PERSIA, IRAN AND INDIA. Contents. Army Lists
|
|
|
- Cornelius Cory Gordon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 PERSIA, IRAN AND INDIA Contents Army Lists
3 Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists
4 Historical Introduction
5 ā
6
7 Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 550 BC to 424 BC SubGenerals 03 Any Instinctive Terrain Plains, Coastal, Mountains Internal Allied Generals Camp Unfortified; or Name Achaemenid Persian Royal Army Type Training and Quality Protection Shooting Skill Melee Characteristics Min Mandatory Optional Max Persian chariots (before 484 BATTLE CHARIOTS Experienced 0 2,3,4 Superior BC) Bow 4 Experienced 4 4,6 Guard cavalry Exceptional Short Spear Drilled Loose Bow 6 Satrapal guard cavalry Superior Short Spear Drilled Loose Bow 6 Experienced 6 4,6 Iranian cavalry Short Spear Saka horse archers (from 545 BC) Formed Flexible Bow 6 Unskilled 0 4,6 Indian cavalry (from 516 BC) Javelin 6 CAMELRY Arab camelry (from 538 BC) Combat Shy Bow 6 Guard Immortals Skilled 6 6,8 Superior Short Spear Pavise Orb/Square Applebearers Drilled Loose Bow 8 Skilled 8 6,8 Immortals Short Spear Pavise Orb/Square Drilled Loose Bow 32 Experienced 0 6,8 Sparabara Short Spear Pavise Combat Shy Bow 32 Crescent shield archers (from Experienced 0 6,8 Combat Shy 465 BC) Bow 16 Crescent shield spearmen 0 6,8,9 Short Spear (from 465 BC) 9 Replace crescent shield Experienced 0 6,8 Short Spear Combat Shy archers and spearmen Bow 24 UG Size Version st January 2018
8 Lydian hoplites (from 545 BC) Assyrian and Chaldean foot (from 538 BC) Subject Greek hoplites (from 545 BC) Asiatic hillmen Levied archers Horse archers Thracian, Paphlagonian, Arachosian or similar light horse Asiatic archers Asiatic javelinmen Allies Mede rebel allies Median (only in 550 BC) Saka allies Early Scythian or Saka (530 BC) Historical Notes Achaemenid Persian Royal Army Tribal Close Drilled Close Formed Close 0 6,8 Long Spear Combat Shy Orb/Square 8 0 6,8,9 Short Spear Integral shooters 9 Shove, Shield 0 6,8 Long Spear Orb/Square Cover 8 Unskilled 0 6,8,9 Short Spear Javelin 9 Experienced 0 6,8 Combat Shy Bow 8 Cantabrian Bow 8 Cantabrian Javelin 6 Combat Shy Combat Shy Javelin 18 The Achaemenid empire was founded by Cyrus the Great who conquered the Median (550 BC), Lydian (546 BC) and Babylonian (539 BC) empires. His son Cambyses II conquered Egypt creating the largest empire the world had yet known. In response to mainland Greeks sending aid to rebellious Greek cities in Asia Minor Darius I sent an expedition that was beaten by the Athenians at Marathon (490 BC). Ten years later his son, Xerxes I, launched a full scale invasion of Greece that was defeated at Salamis by sea and Plataea on land. The final defeat of the Persians at Mycale encouraged the Greek cities of Asia to revolt, and the Persians lost all of their territories in Europe. After Xerxes I was assassinated, he was succeeded by his eldest son Artaxerxes I who ruled until 424 BC Hostilities between Persia and the Greeks continued until 450 BC. Version st January 2018
9 Troop Notes Changes from last version Immortals now skilled shooters. Added light horse. Achaemenid Persian Royal Army The Royal army is assumed to be any army commanded by the King of Kings. As such he could levy troops from anywhere in the Empire, as Xerxes did in 480 BC to invade Greece. The core of the Persian army were the Immortals. A division of 10,000 (baivarabam) consisting of the best Persian, Median or Elamite youth. A unit 1,000 picked troops who constituted the King's personal guard and were selected from this division. A guard unit of 1,000 cavalry also accompanied the King. The Persians inherited their military approach from the Medes. The main weapon was the bow, each file of 10 consisting of 9 archers protected by the Spearbearer (sparabara) who carried a spear and pavise. Cavalry were also primarily bow armed. Version st January 2018
10 Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 530 BC to 424 BC SubGenerals 03 Any Instinctive Terrain Plains, Coastal, Mountains Internal Allied Generals Camp Unfortified; or Name Achaemenid Persian Satrapal Army Type Training and Quality Protection Shooting Skill Melee Characteristics Min Mandatory Optional Max Persian chariots (before 484 BATTLE CHARIOTS Experienced 0 2,3,4 Superior BC) Bow 4 Satrapal guard cavalry Superior Short Spear Drilled Loose Bow 6 Iranian cavalry Experienced 6 4,6 Short Spear Bow 24 Saka horse archers (Eastern satrapies) Formed Flexible Scythian horse archers (Western satrapies) Formed Flexible Bow 6 Indian cavalry (Indian Unskilled 0 4,6 satrapy only from 516 BC) Javelin 12 Arab camelry (Arabian, CAMELRY Egyptian and Syrian Combat Shy satrapies only) Bow 12 Immortals Skilled 0 6,8 Short Spear Pavise Orb/Square Drilled Loose Bow 16 Sparabara (Eastern satrapies) Experienced 8 6,8 Short Spear Pavise Combat Shy Bow 64 Sparabara (Western Experienced 0 6,8 Short Spear Pavise Combat Shy satrapies) Bow 32 UG Size Version st January 2018
11 Crescent shield archers (from 465 BC) Crescent shield spearmen (from 465 BC) Replace crescent shield archers and spearmen Lydian hoplites (Lydian satrapy only) Assyrian and Chaldean foot (Syrian, Assyria and Babylonian Satrapies only) Subject Greek hoplites (Thrace, Macedon and Greece, Ionian, Carian and Lydian satrapies only) Achaemenid Persian Satrapal Army Tribal Close Drilled Close Formed Close Experienced 0 6,8 Combat Shy Bow ,9 Short Spear 9 Experienced 0 6,8 Short Spear Combat Shy Bow ,8 Long Spear Combat Shy Orb/Square ,8,9 Short Spear Integral shooters ,8 Shove, Shield Long Spear Orb/Square Cover 24 Asiatic hillmen Unskilled 0 6,8,9 Short Spear Javelin 27 Levied archers (Eastern Experienced 0 6,8 Combat Shy satrapies only) Bow 24 Horse archers (Eastern Cantabrian satrapies only) Thracian, Paphlagonian, Arachosian or similar light Cantabrian horse Javelin 12 Asiatic archers Combat Shy Bow 27 Asiatic javelinmen Combat Shy Javelin 27 Allies Medizing Greek allies (only in 479 BC) Thrace, Macedon and Greece satrapy only Version st January 2018
12 Achaemenid Persian Satrapal Army Notes Eastern Satrapies include Persis; Elam; Babylonia and Assyria; Media; Armenia; India; Gandara and Sattagydia; Caspia and Hyrcania; Paricania, Gedrosia and Carmania; Maka, Drangiana and Sargatia; Arachosia; Bactria; Sacae; Dahae; Parthia; Aria; Chorasmia and Sogdia; Scythia. Western satrapies include Pamphyilia, Ionia and Caria; Lydia; Paphalagonia and Hellespontines; Cappadocia; Cilicia; Syria; Egypt and Libya; Arabia; Thrace, Macedon and Greece. The number of Immortals cannot exceed the number of sparabara. From 465 BC mandatory sparabara may be replaced with crescent shield troops. Historical Notes The satrapal system was adopted by Cyrus the Great around 530 BC as the Persian empire was too large to be controlled centrally. Troop Notes Satraps might be given divisions of Immortals to command (such as Mardonius in 479 BC). Troops would be a core of Persian, Median or Elamites supplemented by local levied troops. Changes from last version Immortals now skilled shooters. Added light horse. Version st January 2018
13 Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 500 BC to 170 BC SubGenerals 13 Any Instinctive Terrain Mountains Internal Allied Generals 02 Any Instinctive Camp Unfortified; or Name Characteristics Min Mandatory Optional Max ELEPHANTS 0 2,3 Elephants Shove ,8,9 Spearmen Short Spear Integral shooters Combat Shy 64 Unskilled 0 6,8,9 Spearmen with round shields Short Spear Javelin 9 Unskilled 0 6,8,9 Mercenary javelinmen Short Spear Combat Shy Javelin 32 Experienced 0 6,8 Archers Combat Shy Bow 32 Experienced 8 4,6 Light horse Cantabrian Javelin 18 s with bow Combat Shy Bow 36 Historical Notes Tribes on the northwestern mountains of India included the Assakenoi and Parapamisadae. They were used by both the Persians and Alexander. The Mauryans allied with them. Troop Notes The light horse of the Paropamisadae were brigaded with the Arachosians by the Persians and Alexander. The infantry were described as using both spears and bows but were outshot by the Macedonians. Mercenary javelinmen are described as fighting against Alexander. Changes from last version New list. Type Training and Quality Mountain Indian Protection Shooting Skill Melee UG Size Version st January 2018
14 Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 500 BC to 350 AD SubGenerals 13 Any Instinctive Terrain Plains, Jungle Internal Allied Generals 02 Any Instinctive Camp Unfortified; or Name Type Training and Quality Classical Indian Protection Shooting Skill Melee Characteristics Min Mandatory Optional Max Elephants ELEPHANTS 0 2,3,4 Shove 12 Upgrade elephants with ELEPHANTS Experienced 2,3,4 Shove accompanying foot Bow Any Chariots (before 320 AD) BATTLE CHARIOTS Experienced 0 2,3,4 Superior Bow 12 Replace elephants or chariots BATTLE WAGONS Unskilled 0 4 with bullock or camel carts Bow 8 Horse archers (from 149 BC) Formed Flexible Bow 6 Cavalry Unskilled 4 4,6 Javelin 12 Guard infantry (from Superior Short Spear BC) Drilled Loose 6 Javelinmen Unskilled 9 6,8,9 Short Spear Combat Shy Javelin 60 Spearmen 0 6,8,9 Short Spear Combat Shy 30 Archers Experienced 8 6,8 Combat Shy Bow 90 s with bow Combat Shy Slingers Combat Shy Sling 9 UG Size Version st January 2018
15 Optionally upgrade troops as Mauryans (from 321 to 180 BC) Classical Indian Unskilled 4 4,6 Cavalry Combat Shy Javelin 12 Unskilled 9 6,8,9 Javelinmen Short Spear Combat Shy Javelin ,8,9 Spearmen Short Spear Combat Shy 30 Experienced 8 6,8 Archers Combat Shy Bow 90 Allies Mountain Indian allies (Mauryan from 321 to 180 BC) Notes The number of javelinmen and spearmen cannot exceed the number of archers. Foot TUGs may combine 1/3 spearmen with 2/3 archers in a unit of 6 or 9. Version st January 2018
