SPECTRAL EMG WAVES : Should look low at rest and have no spikes at 60 or 120 or 240 Hz. Large SPIKES AT 60/120/240 Hz indicate poor connection, electrical noise. A big yellow spike shows electrical line frequency signal contamination, which appears as regular 50 Hz or 60 Hz spikes within the display. Squeeze your shoulders and the spectral display should spike up for the duration of a contraction. CHECK UPPER THORACIC MUSCLE TENSION WAVEFORMS: Here the EMG detects muscle and heart electrical activity across the chest. 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 11/49
12 The top graph, EMG, is derived from the Raw EMG signal shown with spikes in the earlier graphs. Here however the EMG signal is mathematically changed to an amplitude signal. The greater the muscle tension, the larger the amplitude. The bottom graph is a smoothed version of the Amplitude signal. By smoothing, it shows a little more clearly the underlying chest muscle activation during a relaxed inhale. The result is a breathing wave, very responsive to any movement [ it over-rides the breathing wave] and to true deep relaxed chest breathing. BREATHING SIDEBAR: Abdominal vs Thoracic Breathing? Breathing experts do emphasize abdominal rather than chest or thoracic breathing. However balanced breathing requires both. At rest, the accessory chest muscles naturally fire on exhale and release on inhale. If you are suspicious about missing abdominal breathing, be sure to go to the next chapter, on HRV. When the Low Frequency Wave on the spectral HRV elevates, the frenic nerve controlling abdominal breathing must be engaged. So to detect good abdominal breathing look at the HR waves, discussed next. WHAT TO TRAIN: UPPER THORACIC MUSCLE TENSION Here the EMG detects muscle and heart electrical activity across the chest. The goal is to become so relaxed in your upper torso that the EMG signal shows only the cyclical contraction of the accessory muscles of respiration. The slightest movement will over-ride the smooth muscle-breathing lines, so you must really concentrate on very deep upper body relaxation. The Tone varies with muscle tension. The top graph shows direct muscle tension. Squeeze and release a fist to see it in action. The second graph shows the same raw signal, but it is smoothed out. If you wait about 30 seconds, each graph will self-center, and the signals will look bigger 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 12/49
13 Here both graphs appear small. Wait a few seconds and they will re-adjust for better viewing... As you relax more and more, the top EMG graph will start to show your background breathing rhythm. We have added a new signal, RESP-emg, which filters and smoothes the raw EMG. As your breathing rhythm becomes stronger, this bottom graph automatically re-centers and amplifies your signal so you get a clear view of your background breathing pattern. 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 13/49
14 When the respiration wave begins to show breathing cycles, the green spectral EEG signal also calms down, and you will see a smooth pulsing wide-band moving up and down with each breath. Some clients like to watch this pulsing band and use it as feedback to shape the breathing response. Here is another example. As breathing slows it becomes more regular, note the raw EMG. It too shows a subtle cycle in the imbedded heart pulses, up and down with each chest inhale-exhale cycle. 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 14/49
15 HEART PULSE [ElectroCardioGram, ECG] The bottom display shows the energy-frequency pattern distributed across every beat of the heart, every interbeat interval. It pulses in harmony with you heart beat, and some find it a pleasant display for relaxation. It will pulse a little faster as you inhale, and a little slower when you exhale. As you get better, you may also see some little bumps that increase when you inhale and decrease when you exhale. Try it for fun. [These bumps are not related to good or bad health practices, but are interesting]. Your HR is calculated after every beat. That is why it is step-like. The HR [AVG] smoothes out your HR to get a longer-term view of your average HR. This is the ideal HR Wave. With practice - lots of practice - you can achieve this. This is a typical beginner s Average HR. This average is good for estimating your overall level of relaxation. 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 15/49
16 Try to keep your muscles relaxed, your breathing relaxed, and see if you can lower your average HR. This may take several minutes. Heart Rate [HR] is updated with each heart beat. HR is derived from the the period detector (bottom). Heart-rate period is also known as Inter-beat interval (IBI) and is measured in milliseconds, from R-wave to R-wave. TECHNICAL NOTE: Period is the signal from which spectral HRV bands (HF, LF, VLF) are calculated. However period as a signal is rarely used. We show it here to demonstrate the direct relationship between period (IBI) and Heart Rate (HR). HR is updated every beat, and is just a mathematical conversion of 'period' measured in milliseconds to HR measured in 60 second epochs. 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 16/49
17 WHAT TO TRAIN Heart Rate and Breathing Waves Got your shoulders relaxed? Breathing a little easier? OK, let's move to the next step. Here we want to explore ways to maximize the difference between highest and lowest Heart Rates. For our purposes, think of this as a HR Wave. Watch your HR wave. Let it settle down for a few minutes. When it looks generally stable, try to INHALE at the point HR begins to rise. Keep your shoulders relaxed and inhale from the diaphragm. BE SMART DURING EARLY TRAINING! Just like aerobic exercise, start slowly, and practice in brief work-long rest cycles until you are confident in controlling your HR waves. Exhale slowly using the breath pacer- at about 9 breaths per minute. But do not do it for a minute at first! Do it for a maximum of 3 breaths in the beginning. Some people fell short of breath. If you do, just stop, and stay relaxed. As you gain skills here, go back to one or two breaths, stop forced breathing for about a minute, and try again. Still feel short? Stop, detach, walk around, and try it about 10 minutes If using the Minimum-Maximum HR screens, there is a one-second DELAY in updating. This number updates every time the HR shifts from decelerating to accelerating. If in the middle of a 'cycle' the HR temporarily moves down a beat, this gives the number of HR beats to that point, and resets the HR detector for the next cycle. So to make the Max-Min HR difference as big as possible, a person must learn to smooth the HR cycles. 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 17/49
18 WHAT TO TRAIN BREATHING PACERS AND RESONANT FREQUENCY Breathing pacers are used to help pace breathing. Paced breathing at 5 to 7 breaths per minute help zero in on a person's OPTIMAL HRV- Lf-elevations. Lf-elevations are triggered by different breathing rates for different persons.. Each person has an optimal rate, usually between 5.5 and 6.5 bpm. This optimal rate is called the Resonant Frequency Rate. You have several Breathing pacers: A line, a balloon, and a circle. Breathing Pattern Whrn three different signals are displayed on screen a breathing pacer, a respiration wave form, and a heart rate variability wave form, the effect of correct breathing can be easily observed as an increase in heart rate variability and an increase in synchrony between the HR waveform and the Respiration signal. The HR signal can be hidden with the Show/Hide button if just the pacer and Respiration signal are desired. 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 18/49
19 Adjusting the Breathing Pacer To adjust the breathing pacer, click on the small green box near the top of your screen next to the word Pattern. The white dot that appears indicates that the breathing pattern signal has been selected. The buttons in the left hand signal control bar are used to modify all signals on all screens. By selecting Pattern you have assigned the signal control bar to the breathing pattern signal so that you can modify it. Click on the Modify Settings button In the Breath Parameter box, adjust the target breath rate and inhalation time. These are expressed as percentages of the total breath time, with the sum of inhale time, inhale hold, exhale time and exhale hold equal to 100%. (The numbers of hold times are part of the inhale and exhale percentages). By adjusting the inhale time the exhale time automatically adjusts, and adjusting the exhale time automatically alters the inhale time. Also notice the changes in the wave form. Click on the small x in the upper right hand corner of the Breath Parameter window to close it. WHAT TO TRAIN CARDIO-RESPIRATORY SYNCHRONY This graph shows that HR waves and Breath waves are starting to synchronize, a good beginning. Here is another beginning pattern. Note that HR waves are not yet cyclical.. Remember that movement, including talking, can keep the signals from forming waves. 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 19/49
20 Here the client is prompted to start an inhale each time the HR wave drops, then starts upwards. At first, this is difficult.. Trying to inhale as HR rises takes practice but not a lot of practice.breathing is starting to follow HR Now HR follows breathing pretty closely. WHAT TO TRAIN Increase the Minimum-Maximum Heart Rate Waves The Minimum-Maximum HR Wave signal is a wave detector. Every time the HR wave goes up [HR increases], it resets a counter to zero and counts the number of heart beats until the wvae goes down again. It give a graph of the total number of beats per wave. 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 20/49
21 However it is never IMMEDIATE. It provides a number only after the wave starts descending, providing accurate but slightly delayed information. The AVERAGE Min-Max HR gives you a running average of the Min-Max HR. It provides a baseline, an average, over about 20 seconds. When there is a big upwards shift in Min-Max HR, the wave shows a rainbow of red and yellow. These colored elements are an easy way of tracking progress, and how constant or regular the client is in producing waves at the same maximum number of beats. The closer the Min-Max HR is to the Average Min-Max, the more stable is the HRV. NOTE: The Max-Min HR(AVG) signal is a useful way to detect the trend in Max-Min HR, smoothed out over 60 seconds. Max-Min HR It is also an easy way of looking at overall stress or arousal levels across longer periods. As a person deeply relaxes, the trend should also go up over time. Note the drop out here. For a period of time, we lost a good HRV signal. HR [middle graph] began to flatten out here, then came back to a good wave. 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 21/49
22 Another example of Minimum-Maximum Heart Rate. Here is a good burst of Min-Max HR after a period of instability. 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 22/49
23 WHAT TO TRAIN Increase the Average Heart Rate Waves This is an ideal HR Wave. With practice - lots of practice - you can achieve this. In the beginning, most of us have good periods and periods like this. Be patient, clear your mind and focus on your breathing. 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 23/49
