Physiological Basis of Mechanical Ventilation
|
|
|
- Ira Rodgers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Physiological Basis of Mechanical Ventilation Wally Carlo, M.D. University of Alabama at Birmingham Department of Pediatrics Division of Neonatology
2
3 Fine Tuning Mechanical Ventilation (Outline) 1. Pulmonary mechanics 2. Gas exchange 3. Mechanoreceptor reflexes 4. Lung injury 5. Ventilatory strategies
4 COMPLIANCE 1. Is a measure of elasticity or distensibility of the lungs (and chest wall) 2. Can be calculated as: Compliance = Volume = V T Pressure PIP-PEEP
5
6 C C 20 Volume Above FRC (ml) cmh 2 O P max 0.8 P max High inflection point Low inflection point 20
7 Tidal Volume (% Max) 100 Effect of Decreased Compliance and Inspiratory Time on Tidal Volume Time (msec) Both Left Right
8 RESISTANCE 1. Is a measure of the friction generated by: - movement of gas in the airways (airway resistance) and - movement of lung tissue (tissue resistance) 2. Can be calculated as: Resistance = Pressure Flow
9
10 TIME CONSTANT 1. Is a measure of the time necessary for a 63% of a step change (e.g. airway pressure gradient) to equilibrate. 2. Calculated from the product of compliance and resistance. Time constant = Compliance x Resistance
11 Change in Pressure (%) TIME CONSTANT 63% 86% 95% 98% 99% Time Time Constants
12 Calculations of Pulmonary Mechanics 3 kg Term Normal PIP/PEEP 10/3 Tidal volume (cc) 14 Resistance (cmh 2 O/L/sec) 50 2 kg RDS 14/ Compliance Δ V = 14 = 14 = 2 Δ P Time constant = C x R Time constant = 2 x 50 = 100 msec 6 = 6 = x 100 = 60 msec
13
14 Chest wall motion Short TI Optimal TI Long TI Inadequate tidal volume Short insp. plateau Long plateau Time Chest wall motion Short TE Optimal TE Long TE Gas trapping, inadvertent PEEP Expiratory plateau Long expiratory plateau Time
15 Effect of Incomplete Inspiration on Gas Exchange Incomplete Inspiration Tidal volume Mean airway pressure Hypercapnia Hypoxemia
16 Effect of Incomplete Expiration on Gas Exchange Incomplete expiration Gas trapping Compliance Tidal volume Mean airway pressure Tidal volume Cardiac output Hypercapnia Hyperoxemia
17 Detection of Gas Trapping Anticipate with high respiratory rates, normal C, and high R Decreased chest wall movement Inadvertent PEEP Overexpansion on chest radiograph CO 2 retention; or PaO 2 Increased lung volume Depressed cardiovascular function Increased CVP, decreased blood pressure Metabolic acidosis, peripheral edema Increased intrathoracic or esophageal pressure
18 Because the interaction of the ventilator and the lungs is strongly dependent on the mechanical properties of the respiratory system, the pathophysiology of the pulmonary disease deserves serious consideration when developing ventilatory strategies.
19 Birmingham Civil Rights Institute Vulcan Vulcan Park City of Birmingham McWane Center Historic Tutwiler Hotel
20 Fine Tuning Mechanical Ventilation (Outline) 1. Pulmonary mechanics 2. Gas exchange 3. Mechanoreceptor reflexes 4. Lung injury 5. Ventilatory strategies
21 Mechanisms of Hypoxemia 1. V/Q mismatch 2. Shunt 3. Hypoventilation 4. Diffusion limitation
22 Ventilation Perfusion (V/Q) Mismatch a. Is an important and frequent cause of hypoxemia in neonates (e.g. RDS) b. Normal ratio of ventilation to perfusion should approximate 1, but in V/Q mismatch it does not approximate 1 c. Supplemental oxygen can largely overcome the hypoxemia
23 Shunt a. Common cause of hypoxemia in neonates b. May be physiologic, intracardiac (e.g. PPHN, CHD), or pulmonary (e.g. atelectasis) c. Supplemental O 2 cannot reverse the hypoxemia
24 Hypoventilation a. Common cause of transient hypoxemia (e.g. apnea) b. Rate of oxygen uptake from the alveoli exceeds its replenishment c. Supplemental O 2 can easily overcome the hypoxemia
25 Diffusion Limitation a. Is an uncommon cause of severe hypoxemia, even in the presence of lung disease (e.g. pulmonary edema) b. Occurs when mixed venous blood does not equilibrate with alveolar gas c. Supplemental O 2 can easily overcome the hypoxemia
26 Summary of Mechanisms of Hypoxemia Common Responsive to O 2 V/Q mismatch Yes Somewhat Shunt Yes No Hypoventilation Transient Very Diffusion limitation No Very
27 FiO 2 OXYGENATION Ventilation parameters that determine oxygenation MEAN AIRWAY PRESSURE PEAK INSP. PRESSURE FLOW END EXP. PRESSURE I:E RATIO
28 Mechanisms of Hypercapnia 1. Hypoventilation (decreased V T or f) 2. Increased dead space a. Gas exchange is inefficient because of wasted ventilation b. Includes ventilation to conducting airways and to alveolar spaces not perfused 3. V/Q mismatch 4. Shunt
29 CO 2 ELIMINATION Ventilation parameters that determine CO 2 elimination MINUTE VENTILATION FREQUENCY TIDAL VOLUME RESISTANCE EXP TIME INSP TIME TIME CONSTANT I:E RATIO PRESSURE GRADIENT COMPLIANCE END EXP PRESSURE PEAK INSP PRESSURE
30
31 UAB
32 Fine Tuning Mechanical Ventilation (Outline) 1. Pulmonary mechanics 2. Gas exchange 3. Mechanoreceptor reflexes 4. Lung injury 5. Ventilatory strategies
33 Respiratory Mechanoreflexes Hering-Breuer reflex Head s paradoxical reflex Intercostal phrenic inhibitory reflex
34 Hering-Breuer Reflex In response to lung inflation there is cessation of inspiration and prolongation of the expiratory time In response to an end expiratory occlusion there is a prolongation of the inspiratory time (because the lungs do not inflate and the reflex is not active)
35 Example of a Potent Hering-Breuer Reflex
36 Head s Paradoxical or the Augmenting Inspiratory Reflex 15 Volume (ml) 2 sec Oesophageal pressure (mmh 2 O) Ventilator pressure (cmh 2 O) 0 Greenough et al. Neonatal Respiratory Disorders 1996
37 Fine Tuning Mechanical Ventilation (Outline) 1. Pulmonary mechanics 2. Gas exchange 3. Mechanoreceptor reflexes 4. Lung injury 5. Ventilatory strategies
38 LUNG INJURY DURING ASSISTED VENTILATION 1. Chest wall restriction limits pressure-induced lung injury (Hernandez, et al., 1988) 2. Overexpansion of the thorax with negative pressures causes lung injury (Dreyfus, et al. 1988)
39 VOLUME vs PRESSURE IN LUNG INJURY Pulm. Epith. Hyaline Lymph Filtr. Volume Pressure Edema Injury Memb. Flow Coef. IPPV High High Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Iron Lung High Low Yes Yes Yes N/A N/A Strapping Low High No No No No No Dreyfus et al, 1988; Bshouty et al, 1988; Hernandez et al, 1989; Corbridge et al, 1990; Carlton et al 1990; Zhenxing et al, 1992
