Appendix D. Hangingwall failure mechanisms. Analysis of the literature review
|
|
|
- Vanessa Short
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Appendix D Hangingwall failure mechanim D1 Analyi of the literature review D1.1 Elatic beam invetigation The freely upported beam and the beam with built in end were compared uing the equation for maximum tenile tre (Chapter 4.1). The analyi howed the maximum beam thickne where the induced tre wa equal to an aumed tenile trength of 10 MPa for variou panel pan. The invetigation reult are provided in Figure D 1 and how that the end at the top of a beam with built-in end will alway fail before the bottom centre of a freely upported beam, auming the ame material propertie throughout the beam. Once failure ha occurred at the end of a beam with built-in end, the beam immediately become a freely upported beam or ome combination of the two mechanim. Thu the analytical olution for a beam with built-in end i not uitable for panel pan deign purpoe, and the freely upported beam theory may be lightly conervative due to the compreive tree generated at the bottom edge once the beam with built-in end ha failed. 1
2 3 2.5 Beam thickne (m) Stable Failed Built in end Freely upported Panel pan (m) Figure D 1 Tenile limit for a beam with built-in end and a freely upported beam. A material tenile trength of 10 MPa wa aumed A econd et of analye were done to explore the effect of material tenile trength on beam behaviour. The invetigation wa done uing the analytical olution for the maximum tenile tre in a freely upported beam and a depth below urface and k of 230 m and 2.0 repectively were aumed. The reult of the invetigation are provided in Figure D 2, which how the maximum beam thickne where tenile failure will occur for variou panel pan. Tenile failure will occur at the bae of a beam decribing the relevant material trength if it i narrower than depicted by the curve. The analye indicate that tenile failure cannot occur at the bae of a beam in a 30 m wide panel if the upport capacity can carry the deadweight of a 1.5 m thick beam and the depth of working i deeper than 230 m below urface, auming a k of 2. Note that tenile failure doe not necearily mean a collape but rather progreion toward ome form of a Vouoir beam. 2
3 4.5 4 Beam thickne (m) Stable Failure T = -2 MPa T = -5 MPa T = -10 MPa T = 0 MPa Panel pan (m) Figure D 2 Tenile limit for a imply upported elatic beam for variou material tenile trength Figure D 3 how the effect of k on the behaviour of a freely upported beam. A material tenile trength of 10 MPa and a depth of 200 m were aumed in the invetigation. The effect of k on beam trength i more ignificant than the material propertie at thi depth, clearly illutrating the detrimental effect of low k on beam behaviour at hallow depth Beam thickne (m) Stable Failed k = 0.5 k = Panel pan (m) Figure D 3 Tenile limit for a imply upported elatic beam for variou k 3
4 Further analyi wa done to how the effect of depth below urface on beam behaviour. An aumed common cenario of k=1.3 wa applied with a material tenile trength of 1 MPa. Under thee condition tenile failure and the development of ome kind of Vouoir Beam i almot guaranteed in a pan of 30 m at hallow depth (Figure D 4). 25 Beam thickne (m) Stable 50 m 100 m 200 m Panel pan (m) Failed Figure D 4 Tenile limit for a imply upported elatic beam for variou depth Finally, the maximum height of a parting plane for Vouoir beam formation wa invetigated uing the analytical olution for a imply upported beam. A typical k of 1.3 wa again elected and the tenile trength of the material wa et to zero. In effect the tenile tre that developed at the bottom centre of the beam wa equal to the applied horizontal compreive tre. The reult of the invetigation are provided in Figure D 5. The analyi how that any parting plane at greater height than indicated by the curve cannot form a Vouoir beam in an environment where k=1.3. 4
5 Parting height (m) Vouoir beam formation impoible Panel pan (m) Vouoir beam formation poible 100 m 200 m 400 m Figure D 5 Parting height limit for Vouoir beam formation The graph above are not meant to be ued a deign curve but rather to illutrate condition under which partial or full Vouoir beam theory may be applicable. It hould be noted that the debilitating and trengthening effect of joint and upport repectively have generally not been conidered in the analyi. D1.2 Vouoir beam analyi Should Vouoir beam form, the analye hown in Figure D 6 are uggeted by the literature for deign purpoe. Cruhing failure i the mot likely mode (Ryder and Jager, 2002), and will occur if the beam thickne i le than the limit indicated in Figure D 6. An admiible train of 3 mm/m in the rock abutment wa aumed for the analyi. A low rock ma modulu i uggeted to account for the dicontinuitie (Ryder and Jager, 2002). Where there are adverely oriented, peritent dicontinuitie at the abutment, hear failure will occur firt on a vertical joint of friction angle φ=30 if the beam thickne exceed the limit hown in Figure D 6. 5
6 Beam thickne (m) Failed if appropriate dicontinuity preent Stable 1 Failed Panel pan (m) Shear 20 GPa 3 mm/m 40 GPa 3 mm/m 60 GPa 3 mm/m Figure D 6 Stability limit in a Vouoir beam for different value of E (after Sofiano, 1996) The analyi hown in Figure D 6 indicate a maximum untable beam thickne of 1 m at a panel pan of 30 m. Auming that the lowet beam i not loaded by other, narrower beam above, current Vouoir beam theory ugget that untable arch formation cannot occur if the upport reitance requirement hown in Figure D 7 are atified. The theory ha potential a a deign tool. However, the majority of collape occur on peritent, hallow-dipping dicontinuitie and the Vouoir beam analye may only be applicable, therefore, if it i aumed that thee dicontinuitie are detected early and appropriately upported. 120 Support reitance (kn/m2) Panel pan (m) Figure D 7 Panel pan and upport requirement deign curve baed on current Vouoir beam theory 6
7 D1.3 Dicuion Pure elatic theory ugget that Vouoir beam only form under limited mining condition. Under normal mining condition deeper than about 230 m below urface, where the upport capacity i able to carry a burden height of about 1.5 m and the panel pan i about 30 m, tenile failure hould not occur at the bae of the beam and therefore a Vouoir beam hould not form. In addition, a Vouoir beam cannot form if the lowet parting occur at a greater height than hown by the curve in Figure D 5 (providing the k-ratio and depth below urface are not le than aumed in the analyi). Should Vouoir beam form, a maximum thickne of 1 m i expected in panel pan of 30 m. Thu a nominal upport reitance of about 30 kn/m 2 i required if it i aumed that the beam i not loaded from above. The analyi how that Vouoir beam appear unlikely to form in 30 m wide panel at depth, particularly a the current pre-treed upport ytem are in exce of 50 kn/m 2. D2 Numerical modelling to determine the effect of vertical and horizontal dicontinuitie on the VTZ D2.1 Introduction Several panel uggeted that parting occurred ome 3.5 m above the working when the panel pan were about 30 m x 100 m. A 2D model wa et up under imilar tre condition to collape to conider the effect of the VTZ on an iolated panel in the preence of vertical and horizontal dicontinuitie. The pan at which the model predicted intabilitie were compared to the analytical olution for the VTZ height of an iolated panel and where cruh pillar have been cut. 7
8 D2.2 Model decription Large platen with applied preure load were modelled to obtain realitic cloure behaviour. The model conited of a blocky hangingwall part and the platen, a illutrated in Figure D 8. 2D plane train condition were applied. Figure D 8 Hangingwall model geometry The platen extended acro the total model dimenion to 460 m X 200 m. The blocky part of the model wa 60 m X 45 m and wa made up of an upper portion, coniting of 1.5 m X 1.5 m quare block, and a lower beam 15 m in height, coniting of 1.5 m wide block. Thi beam contained a ingle horizontal dicontinuity placed at a different height for each analyi. The preure load were applied via platen of the ame material a the hangingwall. A frictionle interface wa introduced between the platen and the hangingwall (and between the platen and reef). For the ret of the model, zero coheion and a contant friction angle were applied throughout. Initially, the friction angle wa et to a typical value of 30. Dicrete contact wa managed through a penalty ytem, whereby bodie were permitted to penetrate each other, with an oppoing load applied which wa proportional to the penalty parameter and the amount of interpenetration. Thi produced a dynamic ytem which relied on an appropriate choice of the penalty parameter. Experience ha hown that penalty value twenty percent greater than the material Young modulu are appropriate for the choen contact algorithm. 8
9 The choen elatic material propertie are aumed generic value for platinum mining: Young modulu 80 GPa Poion ratio 0.2 Denity 3000 kg/m 3 The modelled dicontinuity height were: 1.5 m, 3 m, 5 m, 7.5 m and 10 m. The modelled pan wa increaed to a maximum of 54 m. A depth of 500 m wa modelled with a k of 2.0. The reult were interpreted in term of cloure, the VTZ and the vertical eparation between the two part of the lower beam (at centre-pan). Cloure wa obtained by tracking the diplacement of the centre-pan node uing highreolution hitorie. The VTZ i imply the height of the zone indicating vertical tenile tre, and wa quantified by tracking the vertical tre along a vertical row of element extending from the reef horizon to the top of the beam. The vertical eparation wa obtained by tracking the difference between centre-pan nodal diplacement at the top of the lower portion and the bottom of the upper portion of the beam. D2.3 Model reult The general characteritic of the ytem are bet illutrated by examining the vertical tre ditribution over the coure of a full excavation. The evolution of the vertical tre ditribution for the 7.5 m high layer i preented in Figure D 9 to Figure D 13. The dark blue contour repreent vertical compreion. All other contour band indicate tenion, increaing in magnitude from light blue to red. 9
10 Figure D 9 Vertical tenile tre ditribution for a 7.5 m high dicontinuity at a pan of 12 m Figure D 10 Vertical tenile tre ditribution for a 7.5 m high dicontinuity at a pan of 38 m Figure D 11 Vertical tenile tre ditribution for a 7.5 m high dicontinuity at a pan of 42 m 10
11 Figure D 12 Vertical tenile tre ditribution for a 7.5 m high dicontinuity at a pan of 48 m Figure D 13 Vertical tenile tre ditribution for a 7.5 m high dicontinuity at a pan of 54 m Vertical tenion i initially manifeted at the oppoite lower urface of individual block (Figure D 9). A gradual increae in the extent of the VTZ i oberved at the centre of the pan. The greatet magnitude of vertical tenile tre are concentrated at the bottom of the block, while a zone of lower tenile tre extend upward from centre-pan (Figure D 10). Thi zone eventually reache the height of the horizontal dicontinuity at 7.5 m, whereupon the appearance of the VTZ become chaotic (Figure D 11). After a few more metre of excavation, the behaviour oberved for the lower portion of the beam appear to be reetablihed in the upper portion of the beam (Figure D 12). Thi trend continue with the extenion of the VTZ into the blocky portion of the model. Interetingly, the block within the lower portion of the beam how very high value of vertical 11
