Lab exercise 8: Fish and Amphibians General Zoology Laborarory. Matt Nelson
|
|
|
- Edmund Sharp
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lab exercise 8: Fish and Amphibians General Zoology Laborarory. Matt Nelson Superclass: Agnatha The jawless fish represent the most basal group of Craniata. At one time, the two classes of jawless fish were thought to be polyphyletic, but they have since been established as monophyletic by multiple comprehensive molecular studies. Classification The superclass Agnatha comprises two classes: Myxini and Petromyzontes (also known as Cephalospidomorphi). This group was formerly called Cephalospidomorphi, but it is no longer thought to be closely related to the group of ancient fish for which this group was named. As a result, the Petromyzontes is used to denote the more specific group that contains the lampreys. Class Myxini - This class includes the hagfish, which are mostly scavengers feeding on dead and decaying material. The carcasses of dead fish and mammals may harbor many hagfish. Hagfish possess no eyes, but find their prey using tactile and olfactory cues. Class Petromyzontes - These are the lampreys. Mostly parasitic jawless fish. Ammocoetes larvae of this group are similar in appearance and lifestyle to Cephalochordates. Organization Myxini The body of a hagfish is eel-like, long and slender with only a single gill pore (atriopore) on each side. They possess no paired appendages. The only fin is a single diphycercal caudal fin. Hagfish are also absent of scales. A row of pores which look like gill pores runs down the length of the body. Most of these pores connect to slime sacs, which produce enormous amounts of hagfish slime. This slime is used as a defense mechanism. Observe the example preserved hagfish specimen. Cephalospidomorphi (Petromyzontes) The Cephalospidomorphi include the lampreys. The lampreys are all either anadromous or strictly freshwater fish. Many lampreys are parasitic. These often suck the blood of living fish. The nonparasitic forms only feed as larvae, and are short-lived as adults. The body of lampreys is superficially similar to that of the hagfish. They are long and slender, lacking paired appendages. The gill openings are multiple pores in a lateral arrangement down the length of the body. (They do not have slime pores, as they do not produce slime like the hagfish.) A single nostril opens into the olfactory sac and the hypophyseal sac. Water is 1 General Zoology Laboratory. Matthew K Nelson (2011)
2 ventilated into and out of the nostril by muscular contractions associated with feeding. The lamprey has three eyes: two lateral eyes located on either side of the head, and a pineal eye located just posterior to the nostril. The mouth of the lamprey consists of a circular buccal funnel with horny teeth used for attaching to a host. The buccal funnel is surrounded by tiny finger-like papillae. Just posterior (interiorly) to the mouth is the buccal cavity. At the back of the buccal cavity is a rasping tongue, used for rasping the flesh of a host. The tongue can be extended forward into the buccal funnel for scraping flesh. A valve called the velum separates the digestive tract from the respiratory pathway. This prevents food from entering the gills, but keeps water flowing over the gills even while feeding. Preserved lamprey Rasping action of the lamprey tongue. Locate the following structures and become familiar with them: median nostril, external gill pores, lateral line, lateral eyes, pineal eye, buccal funnel, papillae, urogenital papillae, cloacal aperture, anterior and posterior dorsal fins, caudal fin. Examine the internal anatomy of the lamprey as demonstrated by the sagittal section of the pharyngeal region of the lamprey. Using your Zoology Atlas if you have one, label the following structures on the drawing provided below: buccal funnel, buccal cavity, rasping tongue, pharynx, median nostril, olfactory sac, hypophyseal sac, brain, spinal cord, notochord, gill pores, velum, heart, liver, rasping tongue. Superclass: Gnathostomata The jawed vertebrates are placed in the superclass Gnathostomata. The this group is sometimes referred to as the jawed fish, but as tetrapods definitely belong in this group, the use of the term fish is somewhat dubious. The gnathostomes include the cartilage fish, the bony fish, and the tetrapods. The jaws of gnathostomes are derived from the first and second gill arches of ancestral groups. Chondrichthyes The Class Chondrichthyes includes sharks, skates, rays, and chimera. These are often referred to as the cartilage fish, although the cartilaginous skeleton found in members of this class is by no means exclusive to this group. Both Agnathans and some Osteichthyes share this characteristic. Although ancestral chondrichthians had large bony plates covering their bodies, these remain only as dermal denticles (placoid scales) which cover the body. These dermal denticles are most likely homologous with the teeth of chondrichthian fish and possibly all gnathostomes. 2 General Zoology Laboratory. Matthew K Nelson (2011)
3 The jaws of chondrichthyes are connected to the chondrocranium (cartilaginous cranium) by the hyomandibular apparatus. This gives the lower jaw great flexibility and allows it to articulate forward and backward underneath the upper jaw. The fins usually include a heterocercal tail, anterior dorsal fin, posterior dorsal fin, pectoral fins, pelvic fins, and an anal fin. Reproduction in the Chondrichthyes is greatly varied, with examples of oviparity, ovoviviparity, and true viviparity (complete with a placenta-like structure). In viviparous chondrichthyes, fertilization is internal and the egg cases are sometimes referred to as mermaid s purses. Males have modified pelvic fins referred to as claspers which are used to grasp the female and deliver sperm during copulation. Observe the various examples of chondrichthians. Subclass Elasmobranchii The sharks, skates and rays are in the subclass Elasmobranchii. This group has external gill slits (usually 5 per side) and one spiracle. The spiracle is a derived structure which allows the gills to be ventilated even if the mouth is closed. The elasmobranchs possess a well-developed lateral line system, as well as a related system of pores and canals referred to as the ampullae of Lorinzini. Preserved dogfish Examine the specimen of Squalus the dogfish. Be sure you can identify the following external structures: rostrum, eyes, spiracle, gill slits, anterior dorsal fin, posterior dorsal fin, pectoral fins, pelvic fins, anal fin, caudal fin, lateral line, and the claspers if it is a male. Subclass Holocephali There are only a few genera of extant holocephalans. These are referred to as chimaeras or ratfish. They possess many primitive chondrichthian characteristics, including a median nostril, gill pouches (and an operculum), a lower jaw which is fused to the chondrocranium, and a more primitive lateral line system. Observe the preserved Chimaera specimen. Note the following structures: operculum, nostril, claspers (if male), diphycercal tail, pectoral fins, pelvic fins, dorsal fin, anterior dorsal spine. Actinopterygii The Class Actinopterygii was previously in the Class Osteichthyes, which is no longer recognized. The Actinopterygii are the ray-finned fishes. Both the Actinopterygii and the Sarcopterygii are considered to be bony fish (although the Sarctopterygii actually include the tetrapods [which are not fish]). The ray-finned fish include over 90% of all living fish. The teleosts are the largest group. 3 General Zoology Laboratory. Matthew K Nelson (2011)
