COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THE MATRIKA MARMA W..R.T RECEPTORS IN NECK
|
|
|
- Joseph Caldwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Review Article International Ayurvedic Medical Journal ISSN: COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THE MATRIKA MARMA W..R.T RECEPTORS IN NECK Dr. Omkar S. Barge Assistant Professor, Departmentt of Rachana Shareer, Government Ayurved College, Vadodara, Gujarat, India ABSTRACT Sushruta has explained the Marma i.e vital points of the body. On the basis of conse- that means in- quences, there are five types of Marma in which one is SadyapranaharaMarma jury to these Marma leads to sudden death. MatrikaMarmas are eight in number; lie in the neck on either side of Kanthnadi which is a Sadhyapranahara Marma. In the internal carotid arteries, there is carotid sinus which is a major vital point of the body. It regulates the blood pressure of the body. Carotid body is also situated in common carotid artery which regulates the chemical composition of the body. So Matrika Marma can be compared with carotid sinus and carotid body i.e baroreceptor and chemoreceptor. This study will be beneficial for surgery and also for medicine. Keywords: MatrikaMarma, Marma,Sadhyapranhara, Carotid body, Carotid sinus. INTRODUCTION Ayurveda is an eternal science of life. Sushruta has explained the Marma i.e vital points of the body which have major importance while doing surgery. These Marma should be avoided from injury othoccur. Mar- erwise fatal consequences may ma are said to be cover half of surgery beif injury at cause persons die immediately Marma point. On the basis of consequences, there are five types of Marma in which one is Sadyapranahara- Marma Marma that means injury to these leads to sudden death. MatrikaMarma is one of the Sadyapranahara Marma. Matrika Marma are eight in number, lie in the neck on either side of Kanthnadi (8). These measure about four anguli. Many peers considered Matrika Marma as carotid arteries and jugular veins. But only these arteries are not Marma points but also the internal structures of these arteries have to be considered. In the internal carotid artewhich is a major ries, there is carotid sinus vital point of the body. It regulates the blood pressure of the body (14). Any compressive injury to the internal carotid artery leads to stretching of carotid sinuss which contains baroreceptors which give impulses to cardi- ovascular centre in medulla oblongata. Then inhibitory action takes place. It lowers the blood pressure and the heart rate. Further compression of this site leads to syncope, unconsciousness and sudden death. Carotid body is also situated in com- regulates the mon carotid artery whichh chemical composition of the body (14). These two structures are important in body. So Matrika Marma can be compared with carotid sinus and carotid body i.e barorecep- tor and chemoreceptor. This Study will be beneficial for surgery and also for medicine. How to cite this URL: Dr. Omkar S. Barge: Comparative Study Of The Matrika Marma W.R.T Receptors In Neck. International Ayurvedic medical Journal {online} 2016 {cited 2016 July} Available from:
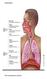
2 Dr. Omkar S. Barge: Comparative Study Of The Matrika Marma W.R.T Receptors In Neck Aim: To compare Matrika Marma with carotid sinus and carotid body. Objectives: 1. To decide the site of MatrikaMarma. 2. To collect the references of Matrika- Marma from different ayurvedic texts. 3. To collect the references of carotid sinus and carotid body from different modern texts. 4. To come to a conclusion regarding the site of Matrika Marma. Materials and methods: 1. Literature regarding Matrika Marma. 2. Literature regarding carotid sinus and carotid body. Observation: 1. Marmas consist of aggregate of muscle, blood vessel, ligaments, and bones and joint in which particularly pranas by nature stay; that is why injury to marma lead to respective consequences (1). 2. MartikaMarma: In neck, on both sides are four blood vessels named Matrika. These lead to immediate death (2). 3. Type of Matrika marma : It is a type Sira marma (according to Rachana) and SadhyapranharMarma marma (according to effect of injury) (3). 4. Location of Matrika marma: It is Urdhvajatrugata, lies above the clavicle (4). The four different Sira going to different part of neck, face, Orbital, temporal regions and nose, on both sides of the Kanthanadi are called as Matrika and cutting of these sira leads to sudden death (8). Four major vessels found in the area of Matruka marma are 1) Common Carodit artery 2) External carotid artery 3) Internal Carotid artery 4) Internal Jugular Vein 5. Anguli pramana or measurement ofmatrika marma site ( according to Ayurvedic text) It measures four fingers (5). 6. Composition of all Marmas: All the four types of Sira (bloodvessles/veins) are generally situated in Marmas and by nourishing bones, ligaments, muscles and joints maintain body (6). 7. Four types of sira: Vata, Pitta, Kapha, Rakta(7). 8. Normal functioning of Marma: There are seven hundred sira by which the body is nourished like garden by water carriers and like field by irrigating channels and also benefited with activities such as contractions and extension (9). 9. Effect of injury to Marma: Injury to neighboring part by cutting, breaking, trauma, burning and tearing should be known to have features similar to those of Marma (10). 10. Carotid sinus: The termination of the common carotid artery or the beginning of internal carotid artery shows a slight dilation known as the carotid sinus. In this region the tunica media is thin but the adventia is relatively thick and receives rich innervations from the glassopharongeal and sympathetic nerves. The carotid sinus acts as baroreceptor or pressure receptor and regulates blood pressure (11). Carotid body: Carotid body is a small, oval reddish-brown structure situated behind the bifurcation of the common carotid artery. It receives a rich nerve supply mainly from glossopharyngeal nerve bur also from the vagus and sympathetic nerves. It acts as a chemoreceptor and responds to changes in the O2, CO2 and ph content of the blood (11) 3162
3 Dr. Omkar S. Barge: Comparative Study Of The Matrika Marma W.R.T Receptors In Neck Diagram showing Carotid sinus & Carotid body DISCUSSION Matrika Marma is located in theneck on both side of Kanthanadi (8). These are eight in number i.e four on one side and four on other side. Its measurement is four Anguli Pramana. In neck, major vessels are carotid arteries and jugular vein. These are also eight in number; four on one side and four on other side of the neck. These are located in carotid triangle of neck region. The major structure which lies in the carotid arteries is carotid sinus and carotid body. Carotid sinus acts as a baroreceptor and carotid body acts as a chemoreceptor. These two have major function in regulation of blood pressure and O2, CO2, H+ ion content of blood respectively (14). Carotid sinus lies at the termination of common carotid artery or the beginning of internal carotid artery which is a slight dilation i.e carotid sinus may be located in either common carotid artery or internal carotid artery. Carotid body is a small reddishbrown structure situated behind the bifurcation of the common carotid artery (12). Measurement of Matrika Marma is four Anguli Pramana. Carotid sinus lies at the termination of common carotid or in internal carotid artery and carotid body lies before the bifurcation that means there is a distance between carotid body and carotid sinus which measures within four Anguli- Pramana. Considering this structure there is an associate structure, internal and external jugular veins which have also a major importance. Hence situational point of view we can consider Matrika Marma is nothing but carotid sinus and carotid body which lie in carotid vessels. So Sushruta should have considered the vessel as MatrikaMarma. Matrika Marmais a Sadyapranahara Marma that means any injury to this lead to sudden death. Many ayurved peers consider that in- 3163
