Types of Estuaries and Mixing Patterns. Mrs. Stahl Marine Science Honors
|
|
|
- Bertina Lyons
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Types of Estuaries and Mixing Patterns Mrs. Stahl Marine Science Honors
2 Coastal Plain Form between glacial periods, when water from melting glaciers raises the sea level and floods coastal plains and low lying rivers. Ex- Gulf of Mexico, Eastern Atlantic, Chesapeake Bay, and Long Island Sound
3
4
5 Tectonic Estuary Form when geological events, such as earthquakes, cause the land to sink below sea level, allowing seawater to cover it. Ex- San Francisco Bay
6
7 Bar Built Estuary When geographical barriers, such as islands, form walls between FW and SW. Ex- Cape Hatteras, N.C., Texas and Florida Gulf Coasts, Indian River, Fl., and the Coast of Northern Europe.
8 Indian River Lagoon
9 Cape Hatteras, N.C.
10 Fjord Form when glaciers carve large valleys in coastal areas. After the glaciers retreated these valleys filled with water and formed a type of estuary. Ex- Alaska, Along the coast of Scandinavia
11
12
13 Norway Fjord
14 Salinity and Mixing Patterns Foldable Terms to know portion of the foldable: Tidal over-mixing Positive estuary Negative estuary Brackish water Salt wedge Tidal flats Embayments Notes
15 Vocabulary Tidal over-mixing- The denser seawater at the surface tends to sink as the lighter FW beneath it rises, creating a mixing action from the surface to the bottom. Positive estuary- Surface water from the river flows out to sea and SW from the ocean moves into the estuary along the bottom. Negative estuary- Surface water flows toward the river and the water along the bottom moves out to sea. Brackish water- Mixture of FW and SW that is less saline than ocean water.
16 Salt wedge- The angled boundary between SW and FW in an estuary that occurs when the rapid flow of river water prevents the SW from mixing with the FW. Tidal flats- An area of estuary that is exposed at low tide and covered at high tide. Embayments- a recess in a coastline forming a bay.
17
18 Positive estuary
19 Salt Wedge
20 Tidal Flats
21 Embayments
22 Notes to the right of vocab Average salinity is 35 ppt. Strongly influences marine organisms as they work to maintain appropriate levels of salt and water in their bodies. Six ions are responsible for 99% of the dissolved salts in the ocean Sodium Magnesium Calcium Potassium Chloride Sulfate Other 1% are called trace elements
23 Temperature- on the back Relatively shallow- the water temp changes rapidly with changes in air temp. Fluctuates seasonally and daily. Depending on location, some estuaries may freeze in the winter. Tidal currents warm or cool an estuary.
24 Surface water can be cooler in the winter and warmer in the summer than deeper water, as a result of the amount of solar energy reaching the surface. Produces a winter turnover in which cooler / denser surface water sinks and is replaced by warmer, deeper water. Vertical mixing of nutrients gets mixed up and swept back out to sea with the next tide. The mixing that occurs because of turnover circulates nutrients vertically between the water and bottom sediments (upwelling and downwelling).
25
26 Salt Wedge Occur in the mouths of rivers that are flowing into SW. At the surface, FW flows rapidly out to sea, and at the bottom the denser SW flows upstream along the river bottom. Produces an angled boundary known as a salt wedge between the two. Example- Mississippi
27 Mississippi Salt Wedge
28 Well Mixed Estuary River flow is low and tidal currents play a major role in the circulation of the water. Result= seaward flow of water and uniform salinity at all depths. Ex- Delaware Bay
29
30 Partially Mixed Estuary Have a strong surface flow of FW and a strong influx of seawater, which increases salinity. Tidal currents force the seawater upward where it mixes with the surface water, producing a seaward flow of surface water. Rapid exchange of surface water between the estuary and ocean. Examples- Puget Sound and Chesapeake Bay
31
32 Fjord River water remains at the surface and mixes very little with the seawater beneath it.
What is an Estuary? Importance of Estuaries. Importance of Estuaries. Importance of Estuaries
 Oceanography 101, Richard Strickland Lecture 20 What is an Estuary? Portion of the ocean that is semi-enclosed by land and diluted by freshwater runoff All estuaries are embayments But embayments without
Oceanography 101, Richard Strickland Lecture 20 What is an Estuary? Portion of the ocean that is semi-enclosed by land and diluted by freshwater runoff All estuaries are embayments But embayments without
Marginal Marine Environments
 Marginal Marine Environments Delta: discrete shoreline protuberances formed where rivers enter oceans, semi-enclosed seas, lakes or lagoons and supply sediment more rapidly than it can be redistributed
Marginal Marine Environments Delta: discrete shoreline protuberances formed where rivers enter oceans, semi-enclosed seas, lakes or lagoons and supply sediment more rapidly than it can be redistributed
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint. Chapter 15 Earth Science, 12e Tarbuck/Lutgens
 Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 15 Earth Science, 12e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 15 Earth Science, 12e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Ocean Motion Notes. Chapter 13 & 14
 Ocean Motion Notes Chapter 13 & 14 What is a Wave? Wave: movement of energy through a body of water How are Waves Caused? Caused mostly by wind Wind blowing on the water transmits energy to the water Size
Ocean Motion Notes Chapter 13 & 14 What is a Wave? Wave: movement of energy through a body of water How are Waves Caused? Caused mostly by wind Wind blowing on the water transmits energy to the water Size
Tidally influenced environments. By Alex Tkaczyk, Henrique Menezes, and Isaac Foli
 Tidally influenced environments By Alex Tkaczyk, Henrique Menezes, and Isaac Foli Goals and aims Describe the role of tidal influence in depositional environments. - Deltas - Estuaries Provide an overview
Tidally influenced environments By Alex Tkaczyk, Henrique Menezes, and Isaac Foli Goals and aims Describe the role of tidal influence in depositional environments. - Deltas - Estuaries Provide an overview
170 points. 38 points In your textbook, read about modern oceanography. For each item write the word that meets the description.