12 tenile tre at all four corner, with a ditribution of lower tenile tree within (Figure D 13). Thi analyi how a ignificant behavioural change when the VTZ extend through the dicontinuity. Thi wa oberved in all reult (except the 10 m high layer) and can be demontrated more clearly in the vertical eparation and VTZ ditribution. Figure D 14 how the height of the VTZ a a function of pan for each analyi. The dahed line indicate the height of the dicontinuity. In each analyi (except the 10 m high layer), the greatet increae in the height of the VTZ occur when it croe through the dicontinuity Height [m] Span [m] Layer at 1.5 m Layer at 3.0 m Layer at 5.0 m Layer at 7.5 m Layer at 10.0 m Figure D 14 Height of vertical tenile tre ditribution a a function of pan for each analyi Thi i even more clearly demontrated in Figure D 15, which how the maximum tenile tre along the vertical line at centre-pan. For layer up to 7.5 m high, the pan at which the VTZ croe into the next layer i indicated by a udden jump in the magnitude of the maximum tenile tre. Prior to thi jump, all of the model how a gradual decreae in tenile tre magnitude. For the 10 m high layer, thi trend continue for the duration of the analyi, a the VTZ 12
13 doe not cro into the upper layer for a 54 m pan. Interetingly, the height of the maximum vertical tenile tre at firt remain cloe to the bottom of the lower beam, however, following the croing over of the VTZ into the upper beam, the highet vertical tenile tre i recorded at the top of the lower beam Vertical tre [MPa] Layer at 1.5 m Layer at 3.0 m Layer at 5.0 m Layer at 7.5 m Layer at 10.0 m Span [m] Figure D 15 Maximum vertical tenile tre ditribution a a function of pan for each analyi The abruptne of the change when the VTZ extend into the upper beam i alo dicernible in the eparation of the beam layer. Figure D 16 how the vertical eparation between beam layer a a function of pan. In all cae, the eparation increae at firt and then tend to a contant value, however, where the VTZ ha croed over, a udden increae in eparation i oberved, which how no ign of attaining a contant value with increaing pan. The pan at which thi change occur are the ame a for the change decribed above. Interetingly the ytem itelf how a natural limit in the layer eparation prior to the VTZ croing into the next layer. Thi eparation i upected to be due to a reduction in compreive tre. 13
14 Vertical eparation [mm] Span [m] Layer at 1.5 m Layer at 3.0 m Layer at 5.0 m Layer at 7.5 m Layer at 10.0 m Figure D 16 Vertical layer eparation a a function of pan for each analyi Change are alo oberved in the cloure profile. It i more intructional to examine the rate of cloure (millimetre of cloure per metre of face advance), which i preented in Figure D 17. The general trend prior to the VTZ croing over i toward a lightly increaing cloure rate, which varie from 0.19 mm/m to 0.29 mm/m over the duration of the analyi for the 10 m high layer. Following the VTZ croing over, cloure rate increae dramatically. Note that the increae in cloure rate i only evident after the tranition ha taken place. For example, the VTZ change for the 5 m layer occur between 28 m and 32 m, according to Figure D 14. Thi change i evident in the cloure rate graph (Figure D 17) at around 35 m. 14
15 Cloure rate [mm/m] Layer at 1.5 m Layer at 3.0 m Layer at 5.0 m Layer at 7.5 m Layer at 10.0 m Span [m] Figure D 17 Rate of cloure a a function of pan for each analyi D2.4 Dicuion The numerical modelling reult have revealed a relationhip between hangingwall tructure, the excavated pan and the occurrence of an abrupt change in the deformational characteritic of the hangingwall. Thi change coincide with the croing over of the VTZ from one horizontal layer to another. It appear that the behaviour i cyclic in nature: the VTZ croe into a new layer, which behave imilarly to the layer below it until the VTZ croe into the next layer, etc. Thi appear to be the cae, but more layer hould be modelled to obtain clear evidence of thi behaviour. The pan at which thi change occur, for each modelled layer height, i preented in Figure D 18. A power-law fit i uggeted. 15
16 60 Span at VTZ change [m] y = 7.178x R 2 = Layer height [m] Figure D 18 Span at which the VTZ croing occur for different layer height The reult hown in Figure D 18 depict the behaviour of an iolated panel. The analytical olution for an iolated panel (Ryder and Jager, 2002) and a panel bounded by cruh pillar (auming a pillar reidual trength of 20 MPa with dimenion 6 m X 3 m and a 2 m holing) (Ryder et al, 2005) i hown for comparion in Figure D 19. The model predict a more conervative pan/vtz ratio and therefore untable condition at maller pan than the elatic model for an iolated condition. Collape invetigation at Paardekraal platinum mine (Appendix B) indicated untable condition at pan of 30 m X 100 m and a parting plane at 3.5 m above the tope. The depth of working wa imilar to the model and how a critical pan between the model and the analytical olution. It hould be noted, however, that the tope wa upported and untable condition could have occurred at maller pan in an unupported cenario. In addition, parting above the panel may well have occurred earlier and remained undetected. When the pillar between panel cruh there i a ignificant increae in the height of the tenile zone, commenurate with a decreae in the loadbearing capacity of the pillar. The tenile height then become dependent on the reidual trength of the pillar rather than depth below urface. Furthermore it hould be noted that the VTZ i independent of k. 16
17 60 Panel pan (m) y = x 0.66 R 2 = 1 y = x 0.5 R 2 = Height of vertical tenile zone (m) Cruh pillar Iolated panel Model Collape ite Power (Iolated panel) Power (Cruh pillar) Figure D 19 Analytic olution for the height of the vertical tenile zone a a function of pan. The iolated panel aumed a depth of 500 m below urface While it i tempting to treat the derived relationhip a a deign chart, it mut be noted that the reult of the blocky model are pecific to the choen input. Thi tudy ha not conidered the effect of depth, tre ratio, contact propertie or material trength. One variation wa modelled to demontrate the enitivity of the model to input parameter: the contact friction angle wa changed to 6 for the 1.5 m high layer. The reulting vertical tenile tre ditribution at a pan of 12 m i preented in Figure D 20. Clearly, thi i very different to the reult for a 30 friction angle: the VTZ extend to 16 m for a 12 m pan. At 26 m pan, the VTZ extend for the entire height of the blocky hangingwall portion of the model, and further excavation with thi model i not meaningful. Figure D 20 Tenile tre ditribution for a layer height of 1.5 m and a contact friction angle of 6 (12 m pan) 17
18 The macrocopic behaviour of a dicontinuou beam i imilar to that of an intact beam in that the vertical tenile tre increae with pan, and i dependent on the thickne of the beam. However, the fundamental apect controlling the behaviour of a dicontinuou beam are very different to thoe in the intact cae. Of particular interet i the fact that the highet vertical tenile tree are recorded near the top of the beam. The top of the beam alo how alternating region of compreion and tenion within the VTZ (Figure D 13). It eem that the behaviour of the individual block, and the variation of the tre within thee block, determine the fundamental behaviour of the dicontinuou beam. Further work hould examine how individual block behave, and how the block combine to produce the overall behaviour. Further work in thi area hould alo involve the following tak: The combination of a blocky hangingwall and cruh pillar; Model multiple layer in the dicontinuou beam zone; Invetigate whether the overlying block tructure affect the reult; Calibration with in itu cloure data and tre meaurement; and Senitivity analye including: o Depth; o Stre ratio; o Contact propertie; o Elatic material propertie; and o Material trength. 18
19 D3 Numerical modelling to determine the effect of hallow-dipping dicontinuitie on tability D3.1 Introduction Since mot of the FOG tudied in thi project involved hallow-dipping or curved dicontinuitie a the primary releae urface, it wa neceary to tudy the effect of uch dicontinuitie on tability. A wort-cae cenario wa choen with infinite dip panel pan and infinitely long dicontinuitie (2D plane train condition). Such condition exited in the original tope at Lebowa Platinum Mine, Middelpunt ection (LPM). The colloquial UCB wa a hallow-dipping thrut fault dipping in and out of the UG2 reef horizon. Many of the original tope formed tet cae imilar to the model, which could be ued to check the validity of the model. The joint et were imilar to the common joint oberved on the platinum mine. 2-D UDEC model (with the Barton Bandi joint addition) incorporating the two commonly oberved joint et, the triplet and a hallow-dipping dicontinuity at 20 to the trata (UCB) were et up. The analye were performed uing laboratory-derived input parameter and meaurement made at the mine (Table D 1 and Table D 2). A k value of 1.5 wa aumed in all the aement. 19
20 Table D 1 Parameter ued in the UDEC model for a horizontal tre of 3 MPa Block propertie Joint et I UCB Shear modulu (G) 40 GPa Joint friction angle Bulk modulu 42 GPa Joint (K) coheion Friction angle 48 0 Joint tenile trength Coheion 14.6 MPa Joint et II Tenile 8.9 MPa Joint friction trength angle Joint coheion Joint tenile trength 36 0 Joint friction angle 0.13 MPa Joint coheion 0 MPa Joint tenile trength Triplet 37 0 Joint friction angle 0.27 MPa Joint coheion 0 MPa Joint tenile trength MPa 0 MPa MPa 7.1 MPa Note: The friction angle were determined uing the methodology uggeted by Barton (1997). Table D 2 Orientation and depth of geological dicontinuitie in the model. Dicontinuity Height above tope (m) Dip angle (degree) Triplet I 1.6 m 0 Triplet II 2.3 m 0 Triplet III 3.0 m 0 Weak trata (UCB value) 5.0 m 0 Joint et I 80 Joint et II
21 D3.2 Benchmark model - without a hallow dipping dicontinuity or upport A uite of model wa run without the UCB plane. The model were et up uing the input parameter provided in Table D 1 and Table D 2 o that an initial pan of 3 m could be increaed in tep of 2 m. The model were terminated when the unupported pan reached 40 m. No failure occurred (table condition) although parting took place on the triplet and the plane at 5 m above the tope, creating four beam a hown in Figure D 21. The maximum vertical deformation wa 15 mm and an exaggeration of 35 wa applied to the reult hown in the figure. Figure D 21 Reult of a UDEC model without upport and without the UCB, a pan of 40 m and the vertical deformation magnified by 35 time D3.3 Model with a hallow dipping dicontinuity but no upport The model above wa modified to include the UCB and a uite of tet were run without upport a hown in Figure D 22. Block that formed between the UCB and the two joint et fell out a the pan wa increaed, howing that there i no table, elf upporting pan. At a pan of 5 m the rock ma up to the firt triplet (1.6 m above the tope) became untable. An increae of the pan by 2 m reulted in a migration of the untable zone up to the econd triplet at 2.3 m above the tope. Both the condition at 5 m and 7 m were oberved at LPM in unupported or poorly upported panel. At a pan of 9 m, everything below 21