4 Teleosts possess gills covered by an operculum. In many cases teleosts have a swim bladder or lung which may or may not be connected to the esophagus. This structure has multiple uses including maintaining buoyancy in the water, and supplementing gas exchange by holding air. The overlapping scales of teleosts are either cycloid or ctenoid. Ctenoid scales usually have concentric growth rings, radial grooves, and tiny spines. Cycloid scales are smooth, with concentric growth rings. Some primitive actinopterygians have ganoid scales. These scales are non-overlapping bony scales that are usually parallelogram-shaped. Observe the external features of the perch (a teleost fish). Note the following features: operculum, anterior and posterior dorsal fins, pelvic fins, pectoral fins, anal fin, anus, urogenital opening, homocercal tail, lateral line. Remove a scale from the skin and view it under the light microscope as a whole mount. Perch dissection Begin by making a mid-sagittal dorsal incision through the skin (not the muscle) from the back of the head to the dorsal edge of the tail fin, to the left of the dorsal fins. Continue this incision down the left side of the tail just anterior to the caudal fin. From the ventral edge of the caudal fin, continue the incision in an anterior direction, cutting through the anus down the length of the body until even with the pectoral fins. Extend the incision dorsally just posterior to the pectoral fins until it meets the origin of the incision. Remove the skin from this incision. Note the myomeric muscles beneath the skin. Make another incision, but this time through the muscles. Begin the incision at the anus and cut dorsally to the dorsal anterior edge of the caudal fin. Continue the incision anteriorly until you reach the posterior edge of the operculum. Cut ventrally posterior to the pectoral fins until the incision meets your original mid-ventral incision. Fold down the muscle to reveal the internal organs. Make another incision around the anterior edge of the operculum, and remove it to reveal the gill slits. Note the following internal organs: gill arches, gill lamellae, opercular cavity, stomach, pyloric caeca, liver, spleen, gall bladder, intestine, rectum, anus, gonads, urinary bladder, swim bladder. Sarcopterygii The lobe-finned fish include the lungfishes and the coelacanth. Coelacanths were thought to be extinct for many years, until 1938 when a live coelacanth was discovered off the coast of Madagascar. Today only one known species of coelacanth exists, Latimeria chalumnae (as far was we know,...and what do we know?). The coelocanths possess cosmoid scales. Cosmoid scales are roughly oval shaped and are covered in a dentine like material. Observe the plaster model of the coelacanth Latimeria chalumnae. Note the fleshy, muscular pectoral, pelvic, and anal fins. Examine any other examples of sarcopterygians available for viewing. Amphibia It should be noted that the amphibians actually represent a branch of the sarcopterygians, and should be included in that class. The ancestor of all the tetrapods (four-legged vertebrates) was a sarcopterygian. It is 4 General Zoology Laboratory. Matthew K Nelson (2011)
5 worth noting that this ancestor was neither a dipnoan (lungfish) or a coelacanth, but a sarcopterygian, nonetheless. The Sarcopterygii are, therefore, paraphyletic without the inclusion of the tetrapods. As it turns out, the Amphibia have their own problems with respect to monophyly. However, if we consider only the extant amphibians (collectively termed the Lissamphibia), they are monophyletic. Phylogenetic relationships of the Sarcopterygii. The amphibians represent the first group of truly terrestrial vertebrates. Having said that, there are, of course many species of amphibians which are aquatic (freshwater). The amphibians possess lungs, gills, or in some cases no specialized respiratory structures (other than the skin). The heart is three chambered, with two atria and one ventricle. There are two incompletely separated circuits: the pulmocutaneous and systemic circuits. Due to the single ventricle, there is some mixing of oxygenated and de-oxygenated blood in the heart. This is a great improvement in efficiency over the two chambered single-circuit heart of fish. The eggs of amphibians are generally fertilized externally, and usually (although not always) laid in water. The eggs have no specialized membranes to prevent desiccation as in the amniotes. Therefore, the eggs must be kept in very moist conditions. The extant groups of amphibians include the orders Anura (Salientia), Caudata (Urodela), and Gymnophiona. Order Anura (Salientia) The anurans include the frogs and toads. This is easily the most speciose group of modern amphibians with a tally of more than 4000 known species. (It should be noted that this number is fluctuating somewhat due to new species descriptions and extinctions.) Examine the external features of the leopard frog (Rana sp.). Note the following features: nostrils, eyes, tympanic membrane, nictitating membrane, sacral hump, webbed digits, forelegs, hind legs, cloacal opening. Frog Dissection Open the mouth of the frog to examine the buccal cavity. Dissect the frog to examine the internal organs. Make a ventral incision posteriorly from the tip of the lower jaw through the pectoral girdle. Continue the incision down the length of the body wall (being careful not to damage internal organs) to the posterior end of the body between the hind legs. Make two transverse incisions from the midpoint between the forelimbs to the base of the forelimbs. Make a similar set of incisions from the midpoint just anterior to the hind limbs. There should now be two rectangular flaps of skin and muscle that can be pulled back and pinned down to reveal the internal organs. Find and note the following structures associated with the circulatory system (trace the path that blood would travel through the heart): heart, ventricle, left and right atria, truncus arteriosus, conus arteriosus, sinus venosus. Draw your dissection labeling the following organs of the coelomic cavity: liver, stomach, small intestine, duodenum, ileum, pancreatic duct, large intestine, spleen, lungs, bladder, kidneys, fat bodies, ovaries or testes, heart. Frog skeleton Examine the frog skeleton and label the following bones: phalanges, metacarpels, carpels, radio-ulna, humerus, clavicle, scapula, sternum, clavicle, scapula, suprascapula, metatarsals, tarsals, tibio-fibula, femur, ischium, illium, urostyle, sacral vertebrae, thoracic vertebrae, urostyle. (Refer to your textbook or lab atlas for help with this.) 5 General Zoology Laboratory. Matthew K Nelson (2011)
6 Order Caudata (Urodela) The caudata are the salamanders and newts. This group is much less specialized anatomically than the anurans and caecilians. Some salamanders, such as the plethodontids possess no lungs or gills, but breathe only through their skin. Many aquatic salamanders are paedomorphic and possess gills as adults. (Gills are common in larval amphibians.) In some cases paedomorphy is conditional. Competition for resources (or population density) for example, may induce some or all individuals to metamorphose (thus reducing intraspecific competition). Note the external features of preserved salamanders. Order Gymnophiona The caecilians are legless aquatic or burrowing amphibians. They rather resemble a salamander that is missing its legs. The eyes are either absent or reduced, reflecting their lifestyle. Caecilians are unique among extant amphibians in the fact that they have dermal scales. However, their scales are located beneath the surface of the skin and are not visible externally. Actual species numbers of caecilians are difficult to estimate due to their burrowing lifestyle; however, they seem to be most common in the tropics. About 160 species of caecilians have been described. Note the external features (and there are few) of the example caecilians. 6 General Zoology Laboratory. Matthew K Nelson (2011)
7 NAME: SECTION: LAB EXERCISE 8 questions fish 1. What sex was your perch? 2. What are the five scale types that are found in the chondrichthyes and osteichthyes? 3. What type of scales did your perch have? amphibians 1. Sarcopterygii are paraphyletic. What group would need to be included to make them monophyletic? 2. Do any amphibians have scales? If so, which amphibians? 7 General Zoology Laboratory. Matthew K Nelson (2011)
8 Drawings Lamprey sagittal section Kingdom: Phylum: Class: Order: 8 General Zoology Laboratory. Matthew K Nelson (2011)
9 Drawings Frog Dissection Kingdom: Phylum: Class: Order: 9 General Zoology Laboratory. Matthew K Nelson (2011)
10 Drawings Frog Skeleton Kingdom: Phylum: Class: Order: 10 General Zoology Laboratory. Matthew K Nelson (2011)
Chapter 10. Part 1: Cartilaginous Fishes
 Chapter 10 Part 1: Cartilaginous Fishes Objectives Understand how hagfishes and lampreys differ from all other fishes. Describe how sharks, skates, and rays are related. Differentiate between cartilaginous
Chapter 10 Part 1: Cartilaginous Fishes Objectives Understand how hagfishes and lampreys differ from all other fishes. Describe how sharks, skates, and rays are related. Differentiate between cartilaginous
What is a Fish? Fishes are aquatic vertebrates. Most fishes have paired fins, scales, and gills.