4 3164 Dr. Omkar S. Barge: Comparative Study Of The Matrika Marma W.R.T Receptors In Neck jury to Matrika Marma leads to bleeding from carotid and jugular vessel which leads to death but this happen due to bleeding. Any major vessel injury or cut leads to major bleeding. So can any major vessel be considered as a Marma? No, Sushruta has given only countable number of Marma. So we have to consider other causes of death due to injury to the Matrika Marma. Considering this, major structures are carotid sinus i.e baroreceptor and carotid body i.e chemoreceptor responsible for death. Carotid sinus is responsive to changes in arterial blood pressure leading to reflex haemodynamic of brain which accounts for its role as baroreceptor in control of intracranial pressure (12). Activation of carotid sinus baroreceptors give rise to impulse carried through the nerve of hearing, a branch of glassopharyngeal nerve to the medulla oblongata. These efferent impulses activate efferent sympathetic nerve fibers to heart and blood vessels, cardiac vagal efferent nerve fibers or both. These responses may cause sinus arrest or AV block (cardioinhibitory r e- sponse), vasodilatation or both (17). Blood pressure stretches the wall of the carotid sinus which stimulates the baroreceptors. Nerve impulses propagate from the carotid sinus baroreceptor over sensory axon in the glass pharyngeal nerve (IX) to the cardiovascular centre in medulla oblongata. Then nerve impulse from aortic baroreceptor reaches the cardiovascular centre through sensory fibers of Vagus nerve (X) which is parasympathetic i.e inhibitor. Those impulses lower the heart rate and vasodilatation takes place to lower the blood pressure. If the stretching of wall continues again and again, the heart rate continues to lower again and again. Vasodilatation takes place again that leads to the lowest blood pressure. This continuous lowest blood pressure leads to syncope, unconsciousness and death. In hanging one cause of death is vagal inhibition from pressure on carotid sinus. Compression of carotid arteries results in rapid loss of consciousness and death. Carotid arteries are occluded by a tension of 3.5 kg and also another cause is cerebral congestion due to compression of the jugular vein (13). The carotid sinus is close to the anterior surface of neck. So anything that stretches or pressure on carotid sinus such as hypertension of head, tight collars, carrying heavy shoulder loads may also slow heart rate and may cause syncope (14). From above discussion, we can say that any compression of carotid arteries is fatal or leads to death within few minutes following the steps syncope, unconsciousness and death. So carotid sinus is a part of SadyapranaharaMarma which we can consider as part of MatrikaMarma. Carotid body contains chemoreceptors which is responsible for detecting changes in blood chemistry primarily oxygen content and is innervated by branches of glossopharyngeal (IX) and vagus (X) nerve. (15) In hypoxia, acidosis (H+ increase) hypercapnia (CO2 increase) stimulates the chemoreceptors to send impulses to the cardiovascular centre. In response this centre increases sympathetic impulses to vessels which produce vasoconstriction and an increase in blood pressure (16). Sushruta has told that injury to the neighboring part by cutting, breaking and trauma, burning and tearing should be known to have features similar to those of
5 3165 Dr. Omkar S. Barge: Comparative Study Of The Matrika Marma W.R.T Receptors In Neck Marma (18). Similarly injury to above and below or nearby the carotid sinus and carotid body may fatal or may lead to death by destroying its normal function. CONCLUSION Thus from above brief study of the Marma, Marma an important anatomical vital points should be taken in to consideration during treatment which is explained in Sushrutasamhita and Ashtangahridaya. The study correlates the MatrikaMarma with the carotid sinus and carotid body by giving various evidences in the ancient and modern texts. MatrikaMarma is a structurally Sira marma which is Carotid arteries & Jugular veins, carotid arteries shows carotid sinus and carotid body that is baroreceptor and chemoreceptor respectively. REFERENCES 1. Sharma P.V. Sushruta Samhita, vol.2 Chapter 6, shloka 15, page no. 187, 2. Sharma P.V. Sushruta Samhita, vol.2 Chapter 6, shloka, page no. 195 Chaukhamba Vishwabharati Prakashan, 3. Sharma P.V. Sushruta Samhita, vol.2 Chapter 6, shloka 9, page no. 187, ChaukhambaVishwabharati Prakashan, 4. Sharma P.V. Sushruta Samhita, vol.2 Chapter 6, shloka--, page no. 185, 5. Sharma P.V. Sushruta Samhita, vol.2 Chapter 6, shloka 29, page no. 196, 6. Sharma P.V. Sushruta Samhita, vol.2 Chapter 6, shloka 18, page no. 189, 7. Sharma P.V. Sushruta Samhita, vol.2 Chapter 7, shloka --, page no. 201, 8. Ashtangahridaya by Dr. BramhanandTripathi, page no. 393, Chaukhamba Sanskrit pratisthan, Delhi. 9. Sharma P.V. Sushruta Samhita, vol.2 Chapter 7, shloka 3, page no. 200, 10. Sharma P.V. Sushruta Samhita, Chapter 6, shloka 41, page no. 200, s Reprint Human Anatomy vol.3 by B. D. Chaurosia fifth edition, CBS publisher and distributers Pvt Ltd. 12. Gray s Anatomy for Student, 2 nd edition by Richard L. Drake, A. Wayne Vogl, Adam W, M. Mitchell, Publisher- Churchill Livingstone Elsevier. Parikh s Textbook of Medical 13. Jurisprudence, forensic medicine and toxicology, 6 th edition, by Dr, C. K Parikh, publisher CBS publishers page no. 3.40, 14. Principles of Anatomy and Physiology, 11 th edition, Gerard J. Tortora, Bryan Derrickson, publisher- Wiley-John Wiley & sons Inc, page no Gray s Anatomy for Student, 2 nd edition by Richard L. Drake, A. Wayne Vogl, Adam W, M. Mitchell, Publisher- Churchill Livingstone Elsevier, page no Principles of Anatomy and Physiology, 11 th edition, Gerard J. Tortora, Bryan Derrickson, publisher- Wiley-John Wi-
6 Dr. Omkar S. Barge: Comparative Study Of The Matrika Marma W.R.T Receptors In Neck ley & sons Inc, page no Principles of Internal Medicine, 15 th edition, Harrison, vol. 1, Publisher- Mcgraw Hill page no Sharma P.V. Sushruta Samhita, vol.2 Chapter 6, shloka 41, page no. 199,. CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Dr. Omkar S. Barge Assistant Professor Department of Rachana Shareer Government Ayurved College, Vadodara, Gujarat, India Source of Support: Nil Conflict of Interest: None Declared 3166
Conceptual study of the Matrika Marma w.r.t Carotid sinus and Carotid body
 International Journal of Ayurvedic Medicine, 2014, 5(3), 231-236 Conceptual study of the Matrika Marma w.r.t Carotid sinus and Carotid body Review article Nilkanth G Thakare 1* 1. Assisstant professor,
International Journal of Ayurvedic Medicine, 2014, 5(3), 231-236 Conceptual study of the Matrika Marma w.r.t Carotid sinus and Carotid body Review article Nilkanth G Thakare 1* 1. Assisstant professor,
ANATOMICAL STUDY OF KAKSHADHRUKA MARMA WITH SPECIAL REF- ERENCE TO VAGHBHATA SAMHITA
 Observational Study International Ayurvedic Medical Journal ISSN:2320 5091 ANATOMICAL STUDY OF KAKSHADHRUKA MARMA WITH SPECIAL REF- ERENCE TO VAGHBHATA SAMHITA Amrutraj Ashok Patil 1, Pramod Appasaheb
Observational Study International Ayurvedic Medical Journal ISSN:2320 5091 ANATOMICAL STUDY OF KAKSHADHRUKA MARMA WITH SPECIAL REF- ERENCE TO VAGHBHATA SAMHITA Amrutraj Ashok Patil 1, Pramod Appasaheb
Some major points on the Effects of Hypoxia
 Some major points on the Effects of Hypoxia Source: Kings College London http://www.kcl.ac.uk/teares/gktvc/vc/dental/year1/lectures/rbmsmajorpoints/effectsofhypoxia.htm Cells obtain their energy from oxygen.