24 WHAT TO TRAIN Watch the Spectral HRV Waves The goal of breathing training is to achieve a peak in the.08 to.12 range of the LF band, allowing for variation in the breathing rate of the individual. This peak indicates increased Vagal tone. Background Spectral HRV Waves: DFT The DFT (Discrete Frequency Transform) display is a spectral display for HR with a horizontal scale of Hz. All the peaks at different frequencies in this display represent the power of different rhythms present in the inter-beat interval (IBI) measurement. TECHNICAL: The calculation always includes a fixed number of beats, either 64 or 128 beats depending upon the application, recalculated as each new IBI measurement is received. For example, in a subject with a breathing rate of 6 breaths per minute (equaling one breath per 10 seconds =.1 cycles per second =.1 Hz) a cyclic variation of heart rate every ten seconds would occur. This would result in a peak in the DFT display in the green area at.1 Hz on the scale. The bands of color in the DFT display represent the frequency ranges of the Very Low Frequency (VLF), Low Frequency (LF), and High Frequency (HF) signals as follows: VLF= Hz LF = Hz HF = Hz 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 24/49
25 VLF,LF,HF The values for each of these signals, which represent the summation of power in a particular band, are displayed at the top of each DFT display (shown above) and are also used in line graph displays (shown below), bar graph displays (left) and digital number displays. The total power of all frequencies is related to autonomic balance ( for example, people suffering from depression tend to have lower total power). VLF is thought to be influenced primarily by the Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS) with slight Parasympathetic, or Vagal, influence. The VLF value rises when people are intellectually engaged in activities such as thinking, worrying, or self-criticizing. LF seems to be related to both SNS and Vagal activity associated with barorecepter regulation. HF Respiration is a major influence over HF activity. Decreasing the breath rate causes this value to go down, while values of breaths per minute cause the HF value to go up. 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 25/49
26 Wait at least one minute for HRV waves to stabilize. WHAT TO TRAIN : Boost the LF Waves Low Frequency Waves [LF] need to be boosted before we launch into more elaborate stress inoculation strategies. For some people this is as easy as relaxing and slowing breathing. If that is you, be sure you can do this exercise without watching the screen. You will need to apply it later during stress inoculation. For those that may have trouble, be patient. If you are not used to slowing your breathing, this can trigger an alarm reaction. Just stop. Then practice it again, and try to stay relaxed. If you continue to experience frustration, go on to the VLF exercise, as it helps control the physiological expression of both frustration and rumination or trying too hard. 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 26/49
27 Wait at least one minute for HRV waves to stabilize. WHAT TO TRAIN : Lower the VLF Waves Very Low Frequency Waves [VLF] increase to very subtle changes in emotion. They seem to detect transition states, especially those assisted with thinking or preoccupation. If you experience frustration or boredom with the previous exercises, test it here. Get bored or frustrated and see if you can still control the blue signals. Remember your relaxation goal is to lower the blue signal, then boost the green signal. If you have difficulty you may be both frustrated and/or ruminating and/or trying too hard. 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 27/49
28 FIND YOUR OPTIMAL BREATH Resonant Breathing Frequency Analysis What is the goal of Resonant Frequency Analysis? THE GOAL IS TO FIND THE BEST BREATHING TECHNIQUE FOR AN INDIVIDUAL No one breathing technique is right for everyone. However we can find your best technique scientifically, using breathing and heart-rate monitoring. When heart rate matches breathing rhythms (Cardio-Respiratory Synchrony) you are in the optimal breathing 'zone' for you. This is your resonant frequency, because this optimal breathing 'resonates' to help calm the heart, balance the activity of the autonomic nervous system controlling inner organs, and is an excellent start for practical stress reduction exercises, like biofeedback, exercise and improved [productive] sleep. What is the goal of Resonant Frequency Training? RESPIRATION-HEART RATE SYNCHRONY TRAINING Training should make use of the Resonant Frequency Analysis. Start with your personal best resonant frequency as a guide to easy breathing. Biofeedback gives feedback when you are in your optimal resonant frequency zone. Training may start with simply staying in the 'zone,' As you get more skillful, challenges may be explored to learn to maintain or recover quickly from disruptions. What are the results of Resonant Frequency Training? As synchrony becomes more pronounced, studies indicate there is a good chance that blood pressure drops, stress hormones plummet, anti-aging hormones increase, and emotional tone 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 28/49
29 (clarity and calmness) is enhanced. Generally stress-recovery is faster and sleep generally is more productive. Resonant Frequency Testing is divided into three parts: Part I: BASELINE: Record breathing while resting quietly. Part II: MATCH BREATHING RATES: Sample breathing rates, from 5.5 bpm, to 7.0 bpm. 'Match' breathing to the pacer. Part III: TEST WITHOUT PACER: Test best breathing rate without the pacer. Start by attaching the sensors: Bring up the Select Profile Screen: 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 29/49
30 Select a button on the right side to begin an Optimal Breathing Profile. * 8 Minute Profile - A quick test of different breathing rates. * 20 Minute Profile - A Research-Based longer protocol. It has the same sequence as the 8 Minute Profile, but has longer periods of breathing pacing. PROCEDURE: To begin, select either the top button or the bottom button. For a rapid scan, choose the 8 minute profile. For longer, more detailed analysis, choose the 20 minute button. You will be taken to an instruction screen. The first requests you to reduce the Pacer rate to one. Comply and press Click Here To Begin Recording. You will see a pleasant tropical island scene while the computer records breathing, heart rate and HRV bands. When recording is complete, another instruction screen appears. It asks you to adjust the breathing pacer to 6.0 bpm [breaths per minute]. Make the adjustment, and press Click Here To Begin Recording. This sequence repeats itself with instructions to alter breath rates to 5.5, 5.0, 7.0, 6.0, 5.5, and /27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 30/49
31 At the end, select an optimal pacer rate [usually 6.0 or 5.5]. The series finishes with another baseline of no instructions. You are then prompted to EXIT. Follow the instructions on the screen to save and exit. 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 31/49
32 OPTIMAL BREATHING REPORT What to look for? CAUTION: Remember that this test is experimental, and should not be over-interpreted. Many people use other means to find their best or optimal breathing rate. The key point here is that you must not force your breathing too soon. If you have difficulty for example at 6.0 bpm, immediately stop. Go up to 10, 15 or more bpm to begin with, and move up or down slowly as you feel comfortable. You may be out of shape and require an aerobic exercise routine to increase your stamina. Try this test again as your aerobic fitness improves. Consult a medical doctor If you feel you have a medical condition precluding mild exercise. START HERE: Select Manage Data. A window pops up. Select a name, and an Application, in this case, Heart Wave Pro Optimal Breath [ResFreq]. Select View, and a new set of screens pop up: The top row has tabs. Click on each tab to see a different screen. 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 32/49
33 Here are a list of screens: SIDEBAR: NO COLOR IN MANUAL: The original graphs are in COLOR. The manual is printed in black. In some printed graphs it is difficult to distinguish one signal from another. If you want color, conduct a profile, save the data, and view it in color on your computer. This screen shows HR waves on top. Expect lots of little spikes due to movements. Note the regular cycles in most of the screen. The bottom shows the Min-to-Max Heart Rate change. The big spikes are due to movement. Otherwise note how Min-Max HR is largest in the middle and tapers on either side. This Screen shows only the Max Heart Rate change. The big spikes are due to movement. Otherwise note how Min-Max HR is largest in the middle and tapers on either side. The Average Max HR is also in the middle. This says that the biggest HR wave change [i.e., Min-Max HR] occurred when the client paced their breath at 5.5 bpm [ shown on the label Breath 5.5 bpm on the bottom labels row]. 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 33/49
34 This graph puts it all together. The top graph shows the Paced Breaths per Minute*. The Middile graph shows the actual HR Waves and Breathing EMG waves. The bottom graph shows the 3 spectral HRV bands, VLF, LF and HF. To find the Optimal or Resonant Frequecy Breath Rate, look at the LF wave. It is highest at the best Rates. Here LF is highest at 6.0 and 5.5 bpm. * SIDEBAR: BUG If you look closely, the Paced Breaths per Minute signal sometimes surged to 15 bpm for about 20 seconds, then came down to the correct bpm.. This is a calculation background error, a bug. It does not affect the live pacer signal. The real signal bpm is shown 20 seconds after each spike. This will be fixed in a later edition. This graph shows the HF/LF Ratios. The top graphs are based on J&Js HRV calculations [ used in biofeedback studies], and the second converts them to a research standard, task force, used in some research studies. Both show similar cycles. The ratio is lowest at the start and end, and highest in the middle. 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 34/49
35 This graph is the one used to determine where to start with a pacing frequency. The key is to look at LF first and find which pacer frequencies raise LF the most. Here the 6.0 bpm in the middle raised LF highest. The other signals, VLF, and HF, are usually not used to determine the oprimal or resonsnt breathing frequency. This is the same 3 signals VLF, LF and HF calculated as task force signals. Here too LF is the key. The Task Force calculation shows the same trend LF is lowest on the ends and highest at 5.5 bpm. There is also a LF spike at the first 6.0 bpm. CONCLUSION: This person s best Min-Max HR occurred between 5.5 and 6.0 bpm. The highest LF waves occurred at 6.0 bpm.. There was also a spike in LF at 5.5 bpm using the task force norms. So all together, this persons best beginning breathing rate should start at 6.0 to 5.5 bpm. 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 35/49