 Ch 15 Earth s Oceans SECTION 15.1 An Overview of Oceans 38 points In your textbook, read about modern oceanography. For each item write the word that meets the description. (5 points) 1. German research
Ch 15 Earth s Oceans SECTION 15.1 An Overview of Oceans 38 points In your textbook, read about modern oceanography. For each item write the word that meets the description. (5 points) 1. German research
The Chesapeake Bay as an Estuary: An introduction. Istvan A. Urcuyo Gettysburg College
 The Chesapeake Bay as an Estuary: An introduction. Istvan A. Urcuyo Gettysburg College The Chesapeake Bay -Native Americans resided on its shores since 8000 B.C. The Chesapeake Bay -Original Native American
The Chesapeake Bay as an Estuary: An introduction. Istvan A. Urcuyo Gettysburg College The Chesapeake Bay -Native Americans resided on its shores since 8000 B.C. The Chesapeake Bay -Original Native American
Water on Earth. How do oceans relate to weather and the atmosphere? Solar Radiation and Convection Currents
 Earth is often called the Blue Planet because so much of its surface (about 71%) is covered by water. Of all the water on Earth, about 96.5% is held in the world s oceans. As you can imagine, these oceans
Earth is often called the Blue Planet because so much of its surface (about 71%) is covered by water. Of all the water on Earth, about 96.5% is held in the world s oceans. As you can imagine, these oceans
Estuaries: Life on the Interface
 Material adapted from: Estuaries: Interface between sea and land & Sea Margin Diversity, The Water Sourcebook Grades 9-12, EPA http://www.epa.gov/safewater/kids/wsb/ Introduction: Some of the most dynamic
Material adapted from: Estuaries: Interface between sea and land & Sea Margin Diversity, The Water Sourcebook Grades 9-12, EPA http://www.epa.gov/safewater/kids/wsb/ Introduction: Some of the most dynamic
OCEANOGRAPHY STUDY GUIDE
 OCEANOGRAPHY STUDY GUIDE Chapter 2 Section 1 1. Most abundant salt in ocean. Sodium chloride; NaCl 2. Amount of Earth covered by Water 71% 3. Four oceans: What are they? Atlantic, Pacific, Arctic, Indian
OCEANOGRAPHY STUDY GUIDE Chapter 2 Section 1 1. Most abundant salt in ocean. Sodium chloride; NaCl 2. Amount of Earth covered by Water 71% 3. Four oceans: What are they? Atlantic, Pacific, Arctic, Indian
Duckies have been found in Hawaii, Alaska, S. America, Scotland, Washington state and Australia as of 2012.
 Duckies have been found in Hawaii, Alaska, S. America, Scotland, Washington state and Australia as of 2012. We learned that it takes 3 years to complete one circuit of the North Pacific Gyre flow in the
Duckies have been found in Hawaii, Alaska, S. America, Scotland, Washington state and Australia as of 2012. We learned that it takes 3 years to complete one circuit of the North Pacific Gyre flow in the
Ocean Layers. Based on sunlight penetration: Based on water density: Sunlight (photosynthesis is possible) Twilight Midnight
 PART 3 Ocean Layers Based on sunlight penetration: Sunlight (photosynthesis is possible) Twilight Midnight Based on water density: Mixed layer Pycnocline (rapid change of themperature/salinity) Deep ocean
PART 3 Ocean Layers Based on sunlight penetration: Sunlight (photosynthesis is possible) Twilight Midnight Based on water density: Mixed layer Pycnocline (rapid change of themperature/salinity) Deep ocean
Chapter 12: Coasts (after a brief review of Tides)
 Chapter 12: Coasts (after a brief review of Tides) 1 Questions from previous classes: What happens when a wave meets a current? wave = people walking current = bus If wave goes with the current, the wave
Chapter 12: Coasts (after a brief review of Tides) 1 Questions from previous classes: What happens when a wave meets a current? wave = people walking current = bus If wave goes with the current, the wave
5/8/2018. Estuaries are classified by: > Mode of formation e.g. glaciers, deposition, sea level rise. > Patterns of water circulation
 Prepared by Diana Wheat-LBCC Compare and contrast the various types of estuaries, including their origin, size, shape, and general location on earth. Distinguish and describe the different types of habitats
Prepared by Diana Wheat-LBCC Compare and contrast the various types of estuaries, including their origin, size, shape, and general location on earth. Distinguish and describe the different types of habitats
Ocean Currents that Redistribute Heat Globally
 Ocean Currents that Redistribute Heat Globally Ocean Circulation Ocean Currents Fig. CO7 OCEAN CURRENTS Surface ocean currents are similar to wind patterns: 1. Driven by Coriolis forces 2. Driven by winds
Ocean Currents that Redistribute Heat Globally Ocean Circulation Ocean Currents Fig. CO7 OCEAN CURRENTS Surface ocean currents are similar to wind patterns: 1. Driven by Coriolis forces 2. Driven by winds
Lesson: Ocean Circulation
 Lesson: Ocean Circulation By Keith Meldahl Corresponding to Chapter 9: Ocean Circulation As this figure shows, there is a connection between the prevailing easterly and westerly winds (discussed in Chapter
Lesson: Ocean Circulation By Keith Meldahl Corresponding to Chapter 9: Ocean Circulation As this figure shows, there is a connection between the prevailing easterly and westerly winds (discussed in Chapter
Overview. Beach Features. Coastal Regions. Other Beach Profile Features. CHAPTER 10 The Coast: Beaches and Shoreline Processes.
 Overview CHAPTER 10 The Coast: Beaches and Shoreline Processes Coastal regions constantly change. The beach is a dominant coastal feature. Wave activity continually modifies the beach and coastal areas.
Overview CHAPTER 10 The Coast: Beaches and Shoreline Processes Coastal regions constantly change. The beach is a dominant coastal feature. Wave activity continually modifies the beach and coastal areas.
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline. The Restless Oceans
 Chapter 10 Lecture Outline The Restless Oceans Focus Question 10.1 How does the Coriolis effect influence ocean currents? The Ocean s Surface Circulation Ocean currents Masses of water that flow from one
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline The Restless Oceans Focus Question 10.1 How does the Coriolis effect influence ocean currents? The Ocean s Surface Circulation Ocean currents Masses of water that flow from one
Directed Reading. Section: Ocean Currents. a(n). FACTORS THAT AFFECT SURFACE CURRENTS
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Ocean Currents 1. A horizontal movement of water in a well-defined pattern is called a(n). 2. What are two ways that oceanographers identify ocean currents? 3.
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Ocean Currents 1. A horizontal movement of water in a well-defined pattern is called a(n). 2. What are two ways that oceanographers identify ocean currents? 3.
Coastal issues: Beaches and Estuaries. Recent Sea Level: Beaches: Baltimore D.C. Patomac R. Chesapeake Bay
 Coastal issues: Beaches and Estuaries Definitions: Coast = broad zone where both marine & terrestrial processes act It includes the beach, lagoons, marshes, bars etc. Coastal processes act to shape the
Coastal issues: Beaches and Estuaries Definitions: Coast = broad zone where both marine & terrestrial processes act It includes the beach, lagoons, marshes, bars etc. Coastal processes act to shape the
The Movement of Ocean Water. Currents
 The Movement of Ocean Water Currents Ocean Current movement of ocean water that follows a regular pattern influenced by: weather Earth s rotation position of continents Surface current horizontal movement
The Movement of Ocean Water Currents Ocean Current movement of ocean water that follows a regular pattern influenced by: weather Earth s rotation position of continents Surface current horizontal movement
Shore - place where ocean meets land Coast - refers to the larger zone affected by the processes that occur at this boundary.
 Waves, Beaches, and Coasts Shore - place where ocean meets land Coast - refers to the larger zone affected by the processes that occur at this boundary. Waves: energy moving through water The height of
Waves, Beaches, and Coasts Shore - place where ocean meets land Coast - refers to the larger zone affected by the processes that occur at this boundary. Waves: energy moving through water The height of
Questions # 4 7 refer to Figure # 2 (page 321, Fig )
 Shoreline Community College OCEANOGRAPHY 101 Fall 2006 Sample Exam # 3 Instructor: Linda Khandro Questions # 1 3 refer to Figure # 1 (page 284, Fig 11.7) 1. At which position is the moon in its new moon
Shoreline Community College OCEANOGRAPHY 101 Fall 2006 Sample Exam # 3 Instructor: Linda Khandro Questions # 1 3 refer to Figure # 1 (page 284, Fig 11.7) 1. At which position is the moon in its new moon
Chapter 9 Insolation control of monsoons 2004/4/15
 Chapter 9 Insolation control of monsoons 2004/4/15 Introduction Monsoon circulations exist on Earth today because the land responds to seasonal changes in solar radiation much more quickly than does the
Chapter 9 Insolation control of monsoons 2004/4/15 Introduction Monsoon circulations exist on Earth today because the land responds to seasonal changes in solar radiation much more quickly than does the
Chapter 22, Section 1 - Ocean Currents. Section Objectives
 Chapter 22, Section 1 - Ocean Currents Section Objectives Intro Surface Currents Factors Affecting Ocean Currents Global Wind Belts (you should draw and label a diagram of the global wind belts) The Coriolis
Chapter 22, Section 1 - Ocean Currents Section Objectives Intro Surface Currents Factors Affecting Ocean Currents Global Wind Belts (you should draw and label a diagram of the global wind belts) The Coriolis
CHAPTER 7 Ocean Circulation
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 CHAPTER 7 Ocean Circulation Words Ocean currents Moving seawater Surface ocean currents Transfer heat from warmer to cooler areas Similar to pattern of major wind belts
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 CHAPTER 7 Ocean Circulation Words Ocean currents Moving seawater Surface ocean currents Transfer heat from warmer to cooler areas Similar to pattern of major wind belts
Deep Water Currents Lab
 Deep Water Currents Lab Background: Anyone visiting the seashore is struck by the constant motion of water traveling on the surface of the ocean in the form of waves. But beneath the ocean's surface, water
Deep Water Currents Lab Background: Anyone visiting the seashore is struck by the constant motion of water traveling on the surface of the ocean in the form of waves. But beneath the ocean's surface, water
Agronomy 406 World Climates
 Agronomy 406 World Climates January 30, 2018 Monsoons. Ocean properties and circulation. Review for today: Online textbook: 1.3.1 (Sea water) Composition and properties. For Thursday: Rahmstorf, S.: The
Agronomy 406 World Climates January 30, 2018 Monsoons. Ocean properties and circulation. Review for today: Online textbook: 1.3.1 (Sea water) Composition and properties. For Thursday: Rahmstorf, S.: The
Today: Coastal Issues and Estuaries
 Today: Coastal Issues and Estuaries Coastal issues Human effect on coastlines What is an estuary Why are they so important? Circulation of water in estuary Environmental issues Coastal Issues: Problem
Today: Coastal Issues and Estuaries Coastal issues Human effect on coastlines What is an estuary Why are they so important? Circulation of water in estuary Environmental issues Coastal Issues: Problem
Shorelines Earth - Chapter 20 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College
 Shorelines Earth - Chapter 20 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The Shoreline A Dynamic Interface The shoreline is a dynamic interface (common boundary) among air, land, and the ocean. The shoreline
Shorelines Earth - Chapter 20 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The Shoreline A Dynamic Interface The shoreline is a dynamic interface (common boundary) among air, land, and the ocean. The shoreline
Montessori for Everyone 2013 Types of Coastlines
 Coast The coast is the part of the land that borders the sea. It is subject to constant change, as the result of the waves and deposits carried by water onto the land. Coastline The coastline is where
Coast The coast is the part of the land that borders the sea. It is subject to constant change, as the result of the waves and deposits carried by water onto the land. Coastline The coastline is where
There are many different kinds of beaches which are generally characterized by the dominance of waves, tides, rivers and currents, and in particular
 Fig. 11-11, p. 253 There are many different kinds of beaches which are generally characterized by the dominance of waves, tides, rivers and currents, and in particular differ by the amount of energy, which
Fig. 11-11, p. 253 There are many different kinds of beaches which are generally characterized by the dominance of waves, tides, rivers and currents, and in particular differ by the amount of energy, which
OCN-201 Chemistry and Physics section
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ OCN-201 Chemistry and Physics section True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Because of the dissolved salt in seawater its freezing point is lower than that
Name: Class: _ Date: _ OCN-201 Chemistry and Physics section True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Because of the dissolved salt in seawater its freezing point is lower than that
Lecture 5.1 Surface Ocean Circulation. Image from Daily Mail Newspaper, UK
 Lecture 5.1 Surface Ocean Circulation Image from Daily Mail Newspaper, UK Announcements Midterm is Thursday, consists of 25 multiple choice, 3 pages short answer questions No Scantron needed Calculators,
Lecture 5.1 Surface Ocean Circulation Image from Daily Mail Newspaper, UK Announcements Midterm is Thursday, consists of 25 multiple choice, 3 pages short answer questions No Scantron needed Calculators,
Earth s oceans covers 71 % _ of the planet s surface. In reality, Earth s ocean waters are all. interconnected as part of a single large global ocean.