Some major points on the Effects of Hypoxia Source: Kings College London http://www.kcl.ac.uk/teares/gktvc/vc/dental/year1/lectures/rbmsmajorpoints/effectsofhypoxia.htm Cells obtain their energy from oxygen.
Dr. S.K. Joshi M.D.Ay. (B.H.U.) Reader and Head of the Department, Shalya-tantra Additional Medical Superintendent Government Ayurvedic College,
 Dr. S.K. Joshi M.D.Ay. (B.H.U.) Reader and Head of the Department, Shalya-tantra Additional Medical Superintendent Government Ayurvedic College, Gurukul Kangri, Hardwar (U.K.) President Mrityunjay Mission
Dr. S.K. Joshi M.D.Ay. (B.H.U.) Reader and Head of the Department, Shalya-tantra Additional Medical Superintendent Government Ayurvedic College, Gurukul Kangri, Hardwar (U.K.) President Mrityunjay Mission
Indian Journal of Medical Research and Pharmaceutical Sciences August (8) ISSN: ISSN: DOI: /zenodo Impact Factor: 3.
 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF MARMA (VITAL POINTS IN AYURVEDA) IN HANDS, ACUPUNCTURE AND ACUPRESSURE- A REVIEW Dr. Darasing Govind Rathod *, Dr. Chandrashekhar Dattatray Vaikos, Dr. Suryakant
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF MARMA (VITAL POINTS IN AYURVEDA) IN HANDS, ACUPUNCTURE AND ACUPRESSURE- A REVIEW Dr. Darasing Govind Rathod *, Dr. Chandrashekhar Dattatray Vaikos, Dr. Suryakant
A Study of Adhoshakhagata Marma with special reference to Kshipra Marma Mehak kamboj 1 *, Tanvi Mahajan 2 and Pramod Anand Tiwari 3
 RESEARCH ARTICLE www.ijapc.com e-issn 2350-0204 A Study of Adhoshakhagata Marma with special reference to Kshipra Marma Mehak kamboj 1 *, Tanvi Mahajan 2 and Pramod Anand Tiwari 3 1,2,3 Deptt. of Rachna
RESEARCH ARTICLE www.ijapc.com e-issn 2350-0204 A Study of Adhoshakhagata Marma with special reference to Kshipra Marma Mehak kamboj 1 *, Tanvi Mahajan 2 and Pramod Anand Tiwari 3 1,2,3 Deptt. of Rachna
Human Biology Respiratory System
 Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
Human Biology Respiratory System Respiratory System Responsible for process of breathing Works in cooperation with Circulatory system Three types: 1. Internal Respiration 2. External Respiration 3. Cellular
Breathing: The normal rate is about 14 to 20 times a minute. Taking in of air is called Inspiration and the forcing out of air is called Expiration.
 Biology 12 Respiration Divisions of Respiration Breathing: entrance and exit of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration: exchange of gases(o2 and CO2) between air (in alveoli) and blood Internal
Biology 12 Respiration Divisions of Respiration Breathing: entrance and exit of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration: exchange of gases(o2 and CO2) between air (in alveoli) and blood Internal
Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment
 Name: Date: Mark: / 45 Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following
Name: Date: Mark: / 45 Chapter 11: Respiratory System Review Assignment Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following
Exam Key. NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 Exam # 2 October 28, 2016 Total POINTS: % of grade in class
 NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 Exam # 2 October 28, 2016 Total POINTS: 100 20% of grade in class 1) An arterial blood sample for a patient at sea level is obtained, and the following physiological values
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 Exam # 2 October 28, 2016 Total POINTS: 100 20% of grade in class 1) An arterial blood sample for a patient at sea level is obtained, and the following physiological values
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Atmosphere Tissue cell External respiration Alveoli of lungs 1 Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Atmosphere Tissue cell External respiration Alveoli of lungs 1 Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere
Respiratory Physiology. Adeyomoye O.I
 Respiratory Physiology By Adeyomoye O.I Outline Introduction Hypoxia Dyspnea Control of breathing Ventilation/perfusion ratios Respiratory/barometric changes in exercise Intra-pulmonary & intra-pleural
Respiratory Physiology By Adeyomoye O.I Outline Introduction Hypoxia Dyspnea Control of breathing Ventilation/perfusion ratios Respiratory/barometric changes in exercise Intra-pulmonary & intra-pleural
Respiration. The resspiratory system
 Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
ANVESHANA OBSERVATIONAL STUDY ON KSHIPRA MARMA IN URDHVASHAKHA Professor of Rachana Sharir, ADAMC, Ashta, Maharashtra, India 2
 www.aamj.in ANVESHANA Research Article AYURVEDA MEDICAL JOURNAL ISSN: 2395-4159 OBSERVATIONAL STUDY ON KSHIPRA MARMA IN URDHVASHAKHA Pramod Appasaheb Budruk 1, Amrutraj Ashok Patil 2 1 Professor of Rachana
www.aamj.in ANVESHANA Research Article AYURVEDA MEDICAL JOURNAL ISSN: 2395-4159 OBSERVATIONAL STUDY ON KSHIPRA MARMA IN URDHVASHAKHA Pramod Appasaheb Budruk 1, Amrutraj Ashok Patil 2 1 Professor of Rachana
Physiology of Respiration
 Physiology of Respiration External Respiration = pulmonary ventilation breathing involves 2 processes: inspiration expiration Inspiration an active process involves contraction of diaphragm innervated
Physiology of Respiration External Respiration = pulmonary ventilation breathing involves 2 processes: inspiration expiration Inspiration an active process involves contraction of diaphragm innervated
- How do the carotid bodies sense arterial blood gases? o The carotid bodies weigh 25mg, yet they have their own artery. This means that they have
 - How do the carotid bodies sense arterial blood gases? o The carotid bodies weigh 25mg, yet they have their own artery. This means that they have the highest blood flow of all organs, which makes them
- How do the carotid bodies sense arterial blood gases? o The carotid bodies weigh 25mg, yet they have their own artery. This means that they have the highest blood flow of all organs, which makes them
CONCEPTUAL STUDY OF PRANAYAMA AS ALTERATION PROCESS OF MARMA
 Review Article International Ayurvedic Medical Journal ISSN:2320 5091 CONCEPTUAL STUDY OF PRANAYAMA AS ALTERATION PROCESS OF MARMA 1 Shrimali Dipakkumar Jayantkumar 2 Vikash Bhatnagar 1 P.G. Scholar P.G
Review Article International Ayurvedic Medical Journal ISSN:2320 5091 CONCEPTUAL STUDY OF PRANAYAMA AS ALTERATION PROCESS OF MARMA 1 Shrimali Dipakkumar Jayantkumar 2 Vikash Bhatnagar 1 P.G. Scholar P.G
Respiratory system. Role. Ventilation consists of 4 (5) steps : oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide elimination ph balance sound and voice formation
 Respiratory system Role oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide elimination ph balance sound and voice formation Ventilation consists of 4 (5) steps : 1. pulmonary ventilation gas exchange between lungs and
Respiratory system Role oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide elimination ph balance sound and voice formation Ventilation consists of 4 (5) steps : 1. pulmonary ventilation gas exchange between lungs and
Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 3
 Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 3 1. The pressure of a gas: a. is inversely proportional to its volume b. is unaffected by temperature changes c. is directly proportional to its volume d. does not
Respiratory Lecture Test Questions Set 3 1. The pressure of a gas: a. is inversely proportional to its volume b. is unaffected by temperature changes c. is directly proportional to its volume d. does not
J. Physiol. (I941) I00, I98-21I 6I :6I2.825
 198 J. Physiol. (I941) I00, I9821I 6I2.22.02:6I2.825 THE EFFECT OF OXYGEN LACK ON THE CEREBRAL CIRCULATION BY F. C. COURTICE From the Departments of Physiology and of Surgery, Oxford (Received 24 March
198 J. Physiol. (I941) I00, I9821I 6I2.22.02:6I2.825 THE EFFECT OF OXYGEN LACK ON THE CEREBRAL CIRCULATION BY F. C. COURTICE From the Departments of Physiology and of Surgery, Oxford (Received 24 March
Chapter 16 Respiratory System
 Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Introduction Chapter 16 Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of tubes that filter incoming air and transport it to alveoli where gases are exchanged. Think pair share: what organs are associated
Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY
 Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Respiration External respiration ventilation gas exchange Internal respiration cellular respiration gas exchange Respiratory Cycle Inspiration
Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Respiration External respiration ventilation gas exchange Internal respiration cellular respiration gas exchange Respiratory Cycle Inspiration
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY. Anaesthesiology Block 18 (GNK 586) Prof Pierre Fourie
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Anaesthesiology Block 18 (GNK 586) Prof Pierre Fourie Outline Ventilation Diffusion Perfusion Ventilation-Perfusion relationship Work of breathing Control of Ventilation 2 This image
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Anaesthesiology Block 18 (GNK 586) Prof Pierre Fourie Outline Ventilation Diffusion Perfusion Ventilation-Perfusion relationship Work of breathing Control of Ventilation 2 This image
GAS EXCHANGE & PHYSIOLOGY
 GAS EXCHANGE & PHYSIOLOGY Atmospheric Pressure Intra-Alveolar Pressure Inspiration 760 mm HG at Sea Level (= 1 atm) Pressure due to gases (N2, O2, CO2, Misc.) Pressure inside the alveolus (air sac) Phrenic
GAS EXCHANGE & PHYSIOLOGY Atmospheric Pressure Intra-Alveolar Pressure Inspiration 760 mm HG at Sea Level (= 1 atm) Pressure due to gases (N2, O2, CO2, Misc.) Pressure inside the alveolus (air sac) Phrenic
P215 Respiratory System, Part 2
 P15 Respiratory System, Part Gas Exchange Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide constant need for oxygen constant production of carbon dioxide exchange (and movement) lung alveoli pulmonary arteries pulmonary capillaries
P15 Respiratory System, Part Gas Exchange Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide constant need for oxygen constant production of carbon dioxide exchange (and movement) lung alveoli pulmonary arteries pulmonary capillaries
Chapter 16 Respiration. Respiration. Steps in Respiration. Functions of the respiratory system
 Chapter 16 Respiration Functions of the respiratory system Respiration The term respiration includes 3 separate functions: Ventilation: Breathing. Gas exchange: Occurs between air and blood in the lungs.
Chapter 16 Respiration Functions of the respiratory system Respiration The term respiration includes 3 separate functions: Ventilation: Breathing. Gas exchange: Occurs between air and blood in the lungs.
Lab #2: Blood pressure and peripheral circulation
 Lab #2: Blood pressure and peripheral circulation Vertebrates have a closed circulatory system where the blood is always enclosed within blood vessels or the heart. Blood is pumped from the heart (the
Lab #2: Blood pressure and peripheral circulation Vertebrates have a closed circulatory system where the blood is always enclosed within blood vessels or the heart. Blood is pumped from the heart (the
4. For external respiration to occur effectively, you need three parameters. They are:
 Self Assessment Module D Name: ANSWER KEY 1. Hypoxia should be assumed whenever the PaO 2 is below 45 mm Hg. 2. Name some clinical conditions that will result in hyperventilation (respiratory alkalosis).
Self Assessment Module D Name: ANSWER KEY 1. Hypoxia should be assumed whenever the PaO 2 is below 45 mm Hg. 2. Name some clinical conditions that will result in hyperventilation (respiratory alkalosis).
HCO - 3 H 2 CO 3 CO 2 + H H H + Breathing rate is regulated by blood ph and C02. CO2 and Bicarbonate act as a ph Buffer in the blood
 Breathing rate is regulated by blood ph and C02 breathing reduces plasma [CO2]; plasma [CO2] increases breathing. When C02 levels are high, breating rate increases to blow off C02 In low C02 conditions,
Breathing rate is regulated by blood ph and C02 breathing reduces plasma [CO2]; plasma [CO2] increases breathing. When C02 levels are high, breating rate increases to blow off C02 In low C02 conditions,
Control of Respiration. Central Control of Ventilation
 Central Control of Goal: maintain sufficient ventilation with minimal energy Process steps: mechanics + aerodynamics Points of Regulation Breathing rate and depth, coughing, swallowing, breath holding
Central Control of Goal: maintain sufficient ventilation with minimal energy Process steps: mechanics + aerodynamics Points of Regulation Breathing rate and depth, coughing, swallowing, breath holding
Pulmonary Circulation
 Pulmonary Circulation resin cast of pulmonary arteries resin cast of pulmonary veins Blood Flow to the Lungs Pulmonary Circulation Systemic Circulation Blood supply to the conducting zone provided by the
Pulmonary Circulation resin cast of pulmonary arteries resin cast of pulmonary veins Blood Flow to the Lungs Pulmonary Circulation Systemic Circulation Blood supply to the conducting zone provided by the
Chapter 17 The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and Regulation of Breathing
 Chapter 17 The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and Regulation of Breathing Overview of Pulmonary Circulation o Diffusion of Gases o Exchange of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide o Transport of Gases in the Blood
Chapter 17 The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and Regulation of Breathing Overview of Pulmonary Circulation o Diffusion of Gases o Exchange of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide o Transport of Gases in the Blood
Figure 1. A schematic diagram of the human respiratory system.
 Introduction to Respiration In this experiment, you will investigate various aspects of normal breathing, hyperventilation, rebreathing the effect of changing airway resistance and ways in which to measure
Introduction to Respiration In this experiment, you will investigate various aspects of normal breathing, hyperventilation, rebreathing the effect of changing airway resistance and ways in which to measure
Review. 1. Which of the following statements regarding the Adam s apple is FALSE?