36 APPENDIX: FINE-TUNING SIGNALS MOST OF OUR SCREENS ARE AUTO-ADJUSTING: The computer is constantly calculating the best gain and offset to display a signal. However, you must wait at least 20 seconds for the screen to recalculate and redraw so the signal fits the entire screen. A few screens may need manual adjustment. Use these instructions for manual fine-tuning. Signal Control Toolbar Use the left edge Signal Control Toolbar buttons to change display characteristics. These buttons will modify only one display or signal at a time. To select an individual display from a multi-display screen, click on the display. The display will become highlighted with light blue to indicate it has been selected and that the Signal Control buttons have been assigned to it. Modify the signal using the icons to the left. If more than one signal appears in the same display and the signal names are clickable, it means that separate scales are available for each signal and that signals can be manipulated separately. Select the signal you wish to modify by clicking on the tiny colored square next to the name of the signal within the top of the display. A white dot in the center of the square indicates that particular signal is selected. Use the Signal Control Toolbar to modify the selected signal. If the signal names are not clickable, it means that the signals have the same scale and are locked together so that the signal controls modify all signals together. The Signal Up button and the Signal Down button are used to move the signal line higher or lower on the display. o The Auto-offset button toggles on and off the Autocenter feature which automatically keeps the signal centered on the screen. To manually adjust the signal higher or lower on the screen, click Auto-offset OFF and use the above Signal Up and Signal Down buttons. The Gain Up button is used to increase signal size and sensitivity. Spaces between scale units increase indicating greater signal sensitivity. The Gain Down button is used to decrease signal size and sensitivity. The combination of Gain Up and Gain Down plus the Signal Up and Down arrows allow you to size and position the signal anywhere on the display. 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 36/49
37 o The Autogain button toggles the Autogain feature on and off. For your convenience you can leave Autogain on or you have the option of turning this feature off and manually adjusting the gain according to your preference. After you click Autogain on, wait up to 30 seconds for the signal to self-adjust. COMMENT: Turning the Autogain or Autocenter features on or off for one signal will not change the settings for the other signals on the screen. Each signal s settings are adjusted individually. The Faster Graph and Slower Graph buttons are used to increase and decrease sweep speed for all signals except FFT. This increases/decreases the time span that can be displayed within a single window. COMMENT: For FFT displays the Faster Graph & Slower Graph buttons change the frequency span of the FFT displays. It is recommended that you leave FFT displays at the maximum frequency scale. The Averaging Interval button changes signal appearance. This button brings up the Select Averaging Interval window which allows you to increase or decrease the averaging interval by seconds or fractions of seconds. Increasing the averaging interval smoothes the selected signal. Decreasing the interval makes signal detail more visible. The Zoom button is used to magnify any individual display to fill up the entire screen. Simply click on the desired display to select it, then click on the Zoom button. To return to the original display, re-click the Zoom button. This feature is particularly useful for simplifying feedback to one signal, then toggling back to a multi-signal display. Clicking on the Adjust Threshold button is enabled if THR is in the signal name of one of the available signals for a particular display. This button brings up the Threshold Control window. An empty checkbox indicates that Auto Threshold is OFF. To turn this feature ON, click in the checkbox next to Enable Auto Threshold. To manually set the threshold, click on the check mark next to Enable Auto Threshold in order to deselect it. Click on the Down/Up arrows next to the Level box or type a numerical value in the box. Close the control box by clicking on the small x. COMMENT: There are many ways to change threshold values. You can drag and drop the threshold line on the display screen. Place the cursor in the display area and click the mouse once to activate the drag-and-drop feature for that display. As you move the cursor over the threshold line, a hand appears. Hold down the left mouse button when the hand appears and drag the threshold line up and down on the screen, releasing the button at the point where you want the threshold line to stay. The Show/Hide Signal button brings up a control box to turn on or off the display of a signal on the selected display. Simply click on the check marks of each signal you wish to 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 37/49
38 hide. To make the signals reappear, again click on the Show/Hide signal icon and click on the empty boxes next to the names of the signal(s) to you wish to re-display. Close the control box by clicking on the small x. The Select Sound button brings up the Audio Control Window. Please see the Audio Features section for information on the use of audio controls. The Sound button toggles the speakers on and off. This button must be down in order for Media Player feedback screens to work. The Modify Settings button is used to specify numerical parameters, such as 1. breathing rate. 2. duration of inhale/exhale and hold times for the Breathing Pacer The Select Second Screen button for Dual Screen Mode will open a window with a list of available second screen displays. It is not used in this set of applications. Exiting a Session Exit each session using the arrow in the lower left hand corner In order to review data, generate reports, export data into a database, manage client or session data, or to quit the program, you must first exit the session. In order to exit the software both the Pause and the Record buttons must be OFF. If you have recorded data, the Save Session Data window will automatically open when you exit the software (See the Saving Session Data section). EXITING A SESSION EXITING SOMETIMES REQUIRES TWO OR THREE STEPS. The key is to follow the instructions in the bottom Information Bar's BLACK BOX. EXIT when CLEAR: If the box is blank..., or says a simple pause, like this. PAUSE just press EXIT. PROBLEMS EXITING and SOLUTIONS: However-If box says REC. First STOP RECORDING: If box turns blank... press EXIT However If box says PAUSE 1:33 remain,, your Task Sequence is still enabled. To abort, first GET OUT of Pause. Press the grey toolbar [] [] Pause button. REC resumes. 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 38/49
39 This is correct. When REC resumes, click on the red Rec Button. The black box will clear and Now you can EXIT.. Reset and Freeze Features Use these buttons while training. Freeze a screen to discuss what happened, to coach a new behavior, to point out a change, or to ask a question. Different buttons allow you to freeze the screen but keep recording or freeze both the screen and pause recording. The Reset Screen button refreshes all of the displays on the screen. Resetting the screen has no effect on data recording. The Freeze Screen button freezes all screen displays to allow for discussion of the signals with the client while USE3 Physiolab continues to monitor and record data. The AutoFreeze button freezes all graph displays when the selected signal display reaches the end of its signal sweep. This does not affect data recording. To restart the signal display, click the Freeze Screen button. The Pause Game Windows button pauses certain game and feedback screens without affecting data recording. To resume the game, re-click the button. o The Pause Task button pauses both the data recording and the feedback screen. The Unpause Task button [][] resets the feedback screen and resumes recording of the current task. o The Pause Game button does not effect recording. It merely freezes the feedback screen while the underlying data recording continues. Printing Screens During the Session The Print Screen button allows you to print the current screen. Click this icon and wait a few moments for the screen image to appear. Click Print in the top menu, modify printer settings as needed, and click OK. You are given the opportunity to abort without printing by selecting Close instead of Print. Recording Data The Record button toggles recording on and off. NOTE: The color difference between on and off is hard to see. Look on the black event box on the bottom center toolbar to see if it says REC. or is blank The Pause button pauses data recording. Re-click it to resume recording. Look on the black event box on the bottom center toolbar to see if it says PAUSE. or is blank 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 39/49
40 o The Menu button allows you to specify the erase time interval invoked by the Record Backup button. o The Record Backup button erases a specified time interval of recorded data, and records over the erased portion so that the data record is seamless. You can change the Backup interval using the Menu button. o The Task Averaging button opens a window that lists the mean average for each signal and each task as it is recorded. It verifies what is being recorded. Event Marking The Event Mark button enables you to add data markers into the recorded data when significant events occur during the session. The button pops up a window into which you can type a name or brief comment which is inserted with the marker into the data record. Character limit for marker label is 3 characters, like 123, abc, or bl1. END OF SECTION 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 40/49
41 APPENDIX: PRO-SERIES ADVANCED TRAINING DISPLAYS PRO SERIES : Imbeded in these applications are a few screens that have lots of information on them. These screens are provided for students and researchers who requested screens showing live relationships among signals. These screens are especially prominent in the Pro Scries. Try our advanced screens. These help put it all together breathing, HR, Cardio-Respiratory Synchrony and LF/VLF balance. Here are some examples: Note how the green LF wave emerges as HR waves become more and more symmetrical. PRO-SERIES HRV Forward-scroll screen. PRO-SERIES HRV Reverse-scroll screen. 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 41/49
42 PRO-SERIES Average HR-Wave+HRV Forward-scroll screen. PRO-SERIES RawHR+Resp -Wave+HRV Forward-scroll screen. PRO-SERIES Average HR-Wave+LF/HF Ratio screen. 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 42/49
43 PRO-SERIES HR+RESP -Wave+HRV +EMG FFT Quad screen. The pro series screens are not for everyone. However for advanced users, they can provide valuable information to guide a peak performance or stress management discussion. 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 43/49
