Extracellular acid base regulation during short-term hypercapnia is effective in a shallow-water crab, but ineffective in a deep-sea crab
|
|
|
- Hugh Hardy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MARINE ECOLOGY PROGRESS SERIES Vol. 33: 1 9, 2007 Pulished Mrch 2 Mr Ecol Prog Ser FEATURE ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Extrcellulr cid se regultion during short-term hypercpni is effective in shllow-wter cr, ut ineffective in deep-se cr Eric F. Pne*, Jmes P. Brry Monterey By Aqurium Reserch Institute, 7700 Sndholdt Rod, Moss Lnding, Cliforni 95039, USA ABSTRACT: Rising levels of tmospheric cron dioxide could e cured y lrge-scle sequestrtion of CO 2 in the deep se. Such solution requires prior ssessment of the impct of hypercpnic, cidic sewter on deep-se fun. Lortory studies were conducted to ssess the short-term hypercpnic tolernce of the deep-se Tnner cr Chionoecetes tnneri, collected from 1000 m depth in Monterey Cnyon off the cost of centrl Cliforni, USA. Hemolymph cid se prmeters were monitored over 2 h of exposure to sewter equilirted with ~1% CO 2 (sewter P CO2 ~ torr or 0. kp, ph 7.1), nd compred with those of the shllow-living Dungeness cr Cncer mgister. Short-term hypercpni-induced cidosis in the hemolymph of Chionoecetes tnneri ws lmost uncompensted, with net 2 h ph reduction of 0.32 units nd net icronte ccumultion of only 3 mm. Under simultneous hypercpni nd hypoxi, short-term extrcellulr cidosis in Chionoecetes tnneri ws completely uncompensted. In contrst, Cncer mgister fully recovered its hemolymph ph over 2 h of hypercpnic exposure y net ccumultion of 12 mm icronte from the surrounding medium. The dt support the hypothesis tht deep-se nimls, which re dpted to stle environment nd exhiit reduced metolic rtes, lck the short-term cid se regultory cpcity to cope with the cute hypercpnic stress tht would ccompny lrge-scle CO 2 sequestrtion. Additionlly, the dt indicte tht sequestrtion in oxygen-poor res of the ocen would e even more detrimentl to deep-se fun. KEY WORDS: CO 2 Deep se Physiology Decpod crustce Acid se regultion Chionoecetes tnneri Cncer mgister Resle or repuliction not permitted without written consent of the pulisher The ocen s lrge-scle sorption, s well s possile future nthropogenic sequestrtion of tmospheric CO 2, will result in long-term cidifiction of the wter. The deep-se cr Chionoecetes tnneri (collected from Monterey Cnyon t 1000 m depth) is unle to regulte extrcellulr ph during short-term CO 2 exposure. The results of Pne & Brry support the hypothesis tht hypercpni will hve profound physiologicl impct on deep-se orgnisms. Photo: MBARI (200) INTRODUCTION Lrge-scle sequestrtion of cron dioxide in the deep se (Mrchetti 1977, 1979), s mens of reducing tmospheric CO 2 emissions nd mitigting greenhouse-gs-induced climte chnge, remins potentil solution to the prolem of esclting tmospheric CO 2 levels. Accordingly, the possiility of lrge-scle nthropogenic inputs of CO 2 into the deep-se hs creted intriguing nd pressing reserch questions. *Emil: epne@mri.org Inter-Reserch
2 2 Mr Ecol Prog Ser 33: 1 9, 2007 Becuse the physiology of deep-se nimls is so poorly understood, puttive deep-se CO 2 sequestrtion must e pproched with cution (Seiel & Wlsh 2001, Portner et l. 200). While in situ microcosmic CO 2 relese studies t depth hve een conducted (Brewer et l. 2000, Tmurri et l. 2000, Brry et l. 200), the direct physiologicl impcts of hypercpni, nd the cid se regultory cpcities of deep-se nimls, hve yet to e systemticlly investigted under lortory conditions. The generl hypothesis tht deep-se niml cid se regultory cpcity will e poorly dptive to hypercpnic exposure rests on 2 sic principles. The first is the trend towrd hypometolism with depth in pelgic, typiclly visul, nimls (Seiel et l. 1997). The theory holds tht limited light with depth reduces visul predtion pressure nd selects for reduced locomotory ility nd metolic cpcity (Childress et l. 1990, Childress & Seiel 199). Although this theory pplies predominntly to pelgic nimls, deep-se enthic nimls (including crustcens) lso exhiit metolic rtes typiclly n order of mgnitude lower thn their shllow-living counterprts (Childress et l. 1990, Henry et l. 1990). While this phenomenon in deep-se enthic crustcens my simply e function of very low tempertures t depth in res of steep therml grdient (Childress et l. 1990), these reduced metolic rtes oserved in deep-se enthic crustcens my still e ecologiclly relevnt (disdvntgeous) in the context of hypercpnic exposure. Secondly, cid se regultory cpcity of deep-se fun my e mldptive to hypercpni due to the nturl invrince of their chemicl environment. The deep se hs een chrcterized for severl thousnds of yers y stle physico-chemicl wter prmeters (Gge & Tyler 1991, Kennett & Ingrm 1995, Portner et l. 200). Unlike some shllow dwelling qutic nimls who hve evolved effective cid se regultory cpilities to comt sesonl, or even dily, fluctutions in wter ph, oxygen nd CO 2 concentrtion, or temperture, deep-se nimls theoreticlly should not possess such well-developed cid se regultory cpcity (Childress & Seiel 199, Seiel & Wlsh 2001). In this study, we took comprtive physiologicl pproch in testing the hypothesis tht deep-se nimls hve limited cid se regultory cpcity. We investigted the response of deep-se enthic decpod cr, Chionoecetes tnneri (Grooved Tnner cr), to cute lortory-sed hypercpnic exposure, nd compred it to tht of shllow-living decpod cr, Cncer mgister (Dungeness cr). Chionoecetes tnneri, of the rchyurn fmily Mjide, is the dominnt decpod cr of the Monterey Cnyon sefloor t 1000 m, nd the only decpod species occurring t densities comptile with remoteoperted vehicle collection t depth. It is sluggish species, lrge enough to fcilitte repetitive lood smpling, yet esily kept in the lortory with very low feeding requirements. Cncer mgister is lrge, highly undnt cr of the fmily Cncride, common to northestern Pcific costl wters. Though predominntly sutidl nd found mostly t depths to 90 m, shorewrd spring migrtions ring them into shllower wter mrgins of sndy eches nd esturies (Morris et l. 190, Airriess & McMhon 199). Hence, Cncer mgister my experience chnges in wter slinity, prtil pressures of oxygen (P O2 ), nd cron dioxide (P CO2 ), nd ph s frequently s ech tidl cycle (Airriess & McMhon 199). Our choice of Cncer mgister s n experimentl species ws lso influenced y its representtion in the existing cid se, respirtory, nd circultory literture (e.g. Johnsen et l. 1970, Airriess & McMhon 199). Additionlly, we explored the influence of oxygen vilility on the response of the deep-se Tnner cr to hypercpni. Chionoecetes tnneri ws collected from the Monterey Cnyon t depths of ~1000 m (Fig. 1), within the oxygen minimum zone (OMZ) typicl of estern Pcific wters nd the Monterey Cnyon (Fig. 2). The OMZ is the ocen zone of lowest oxygen sturtion creted y the processes of iotic oxygen consumption nd ocen circultion (Wyrtki 192). In the estern Pcific it typiclly occurs etween 500 nd 1000 m. Accordingly, we tested the response of Tnner crs to hypercpni when held in oth low oxygen (simulting OMZ levels) nd high oxygen (fully sturted sewter). Fig. 1. Loctions of ROV Ventn dive sites t ~1000 m in Monterey Cnyon (d) for collection of the deep-se decpod Grooved Tnner cr Chionoecetes tnneri
3 Pne & Brry: Acid se regultion in crs 3 Depth (m) Oxygen (mg l 1 ) Fig. 2. Oxygen profile in Monterey Cnyon, showing the oxygen minimum zone (OMZ) etween 00 nd 1200 m. Arrow: smpling depth for Chionoecetes tnneri The level of hypercpni used, (~1% CO 2 ) hs frequently een employed for oth invertertes nd vertertes from freshwter nd mrine systems (Cmeron 197, Truchot 1979, Toews et l. 193, Cliorne & Heisler 19, Lngenuch & Portner 2002, Edwrds et l. 2005). A one-unit reduction in wter ph typiclly occurs with this level of hypercpni, nd the exposure requires competent cid se regultory cpcity to offset the initil extrcellulr cidosis cused y exposure to hypercpnic sewter. MATERIALS AND METHODS Cr collection nd holding. Grooved Tnner crs Chionoecetes tnneri of oth sexes (200 to 00 g) were collected y remote-operted vehicle (ROV Ventn ) from depths of 950 to 1050 m from the sefloor of Monterey Cnyon (Fig. 1). The ROV Ventn ws operted from the RV Point Loos, under the stewrdship of the Monterey By Aqurium Reserch Institute. Once retrieved from depth, crs were held ord ship in 2 C sewter until trnsfer to the lortory. Totl time from collection to lortory trnsfer ws 3 to 5 h nd survivl ws typiclly 75% during this process. In the lortory, crs were held in 3 cuic 110 l tnks under flow-through conditions with oxygen regulted vi computer-controlled gs-regulted qurium system. In rief, oxygen ws controlled using comintion of sensors (Anderr oxygen optodes) nd gs contctors through which mixtures of nitrogen nd oxygen were used to mintin dissolved gses ner prescried setpoints for oxygen. Temperture ws lso regulted. The totl volume of the recirculting system 7 ws ~1000 l. Flow-through ws chieved y ddition of 0.25 l min 1 to ech tnk from common reservoir of sewter equilirted to set oxygen level y the processes descried ove. With the exception of hydrosttic pressure, in situ (~1000 m) sewter conditions were replicted y holding ll crs in constnt drkness in wter of 3 ± 1 C, ph of 7.5 ± 0.10, nd slinity of 3 ppt. All holding nd experimenttion ws conducted t surfce pressure. While we recognize the inconsistency of holding nimls collected from 1000 m t surfce pressure, the technicl chllenges of in vivo work with mcrofun t high hydrosttic pressure in lortory setting re formidle. We therefore weigh ny potentil depth-relted chnges in physiologicl function ginst the following oservtions regrding Chionoecetes tnneri held t surfce pressure: (1) once cclimted to the lortory, survivl is extremely high, with crs surviving >1 mo (cf. Henry et l. 1990); (2) crs molt in the lortory; nd (3) once cclimted, post-rnchil hemolymph ph of resting crs consistently flls within tight rnge (7.9 to.1) consistent with lphstt regultion in qutic nimls held t 3 C (Cmeron 19). The oxygen concentrtion of the sewter ws set to either 90 ± 5% sturtion ( High, ~350 µm), or 10 ± 5% sturtion ( Low, ~0 µm). The lower O 2 tretment mimicked in situ oxygen levels typicl of the oxygen minimum zone t depths etween roughly 00 nd 1200 m off the Cliforni cost nd within the Monterey Cnyon (Childress 1995; our Fig. 2). Pcific Dungeness crs Cncer mgister of oth sexes (500 to 1000 g) were purchsed loclly (Moss Lnding, CA) from commercil fishermn using ited trps t 30 to 0 m. Dungeness crs were held in the lortory in flowing sewter of 10 ± 1 C, ph of 7.9 ± 0.1, slinity of 3 ppt, nd n oxygen sturtion of 90 ± 5%, under 12:12 h light:drk photoperiod. All crs introduced to the lortory were llowed minimum of 3 wk to cclimte efore experimenttion. Both species of cr were fed twice weekly to stition with chopped squid; food ws withheld 72 h prior to experimenttion, nd only hrd-shelled intermolt nimls were used in experiments. In vitro experiments. The non-icronte uffering cpcity (β) of ser ws determined for Cncer mgister nd for Chionoecetes tnneri held in oth low nd high oxygen. In ll experimenttions, post-rnchil hemolymph ws ccessed y drilling smll (1 mm) hole in the dorsl crpce directly ove the hert. A ring of cynocrylte glue ws pplied round the hole nd 1 cm squre piece of dentl dm ws glued into plce (Forgue et l. 1992). Crs were llowed minimum 72 h recovery period prior to experimenttion. All hemolymph ws drwn neroiclly into ice-cold
