Please, after a carefully reading of given references, answer the following questions:
|
|
|
- Georgiana Reynolds
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Report Session 1: Introduction of Respiratory System Student 1 name: Student 2 name: Questionnaire Please, after a carefully reading of given references, answer the following questions: (1) How gas exchange is regulated? (2) Which muscles are implicated in the breathing process and which is their function? (3) What is the activity of diaphragm during active expiration? (4) Where is located respiratory control center anatomically? (5) Which volumes are described in the documentation and what are the relationships between them? (6) Why does total ventilation increase during exercise? (7) Which are normal values of PCO a 2, PO a 2, breathing frequency and tidal volume at rest? Students have to deliver the short answers via Intranet before starting next Lab Session.
2 2 Report Session 2: Respiratory System Response under Ventilatory Stimuli Student 1 name: Student 2 name: EXERCISE 1 Variable Otis equation Mead s equation Widdicombe s equation Table 2.1: Results of simulation in resting conditions with three different equations to calculate the respiratory frequency
3 3 EXERCISE 2 Variable Sea Level 2500 (m) of Altitude Rest Exerc Rest Exerc Table 2.2: Results of exercise simulation at sea level and at 2500 m of altitude Comments at sea level: Comments at high altitude:
4 4 EXERCISE 3 Variable Table 2.3: Results of incremental hypercapnia simulation with Otis equation to calculate respiratory frequency EXERCISE 4 Variable for Mead for Widdicombe for Mead for Widdicombe for Mead for Widdicombe Table 2.4: Results of incremental hypercapnia simulation with Mead and Widdicombe s equation
5 5 EXERCISE 5 EXERCISE 6 Equation Prediction Error (%) Otis Mead Widdicombe V T Table 2.5: Prediction error during hypercapnia with different equations to calculate respiratory frequency f Students have to deliver all the results (Tables, Plots and Comments) via Intranet before starting next Lab Session.
6 6 Report Session 3: Respiratory Diseases based on Mechanical Loads Student 1 name: Student 2 name: EXERCISE 1 Variable Sea Level 2500 (m) of Altitude R=2.6 R=3.6 R=2.6 R=3.6 Table 3.1: Results of variation of airway resistance at sea level and at high altitude EXERCISE 2 Variable Sea Level 2500 (m) of Altitude E=10 E=20 E=10 E=20 Table 3.2: Results of variation of elastance at sea level and at high altitude
7 7 EXERCISE 3 Variable Table 3.3: Results of incremental exercise simulation in a normal subject EXERCISE 4 Variable Table 3.4: Results of incremental exercise simulation in a restrictive patient with E=20 cmh 2 O/l
8 8 EXERCISE 5 Variable Table 3.5: Results of incremental exercise simulation in a restrictive patient with E=30 cmh 2 O/l EXERCISE 6 Settling time: EXERCISE 7
9 9 EXERCISE 8 Elastance (cmh 2 O/l) Prediction Error (%) V T f Table 3.6: Prediction error in exercise with different values of elastance Questionnaire Please, answer the following questions from the results obtained in this Lab Session: (1) Obtain conclusions from the data in table 3.1. How does an increase of airway resistance effect in the respiratory pattern? (2) Obtain conclusions from the data in table 3.1. How does an increase of respiratory elastance effect in the respiratory pattern? (3) Which is the effect of hypoxia in patients with higher respiratory elastance? (4) Which is the effect of exercise in patients with higher respiratory elastance? (5) Obtain conclusions from Figure 3.1 and table 3.1. Experimental data from a restrictive patient could be predicted by RespiLab using higher values of elastance? Which elastance value obtains the best prediction of respiratory system response during exercise for the selected restrictive patient with? (6) Are the graphs of V T vs V E and F vs V E coherent with the prediction error you found? Students have to deliver all the results (Tables and Plots) and answers via Intranet by next week.
LABORATORY GUIDE. Virtual Laboratory for Analysis of Human Respiratory System. May Alher Mauricio Hernández Miguel Ángel Mañanas Ramón Costa
 LABORATORY GUIDE Virtual Laboratory for Analysis of Human Respiratory System May 006 Alher Mauricio Hernández Miguel Ángel Mañanas Ramón Costa Laboratory Guide 3 This guide to be used with a Virtual Laboratory
LABORATORY GUIDE Virtual Laboratory for Analysis of Human Respiratory System May 006 Alher Mauricio Hernández Miguel Ángel Mañanas Ramón Costa Laboratory Guide 3 This guide to be used with a Virtual Laboratory
RESPILAB USER MANUAL
 RESPILAB USER MANUAL Virtual Laboratory for Analysis of Human Respiratory System Version 0.3 April 2006 Alher Mauricio Hernández Miguel Ángel Mañanas Ramón Costa Respilab User Manual Table of Contents
RESPILAB USER MANUAL Virtual Laboratory for Analysis of Human Respiratory System Version 0.3 April 2006 Alher Mauricio Hernández Miguel Ángel Mañanas Ramón Costa Respilab User Manual Table of Contents
Chapter 4: Ventilation Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE
 Instant download and all chapters Test Bank Respiratory Care Anatomy and Physiology Foundations for Clinical Practice 3rd Edition Will Beachey https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-respiratory-care-anatomy-physiologyfoundations-clinical-practice-3rd-edition-will-beachey/
Instant download and all chapters Test Bank Respiratory Care Anatomy and Physiology Foundations for Clinical Practice 3rd Edition Will Beachey https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-respiratory-care-anatomy-physiologyfoundations-clinical-practice-3rd-edition-will-beachey/
HUMAN Sample Experiment High Altitude Simulation (a one variable experiment) (version 5/04/06)
 HUMAN Sample Experiment High Altitude Simulation (a one variable experiment) (version 5/04/06) Students wish to simulate an ascent to the summit of Mount Mckinley (12,500 ft.), perhaps to compare the simulated
HUMAN Sample Experiment High Altitude Simulation (a one variable experiment) (version 5/04/06) Students wish to simulate an ascent to the summit of Mount Mckinley (12,500 ft.), perhaps to compare the simulated
Gas Pressure Volume Relationships Laboratory Simulation
 Gas Pressure Volume Relationships Laboratory Simulation Name Lab Section Problem Statement: How are the pressure and volume of a gas sample related? How do pressure/volume relationships of different gases
Gas Pressure Volume Relationships Laboratory Simulation Name Lab Section Problem Statement: How are the pressure and volume of a gas sample related? How do pressure/volume relationships of different gases
LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
 66 LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB Assignments: Due before lab: Quiz: Three Respiratory Interactive Physiology Animations pages 69 73. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