16 Historical Notes Classical Indian By 6th century BC there were four major kingdoms and many minor kingdoms spread across the IndoGangetic plains of northern India. Early "republics" such as the Vajji (or Vriji) confederation centered in the city of Vaishali also flourished. In 530 BC Cyrus the Great, King of the Persian Achaemenid Empire crossed the HinduKush mountains to seek tribute from the tribes of Kamboja, Gandhara and the transindia region (modern eastern Afghanistan and Pakistan). Persian control and influence persisted for the next two centuries. India supplied troops to Persian armies. Alexander the Great arrived in 326 BC after defeating the Persians. There he defeated King Porus in the Battle of the Hydaspes (near modernday Jhelum, Pakistan) and conquered much of the Punjab. Having reached the Hyphasis (modern Beas River) it refused to march further east. The invasion of Alexander had repercussions in the Northwestern regions of the Indian subcontinent. The Maurya Empire (322 BC to 185 BC) stretched to the north up to the natural boundaries of the Himalayas and to the east into what is now Assam. To the west, it reached the Hindu Kush mountains and into Arachosia (southern Afghanistan). The Satavahana Empire (c. 200 BC to 320 AD) controlled much of central India. To the north and east the Shunga Empire (187 BC to 78 BC) controlled much of the Ganges basin. With the collapse of the Mauryan empire, the GreacoBactrian king Demetrus invaded India and an IndoGreek kingdom was established by 175 BC Under Menander (c. 155 BC to 130 BC) the kingdom expanded greatly covering much of northwest and northern India. It then disintegrated into smaller kingdoms, the last IndoGreek king, Strato II ruled until c 10 AD. Elsewhere the Satavahana Empire (1st century BC to 2nd century AD) competed with the Shunga Empire (187 to 75 BC) and the Kanva Dynasty (75 to 30 BC) in Eastern and Central India. The Greeks were supplanted by the Scythians and then the Kushans. By the 3rd century, the Kushan empire in India was disintegrating. This saw the rise of the Bharshive dynasty from c. 170 to 350 AD. Much of India was then reunited under the Gupta empire. Troop Notes Traditional Indian armies were formed of four troop types, elephants, chariots, cavalry and infantry. Not all states had elephants or chariots. Chariots were probably pulled by two horses with 2 or possibly 3 crew. Cavalry were equipped with shields and short spears. The majority of infantry were archers although some carried javelins or short spears and shields. All troops might carry a sword. Some troops used clubs. Outside of nobles, armour appears to have been rare. s included archers and slingers. The Indians did adopt some weapons and fighting styles from the nations that invaded them. Changes from last version Separated Gupta Empire from Classical Indian list. Bows optional for elephants. Added guard infantry. Version st January 2018
17 Army Commander 1 Any Dates 423 BC to 329 BC SubGenerals 13 Any Terrain Plains, Coastal, Mountains Internal Allied Generals Camp Unfortified; or Name Best cavalry Cavalry with bow Cavalry Levied cavalry Replace best cavalry with armoured cavalry Only if the CinC is the King Characteristics Min Mandatory Optional Max Superior Superior Fully Armoured Unskilled 0 4,6 Short Spear Javelin 12 Short Spear Bow 8 Unskilled 6 4,6 Short Spear Javelin 18 Unskilled 4 4,6 Short Spear Javelin ,6 Short Spear 8 Unskilled 0 4 Kinsmen cavalry Superior Short Spear Drilled Loose Javelin 4 Upgrade kinsmen cavalry Devastating All Superior Melee Expert with lances (only in 331 BC) Chargers Experienced 0 6 Guard infantry Superior Short Spear Orb/Square Drilled Close Bow 6 Bactrian and Saka cavalry Crescent shield spearmen Type Training and Tribal Close Formed Flexible Later Achaemenid Persian Quality Protection Shooting Skill Melee UG Size Bow 8 0 6,8,9 Short Spear 18 Version st January 2018
18 Later Achaemenid Persian Mercenary hoplites Shove, Shield 0 6,8 Long Spear Orb/Square Drilled Close Cover 24 Regrade mercenary hoplites 0 8 as Iphicratean peltasts (from Pike Orb/Square 374 to 353 BC) Formed Close 16 Asiatic hoplites and kardaka Shove, Shield 0 6,8 Long Spear Orb/Square Formed Close Cover 24 Takabara 0 6,8 Short Spear 24 Hillmen Unskilled 0 6,8,9 Short Spear Javelin 18 Thracians Experienced 0 6 Short Spear Javelin 6 Paphlagonian or Arachosian Combat Shy Cantabrian cavalry Javelin 12 Mercenary peltasts Javelin 9 Archers Combat Shy Slingers Combat Shy Sling 18 Javelinmen Combat Shy Javelin 9 Scythed chariots BATTLE CHARIOTS 0 2,3,4 Expendable 4 Notes Iphicretean peltasts are not allowed if the CinC is king. Version st January 2018
19 Historical Notes Later Achaemenid Persian Artaxerxes was succeeded by his son Xerxes II but he was immediately assassinated on the orders of his illegitimate brother, Sogdianus. Sogdianus was captured and killed by his halfbrother Darius II. In 404 BC Darius died. The eldest son Artaxerxes II inherited the throne. His younger brother Cyrus rebelled and hired 10,000 Greek mercenaries including Xenophon. The army of Cyrus was stopped at the battle of Cunaxa (401 BC). At this time Egypt revolted. Artaxerxes ruled for 45 years. Artaxerxes II became involved in a war with Persia's erstwhile allies, the Spartans, who, under Agesilaus II, invaded Asia Minor. In 385 BC he campaigned against the Cadusians. An attempt to reconquer Egypt in 373 BC was completely unsuccessful, but an Egyptian and Spartan effort to conquer Phoenicia was defeated. Between 372 BC and 362 BC he quashed a series of revolts by satraps in Asia Minor. Artaxerxes III inherited the throne in 358 BC He defeated a revolt by Artabazus of Lydia. In 351 BC he attempted to recover Egypt but suffered a crushing defeat that led to Phoenicia, Asia Minor and Cyprus declaring independence. An attempt to recover Phoenicia was defeated and Artaxerxes III personally led an army to recapture Sidon. This was followed by an invasion of Egypt and the rebels were defeated at the battle of Pelusium. Also in 343 BC a force was sent to recover Cyprus. Artaxerxes III and his son were assasinated and Darius III, previously satrap of Armenia was placed on the throne. In 334 BC, just after the Persians had subdued another revolt in Egypt, Alexander the Great led an invasion of Asia Minor. Alexander defeated the Persian armies at Granicus (334 BC), Issue (333 BC) and Gaugamela (331 BC). Darius was taken prisoner by Bessus, satrap of Bactria and murdered. Bessus was captured by Alexander, put on trial in a Persian court and executed. Troop Notes During the 5th century BC the earlier Persian system of paying tribute directly to the King was modified. The satraps retained some of the tribute to pay for local defence. The satraps increasingly relied on mercenaries rather than the households of the Persian nobles. Cavalry adopted shields (probably from the Saka) during the 5th century BC The use of the spear and shock tactics increased, particularly in the west. The bow was still used in the east. During the 4th century BC the quality of much of the cavalry deteriorated. Infantry were largely mercenaries recruited both inside and outside the empire. Large number of Greeks were employed, particularly in the west. The Persians also recruited tribesmen from Pisidia, Mysia and Hyrcania. Kardaka appear to have been Asian troops trained as hoplites to replace the shortage of Greeks in the 4th century BC Iphicrates may have introduced his reforms for the Persian army that invaded Egypt. Scythed chariots. These appear to have been introduced at this time to break up enemy formations before the cavalry charged. Changes from last version None. Version st January 2018
20 Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 300 BC to 130 BC SubGenerals 13 Any Instinctive Terrain Plains Internal Allied Generals Camp Unfortified or Flexible; or Name Nobles and followers Horse archers Upgrade horse archers Foot archers Foot spearmen Horse archers Archers Slingers Historical Notes Increased number of nobles. Cataphracts now Devastating Chargers. Characteristics Min Mandatory Optional Max Fully Armoured Devastating 0 4,6 Long Spear Chargers, Shove 12 Experienced 16 4,6 Bow 72 Skilled 4,6 Bow Up to half Experienced 0 6,8 Combat shy Unskilled 0 6,8,9 Short Spear Javelin 9 Cantabrian Bow 12 Combat Shy Combat Shy Sling 9 Saka tribes including the Parni, Dahae and Massagetae occupied the steppe to the north of the Parthian and Bactrian satrapies. Around 250 BC the Parni invaded Parthia which led to the establishment of the Parthian empire. The migration of the Yeuzhi displaced the remaining Saka who invaded Bactria around 140 BC resulting in the collapse of the Graeco Bactrian kingdom. One group of Saka settled in Seistan. Some Saka then invaded and established kingdoms in India (see IndoScythian list). Troop Notes Type Training and Tribal Close Formed Flexible Formed Flexible Quality Later Saka Protection Shooting Skill Melee During the 4th century the equipment of the nobles became heavier and developed into the cataphract. These were supported by the horse archer. Infantry, if present, were equipped either with bows, slings or javelins and short spears. Changes from last version UG Size Version st January 2018
21 Army Commander 1 Any Professional Dates 250 BC to 140 BC SubGenerals 13 Any Professional Terrain Plains, Mountains Internal Allied Generals Camp Unfortified or Flexible; or Name Elephants Xystophoroi Iranian cavalry Cataphracts Saka horse archers Phalanx Thureophoroi Mountain Indian spearmen Mountain Indian archers Bactrian light horse Mountain Indian cavalry Euzenoi Cretan archers Type Training and ELEPHANTS Drilled Loose Formed Close Formed Flexible Formed Close Drilled Close Quality GraecoBactrian Protection Shooting Skill Melee Characteristics Min Mandatory Optional Max UG Size Superior Fully Armoured 0 2,3,4 Shove 4 Charging 4 4,6 Melee Expert Lancer 6 Charging 4 4,6 Melee Expert Lancer 24 Devastating 0 4,6 Long Spear Chargers, Shove Pike Shove Orb/Square ,8 Long Spear Shove Orb/Square ,8,9 Short Spear Integral shooters Combat Shy 18 Experienced 0 6,8 Combat Shy Experienced 6 4,6 Short Spear Cantabrian Cantabrian Javelin 12 Short Spear Melee Expert Javelin 9 Skilled 0 6,9 Combat Shy Bow 9 Version st January 2018
22 Historical Notes Changes from last version GraecoBactrian Around 250 BC Diodotus, the satrap of Bactria, declared independence by issuing coins with his own portrait. Although forced by Antiochus III to submit, the Bactrian kingdom regained its independence which it maintained until the invasion of the Saka and Yuehzhi tribes (including the Kushans) in around 140 BC. During this time the kingdom was strong enough to invade India undoubtedly helped by the collapse of the Mauryan empire. Troop Notes Elephants: The GraecoBactrian kingdoms used Elephants, presumably obtained from the Mauryans. Cavalry: Greek coins do show cavalry using the Xyston. The Greek cavalry must have been supplemented by Bactrian nobles and their followers who had been present before the invasion by Alexander the Great. Infantry: Pike butts were found during the excavations at Ai Khanum. A pikemen was represented on a Greek coin. The presence of Thureophoroi seems likely given the influx of Greek mercenaries prior to and during this period. Mountain Indians would have been recruited from Arachosia and the Parpamisadae. Increased maximums for cavalry and pike. Cataphracts now Devastaing Chargers. Revised Mountain Indian troops. Camp cannot be Superior. Version st January 2018