 What is a Fish? Fishes are aquatic vertebrates. Most fishes have paired fins, scales, and gills. Feeding and Digestion Every mode of feeding is seen in fish herbivores, carnivores, parasites, filter feeders,
What is a Fish? Fishes are aquatic vertebrates. Most fishes have paired fins, scales, and gills. Feeding and Digestion Every mode of feeding is seen in fish herbivores, carnivores, parasites, filter feeders,
Taxonomy of Fishes. Chapter 18. I. SuperClass Agnatha. A. Class Myxini. Kingdom Animalia. The Fishes
 Taxonomy of Fishes Chapter 18 The Fishes Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata SuperClass Agnatha - jawless fish Class Chondrichthyes - cartilagenous fish Class Osteichthyes - bony fish I. SuperClass Agnatha
Taxonomy of Fishes Chapter 18 The Fishes Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata SuperClass Agnatha - jawless fish Class Chondrichthyes - cartilagenous fish Class Osteichthyes - bony fish I. SuperClass Agnatha
Class Osteichthyes. Bony Fish
 Class Osteichthyes Bony Fish General Characteristics of Class internal skeleton ossified (turned to bone) Paired fins made of rays and spines, or lobed fins swim bladder or lung present bony scales (ganoid,
Class Osteichthyes Bony Fish General Characteristics of Class internal skeleton ossified (turned to bone) Paired fins made of rays and spines, or lobed fins swim bladder or lung present bony scales (ganoid,
Lecture 3 - Early Fishes
 Lecture 3 - Early Fishes 1. Early Chordates 2. Conodonts 3. Early Vertebrates 4. Jawless fishes 5. Agnatha/ Gnathostomes junction 6. Placoderms 7. Chondrichthyes Cephalochordates (lancelets) Early Chordates
Lecture 3 - Early Fishes 1. Early Chordates 2. Conodonts 3. Early Vertebrates 4. Jawless fishes 5. Agnatha/ Gnathostomes junction 6. Placoderms 7. Chondrichthyes Cephalochordates (lancelets) Early Chordates
Chapter 30 Nonvertebrate Chordates, Fishes, and Amphibians Name
 Chapter 30 Nonvertebrate Chordates, Fishes, and Amphibians Name Lab Dissecting a Perch Background Information Fish are the largest group of vertebrates found in fresh and salt water. In fact, over 25,000
Chapter 30 Nonvertebrate Chordates, Fishes, and Amphibians Name Lab Dissecting a Perch Background Information Fish are the largest group of vertebrates found in fresh and salt water. In fact, over 25,000
FISHES. Agnatha Chondrichthyes Osteichthyes
 FISHES Agnatha Chondrichthyes Osteichthyes General Characteristics! Ectothermic! Vertebrates! Have scales! Swim with fins! Almost all exclusively aquatic! Filter oxygen from water over gills Classes of
FISHES Agnatha Chondrichthyes Osteichthyes General Characteristics! Ectothermic! Vertebrates! Have scales! Swim with fins! Almost all exclusively aquatic! Filter oxygen from water over gills Classes of
Class Myxini Order Myxiniformes Family Myxinidae (hagfishes)
 Class Myxini Order Myxiniformes Family Myxinidae (hagfishes) Lacks jaws Mouth not disk-like barbels present Unpaired fins as continuous fin-fold Branchial skeleton not well developed Eyes degenerate 70-200
Class Myxini Order Myxiniformes Family Myxinidae (hagfishes) Lacks jaws Mouth not disk-like barbels present Unpaired fins as continuous fin-fold Branchial skeleton not well developed Eyes degenerate 70-200
Chapter 39. Table of Contents. Section 1 Introduction to Vertebrates. Section 2 Jawless and Cartilaginous Fishes. Section 3 Bony Fishes.
 Fishes Table of Contents Section 1 Introduction to Vertebrates Section 2 Jawless and Cartilaginous Fishes Section 3 Bony Fishes Section 1 Introduction to Vertebrates Objectives Identify the distinguishing
Fishes Table of Contents Section 1 Introduction to Vertebrates Section 2 Jawless and Cartilaginous Fishes Section 3 Bony Fishes Section 1 Introduction to Vertebrates Objectives Identify the distinguishing
Chapter 12 Marine Fishes
 Chapter 12 Marine Fishes Marine Protochordates Phylum: Chordata (nerve cord) Subphylum: Protochordata first chordates/primitive Primitive species of marine vertebrates Do not have advanced features (backbone)
Chapter 12 Marine Fishes Marine Protochordates Phylum: Chordata (nerve cord) Subphylum: Protochordata first chordates/primitive Primitive species of marine vertebrates Do not have advanced features (backbone)
Perch Dissection Lab
 Name: Block: Due Date: Perch Dissection Lab Background The fish in the class Osteichthyes have bony skeletons. There are three groups of the bony fish: ray-finned, lobe-finned, and the lungfish. The perch
Name: Block: Due Date: Perch Dissection Lab Background The fish in the class Osteichthyes have bony skeletons. There are three groups of the bony fish: ray-finned, lobe-finned, and the lungfish. The perch
Dogfish Shark Dissection
 Dogfish Shark Dissection Name Date Period Fun Facts: Materials: The teeth of sharks are modified scales embedded in the skin of its mouth Sharks have pits on their face used to detect electric fields Sharks
Dogfish Shark Dissection Name Date Period Fun Facts: Materials: The teeth of sharks are modified scales embedded in the skin of its mouth Sharks have pits on their face used to detect electric fields Sharks
Exercise 18B Class Chondrichthyes Cartilaginous Fishes
 AP Biology Chapter 24 Exercise #18: Chordates: Fish Cartilaginous Fishes Lab Guide Exercise 18B Class Chondrichthyes Cartilaginous Fishes This group contains about 970 species that are characterized by
AP Biology Chapter 24 Exercise #18: Chordates: Fish Cartilaginous Fishes Lab Guide Exercise 18B Class Chondrichthyes Cartilaginous Fishes This group contains about 970 species that are characterized by
Gen Bio 2 Lab #10: Chondrichthyes and Osteichthyes
 Name: Date Gen Bio 2 Lab #10: Chondrichthyes and Osteichthyes Pre-Lab Reading: pages 687-690 Pre-Lab Vocabulary: 1) Ampullae of Lorenzini 2) Claspers 3) Lateral line 4) Ovoviviparous 5) Squalene 6) Viviparous
Name: Date Gen Bio 2 Lab #10: Chondrichthyes and Osteichthyes Pre-Lab Reading: pages 687-690 Pre-Lab Vocabulary: 1) Ampullae of Lorenzini 2) Claspers 3) Lateral line 4) Ovoviviparous 5) Squalene 6) Viviparous
February 17, Unit 2. Biodiversity. Chordata, the vertebrates
 Unit 2 Biodiversity Chordata, the vertebrates Phylum Chordata Examples: Sea squirts, fish, birds, dinosaurs, humans. General characteristics: 1. Bilaterally symmetrical 2. Coelomate 3. One way digestive
Unit 2 Biodiversity Chordata, the vertebrates Phylum Chordata Examples: Sea squirts, fish, birds, dinosaurs, humans. General characteristics: 1. Bilaterally symmetrical 2. Coelomate 3. One way digestive
Perch Dissection Lab
 Perch Dissection Lab Introduction: The fish in the class Osteichthyes have bony skeletons. There are three groups of the bony fish - -- ray-finned fish, lobe-finned fish, and the lung fish. The perch is
Perch Dissection Lab Introduction: The fish in the class Osteichthyes have bony skeletons. There are three groups of the bony fish - -- ray-finned fish, lobe-finned fish, and the lung fish. The perch is
Fish. Water Dwelling Animals
 Fish Water Dwelling Animals Class Agnatha (Jawless fish) They are believed to be the most primitive and oldest vertebrates. Lamprey and hagfish are the only 2 living members of this class and are placed
Fish Water Dwelling Animals Class Agnatha (Jawless fish) They are believed to be the most primitive and oldest vertebrates. Lamprey and hagfish are the only 2 living members of this class and are placed
Climate Researchers Feeling Heat. By Juliet Eilperin Washington Post Staff Writer Thursday, April 6, 2006; A27
 Biology 2010 April 19, 2006 Readings - From Text (Campbell et al. Biology, 7 th ed.) Chapter 34 pp. 671-707. Climate Researchers Feeling Heat. By Juliet Eilperin Washington Post Staff Writer Thursday,
Biology 2010 April 19, 2006 Readings - From Text (Campbell et al. Biology, 7 th ed.) Chapter 34 pp. 671-707. Climate Researchers Feeling Heat. By Juliet Eilperin Washington Post Staff Writer Thursday,
Classification. Phylum Chordata
 AP Biology Chapter 23 Exercise #17: Chordates: Urochordata & Cephalochordata Lab Guide Chordates show remarkable diversity. Most are vertebrates. All animals that belong to this phylum MUST, at some point
AP Biology Chapter 23 Exercise #17: Chordates: Urochordata & Cephalochordata Lab Guide Chordates show remarkable diversity. Most are vertebrates. All animals that belong to this phylum MUST, at some point
Internal Anatomy of Fish
 Internal Anatomy of Fish The Systems of a Fish Skeletal System Muscular System Respiratory System Digestive System Circulatory System Nervous System Reproductive System Special Organs Skeletal System
Internal Anatomy of Fish The Systems of a Fish Skeletal System Muscular System Respiratory System Digestive System Circulatory System Nervous System Reproductive System Special Organs Skeletal System
Figure Figure Phylum Chordata. Possess a dorsal, tubular nerve cord Notochord Pharyngeal gill slits Postanal tail
 Figure 17.2 Figure 18.3 Phylum Chordata Possess a dorsal, tubular nerve cord Notochord Pharyngeal gill slits Postanal tail 1 Other Characteristics of Phylum Chordata Bilateral symmetry Deuterostome, triploblastic,
Figure 17.2 Figure 18.3 Phylum Chordata Possess a dorsal, tubular nerve cord Notochord Pharyngeal gill slits Postanal tail 1 Other Characteristics of Phylum Chordata Bilateral symmetry Deuterostome, triploblastic,
Shark Lab Key. dorsal surface. click on picture for ventral surface
 Shark Lab Key Study this basic information about the spiny dogfish shark. Print this Shark Lab Report Guide. Pre-Lab Research Study this website. It provides several useful videos of large shark dissections.