66 LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB Assignments: Due before lab: Quiz: Three Respiratory Interactive Physiology Animations pages 69 73. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
Measuring Lung Capacity
 Name Class Date Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Measuring Lung Capacity Introduction The amount of air that you move in and out of your lungs depends on how quickly you are breathing. The
Name Class Date Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Measuring Lung Capacity Introduction The amount of air that you move in and out of your lungs depends on how quickly you are breathing. The
RESPIRATORY REGULATION DURING EXERCISE
 RESPIRATORY REGULATION DURING EXERCISE Respiration Respiration delivery of oxygen to and removal of carbon dioxide from the tissue External respiration ventilation and exchange of gases in the lung Internal
RESPIRATORY REGULATION DURING EXERCISE Respiration Respiration delivery of oxygen to and removal of carbon dioxide from the tissue External respiration ventilation and exchange of gases in the lung Internal
Unit 15 Manual Resuscitators
 15-1 Unit 15 Manual Resuscitators GOAL On completion of this unit, the student should comprehend the proper operation of self-inflating resuscitation bags, flow-inflating resuscitation bags and gas-powered
15-1 Unit 15 Manual Resuscitators GOAL On completion of this unit, the student should comprehend the proper operation of self-inflating resuscitation bags, flow-inflating resuscitation bags and gas-powered
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY, PHYSICS AND PATHOLOGY IN RELATION TO ANAESTHESIA AND INTENSIVE CARE
 Course n : Course 3 Title: RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY, PHYSICS AND PATHOLOGY IN RELATION TO ANAESTHESIA AND INTENSIVE CARE Sub-category: Intensive Care for Respiratory Distress Topic: Pulmonary Function and
Course n : Course 3 Title: RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY, PHYSICS AND PATHOLOGY IN RELATION TO ANAESTHESIA AND INTENSIVE CARE Sub-category: Intensive Care for Respiratory Distress Topic: Pulmonary Function and
Lab 3. The Respiratory System (designed by Heather E. M. Liwanag with T.M. Williams)
 Name Lab Partners Lab 3. The Respiratory System (designed by Heather E. M. Liwanag with T.M. Williams) Part 1. Lung Volumes and Capacities Objectives 1. Obtain graphical representation of lung capacities
Name Lab Partners Lab 3. The Respiratory System (designed by Heather E. M. Liwanag with T.M. Williams) Part 1. Lung Volumes and Capacities Objectives 1. Obtain graphical representation of lung capacities
Introduction. Respiration. Chapter 10. Objectives. Objectives. The Respiratory System
 Introduction Respiration Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body Plays a role in the regulation of acidbase balance during exercise Objectives
Introduction Respiration Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body Plays a role in the regulation of acidbase balance during exercise Objectives
Respiration (revised 2006) Pulmonary Mechanics
 Respiration (revised 2006) Pulmonary Mechanics PUL 1. Diagram how pleural pressure, alveolar pressure, airflow, and lung volume change during a normal quiet breathing cycle. Identify on the figure the
Respiration (revised 2006) Pulmonary Mechanics PUL 1. Diagram how pleural pressure, alveolar pressure, airflow, and lung volume change during a normal quiet breathing cycle. Identify on the figure the
Respiratory Physiology 2
 Respiratory Physiology 2 Session Objectives. What you will cover Gaseous Exchange Control of Breathing Rate Your objectives are State the function of support structures and epithelia of the bronchial tree
Respiratory Physiology 2 Session Objectives. What you will cover Gaseous Exchange Control of Breathing Rate Your objectives are State the function of support structures and epithelia of the bronchial tree
MV-TRAINER USER MANUAL
 MV-TRAINER USER MANUAL Computational Tool for Modeling and Simulation of Mechanically Ventilated Patients Version 0.2 January 2014 Leidy Yanet Serna Mauricio Hernández Miguel Ángel Mañanas MV-TRAINER User
MV-TRAINER USER MANUAL Computational Tool for Modeling and Simulation of Mechanically Ventilated Patients Version 0.2 January 2014 Leidy Yanet Serna Mauricio Hernández Miguel Ángel Mañanas MV-TRAINER User
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY. Anaesthesiology Block 18 (GNK 586) Prof Pierre Fourie
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Anaesthesiology Block 18 (GNK 586) Prof Pierre Fourie Outline Ventilation Diffusion Perfusion Ventilation-Perfusion relationship Work of breathing Control of Ventilation 2 This image
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Anaesthesiology Block 18 (GNK 586) Prof Pierre Fourie Outline Ventilation Diffusion Perfusion Ventilation-Perfusion relationship Work of breathing Control of Ventilation 2 This image
The physiological functions of respiration and circulation. Mechanics. exercise 7. Respiratory Volumes. Objectives
 exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
- How do the carotid bodies sense arterial blood gases? o The carotid bodies weigh 25mg, yet they have their own artery. This means that they have
 - How do the carotid bodies sense arterial blood gases? o The carotid bodies weigh 25mg, yet they have their own artery. This means that they have the highest blood flow of all organs, which makes them
- How do the carotid bodies sense arterial blood gases? o The carotid bodies weigh 25mg, yet they have their own artery. This means that they have the highest blood flow of all organs, which makes them
Respiratory System. Part 2
 Respiratory System Part 2 Respiration Exchange of gases between air and body cells Three steps 1. Ventilation 2. External respiration 3. Internal respiration Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation consists
Respiratory System Part 2 Respiration Exchange of gases between air and body cells Three steps 1. Ventilation 2. External respiration 3. Internal respiration Ventilation Pulmonary ventilation consists
Applying Hooke s Law to Multiple Bungee Cords. Introduction
 Applying Hooke s Law to Multiple Bungee Cords Introduction Hooke s Law declares that the force exerted on a spring is proportional to the amount of stretch or compression on the spring, is always directed
Applying Hooke s Law to Multiple Bungee Cords Introduction Hooke s Law declares that the force exerted on a spring is proportional to the amount of stretch or compression on the spring, is always directed
RSPT 1060 OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES EQUATION OF MOTION. MODULE C Applied Physics Lesson #1 - Mechanics. Ventilation vs.