40 WHICH VOLUMES CAUSE LUNG INJURY? Volutrauma Zone Overdistention Time Volutrauma Zone A B C D Atelectasis A High V T low PEEP W. Carlo 2003 B Normal V T, high PEEP C Normal V T low PEEP D Optimal ventilation
41 EFFECT OF TIDAL VOLUME ON LUNG COMPLIANCE Compliance (cc/cmh 2 O kg) Age (min) 8 cc/kg 16cc/kg 32 cc/kg Bjorklund et al. 39:326A, 1996; Bjorkland et al. Pediatr Res 42:348, 1997
42 EFFECT OF TIMING INFLATION ON LUNG VOLUTRAUMA Compliance (cc/cmh 2 O kg) Age (min) Ingirmarsson et al. Pediatr Res 41:255A, 1997; Bjorkland et al. Pediatr Res 42:348, After Surfactant Before Surfactant
43 EARLY PEEP AND LUNG FUNCTION PEEP 4 PEEP 7 PEEP 0-Nat PEEP 0 Michna et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 160:634, 1999
44 VENTILATOR-ASSOCIATED LUNG INJURY (VALI) Likely mechanisms Volume rather than pressures End expiratory volume rather than V T or FRC Transalveolar pressure and reopening of alveoli Repeated collapse and reopening of alveoli Very low positive end expiratory pressure Oxidant injury
45 REASONS FOR SUSCEPTIBLITY OF NEONATAL LUNG INJURY Poorly compliant alveoli but highly compliant airways Immature antioxidant defense systems Immature macrophages and leukocytes and altered airway clearance mechanisms Poorly developed antioxidants antiproteolytic, antielastolytic systems Increased permeability of alveolar-capillary membrane
46 CONCEPTS IN APPLICATION ASSISTED VENTILATION Assisted ventilation may lead to adverse consequences To minimize side effects, blood gas targets do not have to be in the normal ranges Gas trapping (dynamic hyperinflation) and alveolar overdistention may lead to lung damage and should be limited ACCP Conference. Chest 104:1833, 1993.
47 Fine Tuning Mechanical Ventilation (Outline) 1. Pulmonary mechanics 2. Gas exchange 3. Mechanoreceptor reflexes 4. Lung injury 5. Ventilatory strategies
Neonatal Assisted Ventilation. Haresh Modi, M.D. Aspirus Wausau Hospital, Wausau, WI.
 Neonatal Assisted Ventilation Haresh Modi, M.D. Aspirus Wausau Hospital, Wausau, WI. History of Assisted Ventilation Negative pressure : Spirophore developed in 1876 with manual device to create negative
Neonatal Assisted Ventilation Haresh Modi, M.D. Aspirus Wausau Hospital, Wausau, WI. History of Assisted Ventilation Negative pressure : Spirophore developed in 1876 with manual device to create negative
Principles of mechanical ventilation. Anton van Kaam, MD, PhD Emma Children s Hospital AMC Amsterdam, The Netherlands
 Principles of mechanical ventilation Anton van Kaam, MD, PhD Emma Children s Hospital AMC Amsterdam, The Netherlands Disclosure Research grant Chiesi Pharmaceuticals Research grant CareFusion GA: 27 weeks,
Principles of mechanical ventilation Anton van Kaam, MD, PhD Emma Children s Hospital AMC Amsterdam, The Netherlands Disclosure Research grant Chiesi Pharmaceuticals Research grant CareFusion GA: 27 weeks,
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY. Anaesthesiology Block 18 (GNK 586) Prof Pierre Fourie
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Anaesthesiology Block 18 (GNK 586) Prof Pierre Fourie Outline Ventilation Diffusion Perfusion Ventilation-Perfusion relationship Work of breathing Control of Ventilation 2 This image
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Anaesthesiology Block 18 (GNK 586) Prof Pierre Fourie Outline Ventilation Diffusion Perfusion Ventilation-Perfusion relationship Work of breathing Control of Ventilation 2 This image
Respiration (revised 2006) Pulmonary Mechanics
 Respiration (revised 2006) Pulmonary Mechanics PUL 1. Diagram how pleural pressure, alveolar pressure, airflow, and lung volume change during a normal quiet breathing cycle. Identify on the figure the
Respiration (revised 2006) Pulmonary Mechanics PUL 1. Diagram how pleural pressure, alveolar pressure, airflow, and lung volume change during a normal quiet breathing cycle. Identify on the figure the
Presentation Overview. Monitoring Strategies for the Mechanically Ventilated Patient. Early Monitoring Strategies. Early Attempts To Monitor WOB
 Monitoring Strategies for the Mechanically entilated Patient Presentation Overview A look back into the future What works and what may work What s all the hype about the WOB? Are ventilator graphics really
Monitoring Strategies for the Mechanically entilated Patient Presentation Overview A look back into the future What works and what may work What s all the hype about the WOB? Are ventilator graphics really
Basics of Mechanical Ventilation. Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity
 Basics of Mechanical Ventilation Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity Overview of topics 1. Goals 2. Settings 3. Modes 4. Advantages and disadvantages
Basics of Mechanical Ventilation Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity Overview of topics 1. Goals 2. Settings 3. Modes 4. Advantages and disadvantages
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY, PHYSICS AND PATHOLOGY IN RELATION TO ANAESTHESIA AND INTENSIVE CARE
 Course n : Course 3 Title: RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY, PHYSICS AND PATHOLOGY IN RELATION TO ANAESTHESIA AND INTENSIVE CARE Sub-category: Intensive Care for Respiratory Distress Topic: Pulmonary Function and
Course n : Course 3 Title: RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY, PHYSICS AND PATHOLOGY IN RELATION TO ANAESTHESIA AND INTENSIVE CARE Sub-category: Intensive Care for Respiratory Distress Topic: Pulmonary Function and
Introduction. Respiration. Chapter 10. Objectives. Objectives. The Respiratory System
 Introduction Respiration Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body Plays a role in the regulation of acidbase balance during exercise Objectives
Introduction Respiration Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body Plays a role in the regulation of acidbase balance during exercise Objectives
VENTILATION AND PERFUSION IN HEALTH AND DISEASE. Dr.HARIPRASAD VS
 VENTILATION AND PERFUSION IN HEALTH AND DISEASE Dr.HARIPRASAD VS Ventilation Total ventilation - total rate of air flow in and out of the lung during normal tidal breathing. Alveolar ventilation -represents
VENTILATION AND PERFUSION IN HEALTH AND DISEASE Dr.HARIPRASAD VS Ventilation Total ventilation - total rate of air flow in and out of the lung during normal tidal breathing. Alveolar ventilation -represents
PICU Resident Self-Study Tutorial The Basic Physics of Oxygen Transport. I was told that there would be no math!