22 triplet III (at a height of 3 m) became untable. At a pan of 15 m, a collape occurred up to the parting plane at 5 m above the tope. I II UCB 5 m 3 m pan 5m pan 7 m pan 9 m pan 11 m pan 13 m pan 15 m pan Key Triplet Unmined mining tep I Joint et I II Joint et II Figure D 22 Reult of a UDEC model without upport D3.4 Model with a hallow dipping dicontinuity and 50 kn/m 2 upport reitance A upport ytem of 170 mm diameter mine pole paced 2 m x 2 m on dip and trike wa originally ued at the mine. A down-rated upport reitance of 50 kn/m 2 wa aumed for the invetigation and a curve for the elongate upport ytem wa generated from underground meaurement (Figure D 23). The reult of the model are hown in Figure D 24. Stable condition were predicted up to a pan of 9 m. At a pan of 11 m the model howed that parting had occurred on all three triplet a well a at 5 m above the tope. A collape occurred up to triplet III at a pan of 13 m, which i an improvement of 4 m over the unupported cenario. 22
23 60 Support reitance (kn/m 2 ) Deformation (mm) Figure D 23 Support reitance with a 99% confidence, auming large block (upported by at leat three pole) I II UCB 9 m pan 11 m pan 13 m pan Key Triplet Unmined mining tep I Joint et I II Joint et II Figure D 24 Reult of a UDEC model with a upport reitance of 50 kn/m 2 23
24 D3.5 Model with a hallow-dipping dicontinuity and 135 kn/m 2 upport reitance A new upport ytem wa introduced to the mine which included larger diameter mine pole and pack. Thi condition wa modelled auming a down-rated upport reitance of 135 kn/m 2. In the model, only the mine pole were pretreed (to 150 kn) and the profile of upport reitance to cloure wa determined from underground meaurement (Figure D 25). A great improvement, both in table panel pan and rock ma condition, wa achieved by thi upport ytem (Figure D 26). Untable condition occurred at a pan of 19 m and a final collape at 22 m. Note that parting initiated at 5 m above the hangingwall, when the pan reached 17 m. Support reitance (kn/m 2 ) Deformation (mm) Figure D 25 Support reitance profile for the econd upport ytem 24
25 I UCB II K-ratio 0,16 17 m pan 19 m pan 20 m pan 22 m pan Key Triplet Unmined mining tep I Joint et I II Joint et II Figure D 26 Reult of the UDEC model for a pack-elongate upport ytem with a upport reitance of 136 kn/m 2 D3.6 Model with a hallow dipping dicontinuity and 200 kn/m 2 upport reitance The modelled upport ytem wa intalled at a pre-treed of 100 kn/m 2 and provided a peak reitance of 200 kn/m 2 (Figure D 27). Thu the upport capacity wa technically able to upport a rock height of 5 m, with only about 5 mm deformation. To enure wort cae condition, a econd horizontal dicontinuity, with propertie imilar to the UCB, wa et up at 7 m above the tope. Thi wa jut higher than the upport capacity. The reult are hown in Figure D 28. Span were increaed in the model to a maximum of 36 m and table condition were predicted in all run. However it hould be noted that FOG occurred in the face area when the maximum upport to face ditance wa 3.6 m, a hown in Figure D 29. Thee FOG were not oberved when the 25
26 upport to face ditance wa kept to 2.8 m and thi wa alo confirmed by underground obervation. 250 Support reitance (kn/m 2 ) Cloure (mm) Figure D 27 Final upport reitance profile (100kN/m 2 at intallation) I UCB 32 m pan 34 m pan II 36 m pan Key Triplet Unmined mining tep I Joint et I II Joint et II Support Figure D 28 Reult of the UDEC model for a upport reitance of 200 kn/m 2. The upport to face ditance wa kept to a maximum of 2.8 m 26
27 I UCB 32 m pan 34 m pan II 36 m pan Key Triplet Unmined mining tep I Joint et I II Joint et II Support Figure D 29 Reult of UDEC model for a upport reitance of 200 kn/m 2. FOG occurred when the upport to face ditance wa 3.6 m D3.7 Dicuion of the UDEC modelling reult The initial model that wa run without a peritent, hallow-dipping dicontinuity (cutting through the trata) howed table condition even though parting had occurred on the triplet at 3 m and a weak parting plane at 5 m above the tope. The minor panel pan wa increaed to 40 m without incident of intabilitie or FOG in pite of the fact that no upport wa intalled. However, a oon a a hallow-dipping dicontinuity wa introduced, the confinement inhibiting lip on the teeply dipping joint urface wa removed. Block fell out with every blat and collape enued at very mall pan. Interetingly, thi condition wa alo oberved in the early tope at the mine, where attention to proper intallation of upport wa lacking. The introduction of upport greatly improved condition in the model, and tability wa achieved to a pan of 9 m with a upport reitance of 50 kn/m 2. An increae of upport reitance reulted in improved condition and greater table pan a expected. The final upport configuration with an active upport reitance of 100 kn/m 2 at intallation and a total upport reitance of about 200 kn/m 2, topped the collape on the mine and the model alo howed table condition for the modelled pan. Interetingly, a econd 27
28 weak plane that wa introduced into the model at 7 m above the tope, higher than the reach of the upport, did not affect tability even though the UCB cut through the trata to thi height. The modelling eem to ugget that if a ufficiently high active upport reitance can be achieved at intallation, at leat ome of the force clamping the teeply dipping dicontinuitie are retained thu allowing larger pan to be mined afely. The greatet tability i achieved when the coheion acro the hallow-dipping dicontinuity urface i retained by early intallation of uitable upport, cloe to the face. D4 Summary An analyi of Vouoir beam howed that thi condition only form under limited mining condition. Under normal Buhveld mining condition deeper than about 230 m below urface, where the upport capacity i able to carry a burden height of about 1.5 m and the panel pan i about 30 m, Vouoir beam hould not form. In the collape report urvey, only FOG with a maximum height of 0.5 m could be equated to Vouoir beam. Thee FOG occurred initially between upport before rotating the elongate out. The FOG with a fallout thickne greater than the VTZ height all occurred on hallow-dipping or curved tructure howing that the height of the VTZ doe not retrict the fallout height if thee tructure are preent. The ELFEN modelling reult have revealed a relationhip between hangingwall tructure, the excavated pan and the occurrence of an abrupt change in the deformational characteritic of the hangingwall. Thi change coincide with the croing over of the VTZ from one horizontal layer to another. It appear that the behaviour i cyclic in nature: the VTZ croe into a new layer, which behave imilarly to the layer below it until the VTZ croe into the next layer, etc. Thi appear to be the cae, but more layer hould be modelled to obtain clear evidence of thi behaviour. When the pillar between panel cruh there i a ignificant increae in the height of the VTZ, commenurate with a decreae in the load-bearing capacity of the pillar. The VTZ height then become dependent on the reidual trength of the pillar rather than depth below urface. Furthermore it hould be noted that the VTZ i independent of k. The VTZ can 28
29 extend up to about 5 m above a tope where individual panel of 30 m are eparated by cruh pillar. The modelling ugget that if parting occur within thi height that the effective height of the VTZ i increaed. A UDEC model wa run to determine the effect of hallow-dipping or curved dicontinuitie on tability. The model wa calibrated by mining condition affected by a peritent hallow-dipping, curved tructure that dipped in and out of the reef. The model howed that given the jointing condition of the hangingwall with reef-parallel dicontinuitie above the hangingwall, table condition were likely even at pan of 40 m. However, a oon a the hallow-dipping tructure cut through the trata, untable condition developed at very mall pan. The model howed that a upport configuration with a high pre-tre (100 kn/m 2 at intallation) tabilied condition provided it wa intalled cloe to the face and the panel pan were retricted to 30 m. Thi finding wa hown to work in practice. The model uggeted tability even when the parting plane wa higher than the reach of the upport. The finding of the reearch ugget that hangingwall condition with vertical joint can be mined to ignificantly greater pan than the traditional 30 m, even if there are trata-parallel dicontinuitie. Thu beam and Vouoir beam analyi i generally not applicable. However, a oon a a hallow-dipping, peritent dicontinuity cut through the trata, untable condition can occur at relatively mall pan. Thee condition prevail when a o called dome-tructure i interected. (Thee dome tructure have been found to form part of a larger thrut tructure, dipping in and out of the reef (Perritt and Robert, 2007)). A panel with a good rock ma rating can deteriorate when uch a tructure i interected and thee tructure are often the caue of large FOG and collape. D5 Reference Bandi, S.C., Lumden, A.C., Barton, N.R. (1983). Fundamental of rock joint deformation. Int.J.Rock Mech. Min. Sci. and Geomech. Abtr., Vol.20 no.6. 29
30 Barton, N. (1997). Rock ma characteriation workhop. Workhop note. Bieniawki, Z.T. (1967). The effect of pecimen ize on the compreive trength of rock. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci., Vol.5, no.6, pp Brady, B.H.G. and Brown, E.T. (1993). Rock Mechanic for Underground Mining, 2 nd ed. London: Chapman & Hall, pp 571. Daehnke, A., Anderon, L.M., De Beer, D., Eterhuizen, G.S., Glion, F.J., Grodner, M.W., Hagan, T.O., Jaku, E.P., Kuijper, J.S., Kullmann, D.H., Peake, A.V., Piper, P.S., Quaye, G.B., Reddy, N., Robert, M.K.C., Schweitzer, J.K., Stewart R.D. and Wallmach T. (1998). Stope face upport ytem. SIMRAC Report GAP 330. The afety in mine Reearch Aviory Committee (SIMRAC), Braamfontein, RSA. Diederich, M.S. and Kaier, P.K. (1998). Stability of large excavation in laminated hard rock mae: the vouoir analogue reviited. Int. J. Rock Mech. and Min. Sci., Vol.36, pp Eterhuizen, G.S. (1996). JBlock Uer Manual and Technical Reference, Pretoria. Evan, W.H. (1941). The trength of undermined trata. Tran.IMM. L(50). Fairhurt, C. and Cook, N.G.W. (1966). The phenomenon of rock plitting parallel to a free face under compreive tre. Proc. Au. Int. Metall. Conf., Melbourne, pp Hedley, DGF and Grant, F. (1972). Stope and in-pillar deign for the Elliot Lake Uranium Mine. CIM Bulletin, July. Hutchinon, J.D. and Diederich, M.S. (1996). Cablebolting in Underground Mine, BiTech Publiher Ltd, Richmond, Canada, pp 401. Jaeger, JC and Gay, NC. (1974). Behaviour of lightly confined granular material. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. and Geomech. 30