 RSPT 1060 MODULE C Applied Physics Lesson #1 - Mechanics OBJECTIVES At the end of this module, the student should be able to define the terms and abbreviations used in the module. draw & explain the equation
RSPT 1060 MODULE C Applied Physics Lesson #1 - Mechanics OBJECTIVES At the end of this module, the student should be able to define the terms and abbreviations used in the module. draw & explain the equation
A Liter a Lung Measuring Lung Capacity
 A Liter a Lung Measuring Lung Capacity OBJECTIVE In this investigation, students will compare the actual and expected vital capacities of their classmates. LEVEL Middle Grades Life Science CONNECTIONS
A Liter a Lung Measuring Lung Capacity OBJECTIVE In this investigation, students will compare the actual and expected vital capacities of their classmates. LEVEL Middle Grades Life Science CONNECTIONS
Recitation question # 05
 Recitation and Lab # 05 The goal of this recitations / labs is to review material related to the CV and respiratory lectures for the second test of this course. Info required to answer this recitation
Recitation and Lab # 05 The goal of this recitations / labs is to review material related to the CV and respiratory lectures for the second test of this course. Info required to answer this recitation
VENTILATION AND PERFUSION IN HEALTH AND DISEASE. Dr.HARIPRASAD VS
 VENTILATION AND PERFUSION IN HEALTH AND DISEASE Dr.HARIPRASAD VS Ventilation Total ventilation - total rate of air flow in and out of the lung during normal tidal breathing. Alveolar ventilation -represents
VENTILATION AND PERFUSION IN HEALTH AND DISEASE Dr.HARIPRASAD VS Ventilation Total ventilation - total rate of air flow in and out of the lung during normal tidal breathing. Alveolar ventilation -represents
Initiation and Management of Airway Pressure Release Ventilation (APRV)
 Initiation and Management of Airway Pressure Release Ventilation (APRV) Eric Kriner RRT Pulmonary Critical Care Clinical Specialist Pulmonary Services Department Medstar Washington Hospital Center Disclosures
Initiation and Management of Airway Pressure Release Ventilation (APRV) Eric Kriner RRT Pulmonary Critical Care Clinical Specialist Pulmonary Services Department Medstar Washington Hospital Center Disclosures
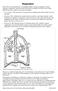
Figure 1. A schematic diagram of the human respiratory system.
 Introduction to Respiration In this experiment, you will investigate various aspects of normal breathing, hyperventilation, rebreathing the effect of changing airway resistance and ways in which to measure
Introduction to Respiration In this experiment, you will investigate various aspects of normal breathing, hyperventilation, rebreathing the effect of changing airway resistance and ways in which to measure
Lung Volumes and Capacities
 Lung Volumes and Capacities Normally the volume of air entering the lungs during a single inspiration is approximately equal to the volume leaving on the subsequent expiration and is called the tidal volume.
Lung Volumes and Capacities Normally the volume of air entering the lungs during a single inspiration is approximately equal to the volume leaving on the subsequent expiration and is called the tidal volume.
Basics of Mechanical Ventilation. Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity
 Basics of Mechanical Ventilation Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity Overview of topics 1. Goals 2. Settings 3. Modes 4. Advantages and disadvantages
Basics of Mechanical Ventilation Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity Overview of topics 1. Goals 2. Settings 3. Modes 4. Advantages and disadvantages
Mechanical power and opening pressure. Fellowship training program Intensive Care Radboudumc, Nijmegen
 Mechanical power and opening pressure Fellowship training program Intensive Care Radboudumc, Nijmegen Mechanical power Energy applied to the lung: Ptp * V (Joule) Power = Energy per minute (J/min) Power
Mechanical power and opening pressure Fellowship training program Intensive Care Radboudumc, Nijmegen Mechanical power Energy applied to the lung: Ptp * V (Joule) Power = Energy per minute (J/min) Power
Lab 17. The Respiratory System. Laboratory Objectives
 Lab 17 The Respiratory System Laboratory Objectives Identify and describe the anatomical structures of the respiratory system. Describe the relationship between volume and pressure. Describe changes in
Lab 17 The Respiratory System Laboratory Objectives Identify and describe the anatomical structures of the respiratory system. Describe the relationship between volume and pressure. Describe changes in
PCO2 levels apparently differed by less than 5 mm Hg. Fowler [1954] and. Godfrey and Campbell [1969] have shown that it is possible to resume a
![PCO2 levels apparently differed by less than 5 mm Hg. Fowler [1954] and. Godfrey and Campbell [1969] have shown that it is possible to resume a PCO2 levels apparently differed by less than 5 mm Hg. Fowler [1954] and. Godfrey and Campbell [1969] have shown that it is possible to resume a](/thumbs/85/91672390.jpg) Q. Ji exp. Physiol. (1969) 54, 129-140 THE INFLUENCE OF LUNG SHRINKAGE ON BREATH HOLDING TIME. By S. GODFREY, R. H. T. EDWARDS and D. A. WARRELL. From the Department of Medicine, Royal Postgraduate Medical
Q. Ji exp. Physiol. (1969) 54, 129-140 THE INFLUENCE OF LUNG SHRINKAGE ON BREATH HOLDING TIME. By S. GODFREY, R. H. T. EDWARDS and D. A. WARRELL. From the Department of Medicine, Royal Postgraduate Medical
Principles of mechanical ventilation. Anton van Kaam, MD, PhD Emma Children s Hospital AMC Amsterdam, The Netherlands
 Principles of mechanical ventilation Anton van Kaam, MD, PhD Emma Children s Hospital AMC Amsterdam, The Netherlands Disclosure Research grant Chiesi Pharmaceuticals Research grant CareFusion GA: 27 weeks,
Principles of mechanical ventilation Anton van Kaam, MD, PhD Emma Children s Hospital AMC Amsterdam, The Netherlands Disclosure Research grant Chiesi Pharmaceuticals Research grant CareFusion GA: 27 weeks,
PROBLEM SET 8. SOLUTIONS April 15, 2004
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.542J: Quantitative Physiology: Organ Transport Systems Instructors: Roger Mark and Jose Venegas MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Departments
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.542J: Quantitative Physiology: Organ Transport Systems Instructors: Roger Mark and Jose Venegas MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Departments
Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange
 Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange Session Objectives. What you will cover Basic anatomy of the lung including airways Breathing movements Lung volumes and capacities Compliance and Resistance in
Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange Session Objectives. What you will cover Basic anatomy of the lung including airways Breathing movements Lung volumes and capacities Compliance and Resistance in
POTENTIAL ENERGY BOUNCE BALL LAB
 Energy cannot be created or destroyed. Stored energy is called potential energy, and the energy of motion is called kinetic energy. Potential energy changes as the height of an object changes due to gravity;
Energy cannot be created or destroyed. Stored energy is called potential energy, and the energy of motion is called kinetic energy. Potential energy changes as the height of an object changes due to gravity;