23 Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 250 BC to 225 AD SubGenerals 03 Any Instinctive Terrain Plains, Mountains Internal Allied Generals Camp Mobile; or Name Royal and nobles guard cataphracts Cataphracts City militia Hillmen Horse archers Archers Slingers Javelinmen Allies Type Training and Tribal Close Tribal Close Formed Close Quality Protection Commagene allies (from 129 to 35 BC) Seleucid allies (only in 129 BC) (Ally general must be Mediocre Professional) Armenian allies (from 127 BC) Hatrene, Adiabene or Edessan subject allies Parthian Vassal (from 127 BC) Elymaian allies Parthian Vassal (from 127 BC) Nomadic Arab allies PreIslamic Arab (from 127 BC) Labienus Roman allies (from 40 to 39 BC) Scythian allies Later Scythian (130 BC to 41 AD) Parthian Shooting Skill Melee Characteristics Min Mandatory Optional Max UG Size Superior Fully Armoured Fully Armoured Devastating 0 4,6 Long Spear Chargers, Shove 12 Devastating 6 4,6 Long Spear Chargers, Shove ,8,9 Long Spear Shove Orb/Square 18 Unskilled 0 6,8,9 Short Spear Javelin 18 Experienced 12 4,6 Cantabrian Bow 90 Combat Shy Bow 12 Combat Shy Sling 12 Combat Shy Javelin 12 Version st January 2018
24 Historical Notes Parthian The Parthians were a Saka tribe, the Parni, who invaded Parthia in the mid3rd century BC. Under Mithridates I (171 to 138 BC) the Parthians expanded into Media and Mesopotamia. They then came into conflict with Armenia and then Rome. They soundly defeated Crassus at the battle of Carrhae (53 BC). In 40 and 39 BC they raided throughout Syria and Asia Minor but were defeated by Ventidius. In the following 250 years the Romans regularly raided deep into Parthian territory, occupying Ctesiphon on multiple occasions but were never able to hold on to the city. The dynasty was ended when Ardashir I established the Sassanid empire in 224 AD. Troop Notes The cavalry appear to have been largely supplied by the nobles and their followers. Cataphracts: Introduced from the steppes but existing in the Seleucid kingdom before the arrival of the Parthians, the cataphracts were fully armoured riders on armoured horses equipped with a long spear. Horse archers: Comprising the largest component of the army, the horse archer was equipped with a bow and some also carried light spears. They relied upon rate of fire and the ability to evade opponents. Once an opponent was disrupted the horse archers might charge in. On at least one occasion the horse archers believed the Romans to be disrupted, charged in and were then beaten. Infantry: Infantry were largely used as garrison troops for cities and frontier defences. 20,000 infantry were raised against the Alanes in 136 AD. Changes from last version Increased cataphract maximum. Cataphracts with devastating chargers. Version st January 2018
25 Army Commander 1 Any Professional Dates 180 BC to 10 AD SubGenerals 13 Any Professional Terrain Plains, Mountains Internal Allied Generals Camp Unfortified or Flexible; or Name Type Training and Quality IndoGreek Protection Shooting Skill Melee Characteristics Min Mandatory Optional Max Elephants ELEPHANTS 0 2,3,4 Shove 6 Greek cavalry Charging 4 4,6 Superior Melee Expert Drilled Loose Lancer 6 Reclassify Greek cavalry Unskilled Superior Short Spear Melee Expert with bows Drilled Loose Bow All or none Iranian cavalry Charging 0 4,6 Melee Expert Lancer 12 Horse archers Formed Flexible Bow 12 Indian cavalry Unskilled 0 4,6 Javelin 6 Phalanx 8 8 Pike Shove Orb/Square Formed Close 16 Thureophoroi 0 6,8 Long Spear Shove Orb/Square Drilled Close 12 Arachosian spearmen 0 6,8,9 Short Spear Integral shooters Combat Shy 27 Arachosian archers Experienced 0 6,8 Combat Shy Indian javelinmen Unskilled 0 6,8,9 Short Spear Combat Shy Javelin 18 Indian spearmen 0 6,8,9 Short Spear Combat Shy 9 Indian archers Experienced 0 6,8 Combat Shy Bow 36 UG Size Version st January 2018
26 Arachosian light horse Euzenoi Cretan archers Archers Notes IndoGreek Cantabrian Javelin 12 Short Spear Melee Expert Javelin 9 Skilled 0 6,9 Combat Shy Bow 9 Combat Shy Bow 9 Sometime after 200 BC the GraecoBactrian kings occupied Arachosia. During the following decades the kings expanded towards India as the Mauryan empire collapsed. This power reached its peak under Menander who probably ruled from 155 BC. Greek rule at this period extended to Ravi river and the Swat valley. After the death of Menander the kingdom disintegrated into a number of smaller states, some of which survived into the 1st century BC. Troop Notes Indian foot can be combined in TuGs of 1/3 spearmen and 2/3 archers in units of 6 or 9. Historical Notes Troop classifications are based upon limited evidence and by association with GraecoBactrian and Indian armies of the period. Elephants: The Elephant scalp headdress is a feature of IndoGreek coins. Cavalry: IndoGreek coins depict a lancer who also carries a bow. Changes from last version Increased cavalry maximums. Reclassified Arachosian spearmen. Version st January 2018
27 Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 150 BC to 500 AD SubGenerals 13 Any Instinctive Terrain Plains, Mountains Internal Allied Generals Camp Mobile or Flexible; or Name Cataphracts Horse archers Only after 70 BC Characteristics Min Mandatory Optional Max Superior Fully Armoured Devastating 4 4,6 Long Spear Chargers, Shove 18 Experienced 6 4,6 Bow 36 ELEPHANTS 0 2,3,4 Elephants Shove 6 Unskilled 0 4,6 Indian cavalry Javelin 6 Unskilled 0 6,8,9 Indian javelinmen Short Spear Combat Shy Javelin 9 0 6,8,9 Indian spearmen Short Spear Combat Shy 9 Experienced 0 6,8 Indian archers Combat Shy Horse archers Arachosian or Mountain Indian light horse Archers Notes Type Training and Tribal Close Formed Flexible Quality Protection Indian foot can be combined in TuGs of 1/3 spearmen and 2/3 archers in units of 6 or 9. Kushan or IndoScythian Shooting Skill Melee Experienced 6 4,6 Cantabrian Bow 48 Cantabrian Javelin 6 Combat Shy UG Size Version st January 2018
28 Troop Notes Kushan or IndoScythian Historical Notes Pressed by the migration of the Yuezhi, the Saka (Scythian) tribes invaded Bactria and Parthia. Against the Parthians they won several battles and it required the Parthian king Mithridates II to reconquer areas including Seistan. From Seistan they advanced south and east into what is now southern Pakistan. They later appear to have also moved northwards replacing some of the IndoGreek kings. In the 1st century AD they also advanced further southeastwards into modern India. Their power declined in the second century AD and they were eventually destroyed by the Gupta Empire towards the end of the 4th century AD. The Kushans were one of the five noble clans of the Yuezhi who conquered the GraecoBactrian kingdom around 135 BC. By 1 AD they had achieved dominance over the other clans. The Yuezhi started encroaching on northern India from c. 70 BC onwards and at the height of its power, the Kushan empire included Bactria, Sogdia and much of Northern India. After 240 AD its western territories were lost to the Sassanid Persians and in the 4th century AD its eastern territories were conquered by the expanding Gupta empire. The remaining Kushan territories fell to the Hephthalite Huns by the end of the 5th century AD. Depictions of Kushan warriors include cataphracts and horse archers. The IndoScythian and Kushans in India also appear to have made use of local warriors. The use of Elephants is also attested. Changes from last version Increased cavalry maximums. Cataphracts with Devastating Chargers. Skirmishing horse archers compulsory. Version st January 2018
29 Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 147 BC to 225 AD SubGenerals 13 Any Instinctive Terrain Mountains Internal Allied Generals Camp Unfortified or Flexible; or Name Royal and nobles guard cataphracts Cataphracts Cataphract camels (only Hatra in 217 AD) Foot archers Horse archers Archers Slingers Javelinmen Historical Notes Type Training and Tribal Close Tribal Close CAMELRY Tribal Close Parthian Vassal States Quality Protection Shooting Skill Melee Characteristics Min Mandatory Optional Max Superior Fully Armoured Fully Armoured Fully Armoured Devastating 0 4,6 Long Spear Chargers, Shove 6 Devastating 0 4,6 Long Spear Chargers, Shove ,6 Short Spear 6 Experienced 8 6,8 Combat Shy Bow 48 Experienced 12 4,6 Cantabrian Bow 48 Combat Shy Bow 36 Combat Shy Sling 18 Combat Shy Javelin 18 The Parthian Arsacid rulers were titled the "King of Kings", as a claim to be the heirs to the Achaemenid Empire. They accepted many local kings as vassals where the Achaemenids would have had centrally appointed, albeit largely autonomous, satraps. This includes the states of Media Atropatene, Osroene (Edessa), Araba (Hatra), Characene, Adiabene, Elymais and Persis. Over time these rulers were either replaced or absorbed into the Arsacid royal family by marriage. Troop Notes The nobility in these states fought in the same way as the Parthians. Larger numbers of locally supplied infantry were also used. Changes from last version Increased cataphract maximum. Cataphracts with devastating chargers. UG Size Version st January 2018
30 Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 75 BC to 100 AD SubGenerals 13 Any Instinctive Terrain Plains, Mountains Internal Allied Generals Camp Unfortified; or Name Elephants Royal and nobles guard cataphracts Cataphracts Hillmen Horse archers Arachosian cavalry Archers Slingers Javelinmen Allies Saka allies IndoScythian Historical Notes Type Training and ELEPHANTS Tribal Close Tribal Close Quality IndoParthian Protection Shooting Skill Melee Characteristics Min Mandatory Optional Max Superior Fully Armoured Fully Armoured Experienced 0 2,3 Shove Bow 3 Devastating 0 4,6 Long Spear Chargers, Shove 6 Devastating 6 4,6 Long Spear Chargers, Shove 12 Unskilled 0 6,8,9 Short Spear Javelin 24 Experienced 12 4,6 Cantabrian Bow 60 Cantabrian Javelin 6 Combat Shy Bow 12 Combat Shy Sling 12 Combat Shy Javelin 12 The House of Suren were a powerful noble family in the Parthian kingdom and controlled areas of Seistan. Surena was a member of the family and best known for defeating Crassus at the Battle of Carrhae in 53 BC. Sometime between 20 and 10 BC Gondophares I, a ruler in Seistan, conquered parts of the former IndoScythian kingdom, seizing Arachosia and the Kabul valley. The kingdom started to decline after his death and from the middle of the 1st century AD the Kushans start to absorb the northern part of the kingdom. The kingdom disappears by about 100 AD. UG Size Version st January 2018
31 IndoParthian Troop Notes It is assumed that the troops fought in the traditional manner of Parthians and Arachosians but this is largely guesswork. Changes from last version Cataphracts devastating chargers. Version st January 2018