Shark Lab Key Study this basic information about the spiny dogfish shark. Print this Shark Lab Report Guide. Pre-Lab Research Study this website. It provides several useful videos of large shark dissections.
Unit 19.2: Fish. Vocabulary fish spawning swim bladder
 Unit 19.2: Fish Lesson Objectives Describe structure and function in fish. Explain how fish reproduce and develop. Give an overview of the five living classes of fish. Summarize the evolution of fish.
Unit 19.2: Fish Lesson Objectives Describe structure and function in fish. Explain how fish reproduce and develop. Give an overview of the five living classes of fish. Summarize the evolution of fish.
Aquatic vertebrates that are characterized by:
 Aquatic vertebrates that are characterized by: Paired fins Used for movement Scales Used for protection Gills Used for exchanging gases Fishes were the first vertebrates to evolve The evolution of jaws
Aquatic vertebrates that are characterized by: Paired fins Used for movement Scales Used for protection Gills Used for exchanging gases Fishes were the first vertebrates to evolve The evolution of jaws
Biol Echinoderms & Chordates. But first a few words about Development
 Biol 1309 Echinoderms & Chordates 1 But first a few words about Development Blastula- zygote first develops into a hollow ball of cells Deuterostome - mouth second Protostome - mouth first Cleavage - describes
Biol 1309 Echinoderms & Chordates 1 But first a few words about Development Blastula- zygote first develops into a hollow ball of cells Deuterostome - mouth second Protostome - mouth first Cleavage - describes
Fish Dissection. Background
 Fish Dissection The Fish Dissection program at Hatfield Marine Science Center is a 50-minute hands-on program for 4th through 12th grade students. Students will work in small groups as they examine a variety
Fish Dissection The Fish Dissection program at Hatfield Marine Science Center is a 50-minute hands-on program for 4th through 12th grade students. Students will work in small groups as they examine a variety
Lecture Notes Chapter 14
 Lecture Notes Chapter 14 I. Chordata- phylum A. 3 subphyla 1. Urochordata 2. Cephalochordata 3. Vertebrata II. Characteristics of all Chordates (found during some part of the life cycle) A. All have a
Lecture Notes Chapter 14 I. Chordata- phylum A. 3 subphyla 1. Urochordata 2. Cephalochordata 3. Vertebrata II. Characteristics of all Chordates (found during some part of the life cycle) A. All have a
Shark Dissection Dogfish Squalus acanthias
 Name Shark Dissection Dogfish Squalus acanthias Fun Facts: The teeth of sharks are modified scales embedded in the skin of its mouth Sharks have pits on their face used to detect electric fields Sharks
Name Shark Dissection Dogfish Squalus acanthias Fun Facts: The teeth of sharks are modified scales embedded in the skin of its mouth Sharks have pits on their face used to detect electric fields Sharks
Animal Evolution: Chordate and Vertebrate Evolution and Diversity (Learning Outline)
 Animal Evolution: Chordate and Vertebrate Evolution and Diversity (Learning Outline) 1. Distinguishing features of the phylum Chordata and representative organisms. 2. Highlights of evolutionary steps
Animal Evolution: Chordate and Vertebrate Evolution and Diversity (Learning Outline) 1. Distinguishing features of the phylum Chordata and representative organisms. 2. Highlights of evolutionary steps
Figure 1: Chordate Characteristics
 I. General Chordate Characteristics Chordates are distinguished as a group by the presence of four embryonic features that may persist into adulthood in some species, but disappear as development progresses
I. General Chordate Characteristics Chordates are distinguished as a group by the presence of four embryonic features that may persist into adulthood in some species, but disappear as development progresses
PHYLUM CHORDATA: Subphylum vertebrata
 PHYLUM CHORDATA: Subphylum vertebrata There are three basic characteristics that distinguish Phylum Chordata from all other animal phyla: The presence of a flexible, rod-like, internal supporting structure
PHYLUM CHORDATA: Subphylum vertebrata There are three basic characteristics that distinguish Phylum Chordata from all other animal phyla: The presence of a flexible, rod-like, internal supporting structure
Chapter 25: Fishes 1
 Chapter 25: Fishes 1 2 Jawless Fishes (Agnatha) Cartilaginous Fishes (Chondrichthyes) Bony Fishes (Osteichthyes) Lamprey Whale shark Scorpion fish 3 Gills Single-loop Blood Circulation Vertebral column
Chapter 25: Fishes 1 2 Jawless Fishes (Agnatha) Cartilaginous Fishes (Chondrichthyes) Bony Fishes (Osteichthyes) Lamprey Whale shark Scorpion fish 3 Gills Single-loop Blood Circulation Vertebral column
The Deuterostomes and the rise of the Vertebrates: from Echinoderms to Man
 The Deuterostomes and the rise of the Vertebrates: from Echinoderms to Man 1 The Deuterostomes Calcarea and Silicea Cnidaria Lophotrochozoa Ecdysozoa Deuterostomia 2 The Ancestral Deuterostome Bilateral
The Deuterostomes and the rise of the Vertebrates: from Echinoderms to Man 1 The Deuterostomes Calcarea and Silicea Cnidaria Lophotrochozoa Ecdysozoa Deuterostomia 2 The Ancestral Deuterostome Bilateral
Chordates 1. Biology 2
 Chordates 1 Biology 2 Kingdom Animals Eukaryotic Multicellular - Many cell types Heterotrophic Feed by ingestion No cell walls Diploid life cycle Phylogenetic Tree Deuterostome Bilateral Symmetry 3 tissues
Chordates 1 Biology 2 Kingdom Animals Eukaryotic Multicellular - Many cell types Heterotrophic Feed by ingestion No cell walls Diploid life cycle Phylogenetic Tree Deuterostome Bilateral Symmetry 3 tissues
Body Plan of the Chordates. Notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal gill slits, blocks of muscle, post-anal tail
 Chordata The Major Groups Invertebrate Chordates Fishes Class: Agnatha Class Condrichthyes Class Osteichthyes Class: Amphibia Class: Reptilia Class: Aves Class: Mammalia Body Plan of the Chordates Notochord,
Chordata The Major Groups Invertebrate Chordates Fishes Class: Agnatha Class Condrichthyes Class Osteichthyes Class: Amphibia Class: Reptilia Class: Aves Class: Mammalia Body Plan of the Chordates Notochord,
AP Biology - Zimmerman Guided Reading Chapter 34
 AP Biology - Zimmerman Guided Reading Chapter 34 1. List the four characteristics of the members of the Phylum Chordata. Name 1. 2. 3. 4. 2. Define the following terms: a. notochord b. Dorsal nerve cord
AP Biology - Zimmerman Guided Reading Chapter 34 1. List the four characteristics of the members of the Phylum Chordata. Name 1. 2. 3. 4. 2. Define the following terms: a. notochord b. Dorsal nerve cord
Fishes and Amphibians Objectives
 Fishes and Amphibians Objectives List the four common body parts of chordates. Describe the two main characteristics of vertebrates. Explain the difference between an ectotherm and an endotherm. Describe
Fishes and Amphibians Objectives List the four common body parts of chordates. Describe the two main characteristics of vertebrates. Explain the difference between an ectotherm and an endotherm. Describe
Is a seahorse a fish, amphibian, or reptile? FISH
 Ch. 30 Loulousis Is a seahorse a fish, amphibian, or reptile? FISH Vertebral Column (Endoskeleton) Gills Single-loop circulation Kidneys Also share all the characteristics of chordates such as notochord,