 Physiology of Oxygen Transport PICU Resident Self-Study Tutorial I was told that there would be no math! INTRODUCTION Christopher Carroll, MD Although cells rely on oxygen for aerobic metabolism and viability,
Physiology of Oxygen Transport PICU Resident Self-Study Tutorial I was told that there would be no math! INTRODUCTION Christopher Carroll, MD Although cells rely on oxygen for aerobic metabolism and viability,
Advanced Ventilator Modes. Shekhar T. Venkataraman M.D. Professor Critical Care Medicine and Pediatrics University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine
 Advanced Ventilator Modes Shekhar T. Venkataraman M.D. Shekhar T. Venkataraman M.D. Professor Critical Care Medicine and Pediatrics University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Advanced modes Pressure-Regulated
Advanced Ventilator Modes Shekhar T. Venkataraman M.D. Shekhar T. Venkataraman M.D. Professor Critical Care Medicine and Pediatrics University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Advanced modes Pressure-Regulated
APRV: Moving beyond ARDSnet
 APRV: Moving beyond ARDSnet Matthew Lissauer, MD Associate Professor of Surgery Medical Director, Surgical Critical Care Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey What is APRV? APRV is different from
APRV: Moving beyond ARDSnet Matthew Lissauer, MD Associate Professor of Surgery Medical Director, Surgical Critical Care Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey What is APRV? APRV is different from
Physiological based management of hypoxaemic respiratory failure
 Physiological based management of hypoxaemic respiratory failure David Tingay 1. Neonatal Research, Murdoch Children s Research Institute, Melbourne 2. Neonatology, Royal Children s Hospital 3. Dept of
Physiological based management of hypoxaemic respiratory failure David Tingay 1. Neonatal Research, Murdoch Children s Research Institute, Melbourne 2. Neonatology, Royal Children s Hospital 3. Dept of
UNIQUE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION MUST, AT ALL TIMES, ACCEPT THE ENTIRE CARDIAC OUTPUT
 UNIQUE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION MUST, AT ALL TIMES, ACCEPT THE ENTIRE CARDIAC OUTPUT UNIQUE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION
UNIQUE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION MUST, AT ALL TIMES, ACCEPT THE ENTIRE CARDIAC OUTPUT UNIQUE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION
mechanical ventilation Arjun Srinivasan
 Respiratory mechanics in mechanical ventilation Arjun Srinivasan Introduction Mechanics during ventilation PV curves Application in health & disease Difficulties & pitfalls The future. Monitoring Mechanics
Respiratory mechanics in mechanical ventilation Arjun Srinivasan Introduction Mechanics during ventilation PV curves Application in health & disease Difficulties & pitfalls The future. Monitoring Mechanics
Principles of Mechanical Ventilation: A Graphics-Based Approach
 Principles of Mechanical Ventilation: A Graphics-Based Approach Steven M. Donn, MD, FAAP Professor of Pediatrics Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine C.S. Mott Children s Hospital University of Michigan Health
Principles of Mechanical Ventilation: A Graphics-Based Approach Steven M. Donn, MD, FAAP Professor of Pediatrics Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine C.S. Mott Children s Hospital University of Michigan Health
INTRODUCTION TO BI-VENT (APRV) INTRODUCTION TO BI-VENT (APRV) PROGRAM OBJECTIVES
 INTRODUCTION TO BI-VENT (APRV) INTRODUCTION TO BI-VENT (APRV) PROGRAM OBJECTIVES PROVIDE THE DEFINITION FOR BI-VENT EXPLAIN THE BENEFITS OF BI-VENT EXPLAIN SET PARAMETERS IDENTIFY RECRUITMENT IN APRV USING
INTRODUCTION TO BI-VENT (APRV) INTRODUCTION TO BI-VENT (APRV) PROGRAM OBJECTIVES PROVIDE THE DEFINITION FOR BI-VENT EXPLAIN THE BENEFITS OF BI-VENT EXPLAIN SET PARAMETERS IDENTIFY RECRUITMENT IN APRV USING
OPEN LUNG APPROACH CONCEPT OF MECHANICAL VENTILATION
 OPEN LUNG APPROACH CONCEPT OF MECHANICAL VENTILATION L. Rudo Mathivha Intensive Care Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Aacademic Hospital & the University of the Witwatersrand OUTLINE Introduction Goals & Indications
OPEN LUNG APPROACH CONCEPT OF MECHANICAL VENTILATION L. Rudo Mathivha Intensive Care Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Aacademic Hospital & the University of the Witwatersrand OUTLINE Introduction Goals & Indications
VENTILATION STRATEGIES FOR THE CRITICALLY UNWELL
 VENTILATION STRATEGIES FOR THE CRITICALLY UNWELL Dr Nick Taylor Visiting Emergency Specialist Teaching Hospital Karapitiya Senior Specialist and Director ED Training Clinical Lecturer, Australian National
VENTILATION STRATEGIES FOR THE CRITICALLY UNWELL Dr Nick Taylor Visiting Emergency Specialist Teaching Hospital Karapitiya Senior Specialist and Director ED Training Clinical Lecturer, Australian National
How does HFOV work? John F Mills MBBS, FRACP, M Med Sc, PhD Neonatologist Royal Children s Hospital. Synopsis
 How does HFOV work? John F Mills MBBS, FRACP, M Med Sc, PhD Neonatologist Royal Children s Hospital Synopsis Definition of an oscillator Historical perspective Differences between HFOV and CMV Determinants
How does HFOV work? John F Mills MBBS, FRACP, M Med Sc, PhD Neonatologist Royal Children s Hospital Synopsis Definition of an oscillator Historical perspective Differences between HFOV and CMV Determinants
EMS INTER-FACILITY TRANSPORT WITH MECHANICAL VENTILATOR COURSE OBJECTIVES
 GENERAL PROVISIONS: EMS INTER-FACILITY TRANSPORT WITH MECHANICAL VENTILATOR COURSE OBJECTIVES Individuals providing Inter-facility transport with Mechanical Ventilator must have successfully completed
GENERAL PROVISIONS: EMS INTER-FACILITY TRANSPORT WITH MECHANICAL VENTILATOR COURSE OBJECTIVES Individuals providing Inter-facility transport with Mechanical Ventilator must have successfully completed
4. For external respiration to occur effectively, you need three parameters. They are:
 Self Assessment Module D Name: ANSWER KEY 1. Hypoxia should be assumed whenever the PaO 2 is below 45 mm Hg. 2. Name some clinical conditions that will result in hyperventilation (respiratory alkalosis).
Self Assessment Module D Name: ANSWER KEY 1. Hypoxia should be assumed whenever the PaO 2 is below 45 mm Hg. 2. Name some clinical conditions that will result in hyperventilation (respiratory alkalosis).
Lung Volumes and Capacities
 Lung Volumes and Capacities Normally the volume of air entering the lungs during a single inspiration is approximately equal to the volume leaving on the subsequent expiration and is called the tidal volume.
Lung Volumes and Capacities Normally the volume of air entering the lungs during a single inspiration is approximately equal to the volume leaving on the subsequent expiration and is called the tidal volume.