31 Jager, AJ. and Robert, MKC. (1986). Support ytem in productive excavation. GOLD 100. Proc. Int. Conf. Gold. Johanneburg. Jeremic, M.L. (1987). Ground Mechanic in Hard Rock Mining. A.A. Balkema, Rotterdam. Joughin, W.C., Swart, A.H. and Stacey, T.R. (1997). Review of fall of ground problem in underground diamond mine and other mine with maive orebodie and make recommendation on reearch need to reduce fall of ground caualtie, particularly in the face area. SIMRAC Report OTH 411. The afety in mine Reearch Aviory Committee (SIMRAC), Braamfontein, RSA. Kotze, T.J. and Streuder, S.B. (1993). A review of the trategy being followed on chrome mine belonging to the Samancor Group. Rock engineering problem related to hard rock mining at hallow to intermediate depth. Proc. Symp. SANGORM. Rutenburg. pp Lougher, D.R. (1994). An in-itu invetigation into the behaviour of the urrounding rock ma in a hard rock pillar mining environment. MSc Thei ubmitted to the Univerity of the Witwaterrand, Johanneburg, RSA. Özbay, MU & Robert, MKC. (1988). Yield pillar in tope upport. Proc. Rock Mechanic in South Africa, SANGORM. Özbay, MU; Ryder, JA & Jager, AJ. (1994). The deign of pillar ytem a practied in hallow hard-rock tabular mine in South Africa. J. S.A. Int. Min. and Metal., Jan/Feb Peck, R.B. (1969). The obervational method in applied oil mechanic 9 th Rankine Lecture, Geotechnique, Vol.19, pp Perritt, S.H. and Robert, M.K.C. (2007). Flexural-lip tructure in the Buhveld Complex, S.A. J. tr. Geol. Vol.29, pp Robert, D.P., Robert, M.K.C. and Jager, A.J. (2004). Alternative upport ytem for mechanied tope. PlatMine report
32 Ryder, J.A. (2004). Peronal Comm. Ryder, J.A. and Jager, A.J. (2002). A textbook on rock mechanic for tabular hard rock mine. The afety in mine Reearch Adviory Committee (SIMRAC), Braamfontein, RSA., pp Ryder, JA and Özbay, MU. (1990). A methodology for deigning pillar layout for hallow mining. ISRM Symp.: Static and Dynamic Conideration in Rock Engineering, Swaziland. Ryder, JA, Waton, BP & Kataka, MO. (2005). Pillar trength back-analye. PlatMine 1.2, Johanneburg. Salamon, M.D.G. (1968). 2D Treatment of problem ariing from mining tabular depoit in iotropic or tranverely iotropic ground. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Salamon, M.D.G. (1976). The roll of pillar in mining. Rock mechanic in mining practice. Ed. S. Budavari. S.A. Int. Min. Metall., Monograph erie M5, pp Salamon, M.D.G. and Munro, A.H. (1967). A tudy of the trength of coal pillar. J. S.A. Int. Min. Metall., Vol.68, pp Shi, G. and Goodman, R.E. (1987). Block theory and it application to rock engineering, Prentice Hall. Sofiano, A.I. (1996). Analyi and deign of an underground hard rock Vouoir beam roof. Int J. Rock Mech.Min. Sci. and Geomech. Abtr., No.2. Spann, H.P. and Napier J.A.L. (1983). The influence of different bolt pattern and anchor type on the deflection of a laminated beam. C.O.M.R.O. technical report no.:rr25/83, Johanneburg. Stacey, T.R. and Page, C.H. (1986). Practical handbook for underground rock mechanic. Tran. Tech. Publication, pp
33 Swart, A.H., Stacey, T.R., Weeloo, J., Joughin, W.C., le Roux, K., Walker, D. and Butcher, R. (2000). Invetigation of factor governing the tability/intability of tope panel in order to define a uitable deign methodology for near urface and hallow mining operation. SIMRAC Project Report OTH 501. The afety in mine Reearch Adviory Committee (SIMRAC), Braamfontein, RSA. Thruh, P.W. (1968). A dictionary of mining, mineral and related term. Wagner, H and Madden, BJ. (1984). Fifteen year experience with the deign of coal pillar in hallow South African collierie: An evaluation of the deign procedure and recent improvement. Deign and Performance of Underground Excavation. ISRM, Cambridge. Wright, F.D. (1974). Deign of Roof Bolt Pattern for Jointed Rock. Bur.of Mine (NTIS), U.S. Dept. Commerce. York, G., Canbulat, I., Kabeya, K.K., Le Bron, K., Waton, B.P. and William S.B. (1998). Develop guideline for the deign of pillar ytem for hallow and intermediate depth, tabular, hard rock mine and provide a methodology for aeing hangingwall tability and upport requirement for the panel between pillar. SIMRAC Report GAP 334. The afety in mine Reearch Adviory Committee (SIMRAC), Braamfontein, RSA. 33
Fluid-structure interaction between trains and noise-reduction barriers: numerical and experimental analysis
 Fluid Structure Interaction V 49 Fluid-tructure interaction between train and noie-reduction barrier: numerical and experimental analyi M. Belloli, B. Pizzigoni, F. Ripamonti & D. Rocchi Mechanical Engineering
Fluid Structure Interaction V 49 Fluid-tructure interaction between train and noie-reduction barrier: numerical and experimental analyi M. Belloli, B. Pizzigoni, F. Ripamonti & D. Rocchi Mechanical Engineering
MEMORANDUM. TNC Fisher Slough Final Design and Permitting Subject: Large Wood Debris Design. Jenny Baker (TNC) Dave Olson (DD3)
 MEMORANDUM TNC Fiher Slough Final Deign and Permitting Subject: Large Wood Debri Deign To: From: Jenny aker (TNC) Dave Olon (DD3) David Cline (Tetra Tech) Jon Olmted (Tetra Tech) Jay lair (Tetra Tech)
MEMORANDUM TNC Fiher Slough Final Deign and Permitting Subject: Large Wood Debri Deign To: From: Jenny aker (TNC) Dave Olon (DD3) David Cline (Tetra Tech) Jon Olmted (Tetra Tech) Jay lair (Tetra Tech)
SEISMIC RESPONSE ANALYSIS OF LONG-SPAN CONTINUOUS RIGID-FRAMED BRIDG
 SEISMIC RESPONSE ANALYSIS OF LONG-SPAN CONTINUOUS RIGID-FRAMED BRIDG Song Wa-li 1, Liu Gao-jun 2, Song Wen-chao 3 and Ren Wen-jie 4 1 Profeor, School of Civil Engineering, Hebei Univerity of Technology,
SEISMIC RESPONSE ANALYSIS OF LONG-SPAN CONTINUOUS RIGID-FRAMED BRIDG Song Wa-li 1, Liu Gao-jun 2, Song Wen-chao 3 and Ren Wen-jie 4 1 Profeor, School of Civil Engineering, Hebei Univerity of Technology,
MEASUREMENT OF DYNAMIC STRESSES ON CARRIERS WITH DETACHABLE GRIP AT STATION ENTRANCE: LA.T.I.F. EXPERIENCES AND FUTURE PROSPECTS
 MEASUREMENT OF DYNAMIC STRESSES ON CARRIERS WITH DETACHABLE GRIP AT STATION ENTRANCE: LA.T.I.F. EXPERIENCES AND FUTURE PROSPECTS dott.ing. Fabio Degaperi Introduction The importance of dynamic tre effect
MEASUREMENT OF DYNAMIC STRESSES ON CARRIERS WITH DETACHABLE GRIP AT STATION ENTRANCE: LA.T.I.F. EXPERIENCES AND FUTURE PROSPECTS dott.ing. Fabio Degaperi Introduction The importance of dynamic tre effect
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING Volume 2, No 3, 2012
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING Volume 2, No 3, 2012 Copyright 2010 All right reerved Integrated Publihing ervice Reearch article ISSN 09 4399 Invetigation on fly ah concrete
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING Volume 2, No 3, 2012 Copyright 2010 All right reerved Integrated Publihing ervice Reearch article ISSN 09 4399 Invetigation on fly ah concrete
Calculation of Actual Concrete Shrinkage Magnitude
 Calculation of Actual Magnitude By: Emilio M. Morale, MSCE - Mater of Science in Civil Engineering major in Geotechnic and Structure, Carnegie Mellon Univerity, Pittburgh Pa. Chairman PICE Geotechnical
Calculation of Actual Magnitude By: Emilio M. Morale, MSCE - Mater of Science in Civil Engineering major in Geotechnic and Structure, Carnegie Mellon Univerity, Pittburgh Pa. Chairman PICE Geotechnical
A Study of Ocean Waves at Fisherman s Wharf, Victoria Harbour
 A Study of Ocean Wave at Fiherman Wharf, Victoria Harbour David B. Fiel, Jianhua Jiang and Dave Billenne ASL Environmental Science Inc., 1986 Mill Rd., Sidney, BC, V8L 5Y3, Canada, Phone Number (250) 656-0177
A Study of Ocean Wave at Fiherman Wharf, Victoria Harbour David B. Fiel, Jianhua Jiang and Dave Billenne ASL Environmental Science Inc., 1986 Mill Rd., Sidney, BC, V8L 5Y3, Canada, Phone Number (250) 656-0177
MEMORANDUM: INTERIM CONCEPTS
 roject 73845 I 15/Tropicana Interchange Feaibility Study MEMORANDUM: INTERIM CONCETS INTRODUCTION During the initial project creening and throughout the development of project concept, alternative concept
roject 73845 I 15/Tropicana Interchange Feaibility Study MEMORANDUM: INTERIM CONCETS INTRODUCTION During the initial project creening and throughout the development of project concept, alternative concept
Cold Formed Steel Tension Members with Two and Three Staggered Bolts
 Miouri Univerity of Science and Technoloy Scholar' Mine International Specialty Conference on Cold- Formed Steel Structure (2010) - 20th International Specialty Conference on Cold-Formed Steel Structure
Miouri Univerity of Science and Technoloy Scholar' Mine International Specialty Conference on Cold- Formed Steel Structure (2010) - 20th International Specialty Conference on Cold-Formed Steel Structure
The Feature of Weak Shock Wave Propagated in a Overlong Tunnel
 Open Journal of Fluid Dynamic 0 85-89 http://d.doi.org/0.436/ojfd.0.4a034 Publihed Online December 0 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojfd) The Feature of Weak Shock Wave Propagated in a Overlong Tunnel Xiao
Open Journal of Fluid Dynamic 0 85-89 http://d.doi.org/0.436/ojfd.0.4a034 Publihed Online December 0 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojfd) The Feature of Weak Shock Wave Propagated in a Overlong Tunnel Xiao
Optimization for Bus Stop Design Based on Cellular Automaton Traffic Model
 Modern Tranportation Volume 6, 2017, PP.1-7 Optimization for Bu Stop Deign Baed on Cellular Automaton Traffic Model Liankui Zhang 1, Chengyou Cui 1 1. Department of Technology Economic and Management,
Modern Tranportation Volume 6, 2017, PP.1-7 Optimization for Bu Stop Deign Baed on Cellular Automaton Traffic Model Liankui Zhang 1, Chengyou Cui 1 1. Department of Technology Economic and Management,
CREST LEVEL OPTIMIZATION OF THE MULTI LEVEL OVERTOPPING BASED WAVE ENERGY CONVERTER SEAWAVE SLOT-CONE GENERATOR. J. P. Kofoed 1 and E.
 6 th European Wave and Tidal Energy Conference Glagow, UK Augut 29 th - September 2 nd 2005 CREST LEVEL OPTIMIZATION OF THE MULTI LEVEL OVERTOPPING BASED WAVE ENERGY CONVERTER SEAWAVE SLOT-CONE GENERATOR
6 th European Wave and Tidal Energy Conference Glagow, UK Augut 29 th - September 2 nd 2005 CREST LEVEL OPTIMIZATION OF THE MULTI LEVEL OVERTOPPING BASED WAVE ENERGY CONVERTER SEAWAVE SLOT-CONE GENERATOR
Original Article. Effectiveness of a specialized climbing method for beginners on the physical and technical fitness of 8-10 year old children
 Journal of Phyical Education and Sport (JPES), 18 Supplement iue 5, Art 308, pp. 2065-2069, 2018 online ISSN: 2247-806X; p-issn: 2247 8051; ISSN - L = 2247-8051 JPES Original Article Effectivene of a pecialized
Journal of Phyical Education and Sport (JPES), 18 Supplement iue 5, Art 308, pp. 2065-2069, 2018 online ISSN: 2247-806X; p-issn: 2247 8051; ISSN - L = 2247-8051 JPES Original Article Effectivene of a pecialized
Experimental Investigation of Pressure Flushing Technique in Reservoir Storages
 Experimental Invetigation of Preure Fluhing Technique in Reervoir Storage M. E. MESKATI SAMIRZADI 1, A. A. DEGANI 1, T. SUMI, A. MOSAEDI 1 and M. MEFTA. 1 1 Dept. of Water Engineering, Gorgan Univerity
