Applied Science SC02 (JUN15SC0201) General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June Energy Transfer Systems TOTAL
|
|
|
- Laureen Tucker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark Applied Science General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June 2015 SC Unit 2 Energy Transfer Systems Tuesday 12 May 2015 For this paper you must have: a pencil a ruler a calculator pm to 3.00 pm TOTAL Time allowed 1 hour 30 minutes A Instructions Use black ink or black ball-point pen. Fill in the es at the top of this page. Answer all questions. You must answer the questions in the spaces provided. around each page or on blank pages. Do all rough work in this book. Cross through any work you do not want to be marked. Show the working of your calculations. Information The marks for questions are shown in brackets. The maximum mark for this paper is 80. You are expected to use a calculator where appropriate. (JUN15SC0201) M/SEM/109504/Jun15/E7 SC02
2 2 Answer all questions in the spaces provided. 1 (a) (i) What does aerobic respiration mean? 1 (a) (ii) Write a balanced chemical equation for aerobic respiration. 1 (b) A group of horticultural students designed a simple respirometer to measure the rate of aerobic respiration in peas. They decided to use a pipette and a respiration chamber as shown in Figure 1. Figure 1 Pipette Stopper Respiration chamber KOH Water Peas Cotton wool Before using the respirometer, the pipette was exposed to the air to allow it to reach equilibrium with the air in the respiration chamber. The pipette was then lowered into the water. The cotton wool prevented the peas from coming into contact with the potassium hydroxide (KOH). Potassium hydroxide absorbs carbon dioxide from the air. (02)
3 3 1 (b) (i) State two measurements that could be made to determine the rate of aerobic respiration in the peas. Measurement 1... Measurement (b) (ii) During the experiment water enters the pipette. Explain why this happens. [3 marks] 1 (b) (iii) Explain how the students could use the measurements, obtained during the experiment, to determine the rate of respiration of the peas. 10 Turn over for the next question Turn over (03)
4 4 2 (a) Figure 2 shows a diagram of the heart with three different valves labelled A, B and C. Figure 2 A B C In the below write the letter, A, B, or C, that shows the position of a semilunar valve. 2 (b) The valves in the heart help to maintain blood flow by preventing the back flow of blood. Name the regions of the heart that blood would flow back into, during contraction of the ventricles, if the following valves were damaged: bicuspid valve... tricuspid valve... (04)
5 5 2 (c) (i) A woman has her cardiovascular fitness assessed before beginning a new exercise regime. Describe how you would assess cardiovascular fitness, using heart rate as an indicator, and using only standard school or college equipment. [4 marks] 2 (c) (ii) The woman exercises regularly by jogging on the spot. This causes an increased demand for blood supply to the muscles. Describe how the brain and nervous system cause the heart rate to increase to meet this demand. [4 marks] Question 2 continues on the next page Turn over (05)
6 6 2 (d) (i) What is the normal value of blood pressure for a healthy 40-year-old woman?... mm Hg 2 (d) (ii) A blood pressure reading consists of two figures. What name is used for the higher of these two figures? 2 (d) (iii) Everyone s blood pressure changes over a 24-hour period. What might a healthy person be doing when their blood pressure is at its lowest? 2 (d) (iv) State three things that might cause a healthy person s blood pressure to rise. [3 marks] (06)
7 7 Turn over for the next question DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAGE ANSWER IN THE SPACES PROVIDED Turn over (07)
8 8 3 (a) A student, studying physiology, was learning how to interpret a spirometer trace. A spirometer is used to test lung function. The spirometer trace in Figure 3 shows the main lung functions of a healthy person. Figure 3 B E Lung volume/ litres C F 1.5 A D Time 3 (a) (i) What is meant by tidal volume? 3 (a) (ii) Which letter on the spirometer trace in Figure 3 shows tidal volume?... 3 (a) (iii) What is meant by vital capacity? (08)
9 9 3 (a) (iv) Which letter on the spirometer trace in Figure 3 shows vital capacity?... 3 (b) (i) What is meant by inspiratory reserve volume? 3 (b) (ii) Which letter on the spirometer trace in Figure 3 shows inspiratory reserve volume?... 3 (b) (iii) Residual volume may be defined as the volume of gases remaining in the alveoli after a person has breathed out as hard as they can. Which letter from the spirometer trace in Figure 3 shows the residual volume?... 3 (c) A pharmaceutical company manufactured a new asthma drug that they needed to test. This involves conducting clinical trials using human beings as subjects. Spirometer traces were obtained to form the basis for the clinical trials. The company has to inform the subjects of any possible risks. Give two pieces of information about the risks involved that the company should tell the subjects before the subjects agree to volunteer Turn over (09)
10 4 A family want to build an extension at the back of their house. 10 Figure 4 Extension The family want the extension to be energy efficient. Their architect showed them Table 1 and Table 2 which give the U-values of possible materials to be used in building the extension. Table 1 U-values for the roof insulation material Insulation thickness (mm) U-value (W m 2 K 1 ) Table 2 U-values for the different parts of the extension Part of extension U-value (W m 2 K 1 ) Cavity wall 1.5 Foam-insulated wall 0.3 Double glazing 2.8 (10)
11 11 4 (a) Each side of the roof of the extension shown in Figure 4 measures 3.5 m by 4.0 m. The average temperature inside the extension is estimated to be 20 C. Calculate the rate of heat loss through the roof when insulation of thickness 50 mm is fitted and the outside temperature is 5 C. Use Table 1 and the following formula to help you answer the question. Rate of heat loss = total surface area U-value temperature difference Rate of heat loss =... W 4 (b) The family would like to have four roof windows in their extension to make the room as light as possible. Would having four roof windows in their extension be energy efficient or would fewer roof windows be better? Use the information in Table 1 and Table 2 to explain your choice. 4 (c) Table 2 shows that when foam insulation is placed in the cavity wall it reduces the U-value from 1.5 W m 2 K 1 to 0.3 W m 2 K 1. Explain how the foam reduces heat losses by conduction and convection. Question 4 continues on the next page Turn over (11)