Ch. 30 Loulousis Is a seahorse a fish, amphibian, or reptile? FISH Vertebral Column (Endoskeleton) Gills Single-loop circulation Kidneys Also share all the characteristics of chordates such as notochord,
deuterostomes eucoelomates pseudocoelomates acoelomate
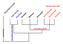 deuterostomes Mollusca Arthropoda Echinodermata Hemichordata Chordata eucoelomates Annelida Rotifera Platyhelminthes Nematoda acoelomate pseudocoelomates Phylum Hemichordata Share characteristics with
deuterostomes Mollusca Arthropoda Echinodermata Hemichordata Chordata eucoelomates Annelida Rotifera Platyhelminthes Nematoda acoelomate pseudocoelomates Phylum Hemichordata Share characteristics with
BIOLOGY 11 CHORDATES
 BIOLOGY 11 CHORDATES All chordates share 4 general characteristics: 1. Notochord a dorsal supporting rod located below the nerve cord toward the back in vertebrates, the embryonic notochord is replaced
BIOLOGY 11 CHORDATES All chordates share 4 general characteristics: 1. Notochord a dorsal supporting rod located below the nerve cord toward the back in vertebrates, the embryonic notochord is replaced
Reference: Chapter Phylum Chordata! Part Two, Fish
 Reference: Chapter 34.1-34.4 Phylum Chordata! Part Two, Fish 2 Clade Craniata v Evolution of a head (cranium) opened up a completely new way of feeding (for chordates): active predation v Craniates share
Reference: Chapter 34.1-34.4 Phylum Chordata! Part Two, Fish 2 Clade Craniata v Evolution of a head (cranium) opened up a completely new way of feeding (for chordates): active predation v Craniates share
/20 Lab #5 The Dissection of the Perch
 /20 Lab #5 The Dissection of the Perch Perch are members of the class Osterichthyes, or bony fishes. They are found in many Canadian waters and are an excellent specimen of boney fish. Food enters the
/20 Lab #5 The Dissection of the Perch Perch are members of the class Osterichthyes, or bony fishes. They are found in many Canadian waters and are an excellent specimen of boney fish. Food enters the
Subphylum Urochordata Subphylum Cephalochordata Subphylum Vertebrata
 Subphylum Urochordata Subphylum Cephalochordata Subphylum Vertebrata The most diverse of all vertebrates My research on fish * PhD Program (Oregon State University) Olfaction
Subphylum Urochordata Subphylum Cephalochordata Subphylum Vertebrata The most diverse of all vertebrates My research on fish * PhD Program (Oregon State University) Olfaction
Phylum Chordata. Chief characteristics (some are embryonic):
 Phylum Chordata Vertebrates, sea squirts or tunicates, lancelets such as Amphioxus. Name: "Chord" means "string," referring to the nerve cord and/or notochord. Geologic range: Cambrian to Holocene. Mode
Phylum Chordata Vertebrates, sea squirts or tunicates, lancelets such as Amphioxus. Name: "Chord" means "string," referring to the nerve cord and/or notochord. Geologic range: Cambrian to Holocene. Mode
External Anatomy Dissection Guide
 External Anatomy Dissection Guide Dissection is the cutting of a dead animal or a plant into separate parts for the purpose of careful and detailed examination and study. The external anatomy is as important
External Anatomy Dissection Guide Dissection is the cutting of a dead animal or a plant into separate parts for the purpose of careful and detailed examination and study. The external anatomy is as important
Phylum Chordata (Focus will be on Subphylum Vertebrata) Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata
 Phylum Chordata (Focus will be on Subphylum Vertebrata) Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata - All members have three basic characteristics: 1) a hollow dorsal nerve cord, - spinal cord has small fluid fill
Phylum Chordata (Focus will be on Subphylum Vertebrata) Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata - All members have three basic characteristics: 1) a hollow dorsal nerve cord, - spinal cord has small fluid fill
Figure 33.25a Free-living nematode
 Figure 33.25a Free-living nematode Bilateraly symmetrical Pseudocoelomates Body covered with secreated, flexible cuticle. No cilia Only longitudinal muscles. No protonephridia Muscular pharynx Gonochoristic
Figure 33.25a Free-living nematode Bilateraly symmetrical Pseudocoelomates Body covered with secreated, flexible cuticle. No cilia Only longitudinal muscles. No protonephridia Muscular pharynx Gonochoristic
Biology 11 - Chapter 31 Assignment
 Name: Class: Date: Biology 11 - Chapter 31 Assignment True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Echinoderms exhibit their invertebrate heritage by their hard exoskeletons made of calcium
Name: Class: Date: Biology 11 - Chapter 31 Assignment True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Echinoderms exhibit their invertebrate heritage by their hard exoskeletons made of calcium
Amphibian Lecture Anatomy of Amphibians
 Amphibian Lecture Anatomy of Amphibians Order Apoda Order Anura Necturus maculosus Order Caudata General Amphibian Traits Tetrapods Skeleton mostly bone 3-5 digits on forelimb (most 4) / 5 digits on hind
Amphibian Lecture Anatomy of Amphibians Order Apoda Order Anura Necturus maculosus Order Caudata General Amphibian Traits Tetrapods Skeleton mostly bone 3-5 digits on forelimb (most 4) / 5 digits on hind
Fish Dissection Background
 Fish Dissection Background Introduction Living things are similar to and different from each other. For example, when we look at the inside of a fish, we learn that the organ systems of fish are similar
Fish Dissection Background Introduction Living things are similar to and different from each other. For example, when we look at the inside of a fish, we learn that the organ systems of fish are similar
Biology 11. Phylum Chordata: Subphylum Vertebrata: The Fishys
 Biology 11 Phylum Chordata: Subphylum Vertebrata: The Fishys Phylum Chordata is typically divided into four subphyla: Higher Chordates We are going to spend the next few classes talking about the Subphylum
Biology 11 Phylum Chordata: Subphylum Vertebrata: The Fishys Phylum Chordata is typically divided into four subphyla: Higher Chordates We are going to spend the next few classes talking about the Subphylum
Outline 15: Paleozoic Life
 Outline 15: Paleozoic Life The Evolution of Vertebrates: Fish and Amphibians Phylum Chordata All chordates have a dorsal nerve cord. Chordates with vertebrae are the vertebrates. The vertebrae surround
Outline 15: Paleozoic Life The Evolution of Vertebrates: Fish and Amphibians Phylum Chordata All chordates have a dorsal nerve cord. Chordates with vertebrae are the vertebrates. The vertebrae surround
Outline 15: Paleozoic Life. The Evolution of Vertebrates: Fish and Amphibians
 Outline 15: Paleozoic Life The Evolution of Vertebrates: Fish and Amphibians Phylum Chordata All chordates have a dorsal nerve cord. Chordates with vertebrae are the vertebrates. The vertebrae surround
Outline 15: Paleozoic Life The Evolution of Vertebrates: Fish and Amphibians Phylum Chordata All chordates have a dorsal nerve cord. Chordates with vertebrae are the vertebrates. The vertebrae surround
Fish Dissection. 1. Place the preserved perch on the dissecting tray. Locate the head region. Examine the eyes. 6. What is the name of these flaps?