Experimental Invetigation of Preure Fluhing Technique in Reervoir Storage M. E. MESKATI SAMIRZADI 1, A. A. DEGANI 1, T. SUMI, A. MOSAEDI 1 and M. MEFTA. 1 1 Dept. of Water Engineering, Gorgan Univerity
Turbulence and waves in numerically simulated slope flows
 9 ème Congrè Françai de Mécanique Mareille, 4-8 août 9 Turbulence and wave in numerically imulated lope flow E. FEDOROVICH, A. SHAPIRO School of Meteorology, Univertiy of Oklahoma, David L. Boren Blvd.,
9 ème Congrè Françai de Mécanique Mareille, 4-8 août 9 Turbulence and wave in numerically imulated lope flow E. FEDOROVICH, A. SHAPIRO School of Meteorology, Univertiy of Oklahoma, David L. Boren Blvd.,
Heat Transfer Effect of Inert Gas on Multi-Tubular Reactor for Partial Oxidation Reaction
 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 18(2), 184-189 (2001) Heat Tranfer Effect of Inert Ga on Multi-Tubular Reactor for Partial Oxidation Reaction Kwang Ho Song, Sang Eon Han and Kwang-Ho Park LG Chem Reearch Park, LG
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 18(2), 184-189 (2001) Heat Tranfer Effect of Inert Ga on Multi-Tubular Reactor for Partial Oxidation Reaction Kwang Ho Song, Sang Eon Han and Kwang-Ho Park LG Chem Reearch Park, LG
Mechanical Waves: Applications in Medicine. How Elastography is Helping Doctors Avoid the Biopsy Needle
 Mechanical Wave: Application in Medicine How Elatography i Helping Doctor Avoid the Biopy Needle Purpoe Thi leon i meant to increae tudent undertanding of mechanical wave and provide them with example
Mechanical Wave: Application in Medicine How Elatography i Helping Doctor Avoid the Biopy Needle Purpoe Thi leon i meant to increae tudent undertanding of mechanical wave and provide them with example
Hydraulic jump in stilling basin with vertical end sill
 International Journal of Phical Science Vol. (), pp. -9, Januar, Available online at http://www.academicjournal.org/ijps ISSN 99-9 Academic Journal Full Length Reearch Paper Hdraulic jump in tilling bain
International Journal of Phical Science Vol. (), pp. -9, Januar, Available online at http://www.academicjournal.org/ijps ISSN 99-9 Academic Journal Full Length Reearch Paper Hdraulic jump in tilling bain
VALIDATION OF THE ASAR WAVE MODE LEVEL 2 PRODUCT USING WAM AND BUOY SPECTRA
 VALIDATION OF THE ASAR WAVE MODE LEVEL 2 PRODUCT USING WAM AND BUOY SPECTRA Harald Johnen (1), Geir Engen (1), Bertrand Chapron (2) (1) Norut Informajonteknologi AS, PP 6463 Forkningparken, N-9294 Tromø,
VALIDATION OF THE ASAR WAVE MODE LEVEL 2 PRODUCT USING WAM AND BUOY SPECTRA Harald Johnen (1), Geir Engen (1), Bertrand Chapron (2) (1) Norut Informajonteknologi AS, PP 6463 Forkningparken, N-9294 Tromø,
Scientia Iranica, Vol. 14, No. 4, pp 358{368 c Sharif University of Technology, August 2007 Research Note Evaluation of Empirically Derived PVT Proper
 Scientia Iranica Vol. 14 No. 4 pp 358{368 c Sharif Univerity of Technoloy Auut 2007 Reearch Note Evaluation of Empirically Derived PVT Propertie for Middle Eat Crude Oil M.N. Hemmati and R. Kharrat 1 PVT
Scientia Iranica Vol. 14 No. 4 pp 358{368 c Sharif Univerity of Technoloy Auut 2007 Reearch Note Evaluation of Empirically Derived PVT Propertie for Middle Eat Crude Oil M.N. Hemmati and R. Kharrat 1 PVT
A Graphic Method to Estimate the Wind Speed under Urban Canopy Layer
 Civil Engineering and Architecture 3(6): 172-188, 2015 DOI: 10.13189/cea.2015.030602 http://www.hrpub.org A raphic Method to Etimate the Wind Speed under Urban Canopy Layer Manoureh Tahba School of Architecture
Civil Engineering and Architecture 3(6): 172-188, 2015 DOI: 10.13189/cea.2015.030602 http://www.hrpub.org A raphic Method to Etimate the Wind Speed under Urban Canopy Layer Manoureh Tahba School of Architecture
VEHICLE NO X AND PM10 EMISSION FACTORS FROM SYDNEY S M5-EAST TUNNEL
 VEHICLE NO X AND PM1 EMISSION FACTORS FROM SYDNEY S M5-EAST TUNNEL Mark F. Hibberd 1 1 CSIRO Atmopheric Reearch, PB 1, Apendale, Vic 3195, Autralia Abtract Reult are preented on the vehicle emiion factor
VEHICLE NO X AND PM1 EMISSION FACTORS FROM SYDNEY S M5-EAST TUNNEL Mark F. Hibberd 1 1 CSIRO Atmopheric Reearch, PB 1, Apendale, Vic 3195, Autralia Abtract Reult are preented on the vehicle emiion factor
CHANGE OF NEARSHORE SIGNIFICANT WAVES IN RESPONSE TO SEA LEVEL RISE. Se-Hyeon Cheon 1 and Kyung-Duck Suh 1
 CHANGE OF NEARSHORE SIGNIFICANT WAVES IN RESPONSE TO SEA EVE RISE Se-Hyeon Cheon 1 and Kyung-Duck Suh 1 In thi paper, a method ha been developed for etimating the change of nearhore ignificant wave in
CHANGE OF NEARSHORE SIGNIFICANT WAVES IN RESPONSE TO SEA EVE RISE Se-Hyeon Cheon 1 and Kyung-Duck Suh 1 In thi paper, a method ha been developed for etimating the change of nearhore ignificant wave in
reviewed paper Public transport travel time simulation Tomáš CHLEBNICAN, Jiří CTYROKY, Marek ZDERADICKA
 reviewed paper Public tranport travel time imulation Tomáš CHLEBNICAN, Jiří CTYROKY, Marek ZDERADICKA (Mgr. Jiří ČTYROKÝ, Útvar rozvoje hl. m. Prahy, Vyšehradká 57, Prague, 18 00, ctyroky@urm.mepnet.cz)
reviewed paper Public tranport travel time imulation Tomáš CHLEBNICAN, Jiří CTYROKY, Marek ZDERADICKA (Mgr. Jiří ČTYROKÝ, Útvar rozvoje hl. m. Prahy, Vyšehradká 57, Prague, 18 00, ctyroky@urm.mepnet.cz)
Semi-Quantitative Freshwater Mussel Survey Date Prepared: 11/20/2017
 PARTNERSHIP FOR THE DELAWARE ESTUARY Science Group Semi-Quantitative Frehwater Muel Survey Date Prepared: 11/20/2017 Prepared By: Kurt Cheng Suggeted Citation: Cheng, K. 2017. Semi-Quantitative Frehwater
PARTNERSHIP FOR THE DELAWARE ESTUARY Science Group Semi-Quantitative Frehwater Muel Survey Date Prepared: 11/20/2017 Prepared By: Kurt Cheng Suggeted Citation: Cheng, K. 2017. Semi-Quantitative Frehwater
A New Surface Model for Cyclone Anticyclone Asymmetry
 VOL. 59, NO. 16 JOURNAL OF THE ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES 15 AUGUST 2002 A New Surface Model for Cyclone Anticyclone Aymmetry GREGORY J. HAKIM Univerity of Wahington, Seattle, Wahington CHRIS SNYDER National
VOL. 59, NO. 16 JOURNAL OF THE ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES 15 AUGUST 2002 A New Surface Model for Cyclone Anticyclone Aymmetry GREGORY J. HAKIM Univerity of Wahington, Seattle, Wahington CHRIS SNYDER National
Coordination in CPG and its Application on Bipedal Walking
 Coordination in CPG and it Application on Bipedal Walking Weiwei Huang Department of Mechanical Engineering National Univerity of Singapore Singapore 96 huangweiwei@nu.edu.g Chee-Meng Chew Department of
Coordination in CPG and it Application on Bipedal Walking Weiwei Huang Department of Mechanical Engineering National Univerity of Singapore Singapore 96 huangweiwei@nu.edu.g Chee-Meng Chew Department of
INFLUENCE OF THE EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION ON THE OXYGEN CONTENTS AND ITS EXCESS RATIO IN THE ENGINE COMBUSTION CHAMBER
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Tranport Vol. 0 No. 3 013 INFLUENCE OF THE EXHAUST GAS ECICULATION ON THE OXYGEN CONTENTS AND ITS EXCESS ATIO IN THE ENGINE COMBUSTION CHAMBE Stan Potrzednik Zbigniew mudka
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Tranport Vol. 0 No. 3 013 INFLUENCE OF THE EXHAUST GAS ECICULATION ON THE OXYGEN CONTENTS AND ITS EXCESS ATIO IN THE ENGINE COMBUSTION CHAMBE Stan Potrzednik Zbigniew mudka
Wave Crest Distributions: Observations and Second-Order Theory
 1AUGUST 000 FORRISTALL 1931 Wave Cret Ditribution: Obervation and Second-Order Theory GEORGE Z. FORRISTALL Shell E&P Technology, Houton, Texa (Manucript received February 1999, in final form 14 September
1AUGUST 000 FORRISTALL 1931 Wave Cret Ditribution: Obervation and Second-Order Theory GEORGE Z. FORRISTALL Shell E&P Technology, Houton, Texa (Manucript received February 1999, in final form 14 September
ABSTRACT: Ocean wave energy contains the largest energy density
 Deign and Modelling of Wave Energy Converter and Power Take-Off Sytem DESIGN AND MODELLING OF WAVE ENERGY CONVERTER AND POWER TAKE-OFF SYSTEM E. Chuah 1, K. Magawaran and M.Z. Haan 3 1 School of Engineering,
Deign and Modelling of Wave Energy Converter and Power Take-Off Sytem DESIGN AND MODELLING OF WAVE ENERGY CONVERTER AND POWER TAKE-OFF SYSTEM E. Chuah 1, K. Magawaran and M.Z. Haan 3 1 School of Engineering,
DESIGN & MODIFICATION OF ROLLERS IN TRACKS OF SURFACE DRILLING MACHINES
 DESIGN & ODIFICATION OF ROLLERS IN TRACKS OF SURFACE DRILLING ACHINES r. S.N. Shinde P.D.V.V.P.C.O.E.Ahmednagar Prof. R.R. Navthar Aociate Profeor Dept. of ech Engg. P.D.V.V.P.C.O.E.Ahmednagar ABSTRACT
DESIGN & ODIFICATION OF ROLLERS IN TRACKS OF SURFACE DRILLING ACHINES r. S.N. Shinde P.D.V.V.P.C.O.E.Ahmednagar Prof. R.R. Navthar Aociate Profeor Dept. of ech Engg. P.D.V.V.P.C.O.E.Ahmednagar ABSTRACT
Application of single-step genomic evaluation for crossbred performance in pig 1
 Application of ingle-tep genomic evaluation for crobred performance in pig 1 T. Xiang* B. Nielen G. Su* A. Legarra and O. F. Chritenen* *Center for Quantitative Genetic and Genomic Department of Molecular
Application of ingle-tep genomic evaluation for crobred performance in pig 1 T. Xiang* B. Nielen G. Su* A. Legarra and O. F. Chritenen* *Center for Quantitative Genetic and Genomic Department of Molecular
A Review on Experimental Analysis for Rectangular Perforated Fin Array
 A Review on Experimental Analyi for Rectangular Perforated Fin Array I.N. Wankhede 1, N. P. Salunke 2 1 PG Student, Mechanical Department, RCPIT Shirpur, Maharahtra, India 2 H. O. D., Mechanical Department,RCPIT
A Review on Experimental Analyi for Rectangular Perforated Fin Array I.N. Wankhede 1, N. P. Salunke 2 1 PG Student, Mechanical Department, RCPIT Shirpur, Maharahtra, India 2 H. O. D., Mechanical Department,RCPIT
Roulette Deluxe. Roulette Deluxe is a fixed odds betting game based on roulette.
 Roulette Deluxe Roulette Deluxe i a fixed odd betting game baed on roulette. The Roulette wheel ha 37 ed lot, 0 to 36 each of which can be bet on. The wheel i pun in one direction and a ball i pun in the
Roulette Deluxe Roulette Deluxe i a fixed odd betting game baed on roulette. The Roulette wheel ha 37 ed lot, 0 to 36 each of which can be bet on. The wheel i pun in one direction and a ball i pun in the
CORPS OF ENGINEERS, U. S. ARMY PLANS FOR IMPROVEMENT OF NAVIGATION CONDITIONS GREENVILLE BRIDGE, MISSISSIPPI RIVER MODEL INVESTIGATION
 TA7,vJ31 (\0 2..-.:;b c CORPS OF ENGINEERS, U. S. ARMY PLANS FOR IMPROVEMENT OF NAVIGATION CONDITIONS AT GREENVILLE BRIDGE, MISSISSIPPI RIVER MODEL INVESTIGATION TECHNICAL MEMORANDUM NO. 2 366 CONDUCTED
TA7,vJ31 (\0 2..-.:;b c CORPS OF ENGINEERS, U. S. ARMY PLANS FOR IMPROVEMENT OF NAVIGATION CONDITIONS AT GREENVILLE BRIDGE, MISSISSIPPI RIVER MODEL INVESTIGATION TECHNICAL MEMORANDUM NO. 2 366 CONDUCTED
Full Internal Relief Valves Instruction Manual
 Full Internal Relief Valve Intruction Manual MEV200FIR & MEV00FIR Application: Deigned for ue in mobile LPG & NH container a a primary preure relief valve for bobtail and tranport trailer intallation.
Full Internal Relief Valve Intruction Manual MEV200FIR & MEV00FIR Application: Deigned for ue in mobile LPG & NH container a a primary preure relief valve for bobtail and tranport trailer intallation.