Respiratory System. Prepared by: Dorota Marczuk-Krynicka, MD, PhD
 Respiratory System Prepared by: Dorota Marczuk-Krynicka, MD, PhD Lungs: Ventilation Perfusion Gas Exchange - Diffusion 1. Airways and Airway Resistance (AWR) 2. Mechanics of Breathing and Lung (Elastic)
Respiratory System Prepared by: Dorota Marczuk-Krynicka, MD, PhD Lungs: Ventilation Perfusion Gas Exchange - Diffusion 1. Airways and Airway Resistance (AWR) 2. Mechanics of Breathing and Lung (Elastic)
Initiation and Management of Airway Pressure Release Ventilation (APRV)
 Initiation and Management of Airway Pressure Release Ventilation (APRV) Eric Kriner RRT Pulmonary Critical Care Clinical Specialist Pulmonary Services Department Medstar Washington Hospital Center Disclosures
Initiation and Management of Airway Pressure Release Ventilation (APRV) Eric Kriner RRT Pulmonary Critical Care Clinical Specialist Pulmonary Services Department Medstar Washington Hospital Center Disclosures
Capnography in the Veterinary Technician Toolbox. Katie Pinner BS, LVT Bush Advanced Veterinary Imaging Richmond, VA
 Capnography in the Veterinary Technician Toolbox Katie Pinner BS, LVT Bush Advanced Veterinary Imaging Richmond, VA What are Respiration and Ventilation? Respiration includes all those chemical and physical
Capnography in the Veterinary Technician Toolbox Katie Pinner BS, LVT Bush Advanced Veterinary Imaging Richmond, VA What are Respiration and Ventilation? Respiration includes all those chemical and physical
PART TWO CHAPTER 4 THE RAMIFICATIONS OF INTRAPULMONARY PERCUSSIVE VENTILATION (IPV ) and associated MECHANICAL INTRATHORACIC VESICULAR PERISTALSIS
 PART TWO CHAPTER 4 THE RAMIFICATIONS OF INTRAPULMONARY PERCUSSIVE VENTILATION (IPV ) and associated MECHANICAL INTRATHORACIC VESICULAR PERISTALSIS A DISCUSSION In 1979 F. M. Bird conceived the technology
PART TWO CHAPTER 4 THE RAMIFICATIONS OF INTRAPULMONARY PERCUSSIVE VENTILATION (IPV ) and associated MECHANICAL INTRATHORACIC VESICULAR PERISTALSIS A DISCUSSION In 1979 F. M. Bird conceived the technology
RSPT 1060 OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES EQUATION OF MOTION. MODULE C Applied Physics Lesson #1 - Mechanics. Ventilation vs.
 RSPT 1060 MODULE C Applied Physics Lesson #1 - Mechanics OBJECTIVES At the end of this module, the student should be able to define the terms and abbreviations used in the module. draw & explain the equation
RSPT 1060 MODULE C Applied Physics Lesson #1 - Mechanics OBJECTIVES At the end of this module, the student should be able to define the terms and abbreviations used in the module. draw & explain the equation
Lung Volumes and Ventilation
 Respiratory System ssrisuma@rics.bwh.harvard.edu Lung Volumes and Ventilation Minute ventilation Volume of an inspired or expired air per minute = tidal volume (V T ) x respiratory rate Dead space ventilation
Respiratory System ssrisuma@rics.bwh.harvard.edu Lung Volumes and Ventilation Minute ventilation Volume of an inspired or expired air per minute = tidal volume (V T ) x respiratory rate Dead space ventilation
3100A Competency Exam
 NAME DATE (Circle the appropriate answer) 3100A Competency Exam 1. Of the following, which best describes the mechanics of ventilation used by the 3100A? a. Active inspiration with passive exhalation b.
NAME DATE (Circle the appropriate answer) 3100A Competency Exam 1. Of the following, which best describes the mechanics of ventilation used by the 3100A? a. Active inspiration with passive exhalation b.
Respiratory Physiology. Adeyomoye O.I
 Respiratory Physiology By Adeyomoye O.I Outline Introduction Hypoxia Dyspnea Control of breathing Ventilation/perfusion ratios Respiratory/barometric changes in exercise Intra-pulmonary & intra-pleural
Respiratory Physiology By Adeyomoye O.I Outline Introduction Hypoxia Dyspnea Control of breathing Ventilation/perfusion ratios Respiratory/barometric changes in exercise Intra-pulmonary & intra-pleural
RESPIRATORY REGULATION DURING EXERCISE
 RESPIRATORY REGULATION DURING EXERCISE Respiration Respiration delivery of oxygen to and removal of carbon dioxide from the tissue External respiration ventilation and exchange of gases in the lung Internal
RESPIRATORY REGULATION DURING EXERCISE Respiration Respiration delivery of oxygen to and removal of carbon dioxide from the tissue External respiration ventilation and exchange of gases in the lung Internal
Collin County Community College. Lung Physiology
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 9 Respiratory System 1 Lung Physiology Factors affecting Ventillation 1. Airway resistance Flow = Δ P / R Most resistance is encountered
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 9 Respiratory System 1 Lung Physiology Factors affecting Ventillation 1. Airway resistance Flow = Δ P / R Most resistance is encountered
Respiratory System. Part 2
 Respiratory System Part 2 Respiration Exchange of gases between air and body cells Three steps 1. Ventilation 2. External respiration 3. Internal respiration Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation consists
Respiratory System Part 2 Respiration Exchange of gases between air and body cells Three steps 1. Ventilation 2. External respiration 3. Internal respiration Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation consists
Section Two Diffusion of gases
 Section Two Diffusion of gases Lecture 5: Partial pressure and the composition of gasses in air. Factors affecting diffusion of gases. Ventilation perfusion ratio effect on alveolar gas concentration.
Section Two Diffusion of gases Lecture 5: Partial pressure and the composition of gasses in air. Factors affecting diffusion of gases. Ventilation perfusion ratio effect on alveolar gas concentration.
PROBLEM SET 9. SOLUTIONS April 23, 2004
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.542J: Quantitative Physiology: Organ Transport Systems Instructors: Roger Mark and Jose Venegas MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Departments
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.542J: Quantitative Physiology: Organ Transport Systems Instructors: Roger Mark and Jose Venegas MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Departments
Pulmonary Circulation
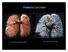 Pulmonary Circulation resin cast of pulmonary arteries resin cast of pulmonary veins Blood Flow to the Lungs Pulmonary Circulation Systemic Circulation Blood supply to the conducting zone provided by the
Pulmonary Circulation resin cast of pulmonary arteries resin cast of pulmonary veins Blood Flow to the Lungs Pulmonary Circulation Systemic Circulation Blood supply to the conducting zone provided by the
Chapter 4: Ventilation Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE
 Instant download and all chapters Test Bank Respiratory Care Anatomy and Physiology Foundations for Clinical Practice 3rd Edition Will Beachey https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-respiratory-care-anatomy-physiologyfoundations-clinical-practice-3rd-edition-will-beachey/
Instant download and all chapters Test Bank Respiratory Care Anatomy and Physiology Foundations for Clinical Practice 3rd Edition Will Beachey https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-respiratory-care-anatomy-physiologyfoundations-clinical-practice-3rd-edition-will-beachey/
Neonatal tidal volume targeted ventilation
 Neonatal tidal volume targeted ventilation Colin Morley Retired Professor of Neonatal Medicine, Royal Women s Hospital, Melbourne, Australia. Honorary Visiting Fellow, Dept Obstetrics and Gynaecology,
Neonatal tidal volume targeted ventilation Colin Morley Retired Professor of Neonatal Medicine, Royal Women s Hospital, Melbourne, Australia. Honorary Visiting Fellow, Dept Obstetrics and Gynaecology,
Module Two. Objectives: Objectives cont. Objectives cont. Objectives cont.