 Ocean Motion Met 101: Introduction to the World's Oceans Produced by The COMET Program Geography: Name Pd. Earth s oceans covers 71 % _ of the planet s surface. In reality, Earth s ocean waters are all
Ocean Motion Met 101: Introduction to the World's Oceans Produced by The COMET Program Geography: Name Pd. Earth s oceans covers 71 % _ of the planet s surface. In reality, Earth s ocean waters are all
W3 Global Circulation Systems
 W3 Global Circulation Systems Which regions of Earth receive the most energy from the Sun? If not for global circulation systems There would only be two narrow regions that would support life What
W3 Global Circulation Systems Which regions of Earth receive the most energy from the Sun? If not for global circulation systems There would only be two narrow regions that would support life What
What is an ocean current? 1. wind action: the force of the wind blowing over the top of the water 2. spin of Earth 3. shape of the continents
 Ocean Currents Textbook pages 414 427 Before You Read Section 11.2 Summary What forces do you think cause ocean water to move? Do you think ocean water moves the same way everywhere in the ocean? Write
Ocean Currents Textbook pages 414 427 Before You Read Section 11.2 Summary What forces do you think cause ocean water to move? Do you think ocean water moves the same way everywhere in the ocean? Write
The ocean water is dynamic. Its physical
 CHAPTER MOVEMENTS OF OCEAN WATER The ocean water is dynamic. Its physical characteristics like temperature, salinity, density and the external forces like of the sun, moon and the winds influence the movement
CHAPTER MOVEMENTS OF OCEAN WATER The ocean water is dynamic. Its physical characteristics like temperature, salinity, density and the external forces like of the sun, moon and the winds influence the movement
Our Climate: A Global Challenge. Academy of Lifelong Learning Denver, CO April 9, 2015
 Our Climate: A Global Challenge Academy of Lifelong Learning Denver, CO April 9, 2015 Oceans Thermohaline Circulation It takes water 500 to 1000 years to go around the planet. Thermohaline Circulation,
Our Climate: A Global Challenge Academy of Lifelong Learning Denver, CO April 9, 2015 Oceans Thermohaline Circulation It takes water 500 to 1000 years to go around the planet. Thermohaline Circulation,
Chapter - Oceans and Coasts
 Chapter - Oceans and Coasts Discussion: What do oceans contribute to the environment of Earth? How do Earth s major systems relate to the oceans? Oceans and Coasts Oceans are important - Thermal regulation
Chapter - Oceans and Coasts Discussion: What do oceans contribute to the environment of Earth? How do Earth s major systems relate to the oceans? Oceans and Coasts Oceans are important - Thermal regulation
The Composition of Seawater
 The Composition of Seawater Salinity Salinity is the total amount of solid material dissolved in water. Most of the salt in seawater is sodium chloride, common table salt. Element Percent Element Percent
The Composition of Seawater Salinity Salinity is the total amount of solid material dissolved in water. Most of the salt in seawater is sodium chloride, common table salt. Element Percent Element Percent
Assessment Schedule 2016 Earth and Space Science: Demonstrate understanding of processes in the ocean system (91413)
 NCEA Level 3 Earth & Space Science (91413) 2016 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2016 Earth and Space Science: Demonstrate processes in the ocean system (91413) Evidence Statement Q Evidence with with Excellence
NCEA Level 3 Earth & Space Science (91413) 2016 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2016 Earth and Space Science: Demonstrate processes in the ocean system (91413) Evidence Statement Q Evidence with with Excellence
Introduction to Physical Oceanography STUDENT NOTES Date: 1. What do you know about solar radiation at different parts of the world?
 Introduction to Physical Oceanography STUDENT NOTES Date: 1 Warm up What do you know about solar radiation at different parts of the world? What affect does the tilt of the Earth have on the northern and
Introduction to Physical Oceanography STUDENT NOTES Date: 1 Warm up What do you know about solar radiation at different parts of the world? What affect does the tilt of the Earth have on the northern and
Essentials of Oceanography Eleventh Edition
 Chapter Chapter 1 10 Clickers Lecture Essentials of Oceanography Eleventh Edition The Coast: Beaches and Shoreline Processes Alan P. Trujillo Harold V. Thurman Chapter Overview Coastal regions have distinct
Chapter Chapter 1 10 Clickers Lecture Essentials of Oceanography Eleventh Edition The Coast: Beaches and Shoreline Processes Alan P. Trujillo Harold V. Thurman Chapter Overview Coastal regions have distinct
EARTH, PLANETARY, & SPACE SCIENCES 15 INTRODUCTION TO OCEANOGRAPHY. LABORATORY SESSION #6 Fall Ocean Circulation
 EARTH, PLANETARY, & SPACE SCIENCES 15 INTRODUCTION TO OCEANOGRAPHY LABORATORY SESSION #6 Fall 2017 Ocean Circulation The focus of the Lab this week is circulation of the ocean and atmosphere. Here, you
EARTH, PLANETARY, & SPACE SCIENCES 15 INTRODUCTION TO OCEANOGRAPHY LABORATORY SESSION #6 Fall 2017 Ocean Circulation The focus of the Lab this week is circulation of the ocean and atmosphere. Here, you
OCN 201, Chemistry & Physics Section
 , A 1-April-2015 Name: Answer the True/False and Multiple Choice questions on the scantron sheet. Answer the remaining questions on this exam handout. Turn in both the scantron and exam at the end of class.
, A 1-April-2015 Name: Answer the True/False and Multiple Choice questions on the scantron sheet. Answer the remaining questions on this exam handout. Turn in both the scantron and exam at the end of class.
Examples of estuaries include bays, sounds, salt marshes, mangrove forests, mud flats, swamps, inlets, and sloughs.
 An estuary is a partially enclosed body of water where incoming seawater is mixed with fresh water coming from the land. Examples of estuaries include bays, sounds, salt marshes, mangrove forests, mud
An estuary is a partially enclosed body of water where incoming seawater is mixed with fresh water coming from the land. Examples of estuaries include bays, sounds, salt marshes, mangrove forests, mud
NYS Coastal Waters. Water Resources of NYS: THE NATURE of the COASTAL ZONE. NYS Coastal Waters. NYS Coastal Atlas. Coastal Zone Management 10/10/2014
 Water Resources of NYS: THE NATURE of the COASTAL ZONE NYS Coastal Waters NYS is the only state to border the Atlantic Ocean and the Great Lakes (Lakes Erie and Ontario). Great Lakes shoreline: 577 miles
Water Resources of NYS: THE NATURE of the COASTAL ZONE NYS Coastal Waters NYS is the only state to border the Atlantic Ocean and the Great Lakes (Lakes Erie and Ontario). Great Lakes shoreline: 577 miles
Role of the oceans in the climate system
 Role of the oceans in the climate system heat exchange and transport hydrological cycle and air-sea exchange of moisture wind, currents, and upwelling gas exchange and carbon cycle Heat transport Two Primary
Role of the oceans in the climate system heat exchange and transport hydrological cycle and air-sea exchange of moisture wind, currents, and upwelling gas exchange and carbon cycle Heat transport Two Primary
Midterm Exam III November 25, 2:10
 Midterm Exam III November 25, 2:10 25, 2:10 3:25 pm, HW714 Chapters 7 (7.12 7.17), 8 and 9 (through section 9.15, included) 60 multiple choice questions this exam constitutes 22% (only) of your total (overall)
Midterm Exam III November 25, 2:10 25, 2:10 3:25 pm, HW714 Chapters 7 (7.12 7.17), 8 and 9 (through section 9.15, included) 60 multiple choice questions this exam constitutes 22% (only) of your total (overall)
Chapter. The Dynamic Ocean
 Chapter The Dynamic Ocean An ocean current is the mass of ocean water that flows from one place to another. 16.1 The Composition of Seawater Surface Circulation Surface Currents Surface currents are movements
Chapter The Dynamic Ocean An ocean current is the mass of ocean water that flows from one place to another. 16.1 The Composition of Seawater Surface Circulation Surface Currents Surface currents are movements
Name Date Class. Overview Oceans. Directions: Use the following terms to complete the concept map below. wind salts climate gases.
 Directed Reading for Content Mastery Overview Oceans Directions: Use the following terms to complete the concept map below. wind salts climate gases densitytides nekton Seawater contains dissolved 1. and
Directed Reading for Content Mastery Overview Oceans Directions: Use the following terms to complete the concept map below. wind salts climate gases densitytides nekton Seawater contains dissolved 1. and
Name: OBJECTIVES: By the end of today s lesson, you will be able to
 7 th Grade Science Unit: Water s Cycles and Patterns Lesson: WCP 21 Name: Date: Monday, October 3, 2016 Homeroom: _ OBJECTIVES: By the end of today s lesson, you will be able to SWBAT Explain how currents
7 th Grade Science Unit: Water s Cycles and Patterns Lesson: WCP 21 Name: Date: Monday, October 3, 2016 Homeroom: _ OBJECTIVES: By the end of today s lesson, you will be able to SWBAT Explain how currents
Winds and Ocean Circulations
 Winds and Ocean Circulations AT 351 Lab 5 February 20, 2008 Sea Surface Temperatures 1 Temperature Structure of the Ocean Ocean Currents 2 What causes ocean circulation? The direction of most ocean currents
Winds and Ocean Circulations AT 351 Lab 5 February 20, 2008 Sea Surface Temperatures 1 Temperature Structure of the Ocean Ocean Currents 2 What causes ocean circulation? The direction of most ocean currents
Section 6. The Surface Circulation of the Ocean. What Do You See? Think About It. Investigate. Learning Outcomes
 Chapter 5 Winds, Oceans, Weather, and Climate Section 6 The Surface Circulation of the Ocean What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Understand the general paths of surface ocean currents.
Chapter 5 Winds, Oceans, Weather, and Climate Section 6 The Surface Circulation of the Ocean What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Understand the general paths of surface ocean currents.
Earth Science Chapter 16 Section 3 Review
 Name: Class: Date: Earth Science Chapter 16 Section 3 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The movement of water that parallels the shore
Name: Class: Date: Earth Science Chapter 16 Section 3 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The movement of water that parallels the shore
Introduction to Oceanography OCE 1001
 Introduction to Oceanography OCE 1001 Lecture Notes Chantale Bégin & Jessica Fry Version 2.1 10. Ocean Circulation (Trujillo, Chapter 7) Major ocean currents are stable and predictable; they have been
Introduction to Oceanography OCE 1001 Lecture Notes Chantale Bégin & Jessica Fry Version 2.1 10. Ocean Circulation (Trujillo, Chapter 7) Major ocean currents are stable and predictable; they have been
HYDROSPHERE, OCEANS AND TIDES
 HYDROSPHERE, OCEANS AND TIDES Revision 10x10learning.com 1 Chapter 12. In the Earth s Atmosphere On surface of the Earth Under the ground Hydrosphere comprises of ALL WATER Water Vapour = 0.001% Is very
HYDROSPHERE, OCEANS AND TIDES Revision 10x10learning.com 1 Chapter 12. In the Earth s Atmosphere On surface of the Earth Under the ground Hydrosphere comprises of ALL WATER Water Vapour = 0.001% Is very
UNDERSTANDING YOUR ESTUARY Level IA- ESTUARY SEARCH
 UNDERSTANDING YOUR ESTUARY Level IA- ESTUARY SEARCH Kakagon/Bad River Sloughs, a Lake Superior estuary located on the Bad River Reservation near Ashland, WI. GOAL Select one Wisconsin estuary to study
UNDERSTANDING YOUR ESTUARY Level IA- ESTUARY SEARCH Kakagon/Bad River Sloughs, a Lake Superior estuary located on the Bad River Reservation near Ashland, WI. GOAL Select one Wisconsin estuary to study
The Ocean is a Geophysical Fluid Like the Atmosphere. The Physical Ocean. Yet Not Like the Atmosphere. ATS 760 Global Carbon Cycle The Physical Ocean
 The Physical Ocean The Ocean is a Geophysical Fluid Like the Atmosphere Three real forces: Gravity Pressure gradients Friction Two apparent forces: Coriolis and Centrifugal Geostrophic & Hydrostatic balances
The Physical Ocean The Ocean is a Geophysical Fluid Like the Atmosphere Three real forces: Gravity Pressure gradients Friction Two apparent forces: Coriolis and Centrifugal Geostrophic & Hydrostatic balances
10% water in the world is tied up in the surface ocean currents. (above the pycnocline) Primary source is wind: Westerlies, Trades, Polar Easterlies
 Oceanography Chapter 9 10% water in the world is tied up in the surface ocean currents. (above the pycnocline) Primary source is wind: Westerlies, Trades, Polar Easterlies Coriolis deflects winds (and
Oceanography Chapter 9 10% water in the world is tied up in the surface ocean currents. (above the pycnocline) Primary source is wind: Westerlies, Trades, Polar Easterlies Coriolis deflects winds (and
OCN201 Spring14 1. Name: Class: Date: True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false.
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ OCN201 Spring14 1 True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Short residence time elements are uniformly distributed in the oceans 2. Thermohaline circulation
Name: Class: _ Date: _ OCN201 Spring14 1 True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Short residence time elements are uniformly distributed in the oceans 2. Thermohaline circulation
Essential Fish Habitat Description Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua)
 Description Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) In its Report to Congress: Status of the Fisheries of the United States (September 1997), NMFS determined the Gulf of Maine stock of cod is considered overfished,
Description Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) In its Report to Congress: Status of the Fisheries of the United States (September 1997), NMFS determined the Gulf of Maine stock of cod is considered overfished,
surface salinities temperature profiles of the ocean; the thermocline seawater density dynamics deep ocean pressures
 NATURE OF SEAWATER: SALINITY, TEMPERATURE, DENSITY, AND PRESSURE surface salinities temperature profiles of the ocean; the thermocline seawater density dynamics deep ocean pressures Part A. Surface Salinities
NATURE OF SEAWATER: SALINITY, TEMPERATURE, DENSITY, AND PRESSURE surface salinities temperature profiles of the ocean; the thermocline seawater density dynamics deep ocean pressures Part A. Surface Salinities
Coastal management has lagged behind the growth in population leading to problems with pollution
 Fifty percent of the population of the industrialized world lives within 100 km of a coast. Coastal management has lagged behind the growth in population leading to problems with pollution and natural
Fifty percent of the population of the industrialized world lives within 100 km of a coast. Coastal management has lagged behind the growth in population leading to problems with pollution and natural
Coastal Zones. Coastal Zones
 Page 1 of 15 EENS 3050 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Coastal Zones Coastal Zones A coastal zone is the interface between the land and water. These zones are important because
Page 1 of 15 EENS 3050 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Coastal Zones Coastal Zones A coastal zone is the interface between the land and water. These zones are important because
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore ESTU ARY wetland For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources,
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore ESTU ARY wetland For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources,
COASTAL ENVIRONMENTS. 454 lecture 12
 COASTAL ENVIRONMENTS Repeated movement of sediment & water constructs a beach profile reflecting the balance between average daily or seasonal wave forces and resistance of landmass to wave action Coasts
COASTAL ENVIRONMENTS Repeated movement of sediment & water constructs a beach profile reflecting the balance between average daily or seasonal wave forces and resistance of landmass to wave action Coasts
Ocean Motion. Ocean Currents. Before You Read. Read to Learn
 chapter 18 3 Ocean Motion section 2 Ocean Currents What You ll Learn the Coriolis effect what influences surface currents the temperature of coastal waters about density currents Before You Read Imagine
chapter 18 3 Ocean Motion section 2 Ocean Currents What You ll Learn the Coriolis effect what influences surface currents the temperature of coastal waters about density currents Before You Read Imagine
Currents & Gyres Notes
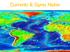 Currents & Gyres Notes Current A river of water flowing in the ocean. 2 Types of Currents Surface Currents wind-driven currents that occur in the top 100m or less Deep Currents density-driven currents
Currents & Gyres Notes Current A river of water flowing in the ocean. 2 Types of Currents Surface Currents wind-driven currents that occur in the top 100m or less Deep Currents density-driven currents
4/20/17. #30 - Coastlines - General Principles Coastlines - Overview
 Writing Assignment Due one week from today by 11:59 pm See main class web pages for detailed instructions Essays will be submitted in Illinois Compass (instructions later) Pick one: Earthquakes, tsunamis,
Writing Assignment Due one week from today by 11:59 pm See main class web pages for detailed instructions Essays will be submitted in Illinois Compass (instructions later) Pick one: Earthquakes, tsunamis,
Current: large mass of continuously moving ocean water
 Ocean Currents Current: large mass of continuously moving ocean water Surface Currents--Wind Circulation These waters make up about 10% of all the water in the ocean. These waters are the upper 400 meters
Ocean Currents Current: large mass of continuously moving ocean water Surface Currents--Wind Circulation These waters make up about 10% of all the water in the ocean. These waters are the upper 400 meters
Ocean Circulation. Si Hui Lee and Frances Wen. You can access ME at
 Ocean Circulation Si Hui Lee and Frances Wen You can access ME at http://tinyurl.com/oceancirculation Earth - the blue planet - 71% area covered by the oceans - 3/4 of ocean area between 3000-6000m deep
Ocean Circulation Si Hui Lee and Frances Wen You can access ME at http://tinyurl.com/oceancirculation Earth - the blue planet - 71% area covered by the oceans - 3/4 of ocean area between 3000-6000m deep
General Oceanography Geology 105 Expedition #19 The Ocean and Climate
 General Oceanography Geology 105 Expedition #19 The Ocean and Climate Name Not attempting to answer questions on expeditions will result in point deductions on course workbook (two or more blank answers
General Oceanography Geology 105 Expedition #19 The Ocean and Climate Name Not attempting to answer questions on expeditions will result in point deductions on course workbook (two or more blank answers
Write about this. Have you ever experienced a very strong wind gust? What happened? Have you ever felt a gentle breeze? What did it feel like?