44 APPENDIX: ABOUT HRV & HR FEEDBACK What is HRV?... Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback is being taught is a variety of formats, and definitions do vary. In this manual, we will try to reduce confusion by using separate terminology for the different kinds of feedback: Check ECG Signal: ECG: The electro cardiogram is picked up as a signal across the chest, reflecting a rhythmic cyclical discharge from heart muscle. Do not expect to get ECG signals from your equipment that are identical to the medical ECG signals. Placements are different. Do however place the positive sensor on the left and the negative on the right to keep the wave upright. The ground can go on the wrist. This is a good ECG with no artifact. This ECG has a peak at 60 Hz. Line voltage is being radiated nearby. Check your impedance and the operation of high voltage lights or machinery. If you get an unexpected reading on an HRV display, you can use the raw ECG signal to evaluate whether the anomaly is due to EMG artifact, indistinct R-wave, or missing or premature beats. Individual physiology may vary and some individuals may have an indistinct R-wave point in their ECG signal. The software needs to be able to detect the R-wave in order to calculate the IBI (Inter-Beat Interval) for HRV displays. If heart rate tracking appears to be unreliable, try a right ankle, left wrist placement with either gel-free or disposable electrodes instead of wrist-to-wrist placement. HR The Heart Rate signal reflects beats per minute and is recalculated and updated in the display on each beat. No averaging is performed. This produces a heart rate waveform display which is a good graphical representation of HRV (Heart Rate Variability). This signal is used in line graph displays along with the Respiration waveform so that the impact of correct breathing on HRV can be easily observed as (1.) increases in variability in the HR waveform and in (2.) increased synchrony between the HR and Respiration waveforms. (Examples are pictured in the HR+Resp1+Resp2 display in the Overview of Screens and Displays and under Breathing Pattern in the discussion Respiration Displays above) The Breathing Pattern screen has a unique way of displaying HR that differs from the standard graph display. When a new heartbeat occurs, its value in beats per minute is plotted as a square dot and a line is drawn from each previous beat to each new beat, producing a graphing point display. 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 44/49
45 The Heart Rate signal is also found in bar displays (Pictured in the second Check Signals screen example in the Overview of Screens and Displays section) and in digital displays (Pictured under Numerical Displays above). Min-Max HR also known as HRV_30 This is a display of heart rate variability averaged over 30 seconds. The software measures the minimum and maximum heart rate values for 30 seconds, then averages the difference of these values and displays them in a line graph. HRV_30 is a good graphical display of increasing or decreasing HRV trends. HRV Feedback : Refers strictly to the HR wave, the min-max HR. RSA Feedback: Refers to the HR wave associated with easy breathing. Traditionally respiration was not recorded, so RSA should be restricted to simple HRV [min-max HR] feedback. Spectral HRV Feedback. Refers to any feedback training that involves watching either the spectral DFT graph or the VLF, LF and/or HF bands. CardioRespiratory Synchrony/Coherence: Refers strictly to the synchrony [timing] between HR acceleration and Inhaling. [If you like, it also refers to HR deceleration timed with the exhale as well]. Resonant Frequency Training. Refers to Paul Leher's protocol combining Breathing Pacer and Cardio- Respiratory Feedback. Spectral HRV is involved, too. Resonant Frequency Training is focused on the LF elevations and min-max HR. 4/27/2009 Smart Heart Instructions 45/49
On Spectral Analysis of Heart Rate Variability during Very Slow Yogic Breathing
 On Spectral Analysis of Heart Rate Variability during Very Slow Yogic Breathing Emil Jovanov Electrical and Computer Engineering Dept. University of Alabama in Huntsville http://www.ece.uah.edu/~jovanov
On Spectral Analysis of Heart Rate Variability during Very Slow Yogic Breathing Emil Jovanov Electrical and Computer Engineering Dept. University of Alabama in Huntsville http://www.ece.uah.edu/~jovanov
Module No GETTING ACQUAINTED GENERAL GUIDE TIMEKEEPING
 Module No. 2196 2196-1 GETTING ACQUAINTED Congratulations upon your selection of this CASIO Pressure Monitor Watch (BP-1B, Module No. 2196). To get the most out of your purchase, be sure to carefully read
Module No. 2196 2196-1 GETTING ACQUAINTED Congratulations upon your selection of this CASIO Pressure Monitor Watch (BP-1B, Module No. 2196). To get the most out of your purchase, be sure to carefully read
Biology 347 General Physiology Lab Basic Pulmonary Functions: Respirometry and Factors that Effect Respiration
 Biology 347 General Physiology Lab Basic Pulmonary Functions: Respirometry and Factors that Effect Respiration Objectives Students will measure breathing parameters in a resting subject. Students will
Biology 347 General Physiology Lab Basic Pulmonary Functions: Respirometry and Factors that Effect Respiration Objectives Students will measure breathing parameters in a resting subject. Students will
For use with version or later
 Thought Technology Ltd. 8205 Montreal/ Toronto Blvd. Suite 223, Montreal West, QC H4X 1N1 Canada Tel: +1 (800) 361-3651 ۰ +1 (514) 489-8251 Fax: +1 (514) 489-8255 E-mail: mail@thoughttechnology.com Webpage:
Thought Technology Ltd. 8205 Montreal/ Toronto Blvd. Suite 223, Montreal West, QC H4X 1N1 Canada Tel: +1 (800) 361-3651 ۰ +1 (514) 489-8251 Fax: +1 (514) 489-8255 E-mail: mail@thoughttechnology.com Webpage:
Users Group Conference 2018
 Users Group Conference 2018 Compressor Analysis Special Circumstances Tracy Wimberly Sr. Reciprocating Equipment Analyst, Windrock 1 Topics, top compressor questions Ultrasound Baseline Cat Eyes Leak Index
Users Group Conference 2018 Compressor Analysis Special Circumstances Tracy Wimberly Sr. Reciprocating Equipment Analyst, Windrock 1 Topics, top compressor questions Ultrasound Baseline Cat Eyes Leak Index
SOLUTIONS Homework #1
 SOLUTIONS Homework #1 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING IN MEDICINE AND BIOLOGY ECEN 1001- Fall 2003 R. Mihran Due Tuesday, 9/9/03 Question 1: a) Chapter 1 of the text discusses the fact that a significant fraction
SOLUTIONS Homework #1 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING IN MEDICINE AND BIOLOGY ECEN 1001- Fall 2003 R. Mihran Due Tuesday, 9/9/03 Question 1: a) Chapter 1 of the text discusses the fact that a significant fraction
LifeBeat should be worn during daytime as well as night time as it can record activity levels as well as sleep patterns.
 myhealth FAQ V1.0.5 GENERAL What is LifeBeat Stress Tracker? LifeBeat Stress Tracker is a system that lets you track your activity, sleep, and especially your various stress levels, so that you can improve
myhealth FAQ V1.0.5 GENERAL What is LifeBeat Stress Tracker? LifeBeat Stress Tracker is a system that lets you track your activity, sleep, and especially your various stress levels, so that you can improve
Confidence comes with knowing you are Code-Ready.
 Confidence comes with knowing you are Code-Ready. The First and Only Code-Ready Defibrillator. The worst time to find out a defibrillator isn t ready is at the code. Quick action is essential and stress
Confidence comes with knowing you are Code-Ready. The First and Only Code-Ready Defibrillator. The worst time to find out a defibrillator isn t ready is at the code. Quick action is essential and stress
For use with version 6.1 or later
 Thought Technology Ltd. 8205 Montreal/ Toronto Blvd. Suite 223, Montreal West, QC H4X 1N1 Canada Tel: +1 (800) 361-3651 ۰ +1 (514) 489-8251 Fax: +1 (514) 489-8255 E-mail: mail@thoughttechnology.com Webpage:
Thought Technology Ltd. 8205 Montreal/ Toronto Blvd. Suite 223, Montreal West, QC H4X 1N1 Canada Tel: +1 (800) 361-3651 ۰ +1 (514) 489-8251 Fax: +1 (514) 489-8255 E-mail: mail@thoughttechnology.com Webpage:
ELIMINATOR COMPETITION DRAG RACE Program Manual Firm Ver 4.11
 ELIMINATOR COMPETITION DRAG RACE Program Manual Firm Ver 4.11 The Portatree Eliminator Super 2000 Competition Track Timer can be used with an IBM Compatible Personal Computer connected through Com Port
ELIMINATOR COMPETITION DRAG RACE Program Manual Firm Ver 4.11 The Portatree Eliminator Super 2000 Competition Track Timer can be used with an IBM Compatible Personal Computer connected through Com Port
Lab 3. The Respiratory System (designed by Heather E. M. Liwanag with T.M. Williams)
 Name Lab Partners Lab 3. The Respiratory System (designed by Heather E. M. Liwanag with T.M. Williams) Part 1. Lung Volumes and Capacities Objectives 1. Obtain graphical representation of lung capacities
Name Lab Partners Lab 3. The Respiratory System (designed by Heather E. M. Liwanag with T.M. Williams) Part 1. Lung Volumes and Capacities Objectives 1. Obtain graphical representation of lung capacities
Boyle s Law: Pressure-Volume Relationship in Gases
 Boyle s Law: Pressure-Volume Relationship in Gases The primary objective of this experiment is to determine the relationship between the pressure and volume of a confined gas. The gas we will use is air,
Boyle s Law: Pressure-Volume Relationship in Gases The primary objective of this experiment is to determine the relationship between the pressure and volume of a confined gas. The gas we will use is air,
Respiratory Response to Physiologic Challenges. Evaluation copy
 Respiratory Response to Physiologic Challenges Computer 20 The respiratory cycle of inspiration and expiration is controlled by complex mechanisms involving neurons in the cerebral cortex, brain stem,
Respiratory Response to Physiologic Challenges Computer 20 The respiratory cycle of inspiration and expiration is controlled by complex mechanisms involving neurons in the cerebral cortex, brain stem,
FireHawk M7 Interface Module Software Instructions OPERATION AND INSTRUCTIONS
 FireHawk M7 Interface Module Software Instructions OPERATION AND INSTRUCTIONS WARNING THE WARRANTIES MADE BY MSA WITH RESPECT TO THE PRODUCT ARE VOIDED IF THE PRODUCT IS NOT USED AND MAINTAINED IN ACCORDANCE
FireHawk M7 Interface Module Software Instructions OPERATION AND INSTRUCTIONS WARNING THE WARRANTIES MADE BY MSA WITH RESPECT TO THE PRODUCT ARE VOIDED IF THE PRODUCT IS NOT USED AND MAINTAINED IN ACCORDANCE
A Hare-Lynx Simulation Model
 1 A Hare- Simulation Model What happens to the numbers of hares and lynx when the core of the system is like this? Hares O Balance? S H_Births Hares H_Fertility Area KillsPerHead Fertility Births Figure
1 A Hare- Simulation Model What happens to the numbers of hares and lynx when the core of the system is like this? Hares O Balance? S H_Births Hares H_Fertility Area KillsPerHead Fertility Births Figure
SmartMan Code User Manual Section 5.0 Results
 SmartMan Code User Manual Section 5.0 Results For SmartMan Code, Megacode and Megacode Low Volume Table of Contents SmartMan Code User Manual Section 5.0 Results... 1 SMARTMAN CODE MEGACODE MEGACODE LOW
SmartMan Code User Manual Section 5.0 Results For SmartMan Code, Megacode and Megacode Low Volume Table of Contents SmartMan Code User Manual Section 5.0 Results... 1 SMARTMAN CODE MEGACODE MEGACODE LOW
Respiration. Exercise 1A: Breathing in Resting Volunteers Aim: To measure breathing parameters in a resting individual.