32 Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 224 AD to 337 AD SubGenerals 03 Any Instinctive Terrain Plains Internal Allied Generals Camp Unfortified or Flexible; or Name Elephants Royal asvaran Best asvaran Asvaran Horse archers Paighan Kamandaran Levy foot Skirmishing horse archers Archers Slingers Javelinmen Type Training and ELEPHANTS Formed Close Formed Close Formed Close Formed Flexible Formed Close Early Sassanid Persian Quality Protection Shooting Skill Melee Characteristics Min Mandatory Optional Max UG Size Superior Superior Fully Armoured Fully Armoured Fully Armoured 0 2,3,4 Shove 6 Devastating 0 4,6 Long Spear Chargers, Shove 6 Devastating 0 4,6 Long Spear Chargers, Shove 6 Devastating 6 4,6 Long Spear Chargers, Shove 18 Experienced 6 4,6 Bow ,8,9 Short Spear 24 Experienced 0 6,8 0 6,8,9 Long Spear Shove Orb/Square 36 Experienced 6 4,6 Cantabrian Bow 36 Combat Shy Combat Shy Sling 18 Combat Shy Javelin 18 Version st January 2018
33 Allies Azd Oman nomad allies PreIslamic Arab Armenian subject allies (from 259 to 287 AD) Kushan vassal allies (from 262 AD) Lahkmid allies Later PreIslamic Bedouin allies (from 300 AD) Notes Only one ally may be taken. Historical Notes Early Sassanid Persian The Sassanid Persian dynasty was founded by Ardashir I, ruler of Persis, who revolted against and defeated the last Parthian king, Artabanus V. He then consolidated central control despite various local rebellions. In 230 AD he raided deep into Roman territory and a Roman counteroffensive two years later ended inconclusively. Ardashir's son Shapur I continued the expansion of the empire, conquering Bactria and the western portion of the Kushan empire. Shapur captured Carrhae and Nisibis but was then defeated in 243 AD at Rhesaina. The Rpman emperor Gordian III subsequently advanced down the Euphrates but was defeated at Meshike (244 AD). War resumed in 253 AD when Shapur defeated the Romans at Barbalissos. Roman counterattacks ended in disaster when the emperor Valerian was captured. He advanced into Anatolia but was repulsed by the Romans and their Palmyrene ally Odaenathus. The Romans sacked Ctesiphon in 283 BC under the emperor Carus. In 296 AD the emperor Galerius was defeated Narseh near Callinicium but in 298 A.D Galerius took the offensive and won successive victories and sacked Ctesiphon. The Romans inflicted a severe peace treaty. Unrest spread throughout the empire until supressed by Sharpur II. Troop Notes The Sassanid dynasty usurped the Arascid dynasty and early Sassanid armies were similar to later Parthian armies. Adarshir I introduced Elephants that had not been used by the Parthian dynasties. Cataphracts. Early Sassanid armies retained the use of Cataphracts. The leaders were fully armoured but some of the followers may not have been able to acquire full panoply. Overall the classification of fully armoured seems justified. Horse archers. The Sassanids used horse archers but perhaps used them more aggresively than the Parthians had. Infantry: Paighan were equipped with spears and wicker shields whilst Kamandaran were equipped with bows. Sassanid infantry were not able to match Roman infantry. Changes from last version Revised list of allies. Skirmishing horse archers compulsory. Cataphracts with Devastating Chargers. Version st January 2018
34 Army Commander 1 Any Dates 338 AD to 488 AD SubGenerals 03 Any Terrain Plains Internal Allied Generals Camp Unfortified or Flexible; or Name Elephants Royal asvaran Asvaran Asvaran and Zhayedan Asvaran Paighan Kamandaran Levy foot Horse archers Archers Slingers Javelinmen Type Training and ELEPHANTS Formed Close Formed Close Formed Close Middle Sassanid Persian Quality Protection Shooting Skill Melee Characteristics Min Mandatory Optional Max UG Size Superior Superior Fully Armoured Fully Armoured 0 2,3,4 Shove 6 Devastating 0 4,6 Long Spear Chargers, Shove 6 Devastating 0 4,6 Long Spear Chargers, Shove 8 Experienced 6 4,6 Short Spear Experienced 6 4,6 Short Spear Bow ,8,9 Short Spear 24 Experienced 0 6,8 0 6,8,9 Long Spear Shove Orb/Square 36 Cantabrian Combat Shy Combat Shy Sling 18 Combat Shy Javelin 18 Version st January 2018
35 Middle Sassanid Persian Allies Azd Oman nomad allies PreIslamic Arab Lahkmid allies Later PreIslamic Bedouin allies Kushan vassal allies (from 338 to 356 and 359 to 370 AD) Armenian subject allies (from 387 AD) Hepthalite Hunnic allies (from 356 AD) Sabir allies (from 463 AD) Notes Only one ally may be taken. Historical Notes Shapur II ruled from 309 AD to 379 AD In 337 AD he broke the peace concluded in 297 AD This led to a series of long drawnout wars (nine major battles were fought) which continued until 363 AD when the Emperor Julian was killed and his successor Jovian agreed to an unfavourable peace treaty. During this period he was attacked by central Asian tribes. Towards the end of his reign he subdued the Kushans. From Shapur II's death until Kavadh I's first coronation (488 AD), there was a largely peaceful period with the Romans interupted only by two brief wars in 421 AD and 440 AD Several invasions by the Huns were defeated but they returned in 483 AD and defeated the Sassanid emperor Peroz I. Peroz I attempted to drive out the Huns but was defeated and killed. Troop Notes Over time, Sassanid armies relied less on the cataphract and more on the armoured horse archer. Changes from last version Increased cavalry maximums. Cataphracts now Devastating Chargers. Revised list of allies. Version st January 2018
36 Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 356 AD to 560 AD SubGenerals 13 Any Instinctive Terrain Plains Internal Allied Generals Camp Mobile; or Name Nobles and followers Horse archers Skilled horse archers Subject Indians (from 475 AD) Characteristics Min Mandatory Optional Max Superior Short Spear Melee Expert Experienced 10 4,6 Melee Expert Bow 36 Skilled 0 4,6 Melee Expert Bow 20 ELEPHANTS 0 2,3,4 Elephants Shove 6 Unskilled 0 4,6 Indian cavalry Javelin 6 Unskilled 0 6,8,9 Indian javelinmen Short Spear Combat Shy Javelin 9 0 6,8,9 Indian spearmen Short Spear Combat Shy 9 Experienced 0 6,8 Indian archers Combat Shy Light horse archers Notes Type Training and Formed Flexible Formed Flexible Hephthalite Hunnic Quality Protection Shooting Skill Melee Cantabrian Indian subjects must be in a separate command. If used, the number of Indian infantry must exceed the number of Elephants. Indian foot can be combined in TuGs of 1/3 spearmen and 2/3 archers in units of 6 or 9. An ally contingent may not use Indian subjects. UG Size Version st January 2018
37 Historical Notes Troop Notes The Huns were classic horse archers but were also prepared to fight at close quarters. Changes from last version Revised date of list to include Chionites. Hephthalite Hunnic A group of nomads called Chionites (or Xionites) are mentioned by the Armenian historian, Moses of Khorene (5th century) as capturing the city of Balkh sometime between 194 and 214 AD. At the end of the 4th century a new wave of Hunnic tribes invaded Bactria. Called Ephthalites by the Greeks, the origin of the Hephthalites is uncertain but they arrived northeast of the Sassanid Persian empire, raided its provinces and by 485 AD had reduced the Sassanids to tributary status. A series of wars from 503 to 513 AD drove them out of Persia. The Hunas, based north of the HinduKush, had established themselves in northwest Pakistan by the early 5th century. In 455 AD Skandagupta repelled a Hunas invasion. Around 475 AD the Hunas conquered Gandhara. They were defeated in 528 AD and had been driven out of the northern Indian plains by 542 AD. An alliance of the Sassanids and Gokturks defeated them c 560 AD after which they disappear from the historical record. This list includes both the Chionites and the Hephthalite Huns. Version st January 2018
Army Lists. Persia. Contents
 Army Lists Contents Early Achaemenid n Later Achaemenid n Parthian Parthian Vassal States Early Sassanid n Middle Sassanid n Version: 1.01 Published: 16 th July 2016 Creating an army with the Mortem et
Army Lists Contents Early Achaemenid n Later Achaemenid n Parthian Parthian Vassal States Early Sassanid n Middle Sassanid n Version: 1.01 Published: 16 th July 2016 Creating an army with the Mortem et
Syria and Asia Minor. Contents. Army Lists
 Syria and Asia Minor Contents Army Lists Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 525 BC to 300 BC SubGenerals 13 Any Instinctive
Syria and Asia Minor Contents Army Lists Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 525 BC to 300 BC SubGenerals 13 Any Instinctive
Army Lists. Syria and Asia Minor. Contents
 Syria and Asia Minor Contents Army Lists Asiatic Greek 670 to 129 BCE Lycian 525 to 300 BCE Bithynian 434 to 74 BCE Armenian 330 BCE to 252 CE Asiatic Successor 323 to 280 BCE Cappadocian 300 BCE to 17
Syria and Asia Minor Contents Army Lists Asiatic Greek 670 to 129 BCE Lycian 525 to 300 BCE Bithynian 434 to 74 BCE Armenian 330 BCE to 252 CE Asiatic Successor 323 to 280 BCE Cappadocian 300 BCE to 17
Army Lists. Egypt and Judaea. Contents
 Army Lists Egypt and Judaea Contents Cyrenean Greek 630 to 74 BCE Meroitic Kushite 592 BCE to 350 CE Late Period Egyptian 405 to 343 BCE Nabatean 312 BCE to 106 CE PreIslamic Arab 300 BCE to 400 CE Ptolemaic
Army Lists Egypt and Judaea Contents Cyrenean Greek 630 to 74 BCE Meroitic Kushite 592 BCE to 350 CE Late Period Egyptian 405 to 343 BCE Nabatean 312 BCE to 106 CE PreIslamic Arab 300 BCE to 400 CE Ptolemaic
Introduction. The conqueror takes over the possessions of the conquered
 Introduction The careers of these men embrace such a multitude of events that my preamble shall consist of nothing more than one plea: if I do not record all of their most celebrated achievements or describe
Introduction The careers of these men embrace such a multitude of events that my preamble shall consist of nothing more than one plea: if I do not record all of their most celebrated achievements or describe
Army Lists. Sumer and Akkad. Contents
 Army Lists Sumer and Akkad Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction A note on chronology Early Sumerian Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 3000 BC to
Army Lists Sumer and Akkad Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction A note on chronology Early Sumerian Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 3000 BC to
Army Lists. India. Contents
 Army Lists India Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander SubGenerals Internal Allied Generals Name Type Training and Anuradhapura Kingdom
Army Lists India Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander SubGenerals Internal Allied Generals Name Type Training and Anuradhapura Kingdom
Kings of War Historical Ancient Combat Hoplon, Pike & Arrow!