 Chapter 25 Review 1. Which of the following statements regarding the Adam s apple is FALSE? A. It is inferior to the cricoid cartilage. B. It is formed by the thyroid cartilage. C. It is the uppermost
Chapter 25 Review 1. Which of the following statements regarding the Adam s apple is FALSE? A. It is inferior to the cricoid cartilage. B. It is formed by the thyroid cartilage. C. It is the uppermost
The Effect of Blood Pressure Pulsatility on the Baroreflex Gain
 The Effect of Blood Pressure Pulsatility on the Baroreflex Gain Méabh Loughman 1,2,3, Annraoi de Paor 4, John V. Ringwood 1 Department of Electronic Engineering, Maynooth University, Co. Kildare 1, The
The Effect of Blood Pressure Pulsatility on the Baroreflex Gain Méabh Loughman 1,2,3, Annraoi de Paor 4, John V. Ringwood 1 Department of Electronic Engineering, Maynooth University, Co. Kildare 1, The
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
Chapter 15. Lecture and Animation Outline
 Chapter 15 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
Chapter 15 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
Effective Strikes are KING!
 VITAL TARGETS The body is divided into three sections: high, middle, and low. Each section contains vital targets. The effects of striking these targets follow: Effective Strikes are KING! Effective striking
VITAL TARGETS The body is divided into three sections: high, middle, and low. Each section contains vital targets. The effects of striking these targets follow: Effective Strikes are KING! Effective striking
The Muscular System. Biology 105 Lecture 12 Chapter 6
 The Muscular System Biology 105 Lecture 12 Chapter 6 Outline I. Characteristics of muscles II. Three types of muscles III. Functions of muscles IV. Structure of skeletal muscles V. Mechanics of muscle
The Muscular System Biology 105 Lecture 12 Chapter 6 Outline I. Characteristics of muscles II. Three types of muscles III. Functions of muscles IV. Structure of skeletal muscles V. Mechanics of muscle
2/28/18. Respiratory System. 1 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Introduction. Anatomy. Physiology. Respiratory System
 Introduction Respiratory System Chapter 28 Respiration: We inhale air, extract oxygen from it, exhale air Cardiovascular and respiratory systems work together Failure of either system: - Disruption of
Introduction Respiratory System Chapter 28 Respiration: We inhale air, extract oxygen from it, exhale air Cardiovascular and respiratory systems work together Failure of either system: - Disruption of
 Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 Exam # 2 October 28, 2016 Total POINTS: % of grade in class
 NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 Exam # 2 October 28, 2016 Total POINTS: 100 20% of grade in class 1) An arterial blood sample for a patient at sea level is obtained, and the following physiological values
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 Exam # 2 October 28, 2016 Total POINTS: 100 20% of grade in class 1) An arterial blood sample for a patient at sea level is obtained, and the following physiological values
Gray's Atlas Of Anatomy, 1e (Gray's Anatomy) By Richard L. Drake, A. Wayne Vogl
 Gray's Atlas Of Anatomy, 1e (Gray's Anatomy) By Richard L. Drake, A. Wayne Vogl Grays Anatomy Review 2nd Edition - Medical ebooks pdf - Grays Anatomy Review 2nd Edition download pdf, gray's anatomy pdf
Gray's Atlas Of Anatomy, 1e (Gray's Anatomy) By Richard L. Drake, A. Wayne Vogl Grays Anatomy Review 2nd Edition - Medical ebooks pdf - Grays Anatomy Review 2nd Edition download pdf, gray's anatomy pdf
Chapter 10 First Aid and Field Sanitation
 Review Questions Chapter 10 First Aid and Field Sanitation 1. True or False. The three reasons for performing first aid are to save lives, prevent further injuries, and prevent infection? 1. True 2. False
Review Questions Chapter 10 First Aid and Field Sanitation 1. True or False. The three reasons for performing first aid are to save lives, prevent further injuries, and prevent infection? 1. True 2. False
Chapter 4: Ventilation Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE
 Instant download and all chapters Test Bank Respiratory Care Anatomy and Physiology Foundations for Clinical Practice 3rd Edition Will Beachey https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-respiratory-care-anatomy-physiologyfoundations-clinical-practice-3rd-edition-will-beachey/
Instant download and all chapters Test Bank Respiratory Care Anatomy and Physiology Foundations for Clinical Practice 3rd Edition Will Beachey https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-respiratory-care-anatomy-physiologyfoundations-clinical-practice-3rd-edition-will-beachey/
Module Two. Objectives: Objectives cont. Objectives cont. Objectives cont.
 Transition to the New National EMS Education Standards: EMT-B B to EMT Module Two Objectives: Upon completion, each participant will do the following to a degree of accuracy that meets the Ntl EMS Education
Transition to the New National EMS Education Standards: EMT-B B to EMT Module Two Objectives: Upon completion, each participant will do the following to a degree of accuracy that meets the Ntl EMS Education
3/24/2009 LAB D.HAMMOUDI.MD. 1. Trachea 2. Thoracic wall 3. Lungs 4. Primary bronchi 5. Diaphragm
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY LAB D.HAMMOUDI.MD 1. Trachea 2. Thoracic wall 3. Lungs 4. Primary bronchi 5. Diaphragm 1 KEY WORDS TO KNOW BOYLE S LAW INTERCOSTAL NERVES PHRENIC NERVE DIAPHRAGM EXTERNAL INTERCOSTAL
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY LAB D.HAMMOUDI.MD 1. Trachea 2. Thoracic wall 3. Lungs 4. Primary bronchi 5. Diaphragm 1 KEY WORDS TO KNOW BOYLE S LAW INTERCOSTAL NERVES PHRENIC NERVE DIAPHRAGM EXTERNAL INTERCOSTAL
The Respiratory System. Medical Terminology
 The Respiratory System Medical Terminology The respiratory system is where gas exchange occurs via respiration; inhalation/exhalation. pick up oxygen from inhaled air expels carbon dioxide and water sinus
The Respiratory System Medical Terminology The respiratory system is where gas exchange occurs via respiration; inhalation/exhalation. pick up oxygen from inhaled air expels carbon dioxide and water sinus
transients' of large amplitude can be imposed on the arterial, cardiac and Since both coughing and the Valsalva manoeuvre raise intrathoracic pressure
 351 J. Physiol. (I953) I22, 35I-357 EFFECTS OF COUGHING ON INTRATHORACIC PRESSURE, ARTERIAL PRESSURE AND PERIPHERAL BLOOD FLOW BY E. P. SHARPEY-SCHAFER From the Department of Medicine, St Thomas's Hospital
351 J. Physiol. (I953) I22, 35I-357 EFFECTS OF COUGHING ON INTRATHORACIC PRESSURE, ARTERIAL PRESSURE AND PERIPHERAL BLOOD FLOW BY E. P. SHARPEY-SCHAFER From the Department of Medicine, St Thomas's Hospital
Cardiovascular Laboratory Biol 106. In this exercise, you will:
 Cardiovascular Laboratory Biol 106 In this exercise, you will: 1) measure an electrical cardiogram of your own heart. 2) Investigate the human dive response 3) Dissect a mammalian heart 4) observe the
Cardiovascular Laboratory Biol 106 In this exercise, you will: 1) measure an electrical cardiogram of your own heart. 2) Investigate the human dive response 3) Dissect a mammalian heart 4) observe the
LIFE SAVING GUIDE. of life savers
 LIFE SAVING GUIDE Training a nation of life savers HEARTSTART TAUGHT MY SON The British Heart Foundation has a vision to create a nation of life savers. As part of that vision, we re doing everything we
LIFE SAVING GUIDE Training a nation of life savers HEARTSTART TAUGHT MY SON The British Heart Foundation has a vision to create a nation of life savers. As part of that vision, we re doing everything we
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
Respiratory Response to Physiologic Challenges. Evaluation copy
 Respiratory Response to Physiologic Challenges Computer 20 The respiratory cycle of inspiration and expiration is controlled by complex mechanisms involving neurons in the cerebral cortex, brain stem,
Respiratory Response to Physiologic Challenges Computer 20 The respiratory cycle of inspiration and expiration is controlled by complex mechanisms involving neurons in the cerebral cortex, brain stem,
Chapter 23: Respiratory System
 Chapter 23: Respiratory System I. Functions of the Respiratory System A. List and describe the five major functions of the respiratory system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. II. Anatomy and Histology of the Respiratory
Chapter 23: Respiratory System I. Functions of the Respiratory System A. List and describe the five major functions of the respiratory system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. II. Anatomy and Histology of the Respiratory
Essential Skills Course Acute Care Module. Respiratory Day 2 (Arterial Blood Gases) Pre course Workbook
 Essential Skills Course Acute Care Module Respiratory Day 2 (Arterial Blood Gases) Pre course Workbook Acknowledgements This pre course workbook has been complied and updated with reference to the original
Essential Skills Course Acute Care Module Respiratory Day 2 (Arterial Blood Gases) Pre course Workbook Acknowledgements This pre course workbook has been complied and updated with reference to the original
Observations of the Properties of the Human Respiratory System. April Ramos Dela Fuente. Bill Keenen; Tommy Kham; Grace Park
 P a g e 1 Observations of the Properties of the Human Respiratory System April Ramos Dela Fuente Bill Keenen; Tommy Kham; Grace Park NPB 101L - Section 06 - Ailsa Dalgliesh 11/25/14 P a g e 2 INTRODUCTION
P a g e 1 Observations of the Properties of the Human Respiratory System April Ramos Dela Fuente Bill Keenen; Tommy Kham; Grace Park NPB 101L - Section 06 - Ailsa Dalgliesh 11/25/14 P a g e 2 INTRODUCTION
Exercise 1/Microscopy Dr. Marvin E. Holtz Human Anatomy and Physiology Lab I
 Exercise 1/Microscopy Parts of the Microscope (page 1) Each student will locate, identify and familiarize themselves with all of the parts and associated functions for each microscope part listed in the
Exercise 1/Microscopy Parts of the Microscope (page 1) Each student will locate, identify and familiarize themselves with all of the parts and associated functions for each microscope part listed in the
Under 17 and Under 15 Competition Theory Paper
 Surf Life Saving Australia Champion Lifesaver 2009 Under 17 and Under 15 Competition Theory Paper Mark the best answer to each question on the answer sheet. The best answer is the one that can be found
Surf Life Saving Australia Champion Lifesaver 2009 Under 17 and Under 15 Competition Theory Paper Mark the best answer to each question on the answer sheet. The best answer is the one that can be found
FIRST AID. Study Topics. At a minimum, the following topics are to be studied for the first aid exam.
 FIRST AID Study Topics At a minimum, the following topics are to be studied for the first aid exam. TOPIC Avoid getting air in stomach during rescue breathing Burns Kinds of Burns & Care Calling for Help
FIRST AID Study Topics At a minimum, the following topics are to be studied for the first aid exam. TOPIC Avoid getting air in stomach during rescue breathing Burns Kinds of Burns & Care Calling for Help
Regulation of Breathing
 Regulation of Breathing Introduction Breathing involves a complex interaction between many important respiratory organs and the blood. Air is brought into the lungs through the active process of inhalation,
Regulation of Breathing Introduction Breathing involves a complex interaction between many important respiratory organs and the blood. Air is brought into the lungs through the active process of inhalation,
Respiratory Anatomy and Physiology. Respiratory Anatomy. Function of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory Anatomy and Physiology Michaela Dixon Clinical Development Nurse PICU BRHFC Respiratory Anatomy Function of the Respiratory System - In conjunction with the cardiovascular system, to supply
Respiratory Anatomy and Physiology Michaela Dixon Clinical Development Nurse PICU BRHFC Respiratory Anatomy Function of the Respiratory System - In conjunction with the cardiovascular system, to supply
UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 9.01 GENERAL FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. Brings oxygenated air to the alveoli B. Removes air containing carbon dioxide C. Filters, warms, and humidifies
UNIT 9 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 9.01 GENERAL FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. Brings oxygenated air to the alveoli B. Removes air containing carbon dioxide C. Filters, warms, and humidifies
Hyndland Secondary School Biology Department
 Hyndland Secondary School Biology Department Body in Action Homework and Question Booklet 1 Body in Action (a) Movement... 2 Skeleton... 2 Joints... 3 Body in Action (b) The need for Energy... 5 Heart...
Hyndland Secondary School Biology Department Body in Action Homework and Question Booklet 1 Body in Action (a) Movement... 2 Skeleton... 2 Joints... 3 Body in Action (b) The need for Energy... 5 Heart...
R S A B C CPR. Basic Life Support Flow Chart Check for danger. Check Response. Send for Help. Check Airway. Check for Breathing.
 CPR CPR is the technique of the manual inflation of the lungs with oxygen, and compression of the heart, therefore pumping oxygenated blood around the body, and keeping the vital organs supplied with oxygen.
CPR CPR is the technique of the manual inflation of the lungs with oxygen, and compression of the heart, therefore pumping oxygenated blood around the body, and keeping the vital organs supplied with oxygen.
FUNDAMENTAL CRITERIA FOR FIRST AID INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 1 FUNDAMENTAL CRITERIA FOR FIRST AID INTRODUCTION Soldiers may have to depend upon their first aid knowledge and skills to save themselves or other soldiers. They may be able to save a life, prevent
CHAPTER 1 FUNDAMENTAL CRITERIA FOR FIRST AID INTRODUCTION Soldiers may have to depend upon their first aid knowledge and skills to save themselves or other soldiers. They may be able to save a life, prevent
2.1.1 List the principal structures of the
 physiology 2.1.1 List the principal structures of the The principle structures of the respiratory are: Nose/Mouth used for inhalation of oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide rich air Pharynx -
physiology 2.1.1 List the principal structures of the The principle structures of the respiratory are: Nose/Mouth used for inhalation of oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide rich air Pharynx -
Pulmonary Circulation Linda Costanzo Ph.D.