 Respiration Background The amount of air that moves in or out of the lungs during any one breathing cycle is called the tidal volume. Above and beyond normal inspiration, it is possible to breathe in additional
Respiration Background The amount of air that moves in or out of the lungs during any one breathing cycle is called the tidal volume. Above and beyond normal inspiration, it is possible to breathe in additional
Meditation Trainer. Created by Collin Cunningham. Last updated on :36:45 PM UTC
 Meditation Trainer Created by Collin Cunningham Last updated on 2018-03-26 09:36:45 PM UTC Guide Contents Guide Contents Overview What is HRV? What you'll need: Wiring Making connections Software Setup
Meditation Trainer Created by Collin Cunningham Last updated on 2018-03-26 09:36:45 PM UTC Guide Contents Guide Contents Overview What is HRV? What you'll need: Wiring Making connections Software Setup
Model AUTOMATIC UPPER ARM Blood Pressure Monitor
 AUTOMATIC UPPER ARM Blood Pressure Monitor Model 1130 Real Fuzzy t e c h n o log y Features: Real Fuzzy Technology Automatic 60 sets of memory One-Touch Operation Easy-to-read Display Table of Contents:
AUTOMATIC UPPER ARM Blood Pressure Monitor Model 1130 Real Fuzzy t e c h n o log y Features: Real Fuzzy Technology Automatic 60 sets of memory One-Touch Operation Easy-to-read Display Table of Contents:
UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS WEAPONS TRAINING BATTALION MARINE CORPS COMBAT DEVELOPMENT COMMAND QUANTICO, VIRGINIA
 UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS WEAPONS TRAINING BATTALION MARINE CORPS COMBAT DEVELOPMENT COMMAND QUANTICO, VIRGINIA 22134-5040 DETAILED INSTRUCTOR GUIDE LESSON TITLE FUNDAMENTALS OF RIFLE MARKSMANSHIP COURSE
UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS WEAPONS TRAINING BATTALION MARINE CORPS COMBAT DEVELOPMENT COMMAND QUANTICO, VIRGINIA 22134-5040 DETAILED INSTRUCTOR GUIDE LESSON TITLE FUNDAMENTALS OF RIFLE MARKSMANSHIP COURSE
Experiment B-18 Heart Rate and Coughing
 1 Experiment B-18 Heart Rate and Coughing Objectives To study the changes in heart rate at rest and after coughing. Modules and Sensors PC + NeuLog application USB-200 module NUL-208 Heart rate & pulse
1 Experiment B-18 Heart Rate and Coughing Objectives To study the changes in heart rate at rest and after coughing. Modules and Sensors PC + NeuLog application USB-200 module NUL-208 Heart rate & pulse
The physiological functions of respiration and circulation. Mechanics. exercise 7. Respiratory Volumes. Objectives
 exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
iworx Sample Lab Experiment HE-4: Respiratory Exchange Ratio (RER)
 Experiment HE-4: Respiratory Exchange Ratio (RER) Before Starting 1. Read the procedures for the experiment completely before beginning the experiment. Have a good understanding of how to perform the experiment
Experiment HE-4: Respiratory Exchange Ratio (RER) Before Starting 1. Read the procedures for the experiment completely before beginning the experiment. Have a good understanding of how to perform the experiment
CONTENTS SPECIFICATIONS GENERAL INFORMATION RECOMMENDED USE OPERATING PRINCIPLE TIPS ON TAKING YOUR BLOOD PRESSURE 3-4 BATTERY INSTALLATION
 IFU SBPMON107 CONTENTS SPECIFICATIONS GENERAL INFORMATION RECOMMENDED USE OPERATING PRINCIPLE TIPS ON TAKING YOUR BLOOD PRESSURE BATTERY INSTALLATION CORRECT POSITION FOR MEASUREMENT POSITIONING THE CUFF
IFU SBPMON107 CONTENTS SPECIFICATIONS GENERAL INFORMATION RECOMMENDED USE OPERATING PRINCIPLE TIPS ON TAKING YOUR BLOOD PRESSURE BATTERY INSTALLATION CORRECT POSITION FOR MEASUREMENT POSITIONING THE CUFF
Figure 1. A schematic diagram of the human respiratory system.
 Introduction to Respiration In this experiment, you will investigate various aspects of normal breathing, hyperventilation, rebreathing the effect of changing airway resistance and ways in which to measure
Introduction to Respiration In this experiment, you will investigate various aspects of normal breathing, hyperventilation, rebreathing the effect of changing airway resistance and ways in which to measure
Homeostasis and Negative Feedback Concepts and Breathing Experiments 1
 Homeostasis and Negative Feedback Concepts and Breathing Experiments 1 I. Homeostasis and Negative Feedback Homeostasis refers to the maintenance of relatively constant internal conditions. For example,
Homeostasis and Negative Feedback Concepts and Breathing Experiments 1 I. Homeostasis and Negative Feedback Homeostasis refers to the maintenance of relatively constant internal conditions. For example,
Semi-Automatic Blood Pressure Monitor with Memory
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Semi-Automatic Blood Pressure Monitor with Memory 61-268-001 (Adult size cuff) Please read this instruction manual completely before operating this unit. English Spanish Limited Five
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Semi-Automatic Blood Pressure Monitor with Memory 61-268-001 (Adult size cuff) Please read this instruction manual completely before operating this unit. English Spanish Limited Five
iworx Sample Lab Experiment HE-5: Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR)
 Experiment HE-5: Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR) Before Starting 1. Read the procedures for the experiment completely before beginning the experiment. Have a good understanding of how to perform the experiment
Experiment HE-5: Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR) Before Starting 1. Read the procedures for the experiment completely before beginning the experiment. Have a good understanding of how to perform the experiment
WATCH COLLECTION NG701 SERIES INSTRUCTION MANUAL
 WATCH COLLECTION NG701 SERIES INSTRUCTION MANUAL INTRODUCTION This watch features electronic sensors that measure outdoor conditions such as temperature, pressure, and altitude. The watch provides essential
WATCH COLLECTION NG701 SERIES INSTRUCTION MANUAL INTRODUCTION This watch features electronic sensors that measure outdoor conditions such as temperature, pressure, and altitude. The watch provides essential
Standard HRaM Editing Techniques. Standard HRaM Editing Techniques
 Standard HRaM Editing Techniques 1 Opening the Study: Double click on the Sandhill Applications icon on the desktop. Click 'Analysis'. Click 'Select Patient': The path to find the patient file is: C:\Sandhill\Patients\ARM
Standard HRaM Editing Techniques 1 Opening the Study: Double click on the Sandhill Applications icon on the desktop. Click 'Analysis'. Click 'Select Patient': The path to find the patient file is: C:\Sandhill\Patients\ARM
AFG FITNESS APP OWNER S MANUAL AFG MANUEL DU PROPRIÉTAIRE DU TAPIS ROULANT AFG MANUAL DEL PROPIETARIO DE LA CAMINADORA
 AFG FITNESS APP OWNER S MANUAL AFG MANUEL DU PROPRIÉTAIRE DU TAPIS ROULANT AFG MANUAL DEL PROPIETARIO DE LA CAMINADORA Read the GUIDE and OWNER S MANUAL before using this CONNECTED FITNESS MANUAL. Lisez
AFG FITNESS APP OWNER S MANUAL AFG MANUEL DU PROPRIÉTAIRE DU TAPIS ROULANT AFG MANUAL DEL PROPIETARIO DE LA CAMINADORA Read the GUIDE and OWNER S MANUAL before using this CONNECTED FITNESS MANUAL. Lisez
Lesson 12 New Procedure PULMONARY FUNCTION I
 Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Student Lab Lesson 12 New Procedure PULMONARY FUNCTION I Volumes and Capacities For Windows 98SE, Me, 2000 Pro, XP or Mac OS X 10.3-10.4 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D.
Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Student Lab Lesson 12 New Procedure PULMONARY FUNCTION I Volumes and Capacities For Windows 98SE, Me, 2000 Pro, XP or Mac OS X 10.3-10.4 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D.
TR Electronic Pressure Regulator. User s Manual
 TR Electronic Pressure Regulator Page 2 of 13 Table of Contents Warnings, Cautions & Notices... 3 Factory Default Setting... 4 Quick Start Procedure... 5 Configuration Tab... 8 Setup Tab... 9 Internal
TR Electronic Pressure Regulator Page 2 of 13 Table of Contents Warnings, Cautions & Notices... 3 Factory Default Setting... 4 Quick Start Procedure... 5 Configuration Tab... 8 Setup Tab... 9 Internal
Experiment HE-9: Resting, Active, and Exercising Metabolic Rates
 Experiment HE-9: Resting, Active, and Exercising Metabolic Rates Before Starting 1. Read the procedures for the experiment completely before beginning the experiment. Have a good understanding of how to
Experiment HE-9: Resting, Active, and Exercising Metabolic Rates Before Starting 1. Read the procedures for the experiment completely before beginning the experiment. Have a good understanding of how to
Experiment HE-9: Resting, Active, and Exercising Metabolic Rates
 Experiment HE-9: Resting, Active, and Exercising Metabolic Rates Before Starting 1. Read the procedures for the experiment completely before beginning the experiment. Have a good understanding of how to
Experiment HE-9: Resting, Active, and Exercising Metabolic Rates Before Starting 1. Read the procedures for the experiment completely before beginning the experiment. Have a good understanding of how to
EN-MOTION TREADMILL. EN-Motion: the ultimate PHYSIO treadmill
 The EN-Motion treadmill is a valuable asset to the physiotherapy and rehabilitation world. An innovative treadmill, ideal for physiotherapy and rehabilitation purposes. EN-MOTION GETS THE WORLD MOVING
The EN-Motion treadmill is a valuable asset to the physiotherapy and rehabilitation world. An innovative treadmill, ideal for physiotherapy and rehabilitation purposes. EN-MOTION GETS THE WORLD MOVING
UNITY 2 TM. Air Server Series 2 Operators Manual. Version 1.0. February 2008
 UNITY 2 TM Air Server Series 2 Operators Manual Version 1.0 February 2008 1. Introduction to the Air Server Accessory for UNITY 2...2 1.1. Summary of Operation...2 2. Developing a UNITY 2-Air Server method
UNITY 2 TM Air Server Series 2 Operators Manual Version 1.0 February 2008 1. Introduction to the Air Server Accessory for UNITY 2...2 1.1. Summary of Operation...2 2. Developing a UNITY 2-Air Server method