2. State the volume of air remaining in the lungs after a normal breathing.
 CLASS XI BIOLOGY Breathing And Exchange of Gases 1. Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Answer: Vital Capacity (VC): The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration.
CLASS XI BIOLOGY Breathing And Exchange of Gases 1. Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Answer: Vital Capacity (VC): The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration.
Completed downloadable Test Bank for Pilbeams Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 5th Edition by Cairo
 Completed downloadable Test Bank for Pilbeams Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 5th Edition by Cairo Link full download: http://testbankcollection.com/download/pilbeams-mechanicalventilation-physiological-and-clinical-applications-5th-edition-test-bank-cairo
Completed downloadable Test Bank for Pilbeams Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 5th Edition by Cairo Link full download: http://testbankcollection.com/download/pilbeams-mechanicalventilation-physiological-and-clinical-applications-5th-edition-test-bank-cairo
mechanical ventilation Arjun Srinivasan
 Respiratory mechanics in mechanical ventilation Arjun Srinivasan Introduction Mechanics during ventilation PV curves Application in health & disease Difficulties & pitfalls The future. Monitoring Mechanics
Respiratory mechanics in mechanical ventilation Arjun Srinivasan Introduction Mechanics during ventilation PV curves Application in health & disease Difficulties & pitfalls The future. Monitoring Mechanics
Mechanical Ventilation
 Mechanical Ventilation Understanding Modes Rob Chatburn, RRT-NPS, FAARC Research Manager Respiratory Therapy Cleveland Clinic Associate Professor Case Western Reserve University 1 Overview Characteristics
Mechanical Ventilation Understanding Modes Rob Chatburn, RRT-NPS, FAARC Research Manager Respiratory Therapy Cleveland Clinic Associate Professor Case Western Reserve University 1 Overview Characteristics
PICU Resident Self-Study Tutorial The Basic Physics of Oxygen Transport. I was told that there would be no math!
 Physiology of Oxygen Transport PICU Resident Self-Study Tutorial I was told that there would be no math! INTRODUCTION Christopher Carroll, MD Although cells rely on oxygen for aerobic metabolism and viability,
Physiology of Oxygen Transport PICU Resident Self-Study Tutorial I was told that there would be no math! INTRODUCTION Christopher Carroll, MD Although cells rely on oxygen for aerobic metabolism and viability,
Activity 2: Examining the Effect of Changing Airway Resistance on Respiratory Volumes
 1 BGYC34 PhysioEx Lab 7 Respiratory Systems Mechanics Marking Scheme Part 1 Complete PhysioEx lab #7. Hand-in all of the pages associated with the lab. Note that there are 5 activities to be completed.
1 BGYC34 PhysioEx Lab 7 Respiratory Systems Mechanics Marking Scheme Part 1 Complete PhysioEx lab #7. Hand-in all of the pages associated with the lab. Note that there are 5 activities to be completed.
Lab Report Outline the Bones of the Story
 Lab Report Outline the Bones of the Story In this course, you are asked to write only the outline of a lab report. A good lab report provides a complete record of your experiment, and even in outline form
Lab Report Outline the Bones of the Story In this course, you are asked to write only the outline of a lab report. A good lab report provides a complete record of your experiment, and even in outline form
MoLE Gas Laws Activities
 MoLE Gas Laws Activities To begin this assignment you must be able to log on to the Internet using Internet Explorer (Microsoft) 4.5 or higher. If you do not have the current version of the browser, go
MoLE Gas Laws Activities To begin this assignment you must be able to log on to the Internet using Internet Explorer (Microsoft) 4.5 or higher. If you do not have the current version of the browser, go
 http://www.priory.com/cmol/hfov.htm INTRODUCTION The vast majority of patients who are admitted to an Intensive Care Unit (ICU) will need artificial ventilation (Jones et al 1998). The usual means through
http://www.priory.com/cmol/hfov.htm INTRODUCTION The vast majority of patients who are admitted to an Intensive Care Unit (ICU) will need artificial ventilation (Jones et al 1998). The usual means through
Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY
 Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Respiration External respiration ventilation gas exchange Internal respiration cellular respiration gas exchange Respiratory Cycle Inspiration
Physiology Unit 4 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Respiration External respiration ventilation gas exchange Internal respiration cellular respiration gas exchange Respiratory Cycle Inspiration
Lung Volumes and Capacities
 BIOL242 Lung Volumes and Capacities Measurement of lung volumes provides a tool for understanding normal function of the lungs as well as disease states. The breathing cycle is initiated by expansion of
BIOL242 Lung Volumes and Capacities Measurement of lung volumes provides a tool for understanding normal function of the lungs as well as disease states. The breathing cycle is initiated by expansion of
Respiration. Figure 22: Schematic representation of the respiratory system
 Respiration One of the seven characteristics of something which is living is respiration. Strictly speaking, respiration is the process that takes place at cellular level and is one of three different
Respiration One of the seven characteristics of something which is living is respiration. Strictly speaking, respiration is the process that takes place at cellular level and is one of three different
Accumulation of EEV Barotrauma Affect hemodynamic Hypoxemia Hypercapnia Increase WOB Unable to trigger MV
 Complicated cases during mechanical ventilation Pongdhep Theerawit M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Ramathibodi Hospital Case I Presentation Male COPD 50 YO, respiratory failure, on mechanical
Complicated cases during mechanical ventilation Pongdhep Theerawit M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Ramathibodi Hospital Case I Presentation Male COPD 50 YO, respiratory failure, on mechanical
Lectures on Medical Biophysics Department of Biophysics, Medical Faculty, Masaryk University in Brno. Biophysics of breathing.