 Kings of War Historical Ancient Combat Hoplon, Pike & Arrow! This Supplement is not published by Mantic Games. Kings of War and all associated logos are property of Mantic Games and are used without permission.
Kings of War Historical Ancient Combat Hoplon, Pike & Arrow! This Supplement is not published by Mantic Games. Kings of War and all associated logos are property of Mantic Games and are used without permission.
Kings of War Historical Ancient Combat Hoplon, Pike & Arrow!
 Kings of War Historical Ancient Combat Hoplon, Pike & Arrow! This Supplement is not published by Mantic Games. Kings of War and all associated logos are property of Mantic Games and are used without permission.
Kings of War Historical Ancient Combat Hoplon, Pike & Arrow! This Supplement is not published by Mantic Games. Kings of War and all associated logos are property of Mantic Games and are used without permission.
Alexander the Great. Tables Explained Each list has an outline of a number of units. The following is an example unit:
 Alexander the Great These are the armies of Alexander the Great and his Enemies. The armies are based upon those found in DBA. and Might of s. They have been modified based on research and gut instinct.
Alexander the Great These are the armies of Alexander the Great and his Enemies. The armies are based upon those found in DBA. and Might of s. They have been modified based on research and gut instinct.
Army Lists. North America and Oceania. Contents
 Army Lists North America and Oceania Contents Eastern Woodland Culture 900 to 1500 CE Mound-Builder Culture 900 to 1500 CE Plains Culture 900 to 1500 CE Pueblo Culture 900 to 1500 CE Tu i Empire 950 to
Army Lists North America and Oceania Contents Eastern Woodland Culture 900 to 1500 CE Mound-Builder Culture 900 to 1500 CE Plains Culture 900 to 1500 CE Pueblo Culture 900 to 1500 CE Tu i Empire 950 to
Basic Impetus Chinese Army Lists
 Basic Impetus Chinese Army Lists Chinese history can be seen as a succession of barbarian peoples held at bay by a powerful Chinese dynasty which would eventually fail. The resulting invading barbarians
Basic Impetus Chinese Army Lists Chinese history can be seen as a succession of barbarian peoples held at bay by a powerful Chinese dynasty which would eventually fail. The resulting invading barbarians
1. MELEE EXPERT Melee Expert covers troops who were especially good at hand-to-hand combat for their quality grade. So an AVERAGE Melee Expert is
 1. MELEE EXPERT Melee Expert covers troops who were especially good at hand-to-hand combat for their quality grade. So an AVERAGE Melee Expert is good at melee for average troops; a SUPERIOR non-melee
1. MELEE EXPERT Melee Expert covers troops who were especially good at hand-to-hand combat for their quality grade. So an AVERAGE Melee Expert is good at melee for average troops; a SUPERIOR non-melee
Kings of War Historical Ancient Combat Hoplon, Pike & Arrow!
 Kings of War Historical Ancient Combat Hoplon, Pike & Arrow! This Supplement is not published by Mantic Games. Kings of War and all associated logos are property of Mantic Games and are used without permission.
Kings of War Historical Ancient Combat Hoplon, Pike & Arrow! This Supplement is not published by Mantic Games. Kings of War and all associated logos are property of Mantic Games and are used without permission.
Appendix A: Army Lists
 Appendix A: Army Lists BAR includes a set of 6 Army List as part of the core rules which allow you to play with 6 common armies. They will also be revised in future army list supplements. By looking at
Appendix A: Army Lists BAR includes a set of 6 Army List as part of the core rules which allow you to play with 6 common armies. They will also be revised in future army list supplements. By looking at
Army Lists. House of Valois. Contents
 Army Lists House of Valois Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Professional except Legendary Dates 1291 AD to 1405 AD SubGenerals
Army Lists House of Valois Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Professional except Legendary Dates 1291 AD to 1405 AD SubGenerals
Kings of War Historical Ancient Combat Rome s Rise and Fall!
 Kings of War Historical Ancient Combat Rome s Rise and Fall! This supplement is designed for use with Mantic Games Kings of War rules, but it is not an official Mantic Games publication. Kings of War and
Kings of War Historical Ancient Combat Rome s Rise and Fall! This supplement is designed for use with Mantic Games Kings of War rules, but it is not an official Mantic Games publication. Kings of War and
Army Lists. France. Contents
 Army Lists France Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Professional except Legendary Dates 1291 A.D. to 1405 A.D. SubGenerals
Army Lists France Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Professional except Legendary Dates 1291 A.D. to 1405 A.D. SubGenerals
Army Lists. France. Contents
 Army Lists France Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Professional except Legendary Dates 1291 A.D. to 1405 A.D. SubGenerals
Army Lists France Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Professional except Legendary Dates 1291 A.D. to 1405 A.D. SubGenerals
Official amendements for L Art de la Guerre Rules
 Official amendements for L Art de la Guerre Rules This document regroups and assembles the official amendments and corrections to L Art de la Guerre V3. They are presented in the chronological order of
Official amendements for L Art de la Guerre Rules This document regroups and assembles the official amendments and corrections to L Art de la Guerre V3. They are presented in the chronological order of
CHARIOT MINIATURES. PRICING 15mm Historical packs $6.60 All have 8 foot, 4 mounted, single elephant or chariot or 2 artillery pieces.
 CHARIOT MINIATURES PRICING 15mm Historical packs $6.60 All have 8 foot, 4 mounted, single elephant or chariot or 2 artillery pieces. ASS22, ABR1 $6.60 ASS21 $8.25 Chariots 2 Horse 2 Crew $5.50 2 Horse
CHARIOT MINIATURES PRICING 15mm Historical packs $6.60 All have 8 foot, 4 mounted, single elephant or chariot or 2 artillery pieces. ASS22, ABR1 $6.60 ASS21 $8.25 Chariots 2 Horse 2 Crew $5.50 2 Horse
Mandate of Heaven. Contents. Army Lists
 Mandate of Heaven Contents Army Lists Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction ō Chinese names and terms Erlitou Chinese Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 1700
Mandate of Heaven Contents Army Lists Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction ō Chinese names and terms Erlitou Chinese Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 1700
Mortem et Gloriam Magna
 16/10/2018 Mortem et Gloriam Magna Small Table Variant for.. 28mm figures on a 6'x4' or 15mm figures on a 4' x 3' table Introduction Mortem et Gloriam Magna is a simple adaptation of the main MeG game
16/10/2018 Mortem et Gloriam Magna Small Table Variant for.. 28mm figures on a 6'x4' or 15mm figures on a 4' x 3' table Introduction Mortem et Gloriam Magna is a simple adaptation of the main MeG game
Stephan Hess Compiled by Ken Demyen
 By Stephan Hess Compiled by Ken Demyen CONTENTS Introduction... Rules... Characters & Mounts... s... s... Shamans... Mount... Elephant Mount... Unit s... Skirmishers... Warband... Phalanx... Testudo...
By Stephan Hess Compiled by Ken Demyen CONTENTS Introduction... Rules... Characters & Mounts... s... s... Shamans... Mount... Elephant Mount... Unit s... Skirmishers... Warband... Phalanx... Testudo...
Athenian Army. The Army is commanded by the Athenian Polemarch, Perikles, who is an Elected, Reliable and Strong commander.
 Athenian Army My Athenian Army was one of the first I completed and as such has had to suffer fighting through considerable rule changes. It has also undergone several expansion and configuration changes.
Athenian Army My Athenian Army was one of the first I completed and as such has had to suffer fighting through considerable rule changes. It has also undergone several expansion and configuration changes.
Army Lists. Arabia. Contents
 Army Lists Arabia Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Early Arab Conquest Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 629 AD to 637 AD SubGenerals 13 Any
Army Lists Arabia Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Early Arab Conquest Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 629 AD to 637 AD SubGenerals 13 Any
Army Lists ITALY. Contents
 Army Lists ITALY Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 500 BC to 330 BC SubGenerals 03 Any Instinctive Terrain
Army Lists ITALY Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 500 BC to 330 BC SubGenerals 03 Any Instinctive Terrain
This is directly commanded by Leonidas, the Army General, and consists of 5 Divisions.
 Spartan Army The Spartans are perhaps the most well-known of all the Greek armies. Hopefully my version of their army is more historically accurate than some of the portrayals in films and books. The Spartans
Spartan Army The Spartans are perhaps the most well-known of all the Greek armies. Hopefully my version of their army is more historically accurate than some of the portrayals in films and books. The Spartans
Kings in the North. Contents. Army Lists
 Kings in the North Contents Army Lists Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction ŵ Wales ŵ Scotland Ireland Jarls of Orkney Kingdom of the Isles and the Isle of Man
Kings in the North Contents Army Lists Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction ŵ Wales ŵ Scotland Ireland Jarls of Orkney Kingdom of the Isles and the Isle of Man
Army Lists BYZANTIUM. Contents
 Army Lists BYZANTIUM Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Later PreIslamic Bedouin Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 400 A.D. to 636 A.D. SubGenerals
Army Lists BYZANTIUM Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Later PreIslamic Bedouin Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 400 A.D. to 636 A.D. SubGenerals
Spain, Sicily and Africa. Contents. Army Lists
 Spain, Sicily and Africa Contents Army Lists Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 650 BC to 202 AD SubGenerals 13 Any
Spain, Sicily and Africa Contents Army Lists Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 650 BC to 202 AD SubGenerals 13 Any
SunTzuGames presents
 SunTzuGames presents Ancient battles a game by Emil Larsen (4) -0 min 4+ version - Omega.4 Ancient Battles Introduction In ancient battles you get to play out some of ancient history s most iconic battles.