Sports Wrist Digital Blood Pressure Monitor Item #
 Instruction Manual Sports Wrist Digital Blood Pressure Monitor Item # 04-885-001 Please read this guidebook completely before operating this unit. Limited Five-Year Warranty The warrantor guarantees that
Instruction Manual Sports Wrist Digital Blood Pressure Monitor Item # 04-885-001 Please read this guidebook completely before operating this unit. Limited Five-Year Warranty The warrantor guarantees that
BLOOD PRESSURE SENSOR BT17i USER S GUIDE
 BLOOD PRESSURE SENSOR BT17i USER S GUIDE CENTRE FOR MICROCOMPUTER APPLICATIONS http://www.cma-science.nl Short description The Blood Pressure sensor BT17i allows measuring arterial blood pressure. The
BLOOD PRESSURE SENSOR BT17i USER S GUIDE CENTRE FOR MICROCOMPUTER APPLICATIONS http://www.cma-science.nl Short description The Blood Pressure sensor BT17i allows measuring arterial blood pressure. The
18-WEEK MARATHON TRAINING PROGRAM
 18-WEEK MARATHON TRAINING PROGRAM OCTOBER 9TH, 2016 T H E G O A L O F T H I S P L A N I S N T T O G E T Y O U A C R O S S T H E F I N I S H L I N E, I T S T O G E T T H E B E S T V E R S I O N O F Y O
18-WEEK MARATHON TRAINING PROGRAM OCTOBER 9TH, 2016 T H E G O A L O F T H I S P L A N I S N T T O G E T Y O U A C R O S S T H E F I N I S H L I N E, I T S T O G E T T H E B E S T V E R S I O N O F Y O
Completed downloadable Test Bank for Pilbeams Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 5th Edition by Cairo
 Completed downloadable Test Bank for Pilbeams Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 5th Edition by Cairo Link full download: http://testbankcollection.com/download/pilbeams-mechanicalventilation-physiological-and-clinical-applications-5th-edition-test-bank-cairo
Completed downloadable Test Bank for Pilbeams Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 5th Edition by Cairo Link full download: http://testbankcollection.com/download/pilbeams-mechanicalventilation-physiological-and-clinical-applications-5th-edition-test-bank-cairo
3D Inversion in GM-SYS 3D Modelling
 3D Inversion in GM-SYS 3D Modelling GM-SYS 3D provides a wide range of inversion options including inversion for both layer structure and physical properties for gravity and magnetic data. There is an
3D Inversion in GM-SYS 3D Modelling GM-SYS 3D provides a wide range of inversion options including inversion for both layer structure and physical properties for gravity and magnetic data. There is an
Standard HRiM Editing Techniques
 Standard HRiM Editing Techniques Opening the Study: Double click on the Sandhill Applications icon on the desktop. Click 'Analysis'. Click 'Select Patient': The path to find the patient file is: C:\Sandhill\Patients\EFT
Standard HRiM Editing Techniques Opening the Study: Double click on the Sandhill Applications icon on the desktop. Click 'Analysis'. Click 'Select Patient': The path to find the patient file is: C:\Sandhill\Patients\EFT
Line Following with RobotC Page 1
 Line Following with RobotC Page 1 Line Following with By Michael David Lawton Introduction Line following is perhaps the best way available to VEX Robotics teams to quickly and reliably get to a certain
Line Following with RobotC Page 1 Line Following with By Michael David Lawton Introduction Line following is perhaps the best way available to VEX Robotics teams to quickly and reliably get to a certain
18-week training program
 MARA T HON 18-week training program T H E G O A L O F T H I S P L A N I S N T T O G E T Y O U A C R O S S T H E F I N I S H L I N E, I T S T O G E T T H E B E S T V E R S I O N O F Y O U A C R O S S T
MARA T HON 18-week training program T H E G O A L O F T H I S P L A N I S N T T O G E T Y O U A C R O S S T H E F I N I S H L I N E, I T S T O G E T T H E B E S T V E R S I O N O F Y O U A C R O S S T
INSTRUCTION MANUAL. Automatic Blood Pressure Monitor with Fit Cuff. =Fit Cuff=!"#$% IA1B. Model
 IA1B INSTRUCTION MANUAL Automatic Blood Pressure Monitor with Fit Cuff =Fit Cuff=!"#$% Model IA1B Contents Introduction... 2 Notes on Safety... 3 Know Your Unit... 5 Quick Reference Guide... 7 Initial
IA1B INSTRUCTION MANUAL Automatic Blood Pressure Monitor with Fit Cuff =Fit Cuff=!"#$% Model IA1B Contents Introduction... 2 Notes on Safety... 3 Know Your Unit... 5 Quick Reference Guide... 7 Initial
14A. Neuromuscular Reflexes. Experiment
 Experiment 14A The automatic response of a muscle to a stimulus is called a reflex. The patellar reflex results from tapping the patellar tendon below the knee with a reflex hammer. This causes contraction
Experiment 14A The automatic response of a muscle to a stimulus is called a reflex. The patellar reflex results from tapping the patellar tendon below the knee with a reflex hammer. This causes contraction
Neuromuscular Reflexes
 Name: Neuromuscular Reflexes Experiment 14A The automatic response of a muscle to a stimulus is called a reflex. The patellar reflex results from tapping the patellar tendon below the knee with a reflex
Name: Neuromuscular Reflexes Experiment 14A The automatic response of a muscle to a stimulus is called a reflex. The patellar reflex results from tapping the patellar tendon below the knee with a reflex
In addition to reading this assignment, also read Appendices A and B.
 1 Kinematics I Introduction In addition to reading this assignment, also read Appendices A and B. We will be using a motion detector to track the positions of objects with time in several lab exercises
1 Kinematics I Introduction In addition to reading this assignment, also read Appendices A and B. We will be using a motion detector to track the positions of objects with time in several lab exercises
EXPERIMENT XI. Careful!! Improper handling of the vacuum line may result in the release of SO 2 which is an irritating and suffocating gas.
 Chem 366-3 Page XI - 1 EXPERIMENT XI INFRARED SPECTRUM OF SO2 (S&G, 5th ed. Expt 36, 6th ed. Expt. 35) 1. Pre-Lab preparation. The description of this experiment has disappeared from the more recent editions
Chem 366-3 Page XI - 1 EXPERIMENT XI INFRARED SPECTRUM OF SO2 (S&G, 5th ed. Expt 36, 6th ed. Expt. 35) 1. Pre-Lab preparation. The description of this experiment has disappeared from the more recent editions
15KM 14-WEEK TRAINING PROGRAMME
 15KM 14-WEEK TRAINING PROGRAMME T H E G O A L O F T H I S P L A N I S N T T O G E T Y O U A C R O S S T H E F I N I S H L I N E, I T S T O G E T T H E B E S T V E R S I O N O F Y O U A C R O S S T H E
15KM 14-WEEK TRAINING PROGRAMME T H E G O A L O F T H I S P L A N I S N T T O G E T Y O U A C R O S S T H E F I N I S H L I N E, I T S T O G E T T H E B E S T V E R S I O N O F Y O U A C R O S S T H E
The Crossvent 2i+ 2. Ventilator Concept (brief theory of operation and features)
 The Crossvent 2i+ 1. How is this ventilator classified 2. Ventilator Concept (brief theory of operation and features) -Your Two Choices with this Ventilator 3. An overview of the device (an in-service)
The Crossvent 2i+ 1. How is this ventilator classified 2. Ventilator Concept (brief theory of operation and features) -Your Two Choices with this Ventilator 3. An overview of the device (an in-service)
RM-80 respiration monitor
 RM-80 respiration monitor User Manual September 18, 2015 0025-003M 950 North Hague Avenue Columbus, Ohio 43204-2121 USA Sales: sales@colinst.com Service: service@colinst.com Phone: (614) 276-0861 Fax:
RM-80 respiration monitor User Manual September 18, 2015 0025-003M 950 North Hague Avenue Columbus, Ohio 43204-2121 USA Sales: sales@colinst.com Service: service@colinst.com Phone: (614) 276-0861 Fax:
Figure SM1: Front panel of the multipatcher software graphic user interface (GUI) at the beginning of multipatcher operation.
 APPENDIX 2. Multipatcher Software Setup and Operation. The multipatcher program is organized into four panels. There are controls that allow the user to specify various parameters into the system. The
APPENDIX 2. Multipatcher Software Setup and Operation. The multipatcher program is organized into four panels. There are controls that allow the user to specify various parameters into the system. The
Harmonization exercises II
 Harmonization exercises II Pranayama The Sanskrit word meaning "extension of the prāṇa or breath" or "extension of the life force. Prana - life force, or vital energy Ayāma - to extend or draw out. The
Harmonization exercises II Pranayama The Sanskrit word meaning "extension of the prāṇa or breath" or "extension of the life force. Prana - life force, or vital energy Ayāma - to extend or draw out. The
Lab #1 Pressure: Bubblers and Water Balloons CEE 331 Fall 2003
 CEE 331 Lab 1 Page 1 of 9 SAFETY Lab #1 Pressure: Bubblers and Water Balloons CEE 331 Fall 2003 Laboratory exercise based on an exercise developed by Dr. Monroe Weber-Shirk The major safety hazard in this
CEE 331 Lab 1 Page 1 of 9 SAFETY Lab #1 Pressure: Bubblers and Water Balloons CEE 331 Fall 2003 Laboratory exercise based on an exercise developed by Dr. Monroe Weber-Shirk The major safety hazard in this
iworx Sample Lab Experiment HE-5: Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR)
 Experiment HE-5: Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR) Before Starting 1. Read the procedures for the experiment completely before beginning the experiment. Have a good understanding of how to perform the experiment
Experiment HE-5: Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR) Before Starting 1. Read the procedures for the experiment completely before beginning the experiment. Have a good understanding of how to perform the experiment
Race Screen: Figure 2: Race Screen. Figure 3: Race Screen with Top Bulb Lock
 Eliminator Competition Stand Alone Mode - Instruction Manual Main Menu: After startup, the Eliminator Competition will enter the Main Menu. Press the right/left arrow buttons to move through the menu.
Eliminator Competition Stand Alone Mode - Instruction Manual Main Menu: After startup, the Eliminator Competition will enter the Main Menu. Press the right/left arrow buttons to move through the menu.