Name: Answer Key Date: Regents Physics. Projectiles
 Nae: Anwer Key Date: Regent Phyic Tet # 5 Review 1. Equation to know: Projectile (1) A y = Ainθ () A = Acoθ Δv vf vi vf + vi (3) a= = (4) vavg = (5) d=vit+½at Δ t tf ti (6) v f =vi+at (7) vf =vi +ad. Ter
Nae: Anwer Key Date: Regent Phyic Tet # 5 Review 1. Equation to know: Projectile (1) A y = Ainθ () A = Acoθ Δv vf vi vf + vi (3) a= = (4) vavg = (5) d=vit+½at Δ t tf ti (6) v f =vi+at (7) vf =vi +ad. Ter
Effect of Altering Handle Position of a Rolling Walker on Gait in Children with Cerebral Palsy
 Effect of Altering Handle Poition of a Rolling Walker on Gait in Children with Cerebral Paly The purpoe of thi tudy wa to determine whether altering the handle poition on a rolling walker would affect
Effect of Altering Handle Poition of a Rolling Walker on Gait in Children with Cerebral Paly The purpoe of thi tudy wa to determine whether altering the handle poition on a rolling walker would affect
generator's nameplate - Datasheet generator's nameplate - Datasheet
 Åpen informajon Foweb: Wind plant parameter (2018-11) Englih verion of 'Foweb: Data for produkjonanlegg vindkraftverk parameterveileder' (page 1 of 7) www.tatnett.no/foweb Diclaimer: Thi document i an
Åpen informajon Foweb: Wind plant parameter (2018-11) Englih verion of 'Foweb: Data for produkjonanlegg vindkraftverk parameterveileder' (page 1 of 7) www.tatnett.no/foweb Diclaimer: Thi document i an
Center for By-Products Utilization
 Center for By-Product Utilization MECHANICAL PROPERTIES AND DURABILITY OF CONCRETE MADE WITH CLASS C BLY ASH FROM DIFFERENT SOURCES OF WISCONSIN By Tarun R. Naik, Shiw S. Singh, and Mohammad M. Hoain Report
Center for By-Product Utilization MECHANICAL PROPERTIES AND DURABILITY OF CONCRETE MADE WITH CLASS C BLY ASH FROM DIFFERENT SOURCES OF WISCONSIN By Tarun R. Naik, Shiw S. Singh, and Mohammad M. Hoain Report
Surface Tension Measurement with an Optofluidic Sensor
 1t International Conference on Sening Technology November 1-, 005 Palmerton North, New Zealand Surface Tenion eaurement with an Optofluidic Senor Abtract Nam-Trung Nguyen, Sumantri Laemono, Franck Alexi
1t International Conference on Sening Technology November 1-, 005 Palmerton North, New Zealand Surface Tenion eaurement with an Optofluidic Senor Abtract Nam-Trung Nguyen, Sumantri Laemono, Franck Alexi
OPTIMISING A BREAKWATER LAYOUT USING AN ITERATIVE ALGORITHM
 OPTIMISING A BREAKWATER LAYOUT USING AN ITERATIVE ALGORITM Michael Rutell R Wallingford / Univerity of Surrey Due to the remote and expoed coatal location of mot liquefied natural ga (LNG) exportation
OPTIMISING A BREAKWATER LAYOUT USING AN ITERATIVE ALGORITM Michael Rutell R Wallingford / Univerity of Surrey Due to the remote and expoed coatal location of mot liquefied natural ga (LNG) exportation
This document is downloaded from DR-NTU, Nanyang Technological University Library, Singapore.
 Thi document i downloaded from DR-NTU, Nanyang Technological Univerity Library, Singapore. Title A microfluidic enor for dynamic urface tenion meaurement Author() Citation Nguyen, Nam-Trung; Laemono, Sumantri;
Thi document i downloaded from DR-NTU, Nanyang Technological Univerity Library, Singapore. Title A microfluidic enor for dynamic urface tenion meaurement Author() Citation Nguyen, Nam-Trung; Laemono, Sumantri;
Total 0/30. 0/1 points Walker3 2.P.068. [544577]
![Total 0/30. 0/1 points Walker3 2.P.068. [544577] Total 0/30. 0/1 points Walker3 2.P.068. [544577]](/thumbs/79/79107050.jpg) 9/9/13 Aignent Previewer Phy 111.HW#2b (3168643) Current Score: 0/30 Due: Wed Sep 11 2013 10:30 AM PDT Quetion Point 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 0/1 0/2 0/3 0/3 0/3 0/3 0/1 0/1 0/1 0/6 0/6 Total 0/30 Decription
9/9/13 Aignent Previewer Phy 111.HW#2b (3168643) Current Score: 0/30 Due: Wed Sep 11 2013 10:30 AM PDT Quetion Point 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 0/1 0/2 0/3 0/3 0/3 0/3 0/1 0/1 0/1 0/6 0/6 Total 0/30 Decription
Projectile Motion. Physics 6A. Prepared by Vince Zaccone For Campus Learning Assistance Services at UCSB
 Projectile Motion Phic 6A Projectile motion i a combination of Horizontal and Vertical motion We ue eparate et of formula for each, but both motion happen imultaneoul. Horizontal In the cae of projectile,
Projectile Motion Phic 6A Projectile motion i a combination of Horizontal and Vertical motion We ue eparate et of formula for each, but both motion happen imultaneoul. Horizontal In the cae of projectile,
Safe Routes to School Engineering Study
 Safe Route to School Brunwick Local School Ditrict Safe Route to School Plan City of Brunwick, Medina County, Ohio Hickory Ridge Elementary School Viintainer Middle School Edward Middle School Saint Ambroe
Safe Route to School Brunwick Local School Ditrict Safe Route to School Plan City of Brunwick, Medina County, Ohio Hickory Ridge Elementary School Viintainer Middle School Edward Middle School Saint Ambroe
Chapter 14. Gas-liquid Transfer
 Chapter 14 Ga-liquid Tranfer 14.1 GAS TRANSFER By ga tranfer i meant the ma movement of ga to or from olution, which occur when a liquid urface i in contact with a ga phae with which it i not in equilibrium.
Chapter 14 Ga-liquid Tranfer 14.1 GAS TRANSFER By ga tranfer i meant the ma movement of ga to or from olution, which occur when a liquid urface i in contact with a ga phae with which it i not in equilibrium.
How to order: Please prefix the mbo part number or description with R239- example: R /014
 SL-retainer for bolt and haft with goove; compenating for play mbo tandard 8 SL-retainer with relief 2) (mbo tandard 88) SL-retainer without relief SL-retainer for bolt diameter = 1 mm, electroplated galvanied
SL-retainer for bolt and haft with goove; compenating for play mbo tandard 8 SL-retainer with relief 2) (mbo tandard 88) SL-retainer without relief SL-retainer for bolt diameter = 1 mm, electroplated galvanied
CAL. V657, VD57 CHRONOGRAPH
 CL. V657, VD57 TIME/CLENDR l Hour, minute and econd hand l Date diplayed in numeral ENGLISH l Meaure up to 60 minute in 1/10 econd increment l Split time meaurement DISPLY ND /UTTONS SCREW DOWN [for model
CL. V657, VD57 TIME/CLENDR l Hour, minute and econd hand l Date diplayed in numeral ENGLISH l Meaure up to 60 minute in 1/10 econd increment l Split time meaurement DISPLY ND /UTTONS SCREW DOWN [for model
MACHINE MILKING AND DAILY CHANGES OF COW S TEAT CONDITION
 20 th Int. Symp. Animal Science Day, Kranjka gora, Slovenia, Sept. 19 th 21 t, 2012. COBISS: 1.08 Agri category code: L01 ACHINE ILKING AND DAILY CHANGES OF COW S TEAT CONDITION iomir STOJNOVIĆ 1, Damir
20 th Int. Symp. Animal Science Day, Kranjka gora, Slovenia, Sept. 19 th 21 t, 2012. COBISS: 1.08 Agri category code: L01 ACHINE ILKING AND DAILY CHANGES OF COW S TEAT CONDITION iomir STOJNOVIĆ 1, Damir
Redirection of center-of-mass velocity during the step-to-step transition of human walking
 2668 The Journal of Experimental Biology 212, 2668-2678 Publihed by The Company of Biologit 29 doi:1.1242/jeb.27581 Redirection of center-of-ma elocity during the tep-to-tep tranition of human walking
2668 The Journal of Experimental Biology 212, 2668-2678 Publihed by The Company of Biologit 29 doi:1.1242/jeb.27581 Redirection of center-of-ma elocity during the tep-to-tep tranition of human walking
Self-Start Performance Evaluation in Darrieus-Type Vertical Axis Wind Turbines: Methodology and Computational Tool Applied to Symmetrical Airfoils
 Self-Start Performance Evaluation in Darrieu-Type Vertical Axi Wind Turbine: Methodology and Computational Tool Applied to Symmetrical Airfoil N.C. Batita 1, R. Melício 1, J.C.O. Matia 1,2 and J.P.S. Catalão
Self-Start Performance Evaluation in Darrieu-Type Vertical Axi Wind Turbine: Methodology and Computational Tool Applied to Symmetrical Airfoil N.C. Batita 1, R. Melício 1, J.C.O. Matia 1,2 and J.P.S. Catalão
Comfortable and maximum walking speed of adults aged years: reference values and determinants
 Age and Ageing 1997; 26: 15-19 Comfortable and maximum walking peed of adult aged 20-79 year: reference value and determinant RICHAR W. BOHAO School of Allied Hearth, U-101, Univerity of Connecticut Storr,
Age and Ageing 1997; 26: 15-19 Comfortable and maximum walking peed of adult aged 20-79 year: reference value and determinant RICHAR W. BOHAO School of Allied Hearth, U-101, Univerity of Connecticut Storr,
LIFTING SYSTEMS. R-System ACCREDITED. Lifting system. with spherical head
 IFTING SYSTEMS ACCEITE -Sytem 2 ifting ytem with pherical head 3 4 ifting ytem with pherical head WHAT IS? Thouand of heavy precat concrete item are lifted and handled on a daily bai. -Sytem i the lifting
IFTING SYSTEMS ACCEITE -Sytem 2 ifting ytem with pherical head 3 4 ifting ytem with pherical head WHAT IS? Thouand of heavy precat concrete item are lifted and handled on a daily bai. -Sytem i the lifting
CAL. VD50 1/10 SECOND RETROGRADE CHRONOGRAPH
 CL. VD50 1/10 SECOND RETROGRDE CHRONOGRPH TIME/CLENDR l Hour, minute and econd hand l Date diplayed in numeral STOPWTCH l Meaure up to 60 minute in 1/10 econd increment. ENGLISH DISPLY ND /UTTONS SCREW
CL. VD50 1/10 SECOND RETROGRDE CHRONOGRPH TIME/CLENDR l Hour, minute and econd hand l Date diplayed in numeral STOPWTCH l Meaure up to 60 minute in 1/10 econd increment. ENGLISH DISPLY ND /UTTONS SCREW
CAL. VK63, VK67, VK73 CHRONOGRAPH
 CL. VK63, VK67, VK73 TIME/CLENDR l Hour and with mall econd hand l Small 24-hour hand (VK63 & VK73 only) l Date diplayed in numeral ENGLISH l Meaure up to minute or hour in 1/5 econd increment [VK63] Hour
CL. VK63, VK67, VK73 TIME/CLENDR l Hour and with mall econd hand l Small 24-hour hand (VK63 & VK73 only) l Date diplayed in numeral ENGLISH l Meaure up to minute or hour in 1/5 econd increment [VK63] Hour
Synthesis of a multivariate extreme sea climate
 Application of Statitic and Probability in Civil Engineering, Der Kiureghian, Madanat & Petana (ed) 3 Millpre, Rotterdam, ISBN 9 5966 4 8 Synthei of a multivariate extreme ea climate P.B. Webber Minitry
Application of Statitic and Probability in Civil Engineering, Der Kiureghian, Madanat & Petana (ed) 3 Millpre, Rotterdam, ISBN 9 5966 4 8 Synthei of a multivariate extreme ea climate P.B. Webber Minitry