12 4 (d) The family have bought an energy-efficient refrigerator. 12 Refrigerators keep food cool by transferring thermal energy from the food to the surroundings using a liquid called Freon, which passes through the pipes as shown by the arrows in Figure 5. Figure 5 Insulation Fins Pipe 4 (d) (i) Why is the pipe at the back of the refrigerator painted black? 4 (d) (ii) Why does this pipe have fins attached as shown in Figure 5? 4 (e) What effect will the Freon passing through the pipe at the back of the refrigerator have on the air around the refrigerator? (12)
13 13 4 (f) Why is there a layer of insulation between the inside wall and the outside wall of the refrigerator? 4 (g) Why is the outside surface of a refrigerator often coloured white? 10 Turn over for the next question Turn over (13)
14 14 5 A builder plans to knock down a house and garage using demolition equipment as shown in Figure 6. A 1200 kg steel sphere is suspended by a cable and then released. Figure 6 Jib of crane Steel sphere Cable 5 (a) When the steel sphere is raised to its dropping position, its gravitational potential energy is increased by J. The steel sphere is then released. 5 (a) (i) Calculate the velocity of the steel sphere just before it smashes into the house and garage. State the unit in your answer. [4 marks] Velocity =... 5 (a) (ii) What assumption have you made in your calculation? (14)
15 15 5 (b) The house wall and the garage wall are shown in Figure 7. Figure 7 House wall Garage wall Inner wall Insulation Outer wall The steel sphere causes more damage to the garage wall than it does to the house wall. Use your knowledge of momentum to explain this difference. [3 marks] 8 Turn over for the next question Turn over (15)
16 16 6 There are many alternative energy resources that can be used to generate electricity and reduce our dependence on fossil fuels. A company manufactures wind turbines and solar cells. The company wants to be able to give its customers advice on which of these products best suits their needs. 6 (a) (i) State one advantage that is common both to solar cells and to wind turbines compared with using fossil fuels. 6 (a) (ii) State two advantages and one disadvantage of using solar cells compared with wind turbines. [3 marks] Advantage 1... Advantage 2... Disadvantage... 6 (b) The company thinks that solar cells could be the most efficient form of electricity production if their process is developed further. State what advantage solar cells have over all other forms of electricity generation, and explain why that might help solar cells to be more efficient than any other method. (16)
17 17 6 (c) The company has developed several prototype solar cells and wants to conduct some tests to determine which of them is most effective at generating electricity. 6 (c) (i) Draw a diagram indicating what equipment should be used to do this experiment and how it should be arranged. Think carefully about the measurements that need to be taken and the equipment required to do this. [3 marks] 6 (c) (ii) Name the two main variables in this experiment. Independent variable... Dependent variable... 6 (c) (iii) How will the results be used to determine which type of solar cell is the most effective? 6 (c) (iv) Give two precautions that could be taken to ensure the validity of the results. Precaution 1... Precaution Turn over (17)
18 18 7 (a) A climber weighing 750 N ascends a climbing wall. On average, he climbs 0.6 m upwards in one second. 7 (a) (i) Calculate the power output required to do this. [3 marks] Power =... W 7 (a) (ii) State the useful energy change involved in the activity. Remember to include all the useful types of energy involved. 7 (a) (iii) The processes in the climber s muscles are 85% efficient. Using your answer from part (a) (i), calculate the total power his muscles must transfer to give the useful output needed to ascend the wall at this speed. [3 marks] Total power =... W (18)
19 19 7 (a) (iv) Assuming that the wasted energy within the muscles is converted into heat, calculate the rate of heat production in the climber s muscles. Rate of heat production =... W 7 (b) Give three reasons why the total rate of energy transfer in the muscles is actually much higher than the output calculated in part (a) (i). [3 marks] END OF QUESTIONS (19)
20 20 There are no questions printed on this page DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAGE ANSWER IN THE SPACES PROVIDED Copyright 2015 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved. (20)
Applied Science SC02 (JAN12SCO201) General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination January Energy Transfer Systems TOTAL
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Applied Science Unit 2 Energy Transfer Systems Thursday 12 January 2012 For this paper you
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Applied Science Unit 2 Energy Transfer Systems Thursday 12 January 2012 For this paper you
ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE G622 APPLIED SCIENCE
 ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE APPLIED SCIENCE Unit 3: Monitoring the activity of the human body TUESDAY 5 JUNE 2007 G622 Afternoon *CUP/T21601* Additional materials: Electronic calculator Ruler (cm/mm) Time:
ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE APPLIED SCIENCE Unit 3: Monitoring the activity of the human body TUESDAY 5 JUNE 2007 G622 Afternoon *CUP/T21601* Additional materials: Electronic calculator Ruler (cm/mm) Time:
1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives
 1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives To understand the functions of the circulatory system. To be able to identify the differences between veins, arteries
1.2 The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system Learning objectives To understand the functions of the circulatory system. To be able to identify the differences between veins, arteries
Measuring Lung Capacity
 Measuring Lung Capacity 1 Name Measuring Lung Capacity Background Information: We need a constant supply of oxygen in order to stay alive. We use oxygen to break down food to release energy and produce
Measuring Lung Capacity 1 Name Measuring Lung Capacity Background Information: We need a constant supply of oxygen in order to stay alive. We use oxygen to break down food to release energy and produce
AP Biology 12 Cellular Respiration Lab
 AP Biology 12 Cellular Respiration Lab Background: Each individual cell is responsible for the energy exchanges necessary to sustain its ordered structure. Cells accomplish this task by breaking down nutrient
AP Biology 12 Cellular Respiration Lab Background: Each individual cell is responsible for the energy exchanges necessary to sustain its ordered structure. Cells accomplish this task by breaking down nutrient
The diagram shows an alveolus next to a blood capillary in a lung. (a) (i) Draw a ring around the correct answer to complete the sentence. diffusion.