 Lectures on Medical Biophysics Department of Biophysics, Medical Faculty, Masaryk University in Brno Biophysics of breathing. Spirometry 1 Lecture outline Mechanisms of gas exchange between organism and
Lectures on Medical Biophysics Department of Biophysics, Medical Faculty, Masaryk University in Brno Biophysics of breathing. Spirometry 1 Lecture outline Mechanisms of gas exchange between organism and
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system
 CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
Pulmonary Circulation Linda Costanzo Ph.D.
 Pulmonary Circulation Linda Costanzo Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The differences between pressures in the pulmonary and systemic circulations. 2. How
Pulmonary Circulation Linda Costanzo Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The differences between pressures in the pulmonary and systemic circulations. 2. How
Respiratory Physiology. Adeyomoye O.I
 Respiratory Physiology By Adeyomoye O.I Outline Introduction Hypoxia Dyspnea Control of breathing Ventilation/perfusion ratios Respiratory/barometric changes in exercise Intra-pulmonary & intra-pleural
Respiratory Physiology By Adeyomoye O.I Outline Introduction Hypoxia Dyspnea Control of breathing Ventilation/perfusion ratios Respiratory/barometric changes in exercise Intra-pulmonary & intra-pleural
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION #34 NAME: 7200 Ventilator Set Up DATE: INSTRUCTOR:
 PERFORMANCE EVALUATION #34 NAME: 7200 Ventilator Set Up DATE: 1. **Identify and name the filters on the 7200ae. 2. **Explain how each filter is sterilized. 3. **Trace the gas flow through the ventilator
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION #34 NAME: 7200 Ventilator Set Up DATE: 1. **Identify and name the filters on the 7200ae. 2. **Explain how each filter is sterilized. 3. **Trace the gas flow through the ventilator
The Human Respiratory System. Mary McKenna. Lab Partners: Jennifer Daciolas-Semon Veronika Mach Colette Roblee
 1 The Human Respiratory System Mary McKenna Lab Partners: Jennifer Daciolas-Semon Veronika Mach Colette Roblee TA: Pearl Chen NPB 101L Section 1 November 25, 2014 2 Introduction The average human will
1 The Human Respiratory System Mary McKenna Lab Partners: Jennifer Daciolas-Semon Veronika Mach Colette Roblee TA: Pearl Chen NPB 101L Section 1 November 25, 2014 2 Introduction The average human will
Guide to Understand Mechanical Ventilation Waveforms
 Do No Harm Ventilate Gently Guide to Understand Mechanical Ventilation Waveforms Middle East Critical Care Assembly 1/30/2015 Mazen Kherallah, MD, FCCP http://www.mecriticalcare.net Email: info@mecriticalcare.net
Do No Harm Ventilate Gently Guide to Understand Mechanical Ventilation Waveforms Middle East Critical Care Assembly 1/30/2015 Mazen Kherallah, MD, FCCP http://www.mecriticalcare.net Email: info@mecriticalcare.net
Update to RS-232 commands. Changing patient from NIV to INVASIVE Vent Type. SNDF command
 Changing patient from NIV to INVASIVE Vent Type Table 9 shows automatic settings changes that occur when changing the same patient from NIV to INVASIVE Vent Type. Table 9: Automatic settings changes NIV
Changing patient from NIV to INVASIVE Vent Type Table 9 shows automatic settings changes that occur when changing the same patient from NIV to INVASIVE Vent Type. Table 9: Automatic settings changes NIV
EMS INTER-FACILITY TRANSPORT WITH MECHANICAL VENTILATOR COURSE OBJECTIVES
 GENERAL PROVISIONS: EMS INTER-FACILITY TRANSPORT WITH MECHANICAL VENTILATOR COURSE OBJECTIVES Individuals providing Inter-facility transport with Mechanical Ventilator must have successfully completed
GENERAL PROVISIONS: EMS INTER-FACILITY TRANSPORT WITH MECHANICAL VENTILATOR COURSE OBJECTIVES Individuals providing Inter-facility transport with Mechanical Ventilator must have successfully completed
Respiratory system & exercise. Dr. Rehab F Gwada
 Respiratory system & exercise Dr. Rehab F Gwada Objectives of lecture Outline the major anatomical components & important functions of the respiratory system. Describe the mechanics of ventilation. List
Respiratory system & exercise Dr. Rehab F Gwada Objectives of lecture Outline the major anatomical components & important functions of the respiratory system. Describe the mechanics of ventilation. List
Human Respiration and Regulation. Jean Liu. Group Bernard (Group 1): Megan Bailey, Katharine Chew, David Ma. Section 12, TA Justin Van Hoorebeke
 1 Human Respiration and Regulation Jean Liu Group Bernard (Group 1): Megan Bailey, Katharine Chew, David Ma Section 12, TA Justin Van Hoorebeke November 28, 2014 2 Introduction The respiratory system is
1 Human Respiration and Regulation Jean Liu Group Bernard (Group 1): Megan Bailey, Katharine Chew, David Ma Section 12, TA Justin Van Hoorebeke November 28, 2014 2 Introduction The respiratory system is
INTRODUCTION TO BI-VENT (APRV) INTRODUCTION TO BI-VENT (APRV) PROGRAM OBJECTIVES
 INTRODUCTION TO BI-VENT (APRV) INTRODUCTION TO BI-VENT (APRV) PROGRAM OBJECTIVES PROVIDE THE DEFINITION FOR BI-VENT EXPLAIN THE BENEFITS OF BI-VENT EXPLAIN SET PARAMETERS IDENTIFY RECRUITMENT IN APRV USING
INTRODUCTION TO BI-VENT (APRV) INTRODUCTION TO BI-VENT (APRV) PROGRAM OBJECTIVES PROVIDE THE DEFINITION FOR BI-VENT EXPLAIN THE BENEFITS OF BI-VENT EXPLAIN SET PARAMETERS IDENTIFY RECRUITMENT IN APRV USING
Collin County Community College. Lung Physiology