CAL. VK68 CHRONOGRAPH
 CL. VK68 CHRONOGRPH TIME/CLENDR l Hour and minute hand with mall econd and 24-hour hand l Date diplayed in numeral ENGLISH CHRONOGRPH l Meaure up to minute in 1/5 econd increment DISPLY ND CROWN/UTTONS
CL. VK68 CHRONOGRPH TIME/CLENDR l Hour and minute hand with mall econd and 24-hour hand l Date diplayed in numeral ENGLISH CHRONOGRPH l Meaure up to minute in 1/5 econd increment DISPLY ND CROWN/UTTONS
Device-Free Passive Identity Identification via WiFi Signals
 enor Article Device-Free Paive Identity Identification via WiFi Signal Jiguang Lv ID, Wu Yang * and Dapeng Man Information Security Reearch Center, Harbin Engineering Univerity, Harbin 5, China; lvjiguang@hrbeu.edu.cn
enor Article Device-Free Paive Identity Identification via WiFi Signal Jiguang Lv ID, Wu Yang * and Dapeng Man Information Security Reearch Center, Harbin Engineering Univerity, Harbin 5, China; lvjiguang@hrbeu.edu.cn
Architecture and functional morphology of the skeletal apparatus of ozarkodinid conodonts
 Architecture and functional morphology of the keletal apparatu of ozarkodinid conodont MARK A. PURNELL and PHILIP C. J. DONOGHUE Department of Geology, Univerity of Leiceter, Leiceter LE1 7RH, UK (map2@le.ac.uk)
Architecture and functional morphology of the keletal apparatu of ozarkodinid conodont MARK A. PURNELL and PHILIP C. J. DONOGHUE Department of Geology, Univerity of Leiceter, Leiceter LE1 7RH, UK (map2@le.ac.uk)
Event Risk Assessment: <Trackstar>
 Rik Aement: Date: 26/04/18 Aeed by: Zoe Gardham ocation: Suex Down Sport Park, Cro evel Way, BN21 2UF. Reviewed: 26/04/18 What are the Hazard? contact with: Walk Dog Oth athlete Or anyone who
Rik Aement: Date: 26/04/18 Aeed by: Zoe Gardham ocation: Suex Down Sport Park, Cro evel Way, BN21 2UF. Reviewed: 26/04/18 What are the Hazard? contact with: Walk Dog Oth athlete Or anyone who
11 th Prima Pasta Badminton Championships 2018 Technical Guidelines
 11 th Prima Pata Badminton Championhip 2018 Technical Guideline 1. DATE AND VENUE The 11 th Prima Pata Badminton Championhip 2018 will be held at Powermah, Makati City on February 16, 17, 18, 23, 24 and
11 th Prima Pata Badminton Championhip 2018 Technical Guideline 1. DATE AND VENUE The 11 th Prima Pata Badminton Championhip 2018 will be held at Powermah, Makati City on February 16, 17, 18, 23, 24 and
Calorimetric Validation of the Caltrac Accelerometer During Level Walking
 Calorimetric Validation of the Caltrac Accelerometer During Level Walking The primary purpoe of thi tudy wa to compare the Caltrac accelerometer output with meaured energy expenditure (Ee). Twenty-five
Calorimetric Validation of the Caltrac Accelerometer During Level Walking The primary purpoe of thi tudy wa to compare the Caltrac accelerometer output with meaured energy expenditure (Ee). Twenty-five
Hybrid Airfoil Design Method to Simulate Full-Scale Ice Accretion Throughout a Given a Range
 JOURNAL OF AIRCRAFf Vol. 35, No.2, March-April 1998 Hybrid Airfoil Deign Method to Simulate Full-Scale Ice Accretion Throughout a Given a Range Farooq Saeed,* MichaelS. Selig.t and Michael B. Bragg:j:
JOURNAL OF AIRCRAFf Vol. 35, No.2, March-April 1998 Hybrid Airfoil Deign Method to Simulate Full-Scale Ice Accretion Throughout a Given a Range Farooq Saeed,* MichaelS. Selig.t and Michael B. Bragg:j:
Experiments on elastic wave modelling in isotropic and anisotropic media
 Exeriment on elatic wave modelling in iotroic and aniotroic media Fan Jiang, Yiqing Ren, and Shengwen Jin, Halliburton Landmark Software & Service Summary Recent advance in eimic data roceing with multi-comonent
Exeriment on elatic wave modelling in iotroic and aniotroic media Fan Jiang, Yiqing Ren, and Shengwen Jin, Halliburton Landmark Software & Service Summary Recent advance in eimic data roceing with multi-comonent
Mechanical Stabilisation for Permanent Roads
 Mechanical Stabilisation for Permanent Roads Tim Oliver VP Global Applications Technology Tensar International toliver@tensar.co.uk Effect of geogrid on particle movement SmartRock Effect of geogrid on
Mechanical Stabilisation for Permanent Roads Tim Oliver VP Global Applications Technology Tensar International toliver@tensar.co.uk Effect of geogrid on particle movement SmartRock Effect of geogrid on
2011 SEG SEG San Antonio 2011 Annual Meeting 3377
 Source-receiver pretack depth migration uing dreamlet Bangyu Wu *, Ru-han Wu and Jinghuai Gao Modeling and Imaging Laboratory, IGPP, Univerity of California, Santa Cruz Summary The dreamlet method add
Source-receiver pretack depth migration uing dreamlet Bangyu Wu *, Ru-han Wu and Jinghuai Gao Modeling and Imaging Laboratory, IGPP, Univerity of California, Santa Cruz Summary The dreamlet method add
April 29, ,492,391. a. H. S. McQUAD ET AL PROCESS AND APPARATUS FOR HANDLING CHLORINE. Filed Sept. 14, Fig.2. N 3.
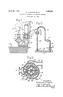 April 29, 1924. 1,492,391 a. H. S. McQUAD ET AL PRCESS AND APPARATUS FR HANDLING CHLRINE Filed Sept. 14, 1923 2-4 19 Fig.2. % 2% 41 N N 3. S E.S. ASE SN SŠ & Si EN gx N.Y. S2 38 A invenor. Howard S.M.
April 29, 1924. 1,492,391 a. H. S. McQUAD ET AL PRCESS AND APPARATUS FR HANDLING CHLRINE Filed Sept. 14, 1923 2-4 19 Fig.2. % 2% 41 N N 3. S E.S. ASE SN SŠ & Si EN gx N.Y. S2 38 A invenor. Howard S.M.
A Double Oracle Algorithm for Zero-Sum Security Games. Graphs, Manish Jain, Dmytro Korzhyk, Ondřej Vaněk, Vincent Conitzer,
 A Double Oracle Algorithm for Zero-Sum Security Game on Graph Manih Jain, Dmytro Korzhyk, Ondřej Vaněk +, Vincent Conitzer, Michal Pěchouček +, Milind Tambe Computer Science Department, Univerity of Southern
A Double Oracle Algorithm for Zero-Sum Security Game on Graph Manih Jain, Dmytro Korzhyk, Ondřej Vaněk +, Vincent Conitzer, Michal Pěchouček +, Milind Tambe Computer Science Department, Univerity of Southern
THE DESIGN AND APPLICATION OF WIRELESS MEMS INERTIAL MEASUREMENT UNITS FOR THE MEASUREMENT AND ANALYSIS OF GOLF SWINGS
 THE DESIGN AND APPLICATION OF WIRELESS MEMS INERTIAL MEASUREMENT UNITS FOR THE MEASUREMENT AND ANALYSIS OF GOLF SWINGS by Kevin W. King A diertation ubmitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for
THE DESIGN AND APPLICATION OF WIRELESS MEMS INERTIAL MEASUREMENT UNITS FOR THE MEASUREMENT AND ANALYSIS OF GOLF SWINGS by Kevin W. King A diertation ubmitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for
Previewer Tools Show All In View: Hide All
 http://www.webaign.net/v4cgiarawon@ater.ny/aignent/previ... 1 of 13 5/28/2008 7:46 AM Aignent Previewer Review #2 About thi Aignent Previewer Tool Show All In View: Hide All Cloe thi window Hidden: Aignent
http://www.webaign.net/v4cgiarawon@ater.ny/aignent/previ... 1 of 13 5/28/2008 7:46 AM Aignent Previewer Review #2 About thi Aignent Previewer Tool Show All In View: Hide All Cloe thi window Hidden: Aignent
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United State US 20080287.036A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0287036A1 McGuire (43) Pub. Date: (54) GAS PERMEABLE ATHLETIC BREAST Publication Claification RESTRAINT (51)
(19) United State US 20080287.036A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0287036A1 McGuire (43) Pub. Date: (54) GAS PERMEABLE ATHLETIC BREAST Publication Claification RESTRAINT (51)
08 Rubble Mound Structure Design
 08 Rubble Mound Structure Deign Ref: Shore Protection Manual, USACE, 1984 Baic Coatal Engineering, R.M. Sorenen, 1997 Coatal Engineering andbook, J.B. erbich, 1991 EM 1110-2-2904, Deign of Breakwater and
08 Rubble Mound Structure Deign Ref: Shore Protection Manual, USACE, 1984 Baic Coatal Engineering, R.M. Sorenen, 1997 Coatal Engineering andbook, J.B. erbich, 1991 EM 1110-2-2904, Deign of Breakwater and
North East Regional Newsletter December 2012
 North Eat Regional Newletter December 2012 Welcome to the December 2012 North Eat Regional Newletter, thi edition i full of club new, good new, opportunitie and development! Now the new regional league
North Eat Regional Newletter December 2012 Welcome to the December 2012 North Eat Regional Newletter, thi edition i full of club new, good new, opportunitie and development! Now the new regional league
NIRSA CLUB BASKETBALL CONFERENCE MANUAL
 2018-2019 NIRSA CLUB BASKETBALL CONFERENCE MANUAL The NIRSA Club Baketball Conference i excited to provide league baketball for collegiate club team acro the country. The miion of the NIRSA Club Baketball
2018-2019 NIRSA CLUB BASKETBALL CONFERENCE MANUAL The NIRSA Club Baketball Conference i excited to provide league baketball for collegiate club team acro the country. The miion of the NIRSA Club Baketball
EFFECTIVE ROOF SUPPORT FOR TABULAR STOPES. RW Ottermann NDL Burger AJ von Wielligh MF Handley GA Fourie
 Safety in Mines Research Advisory Committee Final Project Report EFFECTIVE ROOF SUPPORT FOR TABULAR STOPES RW Ottermann NDL Burger AJ von Wielligh MF Handley GA Fourie Research Agency RE@UP, University
Safety in Mines Research Advisory Committee Final Project Report EFFECTIVE ROOF SUPPORT FOR TABULAR STOPES RW Ottermann NDL Burger AJ von Wielligh MF Handley GA Fourie Research Agency RE@UP, University
CONNECTIONS. Key Words Splices, Bolted Splice, Bolted Column Splice, Minor Axis Splice
 COECTIOS Boled Column Splice wih Minor Axi Bending Auhor: Zahid Hamid, Kevin Cowie Affiliaion: Seel Conrucion ew Zealand Inc. Dae: 19 h February 015 Ref: CO310 Key Word Splice, Boled Splice, Boled Column
COECTIOS Boled Column Splice wih Minor Axi Bending Auhor: Zahid Hamid, Kevin Cowie Affiliaion: Seel Conrucion ew Zealand Inc. Dae: 19 h February 015 Ref: CO310 Key Word Splice, Boled Splice, Boled Column
Simulation of morphological changes induced by large-scale coastal engineering using a 3D wave current interaction model
 Indian Journal of Geo-Marine Science Vol. 45(2), February 2016, pp. 215-223 Simulation of morphological change induced by large-cale coatal engineering uing a 3D wave current interaction model Ting Xu
Indian Journal of Geo-Marine Science Vol. 45(2), February 2016, pp. 215-223 Simulation of morphological change induced by large-cale coatal engineering uing a 3D wave current interaction model Ting Xu
Does culture explain voting biases in association football awards? : The FIFA Ballon d Or 2013 award.