 Pulmonary Circulation Linda Costanzo Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The differences between pressures in the pulmonary and systemic circulations. 2. How
Pulmonary Circulation Linda Costanzo Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The differences between pressures in the pulmonary and systemic circulations. 2. How
S.T.E.M Part 1: Prior Knowledge: Energy and Simple Machines
 S.T.E.M. 2016-7 Part 1: Prior Knowledge: Energy and Simple Machines Prior Knowledge: What is Energy? Redefining: energy, force, work and pressure Experiment 1: Floating Ping Pong Ball You need: - Ping
S.T.E.M. 2016-7 Part 1: Prior Knowledge: Energy and Simple Machines Prior Knowledge: What is Energy? Redefining: energy, force, work and pressure Experiment 1: Floating Ping Pong Ball You need: - Ping
Aquatic vertebrates that are characterized by:
 Aquatic vertebrates that are characterized by: Paired fins Used for movement Scales Used for protection Gills Used for exchanging gases Fishes were the first vertebrates to evolve The evolution of jaws
Aquatic vertebrates that are characterized by: Paired fins Used for movement Scales Used for protection Gills Used for exchanging gases Fishes were the first vertebrates to evolve The evolution of jaws
Respiratory system. Premedical - Biology
 Respiratory system Premedical - Biology Composition of atmosphere Nitrogen (N 2 ) 840 ppmv (78.084%) Oxygen (O 2 ) 209,460 ppmv (20.946%) Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) 387 ppmv (0.0387%) Argon (Ar), Neon (Ne),
Respiratory system Premedical - Biology Composition of atmosphere Nitrogen (N 2 ) 840 ppmv (78.084%) Oxygen (O 2 ) 209,460 ppmv (20.946%) Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) 387 ppmv (0.0387%) Argon (Ar), Neon (Ne),
CPR + AED Topic 6 TECS TECS FIRE & SAFETY TRAINING PTE LTD
 CPR + AED Topic 6 1 Anatomy and physiology of the circulatory system 2 Principles of Resuscitation Principles of resuscitation / Determine if CPR is necessary by examining casualty, which include the following:
CPR + AED Topic 6 1 Anatomy and physiology of the circulatory system 2 Principles of Resuscitation Principles of resuscitation / Determine if CPR is necessary by examining casualty, which include the following:
AMERICAN HEART ASSOCIATION UPDATES:
 INTRODUCTION TO CPR AMERICAN HEART ASSOCIATION UPDATES: October 18, 2010 If a bystander is not trained in CPR, the bystander should provide compression-only CPR (see below) for the adult victim who suddenly
INTRODUCTION TO CPR AMERICAN HEART ASSOCIATION UPDATES: October 18, 2010 If a bystander is not trained in CPR, the bystander should provide compression-only CPR (see below) for the adult victim who suddenly
Hypothermia, the Diving Reflex, and Survival. Briana Martin. Biology 281 Professor McMillan April 17, XXXX
 CSE Paper (Martin) Hypothermia, the Diving Reflex, and Survival Full title, writer s name, name of course, instructor s name, and date (all centered). Briana Martin Biology 281 Professor McMillan April
CSE Paper (Martin) Hypothermia, the Diving Reflex, and Survival Full title, writer s name, name of course, instructor s name, and date (all centered). Briana Martin Biology 281 Professor McMillan April
Nelson Pages
 Nelson Pages 280 309 Biology 20 Unit D: Respiratory and Motor Systems Earth s atmosphere is about: 78 % N2 21 % O2 1 % remaining gases Aerobic organisms require O 2 for cellular respiration Breathing (ventilation).
Nelson Pages 280 309 Biology 20 Unit D: Respiratory and Motor Systems Earth s atmosphere is about: 78 % N2 21 % O2 1 % remaining gases Aerobic organisms require O 2 for cellular respiration Breathing (ventilation).
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System
 VI edit Pag 451-499 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System V edit. Pag 459-509 Tissue cell Alveoli of lungs Atmosphere 1 External respiration Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere and air sacs
VI edit Pag 451-499 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System V edit. Pag 459-509 Tissue cell Alveoli of lungs Atmosphere 1 External respiration Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere and air sacs
Human Respiratory System Experiment
 NPB 101L Human Respiratory System Experiment Name: Zijun Liu Group members: Xiaodong Shi, Conner Tiffany, Allen G. Section 03 TA: Ken Eum Nov 18, 2013 P.1 Liu Introduction: The main purpose of breathing
NPB 101L Human Respiratory System Experiment Name: Zijun Liu Group members: Xiaodong Shi, Conner Tiffany, Allen G. Section 03 TA: Ken Eum Nov 18, 2013 P.1 Liu Introduction: The main purpose of breathing
Recitation question # 05
 Recitation and Lab # 05 The goal of this recitations / labs is to review material related to the CV and respiratory lectures for the second test of this course. Info required to answer this recitation
Recitation and Lab # 05 The goal of this recitations / labs is to review material related to the CV and respiratory lectures for the second test of this course. Info required to answer this recitation
B-immobility from structural or organic damage
 DRAGON'S TOUCH weaknesses of the human anatomy by: Hei Long This volume (and the ones to follow) concentrates on the 43 major pressure points of the body. Of course, there are quite a few more, but these
DRAGON'S TOUCH weaknesses of the human anatomy by: Hei Long This volume (and the ones to follow) concentrates on the 43 major pressure points of the body. Of course, there are quite a few more, but these
SOLUTIONS Homework #1
 SOLUTIONS Homework #1 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING IN MEDICINE AND BIOLOGY ECEN 1001- Fall 2003 R. Mihran Due Tuesday, 9/9/03 Question 1: a) Chapter 1 of the text discusses the fact that a significant fraction
SOLUTIONS Homework #1 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING IN MEDICINE AND BIOLOGY ECEN 1001- Fall 2003 R. Mihran Due Tuesday, 9/9/03 Question 1: a) Chapter 1 of the text discusses the fact that a significant fraction
BASIC KNOWLEDGE OF LABORATORY FIRST AID
 BASIC KNOWLEDGE OF LABORATORY FIRST AID RV: 02/02/2015 prevencio@uv.es Page 1 of 7 . General issues to be considered by the rescuer in the event of an accident are described below: - Proceed as follows:
BASIC KNOWLEDGE OF LABORATORY FIRST AID RV: 02/02/2015 prevencio@uv.es Page 1 of 7 . General issues to be considered by the rescuer in the event of an accident are described below: - Proceed as follows:
Pharynx one of the visceral tubes the common chamber of the respiratory and digestive tracts located behind the nasal and oral cavities funnel-shaped
 Pharynx and soft palate Pharynx one of the visceral tubes the common chamber of the respiratory and digestive tracts located behind the nasal and oral cavities funnel-shaped in form 12 cm in length; its
Pharynx and soft palate Pharynx one of the visceral tubes the common chamber of the respiratory and digestive tracts located behind the nasal and oral cavities funnel-shaped in form 12 cm in length; its
2.This section will move into the Airway Management, Rescue Breaths & Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR).
 Wilderness First Aid Fundamentals The period between the World Wars saw an increased awareness in personal first aid training. To cover all eventualities, from accidents at work to travel in foreign lands.
Wilderness First Aid Fundamentals The period between the World Wars saw an increased awareness in personal first aid training. To cover all eventualities, from accidents at work to travel in foreign lands.