 Transition to the New National EMS Education Standards: EMT-B B to EMT Module Two Objectives: Upon completion, each participant will do the following to a degree of accuracy that meets the Ntl EMS Education
Transition to the New National EMS Education Standards: EMT-B B to EMT Module Two Objectives: Upon completion, each participant will do the following to a degree of accuracy that meets the Ntl EMS Education
Respiratory Anatomy and Physiology. Respiratory Anatomy. Function of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory Anatomy and Physiology Michaela Dixon Clinical Development Nurse PICU BRHFC Respiratory Anatomy Function of the Respiratory System - In conjunction with the cardiovascular system, to supply
Respiratory Anatomy and Physiology Michaela Dixon Clinical Development Nurse PICU BRHFC Respiratory Anatomy Function of the Respiratory System - In conjunction with the cardiovascular system, to supply
Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY
 Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Respiration External respiration ventilation gas exchange Internal respiration cellular respiration gas exchange Respiratory Cycle Inspiration
Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Respiration External respiration ventilation gas exchange Internal respiration cellular respiration gas exchange Respiratory Cycle Inspiration
Introduction to Conventional Ventilation
 Introduction to Conventional Ventilation Dr Julian Eason Consultant Neonatologist Derriford Hospital Mechanics Inspiration diaphragm lowers and thorax expands Negative intrathoracic/intrapleural pressure
Introduction to Conventional Ventilation Dr Julian Eason Consultant Neonatologist Derriford Hospital Mechanics Inspiration diaphragm lowers and thorax expands Negative intrathoracic/intrapleural pressure
I Physical Principles of Gas Exchange
 Respiratory Gases Exchange Dr Badri Paudel, M.D. 2 I Physical Principles of Gas Exchange 3 Partial pressure The pressure exerted by each type of gas in a mixture Diffusion of gases through liquids Concentration
Respiratory Gases Exchange Dr Badri Paudel, M.D. 2 I Physical Principles of Gas Exchange 3 Partial pressure The pressure exerted by each type of gas in a mixture Diffusion of gases through liquids Concentration
Table of Contents. By Adam Hollingworth
 By Adam Hollingworth Table of Contents Oxygen Cascade... 2 Diffusion... 2 Laws of Diffusion... 2 Diffusion & Perfusion Limitations... 3 Oxygen Uptake Along Pulmon Capillary... 4 Measurement of Diffusing
By Adam Hollingworth Table of Contents Oxygen Cascade... 2 Diffusion... 2 Laws of Diffusion... 2 Diffusion & Perfusion Limitations... 3 Oxygen Uptake Along Pulmon Capillary... 4 Measurement of Diffusing
birth: a transition better guidelines better outcomes the birth experience a challenging transition the fountains of life: 2/8/2018
 better guidelines better outcomes neonatal resuscitation Anne G. Wlodaver, MD neonatology OU medical center the birth experience a challenging transition birth requires major and sudden transitions some
better guidelines better outcomes neonatal resuscitation Anne G. Wlodaver, MD neonatology OU medical center the birth experience a challenging transition birth requires major and sudden transitions some
 http://www.priory.com/cmol/hfov.htm INTRODUCTION The vast majority of patients who are admitted to an Intensive Care Unit (ICU) will need artificial ventilation (Jones et al 1998). The usual means through
http://www.priory.com/cmol/hfov.htm INTRODUCTION The vast majority of patients who are admitted to an Intensive Care Unit (ICU) will need artificial ventilation (Jones et al 1998). The usual means through
Accumulation of EEV Barotrauma Affect hemodynamic Hypoxemia Hypercapnia Increase WOB Unable to trigger MV
 Complicated cases during mechanical ventilation Pongdhep Theerawit M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Ramathibodi Hospital Case I Presentation Male COPD 50 YO, respiratory failure, on mechanical
Complicated cases during mechanical ventilation Pongdhep Theerawit M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Ramathibodi Hospital Case I Presentation Male COPD 50 YO, respiratory failure, on mechanical
Pulmonary Circulation Linda Costanzo Ph.D.
 Pulmonary Circulation Linda Costanzo Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The differences between pressures in the pulmonary and systemic circulations. 2. How
Pulmonary Circulation Linda Costanzo Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The differences between pressures in the pulmonary and systemic circulations. 2. How
Respiratory Physiology. ED Primary Teaching
 Respiratory Physiology ED Primary Teaching Functions of the respiratory system Gas exchange with O2 and CO2 Surfactant production Defence - IgA and macrophages Filer - pollutants and thromboembolism Metabolises
Respiratory Physiology ED Primary Teaching Functions of the respiratory system Gas exchange with O2 and CO2 Surfactant production Defence - IgA and macrophages Filer - pollutants and thromboembolism Metabolises
Volume vs Pressure during Neonatal Ventilation
 Volume vs Pressure during Neonatal Ventilation David Tingay 1. Neonatal Research, Murdoch Children s Research Institute, Melbourne 2. Neonatology, Royal Children s Hospital 3. Dept of Paediatrics, University
Volume vs Pressure during Neonatal Ventilation David Tingay 1. Neonatal Research, Murdoch Children s Research Institute, Melbourne 2. Neonatology, Royal Children s Hospital 3. Dept of Paediatrics, University
Test Bank for Pilbeams Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition by Cairo
 Test Bank for Pilbeams Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition by Cairo Link full download: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-pilbeams-mechanicalventilation-physiological-and-clinical-applications-6th-edition-by-cairo/
Test Bank for Pilbeams Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition by Cairo Link full download: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-pilbeams-mechanicalventilation-physiological-and-clinical-applications-6th-edition-by-cairo/
PART ONE CHAPTER ONE PRIMARY CONSIDERATIONS RELATING TO THE PHYSIOLOGICAL AND PHYSICAL ASPECTS OF THE MECHANICAL VENTILATION OF THE LUNG
 PART ONE CHAPTER ONE PRIMARY CONSIDERATIONS RELATING TO THE PHYSIOLOGICAL AND PHYSICAL ASPECTS OF THE MECHANICAL VENTILATION OF THE LUNG POSSIBLE ORIGIN OF THE MECHANICAL VENTILATION OF THE LUNG- The first
PART ONE CHAPTER ONE PRIMARY CONSIDERATIONS RELATING TO THE PHYSIOLOGICAL AND PHYSICAL ASPECTS OF THE MECHANICAL VENTILATION OF THE LUNG POSSIBLE ORIGIN OF THE MECHANICAL VENTILATION OF THE LUNG- The first
Boards and Beyond: Pulmonary
 Boards and Beyond: Pulmonary A Companion Book to the Boards and Beyond Website Jason Ryan, MD, MPH i ii Table of Contents Pulmonary Anatomy 1 Treatment of COPD/Asthma 45 Pulmonary Physiology 4 Pneumonia
Boards and Beyond: Pulmonary A Companion Book to the Boards and Beyond Website Jason Ryan, MD, MPH i ii Table of Contents Pulmonary Anatomy 1 Treatment of COPD/Asthma 45 Pulmonary Physiology 4 Pneumonia
The physiological functions of respiration and circulation. Mechanics. exercise 7. Respiratory Volumes. Objectives
 exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
Respiratory system & exercise. Dr. Rehab F Gwada