 Name: Date: Per: Introduction: Fish Dissection In this lab students will work within a group to learn from the dissection of a Perch. Dissection gives the student the opportunity to observe the location
Name: Date: Per: Introduction: Fish Dissection In this lab students will work within a group to learn from the dissection of a Perch. Dissection gives the student the opportunity to observe the location
Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
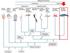 Urochordata (tunicates) Cephalochordata (lancelets) Myxini (hagfishes) Petromyzontiformes (lampreys) Chondrichthyes (sharks, rays) Actinopterygii (ray-finned fish) Actinistia (coelacanths) Dipnoi (lungfishes)
Urochordata (tunicates) Cephalochordata (lancelets) Myxini (hagfishes) Petromyzontiformes (lampreys) Chondrichthyes (sharks, rays) Actinopterygii (ray-finned fish) Actinistia (coelacanths) Dipnoi (lungfishes)
BI 101: Chordate Animals & Biodiversity
 BI 101: Chordate Animals & Biodiversity Final Exam tomorrow Announcements Same time, same place Review Mary s Peak biodiversity results Lab 10 today 1 Deuterostome Development 2 Phylum Chordata Contains
BI 101: Chordate Animals & Biodiversity Final Exam tomorrow Announcements Same time, same place Review Mary s Peak biodiversity results Lab 10 today 1 Deuterostome Development 2 Phylum Chordata Contains
Dogfish Shark Dissection Introduction 1. What are two reasons why spiny dogfish are used for study in laboratories?
 Dogfish Shark Dissection Introduction 1. What are two reasons why spiny dogfish are used for study in laboratories? 2. Someone who studies fish is called an. 3. Sharks and fish belong to the Phylum a.
Dogfish Shark Dissection Introduction 1. What are two reasons why spiny dogfish are used for study in laboratories? 2. Someone who studies fish is called an. 3. Sharks and fish belong to the Phylum a.
Exercise 18A: Subphylum Cephalochordata Amphioxus
 Zoology Exercise #18: Chordates: Fish Lab Guide Chordates show remarkable diversity. Most are vertebrates. All animals that belong to this phylum MUST, at some point in their life cycle, show the following
Zoology Exercise #18: Chordates: Fish Lab Guide Chordates show remarkable diversity. Most are vertebrates. All animals that belong to this phylum MUST, at some point in their life cycle, show the following
Kingdom Animalia part 2.notebook. April 08, The fun continues... Kingdom Animalia
 The fun continues....... Kingdom Animalia 1 2 Joint legged animals (arthropoda) found from the bottom of the ocean to high above the Earth's surface included insects, arachnid, and crustacean hard external
The fun continues....... Kingdom Animalia 1 2 Joint legged animals (arthropoda) found from the bottom of the ocean to high above the Earth's surface included insects, arachnid, and crustacean hard external
LECTURE 6 - OUTLINE. Evolution & Classification - Part II. Agnatha (cont.) Gnathostomata
 LECTURE 6 - OUTLINE Evolution & Classification - Part II Agnatha (cont.) 6. Myxini 7. Cephalaspidomorphi Gnathostomata 1. Phylogenetic relationships 2. Placodermi 3. Acanthodii BIOL 4340 Lecture 6-1 Class
LECTURE 6 - OUTLINE Evolution & Classification - Part II Agnatha (cont.) 6. Myxini 7. Cephalaspidomorphi Gnathostomata 1. Phylogenetic relationships 2. Placodermi 3. Acanthodii BIOL 4340 Lecture 6-1 Class
The Animal Kingdom. The Chordates
 The Animal Kingdom The Chordates Phylum Hemichordata Hemichordata (hemi = half; chordata= cord) acorn worm entirely marine adults show 3 of 4 basic characteristics: 1) pharyngial pouches 2) dorsal tubular
The Animal Kingdom The Chordates Phylum Hemichordata Hemichordata (hemi = half; chordata= cord) acorn worm entirely marine adults show 3 of 4 basic characteristics: 1) pharyngial pouches 2) dorsal tubular
Chapter 34A: The Origin & Evolution of Vertebrates I. 1. Overview of the Chordates 2. Invertebrate Chordates
 Chapter 34A: The Origin & Evolution of Vertebrates I 1. Overview of the Chordates 2. Invertebrate Chordates 1. Overview of Chordates Echinodermata Phylogeny of ANCESTRAL DEUTEROSTOME NOTOCHORD Common ancestor
Chapter 34A: The Origin & Evolution of Vertebrates I 1. Overview of the Chordates 2. Invertebrate Chordates 1. Overview of Chordates Echinodermata Phylogeny of ANCESTRAL DEUTEROSTOME NOTOCHORD Common ancestor
AMPHIBIANS Biology ~ Advanced Studies
 DOL 52 53 AMPHIBIANS Biology ~ Advanced Studies 6. Closed circulation, 3 heart chambers 7. Sexual reproduction a. frogs & toads external fertilization b. salamanders & caecilians internal fert. 8. Metamorphosize
DOL 52 53 AMPHIBIANS Biology ~ Advanced Studies 6. Closed circulation, 3 heart chambers 7. Sexual reproduction a. frogs & toads external fertilization b. salamanders & caecilians internal fert. 8. Metamorphosize
Fishes are vertebrates that have characteristics allowing them to live and reproduce in water.
 Section 1: are vertebrates that have characteristics allowing them to live and reproduce in water. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the features of
Section 1: are vertebrates that have characteristics allowing them to live and reproduce in water. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the features of
For this assignment, use the Chapter about Fish that is found on me website, NOT YOUR BOOK.
 Name: For this assignment, use the Chapter about Fish that is found on me website, NOT YOUR BOOK. 1. Lampreys and hagfish lack (JAWS) and instead, have many rows of (TEETH ) 2. 3. The lamprey is a problem
Name: For this assignment, use the Chapter about Fish that is found on me website, NOT YOUR BOOK. 1. Lampreys and hagfish lack (JAWS) and instead, have many rows of (TEETH ) 2. 3. The lamprey is a problem
Origin and Importance! ! Fish were the first vertebrates to appear on Earth about 500 million years ago.
 2/9/14 Origin and Importance Evolution Marine Fish Fish were the first vertebrates to appear on Earth about 500 million years ago. Fish are the most economically important organism and are a vital source
2/9/14 Origin and Importance Evolution Marine Fish Fish were the first vertebrates to appear on Earth about 500 million years ago. Fish are the most economically important organism and are a vital source
Lecture 8 History of fishes
 Lecture 8 History of fishes Ray Troll Picture = CARD SHARKS Structural Patterns and Trends in Diversification Fish subsumed (since Cope (1889) proposed - Agnatha - jawless fishes and Gnathostome lines
Lecture 8 History of fishes Ray Troll Picture = CARD SHARKS Structural Patterns and Trends in Diversification Fish subsumed (since Cope (1889) proposed - Agnatha - jawless fishes and Gnathostome lines
Chordates. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Chordates Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Vertebrates are members of the kingdom Animalia and the phylum Chordata ([link]). Recall that animals that possess bilateral symmetry can be divided into two groups protostomes
Chordates Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Vertebrates are members of the kingdom Animalia and the phylum Chordata ([link]). Recall that animals that possess bilateral symmetry can be divided into two groups protostomes
Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Subphylum: Vertebrata Class: Amphibians
 1 Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Subphylum: Vertebrata Class: Amphibians Named for the fact that they can live on both land and water amphi = Greek on both sides bian = Greek life 2 Skeleton Clip 1.