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 9 Respiratory System 1 Lung Physiology Factors affecting Ventillation 1. Airway resistance Flow = Δ P / R Most resistance is encountered
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 9 Respiratory System 1 Lung Physiology Factors affecting Ventillation 1. Airway resistance Flow = Δ P / R Most resistance is encountered
It is often said in sports that records are made to be
 L A B 2 THE LIMIT OF SWIMMING SPEED Finding Limits It is often said in sports that records are made to be broken. This saying suggests there is no limit to athletic performance. In some sports, such as
L A B 2 THE LIMIT OF SWIMMING SPEED Finding Limits It is often said in sports that records are made to be broken. This saying suggests there is no limit to athletic performance. In some sports, such as
Respiration - Human 1
 Respiration - Human 1 At the end of the lectures on respiration you should be able to, 1. Describe events in the respiratory processes 2. Discuss the mechanism of lung ventilation in human 3. Discuss the
Respiration - Human 1 At the end of the lectures on respiration you should be able to, 1. Describe events in the respiratory processes 2. Discuss the mechanism of lung ventilation in human 3. Discuss the
Mechanical Ventilation. Flow-Triggering. Flow-Triggering. Advanced Concepts. Advanced Concepts in Mechanical Ventilation
 Mechanical Ventilation Advanced Concepts in Mechanical Ventilation Flow-Triggering Trigger = the variable that causes the vent to begin the inspiratory phase Common triggers 1-2- 3- Effort required to
Mechanical Ventilation Advanced Concepts in Mechanical Ventilation Flow-Triggering Trigger = the variable that causes the vent to begin the inspiratory phase Common triggers 1-2- 3- Effort required to
April KHALED MOUSA BACHA. Physiology #2. Dr. Nayef AL-Gharaibeh. Pulmonary volumes & capacities
 25 th April Physiology #2 Pulmonary volumes & capacities Dr. Nayef AL-Gharaibeh KHALED MOUSA BACHA We will start this lecture by explaining an important concept from the previous one: Intrapleural pressure
25 th April Physiology #2 Pulmonary volumes & capacities Dr. Nayef AL-Gharaibeh KHALED MOUSA BACHA We will start this lecture by explaining an important concept from the previous one: Intrapleural pressure
NAVA Neurally Adjusted Ventilatory Assist In Neonates
 NAVA Neurally Adjusted Ventilatory Assist In Neonates Howard Stein, M.D. Director Neonatology Toledo Children s Hospital Toledo, Ohio Disclaimers Dr Stein: Is on the speaker s bureau for Maquet Is discussing
NAVA Neurally Adjusted Ventilatory Assist In Neonates Howard Stein, M.D. Director Neonatology Toledo Children s Hospital Toledo, Ohio Disclaimers Dr Stein: Is on the speaker s bureau for Maquet Is discussing
exchange of carbon dioxide and of oxygen between the blood and the air in
 M. M. HENRY WILLIAMS, JR.*Cardiorespiratory Laboratory, Grasslands WILLIAMS, JR.* Hospital, Valhalla, New York SOME APPLICATIONS OF PULMONARY PHYSIOLOGY TO CLINICAL MEDICINE During the past ten years a
M. M. HENRY WILLIAMS, JR.*Cardiorespiratory Laboratory, Grasslands WILLIAMS, JR.* Hospital, Valhalla, New York SOME APPLICATIONS OF PULMONARY PHYSIOLOGY TO CLINICAL MEDICINE During the past ten years a
CHAPTER 3: The cardio-respiratory system
 : The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
: The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
How does HFOV work? John F Mills MBBS, FRACP, M Med Sc, PhD Neonatologist Royal Children s Hospital. Synopsis
 How does HFOV work? John F Mills MBBS, FRACP, M Med Sc, PhD Neonatologist Royal Children s Hospital Synopsis Definition of an oscillator Historical perspective Differences between HFOV and CMV Determinants
How does HFOV work? John F Mills MBBS, FRACP, M Med Sc, PhD Neonatologist Royal Children s Hospital Synopsis Definition of an oscillator Historical perspective Differences between HFOV and CMV Determinants
Peter Kremeier, Christian Woll. 2nd. Understanding and comparing modes of ventilation. The Kronberg List of Ventilation Modes
 Extended Edition Revised and 2nd Peter Kremeier, Christian Woll Understanding and comparing modes of ventilation The Kronberg List of Ventilation Modes Contents Preface... 3 Comparison Table - Parameters...6
Extended Edition Revised and 2nd Peter Kremeier, Christian Woll Understanding and comparing modes of ventilation The Kronberg List of Ventilation Modes Contents Preface... 3 Comparison Table - Parameters...6
Introduction to Conventional Ventilation
 Introduction to Conventional Ventilation Dr Julian Eason Consultant Neonatologist Derriford Hospital Mechanics Inspiration diaphragm lowers and thorax expands Negative intrathoracic/intrapleural pressure
Introduction to Conventional Ventilation Dr Julian Eason Consultant Neonatologist Derriford Hospital Mechanics Inspiration diaphragm lowers and thorax expands Negative intrathoracic/intrapleural pressure
The comparison of Work Of Breathing methodologies on a patient model
 The comparison of Work Of Breathing methodologies on a patient model E. Koumoundouros 1, J. Santamaria 2 and J. Patterson 3. 1 Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, The University of Melbourne,
The comparison of Work Of Breathing methodologies on a patient model E. Koumoundouros 1, J. Santamaria 2 and J. Patterson 3. 1 Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, The University of Melbourne,
PROBLEM SET 9. SOLUTIONS April 23, 2004
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.542J: Quantitative Physiology: Organ Transport Systems Instructors: Roger Mark and Jose Venegas MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Departments
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.542J: Quantitative Physiology: Organ Transport Systems Instructors: Roger Mark and Jose Venegas MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Departments
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Atmosphere Tissue cell External respiration Alveoli of lungs 1 Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Atmosphere Tissue cell External respiration Alveoli of lungs 1 Ventilation or gas exchange between the atmosphere
Physiology of the Respiratory System
 Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Physiology of the Respiratory System References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Physiology of the Respiratory System References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
MoLE Gas Laws Activities
 MoLE Gas Laws Activities To begin this assignment you must be able to log on to the Internet using Internet Explorer (Microsoft) 4.5 or higher. If you do not have the current version of the browser, go
MoLE Gas Laws Activities To begin this assignment you must be able to log on to the Internet using Internet Explorer (Microsoft) 4.5 or higher. If you do not have the current version of the browser, go
Presentation Overview. Monitoring Strategies for the Mechanically Ventilated Patient. Early Monitoring Strategies. Early Attempts To Monitor WOB
 Monitoring Strategies for the Mechanically entilated Patient Presentation Overview A look back into the future What works and what may work What s all the hype about the WOB? Are ventilator graphics really
Monitoring Strategies for the Mechanically entilated Patient Presentation Overview A look back into the future What works and what may work What s all the hype about the WOB? Are ventilator graphics really
APRV: Moving beyond ARDSnet
 APRV: Moving beyond ARDSnet Matthew Lissauer, MD Associate Professor of Surgery Medical Director, Surgical Critical Care Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey What is APRV? APRV is different from
APRV: Moving beyond ARDSnet Matthew Lissauer, MD Associate Professor of Surgery Medical Director, Surgical Critical Care Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey What is APRV? APRV is different from
Gas exchange measurement in module M- COVX
 Gas exchange measurement in module M- COVX This document explains how the gas exchange measurement in the gas module M-COVX works. 1. Basic equations To obtain the oxygen consumption VO2 of a patient,
Gas exchange measurement in module M- COVX This document explains how the gas exchange measurement in the gas module M-COVX works. 1. Basic equations To obtain the oxygen consumption VO2 of a patient,
MEDICAL EQUIPMENT IV MECHANICAL VENTILATORS. Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah
 MEDICAL EQUIPMENT IV - 2013 MECHANICAL VENTILATORS Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah Mechanical Ventilator A ventilator is a machine, a system of related elements designed to alter, transmit, and direct energy
MEDICAL EQUIPMENT IV - 2013 MECHANICAL VENTILATORS Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah Mechanical Ventilator A ventilator is a machine, a system of related elements designed to alter, transmit, and direct energy
VT PLUS HF performance verification of Bunnell Life-Pulse HFJV (High Frequency Jet Ventilator)
 VT PLUS HF performance verification of Bunnell Life-Pulse HFJV (High Frequency Jet Ventilator) VT PLUS HF provides a special mode for evaluating the performance of high frequency ventilators while connected
VT PLUS HF performance verification of Bunnell Life-Pulse HFJV (High Frequency Jet Ventilator) VT PLUS HF provides a special mode for evaluating the performance of high frequency ventilators while connected
Hydrostatics Physics Lab XI
 Hydrostatics Physics Lab XI Objective Students will discover the basic principles of buoyancy in a fluid. Students will also quantitatively demonstrate the variance of pressure with immersion depth in
Hydrostatics Physics Lab XI Objective Students will discover the basic principles of buoyancy in a fluid. Students will also quantitatively demonstrate the variance of pressure with immersion depth in
Respiratory System. Prepared by: Dorota Marczuk-Krynicka, MD, PhD
 Respiratory System Prepared by: Dorota Marczuk-Krynicka, MD, PhD Lungs: Ventilation Perfusion Gas Exchange - Diffusion 1. Airways and Airway Resistance (AWR) 2. Mechanics of Breathing and Lung (Elastic)
Respiratory System Prepared by: Dorota Marczuk-Krynicka, MD, PhD Lungs: Ventilation Perfusion Gas Exchange - Diffusion 1. Airways and Airway Resistance (AWR) 2. Mechanics of Breathing and Lung (Elastic)
Lab Midterm 2 - Sample Questions 4/9/04 Human Physiology EPOB 3430
 Lab Midterm 2 - Sample Questions 4/9/04 Human Physiology EPOB 3430 TA: Leif Saul Please Note: These questions were written by me. Any resemblance to past, present or future exam questions is purely coincidental.
Lab Midterm 2 - Sample Questions 4/9/04 Human Physiology EPOB 3430 TA: Leif Saul Please Note: These questions were written by me. Any resemblance to past, present or future exam questions is purely coincidental.
Swimming training and pulmonary variables in women
 8th INSHS International Christmas Sport Scientific Conference, 5-7 December 2013. International Network of Sport and Health Science. Szombathely, Hungary Swimming training and pulmonary variables in women
8th INSHS International Christmas Sport Scientific Conference, 5-7 December 2013. International Network of Sport and Health Science. Szombathely, Hungary Swimming training and pulmonary variables in women
Respiratory Response to Physiologic Challenges. Evaluation copy
 Respiratory Response to Physiologic Challenges Computer 20 The respiratory cycle of inspiration and expiration is controlled by complex mechanisms involving neurons in the cerebral cortex, brain stem,
Respiratory Response to Physiologic Challenges Computer 20 The respiratory cycle of inspiration and expiration is controlled by complex mechanisms involving neurons in the cerebral cortex, brain stem,
Name Student Activity
 Open the TI-Nspire document Boyles_Law.tns. In this activity, you will use a Gas Pressure Sensor to measure the pressure of an air sample inside a syringe. Using graphs, you will apply your results to
Open the TI-Nspire document Boyles_Law.tns. In this activity, you will use a Gas Pressure Sensor to measure the pressure of an air sample inside a syringe. Using graphs, you will apply your results to
Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation. Chad & Angela
 Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation Chad & Angela Respiratory Structures Basic Structures of Respiration Nasal/Oral Cavities Larynx Trachea Bronchi Secondary Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli Mechanics of Ventilation
Chapter 37: Pulmonary Ventilation Chad & Angela Respiratory Structures Basic Structures of Respiration Nasal/Oral Cavities Larynx Trachea Bronchi Secondary Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli Mechanics of Ventilation
BREATH-BY-BREATH METHOD
 BREATH-BY-BREATH METHOD COR-MAN-0000-005-IN / EN Issue A, Rev. 2 2013-07 INNOISION ApS Skovvænge DK-5620 Glamsbjerg Denmark Tel.: +45 65 95 91 00 Fax: +45 65 95 78 00 info@innovision.dk www.innovision.dk
BREATH-BY-BREATH METHOD COR-MAN-0000-005-IN / EN Issue A, Rev. 2 2013-07 INNOISION ApS Skovvænge DK-5620 Glamsbjerg Denmark Tel.: +45 65 95 91 00 Fax: +45 65 95 78 00 info@innovision.dk www.innovision.dk
Medical Ventilators. Presented by: Edwin Lim
 Medical Ventilators Presented by: Edwin Lim 1 Presentation Outline Respiration and You Medical Ventilators: Why? How? Current Medical Ventilators The Future 2 The Importance of Oxygen People can survive
Medical Ventilators Presented by: Edwin Lim 1 Presentation Outline Respiration and You Medical Ventilators: Why? How? Current Medical Ventilators The Future 2 The Importance of Oxygen People can survive
INSTRUMENT INSTRUMENTAL ERROR (of full scale) INSTRUMENTAL RESOLUTION. Tutorial simulation. Tutorial simulation
 Lab 1 Standing Waves on a String Learning Goals: To distinguish between traveling and standing waves To recognize how the wavelength of a standing wave is measured To recognize the necessary conditions
Lab 1 Standing Waves on a String Learning Goals: To distinguish between traveling and standing waves To recognize how the wavelength of a standing wave is measured To recognize the necessary conditions
RESPIRATORY MUSCLES IN HEALTH AND EMPHYSEMA *
 THE OXYGEN CONSUMPTION AND EFFICIENCY OF THE RESPIRATORY MUSCLES IN HEALTH AND EMPHYSEMA * BY REUBEN M. CHERNIACK t (From The Winnipeg General Hospital and the Departments of Medicine and Physiology and
THE OXYGEN CONSUMPTION AND EFFICIENCY OF THE RESPIRATORY MUSCLES IN HEALTH AND EMPHYSEMA * BY REUBEN M. CHERNIACK t (From The Winnipeg General Hospital and the Departments of Medicine and Physiology and
Physiology (3) Pulmonary Function Test:
 Pulmonary Function Test: Today we will continue with the pulmonary function test, and the question is: why do we do pulmonary function tests for patients? Can pulmonary function tests tell us what type
Pulmonary Function Test: Today we will continue with the pulmonary function test, and the question is: why do we do pulmonary function tests for patients? Can pulmonary function tests tell us what type
Circulatory And Respiration
 Circulatory And Respiration Composition Of Blood Blood Heart 200mmHg 120mmHg Aorta Artery Arteriole 50mmHg Capillary Bed Venule Vein Vena Cava Heart Differences Between Arteries and Veins Veins transport
Circulatory And Respiration Composition Of Blood Blood Heart 200mmHg 120mmHg Aorta Artery Arteriole 50mmHg Capillary Bed Venule Vein Vena Cava Heart Differences Between Arteries and Veins Veins transport
Section Two Diffusion of gases
 Section Two Diffusion of gases Lecture 5: Partial pressure and the composition of gasses in air. Factors affecting diffusion of gases. Ventilation perfusion ratio effect on alveolar gas concentration.
Section Two Diffusion of gases Lecture 5: Partial pressure and the composition of gasses in air. Factors affecting diffusion of gases. Ventilation perfusion ratio effect on alveolar gas concentration.
Equation 1: F spring = kx. Where F is the force of the spring, k is the spring constant and x is the displacement of the spring. Equation 2: F = mg
 1 Introduction Relationship between Spring Constant and Length of Bungee Cord In this experiment, we aimed to model the behavior of the bungee cord that will be used in the Bungee Challenge. Specifically,
1 Introduction Relationship between Spring Constant and Length of Bungee Cord In this experiment, we aimed to model the behavior of the bungee cord that will be used in the Bungee Challenge. Specifically,
Driving Pressure. What is it, and why should you care?
 Driving Pressure What is it, and why should you care? Jonathan Pak MD March 2, 2017 Lancet 1967; 290: 319-323 Traditional Ventilation in ARDS Tidal Volume (V T ) = 10-15 ml/kg PBW PEEP = 5-12 cm H 2 O
Driving Pressure What is it, and why should you care? Jonathan Pak MD March 2, 2017 Lancet 1967; 290: 319-323 Traditional Ventilation in ARDS Tidal Volume (V T ) = 10-15 ml/kg PBW PEEP = 5-12 cm H 2 O
Boyle s Law: Pressure-Volume. Relationship in Gases
 Boyle s Law: Pressure-Volume Relationship in Gases The primary objective of this experiment is to determine the relationship between the pressure and volume of a confined gas. The gas we use will be air,
Boyle s Law: Pressure-Volume Relationship in Gases The primary objective of this experiment is to determine the relationship between the pressure and volume of a confined gas. The gas we use will be air,
Lung Volumes and Ventilation
 Respiratory System ssrisuma@rics.bwh.harvard.edu Lung Volumes and Ventilation Minute ventilation Volume of an inspired or expired air per minute = tidal volume (V T ) x respiratory rate Dead space ventilation
Respiratory System ssrisuma@rics.bwh.harvard.edu Lung Volumes and Ventilation Minute ventilation Volume of an inspired or expired air per minute = tidal volume (V T ) x respiratory rate Dead space ventilation