Circulatory And Respiration
 Circulatory And Respiration Composition Of Blood Blood Heart 200mmHg 120mmHg Aorta Artery Arteriole 50mmHg Capillary Bed Venule Vein Vena Cava Heart Differences Between Arteries and Veins Veins transport
Circulatory And Respiration Composition Of Blood Blood Heart 200mmHg 120mmHg Aorta Artery Arteriole 50mmHg Capillary Bed Venule Vein Vena Cava Heart Differences Between Arteries and Veins Veins transport
Medical Center, San Francisco, Cal.,
 628 J. Phy8iol. (1966), 183, 628-636 With 4 text-figure8 Printed in Great Britain THE INTERRELATION OF THERMOREGULATORY AND BARORECEPTOR REFLEXES IN THE CONTROL OF THE BLOOD VESSELS IN THE HUMAN FOREARM
628 J. Phy8iol. (1966), 183, 628-636 With 4 text-figure8 Printed in Great Britain THE INTERRELATION OF THERMOREGULATORY AND BARORECEPTOR REFLEXES IN THE CONTROL OF THE BLOOD VESSELS IN THE HUMAN FOREARM
Outline - Respiratory System. Function of the respiratory system Parts of the respiratory system Mechanics of breathing Regulation of breathing
 Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
A Study on Oxygen Utilization Pattern And Costing In Critical Care Units And Operation Theatre oa Rural Tertiary Care Hospital.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-853, p-issn: 2279-861.Volume 15, Issue 11 Ver. III (November. 216), PP 11-17 www.iosrjournals.org A Study on Oxygen Utilization Pattern
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-853, p-issn: 2279-861.Volume 15, Issue 11 Ver. III (November. 216), PP 11-17 www.iosrjournals.org A Study on Oxygen Utilization Pattern
CPR: A Comprehensive Review of the Concepts Behind the Lifesaving Procedure
 CPR: A Comprehensive Review of the Concepts Behind the Lifesaving Procedure CPR: A Comprehensive Review of the Concepts Behind the Lifesaving Procedure Table of Contents Introduction 2 Section 1: The Anatomy
CPR: A Comprehensive Review of the Concepts Behind the Lifesaving Procedure CPR: A Comprehensive Review of the Concepts Behind the Lifesaving Procedure Table of Contents Introduction 2 Section 1: The Anatomy
Fundamentals and Future Directions in Poultry Stunning. Penny Lawlis Msc. Professional Livestock Auditing Inc.
 Fundamentals and Future Directions in Poultry Stunning Penny Lawlis Msc. Professional Livestock Auditing Inc. Principles of humane stunning Important factors to consider: - How quickly does loss of
Fundamentals and Future Directions in Poultry Stunning Penny Lawlis Msc. Professional Livestock Auditing Inc. Principles of humane stunning Important factors to consider: - How quickly does loss of
Heart Rate Breathing Rate Physical Fitness Student
 We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with heart rate breathing
We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with heart rate breathing
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange elephant seals gills AP Biology
 alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange O 2 & CO 2 exchange exchange between environment & cells provides O 2 for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high
alveoli Chapter 42. Gas Exchange gills elephant seals Gas exchange O 2 & CO 2 exchange exchange between environment & cells provides O 2 for aerobic cellular respiration need moist membrane need high
Respiratory System. Prepared by: Dorota Marczuk-Krynicka, MD, PhD
 Respiratory System Prepared by: Dorota Marczuk-Krynicka, MD, PhD Lungs: Ventilation Perfusion Gas Exchange - Diffusion 1. Airways and Airway Resistance (AWR) 2. Mechanics of Breathing and Lung (Elastic)
Respiratory System Prepared by: Dorota Marczuk-Krynicka, MD, PhD Lungs: Ventilation Perfusion Gas Exchange - Diffusion 1. Airways and Airway Resistance (AWR) 2. Mechanics of Breathing and Lung (Elastic)
COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL. Effective Date: August 31, 2006
 COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION Emergency Procedures POLICY NUMBER: 702 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: CARDIOPULMONARY RESUSCITATION (CPR) 1. PURPOSE: To provide
COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION Emergency Procedures POLICY NUMBER: 702 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: CARDIOPULMONARY RESUSCITATION (CPR) 1. PURPOSE: To provide
Emergency Medical Technician 60 Questions
 Emergency Medical Technician 60 Questions 1. Which of the following is your primary goal during airway management? a. Ensure clear, unobstructed breathing. b. Ensure that CPR is effective. c. Provide a
Emergency Medical Technician 60 Questions 1. Which of the following is your primary goal during airway management? a. Ensure clear, unobstructed breathing. b. Ensure that CPR is effective. c. Provide a
Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42. Gas Exchange pp Gas Exchange. Gas Exchange in Fish pp Gas Exchange in Fish
 Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42 Fig. 42.24 Gas Exchange pp.979-989 Gas exchange involves the uptake of oxygen and the discharge of carbon dioxide (i.e. respiration or breathing). It is necessary for cellular
Topic 13: Gas Exchange Ch. 42 Fig. 42.24 Gas Exchange pp.979-989 Gas exchange involves the uptake of oxygen and the discharge of carbon dioxide (i.e. respiration or breathing). It is necessary for cellular
First Aid Exercises 1
 First Aid Exercises 1 1 A N S W E R T H E Q U E S T I O N S I N Y O U R O W N W O R D S! What are the emergency numbers you should remember? What kind of information should you give when you call for help?
First Aid Exercises 1 1 A N S W E R T H E Q U E S T I O N S I N Y O U R O W N W O R D S! What are the emergency numbers you should remember? What kind of information should you give when you call for help?
Section 01: The Pulmonary System
 Section 01: The Pulmonary System Chapter 12 Pulmonary Structure and Function Chapter 13 Gas Exchange and Transport Chapter 14 Dynamics of Pulmonary Ventilation HPHE 6710 Exercise Physiology II Dr. Cheatham
Section 01: The Pulmonary System Chapter 12 Pulmonary Structure and Function Chapter 13 Gas Exchange and Transport Chapter 14 Dynamics of Pulmonary Ventilation HPHE 6710 Exercise Physiology II Dr. Cheatham
Gas Exchange in Animals. Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2. Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial
 Gas Exchange in Animals Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2 Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial Respiratory surface! skin, gills, lungs Circulatory System O2/CO2
Gas Exchange in Animals Uptake of O2 from environment and discharge of CO2 Respiratory medium! water for aquatic animals, air for terrestial Respiratory surface! skin, gills, lungs Circulatory System O2/CO2
Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation
 1 CPR (HLTCPR201B Perform CPR) 2 Action Plan D anger R esponse S end for help A irway B reathing C PR D efibrillation 3 D anger Check for dangers to: Yourself Bystanders Casualty Walk 360 o around the
1 CPR (HLTCPR201B Perform CPR) 2 Action Plan D anger R esponse S end for help A irway B reathing C PR D efibrillation 3 D anger Check for dangers to: Yourself Bystanders Casualty Walk 360 o around the
1. A.- 2. B.- 3. C.- 4. D.- 5. E.- Anatomy & Physiology 2A Name: FALL 2015 (Take Home) MINI-EXAM #4. Figure 11.2
 Anatomy & Physiology 2A Name: FALL 2015 (Take Home) MINI-EXAM #4 _ Figure 11.2 Using Figure 11.2: Completely define and describe letters A-E in the spaces provided below: 1. A.- 2. B.- 3. C.- 4. D.- 5.
Anatomy & Physiology 2A Name: FALL 2015 (Take Home) MINI-EXAM #4 _ Figure 11.2 Using Figure 11.2: Completely define and describe letters A-E in the spaces provided below: 1. A.- 2. B.- 3. C.- 4. D.- 5.
Merlin Training for Vets and Nurses
 Merlin Training for Vets and Nurses Objectives To familiarise users with the controls of Merlin To familiarise users with the pneumatic connections of Merlin To ensure that users understand the behaviour
Merlin Training for Vets and Nurses Objectives To familiarise users with the controls of Merlin To familiarise users with the pneumatic connections of Merlin To ensure that users understand the behaviour