Previous Release Notes
 Release Notes Shearwater Desktop 3.1.5 Support for NERD 2. Previous Release Notes Version 3.1.4 Improved Bluetooth Reliability with the initial connection. Bug Notes: dded software workaround to allow
Release Notes Shearwater Desktop 3.1.5 Support for NERD 2. Previous Release Notes Version 3.1.4 Improved Bluetooth Reliability with the initial connection. Bug Notes: dded software workaround to allow
Experiment AMe-1: Small Animal Respiratory Exchange Ratio (RER)
 Experiment AMe-1: Small Animal Respiratory Exchange Ratio (RER) Background There are two main sources of energy available for animal metabolism: carbohydrates (CHO) and fats. These molecules are broken
Experiment AMe-1: Small Animal Respiratory Exchange Ratio (RER) Background There are two main sources of energy available for animal metabolism: carbohydrates (CHO) and fats. These molecules are broken
Microsoft Windows Software Manual for FITstep Stream Version 4
 Thank you for purchasing this product from Gopher. If you are not satisfied with any Gopher purchase for any reason at any time, contact us and we will replace the product, credit your account, or refund
Thank you for purchasing this product from Gopher. If you are not satisfied with any Gopher purchase for any reason at any time, contact us and we will replace the product, credit your account, or refund
HEG Neurofeedback with Breathing Software Application User Guide
 MIND-BODY TRAINING TOOLS w w w. s t r e s s r e s i l i e n t m i n d. c o. u k Glyn Blackett HEG Neurofeedback with Breathing Software Application User Guide Contents 1 Introduction...2 2 Launching the
MIND-BODY TRAINING TOOLS w w w. s t r e s s r e s i l i e n t m i n d. c o. u k Glyn Blackett HEG Neurofeedback with Breathing Software Application User Guide Contents 1 Introduction...2 2 Launching the
Technology. In the My Files [My Files] submenu you can store all the programs that you have made on the NXT or downloaded from your computer.
![Technology. In the My Files [My Files] submenu you can store all the programs that you have made on the NXT or downloaded from your computer. Technology. In the My Files [My Files] submenu you can store all the programs that you have made on the NXT or downloaded from your computer.](/thumbs/74/70002303.jpg) NXT Main Menu My Files Files are automatically placed into the appropriate folders. When you download a program using a Sound file to the NXT, the program will be placed under Software files while the
NXT Main Menu My Files Files are automatically placed into the appropriate folders. When you download a program using a Sound file to the NXT, the program will be placed under Software files while the
HEALTHCARE CPR Metrix
 HEALTHCARE CPR Metrix LF03405U CPR Metrix Control Box Only LF03406U CPR Metrix and ipad INSTRUCTION MANUAL *ipad is a trademark of Apple, Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
HEALTHCARE CPR Metrix LF03405U CPR Metrix Control Box Only LF03406U CPR Metrix and ipad INSTRUCTION MANUAL *ipad is a trademark of Apple, Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Overview. The user must follow the instructions below.
 Overview Thank you for purchasing i-pad. This product can be successfully and safely used for a long period if you familiarize yourself with the instructions and precautions by reading the user's manual
Overview Thank you for purchasing i-pad. This product can be successfully and safely used for a long period if you familiarize yourself with the instructions and precautions by reading the user's manual
18-WEEK BANK OF AMERICA CHICAGO MARATHON TRAINING PROGRAM OCTOBER 7, 2018
 18-WEEK BANK OF AMERICA CHICAGO MARATHON TRAINING PROGRAM OCTOBER 7, 2018 CONTENTS 04 INTRODUCTION 05 WEEKLY WORKOUTS 08 PACE CHART 09 GLOSSARY 10 IF YOU... 11 2018 BANK OF AMERICA CHICAGO MARATHON WEEK-BY-WEEK
18-WEEK BANK OF AMERICA CHICAGO MARATHON TRAINING PROGRAM OCTOBER 7, 2018 CONTENTS 04 INTRODUCTION 05 WEEKLY WORKOUTS 08 PACE CHART 09 GLOSSARY 10 IF YOU... 11 2018 BANK OF AMERICA CHICAGO MARATHON WEEK-BY-WEEK
Circulation and Respiration: Vital Signs Student Version
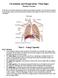 Circulation and Respiration: Vital Signs Student Version In this lab, you will learn about the circulatory and respiratory systems. You will test the capacity of your lungs, measure your blood pressure
Circulation and Respiration: Vital Signs Student Version In this lab, you will learn about the circulatory and respiratory systems. You will test the capacity of your lungs, measure your blood pressure
Application Note AN-107
 SPEC Sensor TM Characterization & Calibration Considerations Scope This document is provided to describe the considerations needed to characterize, calibrate, verify and validate the measurement performance
SPEC Sensor TM Characterization & Calibration Considerations Scope This document is provided to describe the considerations needed to characterize, calibrate, verify and validate the measurement performance
TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 3 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS 3 PACKAGE CONTENTS 4 DEVICE OVERVIEW 4 BUTTON OPERATION SUMMARY 5 BASIC OPERATION 6
 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 3 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS 3 PACKAGE CONTENTS 4 DEVICE OVERVIEW 4 BUTTON OPERATION SUMMARY 5 BASIC OPERATION 6 CURRENT TIME MODE 7 FUNCTIONAL DISPLAY 7 WEATHER FORECAST FEATURE
TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 3 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS 3 PACKAGE CONTENTS 4 DEVICE OVERVIEW 4 BUTTON OPERATION SUMMARY 5 BASIC OPERATION 6 CURRENT TIME MODE 7 FUNCTIONAL DISPLAY 7 WEATHER FORECAST FEATURE
bespoke In general health and rehabilitation Breath-by-breath multi-functional respiratory gas analyser In human performance
 Introduction Expired Gas Analysis or indirect calorimetry, can be used to measure ventilation and the fractions of oxygen and carbon dioxide in expired air. From these measurements, the body's oxygen consumption
Introduction Expired Gas Analysis or indirect calorimetry, can be used to measure ventilation and the fractions of oxygen and carbon dioxide in expired air. From these measurements, the body's oxygen consumption
Data Sheet T 8389 EN. Series 3730 and 3731 Types , , , and. EXPERTplus Valve Diagnostic
 Data Sheet T 8389 EN Series 3730 and 3731 Types 3730-2, 3730-3, 3730-4, 3730-5 and Type 3731-3 Electropneumatic Positioners EXPERTplus Valve Diagnostic Application Positioner firmware to detect potential
Data Sheet T 8389 EN Series 3730 and 3731 Types 3730-2, 3730-3, 3730-4, 3730-5 and Type 3731-3 Electropneumatic Positioners EXPERTplus Valve Diagnostic Application Positioner firmware to detect potential
Advanced Test Equipment Rentals ATEC (2832) OMS 600
 Established 1981 Advanced Test Equipment Rentals www.atecorp.com 800-404-ATEC (2832) OMS 600 Continuous partial discharge monitoring system for power generators and electrical motors Condition monitoring
Established 1981 Advanced Test Equipment Rentals www.atecorp.com 800-404-ATEC (2832) OMS 600 Continuous partial discharge monitoring system for power generators and electrical motors Condition monitoring
CENTER PIVOT EVALUATION AND DESIGN
 CENTER PIVOT EVALUATION AND DESIGN Dale F. Heermann Agricultural Engineer USDA-ARS 2150 Centre Avenue, Building D, Suite 320 Fort Collins, CO 80526 Voice -970-492-7410 Fax - 970-492-7408 Email - dale.heermann@ars.usda.gov
CENTER PIVOT EVALUATION AND DESIGN Dale F. Heermann Agricultural Engineer USDA-ARS 2150 Centre Avenue, Building D, Suite 320 Fort Collins, CO 80526 Voice -970-492-7410 Fax - 970-492-7408 Email - dale.heermann@ars.usda.gov
Series 3730 and Series 3731 EXPERTplus Valve Diagnostics with Partial Stroke Test (PST)
 Series 3730 and Series 3731 EXPERTplus Valve Diagnostics with Partial Stroke Test (PST) Application Positioner firmware for early detection of control valve faults giving maintenance recommendations. Valid
Series 3730 and Series 3731 EXPERTplus Valve Diagnostics with Partial Stroke Test (PST) Application Positioner firmware for early detection of control valve faults giving maintenance recommendations. Valid
To Logon On to your tee sheet, start by opening your browser. (NOTE: Internet Explorer V. 6.0 or greater is required.)
 1. Log-On To Logon On to your tee sheet, start by opening your browser. (NOTE: Internet Explorer V. 6.0 or greater is required.) (NOTE: Logon ID s must be 7 characters or more and passwords are case sensitive.)
1. Log-On To Logon On to your tee sheet, start by opening your browser. (NOTE: Internet Explorer V. 6.0 or greater is required.) (NOTE: Logon ID s must be 7 characters or more and passwords are case sensitive.)
Experiment AMe-1: Small Animal Respiratory Exchange Ratio (RER)
 Experiment AMe-1: Small Animal Respiratory Exchange Ratio (RER) Background There are two main sources of energy available for animal metabolism: carbohydrates (CHO) and fats. These molecules are broken
Experiment AMe-1: Small Animal Respiratory Exchange Ratio (RER) Background There are two main sources of energy available for animal metabolism: carbohydrates (CHO) and fats. These molecules are broken
Tennis...32 Stay above...34 Decimal...36 Bundesliga simulator...38 Shooter management...41 Installation...43 Registration...45 Where do I get the
 Content ShotAnalyzer with Scatt and the Häring target system... 3 ShotAnalyzer with Scatt and the Meyton target system... 5 ShotAnalyzer with Scatt and the Disag target system... 7 ShotAnalyzer with Scatt
Content ShotAnalyzer with Scatt and the Häring target system... 3 ShotAnalyzer with Scatt and the Meyton target system... 5 ShotAnalyzer with Scatt and the Disag target system... 7 ShotAnalyzer with Scatt
OptonPro. High-power laser up to 7000 mw. Laser therapy natural healing with the power of light
 GB High-power laser up to 7000 mw Laser therapy natural healing with the power of light Application of high-power light for targeted penetration of high amounts of energy deep into the tissue. Initiates
GB High-power laser up to 7000 mw Laser therapy natural healing with the power of light Application of high-power light for targeted penetration of high amounts of energy deep into the tissue. Initiates
Xactix XeF2 OPERATION MANUAL
 General Information The Xactix e-1 is a xenon difluoride (XeF 2) isotropic silicon etcher. XeF 2 is a vapor phase etch, which exhibits very high selectivity of silicon to photo-resist, silicon dioxide,
General Information The Xactix e-1 is a xenon difluoride (XeF 2) isotropic silicon etcher. XeF 2 is a vapor phase etch, which exhibits very high selectivity of silicon to photo-resist, silicon dioxide,
Back/Lay Favorite Bot
 Back/Lay Favorite Bot - Updated on 20 th April 2011-2008-2011 http://www.bfbotmanager.com Page 1 Contents 1. Strategy... 3 2. Bot controls... 5 3. Wallet controls... 9 4. User Bets... 14 5. Resources...