 Write about this. Have you ever experienced a very strong wind gust? What happened? Have you ever felt a gentle breeze? What did it feel like? How wind works Winds flow on earth based on differences in
Write about this. Have you ever experienced a very strong wind gust? What happened? Have you ever felt a gentle breeze? What did it feel like? How wind works Winds flow on earth based on differences in
Air Masses and Fronts
 Air Masses and Fronts A huge body of air that has similar temperature, humidity, and air pressure at any given height is called an air mass. A single air mass may spread over millions of square kilometers
Air Masses and Fronts A huge body of air that has similar temperature, humidity, and air pressure at any given height is called an air mass. A single air mass may spread over millions of square kilometers
GEOGRAPHY - STD 8 [ ] Q1.
![GEOGRAPHY - STD 8 [ ] Q1. GEOGRAPHY - STD 8 [ ] Q1.](/thumbs/84/90631870.jpg) GEOGRAPHY - STD 8 Movements of Oceans [2016-2017] Q1. Name the two types of regular movements in the oceans. Ans. The regular movements in the ocean are of two types: 1. Horizontal Ocean currents 2. Vertical
GEOGRAPHY - STD 8 Movements of Oceans [2016-2017] Q1. Name the two types of regular movements in the oceans. Ans. The regular movements in the ocean are of two types: 1. Horizontal Ocean currents 2. Vertical
Ocean Current Worksheet
 Ocean Current Worksheet Temperature Affects and Surface Currents: Surface waters of the Earth s oceans are forced to move, primarily by winds. Where winds blow in the same direction for a long period of
Ocean Current Worksheet Temperature Affects and Surface Currents: Surface waters of the Earth s oceans are forced to move, primarily by winds. Where winds blow in the same direction for a long period of
OCN Second Exam Spring 2010 Test Form
 Name Signature Student ID# OCN 201-1 Second Exam Spring 2010 Test Form Answer questions 1-61 on the computer scan sheet. Use a dark (#2) pencil only, and make your marks neatly within the circles. If you
Name Signature Student ID# OCN 201-1 Second Exam Spring 2010 Test Form Answer questions 1-61 on the computer scan sheet. Use a dark (#2) pencil only, and make your marks neatly within the circles. If you
Physical Geography. Physical Geography III of the United States and Canada. Formation of Great Lakes. Climates of North America. Definitions 2/21/2013
 Physical Geography III of the United States and Canada Ancient Glacial Lakes As the Ice Age ended, areas of North America beyond the terminal moraine were flooded with melt water Prof Anthony Grande AFG
Physical Geography III of the United States and Canada Ancient Glacial Lakes As the Ice Age ended, areas of North America beyond the terminal moraine were flooded with melt water Prof Anthony Grande AFG
Canada s vast size creates a diverse range of weather conditions and climatic conditions. Warming trend for last 10 years Wet Spring Dry five summers
 Chapter 4 Weather and Climate Canada s vast size creates a diverse range of weather conditions and climatic conditions. Weather examples: Rainy today Snow tomorrow Fog on Wednesday 23 degree C today High
Chapter 4 Weather and Climate Canada s vast size creates a diverse range of weather conditions and climatic conditions. Weather examples: Rainy today Snow tomorrow Fog on Wednesday 23 degree C today High
Bell Ringer. taking next year? 1. This is the first day of the last term. Set. 2. What science are you planning on
 Bell Ringer 1. This is the first day of the last term. Set a specific goal for these last 2.5 months (not just get good grades or don t fail or wake up on time. How are you going to do these things. Set
Bell Ringer 1. This is the first day of the last term. Set a specific goal for these last 2.5 months (not just get good grades or don t fail or wake up on time. How are you going to do these things. Set
3/9/2013. Build house on cliff for a view of the ocean - be one with said view Pearson Education, Inc. Shorelines: summary in haiku form
 Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e Edward A. Keller Shorelines: summary in haiku form Chapter 11 Coastal Processes Lecture Presentation prepared by X. Mara Chen, Salisbury University Build house
Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e Edward A. Keller Shorelines: summary in haiku form Chapter 11 Coastal Processes Lecture Presentation prepared by X. Mara Chen, Salisbury University Build house
GEOLOGY 101 Under the Boardwalk: Coastal Geomorphology
 GEOLOGY 101 Under the Boardwalk: Coastal Geomorphology What to look for while you're on the beach during spring break. J.S. Kite, WVU What Causes Changes in Sea Level? Answer Varies with Time Scale. Long-Term
GEOLOGY 101 Under the Boardwalk: Coastal Geomorphology What to look for while you're on the beach during spring break. J.S. Kite, WVU What Causes Changes in Sea Level? Answer Varies with Time Scale. Long-Term
Under the Boardwalk: Coastal Geomorphology
 Under the Boardwalk: Coastal Geomorphology What to look for while you're on the beach during spring break. What Causes Changes in Sea Level? Answer Varies with Time Scale. Long-Term Changes in Sea Level
Under the Boardwalk: Coastal Geomorphology What to look for while you're on the beach during spring break. What Causes Changes in Sea Level? Answer Varies with Time Scale. Long-Term Changes in Sea Level
Chapter 9: Circulation of the Ocean
 Chapter 9: Circulation of the Ocean Tropical gardens on Britain s Scilly Isles. Only 48 kilometers (30 miles) off the coast of Cornwall at 50 N, these scenic islands lie in the path of the warm waters
Chapter 9: Circulation of the Ocean Tropical gardens on Britain s Scilly Isles. Only 48 kilometers (30 miles) off the coast of Cornwall at 50 N, these scenic islands lie in the path of the warm waters
Seawater. Earth is an Ocean Planet
 Seawater Earth is an Ocean Planet Topics Origin of the Ocean and Atmosphere Hydrologic Cycle Biogeochemical Cycle Seawater Salinity Variations in Seawater Chemistry Carbonic Acid System Topics Origin of
Seawater Earth is an Ocean Planet Topics Origin of the Ocean and Atmosphere Hydrologic Cycle Biogeochemical Cycle Seawater Salinity Variations in Seawater Chemistry Carbonic Acid System Topics Origin of