 BREATHING / GAS EXCHANGE. NAME. Q.Gas exchange takes place in the lungs. The diagram shows an alveolus next to a blood capillary in a lung. The arrows show the movement of two gases, A and B. (a) (i) Draw
BREATHING / GAS EXCHANGE. NAME. Q.Gas exchange takes place in the lungs. The diagram shows an alveolus next to a blood capillary in a lung. The arrows show the movement of two gases, A and B. (a) (i) Draw
G622. APPLIED SCIENCE Monitoring the Activity of the Human Body ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE. Thursday 27 May 2010 Afternoon. Duration: 1 hour 30 minutes
 ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE APPLIED SCIENCE Monitoring the Activity of the Human Body G622 *OCE/17533* Candidates answer on the Question Paper OCR Supplied Materials: None Other Materials Required: Electronic
ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE APPLIED SCIENCE Monitoring the Activity of the Human Body G622 *OCE/17533* Candidates answer on the Question Paper OCR Supplied Materials: None Other Materials Required: Electronic
Lab 5- Cellular Respiration
 Lab 5- Cellular Respiration Background: Many cellular processes require energy. Aerobic cellular respiration supplies energy by the oxidation of glucose. This is a complex process involving a number of
Lab 5- Cellular Respiration Background: Many cellular processes require energy. Aerobic cellular respiration supplies energy by the oxidation of glucose. This is a complex process involving a number of
The physiological functions of respiration and circulation. Mechanics. exercise 7. Respiratory Volumes. Objectives
 exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
exercise 7 Respiratory System Mechanics Objectives 1. To explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together to enable gas exchange among the lungs, blood, and body tissues 2. To define respiration,
practices makes perfect
 Human Respiratory system Chapter 1: Respiration PMR 03, 08 1. The human respiratory system consists of: a... b... c.. d... e. Our body has.. lungs (right & left). f. Each lung consists of the, and alveoli.
Human Respiratory system Chapter 1: Respiration PMR 03, 08 1. The human respiratory system consists of: a... b... c.. d... e. Our body has.. lungs (right & left). f. Each lung consists of the, and alveoli.
Explain how the structure of the gas exchange system of an insect ensures that there is a large surface area for gas exchange.
 1 Gas exchange takes place by diffusion. surfacearea differenceinconcentration diffusion lengthof diffusionpath a The diagram shows part of an insect tracheal system. i Explain how the structure of the
1 Gas exchange takes place by diffusion. surfacearea differenceinconcentration diffusion lengthof diffusionpath a The diagram shows part of an insect tracheal system. i Explain how the structure of the
CHAPTER 3: The cardio-respiratory system
 : The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
: The cardio-respiratory system Exam style questions - text book pages 44-45 1) Describe the structures involved in gaseous exchange in the lungs and explain how gaseous exchange occurs within this tissue.
BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
 96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The cell exchange O 2 directly with the air in the
96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The cell exchange O 2 directly with the air in the
Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
 ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE APPLIED SCIENCE Unit 3: Monitoring the activity of the human body FRIDAY 23 MAY 2008 G622 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes *CUP/T44164* Candidates answer on the question paper Additional
ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE APPLIED SCIENCE Unit 3: Monitoring the activity of the human body FRIDAY 23 MAY 2008 G622 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes *CUP/T44164* Candidates answer on the question paper Additional
Respiratory System Lab
 Respiratory System Lab Note: Review the safety materials and wear goggles when working with chemicals. Read the entire exercise before you begin. Take time to organize the materials you will need and set
Respiratory System Lab Note: Review the safety materials and wear goggles when working with chemicals. Read the entire exercise before you begin. Take time to organize the materials you will need and set
Monday, ! Today: Respiratory system! 5/20/14! Transport of Blood! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing!
 Monday, 5.19.14! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing! Transport of Blood! What is transported! Nutrients! Oxygen! Carbon Dioxide! Hormones! Antibodies! What it is/does!
Monday, 5.19.14! What we ve been covering! Circulatory system! Parts of blood! Heart! tubing! Transport of Blood! What is transported! Nutrients! Oxygen! Carbon Dioxide! Hormones! Antibodies! What it is/does!