SunTzuGames presents Ancient battles a game by Emil Larsen (4) -0 min 4+ version - Omega.4 Ancient Battles Introduction In ancient battles you get to play out some of ancient history s most iconic battles.
Spain, Sicily and Africa. Contents. Army Lists
 Spain, Sicily and Africa Contents Army Lists Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 550 B.C. to 380 B.C. SubGenerals 13
Spain, Sicily and Africa Contents Army Lists Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 550 B.C. to 380 B.C. SubGenerals 13
Simple GBoH v1.2 Errata & Clarifications February, 2014
 Simple GBoH v1.2 Errata & Clarifications February, 2014 Rules 4.11 Last Sentence should be: For some, as noted on the Charts, this chain can be traced through one or more vacant hexes that are not in an
Simple GBoH v1.2 Errata & Clarifications February, 2014 Rules 4.11 Last Sentence should be: For some, as noted on the Charts, this chain can be traced through one or more vacant hexes that are not in an
COMITATUS Warfare in the Dark Ages AD
 COMITATUS Warfare in the Dark Ages AD 250-1100 Scenario 1 The Battle of Daras AD 50 Historical Background The young East Roman General Belisarius, in his first major command, was sent to defend the city
COMITATUS Warfare in the Dark Ages AD 250-1100 Scenario 1 The Battle of Daras AD 50 Historical Background The young East Roman General Belisarius, in his first major command, was sent to defend the city
Creating a campaign game of the Teutoburg Forest Disaster in 9AD,
 Creating a campaign game of the Teutoburg Forest Disaster in 9AD, The Ancient Warfare series launched its latest game Roman Civil Wars in December 2011 but did not include a scenario for this famous event.
Creating a campaign game of the Teutoburg Forest Disaster in 9AD, The Ancient Warfare series launched its latest game Roman Civil Wars in December 2011 but did not include a scenario for this famous event.
Western Mediterranean Sea BC
 Western Mediterranean Sea 231 218 BC By the terms of the peace treaty that ended the First Punic War in 241, Carthage was forced to cede Sicily, which became Rome s first province. Three years later, Rome
Western Mediterranean Sea 231 218 BC By the terms of the peace treaty that ended the First Punic War in 241, Carthage was forced to cede Sicily, which became Rome s first province. Three years later, Rome
Army Lists ITALY. Contents
 Army Lists ITALY Contents Early Roman, Latin or Etruscan 500 to 300 BCE Italian Hill Tribes 500 to 290 BCE Umbrian 500 to 290 BCE Early Campanian 500 to 275 BCE Magna Graecia 500 to 267 BCE Apulian 500
Army Lists ITALY Contents Early Roman, Latin or Etruscan 500 to 300 BCE Italian Hill Tribes 500 to 290 BCE Umbrian 500 to 290 BCE Early Campanian 500 to 275 BCE Magna Graecia 500 to 267 BCE Apulian 500
2 nd and 3 rd Punic War
 nd and rd Punic War These are the armies of the second and third Punic war. The armies are based upon those found in DBA. and Might of s. They have been modified based on research and gut instinct. Tables
nd and rd Punic War These are the armies of the second and third Punic war. The armies are based upon those found in DBA. and Might of s. They have been modified based on research and gut instinct. Tables
IMPERIAL WARRIOR ARMY LIST ERRATA To November 2011
 IMPERIAL WARRIOR ARMY LIST ERRATA To November 2011 Any updates or corrections are shown under the specific list. Lines refer to the line starting underneath the list or from the top of the page if the
IMPERIAL WARRIOR ARMY LIST ERRATA To November 2011 Any updates or corrections are shown under the specific list. Lines refer to the line starting underneath the list or from the top of the page if the
Land of the Samurai. Contents. Army Lists
 Land of the Samurai Contents Army Lists Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction ō ō ō ō ō ō ō ō ō ū ō Ō ō Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 500 BCE. to 250
Land of the Samurai Contents Army Lists Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction ō ō ō ō ō ō ō ō ō ū ō Ō ō Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 500 BCE. to 250
CHARIOT THEME LISTS Historicon 2008
 CHARIOT THEME LISTS Historicon 2008 This collection of army lists has been prepared for use with the Warrior rules at the Chariot Theme tournament scheduled for Historicon 2008. It is based upon Biblical
CHARIOT THEME LISTS Historicon 2008 This collection of army lists has been prepared for use with the Warrior rules at the Chariot Theme tournament scheduled for Historicon 2008. It is based upon Biblical
BATTLE OF IBERA Part of the Second Punic War Spring 215 BC
 BATTLE OF IBERA Part of the Second Punic War Spring 215 BC This is a small scenario for Hail Caesar based on the Battle of Ibera. The Troops are not according to any historical account but the unit we
BATTLE OF IBERA Part of the Second Punic War Spring 215 BC This is a small scenario for Hail Caesar based on the Battle of Ibera. The Troops are not according to any historical account but the unit we
PROCONSUL RULES FOR ANCIENT BATTLES
 Index Section Subject Page 1.0 Basic Concepts 2 1.1 Command Groups 2 1.2 Stands and Basing 2 1.3 Strength Points [SP] 2 1.4 Game Play 2 2.0 Command and Control 3 2.1 Moving Commanders 3 2.2 Losing a Commander
Index Section Subject Page 1.0 Basic Concepts 2 1.1 Command Groups 2 1.2 Stands and Basing 2 1.3 Strength Points [SP] 2 1.4 Game Play 2 2.0 Command and Control 3 2.1 Moving Commanders 3 2.2 Losing a Commander
Army Lists. Sumer and Akkad. Contents
 Army Lists Sumer and Akkad Contents Early Sumerian 3000 B.C. to 2801 B.C. Old or Middle Kingdom Egyptian 3000 B.C. to 1550 B.C. Early Nomad 3000 B.C. to 1001 B.C. Highland Raiders 3000 B.C. to 1001 B.C.
Army Lists Sumer and Akkad Contents Early Sumerian 3000 B.C. to 2801 B.C. Old or Middle Kingdom Egyptian 3000 B.C. to 1550 B.C. Early Nomad 3000 B.C. to 1001 B.C. Highland Raiders 3000 B.C. to 1001 B.C.
Rise and Fall of the Roman Empire: Strategic Decision Series Copyright (c) 2016, Two Generals Games LLC Version: 4.9.
 Rise and Fall of the Roman Empire: Strategic Decision Series Copyright (c) 2016, Two Generals Games LLC Version: 4.9 "Dulce et decorum est pro patria mori." -Horace Table of Contents Turns...2 Units and
Rise and Fall of the Roman Empire: Strategic Decision Series Copyright (c) 2016, Two Generals Games LLC Version: 4.9 "Dulce et decorum est pro patria mori." -Horace Table of Contents Turns...2 Units and
The Perfect Persian Plan: Free Deployment in Issus
 C3i Magazine, Nr.2 (1993) The Perfect Persian Plan: Free Deployment in Issus by Ulrich Blennemann In my experience with The Great Battles of Alexander, I have found that the game system captures the essence
C3i Magazine, Nr.2 (1993) The Perfect Persian Plan: Free Deployment in Issus by Ulrich Blennemann In my experience with The Great Battles of Alexander, I have found that the game system captures the essence
Army Lists. Tang China. Contents
 Army Lists Tang China Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Image: Ian Kiu - Tang Dynasty 700 AD from "The T'ang Dynasty, 618-906 A.D.-Boundaries of 700
Army Lists Tang China Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Image: Ian Kiu - Tang Dynasty 700 AD from "The T'ang Dynasty, 618-906 A.D.-Boundaries of 700
Army Lists. Gaul, Germany and Britain. Contents
 Army Lists Gaul, Germany and Britain Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 350 BC to 50 BC SubGenerals 03 Any Instinctive
Army Lists Gaul, Germany and Britain Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 350 BC to 50 BC SubGenerals 03 Any Instinctive
Army Lists. Gaul, Germany and Britain. Contents
 Army Lists Gaul, Germany and Britain Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 350 B.C. to 50 B.C. SubGenerals 13
Army Lists Gaul, Germany and Britain Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 350 B.C. to 50 B.C. SubGenerals 13
Kings of War Historical Ancient Combat Viking Age!
 Kings of War Historical Ancient Combat Viking Age! This Supplement is not published by Mantic Games. Kings of War and all associated logos are property of Mantic Games and are used without permission.
Kings of War Historical Ancient Combat Viking Age! This Supplement is not published by Mantic Games. Kings of War and all associated logos are property of Mantic Games and are used without permission.
PROCONSUL SCENARIO Dacia 87CE
 Dacia 87CE Page 1 of 5 Dacia 87CE The Kingdom of Dacia [present day Romania] frequently launched raids across the Danube into Roman territory. On several occasions the Romans tried to bring them to heel.
Dacia 87CE Page 1 of 5 Dacia 87CE The Kingdom of Dacia [present day Romania] frequently launched raids across the Danube into Roman territory. On several occasions the Romans tried to bring them to heel.
Rules Update for Warmaster Ancients
 Rules Update for Warmaster Ancients P25 Skirmishers Evading a Charge delete all four paragraphs and replace as follows. Note that this new rule replaces the rules addition Evades from close range become
Rules Update for Warmaster Ancients P25 Skirmishers Evading a Charge delete all four paragraphs and replace as follows. Note that this new rule replaces the rules addition Evades from close range become
Weapons and Tactics of Alexander the Great. James Cunningham, Sam O'Connell and Marshall Pease
 Weapons and Tactics of Alexander the Great James Cunningham, Sam O'Connell and Marshall Pease Alexander s Army How was the Macedonian Army able to become so powerful? -The discovery of gold in Amphipolis
Weapons and Tactics of Alexander the Great James Cunningham, Sam O'Connell and Marshall Pease Alexander s Army How was the Macedonian Army able to become so powerful? -The discovery of gold in Amphipolis
Warmaster Ancients Rulebook Errata
 Warmaster Ancients Rulebook Errata When we released Warmaster Ancient Armies we included some rules additions and corrections for Warmaster Ancients and for those who are yet to buy this book, the relevant
Warmaster Ancients Rulebook Errata When we released Warmaster Ancient Armies we included some rules additions and corrections for Warmaster Ancients and for those who are yet to buy this book, the relevant
Rise of Rome through the Punic Wars. Based on the map above, who do you think would be Rome s main opponent?