1.5 How do ocean waves and currents change the face of coastal areas? (Chapter 3)
 1.5 How do ocean waves and currents change the face of coastal areas? (Chapter 3) 1. Hydraulic Action/Pressure - air being forced into crack in rocks. 2. Corrosion (Solution) Minerals such as calcium carbonate
1.5 How do ocean waves and currents change the face of coastal areas? (Chapter 3) 1. Hydraulic Action/Pressure - air being forced into crack in rocks. 2. Corrosion (Solution) Minerals such as calcium carbonate
Quiz name: Oceanography - Land and Sea Interaction - Quiz #2
 Name: Quiz name: Oceanography - Land and Sea Interaction - Quiz #2 ate: 1. What is the direction of spin for gyres in the northern hemisphere? clockwise counter clockwise northern oscillation southern
Name: Quiz name: Oceanography - Land and Sea Interaction - Quiz #2 ate: 1. What is the direction of spin for gyres in the northern hemisphere? clockwise counter clockwise northern oscillation southern
COASTAL UPWELLING - MONTEREY BAY CALIFORNIA (modified from The Maury Project, AMS)
 Name: Date: Per: COASTAL UPWELLING - MONTEREY BAY CALIFORNIA (modified from The Maury Project, AMS) The ocean is composed of 3 distinct layers: the shallow surface mixed zone, the transition zone, and
Name: Date: Per: COASTAL UPWELLING - MONTEREY BAY CALIFORNIA (modified from The Maury Project, AMS) The ocean is composed of 3 distinct layers: the shallow surface mixed zone, the transition zone, and
Reading Material. Inshore oceanography, Anikouchine and Sternberg The World Ocean, Prentice-Hall
 Reading Material Inshore oceanography, Anikouchine and Sternberg The World Ocean, Prentice-Hall BEACH PROCESSES AND COASTAL ENVIRONMENTS COASTAL FEATURES Cross section Map view Terminology for Coastal
Reading Material Inshore oceanography, Anikouchine and Sternberg The World Ocean, Prentice-Hall BEACH PROCESSES AND COASTAL ENVIRONMENTS COASTAL FEATURES Cross section Map view Terminology for Coastal
Estuaries. Lecture 18
 Estuaries Lecture 18 Estuaries. Estuaries are places where fresh and salt water mix. Typically they occur where rivers enter the sea. Estero Limantour, Drakes Bay, Point Reyes National Seashore. Estuary
Estuaries Lecture 18 Estuaries. Estuaries are places where fresh and salt water mix. Typically they occur where rivers enter the sea. Estero Limantour, Drakes Bay, Point Reyes National Seashore. Estuary
Oceans and Coasts. Chapter 18
 Oceans and Coasts Chapter 18 Exploring the oceans The ocean floor Sediments thicken and the age of the seafloor increases from ridge to shore The continental shelf off the northeast United States Constituent
Oceans and Coasts Chapter 18 Exploring the oceans The ocean floor Sediments thicken and the age of the seafloor increases from ridge to shore The continental shelf off the northeast United States Constituent
Essential Fish Habitat Description Atlantic herring (Clupea harengus)
 Description Atlantic herring (Clupea harengus) In its Report to Congress: Status of the Fisheries of the United States (September 1997), NMFS determined Atlantic herring is not currently overfished. This
Description Atlantic herring (Clupea harengus) In its Report to Congress: Status of the Fisheries of the United States (September 1997), NMFS determined Atlantic herring is not currently overfished. This
Chapter 8 Air Masses
 Chapter 8 Air Masses Air Masses - 1 1. An Air Mass is a large body of air usually about 1500 km across and several km thick, that has homogeneous physical properties. 2. The important physical properties
Chapter 8 Air Masses Air Masses - 1 1. An Air Mass is a large body of air usually about 1500 km across and several km thick, that has homogeneous physical properties. 2. The important physical properties
Essential Fish Habitat Description White hake (Urophycis tenuis)
 Description White hake (Urophycis tenuis) In its Report to Congress: Status of the Fisheries of the United States (September 1997), NMFS determined white hake is not currently overfished, but it is approaching
Description White hake (Urophycis tenuis) In its Report to Congress: Status of the Fisheries of the United States (September 1997), NMFS determined white hake is not currently overfished, but it is approaching
Synoptic Lab, MET 421, Test 2
 Name Synoptic Lab, MET 421, Test 2 1) For a 15 ms -1 east wind blowing towards Milwaukee a) Calculate the distance to the east shore of Lake Michigan. You can use a distance calculator website such as
Name Synoptic Lab, MET 421, Test 2 1) For a 15 ms -1 east wind blowing towards Milwaukee a) Calculate the distance to the east shore of Lake Michigan. You can use a distance calculator website such as
Monday, October 2, Watch for new assessment (Week 4/5 review) TA s have your tests, please see key (at course website)
 Monday, October 2, 2017 Watch for new assessment (Week 4/5 review) TA s have your tests, please see key (at course website) Homework 3 Due date Wednesday, Oct 11 (8 pm) Be ready to watch another important
Monday, October 2, 2017 Watch for new assessment (Week 4/5 review) TA s have your tests, please see key (at course website) Homework 3 Due date Wednesday, Oct 11 (8 pm) Be ready to watch another important
BEACH PROCESSES AND COASTAL ENVIRONMENTS
 BEACH PROCESSES AND COASTAL ENVIRONMENTS COASTAL FEATURES Cross section Map view TOPICS: Terminology Waves Beach Morphology Barriers Coastal Migration Tides Tidal Flats and Marshes Sediment Budgets Human
BEACH PROCESSES AND COASTAL ENVIRONMENTS COASTAL FEATURES Cross section Map view TOPICS: Terminology Waves Beach Morphology Barriers Coastal Migration Tides Tidal Flats and Marshes Sediment Budgets Human
CHAPTER 11.1 THE WORLD OCEAN MARINE BIOMES NOTES
 CHAPTER 11.1 THE WORLD OCEAN MARINE BIOMES NOTES 1. The world ocean can be divided into zones both and. The,, and zones that apply to large lakes also apply to the ocean. 2. In addition to the depth zones,
CHAPTER 11.1 THE WORLD OCEAN MARINE BIOMES NOTES 1. The world ocean can be divided into zones both and. The,, and zones that apply to large lakes also apply to the ocean. 2. In addition to the depth zones,