4 Mr Ecol Prog Ser 33: 1 9, 2007 gs-tight Hmilton syringes rinsed with Cr Ringer comprised of (in mm) NCl (0), KCl (10), CCl 2 (20), MgCl 2 (9.5), nd H 3 BO 3 (3), ph 7.0 (Lng & Giner 199). For tonometric nlysis, hemolymph ws drwn nd llowed to clot on ice for 10 min. Hemolymph ws then centrifuged eroiclly t 000 g t 3 C for 3 min, producing seprted, rther thn true, serum (Dvenport 197). Seprted serum ws then dded (~150 µl) to round-ottom flsks nd equilirted with humidified gs mixtures of CO 2 nd nitrogen from prenlyzed cylinders (Airgs). Ser were equilirted for 90 min in shking wter th t the pproprite temperture (10 C for Cncer mgister serum nd 3.5 C for Chionoecetes tnneri serum). After equilirtion, smples were drwn into gstight syringes nd ph ws mesured using microelectrode nd in-line reference electrode (Microelectrodes) thermosttted to the pproprite temperture nd coupled to n Accumet (Fisher Scientific) ph meter. Totl CO 2 (C CO2 ) ws mesured y non-dispersive infrred nlysis (LI-COR model 22), following cidifiction (5% phosphoric cid) of serum nd introduction of stripped gs into n infrred nlyzer (Friederich et l. 2002). ph ws stndrdized with Rdiometer Anlyticl precision uffers djusted to the ionic strength of cr serum (~1050 mosm), while C CO2 ws stndrdized with NCO 3 (Sigm-Aldrich) dried for h t 250 C prior to mking cronte stndrds. Serum CO 2 tension (P CO2 ) nd serum [HCO 3 ], sed on mesured ph nd C CO2, were clculted y rerrngement of the Henderson-Hsselch eqution with vlues for CO 2 soluility (αco 2 ) nd pprent pk (pk ) t the pproprite temperture tken from Boutilier et l. (19) nd Truchot (197). βs were derived from liner regression of ph-icronte plots for ech species nd oxygen tretment (Truchot 1979, Cmeron 195, 19). These speciesnd oxygen-specific slopes pper on the pproprite Dvenport digrms s dshed lines (see Fig. ). In vivo experiments. Crs were plced in individul 12 (Chionoecetes tnneri) or 20 l (Cncer mgister) drkened oxes with no hed spce, modertely tightfitting lids, nd wter flow of pproximtely 50 ml min 1. All Cncer mgister experiments were run t 10 C, nd ll Chionoecetes tnneri exposures were run t 3.5 C. Cncer mgister nd Chionoecetes tnneri in the high O 2 tretment were exposed to sewter equilirted vi n exchnge column (Memrn) to gs mixture of 1% CO 2, 20% O 2 ( high O 2 ), nd lnce N 2 delivered from premixed, clirted gs cylinder (Airgs). Chionoecetes tnneri in the low O 2 tretment were exposed in similr fshion to sewter equilirted with cylinder comprising 1% CO 2, 3% O 2 ( low O 2 ), nd lnce N 2. Nominl levels of oxygen sturtion in sewter equilirted with the 2 gs mixtures were pproximtely 95 nd 1%, respectively. Wter ph ws mesured t the pproprite temperture using Rdiometer immersion electrode clirted with Rdiometer Anlyticl precision ph uffers djusted to the ionic strength of sewter. Men wter ph (from ll 3 tretments) t 2 h of hypercpnic exposure ws 7.0 ± 0.01 (SE, n = 1 mesurement). Post-rnchil hemolymph ws smpled immeditely prior to onset of hypercpnic exposure, nd then t 25 min, 50 min, 75 min, 2.5 h,.25 h, nd 2 h of hypercpni. Hemolymph ph ws mesured s descried ove, while C CO2 ws mesured s descried ove on true serum otined from neroic centrifugtion (12000 g for 1 min). Seprte liquots of seprted serum (see ove) were immeditely snp-frozen in liquid N 2 for lter nlysis of protein concentrtion, nd deproteinized in 2 volumes of ice-cold % perchloric cid prior to snp-freezing for lter nlysis of serum lctte concentrtion. Hemolymph dioxide tension (P CO2 ) nd [HCO 3 ], sed on mesured ph nd C CO2, were clculted s descried ove. Serum protein concentrtion ws nlyzed y the method of Brdford (197) using regent nd BSA stndrds from Pierce Biotechnology. Serum lctte ws mesured with commercil kit (regents nd stndrds) from Trinity Biotech. Sttistics. All mesured vlues re presented s men ± 1 SEM (n = numer of crs). Dt were tested for normlity (Shpiro-Wilk test) nd homogeneity of vrince (Levene test) prior to sttisticl tretment. Dt meeting these ssumptions were nlyzed for significnt differences using 1-wy ANOVA followed y Bonferroni s post-hoc multiple comprison test. Dt not meeting prmetric ssumptions were compred using Kruskl-Wllis test followed y multiple comprison testing ccording to the method of Dunn (19), s descried in Zr (19). Sttisticl significnce in ll cses ws ccepted t the p < 0.05 level. RESULTS Over 2 h of hypercpnic exposure, Cncer mgister exhiited lmost complete extrcellulr cid se regultion despite hemolymph ph dropping more quickly nd more shrply over the first hour of hypercpni thn in either Chionoecetes tnneri tretment (Fig. 3A). Compenstion of hemolymph ph in Cncer mgister egn t 75 min nd continued over the reminder of the exposure period, resulting in lmost complete compenstion y 2 h. In neither Chionoecetes tnneri tretment ws ny ph compenstion oserved over the first h. Only t 2 h ws ph slightly recovered in Chionoecetes tnneri cclimted to oth
5 Pne & Brry: Acid se regultion in crs 5 ΔPCO2 (torr) ΔpH A B existent in the low oxygen tretment (Fig. 3C). In neither Chionoecetes tnneri tretment ws ny pprecile gin in hemolymph icronte oserved over the first h. Viewed on ph-icronte (Dvenport) digrm, the overll pttern of hypercpnic-induced cidotic recovery in Cncer mgister ws consistent with tht of competent qutic cid se regultors. In ll 3 tretments, the first hour of hypercpnic exposure resulted in titrtion of hemolymph lood in n cidic direction, roughly down the non-icronte uffering (β) line nd consistent with CO 2 -derived respirtory cidoses (Fig. ). From 1 to h, hemolymph cid se sttus in Cncer mgister followed typicl pttern of metolic compenstion of respirtory cidosis, consistent with lrge gins in hemolymph icronte concentrtion nd movement in n lklotic direction roughly long the torr P CO2 isopleth (Fig. A). Δ[HCO 3 ] (mm) C C. mgister C. tnneri (High O 2 ) C. tnneri (Low O 2 ) Time (h) 3 2 Fig. 3. Cncer mgister nd Chionoecetes tnneri. Delt profiles of (A) ph, (B) P CO2, nd (C) [HCO 3 ] for post-rnchil hemolymph cid-se prmeters during 2 h hypercpnic (1% CO 2 ) exposure. Dt re men ± SE. Tretment mens not shring the sme letter re significntly different high nd low oxygen (Fig. 3A). The resultnt net reductions in hemolymph ph over the 2 h period were 0.0 (C. mgister), 0.32 (Chionoecetes tnneri, high O 2 ), nd 0.3 (Chionoecetes tnneri, low O 2 ) units, nd the net hemolymph ph reduction t 2 h in Cncer mgister ws significntly less thn tht of either tretment of Chionoecetes tnneri (Fig. 3A). The chnge in hemolymph P CO2 (ΔP CO2 ) profile for Cncer mgister ws consistently higher thn those of oth Chionoecetes tnneri tretments throughout the hypercpnic exposure (Fig. 3B). Internliztion of CO 2 in the 2 Chionoecetes tnneri tretments ws similr throughout the exposure period. A sustntil increse (12 mm) in the icronte concentrtion of Cncer mgister hemolymph occurred over the course of 2 h of hypercpni. In contrst, icronte gins in Chionoecetes tnneri were modest (3 mm) in the high oxygen tretment nd non- [HCO3 ] (mm) h 1.5 h C. tnneri (High O 2 ) C. tnneri (Low O 2 ) P CO2 (torr) h 2.5 h 1 h 1.5 h 2 h h 0.5 h h 1 h 2.5 h 1.5 h 0.5 h 2 h 1 h ph 2 h 0 h 0.5 h Fig.. (A) Cncer mgister nd (B) Chionoecetes tnneri. phicronte (Dvenport) digrms showing the time course of post-rnchil hemolymph cid se compenstion during 2 h hypercpnic (1% CO 2 ) exposure. Dt re men ± SE. Solid curved lines re CO 2 isopleths. Stright dshed lines re serum non-icronte uffer (β) lines determined in vitro (see text for detils) 0 h 0 h A B PCO2 (torr)
6 Mr Ecol Prog Ser 33: 1 9, 2007 Serum lctte (mm) Serum protein (g dl 1 ) A In contrst, the cid se vriles for Chionoecetes tnneri held in low oxygen remined elow the nonicronte uffering (β) line t ll time points fter 1 h. This indictes slight metolic cidosis, which compounds the uncompensted respirtory cidosis oserved in this tretment (Fig. B). The serum protein concentrtion of Cncer mgister ws significntly higher thn mesured for Chionoecetes tnneri cclimted to low O 2, oth prior to the onset of hypercpni nd throughout the exposure (Fig. 5A). Additionlly, under hypercpni, serum protein levels in Cncer mgister from 2.5 h onwrd were significntly greter thn those mesured in Chionoecetes tnneri cclimted to high oxygen (Fig. 5A). Serum lctte in Cncer mgister incresed drmticlly (~25-fold) during the first.25 h of hypercpni, only to return to seline levels y 2 h (Fig. 5B). Conversely, serum lctte in Chionoecetes tnneri ws unffected y hypercpni (Fig. 5B). DISCUSSION The deep-se Tnner cr Chionoecetes tnneri did not regulte extrcellulr cid se sttus during B C. mgister C. tnneri (High O 2 ) C. tnneri (Low O 2 ) Time (h) Fig. 5. Cncer mgister nd Chionoecetes tnneri. Time course of (A) serum protein nd (B) serum lctte during 2 h hypercpnic (1% CO 2 ) exposure. Dt re men ± SE. Tretment mens not shring the sme letter re significntly different short-term (2 h) hypercpnic exposure. Compred to the ner-complete extrcellulr compenstory response of the Dungeness cr Cncer mgister, the Tnner cr response to hypercpni ws ineffective (in high O 2 ) or non-existent (in low O 2 ) over 2 h (Figs. 3 & ). Our results indirectly support the hypothesis of Seiel & Wlsh (2001) tht deep-se nimls exchnge ions t the gills more slowly thn their shllow-living counterprts, nd re consistent with generl pttern of reduced rtes of key metolic nd enzymtic processes in deep-se decpod crs, compred to shllow-living species (Henry et l. 1990, Wlsh & Henry 1990). Bicronte cquisition, the primry mens of ph compenstion in qutic nimls, ws not oserved in Tnner crs cclimted to low oxygen, suggesting mrked reduction (or dely) in ion exchnge. In contrst, rpid, hypercpnic-induced extrcellulr icronte cquisition ( net gin of 12 mm over 2 h; Fig. 3B) oserved in Dungeness crs fits the pttern oserved in nother strong cid se regultor, the mrine shore cr Crcinus mens (Truchot 1979, 19). It should e noted tht the current work with Cncer mgister (t 10 C) nd the work y Truchot (1979, 19) with Crcinus mens (t 1 C) were conducted t sustntilly higher tempertures thn the hypercpnic experiments with Chionoecetes tnneri (3 C). In Crcinus mens exposed to ~1% CO 2 t 1 C, relevnt net trnsfers of cid se equivlents cross the rnchil epithelium were ccomplished in to 10 h. The possiility remins, therefore, tht the dptive extrcellulr response of Chionoecetes tnneri to hypercpni my ctully occur ppropritely, just over longer time period thn 2 h. The discrepncy in hemolymph ΔP CO2 profiles (Fig. 3B) during hypercpnic exposure (with Cncer mgister internlizing more CO 2 thn the 2 Chionoecetes tnneri tretments) is t odds with the common notion tht CO 2 equilirtes rpidly mong the externl medium, the extrcellulr fluid, nd the intrcellulr comprtment. A simple explntion my involve trnsitory experimentl vritions in wter CO 2 tensions cused y vrile gs exchnge with the equilirtion columns employed. While this would esily explin differences occurring in the first h of hypercpnic exposure, 2 h wter phs were very similr mong the 3 tretments, suggesting tht the wter CO 2 prtil pressures were lso very similr t 2 h. Yet the hemolymph ΔP CO2 vlue in Cncer mgister remined greter thn those of the Tnner crs. Cmeron (19) descries in detil the disequilirium conditions of inverterte lood with respect to CO 2 internliztion nd excretion, concluding tht CO 2 in inverterte lood most likely never reches equilirium conditions. Such n occurrence would certinly confound ssumptions nd discussions of CO 2 equilirium dur-
7 Pne & Brry: Acid se regultion in crs 7 ing hypercpnic exposure nd my ccount for the inconsistencies seen in Fig. 3B. It is lso possile tht the CO 2 soluility constnts nd pprent pk vlues employed, derived from literture using Crcinus mens nd temperturedjusted ccordingly, re not entirely consistent with the ctul lood chemistry of Chionoecetes tnneri. Such discrepncy could e function of ltered hydrosttic pressure dynmics involved in working with deep-se nimls t mient pressures, nd could esily explin the minor differences in the ΔP CO2 profiles oserved etween the 2 species. The key point, however, is tht Dungeness crs were le to effectively regulte their hemolymph cid se sttus despite n pprent higher internl CO 2 lod thn tht oserved in Tnner crs. In this study, cid se sttus ws monitored in the extrcellulr fluid for 2 h without mesuring intrcellulr ph (phi). There is evidence tht qutic crustcens cn regulte phi independently of extrcellulr ph (phe) (Henry & Whetly 1992, Whetly & Henry 1992), mintining constnt phi during hypercpnicinduced cidifiction of the extrcellulr fluid (Gillrd & Mln 193). The Chinese mitten cr Eriocheir sinenesis ctully incresed phi during n extrcellulr cidosis, presumly vi rpid exchnge of cid se equivlents etween the intr- nd extr-cellulr comprtments (Whiteley et l. 2001). While constncy of phi in the fce of mrked cifidiction of the extrcellulr comprtment my hve occurred in Chionoecetes tnneri exposed to hypercpni, this strtegy is one more typiclly ssocited with strong cid se regultors ntive to highly vrile environments. Therefore, we postulte tht the intrcellulr ph of Chionoecetes tnneri is likely compromised s consequence of uncompensted cidifiction of the extrcellulr comprtment, though this is n re of reserch we re ctively pursuing. Regrdless of the extent of phi regultion, mintennce of phe within firly tight limits is criticl to proper function of extrcellulr respirtory proteins, nd consequently oxygen delivery to tissues (Whetly & Henry 1992). Using the Dungeness cr, Johnsen et l. (1970) clculted Bohr shift tht would ccount for 50% increse in the hemolymph P 50 (hemolymph oxygen tension t which hemocynin is hlf-sturted) following 0. unit decrese in hemolymph ph. A similr effect with Chionoecetes tnneri hemolymph would gretly reduce oxygen crrying cpcity nd susequent delivery to respiring tissues. The inility of Chionoecetes tnneri to sustntilly ccumulte extrcellulr icronte from the environment my lso involve poor icronte retention cpcity. Even in strong cid se regultors, ph compenstion y uptke of icronte equivlents from the surrounding medium is limited y the mount of icronte tht cn e retined in the extrcellulr fluid (Truchot 1979). Mintennce of elevted concentrtions of extrcellulr icronte requires, within the kidney, commitment of sustntil frction of energeticlly costly proton pumping in order to resor vlule icronte ions tht would otherwise e lost in the urine (Truchot 197). We re currently undertking icronte infusion studies with Chionoecetes tnneri to determine the extent to which poor cid se regultion in Tnner crs is function of limited ility to cquire, or to retin, icronte. Both the net cquisition of sic equivlents from sewter, nd renl retention of icronte in the urine, require energeticlly costly epithelil ion pumping. Net cid excretion (or net se ccumultion) during hypercpni my occur t the direct expense of metolic ATP in the cse of H + -ATPses pumping protons cross epitheli, or indirectly in the cse of electroneutrl exchnge vi N + /H + or Cl /HCO 3 ntiporters (see Ahern et l for review). In the ltter cse, electroneutrl N + /H + nd Cl /HCO 3 exchnge show clerly the close coupling of ionic, osmotic, nd cid se regultion, highlighting the importnce of the primry epithelil ion pump, N + - K + -ATPse in correction of ion grdients distured y the necessity of hypercpnic cid se regultion (Ahern et l. 1999). Furthermore, in the cse of decpod crustcens, N + /H + exchnge is electrogenic (2N + /H + ), possily requiring direct synergistic interction with n ATP-dependent ion pump such s vcuolr, or V-type, H + -ATPse (Kimur et l. 199). Brnchil pumping of cid se relevnt ions to offset cid se disturnces cn e n energeticlly costly process, nd one which my e limited in deepse enthic crustcens which hve metolic rtes typiclly n order of mgnitude lower thn their shllow-living counterprts (Childress et l. 1990). Our results, showing tht the sluggish deep-se Tnner cr hs limited short-term extrcellulr cid se compenstory cpcity following hypercpni, support the theory (Seiel & Wlsh 2001, Childress & Seiel 199) tht deep-se nimls will e prticulrly sensitive to hypercpni. As indirect evidence tht the cid se regultory cpcity of deep-se nimls is mldptive to severe cid se disturnce due to lowered metolic rtes, short-term extrcellulr ph compenstion, nd extrcellulr icronte ccumultion, were modertely improved when Tnner crs were held under conditions of high oxygen, essentilly hyperoxic to their in situ conditions (Fig. 3). In shllow-living decpod crustcens, lctte uildup in the extrcellulr comprtment increses hemocynin oxygen ffinity nd cts s metolic signling compound to increse oxygen consumption rte (Lllier & Truchot 199, De wtcher et l. 1997, Bridges
8 Mr Ecol Prog Ser 33: 1 9, ). Accordingly, lctte moiliztion in Cncer mgister during hypercpni corresponds well with the need for upregultion of metoliclly costly cid se regultory trnsport phenomen (Fig. 5B). In Tnner crs held in oth oxygen levels, however, lctte ws sent from the serum prior to, nd throughout, the 2 h exposure period (Fig. 5B). This devince of the serum lctte pttern of Chionoecetes tnneri from the typicl pttern displyed y Cncer mgister (Fig. 5B) nd other shllow-living decpod crustcens (Bridges 2001), suggests tht Chionoecetes tnneri relies on nother signling molecule, such s urte or mgnesium (Bridges 2001) to effect the pproprite metolic response. Additionlly, it is possile tht Chionoecetes tnneri produces lctic cid intrcellulrly during hypercpnic stress, ut does not relese lctte from the tissue. Extrcellulr relese of the proton ccompnying lctte, however, would explin the metolic cid component evident in the Dvenport digrms for Chionoecetes tnneri (Fig. B). The dt points lying elow the pssive uffering line (1 to h in Tnner crs cclimted to high O 2 nd 1 to 2 h in Tnner crs cclimted to low O 2 ) indicte comintion of respirtory nd metolic cid input into the extrcellulr fluid. While the respirtory component is protons derived from hydrted CO 2, the metolic component could stem from lctic cid-derived protons, nd future work in our lortory will focus on tissue metolic nd cid se nlyses during hypercpnic exposure. CONCLUSIONS This report represents, to our knowledge, one of the first detiled investigtions of cid se regultory ptterns in deep-se niml. Under the cron sequestrtion scenrio, generlly involving deposition of lrge mounts of liquid CO 2 on the deep se floor, short-term tolernce of high CO 2 concentrtions will e vitl. Storge lkes of CO 2 in the deep-se enthos (Ohsumi 1993) will e ccompnied y lrge locl wter ph excursions (Adms et l. 1997). In such cses, the ~0. unit drop in serum ph in Chionoecetes tnneri exposed to 1% CO 2 nd simultneously cclimted to low O 2, over 2 h (Fig. 3A), supports the hypothesis tht the consequences of lrge-scle CO 2 sequestrtion will e physiologiclly chllenging to deep-se nimls t lest in the short term. Additionlly, the dt support the synergistic effects of hypoxi nd hypercpni (see Portner et l. 200 for review). Under lortory conditions, oxygen limittion excerted extrcellulr hypercpnic-induced cidosis in the deep-se Tnner cr. Prcticlly, then, CO 2 sequestrtion in n re of the deep-se tht is nturlly hypoxic (such s the OMZ of the estern Pcific) my hve greter detrimentl effect on deep-se fun. Even in the sence of lrge-scle sequestrtion, elevted tmospheric CO 2 is continully eing sored y the world s ocens, resulting in ph depression of pproximtely 0.1 units to dte, with projected dditionl 0. unit reduction y the yer 2100 (Hugn & Drnge 199, Cldeir & Wickett 2003, Glover & Smith 2003, Sine et l. 200). This process of pssive CO 2 influx, left unted for mny yers nd comined with long-term turnover of deep ocen wter, will eventully result in consistently hypercpnic conditions in the deep se. Accordingly, chronic hypercpnic exposures re needed to understnd how deep-se nimls will fre with such chllenge. Acknowledgements. We grtefully cknowledge the tlent nd effort of the crews of the RV Point Loos nd the ROV Ventn. Additionlly, we thnk Ptrick Whling, Kurt Buck, Chris Lover, Gernot Friederich, Eric Nelson, nd Crig Okud. These studies were supported y the Monterey By Aqurium Reserch Institute (Project ), the Ocen Cron Sequestrtion Reserch Progrm, Biologicl nd Environmentl Reserch (BER), US Deprtment of Energy (Awrd No. DE- FG03-01DF305 nd DE-FG02-0ER3721), nd the Ntionl Energy Technology Lortory (NETL), US Deprtment of Energy (Awrd No. DE-FC2-00NT0929). LITERATURE CITED Adms EE, Culfield AJ, Herzog HJ, Auerch DI (1997) Impcts of reduced ph from ocen CO 2 disposl: sensitivity of zooplnkton mortlity to model prmeters. Wste Mnge 17: Ahern GA, Duerr JM, Zhung Z, Brown RJ, Aslmkhn A, Killerew DA (1999) Ion trnsport processes of crustcen epithelil cells. Physiol Biochem Zool 72:1 1 Airriess CN, McMhon BR (199) Crdiovsculr dpttions enhnce tolernce of environmentl hypoxi in the cr Cncer mgister. J Exp Biol 190:23 1 Brry JP, Buck KR, Lover CL, Kuhnz L, Whling PJ, Peltzer ET, Wlz P, Brewer PG (200) Effects of direct ocen CO 2 injection on deep-se meiofun. J Ocenogr 0:759 7 Boutilier RG, Heming TA, Iwm GK (19) Physiochemicl prmeters for use in fish respirtory physiology. In: Hor WS, Rndll DJ (eds) Fish physiology. Acdemic Press, London, p Brdford MM (197) A rpid nd sensitive method for the quntittion of microgrm quntities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye inding. Anl Biochem 72:2 25 Brewer PG, Peltzer ET, Friederich G, Ay I, Ymne K (2000) Experiments on the ocen sequestrtion of fossil fuel CO 2 : ph mesurements nd hydrte formtion. Mr Chem 72:3 93 Bridges CR (2001) Modultion of hemocynin oxygen ffinity: properties nd physiologicl implictions in chnging world. J Exp Biol 20: Cldeir K, Wickett ME (2003) Anthropogenic cron nd ocen ph. Nture 25:35 Cmeron JN (197) Effects of hypercpni on lood cid se sttus, NCl fluxes, nd trns-gill potentil in freshwter lue crs, Cllinectes spidus. J Comp Physiol 123: Cmeron JN (195) Compenstion of hypercpnic cidosis in the
9 Pne & Brry: Acid se regultion in crs 9 Editoril responsiility: Howrd Browmn (Associte Editorin-Chief), Storeø, Norwy qutic lue cr, Cllinectes spidus: the predominnce of externl sewter over crpce cronte s the proton sink. J Exp Biol 11: Cmeron JN (19) Acid se equiliri in invertertes. In: Heisler N (ed) Acid se regultion in nimls. Elsevier, New York, p Childress JJ (1995) Are there physiologicl nd iochemicl dpttions of metolism in deep-se nimls? Trends Ecol Evol 10:30 3 Childress JJ, Seiel BA (199) Life t stle low oxygen levels: dpttions of nimls to ocenic oxygen minimum lyers. J Exp Biol 201: Childress JJ, Cowles DL, Fvuzzi JA, Mickel TJ (1990) Metolic rtes of enthic deep-se decpod crustcens decline with incresing depth primrily due to the decline in temperture. Deep-Se Res 37: Cliorne JB, Heisler N (19) Acid se regultion nd ion trnsfers in the crp (Cyprinus crpio): ph compenstion during grded long- nd short-term environmentl hypercpni, nd the effect of icronte infusion. J Exp Biol 12:1 1 Dvenport HW (197) The ABC of cid se chemistry. University of Chicgo Press, Chicgo, IL De Wtcher B, Srtoris FJ, Portner HO (1997) The neroic endproduct lctte hs ehviourl nd metolic signling function in the shore cr Crcinus mens. J Exp Biol 200: Dunn OJ (19) Multiple contrsts using rnk sums. Technometrics : Edwrds SL, Wll BP, Morrison-Shetlr A, Sligh S, Wekley JC, Cliorne JB (2005) The effect of environmentl hypercpni nd slinity on the expression of NHE-like isoforms in the gills of euryhline fish (Fundulus heteroclitus). J Exp Zool 303A: 75 Forgue J, Mssuu JC, Truchot JP (1992) When re resting wter-rethers lcking O 2? Arteril P O2 t the neroic threshold in cr. Resp Physiol :27 25 Friederich GE, Wlz PM, Burczynski MG, Chvez FP (2002) Inorgnic cron in the centrl Cliforni upwelling system during the El Niño-L Niñ event. Prog Ocenogr 5: Gge JD, Tyler PA (1991) Deep-se iology nturl history of orgnisms t the deep-se floor. Cmridge University Press, Cmridge Gillrd S, Mln A (193) Intrcellulr ph regultion in response to mient hyperoxi or hypercpni in the cryfish. Mol Physiol : Glover AG, Smith CR (2003) The deep-se floor ecosystem: current sttus nd prospects of nthropogenic chnge y the yer Environ Conserv 30: Hugn PM, Drnge H (199) Effects of CO 2 on the ocen environment. Energy Convers Mnge 37: Henry RP, Whetly MG (1992) Interction of respirtion, ion regultion, nd cid se lnce in the everydy life of qutic crustcens. Am Zool 32:07 1 Henry RP, Perry HM, Trigg CB, Hndley HL, Krrup A (1990) Physiology of two species of deep-wter crs, Chceon fenneri nd C. quinquedens: gill morphology, nd hemolymph ionic nd nitrogen concentrtions. J Crustc Biol 10: Johnsen K, Lenfnt C, Mecklenurg TA (1970) Respirtion in the cr, Cncer mgister. Z Vgl Physiol 70:1 19 Kennett JP, Ingrm BL (1995) A 20,000-yer record of ocen circultion nd climte chnge from the Snt Brr sin. Nture 377: Kimur C, Ahern GA, Busquets-Turner L, Hley SR, Ngo C, De Couet HG (199) Immunolocliztion of n ntigen ssocited with the inverterte electrogenic 2N + /1H + ntiporter. J Exp Biol 19:9 10 Lllier F, Truchot JP (199) Hemolymph oxygen trnsport during environmentl hypoxi in the shore cr, Crcinus mens. Resp Physiol 77: Lng MA, Giner H (199) Isosmotic intrcellulr regultion s mechnism of volume control in cr muscle fiers. Comp Biochem Physiol 30:5 5 Lngenuch M, Portner HO (2002) Chnges in metolic rte nd N excretion in the mrine inverterte Sipunculus nudus under conditions of environmentl hypercpni: identifying effective cid se vriles. J Exp Biol 205: Mrchetti C (1977) On geoengineering nd the CO 2 prolem. Clim Chnge 1:59 Mrchetti C (1979) Constructive solutions to the CO 2 prolem. In: Bch W, Pnkrth J, Kellogg W (eds) Mn s impct on climte. Elsevier Science, Amsterdm, p Morris RH, Aott DP, Hderlie EC (190) Intertidl invertertes of Cliforni. Stnford University Press, Stnford, CA Ohsumi T (1993) Prediction of solute cron dioxide ehviour round liquid cron dioxide pool on deep ocen sins. Energy Convers Mnge 3: Portner HO, Lngenuch M, Reipschlger A (200) Biologicl impct of elevted ocen CO 2 concentrtions: lessons from niml physiology nd erth history. J Ocenogr 0: Sine CL, Feely RA, Gruer N, Key RM nd 11 others (200) The ocen sink for nthropogenic CO 2. Science 305: Seiel BA, Wlsh PJ (2001) Potentil impcts of CO 2 injection on deep-se iot. Science 29: Seiel BA, Thuesen EV, Childress JJ, Gorodezky LA (1997) Decline in pelgic cephlopod metolism with hitt depth reflects differences in locomotory efficiency. Biol Bull 192: Tmurri MN, Peltzer ET, Friederich GE, Ay I, Ymne K, Brewer PG (2000) A field study of the effects of CO 2 ocen disposl on moile deep-se nimls. Mr Chem 72: Toews DP, Holeton GF, Heisler N (193) Regultion of the cid se sttus during environmentl hypercpni in the mrine teleost fish Conger conger. J Exp Biol 107:9 20 Truchot JP (197) Cron dioxide comining properties of the lood of the shore cr Crcinus mens (L.): cron dioxide soluility coefficient nd cronic cid dissocition constnts. J Exp Biol :5 57 Truchot JP (1979) Mechnisms of the compenstion of lood respirtory cid se disturnces in the shore cr, Crcinus mens (L.). J Exp Zool 210:07 1 Truchot JP (19) Wter cronte lklinity s determinnt of hemolymph cid se lnce in the shore cr, Crcinus mens: study t two different mient P CO2 nd P O2 levels. J Comp Physiol B 15:01 0 Truchot JP (197) Comprtive spects of extrcellulr cid se lnce. Springer-Verlg, Berlin Wlsh PJ, Henry RP (1990) Activities of metolic enzymes in the deep-wter crs Chceon fenneri nd C. quinquedens nd the shllow-wter cr Cllinectes spidus. Mr Biol 10: 33 3 Whetly MG, Henry RP (1992) Extrcellulr nd intrcellulr cid se regultion in crustcens. J Exp Zool 22: Whiteley NM, Scott JL, Breeze SJ, McCnn L (2001) Effects of wter slinity on cid se lnce in decpod crustcens. J Exp Biol 20: Wyrtki K (192) The oxygen minim in reltion to ocen circultion. Deep-Se Res 9:11 23 Zr JH (19) Biosttisticl nlysis. Prentice-Hll, Englewood Cliffs, NJ Sumitted: Octoer 10, 200; Accepted: Ferury 15, 2007 Proofs received from uthor(s): Mrch 7, 2007
Department of Animal and Aquacultural Sciences, Norwegian University of life Science, PO-Box N-1432 Ås, Norway.
 Presenttion in session H11.5 * The ehviour of horses in different pddock sizes, with nd without exercise G.H.M. Jørgensen * & K.E. Bøe. Deprtment of Animl nd Aquculturl Sciences, Norwegin University of
Presenttion in session H11.5 * The ehviour of horses in different pddock sizes, with nd without exercise G.H.M. Jørgensen * & K.E. Bøe. Deprtment of Animl nd Aquculturl Sciences, Norwegin University of
TECHNICAL BULLETINApril 2016
 SYN-86 TECHNICAL BULLETINApril 216 Synovex One-Feedlot Implnts in Feedlot Steers: Phse IIIB Studies in Nersk nd Texs Zoetis Florhm Prk, NJ 7932 Summry Two Phse IIIB studies 1,2 were conducted in feedlot
SYN-86 TECHNICAL BULLETINApril 216 Synovex One-Feedlot Implnts in Feedlot Steers: Phse IIIB Studies in Nersk nd Texs Zoetis Florhm Prk, NJ 7932 Summry Two Phse IIIB studies 1,2 were conducted in feedlot
THE EFFECT OF GRADED HYPOXIA ON THE METABOLIC RATE AND BUCCAL ACTIVITY OF A LUNGLESS SALAMANDER (DESMOGNATHUS FUSCUS)
 The Journl of xperimentl iology, 78 79 () Printed in Gret ritin The ompny of iologists Limited J9 78 T FFT OF G YPOXI O T MTOLI T UL TIVITY OF LUGLSS SLM (SMOGTUS FUSUS) LIZT. SFO, STP. WOO GL J. TTTSLL
The Journl of xperimentl iology, 78 79 () Printed in Gret ritin The ompny of iologists Limited J9 78 T FFT OF G YPOXI O T MTOLI T UL TIVITY OF LUGLSS SLM (SMOGTUS FUSUS) LIZT. SFO, STP. WOO GL J. TTTSLL
INVESTIGATION 2. What s the Angle?
 INVESTIGATION 2 Wht s the Angle? In the previous investigtion, you lerned tht when the rigidity property of tringles is comined with the ility to djust the length of side, the opportunities for useful
INVESTIGATION 2 Wht s the Angle? In the previous investigtion, you lerned tht when the rigidity property of tringles is comined with the ility to djust the length of side, the opportunities for useful
Contents TRIGONOMETRIC METHODS PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS
 ontents UNIT 7 TRIGONOMETRI METHODS Lesson 1 Trigonometric Functions................... 462 1 onnecting ngle Mesures nd Liner Mesures.............. 463 2 Mesuring Without Mesuring.........................
ontents UNIT 7 TRIGONOMETRI METHODS Lesson 1 Trigonometric Functions................... 462 1 onnecting ngle Mesures nd Liner Mesures.............. 463 2 Mesuring Without Mesuring.........................
Rapid increase in the partial pressure of NH 3 on the cutaneous surface of airexposed mangrove killifish, Rivulus marmoratus
 1737 The Journl of Experimentl Biology 29, 1737-1745 Pulished y The Compny of Biologists 26 doi:1.1242/je.2197 Rpid increse in the prtil pressure of NH 3 on the cutneous surfce of irexposed mngrove killifish,
1737 The Journl of Experimentl Biology 29, 1737-1745 Pulished y The Compny of Biologists 26 doi:1.1242/je.2197 Rpid increse in the prtil pressure of NH 3 on the cutneous surfce of irexposed mngrove killifish,
Open Access Regression Analysis-based Chinese Olympic Games Competitive Sports Strength Evaluation Model Research
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthmscience.e The Open Cybernetics & Systemics Journl, 05, 9, 79-735 79 Open Access Regression Anlysis-bsed Chinese Olympic Gmes Competitive Sports Strength Evlution
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthmscience.e The Open Cybernetics & Systemics Journl, 05, 9, 79-735 79 Open Access Regression Anlysis-bsed Chinese Olympic Gmes Competitive Sports Strength Evlution
RESEARCH ARTICLE Diet influences salinity preference of an estuarine fish, the killifish Fundulus heteroclitus
 1965 The Journl of Experimentl Biology 2, 1965-1974 12. Pulished y The Compny of Biologists Ltd doi:.1242/je.06 RESEARCH ARTICLE Diet influences slinity preference of n esturine fish, the killifish Fundulus
1965 The Journl of Experimentl Biology 2, 1965-1974 12. Pulished y The Compny of Biologists Ltd doi:.1242/je.06 RESEARCH ARTICLE Diet influences slinity preference of n esturine fish, the killifish Fundulus
APPLICATION OF POLISH CALCIUM SORBENTS IN CARBONATE LOOPING
 Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 49(), 203, 20 www.minproc.pwr.wroc.pl/journl/ Physicochemicl Problems of Minerl Processing ISSN 643-049 (print) ISSN 2084-4735 (online) Received April 3, 202; reviewed;
Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 49(), 203, 20 www.minproc.pwr.wroc.pl/journl/ Physicochemicl Problems of Minerl Processing ISSN 643-049 (print) ISSN 2084-4735 (online) Received April 3, 202; reviewed;
The Discussion of this exercise covers the following points: The open-loop Ziegler-Nichols method. The open-loop Ziegler-Nichols method
 Exercise 6-3 Level Process Control EXERCISE OBJECTIVE In this exercise, you will perform PID control of level process. You will use the open-loop step response method to tune the controller. DISCUSSION
Exercise 6-3 Level Process Control EXERCISE OBJECTIVE In this exercise, you will perform PID control of level process. You will use the open-loop step response method to tune the controller. DISCUSSION
Ferskvannsavlusing small-scale tests: Short-term exposure tests to elucidate handling effects.
 Ferskvnnsvlusing smll-scle tests: Short-term exposure tests to elucidte hndling effects. The use of freshwter to control infesttions of the se louse Lepeophtheirus slmonis K on Atlntic slmon Slmo slr L.
Ferskvnnsvlusing smll-scle tests: Short-term exposure tests to elucidte hndling effects. The use of freshwter to control infesttions of the se louse Lepeophtheirus slmonis K on Atlntic slmon Slmo slr L.
2014 WHEAT PROTEIN RESPONSE TO NITROGEN
 2014 WHEAT PROTEIN RESPONSE TO NITROGEN Aron Wlters, Coopertor Ryford Schulze, Coopertor Dniel Hthcot, Extension Progrm Specilist Dr. Clrk Neely, Extension Stte Smll Grins Specilist Ryn Collett, Extension
2014 WHEAT PROTEIN RESPONSE TO NITROGEN Aron Wlters, Coopertor Ryford Schulze, Coopertor Dniel Hthcot, Extension Progrm Specilist Dr. Clrk Neely, Extension Stte Smll Grins Specilist Ryn Collett, Extension
PILOT PROGRAM FOR THE EVALUATION OF NANOFILTRATION MEMBRANES PREPARED BY: WILMINGTON, MA ON UF PERMEATE
 PILOT PROGRAM FOR THE EVALUATION OF NANOFILTRATION MEMBRANES ON UF PERMEATE PREPARED BY: KOCH MEMBRANE SYSTEMS, INC. 850 MAIN STREET WILMINGTON, MA 01887 NANOPILT. D157 INTRODUCTION This progrm will outline
PILOT PROGRAM FOR THE EVALUATION OF NANOFILTRATION MEMBRANES ON UF PERMEATE PREPARED BY: KOCH MEMBRANE SYSTEMS, INC. 850 MAIN STREET WILMINGTON, MA 01887 NANOPILT. D157 INTRODUCTION This progrm will outline
Metabolic, respiratory and cardiovascular responses to acute and chronic hypoxic exposure in tadpole shrimp Triops longicaudatus
 1639 The Journl of Experimentl Biology 209, 1639-1650 Published by The Compny of Biologists 2006 doi:10.1242/jeb.02180 Metbolic, respirtory nd crdiovsculr responses to cute nd chronic hypoxic exposure
1639 The Journl of Experimentl Biology 209, 1639-1650 Published by The Compny of Biologists 2006 doi:10.1242/jeb.02180 Metbolic, respirtory nd crdiovsculr responses to cute nd chronic hypoxic exposure
Responses of fish communities to sustained removals of perch (Perca fluviatilis)
 Responses of fish communities to sustined removls of perch (Perc fluvitilis) SCIENCE FOR CONSERVATION Benjmin G. Ludgte nd Gerrd P. Closs Pulished y Deprtment of Conservtion PO Box -4 Wellington, New Zelnd
Responses of fish communities to sustined removls of perch (Perc fluvitilis) SCIENCE FOR CONSERVATION Benjmin G. Ludgte nd Gerrd P. Closs Pulished y Deprtment of Conservtion PO Box -4 Wellington, New Zelnd
RESEARCH ARTICLE Ammonia sensing by neuroepithelial cells and ventilatory responses to ammonia in rainbow trout
 2678 The Journl of Experimentl Biology 214, 2678-2689 211. Pulished y The Compny of Biologists Ltd doi:1.1242/je.55541 RESEARCH ARTICLE Ammoni sensing y neuroepithelil cells nd ventiltory responses to
2678 The Journl of Experimentl Biology 214, 2678-2689 211. Pulished y The Compny of Biologists Ltd doi:1.1242/je.55541 RESEARCH ARTICLE Ammoni sensing y neuroepithelil cells nd ventiltory responses to
MAXIMUM CARDIAC PERFORMANCE OF RAINBOW TROUT (ONCORHYNCHUS MYKISS) AT TEMPERATURES APPROACHING THEIR UPPER LETHAL LIMIT
 The Journl of Experimentl Biology 199, 663 672 (1996) Printed in Gret Britin The Compny of Biologists Limited 1996 JEB0137 663 MAXIMUM CARDIAC PERFORMANCE OF RAINBOW TROUT (ONCORHYNCHUS MYKISS) AT TEMPERATURES
The Journl of Experimentl Biology 199, 663 672 (1996) Printed in Gret Britin The Compny of Biologists Limited 1996 JEB0137 663 MAXIMUM CARDIAC PERFORMANCE OF RAINBOW TROUT (ONCORHYNCHUS MYKISS) AT TEMPERATURES
The effects of sustained exercise and hypoxia upon oxygen tensions in the red muscle of rainbow trout
 The Journl of Experimentl Biology 27, 3629-3637 Pulished y The Compny of Biologists 24 doi:1.1242/je.1199 3629 The effects of sustined exercise nd hypoxi upon oxygen tensions in the red muscle of rinow
The Journl of Experimentl Biology 27, 3629-3637 Pulished y The Compny of Biologists 24 doi:1.1242/je.1199 3629 The effects of sustined exercise nd hypoxi upon oxygen tensions in the red muscle of rinow
Small Game Hunter Lead Shot Communication Study. Executive Summary. A cooperative study conducted by:
 8 Smll Gme Hunter Led Shot Communiction Study Executive Summry A coopertive study conducted y: Minnesot Coopertive Fish nd Wildlife Reserch Unit Minnesot Deprtment of Nturl Resources 9 Smll Gme Hunter
8 Smll Gme Hunter Led Shot Communiction Study Executive Summry A coopertive study conducted y: Minnesot Coopertive Fish nd Wildlife Reserch Unit Minnesot Deprtment of Nturl Resources 9 Smll Gme Hunter
Ventilation rates and activity levels of juvenile jumbo squid under metabolic suppression in the oxygen minimum zone
 University of Rhode Islnd DigitlCommons@URI iologicl Sciences Fculty Pulictions iologicl Sciences 213 Ventiltion rtes nd ctivity levels of juvenile jumo squid under metolic suppression in the oxygen minimum
University of Rhode Islnd DigitlCommons@URI iologicl Sciences Fculty Pulictions iologicl Sciences 213 Ventiltion rtes nd ctivity levels of juvenile jumo squid under metolic suppression in the oxygen minimum
Integration of modelling and monitoring to optimize network control: two case studies from Lisbon
 Aville online t www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedi Engineering 70 ( 2014 ) 555 562 12th Interntionl Conference on Computing nd Control for the Wter Industry, CCWI2013 Integrtion of modelling nd
Aville online t www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedi Engineering 70 ( 2014 ) 555 562 12th Interntionl Conference on Computing nd Control for the Wter Industry, CCWI2013 Integrtion of modelling nd
Nanobiophysical exploration of transthyretin amyloid fibrils Final report
 Nnoiophysicl explortion of trnsthyretin myloid firils Finl report Summry In this work we used AFM to follow the myloidogenetic pthwy of trnsthyretin (TTR) y imging the events leding to the formtion of
Nnoiophysicl explortion of trnsthyretin myloid firils Finl report Summry In this work we used AFM to follow the myloidogenetic pthwy of trnsthyretin (TTR) y imging the events leding to the formtion of
CHAPTER 4. Surface Root-zone Water Content and Bentgrass Water Stress. During Drydown for Selected Putting Green Construction.
 CHAPTER 4 Surfce Root-zone Wter Content nd Bentgrss Wter Stress During Drydown for Selected Putting Green Construction Systems ABSTRACT Creeping entgrss, cool-seson grss used extensively in golf courses
CHAPTER 4 Surfce Root-zone Wter Content nd Bentgrss Wter Stress During Drydown for Selected Putting Green Construction Systems ABSTRACT Creeping entgrss, cool-seson grss used extensively in golf courses
Quantifying Efficacy and Avoidance Behavior by Tawny Mole Crickets (Orthoptera: Gryllotalpidae: Scapteriscus vicinus) to Three Synthetic Insecticides
 Quntifying Efficcy nd Avoidnce Behvior y Twny Mole Crickets (Orthopter: Gryllotlpide: Scpteriscus vicinus) to Three Synthetic Insecticides Authors: D. E. Silcox, C. E. Sorenson, nd R. L. Brndenurg Source:
Quntifying Efficcy nd Avoidnce Behvior y Twny Mole Crickets (Orthopter: Gryllotlpide: Scpteriscus vicinus) to Three Synthetic Insecticides Authors: D. E. Silcox, C. E. Sorenson, nd R. L. Brndenurg Source:
Available online at ScienceDirect. Energy Procedia 59 (2014 )
 Aville online t www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedi 59 (2014 ) 182 189 Europen Geosciences Union Generl Assemly 2014, EGU 2014 Turulence chrcteristics in offshore wind frms from LES simultions
Aville online t www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedi 59 (2014 ) 182 189 Europen Geosciences Union Generl Assemly 2014, EGU 2014 Turulence chrcteristics in offshore wind frms from LES simultions
Exploring Impacts of Countdown Timers on Queue Discharge Characteristics of Through Movement at Signalized Intersections
 Avilble online t www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedi - Socil nd Behviorl Scienc es 96 ( 2013 ) 255 264 13th COTA Interntionl Conference of Trnsporttion Professionls (CICTP 2013) Exploring Impcts
Avilble online t www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedi - Socil nd Behviorl Scienc es 96 ( 2013 ) 255 264 13th COTA Interntionl Conference of Trnsporttion Professionls (CICTP 2013) Exploring Impcts
Alterations of Ventilation to Perfusion Ratios Distribution
 Journl of Clinicl Investigtion Vol. 44, No. 9, 1965 Altertions of Ventiltion to Perfusion Rtios Distribution Associted with Successive Clinicl Stges of Pulmonry Emphysem * CLAUDE LENFANT t AND WILLIAM
Journl of Clinicl Investigtion Vol. 44, No. 9, 1965 Altertions of Ventiltion to Perfusion Rtios Distribution Associted with Successive Clinicl Stges of Pulmonry Emphysem * CLAUDE LENFANT t AND WILLIAM
Sparse, decorrelated odor coding in the mushroom body enhances learned odor discrimination
 Sprse, decorrelted odor coding in the mushroom ody enhnces lerned odor discrimintion Andrew C. Lin, Alexei Bygrve, Alix de Clignon, Tzumin Lee, nd Gero Miesenöck Supplementry Mteril R64C08-GAL4 (γ) R35B12-GAL4
Sprse, decorrelted odor coding in the mushroom ody enhnces lerned odor discrimintion Andrew C. Lin, Alexei Bygrve, Alix de Clignon, Tzumin Lee, nd Gero Miesenöck Supplementry Mteril R64C08-GAL4 (γ) R35B12-GAL4
Minnesota s Wild Turkey Harvest Fall 2016, Spring 2017
 Minnesot s Wild Turkey Hrvest Fll 2016, Spring 2017 Lindsey Messinger Frmlnd Wildlife Popultions nd Reserch Group Minnesot Deprtment of Nturl Resources Mdeli, Minnesot 15 August 2017 Summry of Seson Structure
Minnesot s Wild Turkey Hrvest Fll 2016, Spring 2017 Lindsey Messinger Frmlnd Wildlife Popultions nd Reserch Group Minnesot Deprtment of Nturl Resources Mdeli, Minnesot 15 August 2017 Summry of Seson Structure
The infection of tench (Tinca tinca) with Ligula intestinalis plerocercoids in Lake Beysehir (Turkey)
 Bull. Eur. Ass. Fish Pthol., 23(5) 2003, 223 The infection of tench (Tinc tinc) with Ligul intestinlis plerocercoids in Lke Beysehir (Turkey) H. Yvuzcn Yıldız*, A. S. Korkmz nd Ö. Zencir Ankr University,
Bull. Eur. Ass. Fish Pthol., 23(5) 2003, 223 The infection of tench (Tinc tinc) with Ligul intestinlis plerocercoids in Lke Beysehir (Turkey) H. Yvuzcn Yıldız*, A. S. Korkmz nd Ö. Zencir Ankr University,
On the dynamics of low latitude, wide and shallow coastal system: numerical simulations of the Upper Gulf of Thailand
 Ocen Dynmics (214) 64:557 571 DOI 1.17/s1236-14-73-z On the dynmics of low ltitude, wide nd shllow costl system: numericl simultions of the Upper Gulf of Thilnd Suriyn Srmul & Tl Ezer Received: 9 August
Ocen Dynmics (214) 64:557 571 DOI 1.17/s1236-14-73-z On the dynmics of low ltitude, wide nd shllow costl system: numericl simultions of the Upper Gulf of Thilnd Suriyn Srmul & Tl Ezer Received: 9 August
IGF Research Project N Safer High Heels
 IGF Reserch Project 17868 N Sfer High Heels Survivl of compnies in the fshion nd sesonlly dependent sectors such s the footwer industry depends upon their ility to implement the ltest trends. Shoe ottoms
IGF Reserch Project 17868 N Sfer High Heels Survivl of compnies in the fshion nd sesonlly dependent sectors such s the footwer industry depends upon their ility to implement the ltest trends. Shoe ottoms
The Pythagorean Theorem and Its Converse Is That Right?
 The Pythgoren Theorem nd Its Converse Is Tht Right? SUGGESTED LEARNING STRATEGIES: Activting Prior Knowledge, Mrking the Text, Shred Reding, Summrize/Prphrse/Retell ACTIVITY 3.6 How did Pythgors get theorem
The Pythgoren Theorem nd Its Converse Is Tht Right? SUGGESTED LEARNING STRATEGIES: Activting Prior Knowledge, Mrking the Text, Shred Reding, Summrize/Prphrse/Retell ACTIVITY 3.6 How did Pythgors get theorem
United States Patent (19)
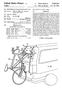 United Sttes Ptent (19) Mobley (11) 45) Ptent Number: Dte of Ptent: Nov. 19, 1991 (54) BICYCLE RACK FORMOUNTING ON A VAN 76 Inventor: Mrk H. Mobley, P.O. Box 636, Norris, Tenn. 37828 21 Appl. No.: 436,492
United Sttes Ptent (19) Mobley (11) 45) Ptent Number: Dte of Ptent: Nov. 19, 1991 (54) BICYCLE RACK FORMOUNTING ON A VAN 76 Inventor: Mrk H. Mobley, P.O. Box 636, Norris, Tenn. 37828 21 Appl. No.: 436,492
A Measurement Framework for National Key Performance Measures
 MINISTERIAL COUNCIL ON EDUCATION, EMPLOYMENT, TRAINING AND YOUTH AFFAIRS Performnce Mesurement nd Reporting Tskforce Working for qulity eduction outcomes A Mesurement Frmework for Ntionl Key Performnce
MINISTERIAL COUNCIL ON EDUCATION, EMPLOYMENT, TRAINING AND YOUTH AFFAIRS Performnce Mesurement nd Reporting Tskforce Working for qulity eduction outcomes A Mesurement Frmework for Ntionl Key Performnce
THE RELATIVE EFFICIENCY OF GASEOUS EXCHANGE ACROSS THE LUNGS AND GILLS OF AN AFRICAN LUNGFISH PROTOPTERUS AETHIOPICUS
 J. Exp. Biol. (1970), 5, 1-15 j With 1 text-figures Printed in Gret Britin THE RELATIVE EFFICIENCY OF GASEOUS EXCHANGE ACROSS THE LUNGS AND GILLS OF AN AFRICAN LUNGFISH PROTOPTERUS AETHIOPICUS BY B. R.
J. Exp. Biol. (1970), 5, 1-15 j With 1 text-figures Printed in Gret Britin THE RELATIVE EFFICIENCY OF GASEOUS EXCHANGE ACROSS THE LUNGS AND GILLS OF AN AFRICAN LUNGFISH PROTOPTERUS AETHIOPICUS BY B. R.
The development of a truck concept to allow improved direct vision of vulnerable road users by drivers
 Loughorough University Institutionl Repository The development of truck concept to llow improved direct vision of vulnerle rod users y drivers This item ws sumitted to Loughorough University's Institutionl
Loughorough University Institutionl Repository The development of truck concept to llow improved direct vision of vulnerle rod users y drivers This item ws sumitted to Loughorough University's Institutionl
Lesson 8: Application Technology
 The type of ppliction equipment used must suit the type of ppliction. In this module, you ll lern the prts of the most common types of ppliction equipment used by ssistnt pplictors, s well s how to properly
The type of ppliction equipment used must suit the type of ppliction. In this module, you ll lern the prts of the most common types of ppliction equipment used by ssistnt pplictors, s well s how to properly
Chapter 4 Group of Volunteers
 CHAPTER 4 SAFETY CLEARANCE, FREEBOARD AND DRAUGHT MARKS 4-1 GENERAL 4-1.1 This chpter specifies the minimum freebord for inlnd wterwy vessels. It lso contins requirements concerning the indiction of the
CHAPTER 4 SAFETY CLEARANCE, FREEBOARD AND DRAUGHT MARKS 4-1 GENERAL 4-1.1 This chpter specifies the minimum freebord for inlnd wterwy vessels. It lso contins requirements concerning the indiction of the
First Aid in School Policy
 First Aid in School Policy Approved y the Governing Body of West Monkton Church of Englnd Primry School: Reviewed y Governors nd Agreed: Septemer 2017 At West Monkton we im to e n inspirtionl community,
First Aid in School Policy Approved y the Governing Body of West Monkton Church of Englnd Primry School: Reviewed y Governors nd Agreed: Septemer 2017 At West Monkton we im to e n inspirtionl community,
Turbulence characteristics in offshore wind farms from LES simulations of Lillgrund wind farm Fruh, Wolf-Gerrit; Creech, Angus C.W.; Maguire, A Eoghan
 Heriot-Wtt University Heriot-Wtt University Reserch Gtewy Turulence chrcteristics in offshore wind frms from LES simultions of Lillgrund wind frm Fruh, Wolf-Gerrit; Creech, Angus C.W.; Mguire, A Eoghn
Heriot-Wtt University Heriot-Wtt University Reserch Gtewy Turulence chrcteristics in offshore wind frms from LES simultions of Lillgrund wind frm Fruh, Wolf-Gerrit; Creech, Angus C.W.; Mguire, A Eoghn
Production of chemical alarm cues in convict cichlids: the effects of diet, body condition and ontogeny
 Ann. Zool. Fennici 41: 487 499 ISSN 3-455X Helsinki 22 June 24 Finnish Zoologicl nd Botnicl Pulishing Bord 24 Production of chemicl lrm cues in convict cichlids: the effects of diet, ody condition nd ontogeny
Ann. Zool. Fennici 41: 487 499 ISSN 3-455X Helsinki 22 June 24 Finnish Zoologicl nd Botnicl Pulishing Bord 24 Production of chemicl lrm cues in convict cichlids: the effects of diet, ody condition nd ontogeny
Supplement of Population-specific responses in physiological rates of Emiliania huxleyi to a broad CO 2 range
 Supplement of Biogeosciences, 15, 3691 371, 21 https://doi.org/1.519/bg-15-3691-21-supplement Author(s) 21. This work is distributed under the Cretive Commons Attribution. License. Supplement of Popultion-specific
Supplement of Biogeosciences, 15, 3691 371, 21 https://doi.org/1.519/bg-15-3691-21-supplement Author(s) 21. This work is distributed under the Cretive Commons Attribution. License. Supplement of Popultion-specific
PRESSURE LOSSES DUE TO THE LEAKAGE IN THE AIR DUCTS - A SAFETY PROBLEM FOR TUNNEL USERS?
 - 7 - PRESSURE LOSSES DUE TO THE LEAKAGE IN THE AIR DUCTS - A SAFETY PROBLEM FOR TUNNEL USERS? Pucher Krl, Grz Uniersity of Technology, Austri E-Mil: pucherk.drtech@gmx.t Pucher Robert, Uniersity of Applied
- 7 - PRESSURE LOSSES DUE TO THE LEAKAGE IN THE AIR DUCTS - A SAFETY PROBLEM FOR TUNNEL USERS? Pucher Krl, Grz Uniersity of Technology, Austri E-Mil: pucherk.drtech@gmx.t Pucher Robert, Uniersity of Applied
a b c Plasma mem. Cytoplasm Total
 DOI: 10.1038/nc1886 c Plsm mem. Cytoplsm Totl 0 µm -0.3 to -1.8 µm 0 to -1.8 µm Rel. Signl Density 1.0 0.6 0.2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 Time (h) Control Isoxen Figure S1 Isoxen cuses loss of YFP::CESA6 signl
DOI: 10.1038/nc1886 c Plsm mem. Cytoplsm Totl 0 µm -0.3 to -1.8 µm 0 to -1.8 µm Rel. Signl Density 1.0 0.6 0.2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 Time (h) Control Isoxen Figure S1 Isoxen cuses loss of YFP::CESA6 signl
Bypass Compensator Cartridge, Size 16
 Bypss Compenstor Crtridge, Size 6 Q mx = 5 l/min, p mx = 42 br Direct cting, djustble compenstor spring Description These direct-cting bypss pressure-compenstor (hydrostt) crtridges, series DWDP-2B -6,
Bypss Compenstor Crtridge, Size 6 Q mx = 5 l/min, p mx = 42 br Direct cting, djustble compenstor spring Description These direct-cting bypss pressure-compenstor (hydrostt) crtridges, series DWDP-2B -6,
Small-scale observations of atypical fire spread caused by the interaction of wind, terrain and fire
 Smll-scle oservtions of typicl fire spred cused y the interction of wind, terrin nd fire Json J. Shrples Applied nd Industril Mthemtics Reserch Group, School of Physicl Environmentl nd Mthemticl Sciences,
Smll-scle oservtions of typicl fire spred cused y the interction of wind, terrin nd fire Json J. Shrples Applied nd Industril Mthemtics Reserch Group, School of Physicl Environmentl nd Mthemticl Sciences,
High rate of prey consumption in a small predatory fish on coral reefs
 Corl Reefs (1) 31:99 918 DOI 1.17/s338-1-894-z High rte of prey consumption in smll predtory fish on corl reefs W. E. Feeney O. M. Lönnstedt Y. Bosiger J. Mrtin G. P. Jones R. J. Rowe M. I. McCormick Received:
Corl Reefs (1) 31:99 918 DOI 1.17/s338-1-894-z High rte of prey consumption in smll predtory fish on corl reefs W. E. Feeney O. M. Lönnstedt Y. Bosiger J. Mrtin G. P. Jones R. J. Rowe M. I. McCormick Received:
Response by anglers to a differential harvest regulation on three black bass species at Skiatook Lake, Oklahoma
 9 Response y nglers to differentil hrvest regultion on three lck ss species t Skitook Lke, Oklhom Jmes M. Long U.S. Geologicl Survey, Oklhom Coopertive Fish nd Wildlife Reserch Unit, Nturl Resource Ecology
9 Response y nglers to differentil hrvest regultion on three lck ss species t Skitook Lke, Oklhom Jmes M. Long U.S. Geologicl Survey, Oklhom Coopertive Fish nd Wildlife Reserch Unit, Nturl Resource Ecology
Workfit -SR, Dual Monitor Short Surface
 User's Guide Workfit -SR, Dul Monitor Short Surfce Do not throw wy! Crdord locks needed for instlltion. Visit http://www.ergotron.com/workfi t-sr-instll for instlltion instructionl video. NOTE: 10 feet
User's Guide Workfit -SR, Dul Monitor Short Surfce Do not throw wy! Crdord locks needed for instlltion. Visit http://www.ergotron.com/workfi t-sr-instll for instlltion instructionl video. NOTE: 10 feet
THE CONTROL OF BLOOD PRESSURE DURING EXTERNAL HYPERCAPNIA IN THE RAINBOW TROUT (ONCORHYNCHUS MYKISS)
 The Journl of Experimentl Biology, 77 9 (999) Printed in Gret Britin The Compny of Biologists Limited 999 JEB9 77 THE CONTROL OF BLOOD PRESSURE DURING EXTERNAL HYPERCAPNIA IN THE RAINBOW TROUT (ONCORHYNCHUS
The Journl of Experimentl Biology, 77 9 (999) Printed in Gret Britin The Compny of Biologists Limited 999 JEB9 77 THE CONTROL OF BLOOD PRESSURE DURING EXTERNAL HYPERCAPNIA IN THE RAINBOW TROUT (ONCORHYNCHUS
Numerical simulations of rip currents off arc-shaped coastlines
 Act Ocenol. Sin., 1, Vol. 37, No. 3, P. 1 3 DOI: 1.17/s13131-1-1197-1 http://www.hyx.org.cn E-mil: hyxe@3.net Numericl simultions of rip currents off rc-shped costlines WANG Hong 1, 3, ZHU Shouxin *, LI
Act Ocenol. Sin., 1, Vol. 37, No. 3, P. 1 3 DOI: 1.17/s13131-1-1197-1 http://www.hyx.org.cn E-mil: hyxe@3.net Numericl simultions of rip currents off rc-shped costlines WANG Hong 1, 3, ZHU Shouxin *, LI
ABSTRACT VARIATION AMONG FISH SPECIES IN THE STOICHIOMETRY OF NUTRIENT EXCRETION. by Lisette Esmeralda Torres
 ABSTRACT VARIATION AMONG FISH SPECIES IN THE STOICHIOMETRY OF NUTRIENT EXCRETION by Lisette Esmerld Torres This study investigtes how nutrient cycling rtes nd rtios vry mong fish species nd with body size,
ABSTRACT VARIATION AMONG FISH SPECIES IN THE STOICHIOMETRY OF NUTRIENT EXCRETION by Lisette Esmerld Torres This study investigtes how nutrient cycling rtes nd rtios vry mong fish species nd with body size,
Ephemeral floodplain habitats provide best growth conditions for juvenile Chinook salmon in a California river. by Carson A.
 Ephemerl floodplin hbitts provide best growth conditions for juvenile Chinook slmon in Cliforni river by Crson A. Jeffres Abstrct We rered juvenile Chinook slmon for two consecutive flood sesons within
Ephemerl floodplin hbitts provide best growth conditions for juvenile Chinook slmon in Cliforni river by Crson A. Jeffres Abstrct We rered juvenile Chinook slmon for two consecutive flood sesons within
Renewable Energy xxx (2011) 1e10. Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect. Renewable Energy
 Renewle Energy xxx () e Contents lists ville t SciVerse ScienceDirect Renewle Energy journl homepge: www.elsevier.com/locte/renene Wke effect in wind frm performnce: Stedy-stte nd dynmic ehvior F. González-Longtt
Renewle Energy xxx () e Contents lists ville t SciVerse ScienceDirect Renewle Energy journl homepge: www.elsevier.com/locte/renene Wke effect in wind frm performnce: Stedy-stte nd dynmic ehvior F. González-Longtt
ANNEX 1 CLASSIFICATION AND LABELLING SUMMARY TABLES
 ANNEX CLASSIFICATION AND LABELLING SUMMARY TABLES ANNEX CLASSIFICATION AND LABELLING SUMMARY TABLES NOTE: The codifiction of hzrd s is further explined in Annex 3 (Section ). The hzrd re intended to be
ANNEX CLASSIFICATION AND LABELLING SUMMARY TABLES ANNEX CLASSIFICATION AND LABELLING SUMMARY TABLES NOTE: The codifiction of hzrd s is further explined in Annex 3 (Section ). The hzrd re intended to be
Design and Calibration of Submerged Open Channel Flow Measurement Structures: Part 3 - Cutthroat Flumes
 Uth Stte University DigitlCommons@USU Reports Uth Wter Reserch Lbortory Jnury 1967 Design nd Clibrtion of Submerged Open Chnnel Flow Mesurement Structures: Prt 3 - Cutthrot Flumes Gylord V. Skogerboe M.
Uth Stte University DigitlCommons@USU Reports Uth Wter Reserch Lbortory Jnury 1967 Design nd Clibrtion of Submerged Open Chnnel Flow Mesurement Structures: Prt 3 - Cutthrot Flumes Gylord V. Skogerboe M.
Chp. 3_4 Trigonometry.notebook. October 01, Warm Up. Pythagorean Triples. Verifying a Pythagorean Triple... Pythagorean Theorem
 Chp. 3_4 Trigonometry.noteook Wrm Up Determine the mesure of the vrile in ech of the following digrms: x + 2 x x 5 x + 3 Pythgoren Theorem - is fundmentl reltionship mongst the sides on RIGHT tringle.
Chp. 3_4 Trigonometry.noteook Wrm Up Determine the mesure of the vrile in ech of the following digrms: x + 2 x x 5 x + 3 Pythgoren Theorem - is fundmentl reltionship mongst the sides on RIGHT tringle.
Assessment of River Herring and Striped Bass in the Connecticut River: Abundance, Population Structure, and Predator/Prey Interactions
 University of Connecticut DigitlCommons@UConn EEB Articles Deprtment of Ecology nd Evolutionry Biology 2009 Assessment of River Herring nd Striped Bss in the Connecticut River: Aundnce, Popultion Structure,
University of Connecticut DigitlCommons@UConn EEB Articles Deprtment of Ecology nd Evolutionry Biology 2009 Assessment of River Herring nd Striped Bss in the Connecticut River: Aundnce, Popultion Structure,
Universidad Juárez Autónoma de Tabasco, Tabasco, Mexico. 2. CIAD A.C. Unidad Mazatlan, Mexico. 3. University of Arizona, Arizona, Tucson, USA
 EFFECT OF STOCKING DENSITY OF RED HYBRID TILAPIA (OREOCHROMIS SP.) ON GROWTH AND SURVIVAL OF JUVENILE TILAPIA AND SHRIMP (LITOPENAEUS VANNAMEI) IN POLYCULTURE. Alejndro Mcdonld-Ver 1,2 Neil J. Duncn 2
EFFECT OF STOCKING DENSITY OF RED HYBRID TILAPIA (OREOCHROMIS SP.) ON GROWTH AND SURVIVAL OF JUVENILE TILAPIA AND SHRIMP (LITOPENAEUS VANNAMEI) IN POLYCULTURE. Alejndro Mcdonld-Ver 1,2 Neil J. Duncn 2
The amphibious fish Kryptolebias marmoratus uses different strategies to maintain oxygen delivery during aquatic hypoxia and air exposure
 214. Pulished y The ompny of iologists Ltd The Journl of Experimentl iology (214) 217, 3988-3995 doi:1.1242/je.1161 RESERH RTILE The mphiious fish Kryptoleis mrmortus uses different strtegies to mintin
214. Pulished y The ompny of iologists Ltd The Journl of Experimentl iology (214) 217, 3988-3995 doi:1.1242/je.1161 RESERH RTILE The mphiious fish Kryptoleis mrmortus uses different strtegies to mintin
S. FURDEAN, D. LALESCU, Sandra Antonia MIHAILOV, A. GROZEA*
 GROWTH DYNAMIC OF THE MAIN MORPHOLOGICAL TRAITS IN A STERLET (ACIPENSER RUTHENUS) POPULATION REARED INTO RECIRCULATING AQUACULTURE SYSTEM, FROM 2 TO 6 MONTHS OLD S. FURDEAN, D. LALESCU, Sndr Antoni MIHAILOV,
GROWTH DYNAMIC OF THE MAIN MORPHOLOGICAL TRAITS IN A STERLET (ACIPENSER RUTHENUS) POPULATION REARED INTO RECIRCULATING AQUACULTURE SYSTEM, FROM 2 TO 6 MONTHS OLD S. FURDEAN, D. LALESCU, Sndr Antoni MIHAILOV,
How To Demonstrate Guide E24 & E26
 Pre-Demonstrtion Checklist Clen the entire mchine Chrge tteries Check squeegee ldes Bring proper rushes nd/or pds Clening cost nlysis Prepre quottion with lese pyments E24 & E26 literture nd fct sheet
Pre-Demonstrtion Checklist Clen the entire mchine Chrge tteries Check squeegee ldes Bring proper rushes nd/or pds Clening cost nlysis Prepre quottion with lese pyments E24 & E26 literture nd fct sheet
Copyright 1983 by ASME NEGATIVE INCIDENCE FLOW OVER A TURBINE ROTOR BLADE
 THE AMERICAN SOCIETY OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERS 345 E. 47 St., New York, N.Y. 7 83-GT-23 ^+ The Society shll not be responsible for sttements or opinions dvnced in ppers or in G discussion t meetings of the
THE AMERICAN SOCIETY OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERS 345 E. 47 St., New York, N.Y. 7 83-GT-23 ^+ The Society shll not be responsible for sttements or opinions dvnced in ppers or in G discussion t meetings of the
THERMOFLO FLUID PUMPS& SYSTEMS THERMOFLO FOR HEATING, COOLING AND WATER SUPPLY APPLICATIONS TO BS7074 SEALED SYSTEMS EXPANSION VESSELS PRESSURIZERS
 THERMOFLO S E A L E D S Y S T E M S THERMOFLO SEALED SYSTEMS FOR HEATING, COOLING AND WATER SUPPLY APPLICATIONS TO BS7074 EXPANSION VESSELS PRESSURIZERS PUMPS& SYSTEMS WALL OR BASE MOUNTING PRESSURIZERS
THERMOFLO S E A L E D S Y S T E M S THERMOFLO SEALED SYSTEMS FOR HEATING, COOLING AND WATER SUPPLY APPLICATIONS TO BS7074 EXPANSION VESSELS PRESSURIZERS PUMPS& SYSTEMS WALL OR BASE MOUNTING PRESSURIZERS
Working Paper: Reversal Patterns
 Remember to welcome ll ides in trding. AND remember to reserve your opinion until you hve independently vlidted the ide! Working Pper: Reversl Ptterns Working Pper In this pper I wnt to review nd (hopefully)
Remember to welcome ll ides in trding. AND remember to reserve your opinion until you hve independently vlidted the ide! Working Pper: Reversl Ptterns Working Pper In this pper I wnt to review nd (hopefully)
Wonderland Road South from Southdale Road to Highway 402 DRAFT Assessment and Evaluation of Road Cross-Section Concepts
 APPENDIX F 1 Socio-Economic 1.1 Property nd Access Impcts to properties Potentil impcts to ccess to existing residences/usinesses Totl numer of properties impcted Impcts to residences (e.g., displcement)
APPENDIX F 1 Socio-Economic 1.1 Property nd Access Impcts to properties Potentil impcts to ccess to existing residences/usinesses Totl numer of properties impcted Impcts to residences (e.g., displcement)
Daytime Habitat Selection by Resident Golden Eagles in Southern Idaho, USA
 Dytime Hbitt Selection by Resident Golden Egles in Southern Idho, USA Environmentl & Sttisticl Consultnts Chd LeBeu 1-04-14 Ryn Nielson, Eric Hllingstd, nd Dve Young cwlebeu@west-inc.com Introduction Risk
Dytime Hbitt Selection by Resident Golden Egles in Southern Idho, USA Environmentl & Sttisticl Consultnts Chd LeBeu 1-04-14 Ryn Nielson, Eric Hllingstd, nd Dve Young cwlebeu@west-inc.com Introduction Risk
USE OF MICROCLIMATE MODELS FOR EVALUATING THERMAL COMFORT: IDENTIFYING THE GAPS
 USE OF MICROCLIMATE MODELS FOR EVALUATING THERMAL COMFORT: IDENTIFYING THE GAPS Tni Shrmin; Koen Steemers The Mrtin Centre for Architecturl nd Urn Studies, Deprtment of Architecture, University of Cmridge,
USE OF MICROCLIMATE MODELS FOR EVALUATING THERMAL COMFORT: IDENTIFYING THE GAPS Tni Shrmin; Koen Steemers The Mrtin Centre for Architecturl nd Urn Studies, Deprtment of Architecture, University of Cmridge,
ERRATA for Guide for the Development of Bicycle Facilities, 4th Edition (GBF-4)
 Dvid Bernhrdt, P.E., President Commissioner, Mine Deprtment of Trnsporttion Bud Wright, Executive Director 444 North Cpitol Street NW, Suite 249, Wshington, DC 20001 (202) 624-5800 Fx: (202) 624-5806 www.trnsporttion.org
Dvid Bernhrdt, P.E., President Commissioner, Mine Deprtment of Trnsporttion Bud Wright, Executive Director 444 North Cpitol Street NW, Suite 249, Wshington, DC 20001 (202) 624-5800 Fx: (202) 624-5806 www.trnsporttion.org
Standard Weight (W s ) Equation and Length Categories for Shovelnose Sturgeon
 North Americn Journl of Fisheries Mngement 18:9 7, 18 Copyright by the Americn Fisheries Society 18 Stndrd Weight (W s ) Eqution nd Length Ctegories for Shovelnose Sturgeon MICHAEL C. QUIST,* CHRISTOPHER
North Americn Journl of Fisheries Mngement 18:9 7, 18 Copyright by the Americn Fisheries Society 18 Stndrd Weight (W s ) Eqution nd Length Ctegories for Shovelnose Sturgeon MICHAEL C. QUIST,* CHRISTOPHER
APPNA SPRING MEETING CHICAGO, ILLINOIS RETAIL BAZAAR REGISTRATION MARRIOTT DOWNTOWN MAGNIFICENT MILE 540 NORTH MICHIGAN AVENUE
 1 PPN SPRING MEETING 2018 CHICGO, ILLINOIS PRIL 26 29, 2018 MRRIOTT DOWNTOWN MGNIFICENT MILE 540 NORTH MICHIGN VENUE RETIL ZR REGISTRTION 2 COMPNY NME CONTCT NME DDRESS RETIL ZR REGISTRTION PREFERRED PHONE
1 PPN SPRING MEETING 2018 CHICGO, ILLINOIS PRIL 26 29, 2018 MRRIOTT DOWNTOWN MGNIFICENT MILE 540 NORTH MICHIGN VENUE RETIL ZR REGISTRTION 2 COMPNY NME CONTCT NME DDRESS RETIL ZR REGISTRTION PREFERRED PHONE
Hot-Air Blowers 12 / / Hot-Air Blowers
 Hot-Air Blowers MISTRAL HOTWIND PREMIUM / HOTWIND SYSTEM MISTRAL Accessories HOTWIND Accessories VULCAN SYSTEM VULCAN SYSTEM Accessories IGNITER BM4/BR4 IGNITER BM4/BR4 Accessories 12 / 13 14 / 15 16 17
Hot-Air Blowers MISTRAL HOTWIND PREMIUM / HOTWIND SYSTEM MISTRAL Accessories HOTWIND Accessories VULCAN SYSTEM VULCAN SYSTEM Accessories IGNITER BM4/BR4 IGNITER BM4/BR4 Accessories 12 / 13 14 / 15 16 17
1991. George W. Sidebotham 1, Gerald L. Wolf 1, Jeffrey Stern 1, and Robert Aftel 1
 George W. Sidebothm 1, Gerld L. Wolf 1, Jeffrey Stern 1, nd Robert Aftel 1 ENDOTRACHEAL TUBE FIRES: A FLAME SPREAD PHENOMENON REFERENCE: Sidebothm, G.W., Wolf, G.L., Stern, J., nd Aftel, R. "Endotrchel
George W. Sidebothm 1, Gerld L. Wolf 1, Jeffrey Stern 1, nd Robert Aftel 1 ENDOTRACHEAL TUBE FIRES: A FLAME SPREAD PHENOMENON REFERENCE: Sidebothm, G.W., Wolf, G.L., Stern, J., nd Aftel, R. "Endotrchel
Lateral Earth Pressure on Lagging in Soldier Pile Wall Systems
 Lterl Erth Pressure on Lgging in Soldier Pile Wll Systems Howrd A. Perko, Ph.D, P.E., CTL Thompson, Fort Collins, CO, USA hperko@ctlthompson.com John J Boulden, SGM, Inc., Grnd Junction, CO johnb@sgm-inc.com
Lterl Erth Pressure on Lgging in Soldier Pile Wll Systems Howrd A. Perko, Ph.D, P.E., CTL Thompson, Fort Collins, CO, USA hperko@ctlthompson.com John J Boulden, SGM, Inc., Grnd Junction, CO johnb@sgm-inc.com
Acoustic measurements of bubbles in the wake of ship model in tank
 Acoustic mesurements of bubbles in the wke of ship model in tnk A. Sutin,b, A. Benilov, H.-S. Roh nd Y.I. Nh c Stevens Institute of Technology, Cstle Point on Hudson, Hoboken, NJ 07030, USA b Artnn Lbortories,
Acoustic mesurements of bubbles in the wke of ship model in tnk A. Sutin,b, A. Benilov, H.-S. Roh nd Y.I. Nh c Stevens Institute of Technology, Cstle Point on Hudson, Hoboken, NJ 07030, USA b Artnn Lbortories,
Impact of Background on Color Performance of False Clownfish, Amphiprion ocellaris, Cuvier
 JOURNAL OF THE Vol. 4, No. 6 WORLD AQUACULTURE SOCIETY Decemer, 29 Impct of Bckground on Color Performnce of Flse Clownfish, Amphiprion ocellris, Cuvier Inyh Ysir School of Biologicl Sciences, Flinders
JOURNAL OF THE Vol. 4, No. 6 WORLD AQUACULTURE SOCIETY Decemer, 29 Impct of Bckground on Color Performnce of Flse Clownfish, Amphiprion ocellris, Cuvier Inyh Ysir School of Biologicl Sciences, Flinders
Ionoregulatory changes in different populations of maturing sockeye salmon Oncorhynchus nerka during ocean and river migration
 The Journl of Experimentl iology 8, 469-478 Pulished y The ompny of iologists 5 doi:.4/je.87 469 Ionoregultory chnges in different popultions of mturing sockeye slmon Oncorhynchus nerk during ocen nd river
The Journl of Experimentl iology 8, 469-478 Pulished y The ompny of iologists 5 doi:.4/je.87 469 Ionoregultory chnges in different popultions of mturing sockeye slmon Oncorhynchus nerk during ocen nd river
WASTE ROCK MANAGEMENT AT SANGATTA COAL MINE A CULTURAL CHANGE. By Peter Scott HLA- Envirosciences Pty Limited
 WASTE ROK MANAGEMENT AT SANGATTA OAL MINE A ULTURAL HANGE By Peter Scott HLA- Envirosciences Pty Limited WASTE ROK MANAGEMENT AT SANGATTA OAL MINE - A ULTURAL HANGE AKNOWLEDGEMENTS Deddi Hndiko Mtthew
WASTE ROK MANAGEMENT AT SANGATTA OAL MINE A ULTURAL HANGE By Peter Scott HLA- Envirosciences Pty Limited WASTE ROK MANAGEMENT AT SANGATTA OAL MINE - A ULTURAL HANGE AKNOWLEDGEMENTS Deddi Hndiko Mtthew
FOR OWNERS OF HORSE BUSINESSES
 W 371-B MANAGEMENT AND COST CONSIDERATIONS FOR OWNERS OF HORSE BUSINESSES Andrew P. Griffith, Assistnt Professor nd UT Extension Specilist Deprtment of Agriculturl nd Resource Economics BACKYARD VEGETABLES
W 371-B MANAGEMENT AND COST CONSIDERATIONS FOR OWNERS OF HORSE BUSINESSES Andrew P. Griffith, Assistnt Professor nd UT Extension Specilist Deprtment of Agriculturl nd Resource Economics BACKYARD VEGETABLES
Characteristics, Expenditures, and Economic Impact of Resident and Nonresident Hunters and Anglers in North Dakota, , Season and Trends
 Agriculturl Economics Report No. 389 June 1998 Chrcteristics, Expenditures, nd Economic Impct of Resident nd Nonresident Hunters nd Anglers in North Dkot, 1996-97, Seson nd Trends Tin D. Lewis Jy A. Leitch
Agriculturl Economics Report No. 389 June 1998 Chrcteristics, Expenditures, nd Economic Impct of Resident nd Nonresident Hunters nd Anglers in North Dkot, 1996-97, Seson nd Trends Tin D. Lewis Jy A. Leitch
OFFSHORE USE OF FLOATING SHEERLEGS
 Proceedings of the ASME 211 3th Interntionl Conference on Ocen, Offshore nd Arctic Engineering OMAE211 June 19-24, 211, Rotterdm, The Netherlnds OMAE211-49394 OFFSHORE USE OF FLOATING SHEERLEGS Vincent
Proceedings of the ASME 211 3th Interntionl Conference on Ocen, Offshore nd Arctic Engineering OMAE211 June 19-24, 211, Rotterdm, The Netherlnds OMAE211-49394 OFFSHORE USE OF FLOATING SHEERLEGS Vincent
Foraging Behavior of Fishes in Aquatic Plants
 Forging Behvior of Fishes in Aqutic Plnts by Sherry L Hrrel, Eric D. Dibble, nd K. Jck Killgore PURPOSE: Forging behvior of juvenile bluegill (Lepomis mcrochirus) nd lrgemouth bss (Micropterus slmoides)
Forging Behvior of Fishes in Aqutic Plnts by Sherry L Hrrel, Eric D. Dibble, nd K. Jck Killgore PURPOSE: Forging behvior of juvenile bluegill (Lepomis mcrochirus) nd lrgemouth bss (Micropterus slmoides)
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring Announcements
 CS 188: Artificil Intelligence Spring 2011 Lecture 19: Dynmic Byes Nets, Nïve Byes 4/6/2011 Pieter Aeel UC Berkeley Slides dpted from Dn Klein. Announcements W4 out, due next week Mondy P4 out, due next
CS 188: Artificil Intelligence Spring 2011 Lecture 19: Dynmic Byes Nets, Nïve Byes 4/6/2011 Pieter Aeel UC Berkeley Slides dpted from Dn Klein. Announcements W4 out, due next week Mondy P4 out, due next
August Forestry Commission Wales Public Funding of Ffynone and Cilgwyn Woodlands
 357A2010 - Ffynone Woodlnds report - pv5:lyout 1 09/08/2010 14:12 Pge 1 August 2010 www.wo.gov.uk Forestry Commission Wles Pulic Funding of Ffynone nd Cilgwyn Woodlnds Forestry Commission Wles Pulic Funding
357A2010 - Ffynone Woodlnds report - pv5:lyout 1 09/08/2010 14:12 Pge 1 August 2010 www.wo.gov.uk Forestry Commission Wles Pulic Funding of Ffynone nd Cilgwyn Woodlnds Forestry Commission Wles Pulic Funding
Phenology of Brown Marmorated Stink Bugs and Distribution near California Pear Orchards
 Phenology of Brown Mrmorted Stink Bugs nd Distriution ner Cliforni Per Orchrds Chuck Ingels 1, Luci Vrel 2, Rchel Elkins 3, nd Cort Hurley 1 1 UC Coopertive Extension, Scrmento County 2 UC Coopertive Extension,
Phenology of Brown Mrmorted Stink Bugs nd Distriution ner Cliforni Per Orchrds Chuck Ingels 1, Luci Vrel 2, Rchel Elkins 3, nd Cort Hurley 1 1 UC Coopertive Extension, Scrmento County 2 UC Coopertive Extension,
Impact of cross-reef fluxes on the Ouano lagoon circulation.
 Impct of cross-reef fluxes on the Ouno lgoon circultion. Cristele Chevlier, Jen-Luc Devenon, Vincent Rey Mediterrnen Institute of Ocenogrphy (MIO), CNRS/INSU, UMR 7294 nd IRD, UR235, 13288 Mrseille Cedex,
Impct of cross-reef fluxes on the Ouno lgoon circultion. Cristele Chevlier, Jen-Luc Devenon, Vincent Rey Mediterrnen Institute of Ocenogrphy (MIO), CNRS/INSU, UMR 7294 nd IRD, UR235, 13288 Mrseille Cedex,
Beetle and plant density as cues initiating dispersal in two species of adult predaceous diving beetles
 DOI 10.1007/s00442-008-9-z POPULATION ECOLOGY - ORIGINAL PAPER Beetle nd plnt density s cues inititing dispersl in two species of dult predceous diving eetles Donld A. Yee Stcy Tylor Steven M. Vmosi Received:
DOI 10.1007/s00442-008-9-z POPULATION ECOLOGY - ORIGINAL PAPER Beetle nd plnt density s cues inititing dispersl in two species of dult predceous diving eetles Donld A. Yee Stcy Tylor Steven M. Vmosi Received:
Valve Proving System for automatic Shutoff Valves
 LGY lve Proving System for utomtic Shutoff lves 11... The 11... vlve proving system is designed for use with shutoff vlves in connection with gs urners nd gs pplinces. n the event of indmissile lekge,
LGY lve Proving System for utomtic Shutoff lves 11... The 11... vlve proving system is designed for use with shutoff vlves in connection with gs urners nd gs pplinces. n the event of indmissile lekge,
PCT MINIMUM DOCUMENTATION
 Ref.: PCT Minimum Documenttion pge: 4.1.1 PCT MINIMUM TION INVENTORY S CCORDING TO PCT RULE 34.1 (PERIOD FROM 1920 TO 2000) Explntory Notes 1. On the following pges is given the inventory of ptent documents,
Ref.: PCT Minimum Documenttion pge: 4.1.1 PCT MINIMUM TION INVENTORY S CCORDING TO PCT RULE 34.1 (PERIOD FROM 1920 TO 2000) Explntory Notes 1. On the following pges is given the inventory of ptent documents,
VB-7253 Series. Application. Features. Applicable Literature
 VB-7253 Series 1/2 to 2 Screwed NPT Stinless Steel Trim with Teflon Disc Stem Up Open, Two-Wy Vlves Generl Instructions Appliction VB-7253 series single set, stem down to close, two wy vlves control wter
VB-7253 Series 1/2 to 2 Screwed NPT Stinless Steel Trim with Teflon Disc Stem Up Open, Two-Wy Vlves Generl Instructions Appliction VB-7253 series single set, stem down to close, two wy vlves control wter
OXYGEN REQUIREMENTS AND THE PHYSIOLOGICAL SUPPRESSION OF SUPERNUMERARY INSECT PARASITOIDS
 p. Biol. (96), 0, 550 textfigures Printed in Gret Britin OXYGEN REQUIREMENTS AND THE PHYSIOLOGICAL SUPPRESSION OF SUPERNUMERARY INSECT PARASITOIDS BY RODERICK C. FISHER Deprtment of Zoology nd Comprtive
p. Biol. (96), 0, 550 textfigures Printed in Gret Britin OXYGEN REQUIREMENTS AND THE PHYSIOLOGICAL SUPPRESSION OF SUPERNUMERARY INSECT PARASITOIDS BY RODERICK C. FISHER Deprtment of Zoology nd Comprtive
Name Class Date SAMPLE. Complete the missing numbers in the sequences below. 753, ,982. The area of the shape is approximately cm 2
 End of term: TEST A You will need penil. Yer 5 Nme Clss Dte 1 2 Complete the missing numers in the sequenes elow. 200 3926 4926 400 500 700 7926 753,982 553,982 Estimte the re of the shpe elow. The re
End of term: TEST A You will need penil. Yer 5 Nme Clss Dte 1 2 Complete the missing numers in the sequenes elow. 200 3926 4926 400 500 700 7926 753,982 553,982 Estimte the re of the shpe elow. The re
ABSTRACT EXPERIMENTAL METHOD AND MODEL
 Proceedings of The Twelfth () Interntionl Offshore nd Polr Engineering Conference Kitkyushu, Jpn, My 31, Copyright by The Interntionl Society of Offshore nd Polr Engineers ISBN 1-53-5-3 (Set); ISSN 19-19
Proceedings of The Twelfth () Interntionl Offshore nd Polr Engineering Conference Kitkyushu, Jpn, My 31, Copyright by The Interntionl Society of Offshore nd Polr Engineers ISBN 1-53-5-3 (Set); ISSN 19-19
and that excessive pronation is one major cause of foot and leg problems of runners. The treatment modahties used on these runners are shown
 Foot orthotic devices to modify selected spects of lower extremity mechnics* B. T. BATES,&dgger; Ph.D., L. R. OSTERNIG, Ph.D., B. MASON, M.S., AND L. S. JAMES, M.D., Eugene, Oregon From the Biomechnics-Sports
Foot orthotic devices to modify selected spects of lower extremity mechnics* B. T. BATES,&dgger; Ph.D., L. R. OSTERNIG, Ph.D., B. MASON, M.S., AND L. S. JAMES, M.D., Eugene, Oregon From the Biomechnics-Sports
Using physiological tools to forecast male life-history types to aid in management of hatchery and wild Oncorhynchus mykiss
 Using physiologicl tools to forecst mle life-history types to id in mngement of htchery nd wild Oncorhynchus mykiss Don Lrsen nd Penny Swnson NOAA Fisheries Mollie Middleton nd Jon Dickey UW, School of
Using physiologicl tools to forecst mle life-history types to id in mngement of htchery nd wild Oncorhynchus mykiss Don Lrsen nd Penny Swnson NOAA Fisheries Mollie Middleton nd Jon Dickey UW, School of
Long Term Retention, Survival, Growth, and Physiological Indicators of Juvenile Salmonids Marked with Passive Integrated Transponder Tags
 Americn Fisheries Society Symposium 76, 2011 2011 y the Americn Fisheries Society Long Term Retention, Survivl, Growth, nd Physiologicl Indictors of Juvenile Slmonids Mrked with Pssive Integrted Trnsponder
Americn Fisheries Society Symposium 76, 2011 2011 y the Americn Fisheries Society Long Term Retention, Survivl, Growth, nd Physiologicl Indictors of Juvenile Slmonids Mrked with Pssive Integrted Trnsponder
STOCK ASSESSMENT OF SHRIMP Pandalus borealis (KRØYER 1838) IN SKJÁLFANDI BAY NORTHERN ICELAND
 P.O. Box 1390, Skulgt 4 120 Reykjvik, Icelnd Finl Project 2008 STOCK ASSESSMENT OF SHRIMP Pndlus borelis (KRØYER 1838) IN SKJÁLFANDI BAY NORTHERN ICELAND Josephus Choe Junior Mmie Ministry of Fisheries
P.O. Box 1390, Skulgt 4 120 Reykjvik, Icelnd Finl Project 2008 STOCK ASSESSMENT OF SHRIMP Pndlus borelis (KRØYER 1838) IN SKJÁLFANDI BAY NORTHERN ICELAND Josephus Choe Junior Mmie Ministry of Fisheries
The role of experience in flight behaviour of Drosophila
 3377 The Journl of Experimentl iology 212, 3377-3386 Pulished y The Compny of iologists 29 doi:1.1242/je.25221 The role of experience in flight ehviour of Drosophil Thoms Hesselerg nd Fritz-Olf Lehmnn*
3377 The Journl of Experimentl iology 212, 3377-3386 Pulished y The Compny of iologists 29 doi:1.1242/je.25221 The role of experience in flight ehviour of Drosophil Thoms Hesselerg nd Fritz-Olf Lehmnn*
Quantitative assessment of surf-produced sea spray aerosol
 Quntittive ssessment of surf-produced se spry erosol Filip P. Neele', Gerrit de Leeuw', Mrtijn Jnsen2 nd Mrcel Stive2' 1TNO Physics nd Electronics Lbortory, The Hgue, The Netherlnds 2Delft Hydrulics, Delft,
Quntittive ssessment of surf-produced se spry erosol Filip P. Neele', Gerrit de Leeuw', Mrtijn Jnsen2 nd Mrcel Stive2' 1TNO Physics nd Electronics Lbortory, The Hgue, The Netherlnds 2Delft Hydrulics, Delft,