Back/Lay Favorite Bot - Updated on 20 th April 2011-2008-2011 http://www.bfbotmanager.com Page 1 Contents 1. Strategy... 3 2. Bot controls... 5 3. Wallet controls... 9 4. User Bets... 14 5. Resources...
DT 630 ALTIMETER, BAROMETER AND COMPASS WATCH OPERATING INSTRUSTIONS
 DT 630 ALTIMETER, BAROMETER AND COMPASS WATCH OPERATING INSTRUSTIONS Overview:--- Positive or Negative Icon Barometric Trend Indicator SELECT Low Battery Indicator AM/FM Indicator Daily Alarm Indicator
DT 630 ALTIMETER, BAROMETER AND COMPASS WATCH OPERATING INSTRUSTIONS Overview:--- Positive or Negative Icon Barometric Trend Indicator SELECT Low Battery Indicator AM/FM Indicator Daily Alarm Indicator
Page 1 Make more profit from your betting at Betting Speed Evolution and the Race Advisor
 Page 1 Introduction The information contained here has been put together to assist you in not only finding winning horses, but making good profits. The software is based around a complex professional strategy.
Page 1 Introduction The information contained here has been put together to assist you in not only finding winning horses, but making good profits. The software is based around a complex professional strategy.
Exercise and Respiration Rate
 Activity 17 PS-2820 Physiology: Breathing, respiration rate Exercise and Respiration Rate DataStudio GLX setup file: respiration.glx Qty Equipment and Materials Part Number 1 PASPORT Xplorer GLX PS-2002
Activity 17 PS-2820 Physiology: Breathing, respiration rate Exercise and Respiration Rate DataStudio GLX setup file: respiration.glx Qty Equipment and Materials Part Number 1 PASPORT Xplorer GLX PS-2002
Basic Shooting Skills Principles of Marksmanship. By: Shannon Carlton
 Basic Shooting Skills Principles of Marksmanship By: Shannon Carlton Agenda Introduction Principles of Coaching 5 Principles of Marksmanship Developing a Routine Making Sight Adjustments Sequences Principles
Basic Shooting Skills Principles of Marksmanship By: Shannon Carlton Agenda Introduction Principles of Coaching 5 Principles of Marksmanship Developing a Routine Making Sight Adjustments Sequences Principles
Experiment 11: The Ideal Gas Law
 Experiment 11: The Ideal Gas Law The behavior of an ideal gas is described by its equation of state, PV = nrt. You will look at two special cases of this. Part 1: Determination of Absolute Zero. You will
Experiment 11: The Ideal Gas Law The behavior of an ideal gas is described by its equation of state, PV = nrt. You will look at two special cases of this. Part 1: Determination of Absolute Zero. You will
Restrictive and Obstructive Airway Diseases
 iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HS-8-1 Restrictive and Obstructive Airway Diseases Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should refer to the User
iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HS-8-1 Restrictive and Obstructive Airway Diseases Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should refer to the User
NanoSight NS300. NanoSight NS300. Operation instructions. Laser Spectroscopy Labs, UCI
 NanoSight NS300 Operation instructions Injection/flushing brief overview: 1. Do not exceed flow of 1 ml per 20 seconds. 2. Inject two 1 ml syringes with nano-pure or DI water. 3. If the water does not
NanoSight NS300 Operation instructions Injection/flushing brief overview: 1. Do not exceed flow of 1 ml per 20 seconds. 2. Inject two 1 ml syringes with nano-pure or DI water. 3. If the water does not
Cover Page for Lab Report Group Portion. Head Losses in Pipes
 Cover Page for Lab Report Group Portion Head Losses in Pipes Prepared by Professor J. M. Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revision: 02 February 2012 Name 1: Name 2: Name 3: [Name 4: ] Date: Section
Cover Page for Lab Report Group Portion Head Losses in Pipes Prepared by Professor J. M. Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revision: 02 February 2012 Name 1: Name 2: Name 3: [Name 4: ] Date: Section
HOW TO USE THE 16-WEEK MARATHON PLAN
 LET S RUN! YOUR MARATHON PLAN STARTS HERE HOW TO USE THE 16-WEEK MARATHON PLAN To ensure you make it to the Start Line in great shape to enjoy your marathon adventure, we ve devised a training plan to
LET S RUN! YOUR MARATHON PLAN STARTS HERE HOW TO USE THE 16-WEEK MARATHON PLAN To ensure you make it to the Start Line in great shape to enjoy your marathon adventure, we ve devised a training plan to
Module 3 Developing Timing Plans for Efficient Intersection Operations During Moderate Traffic Volume Conditions
 Module 3 Developing Timing Plans for Efficient Intersection Operations During Moderate Traffic Volume Conditions CONTENTS (MODULE 3) Introduction...1 Purpose...1 Goals and Learning Outcomes...1 Organization
Module 3 Developing Timing Plans for Efficient Intersection Operations During Moderate Traffic Volume Conditions CONTENTS (MODULE 3) Introduction...1 Purpose...1 Goals and Learning Outcomes...1 Organization
LEO SEM SOP Page 1 of 9 Revision 1.4 LEO 440 SEM SOP. Leica Leo Stereoscan 440i
 LEO SEM SOP Page 1 of 9 LEO 440 SEM SOP Gun (Filament) Column Manual Valves Chamber Window Chamber Stage Movement Leica Leo Stereoscan 440i 1. Scope 1.1 This document provides the procedure for operating
LEO SEM SOP Page 1 of 9 LEO 440 SEM SOP Gun (Filament) Column Manual Valves Chamber Window Chamber Stage Movement Leica Leo Stereoscan 440i 1. Scope 1.1 This document provides the procedure for operating
FIG: 27.1 Tool String
 Bring up Radioactive Tracer service. Click Acquisition Box - Edit - Tool String Edit the tool string as necessary to reflect the tool string being run. This is important to insure proper offsets, filters,
Bring up Radioactive Tracer service. Click Acquisition Box - Edit - Tool String Edit the tool string as necessary to reflect the tool string being run. This is important to insure proper offsets, filters,
Dynamic Positioning Control Augmentation for Jack-up Vessels
 DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE October 9-10, 2012 Design and Control Session Dynamic Positioning Control Augmentation for Jack-up Vessels By Bradley Deghuee L-3 Communications 1 Introduction Specialized
DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE October 9-10, 2012 Design and Control Session Dynamic Positioning Control Augmentation for Jack-up Vessels By Bradley Deghuee L-3 Communications 1 Introduction Specialized
Model UB-328. Wrist Digital Blood Pressure Monitor. Instruction Manual. Manuel d instructions. Manual de Instrucciones. Manuale di Istruzioni
 Wrist Digital Blood Pressure Monitor Model UB-328 Instruction Manual Manuel d instructions Manual de Instrucciones Manuale di Istruzioni WM+PD4000913 ENGLISH Dear Customers Congratulations. You have purchased
Wrist Digital Blood Pressure Monitor Model UB-328 Instruction Manual Manuel d instructions Manual de Instrucciones Manuale di Istruzioni WM+PD4000913 ENGLISH Dear Customers Congratulations. You have purchased
Lung Volumes and Capacities
 BIOL242 Lung Volumes and Capacities Measurement of lung volumes provides a tool for understanding normal function of the lungs as well as disease states. The breathing cycle is initiated by expansion of
BIOL242 Lung Volumes and Capacities Measurement of lung volumes provides a tool for understanding normal function of the lungs as well as disease states. The breathing cycle is initiated by expansion of
Golfshot : Golf GPS Android User Guide
 Golfshot : Golf GPS Android User Guide Version 3.5 Scorecard Version 3.5 QUICK TIPS: New in 3.5: Track Menu Track Menu Press the Golf Ball icon in the upper left corner to slide down the Track Menu. Here
Golfshot : Golf GPS Android User Guide Version 3.5 Scorecard Version 3.5 QUICK TIPS: New in 3.5: Track Menu Track Menu Press the Golf Ball icon in the upper left corner to slide down the Track Menu. Here
Instruction Manual. Auto Inflate Blood Pressure Monitor
 TM Auto Inflate Blood Pressure Monitor Instruction Manual Features: Fuzzy Logic Technology Auto memory for up to 90 readings One-Touch Operation Easy-to-read Display Date and Time indications AC Adapter
TM Auto Inflate Blood Pressure Monitor Instruction Manual Features: Fuzzy Logic Technology Auto memory for up to 90 readings One-Touch Operation Easy-to-read Display Date and Time indications AC Adapter
SENSUS PRO MANAGER (for SENSUS or SENSUS PRO devices) User s Guide -- Windows. Version 2.0 Published October 17, ReefNet Inc.
 SENSUS PRO MANAGER (for SENSUS or SENSUS PRO devices) User s Guide -- Windows Version 2.0 Published October 17, 2002 2002 ReefNet Inc. 1.0 Introduction The SENSUS PRO data recorder captures the time, depth,
SENSUS PRO MANAGER (for SENSUS or SENSUS PRO devices) User s Guide -- Windows Version 2.0 Published October 17, 2002 2002 ReefNet Inc. 1.0 Introduction The SENSUS PRO data recorder captures the time, depth,
Wave Motion. interference destructive interferecne constructive interference in phase. out of phase standing wave antinodes resonant frequencies
 Wave Motion Vocabulary mechanical waves pulse continuous periodic wave amplitude period wavelength period wave velocity phase transverse wave longitudinal wave intensity displacement amplitude phase velocity
Wave Motion Vocabulary mechanical waves pulse continuous periodic wave amplitude period wavelength period wave velocity phase transverse wave longitudinal wave intensity displacement amplitude phase velocity
Gravity: How fast do objects fall? Teacher Version (Grade level: 4 7)
 Gravity: How fast do objects fall? Teacher Version (Grade level: 4 7) *** Experiment with Audacity to be sure you know how to do what s needed for the lab*** Kinematics is the study of how things move
Gravity: How fast do objects fall? Teacher Version (Grade level: 4 7) *** Experiment with Audacity to be sure you know how to do what s needed for the lab*** Kinematics is the study of how things move