 Respiratory system & exercise Dr. Rehab F Gwada Objectives of lecture Outline the major anatomical components & important functions of the respiratory system. Describe the mechanics of ventilation. List
Respiratory system & exercise Dr. Rehab F Gwada Objectives of lecture Outline the major anatomical components & important functions of the respiratory system. Describe the mechanics of ventilation. List
Mechanical Ventilation. Flow-Triggering. Flow-Triggering. Advanced Concepts. Advanced Concepts in Mechanical Ventilation
 Mechanical Ventilation Advanced Concepts in Mechanical Ventilation Flow-Triggering Trigger = the variable that causes the vent to begin the inspiratory phase Common triggers 1-2- 3- Effort required to
Mechanical Ventilation Advanced Concepts in Mechanical Ventilation Flow-Triggering Trigger = the variable that causes the vent to begin the inspiratory phase Common triggers 1-2- 3- Effort required to
CHAPTER 6. Oxygen Transport. Copyright 2008 Thomson Delmar Learning
 CHAPTER 6 Oxygen Transport Normal Blood Gas Value Ranges Table 6-1 OXYGEN TRANSPORT Oxygen Dissolved in the Blood Plasma Dissolve means that the gas maintains its precise molecular structure About.003
CHAPTER 6 Oxygen Transport Normal Blood Gas Value Ranges Table 6-1 OXYGEN TRANSPORT Oxygen Dissolved in the Blood Plasma Dissolve means that the gas maintains its precise molecular structure About.003
4/18/12 MECHANISM OF RESPIRATION. Every Breath You Take. Fun Facts
 Objectives MECHANISM OF RESPIRATION Dr Badri Paudel Explain how the intrapulmonary and intrapleural pressures vary during ventilation and relate these pressure changes to Boyle s law. Define the terms
Objectives MECHANISM OF RESPIRATION Dr Badri Paudel Explain how the intrapulmonary and intrapleural pressures vary during ventilation and relate these pressure changes to Boyle s law. Define the terms
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Atmosphere Tissue cell External respiration Alveoli of lungs 1 Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Atmosphere Tissue cell External respiration Alveoli of lungs 1 Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere
Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation
 Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation - Physical principles of gases: Pressure of a gas is caused by the movement of its molecules against a surface (more concentration
Unit II Problem 4 Physiology: Diffusion of Gases and Pulmonary Circulation - Physical principles of gases: Pressure of a gas is caused by the movement of its molecules against a surface (more concentration
Indications for Mechanical Ventilation. Mechanical Ventilation. Indications for Mechanical Ventilation. Modes. Modes: Volume cycled
 Mechanical Ventilation Eric A. Libré, MD VCU School of Medicine Inova Fairfax Hospital and VHC Indications for Mechanical Ventilation Inadequate ventilatory effort Rising pco2 with resp acidosis (7.25)
Mechanical Ventilation Eric A. Libré, MD VCU School of Medicine Inova Fairfax Hospital and VHC Indications for Mechanical Ventilation Inadequate ventilatory effort Rising pco2 with resp acidosis (7.25)
Disclosures. The Pediatric Challenge. Topics for Discussion. Traditional Anesthesia Machine. Tidal Volume = mls/kg 2/13/14
 2/13/14 Disclosures Optimal Ventilation of the Pediatric Patient in the OR Consulting Draeger Medical Jeffrey M. Feldman, MD, MSE Division Chief, General Anesthesia Dept. of Anesthesiology and Critical
2/13/14 Disclosures Optimal Ventilation of the Pediatric Patient in the OR Consulting Draeger Medical Jeffrey M. Feldman, MD, MSE Division Chief, General Anesthesia Dept. of Anesthesiology and Critical
Mechanical Ventilation. Mechanical Ventilation is a Drug!!! is a drug. MV: Indications for use. MV as a Drug: Outline. MV: Indications for use
 Mechanical Ventilation is a Drug!!! Mechanical Ventilation is a drug I am an employee of Philips Healthcare Hospital Respiratory Care Group and they help me pay for my kids education Jim Laging, RRT, RCP
Mechanical Ventilation is a Drug!!! Mechanical Ventilation is a drug I am an employee of Philips Healthcare Hospital Respiratory Care Group and they help me pay for my kids education Jim Laging, RRT, RCP
Figure 11 iron lung. Dupuis, Ventilators, 1986, Mosby Year Book. early negative pressure ventilators were often bulky and cumbersome
 HISTORY MECHANICAL VENTILATION Mechanical ventilatory support is now a major aspect of critical care. The lungs are often central in a patient with multi-organ system failure, and many patients have cardiopulmonary
HISTORY MECHANICAL VENTILATION Mechanical ventilatory support is now a major aspect of critical care. The lungs are often central in a patient with multi-organ system failure, and many patients have cardiopulmonary
PART SEVEN THE HISTORY AND APPLICATION OF HIGH FREQUENCY OSCILLATORY VENTILATION (HFOV)
 PART SEVEN THE HISTORY AND APPLICATION OF HIGH FREQUENCY OSCILLATORY VENTILATION (HFOV) Reciprocating pistons with an eccentric travel speed, moving to and fro within a cylinder (with a common inlet/outlet),
PART SEVEN THE HISTORY AND APPLICATION OF HIGH FREQUENCY OSCILLATORY VENTILATION (HFOV) Reciprocating pistons with an eccentric travel speed, moving to and fro within a cylinder (with a common inlet/outlet),
Mechanical Ventilation. Which of the following is true regarding ventilation? Basics of Ventilation
 Mechanical Ventilation Jeffrey L. Wilt, MD, FACP, FCCP Associate Professor of Medicine Michigan State University Associate Program Director MSU-Grand Rapids Internal Medicine Residency Which of the following
Mechanical Ventilation Jeffrey L. Wilt, MD, FACP, FCCP Associate Professor of Medicine Michigan State University Associate Program Director MSU-Grand Rapids Internal Medicine Residency Which of the following
LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
 66 LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB Assignments: Due before lab: Quiz: Three Respiratory Interactive Physiology Animations pages 69 73. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
66 LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB Assignments: Due before lab: Quiz: Three Respiratory Interactive Physiology Animations pages 69 73. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY RELEVANT TO HFOV
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY RELEVANT TO Physiology of CMV 1 What is? Ventilation using a relatively high continuous distending pressure at the airway opening, around which an oscillatory wave is generated to
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY RELEVANT TO Physiology of CMV 1 What is? Ventilation using a relatively high continuous distending pressure at the airway opening, around which an oscillatory wave is generated to
By: Aseel Jamil Al-twaijer. Lec : physical principles of gas exchange
 By: Aseel Jamil Al-twaijer Lec : physical principles of gas exchange Date:30 /10/2017 this lecture is about the exchange of gases between the blood and the alveoli. I might add some external definitions
By: Aseel Jamil Al-twaijer Lec : physical principles of gas exchange Date:30 /10/2017 this lecture is about the exchange of gases between the blood and the alveoli. I might add some external definitions
Respiratory Physiology 2