1 Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Subphylum: Vertebrata Class: Amphibians Named for the fact that they can live on both land and water amphi = Greek on both sides bian = Greek life 2 Skeleton Clip 1.
Readings in Chapter 2, 3, and 7.
 Early Vertebrates Readings in Chapter 2, 3, and 7. Using the Tree of Life Web Project www.tolweb.org org A project to put the entire tree of life, a phylogeny of all life, on the web. Biologists world-wide
Early Vertebrates Readings in Chapter 2, 3, and 7. Using the Tree of Life Web Project www.tolweb.org org A project to put the entire tree of life, a phylogeny of all life, on the web. Biologists world-wide
What is it? Affinities and systematic position of Dipnoi DBS 402B.1 Presidency University, 2015
 What is it? Affinities and systematic position of Dipnoi DBS 402B.1 Presidency University, 2015 What is the question? I ve decided to discuss the controversy, therefore the argument and philosophy of classification/systematics
What is it? Affinities and systematic position of Dipnoi DBS 402B.1 Presidency University, 2015 What is the question? I ve decided to discuss the controversy, therefore the argument and philosophy of classification/systematics
Biology 3315 Comparative Vertebrate Morphology Protochordates and Fishes
 Biology 3315 Comparative Vertebrate Morphology Protochordates and Fishes 1. Echinodermata If fossil forms are included, echinoderms are a very diverse assemblage; several classes are now entirely extinct.
Biology 3315 Comparative Vertebrate Morphology Protochordates and Fishes 1. Echinodermata If fossil forms are included, echinoderms are a very diverse assemblage; several classes are now entirely extinct.
1. Myxinoides (hagfish) are sister to. what monophyletic group? 2. Which is NOT a characteristic of chordata?
 1. Myxinoides (hagfish) are sister to a) Verterbrata what monophyletic group? b) Gnathastomata c) Urochordata d) Cephalachordata 2. Which is NOT a characteristic of chordata? a) Pharyngeal pouches b) Notochord
1. Myxinoides (hagfish) are sister to a) Verterbrata what monophyletic group? b) Gnathastomata c) Urochordata d) Cephalachordata 2. Which is NOT a characteristic of chordata? a) Pharyngeal pouches b) Notochord
CHAPTER 25 Early Tetrapods and Modern Amphibians
 CHAPTER 25 Early Tetrapods and 25-1 Physical Adaptations: Oxygen content Movement Onto Land Oxygen is 20 times more abundant in air so terrestrial animals can obtain oxygen much more easily once they possess
CHAPTER 25 Early Tetrapods and 25-1 Physical Adaptations: Oxygen content Movement Onto Land Oxygen is 20 times more abundant in air so terrestrial animals can obtain oxygen much more easily once they possess
DISSECTION 101 THE FROG
 DISSECTION 101 THE FROG Dissection helps us understand how living things function. Dissection is analytical. Dissection is an adventure. Discussion Frog anatomy is unique in that it does resemble human
DISSECTION 101 THE FROG Dissection helps us understand how living things function. Dissection is analytical. Dissection is an adventure. Discussion Frog anatomy is unique in that it does resemble human
Invertebrate Chordates
 Invertebrate Chordates Chapter 11.2 - Fishes And Invertebrate Chordates... Invertebrate Chordates Lancelets Filter feed and spend most of their time buried in the sand. Only 2 invertebrate chordates Tunicates
Invertebrate Chordates Chapter 11.2 - Fishes And Invertebrate Chordates... Invertebrate Chordates Lancelets Filter feed and spend most of their time buried in the sand. Only 2 invertebrate chordates Tunicates
Phylum Chordata Subphylum Vertebrata Superclass Agnatha Class Myxini - hagfishes Class Cephalaspidomorphi - lampreys
 Although it is debatable whether hagfish are vertebrates current classification places the hagfish within the Subphylum Vertebrata. Hagfish and Lampreys are placed in different classes of the Superclass
Although it is debatable whether hagfish are vertebrates current classification places the hagfish within the Subphylum Vertebrata. Hagfish and Lampreys are placed in different classes of the Superclass
Marine Fishes. Chapter 8
 Marine Fishes Chapter 8 Fish Gills The construction of the gill is the same in all fish gill arch supports the entire structure, gill rakers are on the forward surface of the gill arch and gill filaments
Marine Fishes Chapter 8 Fish Gills The construction of the gill is the same in all fish gill arch supports the entire structure, gill rakers are on the forward surface of the gill arch and gill filaments
5/3/15. Vertebrate Evolution Traces a Long and Diverse History. Construction of Complex Chordate Bodies Begins on a Stiffening Scaffold
 Construction of Complex Chordate Bodies Begins on a Stiffening Scaffold Chordata is the most advanced animal phylum. All chordates have, at some time during development, a notochord. Both invertebrate
Construction of Complex Chordate Bodies Begins on a Stiffening Scaffold Chordata is the most advanced animal phylum. All chordates have, at some time during development, a notochord. Both invertebrate
Chordata sm. Other chordates, vertebrata in general, share the additional structures: 1. Segmented body. 2. Endoskeleton.
 Chordata sm Objectives: 1. Identify exterior structures associated with each of the chordates presented. 2. Identify interior morphology associated with respiration, reproduction, digestion and absorption,
Chordata sm Objectives: 1. Identify exterior structures associated with each of the chordates presented. 2. Identify interior morphology associated with respiration, reproduction, digestion and absorption,
Biology. Slide 1 of 53. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 53 Chapter 33 Comparing Chordates 2 of 53 This chapter is a good revision of the material we saw during Unit III. 3 of 53 4 of 53 Controlling Body Temperature The control of body temperature
Biology 1 of 53 Chapter 33 Comparing Chordates 2 of 53 This chapter is a good revision of the material we saw during Unit III. 3 of 53 4 of 53 Controlling Body Temperature The control of body temperature
1. Overview of Chordates
 Chapter 34A: The Origin & Evolution of Vertebrates I 1. Overview of the Chordates 2. Invertebrate Chordates 1. Overview of Chordates Echinodermata ANCESTRAL DEUTEROSTOME NOTOCHORD Common ancestor of chordates
Chapter 34A: The Origin & Evolution of Vertebrates I 1. Overview of the Chordates 2. Invertebrate Chordates 1. Overview of Chordates Echinodermata ANCESTRAL DEUTEROSTOME NOTOCHORD Common ancestor of chordates
Animal Diversity. Kingdom Animalia
 7ch11 Animal Diversity Kingdom Animalia Animal Characteristics 1. animals are eukaryotes and are multicellular 2. cells are specialized for different functions (vision,digestion,reproduction) 3. protein,
7ch11 Animal Diversity Kingdom Animalia Animal Characteristics 1. animals are eukaryotes and are multicellular 2. cells are specialized for different functions (vision,digestion,reproduction) 3. protein,
Animal Diversity III Deuterostomes
 Animal Diversity III Deuterostomes In this third and final animal diversity lab, we will study the deuterostomes, which include phylum echinodermata and phylum chordata. Though echinoderms and chordates
Animal Diversity III Deuterostomes In this third and final animal diversity lab, we will study the deuterostomes, which include phylum echinodermata and phylum chordata. Though echinoderms and chordates
Lesson 27. Objectives: At the end of this lesson you should be able to:
 Lesson 27 Lesson Outline: Evolution of Respiratory Mechanisms Cutaneous Exchange Evolution of Respiratory Mechanisms - Water Breathers o Origin of pharyngeal slits from corner of mouth o Origin of skeletal
Lesson 27 Lesson Outline: Evolution of Respiratory Mechanisms Cutaneous Exchange Evolution of Respiratory Mechanisms - Water Breathers o Origin of pharyngeal slits from corner of mouth o Origin of skeletal
Phylum Chordata Featuring Vertebrate Animals
 Phylum Chordata Featuring Vertebrate Animals Prepared by Diana C. Wheat For Linn-Benton Community College Characteristics All have a notochord: a stiff but flexible rod that extends the length of the body
Phylum Chordata Featuring Vertebrate Animals Prepared by Diana C. Wheat For Linn-Benton Community College Characteristics All have a notochord: a stiff but flexible rod that extends the length of the body
CHAPTER 16 FISHES STUDY GUIDE 16.1 What Is a Fish? A. Approximately 28,000 living species more than all other species of vertebrates combined B.
 CHAPTER 16 FISHES STUDY GUIDE 16.1 What Is a Fish? A. Approximately 28,000 living species more than all other species of vertebrates combined B. Adaptations that have fitted them to almost every conceivable
CHAPTER 16 FISHES STUDY GUIDE 16.1 What Is a Fish? A. Approximately 28,000 living species more than all other species of vertebrates combined B. Adaptations that have fitted them to almost every conceivable
Dorsal hollow nerve chord that forms spinal cord and brain. VERTEBRATES [OVERVIEW - OVERHEAD, similar to fig. 19.1, p. 390]:
![Dorsal hollow nerve chord that forms spinal cord and brain. VERTEBRATES [OVERVIEW - OVERHEAD, similar to fig. 19.1, p. 390]: Dorsal hollow nerve chord that forms spinal cord and brain. VERTEBRATES [OVERVIEW - OVERHEAD, similar to fig. 19.1, p. 390]:](/thumbs/73/69272471.jpg) Phylum Chordata (44,000 species) Dorsal hollow nerve chord that forms spinal cord and brain Notochord at some stage of life cycle Gill slits at some point in life cycle VERTEBRATES [OVERVIEW - OVERHEAD,
Phylum Chordata (44,000 species) Dorsal hollow nerve chord that forms spinal cord and brain Notochord at some stage of life cycle Gill slits at some point in life cycle VERTEBRATES [OVERVIEW - OVERHEAD,
Chordates. Chapter 23
 Chordates Chapter 23 Phylum Chordata By the end of the Cambrian period, 540 million years ago, an astonishing variety of animals inhabited Earth s oceans. One of these types of animals gave rise to vertebrates,
Chordates Chapter 23 Phylum Chordata By the end of the Cambrian period, 540 million years ago, an astonishing variety of animals inhabited Earth s oceans. One of these types of animals gave rise to vertebrates,
Frog Dissection. External Observation
 Frog Dissection External Observation Use the diagram below to locate and identify the external features of the head. Find the mouth, external nares, tympani (ear drum), eyes, and nictitating membranes
Frog Dissection External Observation Use the diagram below to locate and identify the external features of the head. Find the mouth, external nares, tympani (ear drum), eyes, and nictitating membranes
FISH ANATOMY DIAGRAM AND QUESTIONS
 Name Block FISH ANATOMY DIAGRAM AND QUESTIONS External: 1. What percentage of fish are bony fish? 2. What is the operculum s function? 3. The nostrils are used for, not. 4. Which fins keeps the fish level
Name Block FISH ANATOMY DIAGRAM AND QUESTIONS External: 1. What percentage of fish are bony fish? 2. What is the operculum s function? 3. The nostrils are used for, not. 4. Which fins keeps the fish level
Myxiniformes Petromyzontiformes Chondrichthyes Osteichthyes. Before we get to jaws, we need to know something about hard tissues.
 Behold the Gnathostomata: gnathos (jaw) + stoma (mouth) Cephalochordata Urochordata Haikouella Myxiniformes Petromyzontiformes Chondrichthyes Osteichthyes jaws skull proto-vertebrae, true gills, two eyes,
Behold the Gnathostomata: gnathos (jaw) + stoma (mouth) Cephalochordata Urochordata Haikouella Myxiniformes Petromyzontiformes Chondrichthyes Osteichthyes jaws skull proto-vertebrae, true gills, two eyes,
 CHORDATA SK.M.BASHA Phylum Chordata Vertebrates, sea squirts or tunicates, lancelets such as Amphioxus. Name: "Chord" means "string", referring to the nerve cord and/or notochord. Chief characteristics:
CHORDATA SK.M.BASHA Phylum Chordata Vertebrates, sea squirts or tunicates, lancelets such as Amphioxus. Name: "Chord" means "string", referring to the nerve cord and/or notochord. Chief characteristics:
Materials: Field notebook and pencil INTRODUCTION:
 Field Methods of Fish Biology 2014 Exercise 1: Basic Anatomy and Finding and Measuring Characters *Labs modified from Caillet et al. 1986 and Eric Schultz s Biology of Fishes lab Materials: Field notebook
Field Methods of Fish Biology 2014 Exercise 1: Basic Anatomy and Finding and Measuring Characters *Labs modified from Caillet et al. 1986 and Eric Schultz s Biology of Fishes lab Materials: Field notebook
For this assignment, use the Chapter about Fish that is found on my website, NOT YOUR BOOK.
 Name: For this assignment, use the Chapter about Fish that is found on my website, NOT YOUR BOOK. 1. Lampreys and hagfish lack (1) and instead, have many rows of (2) 2. 3. The lamprey is a problem because
Name: For this assignment, use the Chapter about Fish that is found on my website, NOT YOUR BOOK. 1. Lampreys and hagfish lack (1) and instead, have many rows of (2) 2. 3. The lamprey is a problem because
Frog Dissection. PreLab: 1. Where do frogs get their energy? Draw a simple food chain to illustrate.
 Name Date Frog Dissection Class # PreLab: Amphibian Reading As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but they must return to water to reproduce. Eggs are laid
Name Date Frog Dissection Class # PreLab: Amphibian Reading As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but they must return to water to reproduce. Eggs are laid
Virtual Shark Lab. Getting Started
 Virtual Shark Lab Getting Started In this lab you will study the anatomy of the shark. Humans are fascinated by sharks. We are at once repulsed and attracted to these predators. We fear them, often unnecessarily,
Virtual Shark Lab Getting Started In this lab you will study the anatomy of the shark. Humans are fascinated by sharks. We are at once repulsed and attracted to these predators. We fear them, often unnecessarily,
VERTEBRATE EVOLUTION & DIVERSITY
 VERTEBRATE EVOLUTION & DIVERSITY 1 ANIMAL DIVERSITY No true tissues Ancestral protist True tissues Radial symmetry True Animals Bilateral symmetry Bilateral Animals Deuterostomes Lophotrochophores Ecdysozoans
VERTEBRATE EVOLUTION & DIVERSITY 1 ANIMAL DIVERSITY No true tissues Ancestral protist True tissues Radial symmetry True Animals Bilateral symmetry Bilateral Animals Deuterostomes Lophotrochophores Ecdysozoans
Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata. The vertebrates and their relatives
 Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata The vertebrates and their relatives Figure 23.02 Phylum Chordata 5 Characteristics of a chordate 1. A dorsal hollow nerve cord (spinal cord in vertebrates) 2. A notochord
Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata The vertebrates and their relatives Figure 23.02 Phylum Chordata 5 Characteristics of a chordate 1. A dorsal hollow nerve cord (spinal cord in vertebrates) 2. A notochord
Symmetry. Asymmetrical- no shape. Radial- same in half when cut any angle. Bilateral- having a distinct right and left side
 Symmetry Asymmetrical- no shape Radial- same in half when cut any angle Bilateral- having a distinct right and left side Invertebrates 95% of Animals No Backbone The simplest animals and they do not have
Symmetry Asymmetrical- no shape Radial- same in half when cut any angle Bilateral- having a distinct right and left side Invertebrates 95% of Animals No Backbone The simplest animals and they do not have