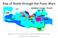 Rise of Rome through the Punic Wars Based on the map above, who do you think would be Rome s main opponent? 753 BC: Rome begins as one of many city states on the Italian Peninsula. 509 BC: Roman Republic
Rise of Rome through the Punic Wars Based on the map above, who do you think would be Rome s main opponent? 753 BC: Rome begins as one of many city states on the Italian Peninsula. 509 BC: Roman Republic
Army Lists. Mandate of Heaven. Contents
 Mandate of Heaven Contents Army Lists Erlitoi Chinese 1700 to 1301 BCE Chinese Northern Barbarians 1700 to 500 BCE Later Shang Chinese 1300 to 1017 BCE Chinese Nomadic Barbarians 1300 to 314 BCE Early
Mandate of Heaven Contents Army Lists Erlitoi Chinese 1700 to 1301 BCE Chinese Northern Barbarians 1700 to 500 BCE Later Shang Chinese 1300 to 1017 BCE Chinese Nomadic Barbarians 1300 to 314 BCE Early
The Scottish Wars against England
 The Scottish Wars against England Male lust and a mole can be blamed for the opening of the Scottish Wars of Independence. The male lust was in the breast of Alexander the Third, The King of Scots. (Note
The Scottish Wars against England Male lust and a mole can be blamed for the opening of the Scottish Wars of Independence. The male lust was in the breast of Alexander the Third, The King of Scots. (Note
COMMON CORE Lessons & Activities SAMPLE
 COMMON CORE Lessons & Activities TEACH IT TODAY! About this Book This Common Core Lessons and Activities Book allows you to immediately meet new Common Core State Standards for English Language Arts, as
COMMON CORE Lessons & Activities TEACH IT TODAY! About this Book This Common Core Lessons and Activities Book allows you to immediately meet new Common Core State Standards for English Language Arts, as
Order Code. Test reaction if:
 Move Sequence in each period 1. Dice for arrivals and returns 2. Test reaction for first time in charge reach or shot at 3. Declare and Test for charges. Test Reaction for all other causes 5. Charge Response,
Move Sequence in each period 1. Dice for arrivals and returns 2. Test reaction for first time in charge reach or shot at 3. Declare and Test for charges. Test Reaction for all other causes 5. Charge Response,
Page. Blades (Bd) classed as foot troop description figures per base recoil interpenetration combat factors flank support
 Aggression defender selection in the army lists Allies can t garrison can t guard a camp moving in groups in tournaments BBDBA allies BBDBA allied camps BBDBA allied PIPs allied contingents Arable Homeland
Aggression defender selection in the army lists Allies can t garrison can t guard a camp moving in groups in tournaments BBDBA allies BBDBA allied camps BBDBA allied PIPs allied contingents Arable Homeland
Time of Day Display. DBA 3.0 doesn t have any kind of time limit, and this can seriously distort the re-creation of many historical battles.
 Time of Day Display...by Super Stevie, Jan 10th 2017 DBA 3.0 doesn t have any kind of time limit, and this can seriously distort the re-creation of many historical battles. Take Hastings for example. Why
Time of Day Display...by Super Stevie, Jan 10th 2017 DBA 3.0 doesn t have any kind of time limit, and this can seriously distort the re-creation of many historical battles. Take Hastings for example. Why
Pig Wars Late Medieval Variant
 Pig Wars Late Medieval Variant 1337 to 1485 Introduction Pig Wars LMV is a variant of Tod Kershner s Pig Wars Dark Age skirmish rules that covers the period of the Hundred Years War to the end of the Wars
Pig Wars Late Medieval Variant 1337 to 1485 Introduction Pig Wars LMV is a variant of Tod Kershner s Pig Wars Dark Age skirmish rules that covers the period of the Hundred Years War to the end of the Wars
Army Lists. Tang China. Contents
 Army Lists Tang China Contents Pre Dynastic Khitan 432 to 1000 CE T'ang China Biejayun Fuzijen 655 to 750 CE Sogdian 500 to 730 CE Balhae Korean 698 to 926 CE Tarim Basin States 500 to 1063 CE Turgesh
Army Lists Tang China Contents Pre Dynastic Khitan 432 to 1000 CE T'ang China Biejayun Fuzijen 655 to 750 CE Sogdian 500 to 730 CE Balhae Korean 698 to 926 CE Tarim Basin States 500 to 1063 CE Turgesh
Army Lists. Africa. Contents
 Army Lists Africa Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 550 CE to 1500 CE Sub-Generals 0-3 Any Instinctive Terrain
Army Lists Africa Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 550 CE to 1500 CE Sub-Generals 0-3 Any Instinctive Terrain
Army Lists. The Steppes and Eastern Europe. Contents
 Army Lists The Steppes and Eastern Europe Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 476 A.D. to 896 A.D. Sub-Generals
Army Lists The Steppes and Eastern Europe Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 476 A.D. to 896 A.D. Sub-Generals
CIVITATES BELLANTES. Rules for Ancient Wargames with Miniatures 500 BC to AD 200 by Simon MacDowall & Caoimhín Boru
 CIVITATES BELLANTES Rules for Ancient Wargames with Miniatures 500 BC to AD 200 by Simon MacDowall & Caoimhín Boru O n the fourth day both generals lead out their forces and drew them up for battle. Scipio
CIVITATES BELLANTES Rules for Ancient Wargames with Miniatures 500 BC to AD 200 by Simon MacDowall & Caoimhín Boru O n the fourth day both generals lead out their forces and drew them up for battle. Scipio
THE ART OF WAR IN ANCIENT INDIA. Maj Gen (Dr) G D Bakshi SM, VSM (retd)
 THE ART OF WAR IN ANCIENT INDIA By Maj Gen (Dr) G D Bakshi SM, VSM (retd) The Impact of Techno-Economic and Techno-Military Triggers. Indian history can be scientifically studied in terms of the impacts
THE ART OF WAR IN ANCIENT INDIA By Maj Gen (Dr) G D Bakshi SM, VSM (retd) The Impact of Techno-Economic and Techno-Military Triggers. Indian history can be scientifically studied in terms of the impacts
Tips on How to Assemble the Persian Scythed Chariot (60 PSN 07 Y) By scott lam
 Tips on How to Assemble the Persian Scythed Chariot (60 PSN 07 Y) By scott lam Introduction The war chariot is invented during the Bronze Age circa 1800 B.C. by the nomadic people of Central Asia. It starts
Tips on How to Assemble the Persian Scythed Chariot (60 PSN 07 Y) By scott lam Introduction The war chariot is invented during the Bronze Age circa 1800 B.C. by the nomadic people of Central Asia. It starts
Army Lists. Mandate of Heaven. Contents
 Mandate of Heaven Contents Army Lists Erlitoi Chinese 1700 to 1301 BCE Chinese Northern Barbarians 1700 to 500 BCE Later Shang Chinese 1300 to 1017 BCE Chinese Nomadic Barbarians 1300 to 314 BCE Early
Mandate of Heaven Contents Army Lists Erlitoi Chinese 1700 to 1301 BCE Chinese Northern Barbarians 1700 to 500 BCE Later Shang Chinese 1300 to 1017 BCE Chinese Nomadic Barbarians 1300 to 314 BCE Early
Imperial Meltdown 2004 A themed Successor s Civil War tournament
 version 1.8 06/06/04 www.ancientbattles.com/imperial_meltdown_04.htm Imperial Meltdown 2004 A themed Successor s Civil War tournament Introduction The point of this "Imperial Meltdown" Campaign scenario
version 1.8 06/06/04 www.ancientbattles.com/imperial_meltdown_04.htm Imperial Meltdown 2004 A themed Successor s Civil War tournament Introduction The point of this "Imperial Meltdown" Campaign scenario
IN DEATH GROUND : ADDITIONAL ARMY LISTS. PART 1). THE GOLDEN HORDE AND ITS ENEMIES, c to 1300 AD.
 IN DEATH GROUND : ADDITIONAL ARMY LISTS. PART 1). THE GOLDEN HORDE AND ITS ENEMIES, c. 1220 to 1300 AD. For the first of the planned free army list downloads for In Death Ground, we have chosen the armies
IN DEATH GROUND : ADDITIONAL ARMY LISTS. PART 1). THE GOLDEN HORDE AND ITS ENEMIES, c. 1220 to 1300 AD. For the first of the planned free army list downloads for In Death Ground, we have chosen the armies
Year 7 History Key Terms Homework. How England Began
 Year 7 History Key Terms Homework How England Began New Words: How England Began #1 New Words: How England Began #2 Migration Invasion Chronology Huguenots The movement of people from one place, usually
Year 7 History Key Terms Homework How England Began New Words: How England Began #1 New Words: How England Began #2 Migration Invasion Chronology Huguenots The movement of people from one place, usually
Army Lists. Britain after the Romans to the Norman conquest. Contents
 Army Lists Britain after the Romans to the Norman conquest Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 407 AD to 468
Army Lists Britain after the Romans to the Norman conquest Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 407 AD to 468
Army Lists. The Franks. Contents
 Army Lists The Franks Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 419 AD to 621 AD Sub-Generals 0-3 Any Instinctive
Army Lists The Franks Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 419 AD to 621 AD Sub-Generals 0-3 Any Instinctive
The Battle of Chalons 20 th June 451 AD
 Introduction The Battle of Chalons This project has been designed as a Kings of War battle supplement for use with Rome's Rise and Fall from www.hourofwolves.org This battle, fought from mid-afternoon
Introduction The Battle of Chalons This project has been designed as a Kings of War battle supplement for use with Rome's Rise and Fall from www.hourofwolves.org This battle, fought from mid-afternoon
Overview Background Causes of the Hundred Years War Succession Controversy
 Overview 1337-1453 (116 years) Began as a dispute over who was the rightful king of France War consisted of a handful of land battles, raids, sea battles, many sieges, and long periods of tense truces
Overview 1337-1453 (116 years) Began as a dispute over who was the rightful king of France War consisted of a handful of land battles, raids, sea battles, many sieges, and long periods of tense truces
Army Lists. The Steppes and Eastern Europe. Contents
 Army Lists The Steppes and Eastern Europe Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 476 AD to 896 AD Sub-Generals 0-2
Army Lists The Steppes and Eastern Europe Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 476 AD to 896 AD Sub-Generals 0-2
THE SUCCESSORS. And the wars for Alexanders s Empire. By Jeff Jonas.