 Doe culture explain voting biae in aociation football award? : The FIFA Ballon d Or 2013 award. Author: Rutger Ruizendaal Univerity of Twente P.O. Box 217, 7500AE Enchede The Netherland r.ruizendaal@tudent.utwente.nl
Doe culture explain voting biae in aociation football award? : The FIFA Ballon d Or 2013 award. Author: Rutger Ruizendaal Univerity of Twente P.O. Box 217, 7500AE Enchede The Netherland r.ruizendaal@tudent.utwente.nl
Flail Mowers FM2060 & FM2072
 Table of Content Flail Mower FM2060 & FM2072 17962! 309-100M Operator Manual Read the Operator manual entirely. When you ee thi ymbol, the ubequent intruction and warning are eriou - follow without exception.
Table of Content Flail Mower FM2060 & FM2072 17962! 309-100M Operator Manual Read the Operator manual entirely. When you ee thi ymbol, the ubequent intruction and warning are eriou - follow without exception.
Feb. 6, W. C. HAMPTON 1,946,208 METHOD OF COATING ARTICLES WITH PYROXYLIN or THE LIKE
 Feb. 6, 1934. W. C. HAMPTN 1,946,8 METHD F CATING ARTICLES WITH PYRXYLIN or THE LIKE Filed June 12, 19 SN 2 26 Z2 28S 37 6 N Patented Feb. 6, 1934 1946,8 3 40 4 UNITED STATES PATENT FFICE 1946,8 METHD
Feb. 6, 1934. W. C. HAMPTN 1,946,8 METHD F CATING ARTICLES WITH PYRXYLIN or THE LIKE Filed June 12, 19 SN 2 26 Z2 28S 37 6 N Patented Feb. 6, 1934 1946,8 3 40 4 UNITED STATES PATENT FFICE 1946,8 METHD
draft 5.2 CITY OF LARKSPUR
 5 Acce, Circulation and ing A dicued in the Viion Chapter, thi Plan take an integrated land ue and tranportation approach which provide flexibility and monitor development o a to avoid or minimize traffic
5 Acce, Circulation and ing A dicued in the Viion Chapter, thi Plan take an integrated land ue and tranportation approach which provide flexibility and monitor development o a to avoid or minimize traffic
A Method for Estimating Sound Speed and the Void Fraction of Bubbles from Sub-Bottom Sonar Images of Gassy Seabeds. T.G. Leighton
 A Method for Etimating Sound Speed and the Void Fraction of Bubble from Sub-Bottom Sonar Image of Gay Seabed T.G. Leighton ISVR Technical Report No 320 December 2007 SCIENTIFIC PUBLICATIONS BY THE ISVR
A Method for Etimating Sound Speed and the Void Fraction of Bubble from Sub-Bottom Sonar Image of Gay Seabed T.G. Leighton ISVR Technical Report No 320 December 2007 SCIENTIFIC PUBLICATIONS BY THE ISVR
Physics 20 Lesson 13 Projectile Motion
 Pyic 0 Leon 13 Projectile Motion In Leon 1 to 9 we learned ow to decribe te otion of object wic were eiter oving orizontally or vertically. Now we wi to conider otion were te object i oving bot orizontally
Pyic 0 Leon 13 Projectile Motion In Leon 1 to 9 we learned ow to decribe te otion of object wic were eiter oving orizontally or vertically. Now we wi to conider otion were te object i oving bot orizontally
Bearing Capacity and Settlement Response of PMS Tanks on Cohesionless Soil Lithology in Lekki, Lagos of Nigeria
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Applied Engineering and Scientific Research,, ():- (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN: 8 Bearing Capacity and
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Applied Engineering and Scientific Research,, ():- (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN: 8 Bearing Capacity and
Convective entrainment and large-scale organization of tropical precipitation: sensitivity of the CNRM-CM5 hierarchy of models
 Convective entrainment and large-cale organization of tropical precipitation: it ti enitivity of the CNRM-CM5 hierarchy of model Boutheina Ouelati & Gille Bellon CNRM, CNRS/Météo-France, Touloue, France
Convective entrainment and large-cale organization of tropical precipitation: it ti enitivity of the CNRM-CM5 hierarchy of model Boutheina Ouelati & Gille Bellon CNRM, CNRS/Météo-France, Touloue, France
UNIT-I SOIL EXPLORATION
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : Geotechnical Engineering - II (16CE127) Year & Sem: III-B.Tech & II-Sem
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : Geotechnical Engineering - II (16CE127) Year & Sem: III-B.Tech & II-Sem
Combination Analysis Tutorial
 Combination Analysis Tutorial 3-1 Combination Analysis Tutorial It is inherent in the Swedge analysis (when the Block Shape = Wedge), that tetrahedral wedges can only be formed by the intersection of 2
Combination Analysis Tutorial 3-1 Combination Analysis Tutorial It is inherent in the Swedge analysis (when the Block Shape = Wedge), that tetrahedral wedges can only be formed by the intersection of 2
WALTON-VERONA YOUTH FOOTBALL ASSOCIATION 2018 REGISTRATION FORM
 WALTON-VERONA YOUTH FOOTBALL AOCIATION 2018 REGITRATION FORM Pleae circle appropriate team / age for fall 2018: Refer to Helpful Fact and Tip heet for cut off date for each team. FLAG TARTER PEEWEE / MIDGET
WALTON-VERONA YOUTH FOOTBALL AOCIATION 2018 REGITRATION FORM Pleae circle appropriate team / age for fall 2018: Refer to Helpful Fact and Tip heet for cut off date for each team. FLAG TARTER PEEWEE / MIDGET
is. ? S. Z7zvezzar; AA-7/w/ Zoza, ZvZAegea, 62/. y-p2 se Aug. 5, W. W. PAGET-- 2,425,000 & Filed March 27, Sheets-Sheet l
 Aug. 5, 1947. W. W. PAGET-- 2,425,000 APPARATUS FOR AUTOMATICALLY ROLLING PRESSURE AND TEMPERATURE WITHiiN AIRCRAFT CABINS m Filed March 27, 1943 8 Sheet-Sheet l S \4. - - e o 2 y-p2 e R Ea i. V El N O
Aug. 5, 1947. W. W. PAGET-- 2,425,000 APPARATUS FOR AUTOMATICALLY ROLLING PRESSURE AND TEMPERATURE WITHiiN AIRCRAFT CABINS m Filed March 27, 1943 8 Sheet-Sheet l S \4. - - e o 2 y-p2 e R Ea i. V El N O
U.S. UNCONVENTIONAL MONETARY POLICY AND TRANSMISSION TO EMERGING MARKET ECONOMIES. David Bowman, Juan M. Londono and Horacio Sapriza
 U.S. UNCONVENTIONAL MONETARY POLICY AND TRANSMISSION TO EMERGING MARKET ECONOMIES 1 David Bowman, Juan M. Londono and Horacio Sapriza Dicuion by Emmanuel C Mamatzaki Univerity of Suex Fifth BIS Conultative
U.S. UNCONVENTIONAL MONETARY POLICY AND TRANSMISSION TO EMERGING MARKET ECONOMIES 1 David Bowman, Juan M. Londono and Horacio Sapriza Dicuion by Emmanuel C Mamatzaki Univerity of Suex Fifth BIS Conultative
Essential Ingredients for Heavy Orographic Rainfall and their Potential Application for Prediction
 7.6 Eential Ingredient for eavy Orographic Rainfall and their Potential Application for Prediction Yuh-Lang Lin, Sen Chiao, Jame A. Thurman and Michael L. Kaplan North Carolina State Univerity, Raleigh,
7.6 Eential Ingredient for eavy Orographic Rainfall and their Potential Application for Prediction Yuh-Lang Lin, Sen Chiao, Jame A. Thurman and Michael L. Kaplan North Carolina State Univerity, Raleigh,
CAPSIZING OF VESSELS IN FOLLOWING SEAS
 CAPSIZING OF VESSELS IN FOLLOWING SEAS By: M Reniton For Preentation at AQUAMARINE '95 OCTOBER 1995 REPORT AMECRC C 95/17 AUSTRALIAN MARITIME ENGINEERING CRC LIMITED ACN 060 208 577 Capizing of Veel in
CAPSIZING OF VESSELS IN FOLLOWING SEAS By: M Reniton For Preentation at AQUAMARINE '95 OCTOBER 1995 REPORT AMECRC C 95/17 AUSTRALIAN MARITIME ENGINEERING CRC LIMITED ACN 060 208 577 Capizing of Veel in
COMPARISONS OF WAVE OVERTOPPING DISCHARGES AND DAMAGES OF THE NTOU VERTICAL SEAWALL DUE TO TWO SIMILAR SUPER TYPHOONS ON KEELUNG COAST OF TAIWAN
 COMPAISONS OF WAVE OVETOPPING DISCAGES AND DAMAGES OF TE NTOU VETICAL SEAWALL DUE TO TWO SIMILA SUPE TYPOONS ON KEELUNG COAST OF TAIWAN Da-Wei Chen 1 Shiaw-Yih Tzang Shan-wei Ou In thi tudy, SWAN model
COMPAISONS OF WAVE OVETOPPING DISCAGES AND DAMAGES OF TE NTOU VETICAL SEAWALL DUE TO TWO SIMILA SUPE TYPOONS ON KEELUNG COAST OF TAIWAN Da-Wei Chen 1 Shiaw-Yih Tzang Shan-wei Ou In thi tudy, SWAN model
Analysis of Shear Lag in Steel Angle Connectors
 University of New Hampshire University of New Hampshire Scholars' Repository Honors Theses and Capstones Student Scholarship Spring 2013 Analysis of Shear Lag in Steel Angle Connectors Benjamin Sawyer
University of New Hampshire University of New Hampshire Scholars' Repository Honors Theses and Capstones Student Scholarship Spring 2013 Analysis of Shear Lag in Steel Angle Connectors Benjamin Sawyer
FORUMS INSIGHTS BLOG VIDEOS PHYSICS NEWS INFO SEARCH Forums Physics Classical Physics
 FORUMS INSIGHTS BLOG VIDEOS PHYSICS NEWS INFO SEARCH Forum Phyi Claial Phyi PF thrive by your haring of our ommunity with your friend, family and oial media. If you do, tell me and I'll give you Gold Memberhip.
FORUMS INSIGHTS BLOG VIDEOS PHYSICS NEWS INFO SEARCH Forum Phyi Claial Phyi PF thrive by your haring of our ommunity with your friend, family and oial media. If you do, tell me and I'll give you Gold Memberhip.
Some rankings for the Athens Olympic Games using DEA models with a constant input
 J.S. MELLO et al. / Invetigação Operacional, 28 (2008) 77-89 77 Some ranking for the Athen Olympic Game uing DEA model with a contant input João Carlo Correia Baptita Soare de Mello Lidia Angulo Meza Brenda
J.S. MELLO et al. / Invetigação Operacional, 28 (2008) 77-89 77 Some ranking for the Athen Olympic Game uing DEA model with a contant input João Carlo Correia Baptita Soare de Mello Lidia Angulo Meza Brenda
The tensile capacity of suction caissons in sand under rapid loading
 Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics: ISFOG 25 Gourvenec & Cassidy (eds) 25 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 415 3963 X The tensile capacity of suction caissons in sand under rapid loading Guy T. Houlsby,
Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics: ISFOG 25 Gourvenec & Cassidy (eds) 25 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 415 3963 X The tensile capacity of suction caissons in sand under rapid loading Guy T. Houlsby,
Hydrostatic Force on a Submerged Surface
 Experiment 3 Hydrostatic Force on a Submerged Surface Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to experimentally locate the center of pressure of a vertical, submerged, plane surface. The experimental
Experiment 3 Hydrostatic Force on a Submerged Surface Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to experimentally locate the center of pressure of a vertical, submerged, plane surface. The experimental
Measuring and Evaluation on Priority Lanes
 I.J. Intelligent Sytem and Application, 2010, 2, 56-63 Publihed Online December 2010 in MECS (http://www.mec-pre.org/) Meauring and Evaluation on Priority Lane Shan Jiang Beijing Intitute of Technology,
I.J. Intelligent Sytem and Application, 2010, 2, 56-63 Publihed Online December 2010 in MECS (http://www.mec-pre.org/) Meauring and Evaluation on Priority Lane Shan Jiang Beijing Intitute of Technology,