Supporting inquiry based teaching and learning. Respiration. Student Name: Class:
 Supporting inquiry based teaching and learning Respiration Student Name: Class: Teacher Name: School: Question 1 a) Respiration is the process that the swimmer uses to release energy from the digested
Supporting inquiry based teaching and learning Respiration Student Name: Class: Teacher Name: School: Question 1 a) Respiration is the process that the swimmer uses to release energy from the digested
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 4
 Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 4 64 minutes 64 marks Page of 0 Q. (a) The table shows an athlete s breathing rate after the end of a race. Use the information shown in the table to draw a line
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 4 64 minutes 64 marks Page of 0 Q. (a) The table shows an athlete s breathing rate after the end of a race. Use the information shown in the table to draw a line
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system
 CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
CHAPTER 3: The respiratory system Practice questions - text book pages 56-58 1) When the inspiratory muscles contract, which one of the following statements is true? a. the size of the thoracic cavity
General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier
 Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Pages 3 Mark General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier 4 5 6 7 Mathematics (Linear) B Paper 2
Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Pages 3 Mark General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier 4 5 6 7 Mathematics (Linear) B Paper 2
C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 6H CO kilocalories of energy/mole of glucose
 Objectives Before doing this lab you should understand respiration, dormancy, and germination. After doing this lab you should be able to relate gas production to respiration rate. Introduction Aerobic
Objectives Before doing this lab you should understand respiration, dormancy, and germination. After doing this lab you should be able to relate gas production to respiration rate. Introduction Aerobic
BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
 96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The tissues exchange O 2 directly with the air in
96 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 17 BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Respiration in insects is called direct because a. The tissues exchange O 2 directly with the air in
Collin County Community College. Lung Physiology
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 9 Respiratory System 1 Lung Physiology Factors affecting Ventillation 1. Airway resistance Flow = Δ P / R Most resistance is encountered
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 9 Respiratory System 1 Lung Physiology Factors affecting Ventillation 1. Airway resistance Flow = Δ P / R Most resistance is encountered
F For this paper you must have:
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Mathematics Unit 1 General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier March 2011 43601F
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Mathematics Unit 1 General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier March 2011 43601F
Candidate Number. General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier March 2013
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier March 2013 Pages 2 3 4 5 Mark Mathematics
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier March 2013 Pages 2 3 4 5 Mark Mathematics
Engineering (JUN ) General Certificate of Secondary Education June 2014 TOTAL. Time allowed 1 hour
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark General Certificate of Secondary Education June 2014 Engineering 48501 Unit 1
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark General Certificate of Secondary Education June 2014 Engineering 48501 Unit 1
Statistics Unit Statistics 1A
 Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Mathematics Unit Statistics 1A Statistics Unit Statistics 1A Friday 14 January 2011 General
Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Mathematics Unit Statistics 1A Statistics Unit Statistics 1A Friday 14 January 2011 General
Tuesday 23 May 2017 Morning Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes
 Oxford Cambridge and RSA AS Level Physical Education H155/01 Physiological factors affecting performance Tuesday 23 May 2017 Morning Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes *6962735173* You may use: A scientific
Oxford Cambridge and RSA AS Level Physical Education H155/01 Physiological factors affecting performance Tuesday 23 May 2017 Morning Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes *6962735173* You may use: A scientific
Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange
 Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange Session Objectives. What you will cover Basic anatomy of the lung including airways Breathing movements Lung volumes and capacities Compliance and Resistance in
Respiratory Physiology Gaseous Exchange Session Objectives. What you will cover Basic anatomy of the lung including airways Breathing movements Lung volumes and capacities Compliance and Resistance in
Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class
 I. Name the following : Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class 1. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. 2. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous
I. Name the following : Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system,9 class 1. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. 2. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous
Sc ienc e 9-Biology Work sheet 8-2 A Single Breat h & Tak ing Care
 Unit 2 Your Living Body Sc ienc e 9-Biology Work sheet 8-2 A Single Breat h & Tak ing Care Name No pen or pencil No Textbook 20 Due Date Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Read pages 159-167
Unit 2 Your Living Body Sc ienc e 9-Biology Work sheet 8-2 A Single Breat h & Tak ing Care Name No pen or pencil No Textbook 20 Due Date Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Read pages 159-167
Chapter 1: Respiration
 Chapter 1: Respiration Respiration Human Breathing Mechanism Transport of oxygen Importance of a healthy respiratory system Respiratory system lungs inhalation exhalation Diffusion of oxygen by blood Transport
Chapter 1: Respiration Respiration Human Breathing Mechanism Transport of oxygen Importance of a healthy respiratory system Respiratory system lungs inhalation exhalation Diffusion of oxygen by blood Transport
SCIENCE- NOTES. Q1. Draw the diagram of human respiratory system and explain the function of the following parts:
 SCIENCE- NOTES NAME: RESPIRATION IN ORGANISMS STD.VII DIV: Q1. Draw the diagram of human respiratory system and explain the function of the following parts: i. Nasal cavity ii. Trachea iii. Lungs iv. Bronchioles
SCIENCE- NOTES NAME: RESPIRATION IN ORGANISMS STD.VII DIV: Q1. Draw the diagram of human respiratory system and explain the function of the following parts: i. Nasal cavity ii. Trachea iii. Lungs iv. Bronchioles
Additional Science Unit Physics P2. Physics Unit Physics P2 PHY2H. (Jan11PHY2H01) General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier January 2011
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Additional Science Unit Physics P2 Physics Unit Physics P2 General Certificate of Secondary
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Additional Science Unit Physics P2 Physics Unit Physics P2 General Certificate of Secondary
Unit 8 B: Respiration
 Unit 8 B: Respiration Respiration: Respiration is a chemical reaction that happens in all living cells. It is the way that energy is released from glucose, for our cells to use to keep us functioning.
Unit 8 B: Respiration Respiration: Respiration is a chemical reaction that happens in all living cells. It is the way that energy is released from glucose, for our cells to use to keep us functioning.
Respiratory System Review
 KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
KEY THIS TEST WILL BE COMPLETED IN ONE CLASS PERIOD MONDAY, MARCH 10. 2014 Respiratory System Review Name A. Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate vocabulary word or words (several examples
April KHALED MOUSA BACHA. Physiology #2. Dr. Nayef AL-Gharaibeh. Pulmonary volumes & capacities
 25 th April Physiology #2 Pulmonary volumes & capacities Dr. Nayef AL-Gharaibeh KHALED MOUSA BACHA We will start this lecture by explaining an important concept from the previous one: Intrapleural pressure
25 th April Physiology #2 Pulmonary volumes & capacities Dr. Nayef AL-Gharaibeh KHALED MOUSA BACHA We will start this lecture by explaining an important concept from the previous one: Intrapleural pressure
(JUN10SS0501) General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination June Unit Statistics TOTAL.
 Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Statistics Unit Statistics 5 Friday 18 June 2010 General Certificate of Education Advanced
Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Statistics Unit Statistics 5 Friday 18 June 2010 General Certificate of Education Advanced
Q1. Which activity is most likely to use aerobic respiration for energy?
 Q1. Which activity is most likely to use aerobic respiration for energy? 10 km cross country run Vault in gymnastics Shot put Jumping to block a shot in basketball (Total 1 mark) Q. All of the following
Q1. Which activity is most likely to use aerobic respiration for energy? 10 km cross country run Vault in gymnastics Shot put Jumping to block a shot in basketball (Total 1 mark) Q. All of the following
AP Biology Lab - Cell Respiration
 AP Biology Lab - Cell Respiration This investigation uses respirometry techniques to calculate the rate of oxygen consumption (cellular respiration) in germinating pea seeds. The effect of temperature
AP Biology Lab - Cell Respiration This investigation uses respirometry techniques to calculate the rate of oxygen consumption (cellular respiration) in germinating pea seeds. The effect of temperature
Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired
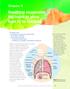 Chapter 6 Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired This chapter covers: the structure of the human gas exchange system the mechanism of breathing gas exchange in the alveoli the concept
Chapter 6 Breathing oxygenates the blood to allow food to be respired This chapter covers: the structure of the human gas exchange system the mechanism of breathing gas exchange in the alveoli the concept
Hyndland Secondary School Biology Department
 Hyndland Secondary School Biology Department Body in Action Homework and Question Booklet 1 Body in Action (a) Movement... 2 Skeleton... 2 Joints... 3 Body in Action (b) The need for Energy... 5 Heart...
Hyndland Secondary School Biology Department Body in Action Homework and Question Booklet 1 Body in Action (a) Movement... 2 Skeleton... 2 Joints... 3 Body in Action (b) The need for Energy... 5 Heart...
A Liter a Lung Measuring Lung Capacity
 A Liter a Lung Measuring Lung Capacity OBJECTIVE In this investigation, students will compare the actual and expected vital capacities of their classmates. LEVEL Middle Grades Life Science CONNECTIONS
A Liter a Lung Measuring Lung Capacity OBJECTIVE In this investigation, students will compare the actual and expected vital capacities of their classmates. LEVEL Middle Grades Life Science CONNECTIONS
Honors Physiology The Respiratory System
 Honors Physiology Name: The Respiratory System Objective: To create a model of our respiratory system, understanding the relationship between structure and function. Warm Up Questions: 1. What is the function
Honors Physiology Name: The Respiratory System Objective: To create a model of our respiratory system, understanding the relationship between structure and function. Warm Up Questions: 1. What is the function
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
BIOLOGY 12: UNIT J - CHAPTER 15 - REVIEW WORKSHEET RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. Define the four components of respiration. 2. What happens to the air as it moves along the air passages? What
Video. Respiration System. You will use 3 pages of your journal for this lesson. 1. One page for hand written notes onto a journal page
 Respiratory System Video Respiration System You will use 3 pages of your journal for this lesson. 1. One page for hand written notes onto a journal page 2. 2 nd page for diagram 3. 3 rd page for chart
Respiratory System Video Respiration System You will use 3 pages of your journal for this lesson. 1. One page for hand written notes onto a journal page 2. 2 nd page for diagram 3. 3 rd page for chart
[2] Explain how the alveoli create a surface for efficient gaseous exchange
![[2] Explain how the alveoli create a surface for efficient gaseous exchange [2] Explain how the alveoli create a surface for efficient gaseous exchange](/thumbs/89/98827571.jpg) 1 (a) (i) Name the two types of epithelial tissue found in the lungs and airways.... [2] (ii) The epithelial cells in the lungs are arranged into structures called alveoli. Explain how the alveoli create
1 (a) (i) Name the two types of epithelial tissue found in the lungs and airways.... [2] (ii) The epithelial cells in the lungs are arranged into structures called alveoli. Explain how the alveoli create
Respiration in Organisms MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS NCERT
 10 Respiration in Organisms MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Sometimes when we do heavy exercise, anaerobic respiration takes place in our muscle cells. What is produced during this process? alcohol and lactic
10 Respiration in Organisms MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Sometimes when we do heavy exercise, anaerobic respiration takes place in our muscle cells. What is produced during this process? alcohol and lactic
Physiology of the Respiratory System
 Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Physiology of the Respiratory System References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Physiology of the Respiratory System References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning
The Human Body. Everyone Needs Healthy Systems. Blood Vessels
 The Human Body Everyone Needs Healthy Systems There are several systems that make up the human body. Although their functions differ, they all work together to keep your body running smoothly. Some of
The Human Body Everyone Needs Healthy Systems There are several systems that make up the human body. Although their functions differ, they all work together to keep your body running smoothly. Some of
 Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
Question 1: Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration. It is about 3.5 4.5 litres in the human body. It
Cornell Institute for. Biology Teachers. Respirometry Part I: Lung Volumes and Capacities. Lab issue/rev. date: 12/12/96. Title:
 Cornell Institute for Biology Teachers Copyright Cornell Institute for Biology Teachers, 1999. This work may be copied by the original recipient from CIBT to provide copies for users working under the
Cornell Institute for Biology Teachers Copyright Cornell Institute for Biology Teachers, 1999. This work may be copied by the original recipient from CIBT to provide copies for users working under the
Respiratory Physiology
 Respiratory Physiology Background Information: When inspiring, the pleura attached to the internal chest wall is pulled outward as the thoracic cavity expands. The pleural cavity [space between the outer
Respiratory Physiology Background Information: When inspiring, the pleura attached to the internal chest wall is pulled outward as the thoracic cavity expands. The pleural cavity [space between the outer
Outline - Respiratory System. Function of the respiratory system Parts of the respiratory system Mechanics of breathing Regulation of breathing
 Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
Respiratory system Function Outline - Respiratory System I. II. III. IV. Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. Function
Respiration. Figure 22: Schematic representation of the respiratory system
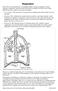 Respiration One of the seven characteristics of something which is living is respiration. Strictly speaking, respiration is the process that takes place at cellular level and is one of three different
Respiration One of the seven characteristics of something which is living is respiration. Strictly speaking, respiration is the process that takes place at cellular level and is one of three different
Measuring Carbon Dioxide in Breath
 Measuring Carbon Dioxide in Breath OBJECTIVES 1. Measure the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in your breath 2. Estimate the volume of air you exhale per day 3. Estimate the volume and mass of CO2 you
Measuring Carbon Dioxide in Breath OBJECTIVES 1. Measure the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in your breath 2. Estimate the volume of air you exhale per day 3. Estimate the volume and mass of CO2 you
Human Respiration Laboratory Experiment By
 Human Respiration Laboratory Experiment By Alison L., Thurow, Brittany Baierlein, Rachel C. Holsinger and Robin L. Cooper Department of Biology, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY 40506 0225, USA. Purpose:
Human Respiration Laboratory Experiment By Alison L., Thurow, Brittany Baierlein, Rachel C. Holsinger and Robin L. Cooper Department of Biology, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY 40506 0225, USA. Purpose:
SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION
 SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION WHEN WE BREATHE, WHAT DO WE BREATHE IN? O2, N2, CO2, O3, NO2 (gas fumes), CO, pollutant, fragrants, toxins, etc. WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF BREATHING IN? WHAT DOES OUR BODY WANT? O2 WHY?