 13:22 Page 1 THE SUCCESSORS And the wars for Alexanders s Empire. By Jeff Jonas. When Alexander the Great died in 323 BC, he left his newly conquered empire in disarray. He was the first to conquer the
13:22 Page 1 THE SUCCESSORS And the wars for Alexanders s Empire. By Jeff Jonas. When Alexander the Great died in 323 BC, he left his newly conquered empire in disarray. He was the first to conquer the
Army Lists. Spain, Sicily and Africa. Contents
 Spain, Sicily and Africa Contents Army Lists Libyan 650 BCE to 202 CE Sicel 550 to 380 BCE Early Carthaginian (02) 550 to 275 BCE Sardinian 550 to 215 BCE Siciliot Greek 550 to 241 BCE Syracusan 411 to
Spain, Sicily and Africa Contents Army Lists Libyan 650 BCE to 202 CE Sicel 550 to 380 BCE Early Carthaginian (02) 550 to 275 BCE Sardinian 550 to 215 BCE Siciliot Greek 550 to 241 BCE Syracusan 411 to
ARE YE FOR KING OR PARLIAMENT?
 ARE YE FOR KING OR PARLIAMENT? A Warmaster Ancients Variant For The Period 1641-52 Written by Jimi Tubman Assisted by the members of the Washington Wargames Club ( http://www.washingtonwargames.co.uk ).
ARE YE FOR KING OR PARLIAMENT? A Warmaster Ancients Variant For The Period 1641-52 Written by Jimi Tubman Assisted by the members of the Washington Wargames Club ( http://www.washingtonwargames.co.uk ).
COMMON TRAINING PROFICIENCY LEVEL FOUR INSTRUCTIONAL GUIDE SECTION 5 EO C DISCUSS THE HISTORY OF DRILL PREPARATION
 COMMON TRAINING PROFICIENCY LEVEL FOUR INSTRUCTIONAL GUIDE SECTION 5 EO C408.01 DISCUSS THE HISTORY OF DRILL Total Time: 30 min PREPARATION PRE-LESSON INSTRUCTIONS Resources needed for the delivery of
COMMON TRAINING PROFICIENCY LEVEL FOUR INSTRUCTIONAL GUIDE SECTION 5 EO C408.01 DISCUSS THE HISTORY OF DRILL Total Time: 30 min PREPARATION PRE-LESSON INSTRUCTIONS Resources needed for the delivery of
IMPETVS ANCIENTS BETA LISTS
 IMPETVS ANCIENTS BETA LISTS Version 2.2 December2017 Since last version: Early Franks list added. Dadi&Piombo PAGE ARMY 2 Early Sumerians 2 Nubians 2 Akkadian Empire 3 Minoans and Early Mycaeneans 3 Achaians
IMPETVS ANCIENTS BETA LISTS Version 2.2 December2017 Since last version: Early Franks list added. Dadi&Piombo PAGE ARMY 2 Early Sumerians 2 Nubians 2 Akkadian Empire 3 Minoans and Early Mycaeneans 3 Achaians
Dark Age Britain. Tables Explained Each list has an outline of a number of units. The following is an example unit:
 Dark Age Britain These are the armies of Post Roman Britain and the Age of Arthur. The armies are based upon those found in DBA. and Might of s. They have been modified based on research and gut instinct.
Dark Age Britain These are the armies of Post Roman Britain and the Age of Arthur. The armies are based upon those found in DBA. and Might of s. They have been modified based on research and gut instinct.
Surprise, surprise: The Tactical Response of Alexander to Guerilla Warfare and Fighting in Difficult Terrain
 South Dakota State University Open PRAIRIE: Open Public Research Access Institutional Repository and Information Exchange History, Political Science, Philosophy, and Religion Faculty Publications Department
South Dakota State University Open PRAIRIE: Open Public Research Access Institutional Repository and Information Exchange History, Political Science, Philosophy, and Religion Faculty Publications Department
Holy Roman Empire. Contents. Army Lists
 Holy Roman Empire Contents Army Lists Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 1029 AD to 1150 AD SubGenerals 01 Any Instinctive
Holy Roman Empire Contents Army Lists Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 1029 AD to 1150 AD SubGenerals 01 Any Instinctive
Army Lists. The Crusades. Contents
 Army Lists The Crusades Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 1008 AD to 1403 AD SubGenerals 03 Any Instinctive
Army Lists The Crusades Contents Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction Army Commander 1 Any Instinctive Dates 1008 AD to 1403 AD SubGenerals 03 Any Instinctive
15mm Mirliton Catalogue - Medieval Ranges
 15mm Mirliton Catalogue - Medieval Ranges Ranges The Empire and Italy, 1090-1190 AD Italian Commune Wars, 1200-1300 AD Crusaders and Teutonic Knights, 1200-1291 AD Muslim Armies of the Crusades, 1096-1350
15mm Mirliton Catalogue - Medieval Ranges Ranges The Empire and Italy, 1090-1190 AD Italian Commune Wars, 1200-1300 AD Crusaders and Teutonic Knights, 1200-1291 AD Muslim Armies of the Crusades, 1096-1350
Soldiers of Iran. Imperial Achaemenian (Homa) Standard- Achaemenian. Period. Period. Persian Officer- Achaemenian. Period. Period
 Soldiers of Iran The Akhtar Kavian Banner- Prehistoric Imperial (Homa) Standard- Golden Eagle Standard- Persian Spearman- Persian Soldier with Lotus-shaped Banner- Persian Soldier with Lotus Shaped Banner-
Soldiers of Iran The Akhtar Kavian Banner- Prehistoric Imperial (Homa) Standard- Golden Eagle Standard- Persian Spearman- Persian Soldier with Lotus-shaped Banner- Persian Soldier with Lotus Shaped Banner-
Hambone Barca vs. Miles Gloriousus GAME RULES By George Sivess
 Hambone Barca vs. Miles Gloriousus GAME RULES By George Sivess Two of my favorite Ancient Generals, Hambone Barca (the illegitimate and slightly less capable son of Hamilcar), and Miles, the star of A
Hambone Barca vs. Miles Gloriousus GAME RULES By George Sivess Two of my favorite Ancient Generals, Hambone Barca (the illegitimate and slightly less capable son of Hamilcar), and Miles, the star of A
Warring States and Han. Contents. Army Lists
 Warring States and Han Contents ệ Army Lists Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction ệ Chinese names and terms Early Warring States Army Commander 1 Any Professional
Warring States and Han Contents ệ Army Lists Creating an army with the Mortem et Gloriam Army Lists Historical Introduction ệ Chinese names and terms Early Warring States Army Commander 1 Any Professional
66 Jones (1988) Scullard (1974). 68 Livy 10.28; Arr. Anab
 battle 417 interactions far broader than in the heavy infantry clashes of the hoplite era. Each troop type had its own strengths and weaknesses relative to other troop types, giving the interaction a rock,
battle 417 interactions far broader than in the heavy infantry clashes of the hoplite era. Each troop type had its own strengths and weaknesses relative to other troop types, giving the interaction a rock,
DBA-RRR. Renaissance, Reformation and Restoration Extension Rules v By Tony Aguilar
 DBA-RRR Renaissance, Reformation and Restoration 1500-1700 Extension Rules v. 1.21 By Tony Aguilar DBA-RRR Renaissance, Reformation and Restoration Rules v. 1.21 (January 2012) Page 1 DESIGNER NOTES This
DBA-RRR Renaissance, Reformation and Restoration 1500-1700 Extension Rules v. 1.21 By Tony Aguilar DBA-RRR Renaissance, Reformation and Restoration Rules v. 1.21 (January 2012) Page 1 DESIGNER NOTES This
Army Lists. Land of the Samurai. Contents
 Land of the Samurai Contents Army Lists Yayoi Japanese 500 BCE to 250 CE Yamoto Era Japanese 251 to 790 CE Emishi 400 to 802 CE Heian Japanese 794 to 1179 CE Sohei Monks (02) 980 to 1550 CE Kamakura Samurai
Land of the Samurai Contents Army Lists Yayoi Japanese 500 BCE to 250 CE Yamoto Era Japanese 251 to 790 CE Emishi 400 to 802 CE Heian Japanese 794 to 1179 CE Sohei Monks (02) 980 to 1550 CE Kamakura Samurai
The Gladiator s Present:
 The Gladiator s Present: Here are the Troop Types in the Roman legion The Roman Legionnaire Only Roman citizens could sign up for the army. They had to be fit and able to fight. These lower soldiers were
The Gladiator s Present: Here are the Troop Types in the Roman legion The Roman Legionnaire Only Roman citizens could sign up for the army. They had to be fit and able to fight. These lower soldiers were
GMT Games, LLC P.O. Box 1308, Hanford, CA
 (1.0) Introduction... 2 (2.0) Game Components... 2 (3.0) Sequence of Play... 7 (4.0) Leaders... 8 (5.0) Leader Activation & Orders... 10 (6.0) Movement... 14 (7.0) Facing & ZOCs... 20 (8.0) Missile Combat...
(1.0) Introduction... 2 (2.0) Game Components... 2 (3.0) Sequence of Play... 7 (4.0) Leaders... 8 (5.0) Leader Activation & Orders... 10 (6.0) Movement... 14 (7.0) Facing & ZOCs... 20 (8.0) Missile Combat...
Lesson Four. Aims. Context. In this lesson you will learn about how William and his successors extended their power: in England. into other countries
 KS3 History (Year 7) Module Two: Medieval Monarchs Lesson Four Gaining control, consolidating power Aims In this lesson you will learn about how William and his successors extended their power: in England
KS3 History (Year 7) Module Two: Medieval Monarchs Lesson Four Gaining control, consolidating power Aims In this lesson you will learn about how William and his successors extended their power: in England
PREFACE. Invasions and Conquests_FM_ppi-xviii.indd 15
 PREFACE The greatest difficulty in undertaking a work such as this is defining the terms invasion and conquest. Both have overtly military connotations, though not all conquests are accomplished totally
PREFACE The greatest difficulty in undertaking a work such as this is defining the terms invasion and conquest. Both have overtly military connotations, though not all conquests are accomplished totally
Bundok and Bayonet Colonial Wargames Rules by Bob Cordery
 Introduction Bundok and Bayonet Colonial Wargames Rules by Bob Cordery Part 1 - The Basic Rules The following Colonial Wargames rules were written for my own personal use and reflect my philosophy that
Introduction Bundok and Bayonet Colonial Wargames Rules by Bob Cordery Part 1 - The Basic Rules The following Colonial Wargames rules were written for my own personal use and reflect my philosophy that
Part1 Setting up the Game. Sample file
 Part1 Setting up the Game Setting up the game Necessary equipment All you need to play Polemos American Civil War is: A number of ordinary six-sided dice, numbered 1-6, known hereafter as D6. A ten-sided
Part1 Setting up the Game Setting up the game Necessary equipment All you need to play Polemos American Civil War is: A number of ordinary six-sided dice, numbered 1-6, known hereafter as D6. A ten-sided