 Respiratory Physiology 2 Session Objectives. What you will cover Gaseous Exchange Control of Breathing Rate Your objectives are State the function of support structures and epithelia of the bronchial tree
Respiratory Physiology 2 Session Objectives. What you will cover Gaseous Exchange Control of Breathing Rate Your objectives are State the function of support structures and epithelia of the bronchial tree
Mechanical Ventilation
 PROCEDURE - Page 1 of 5 Purpose Scope Physician's Order Indications Procedure Mechanical Artificial Ventilation refers to any methods to deliver volumes of gas into a patient's lungs over an extended period
PROCEDURE - Page 1 of 5 Purpose Scope Physician's Order Indications Procedure Mechanical Artificial Ventilation refers to any methods to deliver volumes of gas into a patient's lungs over an extended period
RESPIRATORY GAS EXCHANGE
 RESPIRATORY GAS EXCHANGE Alveolar PO 2 = 105 mmhg; Pulmonary artery PO 2 = 40 mmhg PO 2 gradient across respiratory membrane 65 mmhg (105 mmhg 40 mmhg) Results in pulmonary vein PO 2 ~100 mmhg Partial
RESPIRATORY GAS EXCHANGE Alveolar PO 2 = 105 mmhg; Pulmonary artery PO 2 = 40 mmhg PO 2 gradient across respiratory membrane 65 mmhg (105 mmhg 40 mmhg) Results in pulmonary vein PO 2 ~100 mmhg Partial
Respiratory Medicine. A-A Gradient & Alveolar Gas Equation Laboratory Diagnostics. Alveolar Gas Equation. See online here
 Respiratory Medicine A-A Gradient & Alveolar Gas Equation Laboratory Diagnostics See online here Alveolar gas equation helps to calculate the partial pressure of oxygen in alveoli and A-a gradient is the
Respiratory Medicine A-A Gradient & Alveolar Gas Equation Laboratory Diagnostics See online here Alveolar gas equation helps to calculate the partial pressure of oxygen in alveoli and A-a gradient is the
6 th Accredited Advanced Mechanical Ventilation Course for Anesthesiologists. Course Test Results for the accreditation of the acquired knowledge
 6 th Accredited Advanced Mechanical Ventilation Course for Anesthesiologists Course Test Results for the accreditation of the acquired knowledge Q. Concerning the mechanics of the newborn s respiratory
6 th Accredited Advanced Mechanical Ventilation Course for Anesthesiologists Course Test Results for the accreditation of the acquired knowledge Q. Concerning the mechanics of the newborn s respiratory
MEDICAL EQUIPMENT IV MECHANICAL VENTILATORS. Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah
 MEDICAL EQUIPMENT IV - 2013 MECHANICAL VENTILATORS Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah Mechanical Ventilator A ventilator is a machine, a system of related elements designed to alter, transmit, and direct energy
MEDICAL EQUIPMENT IV - 2013 MECHANICAL VENTILATORS Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah Mechanical Ventilator A ventilator is a machine, a system of related elements designed to alter, transmit, and direct energy
Bunnell LifePulse HFV Quick Reference Guide # Bunnell Incorporated
 Bunnell Incorporated n www.bunl.com n 800-800-4358 (HFJV) n info@bunl.com 436 Lawndale Drive n Salt Lake City, Utah 84115 n intl 801-467-0800 n f 801-467-0867 Bunnell LifePulse HFV Quick Reference Guide
Bunnell Incorporated n www.bunl.com n 800-800-4358 (HFJV) n info@bunl.com 436 Lawndale Drive n Salt Lake City, Utah 84115 n intl 801-467-0800 n f 801-467-0867 Bunnell LifePulse HFV Quick Reference Guide
ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENT. First 24 hours: All patients with ARDS criteria were ventilated during 24 hours with low V T (6-8 ml/kg
 APPENDIX 1 Appendix 1. Complete respiratory protocol. First 24 hours: All patients with ARDS criteria were ventilated during 24 hours with low V T (6-8 ml/kg predicted body weight (PBW)) (NEJM 2000; 342
APPENDIX 1 Appendix 1. Complete respiratory protocol. First 24 hours: All patients with ARDS criteria were ventilated during 24 hours with low V T (6-8 ml/kg predicted body weight (PBW)) (NEJM 2000; 342
Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation. Chad & Angela
 Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation Chad & Angela Respiratory Structures Basic Structures of Respiration Nasal/Oral Cavities Larynx Trachea Bronchi Secondary Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli Mechanics of Ventilation
Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation Chad & Angela Respiratory Structures Basic Structures of Respiration Nasal/Oral Cavities Larynx Trachea Bronchi Secondary Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli Mechanics of Ventilation
Chapter 16 Respiration. Respiration. Steps in Respiration. Functions of the respiratory system
 Chapter 16 Respiration Functions of the respiratory system Respiration The term respiration includes 3 separate functions: Ventilation: Breathing. Gas exchange: Occurs between air and blood in the lungs.
Chapter 16 Respiration Functions of the respiratory system Respiration The term respiration includes 3 separate functions: Ventilation: Breathing. Gas exchange: Occurs between air and blood in the lungs.
UNDERSTANDING NEONATAL WAVEFORM GRAPHICS. Brandon Kuehne, MBA, RRT-NPS, RPFT Director- Neonatal Respiratory Services
 UNDERSTANDING NEONATAL WAVEFORM GRAPHICS Brandon Kuehne, MBA, RRT-NPS, RPFT Director- Neonatal Respiratory Services Disclosures Purpose: To enhance bedside staff s knowledge of ventilation and oxygenation
UNDERSTANDING NEONATAL WAVEFORM GRAPHICS Brandon Kuehne, MBA, RRT-NPS, RPFT Director- Neonatal Respiratory Services Disclosures Purpose: To enhance bedside staff s knowledge of ventilation and oxygenation
Author: Thomas Sisson, MD, 2009
 Author: Thomas Sisson, MD, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author: Thomas Sisson, MD, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Rodney Shandukani 14/03/2012
 Rodney Shandukani 14/03/2012 OXYGEN THERAPY Aerobic metabolism accounts for 90% of Oxygen consumption by tissues. generates ATP by oxidative phosphorylation. Oxygen cascade: Oxygen exerts a partial pressure,
Rodney Shandukani 14/03/2012 OXYGEN THERAPY Aerobic metabolism accounts for 90% of Oxygen consumption by tissues. generates ATP by oxidative phosphorylation. Oxygen cascade: Oxygen exerts a partial pressure,
Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange
 Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange Session Objectives. What you will cover Basic anatomy of the lung including airways Breathing movements Lung volumes and capacities Compliance and Resistance in
Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange Session Objectives. What you will cover Basic anatomy of the lung including airways Breathing movements Lung volumes and capacities Compliance and Resistance in
The Basics of Ventilator Management. Overview. How we breath 3/23/2019
 The Basics of Ventilator Management What are we really trying to do here Peter Lutz, MD Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Pulmonary Associates, Mobile, Al Overview Approach to the physiology of the
The Basics of Ventilator Management What are we really trying to do here Peter Lutz, MD Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Pulmonary Associates, Mobile, Al Overview Approach to the physiology of the
Javier García Fernández. MD. Ph.D. MBA. Chairman of Anaesthesia and Critical Care Service Puerta de Hierro University Hospital Associate Professor.