SCIENCE 8 RESPIRATION WHEN WE BREATHE, WHAT DO WE BREATHE IN? O2, N2, CO2, O3, NO2 (gas fumes), CO, pollutant, fragrants, toxins, etc. WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF BREATHING IN? WHAT DOES OUR BODY WANT? O2 WHY?
1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT. Medicinal Air, Air Liquide 100%, medicinal gas, compressed. 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Medicinal Air, Air Liquide 100%, medicinal gas, compressed. 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Medicinal air 100% at a pressure of 200 bar (15 C). 3. PHARMACEUTICAL
1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Medicinal Air, Air Liquide 100%, medicinal gas, compressed. 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Medicinal air 100% at a pressure of 200 bar (15 C). 3. PHARMACEUTICAL
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *3585141648* BIOLOGY 0610/62 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical February/March 2018 1 hour Candidates
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *3585141648* BIOLOGY 0610/62 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical February/March 2018 1 hour Candidates
08 Respiration. #79 Respiration realeases energy from food
 08 Respiration #79 Respiration realeases energy from food Respiration is the chemical reactions that break down nutrient molecules in living cells to release energy. In humans, our cells need energy (ATP)
08 Respiration #79 Respiration realeases energy from food Respiration is the chemical reactions that break down nutrient molecules in living cells to release energy. In humans, our cells need energy (ATP)
The Respiratory System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Organs of the Respiratory system
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Organs of the Respiratory system
Introduction. Respiration. Chapter 10. Objectives. Objectives. The Respiratory System
 Introduction Respiration Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body Plays a role in the regulation of acidbase balance during exercise Objectives
Introduction Respiration Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body Plays a role in the regulation of acidbase balance during exercise Objectives
inquiry question How does the respiratory system contribute to energy production for movement? UNCORRECTED PAGE PROOFS
 inquiry question How does the respiratory system contribute to energy production for movement? chapter 7 Structure and functions of the respiratory system The respiratory system is the starting point for
inquiry question How does the respiratory system contribute to energy production for movement? chapter 7 Structure and functions of the respiratory system The respiratory system is the starting point for
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
GASEOUS EXCHANGE 17 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss what is gaseous exchange? Consider requirements of an efficient gaseous exchange surface. Look at diversity in gas exchange systems.
Show Me Hand In. Correct and Hand In Again By. Read pages of SP to help you answer the following questions: 1. Name 4 gases contained in air:,
 Name 20 Due Date Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Read pages 151-157 of SP to help you answer the following questions: 1. Name 4 gases contained in air:, and. 2. What are two types of solid
Name 20 Due Date Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Read pages 151-157 of SP to help you answer the following questions: 1. Name 4 gases contained in air:, and. 2. What are two types of solid
Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan
 Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan Lesson Name Measuring Carbon Dioxide with Vernier Probes Presenter(s) Derek Vigil Currey, Ph.D student in Physics at UCB Grade Level 5th Standards Connection(s)
Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan Lesson Name Measuring Carbon Dioxide with Vernier Probes Presenter(s) Derek Vigil Currey, Ph.D student in Physics at UCB Grade Level 5th Standards Connection(s)
Environmental Studies
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark Environmental Studies Unit 1 The Living Environment Wednesday 14 May 2014 You
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark Environmental Studies Unit 1 The Living Environment Wednesday 14 May 2014 You
Level 3 Cambridge Technical in Engineering 05822/05823/05824/05825/05873 Unit 3: Principles of mechanical engineering
 Level 3 Cambridge Technical in Engineering 05822/05823/05824/05825/05873 Unit 3: Principles of mechanical engineering Monday 16 January 2017 Afternoon Time allowed: 1 hour 30 minutes You must have: the
Level 3 Cambridge Technical in Engineering 05822/05823/05824/05825/05873 Unit 3: Principles of mechanical engineering Monday 16 January 2017 Afternoon Time allowed: 1 hour 30 minutes You must have: the
2. State the volume of air remaining in the lungs after a normal breathing.
 CLASS XI BIOLOGY Breathing And Exchange of Gases 1. Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Answer: Vital Capacity (VC): The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration.
CLASS XI BIOLOGY Breathing And Exchange of Gases 1. Define vital capacity. What is its significance? Answer: Vital Capacity (VC): The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration.
Name period date assigned date due date returned
 Name period date assigned date due date returned procedure 1. Take one balloon and stretch it out 2. Take one deep breath and blow into the balloon until you cannot breath out anymore. Do Not Take A Second
Name period date assigned date due date returned procedure 1. Take one balloon and stretch it out 2. Take one deep breath and blow into the balloon until you cannot breath out anymore. Do Not Take A Second
The bar chart shows the amount of water lost from the body of a student on two different days.
 RESPIRATION (2nd PART) Q1. The bar chart shows the amount of water lost from the body of a student on two different days. The student ate the same amount of food and drank the same amount of liquid on
RESPIRATION (2nd PART) Q1. The bar chart shows the amount of water lost from the body of a student on two different days. The student ate the same amount of food and drank the same amount of liquid on
Candidate Number. General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier January 2013
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier January 2013 Pages 3 4 5 Mark Mathematics
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier January 2013 Pages 3 4 5 Mark Mathematics
BASIC PHYSICS APPLIED TO ANAESTHESIOLOGY
 BASIC PHYSICS APPLIED TO ANAESTHESIOLOGY Dr.R.Selvakumar.M.D.D.A.DNB Professor of Anaesthesiology, K.A.P.Viswanatham Govt medical college, Trichy. The current practice of Anaesthesiology demands knowledge
BASIC PHYSICS APPLIED TO ANAESTHESIOLOGY Dr.R.Selvakumar.M.D.D.A.DNB Professor of Anaesthesiology, K.A.P.Viswanatham Govt medical college, Trichy. The current practice of Anaesthesiology demands knowledge
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System
 Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Respiratory System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Directions: The following two questions refer to the diagram below, which shows a group of cells from the respiratory tract.
 Topic 7 Gas exchange in humans Directions: The following two questions refer to the diagram below, which shows a group of cells from the respiratory tract. X Y 1. What is the function of structure X? A.
Topic 7 Gas exchange in humans Directions: The following two questions refer to the diagram below, which shows a group of cells from the respiratory tract. X Y 1. What is the function of structure X? A.
COMBINED SCIENCE 0653/6 CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/6
 Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Name International General Certificate of Secondary Education UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE LOCAL EXAMINATIONS SYNDICATE COMBINED SCIENCE 0653/6 CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES
Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Name International General Certificate of Secondary Education UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE LOCAL EXAMINATIONS SYNDICATE COMBINED SCIENCE 0653/6 CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES
Respiration - Human 1
 Respiration - Human 1 At the end of the lectures on respiration you should be able to, 1. Describe events in the respiratory processes 2. Discuss the mechanism of lung ventilation in human 3. Discuss the
Respiration - Human 1 At the end of the lectures on respiration you should be able to, 1. Describe events in the respiratory processes 2. Discuss the mechanism of lung ventilation in human 3. Discuss the
A breath of fresh air
 A breath of fresh air BIG IDEAS You are learning to: Describe the structure of the lungs Explain how the lungs clean themselves Interpret patterns in data Where are the lungs and what do they do? The lungs
A breath of fresh air BIG IDEAS You are learning to: Describe the structure of the lungs Explain how the lungs clean themselves Interpret patterns in data Where are the lungs and what do they do? The lungs
1. Read the overview. What is the difference between germinating and nongerminating
 Pre-lab Cell Respiration (# 5) 1. Read the overview. What is the difference between germinating and nongerminating seeds? 2. Why do seeds need oxygen? And, what would measuring the oxygen consumption of
Pre-lab Cell Respiration (# 5) 1. Read the overview. What is the difference between germinating and nongerminating seeds? 2. Why do seeds need oxygen? And, what would measuring the oxygen consumption of
Physiology of Respiration
 Physiology of Respiration External Respiration = pulmonary ventilation breathing involves 2 processes: inspiration expiration Inspiration an active process involves contraction of diaphragm innervated
Physiology of Respiration External Respiration = pulmonary ventilation breathing involves 2 processes: inspiration expiration Inspiration an active process involves contraction of diaphragm innervated
What factors affect the rate of cellular respiration in multicellular organisms?
 INV~t:;TIGATION 6 CELLULAR RESPIRATION* What factors affect the rate of cellular respiration in multicellular organisms? BACKGROUND Living systems require free energy and matter to maintain order, to grow,
INV~t:;TIGATION 6 CELLULAR RESPIRATION* What factors affect the rate of cellular respiration in multicellular organisms? BACKGROUND Living systems require free energy and matter to maintain order, to grow,
Respiration. The resspiratory system
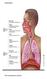 Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
Respiration The resspiratory system The Alveoli The lungs have about 300 million alveoli, with a total crosssec onal area of 50 70 m2.. Each alveolar sac is surrounded by blood capillaries. The walls of
Respiratory Physiology 2
 Respiratory Physiology 2 Session Objectives. What you will cover Gaseous Exchange Control of Breathing Rate Your objectives are State the function of support structures and epithelia of the bronchial tree
Respiratory Physiology 2 Session Objectives. What you will cover Gaseous Exchange Control of Breathing Rate Your objectives are State the function of support structures and epithelia of the bronchial tree
Anatomy and Physiology Part 11: Of Blood and Breath by: Les Sellnow
 Anatomy and Physiology Part 11: Of Blood and Breath by: Les Sellnow There are few similarities between horses and automobiles, but in a manner of speaking, the horse's circulatory and respiratory systems
Anatomy and Physiology Part 11: Of Blood and Breath by: Les Sellnow There are few similarities between horses and automobiles, but in a manner of speaking, the horse's circulatory and respiratory systems
Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system
 Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system 1. Name the following : i. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. ii. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous rings.
Department of Biology Work Sheet Respiratory system 1. Name the following : i. A muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. ii. A respiratory tube supported by cartilaginous rings.
Respiratory System, a Middle School Systems Powerful Classroom Assessment (PCA) Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Middle School Systems Powerful Classroom Assessment (PCA) Published by the Science Assessment Team of the Washington Office of the Superintendent of Public Instruction on September 14,
Respiratory System Middle School Systems Powerful Classroom Assessment (PCA) Published by the Science Assessment Team of the Washington Office of the Superintendent of Public Instruction on September 14,
Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration)
 Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration) 1 Question 1 Why do organisms need food? Organisms need food for obtaining energy to perform the vital functions. Question 2 What is a respiratory substrate?
Assignments for Life Processes(Respiration) 1 Question 1 Why do organisms need food? Organisms need food for obtaining energy to perform the vital functions. Question 2 What is a respiratory substrate?
You must have: Pen, calculator, HB pencil, eraser, ruler graduated in cm and mm, protractor, compasses.
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Functional Skills Centre Number Mathematics Level 1 Candidate Number 13 17 June 2016 Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Paper Reference FSM01/01 You must have:
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Functional Skills Centre Number Mathematics Level 1 Candidate Number 13 17 June 2016 Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Paper Reference FSM01/01 You must have:
EXP: The effect of exercise on the circulatory and respiratory systems
 EXP: The effect of exercise on the circulatory and respiratory systems Miss Werba Introduc;on: When you breathe in, the respiratory system is supplied with fresh oxygen. The oxygen moves into the lungs
EXP: The effect of exercise on the circulatory and respiratory systems Miss Werba Introduc;on: When you breathe in, the respiratory system is supplied with fresh oxygen. The oxygen moves into the lungs
Respiratory System Homework
 Respiratory System Homework The R S is the body s breathing equipment. Similar to the D system, it takes S from outside the body (G, particularly O ), circulates them through the body to C and T, then
Respiratory System Homework The R S is the body s breathing equipment. Similar to the D system, it takes S from outside the body (G, particularly O ), circulates them through the body to C and T, then
Mechanisms of Breathing. Vital Capacity
 Mechanisms of Breathing Mechanics of Breathing Two muscles are involved in the mechanics of breathing: Diaphragm = large sheet of muscle located beneath the lungs that is the primary muscle in breathing
Mechanisms of Breathing Mechanics of Breathing Two muscles are involved in the mechanics of breathing: Diaphragm = large sheet of muscle located beneath the lungs that is the primary muscle in breathing
LAB 06 Organismal Respiration
 LAB 06 Organismal Respiration Objectives: To learn how a respirometer can be used to determine a respiration rate. Identify and explain the effect of seed germination on cell respiration. To design and
LAB 06 Organismal Respiration Objectives: To learn how a respirometer can be used to determine a respiration rate. Identify and explain the effect of seed germination on cell respiration. To design and
SCIENCE PUPIL WORKSHEETS 6A - 6F
 Worksheet 6A: The Lungs PUPIL S 6A - 6F When you ve been running around outside or in a game of football, you sometimes get out of breath. This may cause us to become dizzy. Do you know why this happens?
Worksheet 6A: The Lungs PUPIL S 6A - 6F When you ve been running around outside or in a game of football, you sometimes get out of breath. This may cause us to become dizzy. Do you know why this happens?
What is breathing an respiration?
 LE SSON 15 What is breathing an respiration? You need energy to live. So do birds, trees, and bacteria. All living things need energy to carry out the life processes. And, there can be no life without
LE SSON 15 What is breathing an respiration? You need energy to live. So do birds, trees, and bacteria. All living things need energy to carry out the life processes. And, there can be no life without
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system. Objective sheet 3 Notes
 1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
1. Label a diagram of the respiratory system Objective sheet 3 Notes 2. Functions of the respiratory structures Name Description Function Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchi (Singular Bronchus) Bronchioles Lungs
Respiratory System Physiology. Dr. Vedat Evren
 Respiratory System Physiology Dr. Vedat Evren Respiration Processes involved in oxygen transport from the atmosphere to the body tissues and the release and transportation of carbon dioxide produced in
Respiratory System Physiology Dr. Vedat Evren Respiration Processes involved in oxygen transport from the atmosphere to the body tissues and the release and transportation of carbon dioxide produced in
Lung Capacity. Science and Engineering Practices: S.1A.1; S.1A.2; S.1A.4; S.1A.5; S.1A.7
 SC Academic Standards: NGSS DCI: Science and Engineering Practices: S.1A.1; S.1A.2; S.1A.4; S.1A.5; S.1A.7 Crosscutting Concepts: Patterns; Cause and Effect: Mechanism and Explanation; Systems and Systems
SC Academic Standards: NGSS DCI: Science and Engineering Practices: S.1A.1; S.1A.2; S.1A.4; S.1A.5; S.1A.7 Crosscutting Concepts: Patterns; Cause and Effect: Mechanism and Explanation; Systems and Systems
LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
 66 LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB Assignments: Due before lab: Quiz: Three Respiratory Interactive Physiology Animations pages 69 73. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
66 LAB 7 HUMAN RESPIRATORY LAB Assignments: Due before lab: Quiz: Three Respiratory Interactive Physiology Animations pages 69 73. Complete the charts on pgs. 67 and 68 and read directions for using BIOPAC
GCSE Biology. BL3FP Final Mark Scheme June Version/Stage: v1.0
 GCSE Biology BL3FP Final Mark Scheme 440 June 207 Version/Stage: v.0 Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered, together with the relevant questions, by a panel of subject
GCSE Biology BL3FP Final Mark Scheme 440 June 207 Version/Stage: v.0 Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered, together with the relevant questions, by a panel of subject