 Javier García Fernández. MD. Ph.D. MBA. Chairman of Anaesthesia and Critical Care Service Puerta de Hierro University Hospital Associate Professor. Medical School. UAM CV and Conflict of interest Chairman
Javier García Fernández. MD. Ph.D. MBA. Chairman of Anaesthesia and Critical Care Service Puerta de Hierro University Hospital Associate Professor. Medical School. UAM CV and Conflict of interest Chairman
PROBLEM SET 8. SOLUTIONS April 15, 2004
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.542J: Quantitative Physiology: Organ Transport Systems Instructors: Roger Mark and Jose Venegas MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Departments
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.542J: Quantitative Physiology: Organ Transport Systems Instructors: Roger Mark and Jose Venegas MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Departments
HMP 210: MEDICAL PHYSIOLOGY III. Dr Lee Ngugi Kigera
 HMP 210: MEDICAL PHYSIOLOGY III Dr Lee Ngugi Kigera HMP 200: RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY AND MECHANICS OF RESPIRATION HMP 201: TRANSPORT OF GASES AND RESPIRATORY CONTROL Reference books Review of Medical Physiology
HMP 210: MEDICAL PHYSIOLOGY III Dr Lee Ngugi Kigera HMP 200: RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY AND MECHANICS OF RESPIRATION HMP 201: TRANSPORT OF GASES AND RESPIRATORY CONTROL Reference books Review of Medical Physiology
The Respiratory System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Organs of the Respiratory system
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Organs of the Respiratory system
Respiratory System Physiology. Dr. Vedat Evren
 Respiratory System Physiology Dr. Vedat Evren Respiration Processes involved in oxygen transport from the atmosphere to the body tissues and the release and transportation of carbon dioxide produced in
Respiratory System Physiology Dr. Vedat Evren Respiration Processes involved in oxygen transport from the atmosphere to the body tissues and the release and transportation of carbon dioxide produced in
Respiration - Human 1
 Respiration - Human 1 At the end of the lectures on respiration you should be able to, 1. Describe events in the respiratory processes 2. Discuss the mechanism of lung ventilation in human 3. Discuss the
Respiration - Human 1 At the end of the lectures on respiration you should be able to, 1. Describe events in the respiratory processes 2. Discuss the mechanism of lung ventilation in human 3. Discuss the
Objectives. Respiratory Failure : Challenging Cases in Mechanical Ventilation. EM Knows Respiratory Failure!
 Respiratory Failure : Challenging Cases in Mechanical Ventilation Peter DeBlieux, MD, FAAEM, FACEP LSUHSC University Hospital Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Emergency Medicine pdebli@lsuhsc.edu Objectives
Respiratory Failure : Challenging Cases in Mechanical Ventilation Peter DeBlieux, MD, FAAEM, FACEP LSUHSC University Hospital Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Emergency Medicine pdebli@lsuhsc.edu Objectives
Physiology of Respiration
 Physiology of Respiration External Respiration = pulmonary ventilation breathing involves 2 processes: inspiration expiration Inspiration an active process involves contraction of diaphragm innervated
Physiology of Respiration External Respiration = pulmonary ventilation breathing involves 2 processes: inspiration expiration Inspiration an active process involves contraction of diaphragm innervated
RESPIRATORY MONITORING AND OXIMETRY
 RESPIRATORY MONITORING AND OXIMETRY EE 471 F2016 Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah Introduction Respiratory monitoring includes measurement, evaluation, and monitoring of parameters of respiratory system, First
RESPIRATORY MONITORING AND OXIMETRY EE 471 F2016 Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah Introduction Respiratory monitoring includes measurement, evaluation, and monitoring of parameters of respiratory system, First
Volume Guarantee New Approaches in Volume Controlled Ventilation for Neonates
 Volume Guarantee New Approaches in Volume Controlled Ventilation for Neonates Jag Ahluwalia Colin Morley Hans Georg Wahle Important Notice: Medical knowledge changes constantly as a result of new research
Volume Guarantee New Approaches in Volume Controlled Ventilation for Neonates Jag Ahluwalia Colin Morley Hans Georg Wahle Important Notice: Medical knowledge changes constantly as a result of new research
Mechanical Ventilation Guided by Esophageal Pressure in Acute Lung Injury *
 A teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School Mechanical Ventilation Guided by Esophageal Pressure in Acute Lung Injury * Ray Ritz BA RRT FAARC Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Boston MA * n engl j
A teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School Mechanical Ventilation Guided by Esophageal Pressure in Acute Lung Injury * Ray Ritz BA RRT FAARC Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Boston MA * n engl j
The Respiratory System Part I. Dr. Adelina Vlad
 The Respiratory System Part I Dr. Adelina Vlad The Respiratory Process Breathing automatic, rhythmic and centrally-regulated mechanical process by which the atmospheric gas moves into and out of the lungs
The Respiratory System Part I Dr. Adelina Vlad The Respiratory Process Breathing automatic, rhythmic and centrally-regulated mechanical process by which the atmospheric gas moves into and out of the lungs
Mechanical ven3la3on. Neonatal Mechanical Ven3la3on. Mechanical ven3la3on. Mechanical ven3la3on. Mechanical ven3la3on 8/25/11. What we need to do"
 8/25/11 Mechanical ven3la3on Neonatal Mechanical Ven3la3on Support oxygen delivery, CO2 elimination" Prevent added injury, decrease ongoing injury" Enhance normal development" Mark C Mammel, MD University
8/25/11 Mechanical ven3la3on Neonatal Mechanical Ven3la3on Support oxygen delivery, CO2 elimination" Prevent added injury, decrease ongoing injury" Enhance normal development" Mark C Mammel, MD University
Mechanical Ventilation
 Mechanical Ventilation Chapter 4 Mechanical Ventilation Equipment When providing mechanical ventilation for pediatric casualties, it is important to select the appropriately sized bag-valve mask or endotracheal
Mechanical Ventilation Chapter 4 Mechanical Ventilation Equipment When providing mechanical ventilation for pediatric casualties, it is important to select the appropriately sized bag-valve mask or endotracheal
Respiratory Signs: Tachypnea (RR>30/min), Desaturation, Shallow breathing, Use of accessory muscles Breathing sound: Wheezing, Rhonchi, Crepitation.
 Respiratory Signs: Tachypnea (RR>30/min), Desaturation, Shallow breathing, Use of accessory muscles Breathing sound: Wheezing, Rhonchi, Crepitation. Paradoxical breathing Hyper-resonance on percussion:
Respiratory Signs: Tachypnea (RR>30/min), Desaturation, Shallow breathing, Use of accessory muscles Breathing sound: Wheezing, Rhonchi, Crepitation. Paradoxical breathing Hyper-resonance on percussion:
